Zygomycetes (Mucorales) – Aseptate Molds
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Microscopy: Sporangiophores between rhizoids, pear-shaped sporangia.
Absidia spp. (now Lichtheimia )
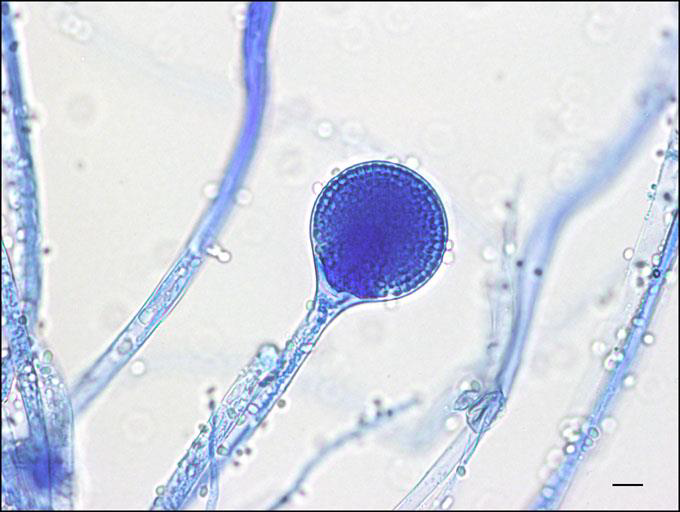
Absidia spp. (now Lichtheimia )
clinically relevant in mucormycosis.
Lichtheimia corymbifera
Microscopy: Branching sporangiophores; no rhizoids.
Mucor spp.
Pathogenicity: Can cause rhinocerebral mucormycosis.
Mucor spp.
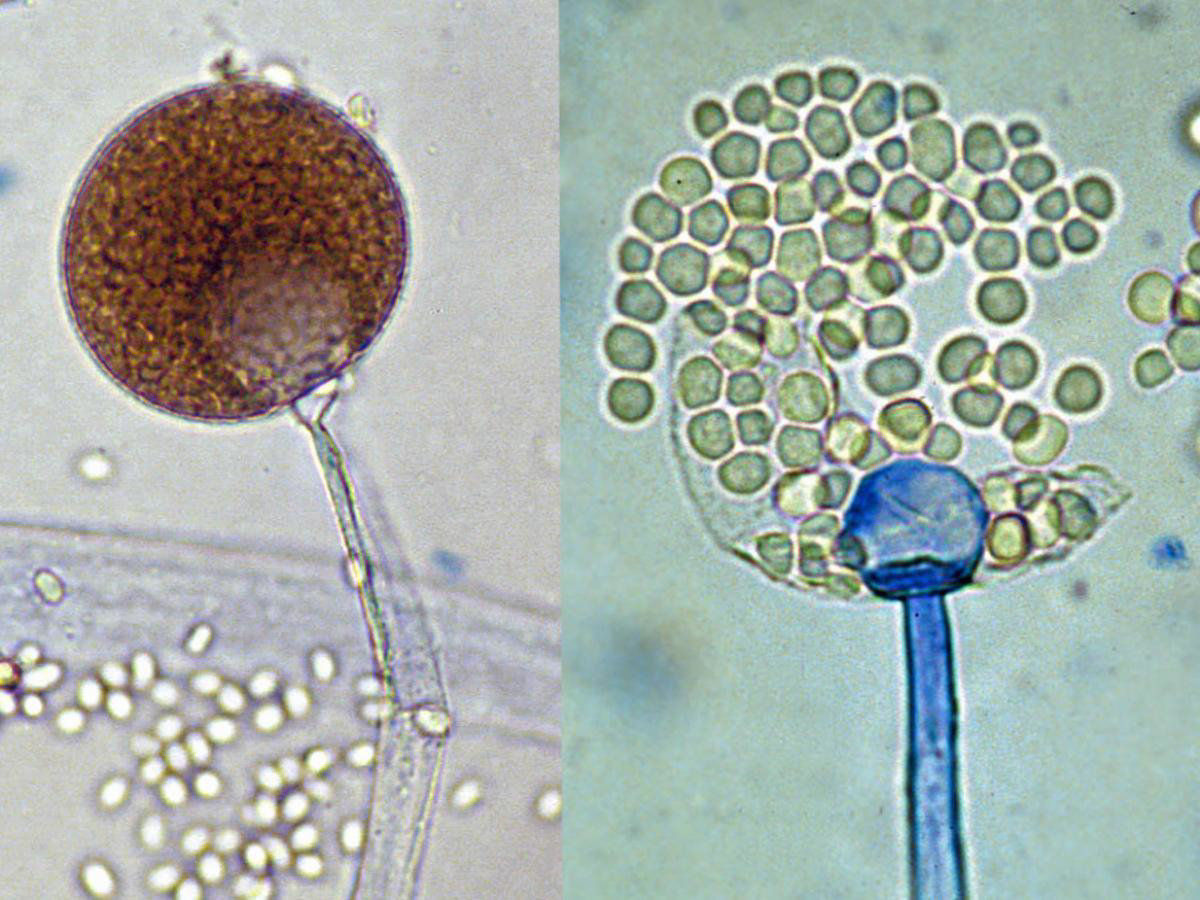
Mucor spp.
