Enteric Viruses
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What adaptations does the GI system have to protect against pathogens?
-Stomach acid/bile
-Digestive enzymes
-Secretory antibody (IgA)
-Epithelium
What are the main veterinary enteric viruses?
-Reoviruses
-Calciviruses
-Flaviviruses
-Coronaviruses
-Parvoviruses
Are enteric viruses mostly RNA or DNA viruses?
RNA - with the exception of parvovirus which is DNA.
What main enteric disease is caused by calciviruses?
-Norovirus: Main cause of diarrhoea and vomitting in humans
-Feline Calicivirus
What main enteric disease is caused by Flaviviruses?
Pestiviruses: Bovine viral diarrhoea (BVD) causes persistent enteritis (through immunotolerance) in calfs (virus can mutate to cause mucosal disease which can be fatal
What main enteric diseases are caused by coronaviruses?
-Canine enteric coronavirus
-Feline infectious peritonitis
-Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus
How does transmissible gastroenteritis virus survive through the GI's defence mechanisms?
It uses the milk in piglets stomach as protection.
What is the significance of Bovine coronavirus with vaccination?
The dam can be vaccinated to elevate and prolong maternal antibodies to protect both the dam and the calf from the disease.
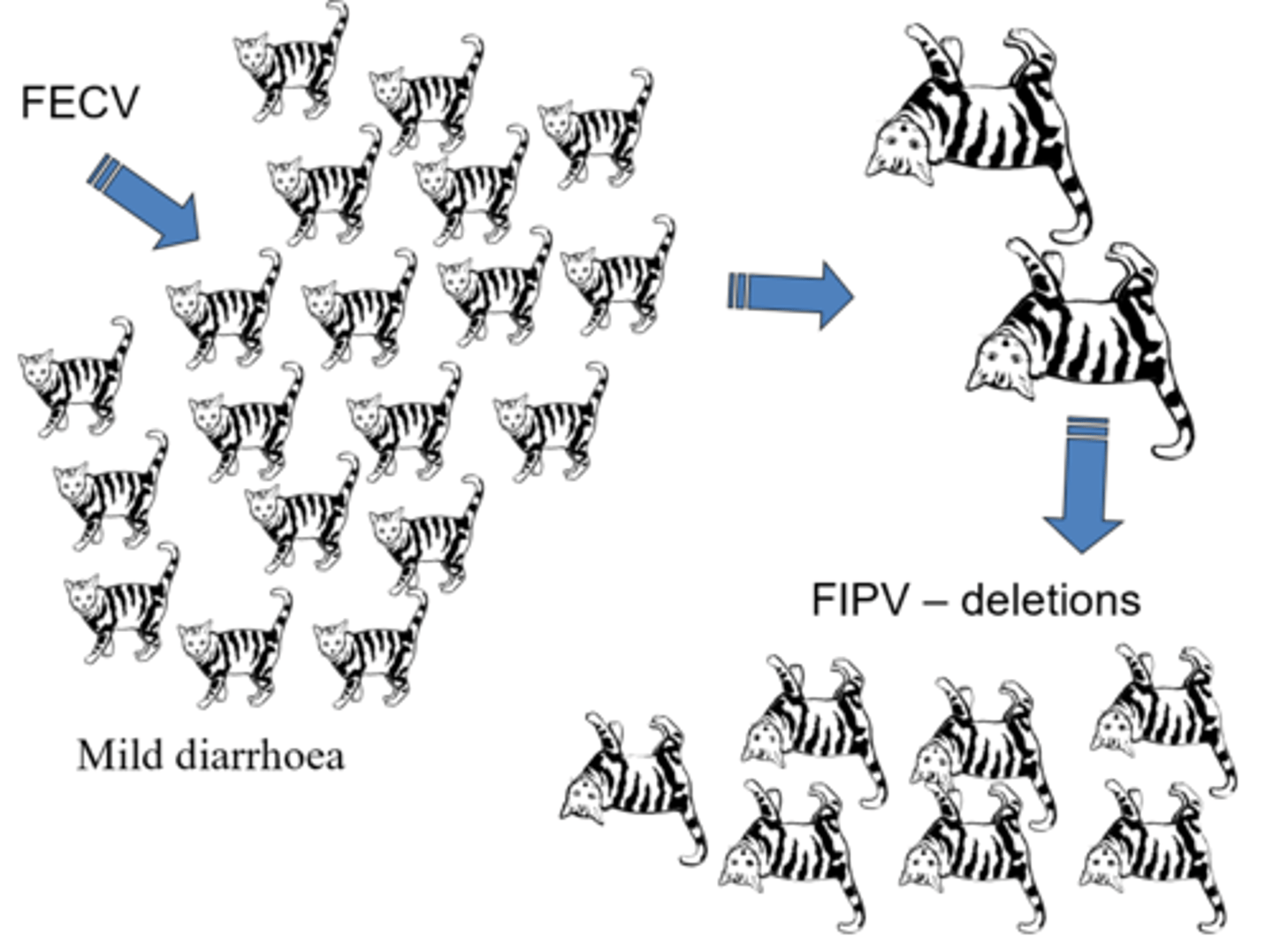
What is the significance of Feline coronaviruses?
2 Biotypes:
-Feline enteric coronaviruses (FECoV): causes intestinal disease (mild)
-Feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV): causes fatal polyserositis
Key example of mutations effect on pathogenesis as the mild version can mutate into the severe fatal form
What are the main methods of controlling enteric viruses?
