AP World History: Unit 4
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Trans-Oceanic Trade
global trading system in the Caribbean and the Americans trade networks extended to all corners of Atlantic Ocean
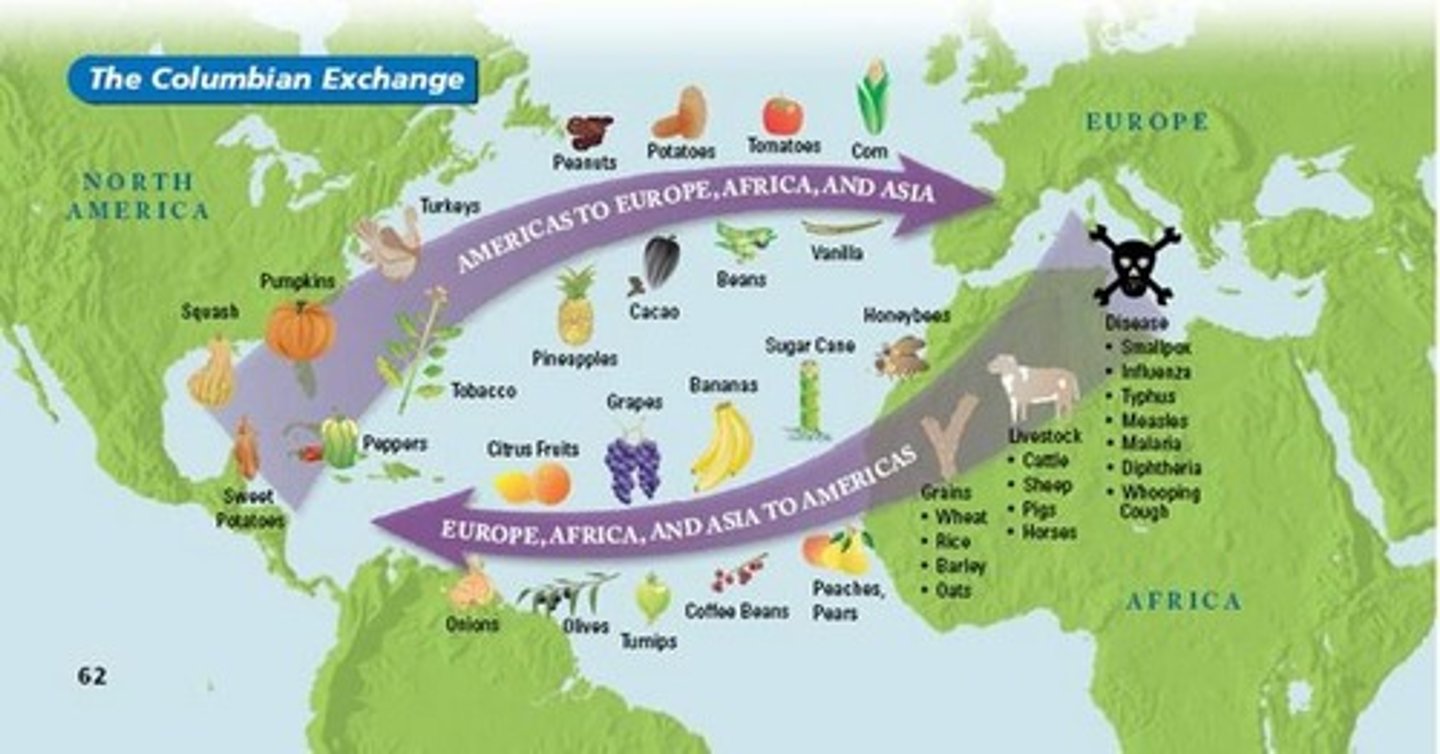
Columbian Exchange
An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa.