Microscopy: Unbranched sporangiophores directly opposite rhizoids.
Rhizopus spp.
Clinical Relevance: Most common cause of mucormycosis.
Rhizopus spp.
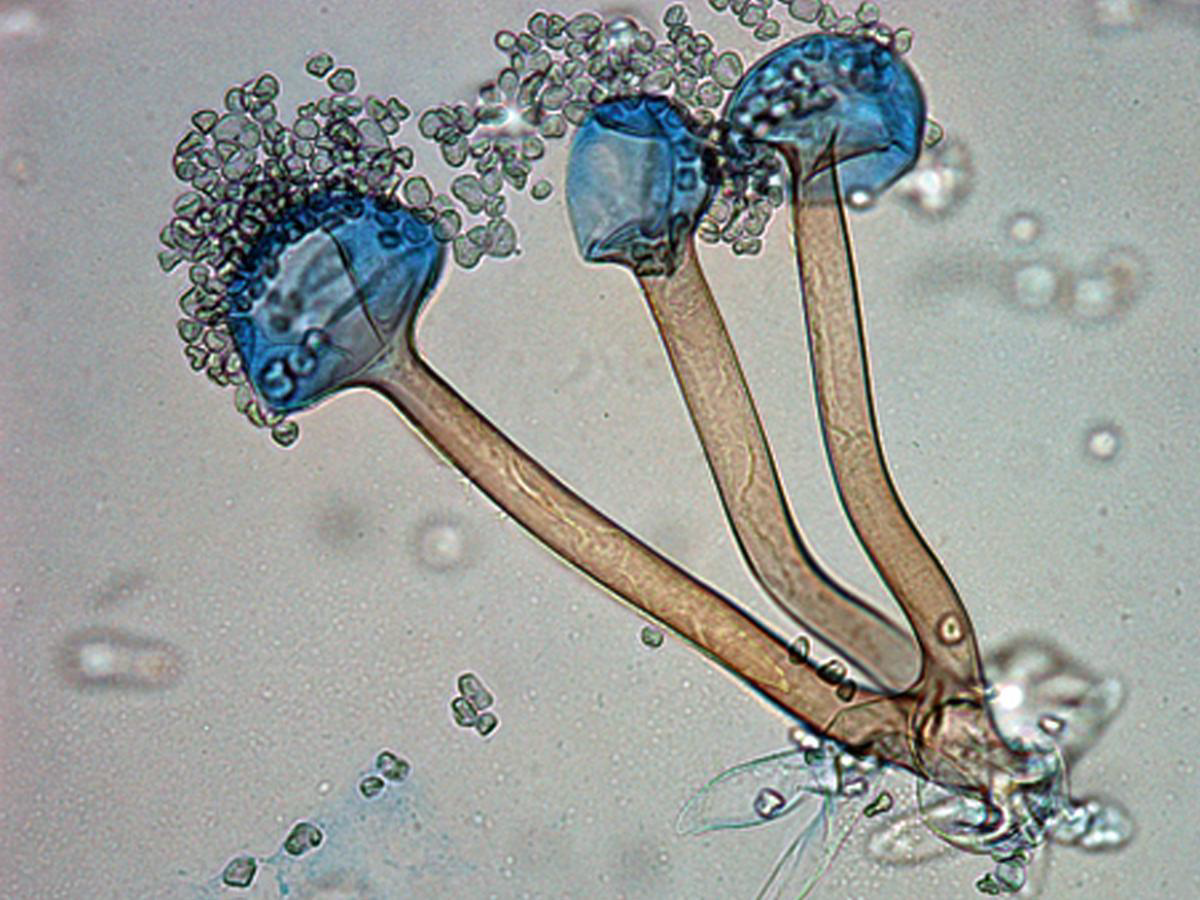
Rhizopus spp.
