5.4 - ds DNA, SS RNA, Influenza
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Is ds DNA curable or for life?
for life
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is what type of virus? (nucleic acid + type of virus)
dsDNA, naked virus
Most strains of HPV cause what symptom?
warts
A few strains of HPV cause what?
cervical cancer
What’s used to screen for cervical cancer?
PAP smear

PAP smears recognize abnormal cervical cells if the cells they scraped are still ______.
replicating
So HPV vacinnes are mostly given to people to prevent ______ _____ rather than warts.
cervical cancer
Are the strains of HPV the same between the one that gives you warts vs cervical cancer? Or different?
different (some cause warts, some cause cancer, they don’t intersect)
HPV is a _____ containing many different strains
family
What are 3 techniques that can be used to diagnose specfic viruses that cause infections?
ELISA test
Bloodwork
Cytological changes
ELISA tests can be bought OTC; they look for?
particular viral antigen

e.g. of virsuses ELISA tests can detect are? (2)
covid-19, influenza A
Bloodwork tests for a variety of things which are: (3)
looks for + or - viral antigen
looks for nucleic acid of virus
looks for antibodies against viral antigen
The gold standard for IDing the virus is:
nucleic acid testing
Through bloodwork that checks + or - antigens, you can ID viruses like: (2)
HIV, Hep B
The antibodies you look for in bloodwork are: (2)
IgG, IgM
IgG indicates →
previous exposure (at some point)
IgM indicates →
active infection
If 2 patients come in, one with IgG positive antibodies, the other with IgM positive, which person is more at risk for spreading the virus?
patient with + IgM
For a person who comes in with IgG + but IgM - antibodies, the person’s virus is in ______.
latency
Cytological changes means →
cell changes
So an example of Cytological Changes is that HPV causes →
changes in cervical cells
Another example of Cytological Changes is that EBV (epstien-barr virus) causes what to our lymphocytes? →
squashes them
A branch of + ss RNA viruses is called →
Picornoviruses
Picornoviruses are described as very small and ______ virus.
naked
2 viruses within the Picornoviruses family are:
Rhinovirus, Poliovirus
Rhinovirus has around ~____ varieites.
100
What does rhinovirus predominantly cause?
common cold
Is there a vaccine for rhinovirus?
no (too many varieties)
For Poliovirus; the portal of entry = _____ and the portal of exit = _____.
oral; feces
What does poliovirus infect?
motor neurons (once these are damages, they can’t be remade)
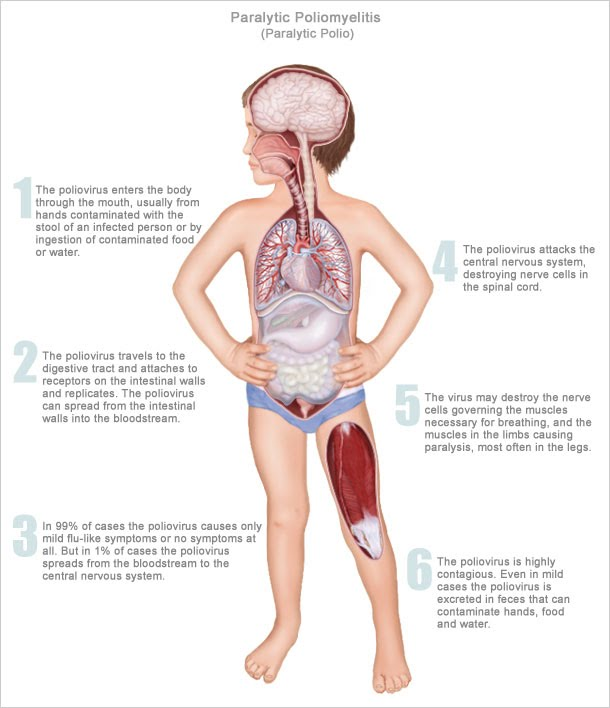
On the extreme end, what can Polio virus lead to?
paralysis
Coronavirus has what nucleic acid strategy and what type of virus?
(-) ss RNA, enveloped virus
What type of penetration and exit method does Coronavirus/COVID-19 use? (2)
fusion (entry), budding (exit)
COVID-19 is transmitted how?
airborne
Influenza is what type of nucleic acid and what type of virus?
(-) ss RNA, enveloped virus
How does Influenza penetrate and exit host cell? (2)
fusion (entry), budding (exit)
How many genes does Influneza have on 8 RNA segments?
10
The Influenza virus has ___ spike and _ spike.
N, H
Influenza spikes have ______ mutations every year.
missense
These missense mutations change the shape of the _____.
spikes
When the RNA has a missense mutation and changes from H1N1 → H2N3 this is called ______ _____.
Antigentic Drift
Antigenic drift is considered a ____ change.
small
When 2 species infects a human at one time, it can lead to a ______.
recombinant
So if a person gets human influenza & avion flu at the same time → there’s a chance that …
the viruses create a recombinant of 2 species that creates a brand new virus
A brand new virus being created will cause a ______.
Pandemic
When a recombinant from 2 entirely different viruses occurs, this is called ______ ____.
Antigenic Shift
Antigenic shifts only happen every couple of ______.
decades