Mercantilism
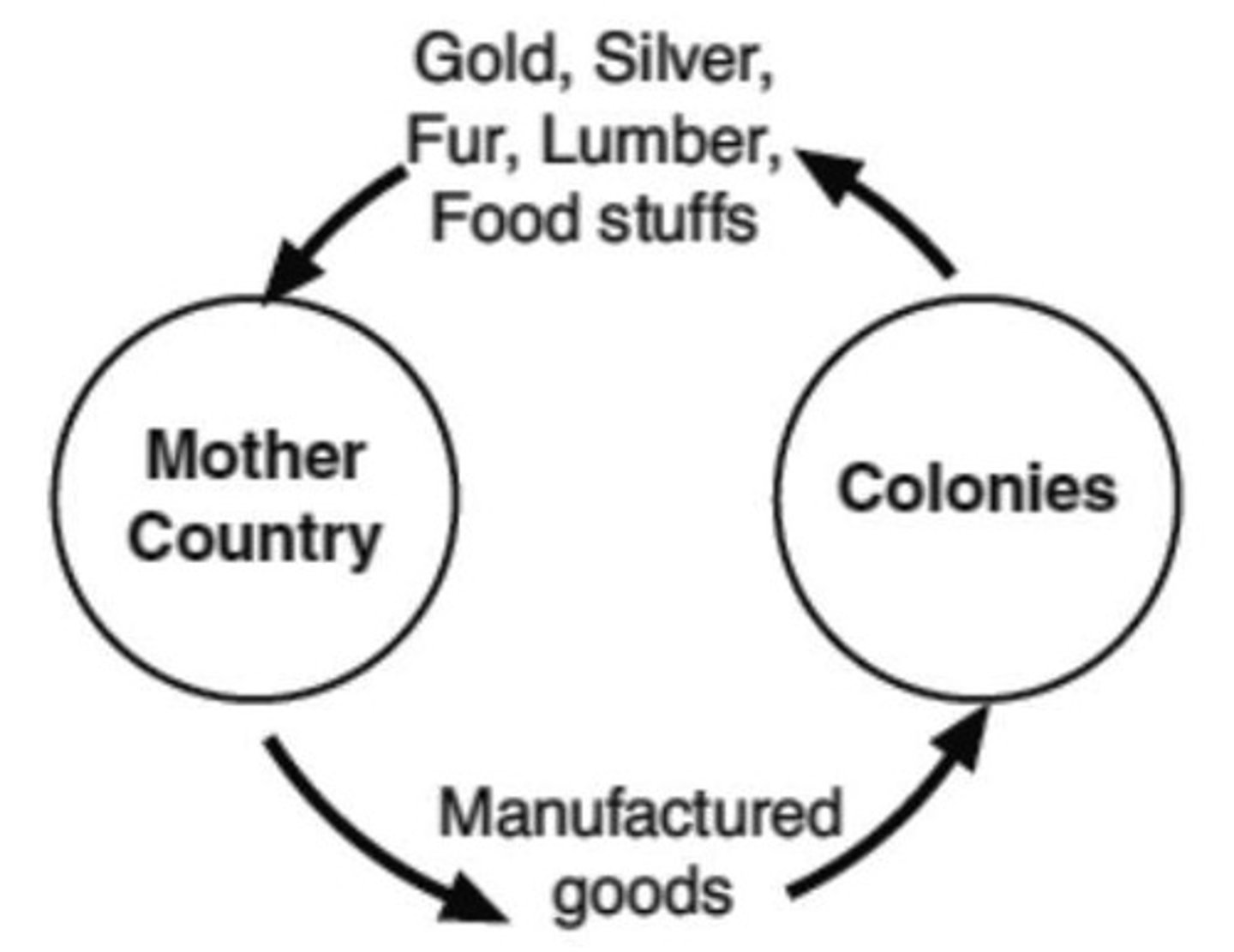
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
Triangular Trade
Trading System between Europe, Africa, and the colonies; European purchased slaves in Africa and sold them to colonies, new materials from colonies went to Europe while European finished products were sold in the colonies.