Microscopy: Flask-shaped sporangia, opposite rhizoids.
Saksenaea spp.
Relevance: May cause necrotizing skin infections and rhino-orbital disease.
Saksenaea spp.
Saksenaea spp.
Microscopy: Vesicles with denticles bearing single sporangiola.
Cunninghamella spp.
Clinical Significance: Rare cause of disseminated mucormycosis.
Cunninghamella spp.
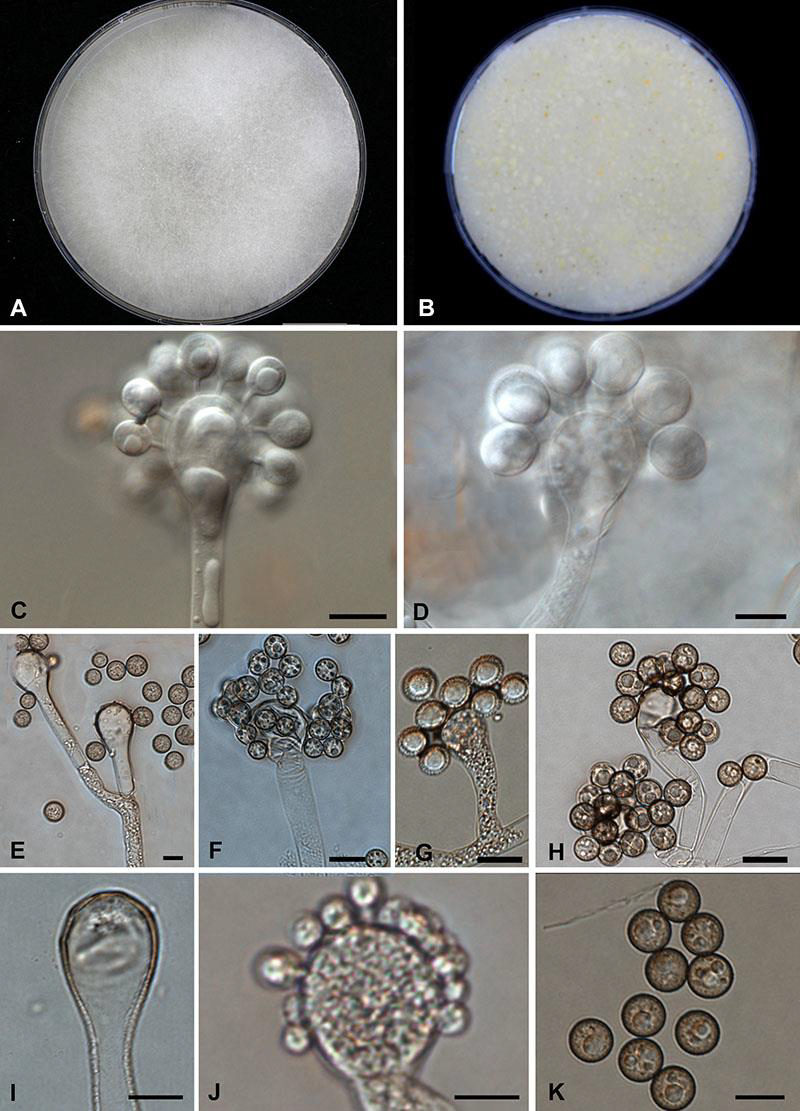
Cunninghamella spp.
.Microscopy: Cylindrical merosporangia radiating around vesicles.
Syncephalastrum spp
Relevance: Rarely pathogenic; may resemble Aspergillus in culture.
