Economic Growth and Economic Cycle
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Short vs long run growth
Short run - the actual annual percentage change in real national output (% change in real GDP): At least one factor of production is fixed
Long run - an increase in the potential productive capacity of the economy (shifts in PPF/LRAS curves)
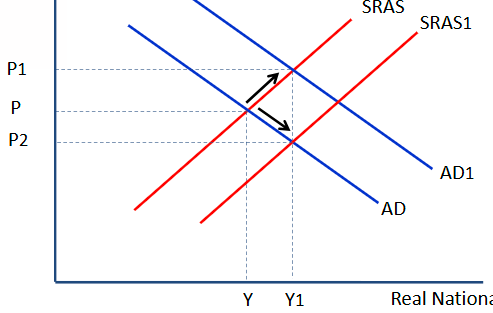
Short run growth graph
Both AD and SRAS shift rightward.
What must increase for long run economic growth to occur
The productive capacity of the economy.
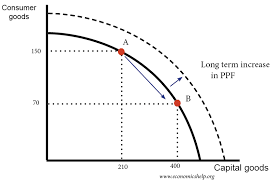
Long run growth - PPF
Initially, with all factor resources fully employed, economy can only produce on solid line.
Increase in factor resources shifts curve right.
Can now produce on dashed line, but this is max capacity, still difficult to achieve.
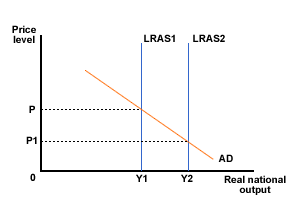
Long run economic growth - LRAS curve
If technological processes become more efficient, will be an increase in productive capacity
LRAS will shift right
Real GDP (national output) will increase to Y2, and price levels will fall to P1
Evaluating short run (demand-side) vs long run (supply side) policies for growth.
Stimulating demand-side is important, but will lead to inflation if supply-side remains constrained.
Equally, improving supply-side has little effect if demand-side is suppressed, leading to spare capacity and unused resources.
However, enhancement of supply side has time lags and doesn’t always improve productive efficiency.
Productive capacity - definition
Maximum amount of goods and services that we can produce with available resources.
GDP - definition
The value of goods + services produced in the economy over a period of time.
Economic Cycle graph
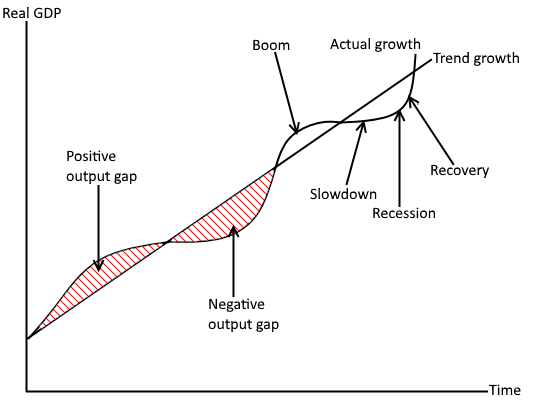
Output gap - definition
Difference between actual GDP and potential GDP (trend line)
Potential GDP - definition
Highest possible level of long term growth, with all factor resources employed.
Real GDP - how does it work?
If GDP growth is 5%, but inflation is 2%, then real GDP is 3%.
Whats a boom characterised by?
Peaks of the economic cycle
High growth rate and demand
Low unemployment
Inflationary pressure
Labour skills shortage
High confidence in economy, so high investment
Downturn vs recession
Downturn is when rate of GDP growth starts to fall. Recession is when a downturn is sustained for 6 months
Recession characterised by?
Demand falls
Unemployment rises
Some firms go bust
Low confidence, reduced investment
Slump (bottom of economic cycle) characterised by:
Low or negative growth
Demand + inflation low
Unemployment high
Confidence in economy low
High rate of bankruptcy
Recovery (green shoots) when growth starts to rise - characterised by:
Economic growth starts to rise
Demand increases
Unemployment falls
Inflation starts to rise
Confidence in the economy increasees
Capital investment increases
Shocks - definition
What might cause unexpected changes in the economic cycle
Demand-side shocks - definition
Unexpected changes in the economy that directly impact Aggregate Demand (Investment, Consumption, Govt spending, Net Exports
Supply-side shocks - definition
Unexpected changes in the economy that directly impact on aggregate supply
Long run: Changes in quality/quantity of factor resources
Short run: Changes in costs of production
Benefits of economic growth (4)
Rise in living standards: Real GDP/ Capita increases
Lower unemployment: Demand rises, so firms require more labour to increase production
Reduced poverty: Rise in avg. incomes leads to fall in absolute poverty
Government’s fiscal position: More jobs = increase in income tax received and decrease in welfare payments
Costs of economic growth (4)
Negative externalities: Damage to the environment, pollution and congestion may all reduce living standards
Scarce resources: may be unsustainable
Inequality: Benefits are unevenly distributed, creating divisions in society
Inflation: As resources become scarcer, demand-pull inflationary pressure arises
How can growth benefit the environment?
May lead to the development of low carbon tech through increased R&D
4 Sources of cyclical instability
Excessive growth in credit + debt
Asset price bubbles
Destabilising speculation
Animal spirits or herding
Excessive growth in credit and debt: explained
During economic boom, high consumer confidence leads to increased borrowing. If there’s a downturn in confidence, many may be unable to afford repayments, magnifying existing instability
Asset price bubbles- definition
When the price of an asset deviates significantly from its intrinsic value, with sharp price rises
Effects of asset price bubbles
They are unsustainable and will eventually burst, negative impact on the economic cycle
Speculation - definition
Trading in an asset or conducting a transaction that has a significant risk of losing initial outlay in expectation of gain due to market fluctuations .
The risk of loss is offset by the possibility of huge gain.
Effects of speculation
Drives sharp movements in the price of a stock, asset or currency due to belief of under/over valuation. This exacerbates booms and busts, linked to price bubbles
Animal spirits - definition
The instincts and emotions that guide behaviour rather than simple, rational and quantifiable facts. H
Herding - definition
Irrational behaviour where there’s a lack of individual decision making as people act like those around them while ignoring the underlying economic facts.