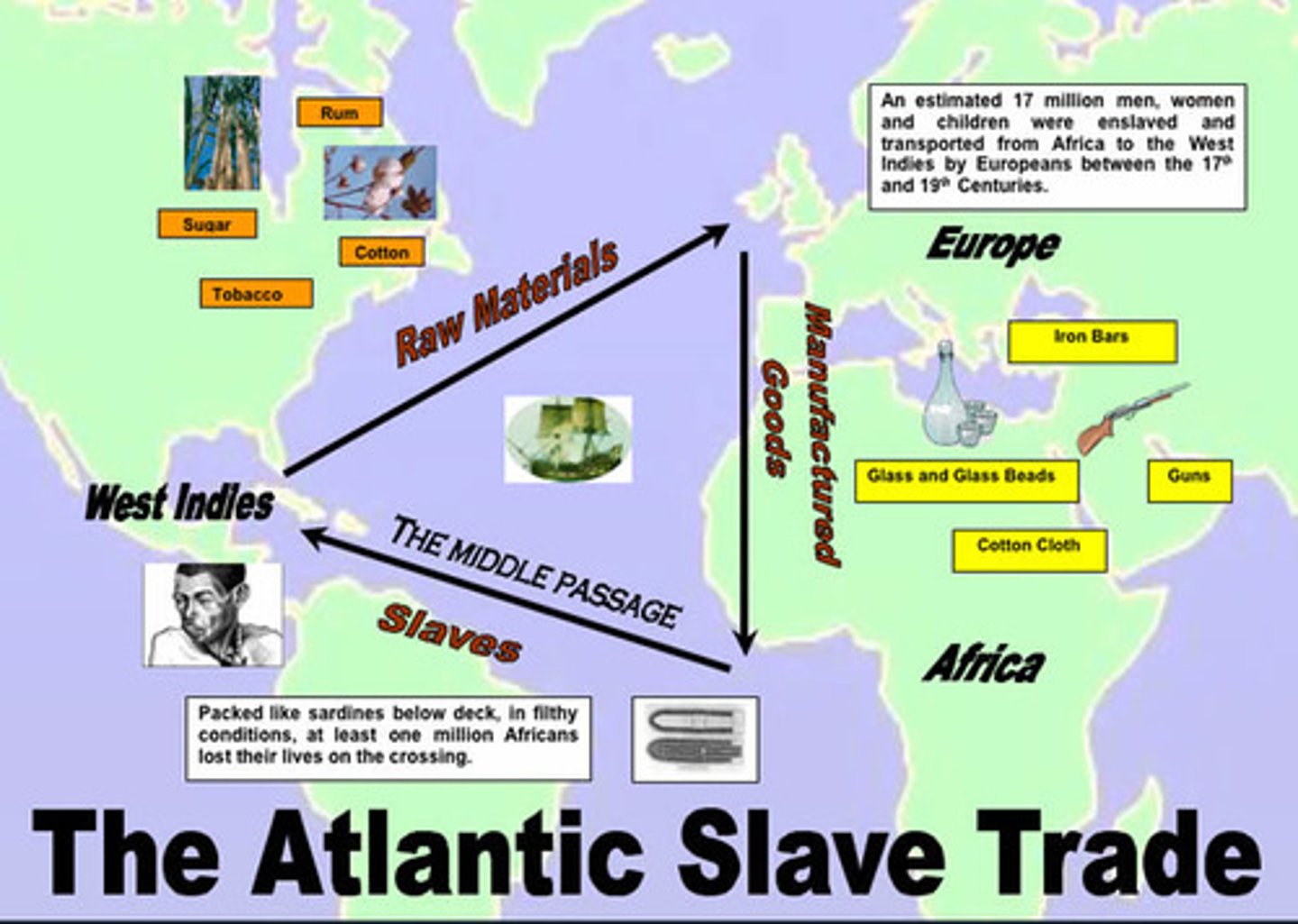
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies

Caravel
A small, highly maneuverable three-masted ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic.

Cartography
the science or the art of making maps
Joint-stock companies
businesses formed by groups of people who jointly make an investment and share in the profits and losses
East India Companies
British, French, and Dutch trading companies that obtained government monopolies of trade to India and Asia; acted independently in their regions.

Vodun
African religious ideas and practices among descendants of African slaves in Haiti.

Jesuits
Members of the Society of Jesus, a Roman Catholic order founded by Ignatius Loyola in 1534. They played an important part in the Catholic Reformation and helped create conduits of trade and knowledge between Asia and Europe.