Syncephalastrum spp
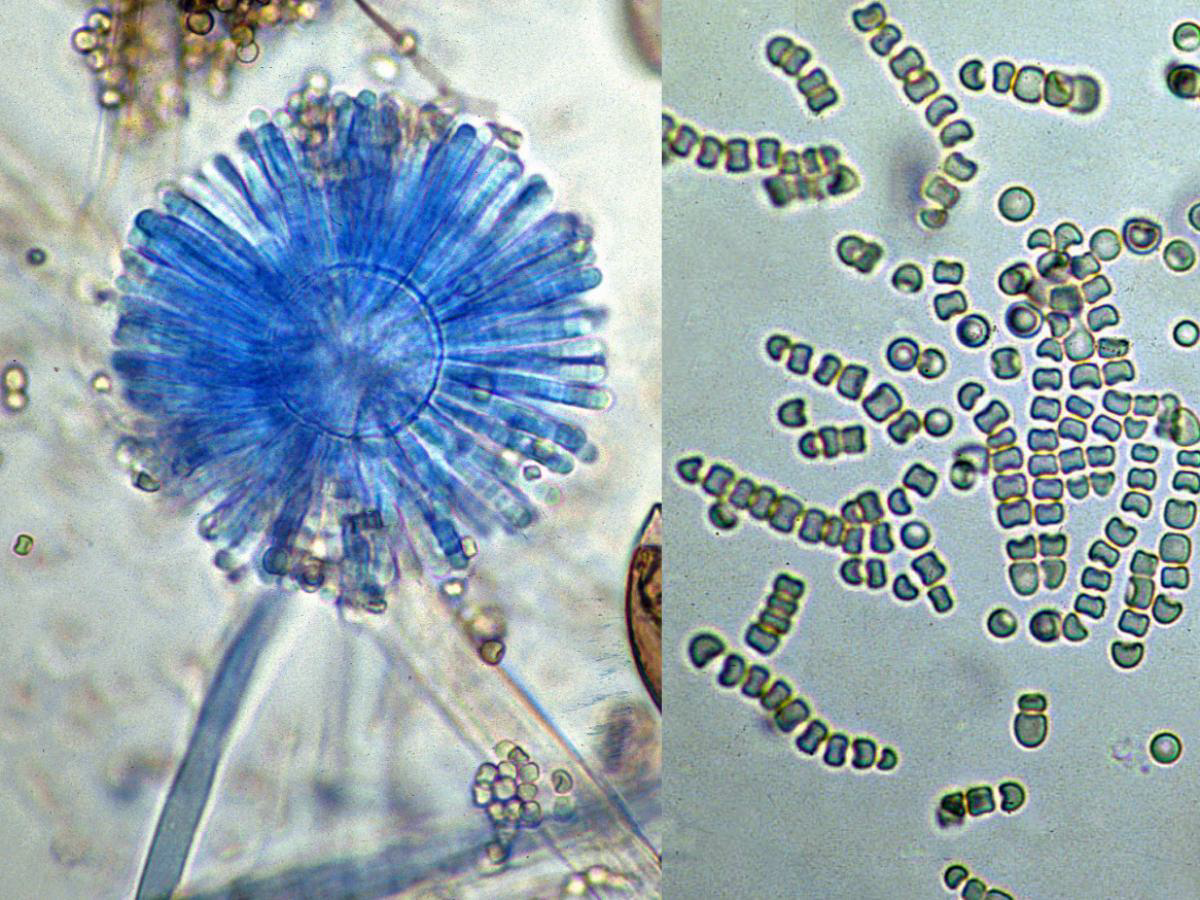
Syncephalastrum spp
Microscopy: Produces pseudohyphae, chlamydospores, and blastoconidia.
Candida albicans
Germ Tube Test: Positive
Sugar Assimilation: Sucrose-positive.
Candida albicans
Clinical Role: Major cause of mucocutaneous and systemic candidiasis.