-Enforcing correct animal husbandry
-Ensuring good biosecurity
-Barrier nursing
-Improving diagnosis
-Vaccination (particularly of the dam)
-Disinfection of potential infection routes
What is the significance of rotavirus?
Common cause of diarrhoea in young animals in species including:
-Calves
-Pigs
-Foals
-Lambs
-Dogs
-Cats
Key example of vaccinating the dam to protect offspring from the virus
What is the significance of Canine/Feline Parvovirus?
-Very environmental resistant virus that causes severe and highly contagious diarrhoea,vomiting and leukopenia
-Uses rapidly dividing cells (E.g. bone marrow) to rapidly replicate itself
-Largely controlled by vaccination
-Can use the antiviral interferon to therapeutically treat the disease
How do viruses generally cause diarrhoea?
-Generally not known
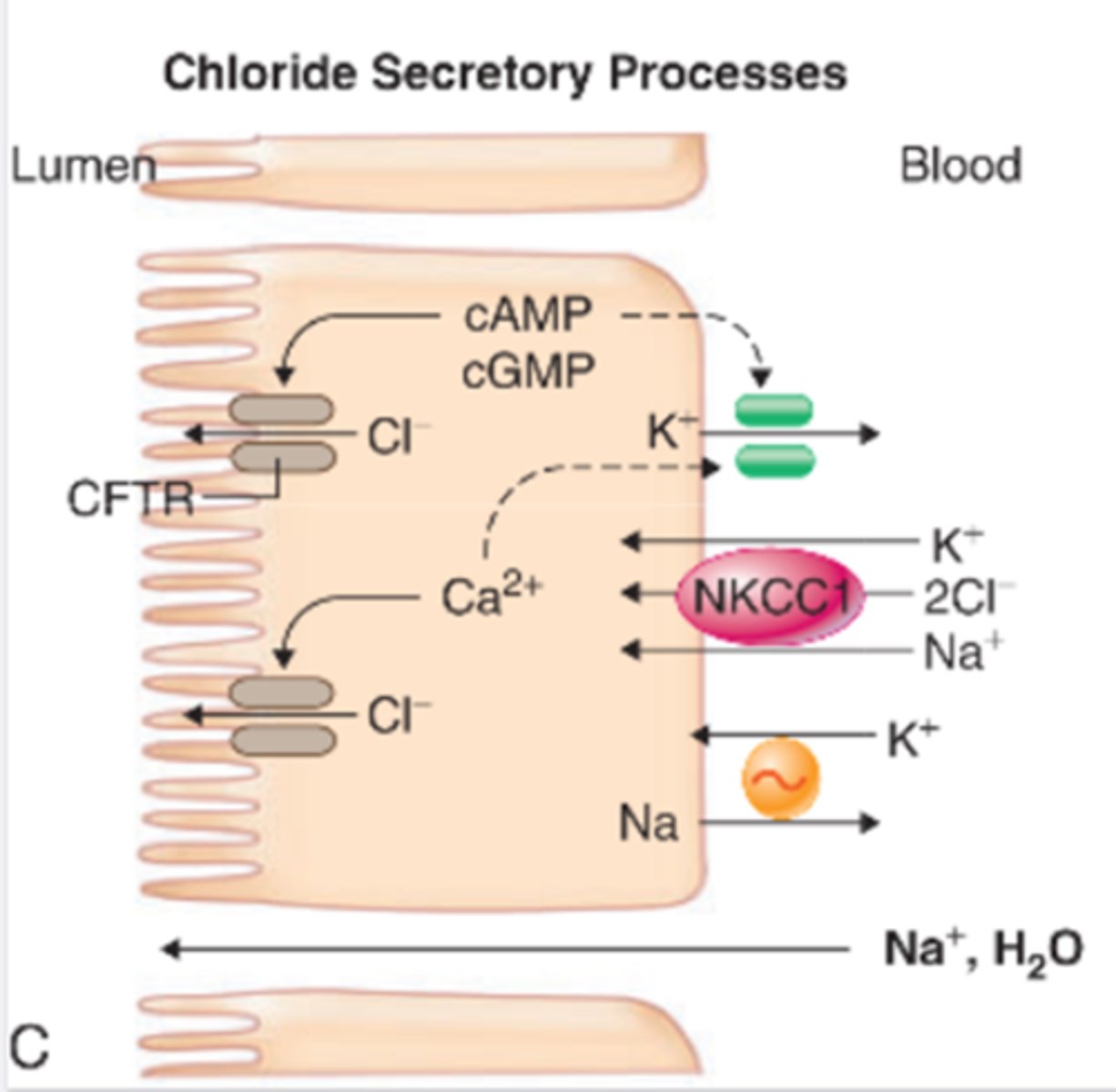
Rotovirus mechanism best understood:
-Control of the flow of water across the intestinal epithelium is disrupted by effecting calcium balance in the intestinal cells
-Protein NSP4 increases the amount of calcium within cell meaning more water is drawn into the cells hence causing diarrhoea upon lysis
How can viruses protect themselves from stomach acid?
-Use stomach enzymes (e.g. trypsin) to increase their infectivity -Capsids to protect the virus from harsh environments
Are there many antivirals available? Are they used often?
-No, they are relatively rare
-The ones that are present are used as they are generally effective at treating disease
Do we know most of the enteric viruses?
-No, a high proportion of diagnostic screening for animals with enteric diseases shows unknown causes of the diseases
-This is indicative of new pathogens that we do not know about yet.