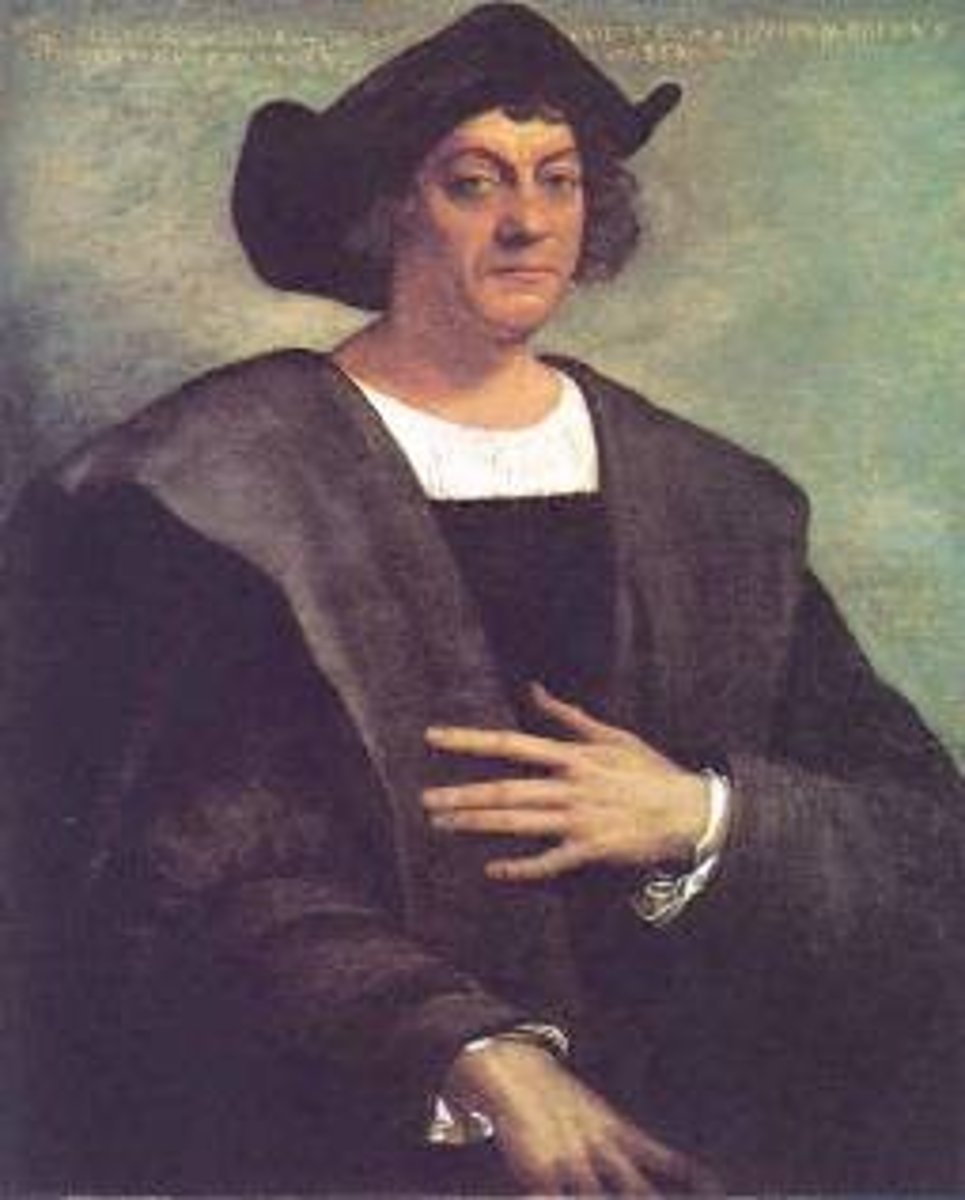
Columbus
Italian navigator who discovered the New World in the service of Spain while looking for a route to China (1451-1506)

Magellan
Portuguese explorer who sailed around the Southern end of South America and eventually reached the Philippines, but was killed in a local war there

Vasco da Gama
the first European to reach India by sea sailing around the tip of Africa.