Candida albicans
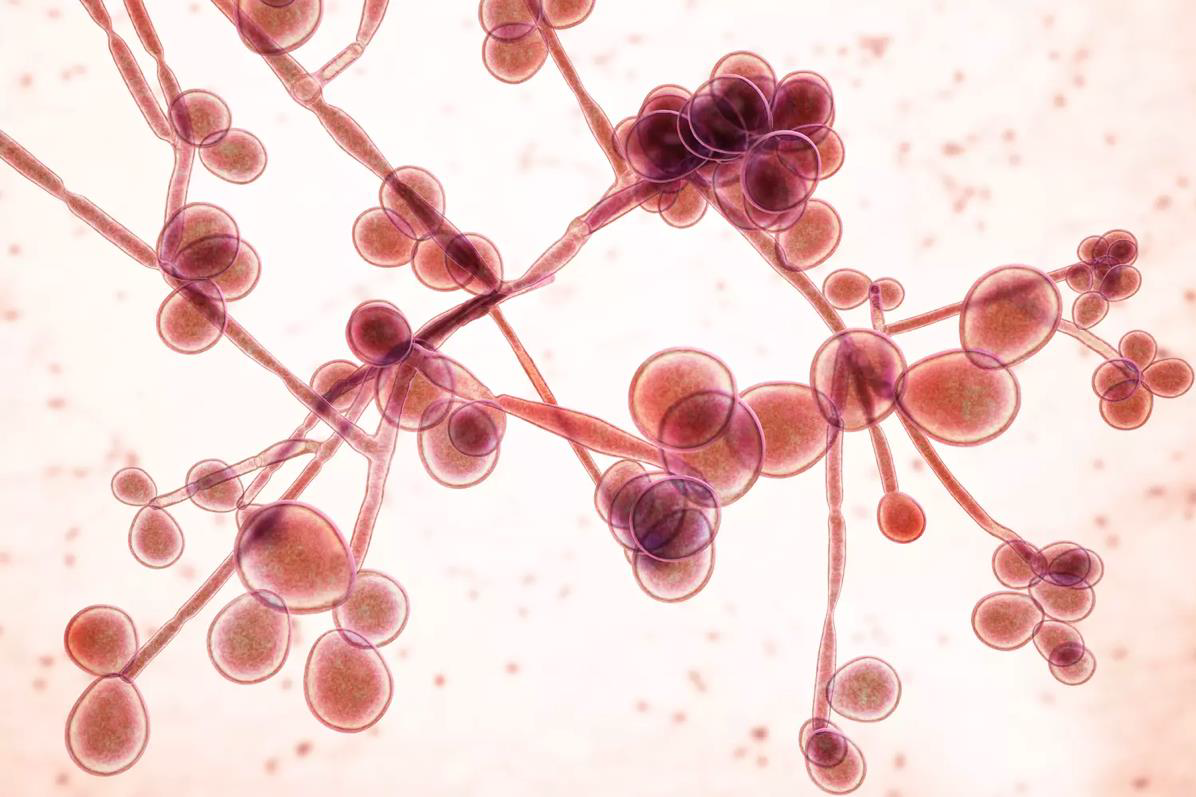
Candida albicans
Microscopy: Small, oval yeasts, no pseudohyphae.
Candida glabrata (formerly Torulopsis glabrata)
Clinical Role: UTI, vaginal infections, and systemic disease; azoles resistant.
Candida glabrata (formerly Torulopsis glabrata)
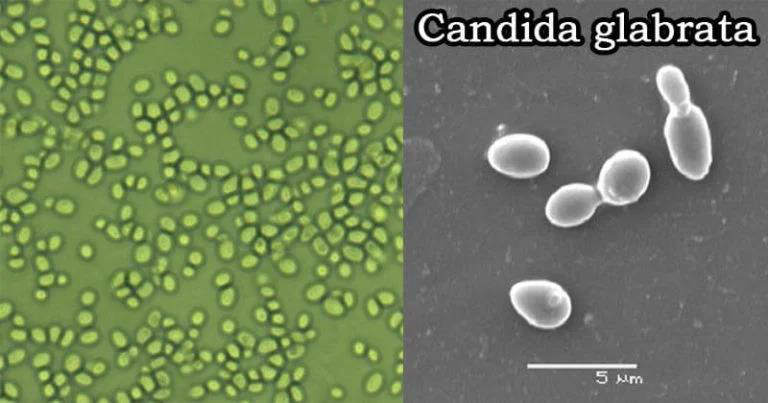
Candida glabrata (formerly Torulopsis glabrata)
Common in neutropenic patients.
C. tropicalis:
Found in catheters and prosthetic devices.
C. parapsilosis:
Intrinsically resistant to fluconazole.
C. krusei