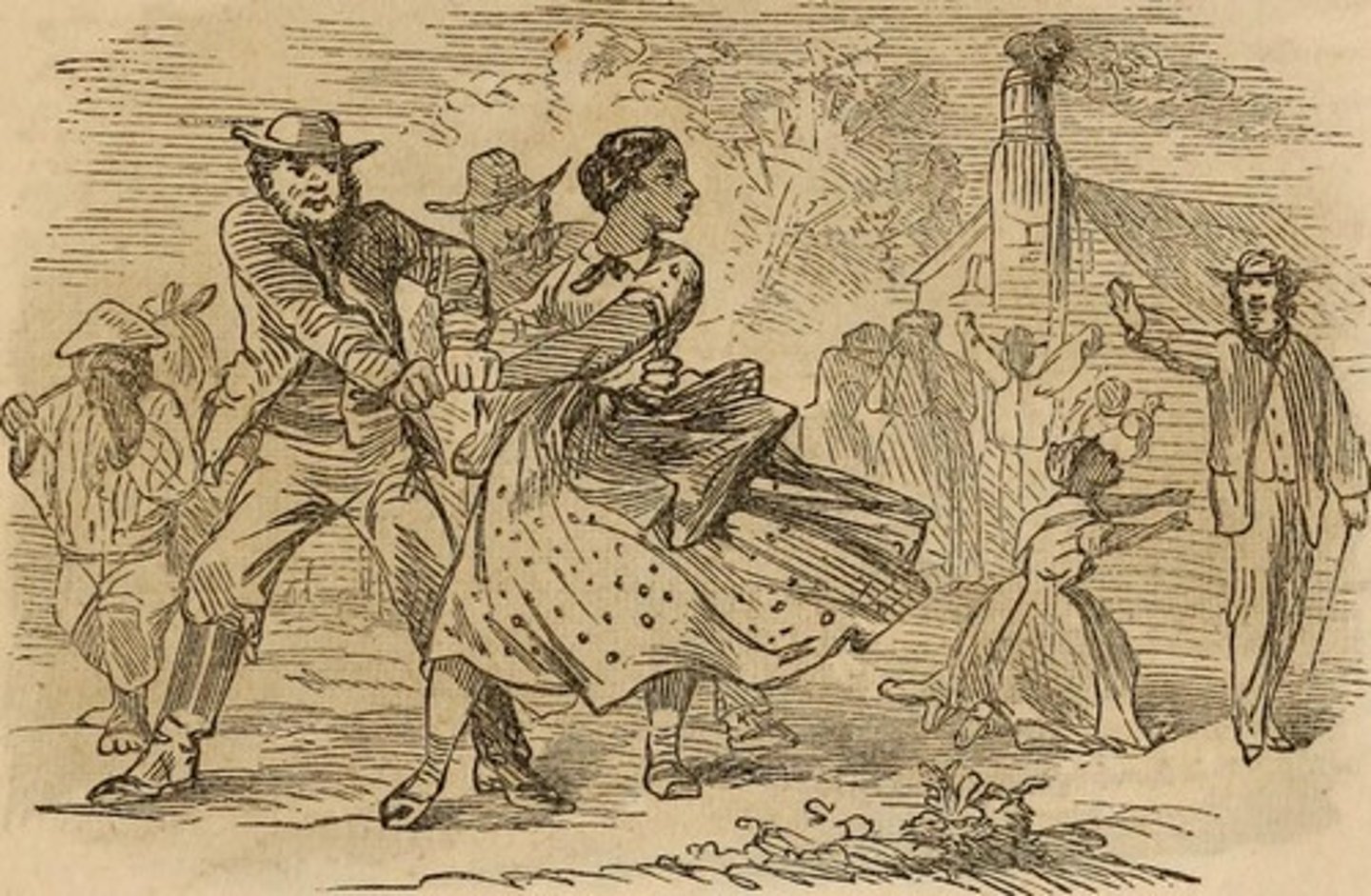
Chattel Slavery
Absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person.

Plantation Economy
This referred to the inefficient, slave-centered economy of the South where all land was used to grow large amounts of cash crops for export.
Indentured servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Before 1800 most were Europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were Asians.
Encomienda System
Spaniards received grants of a number of Indians, from whom they could exact "tribute" in the form of gold or labor
Hacienda System
Similar to feudal system, Rural estates in Spanish colonies in New World; basis of wealth and power for local aristocracy.
Mita System
economic system in Incan society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced, used by Spanish as forced labor
Peninsulare
a Spanish-born Spaniard residing in the New World or the Spanish East Indies, highest social rank in Spanish colonies
Creoles
a person of European ancestry born in the Americas, part of the Spanish casta system
Mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestry
Mulattos
Persons of mixed European and African ancestry
Casta
Spanish social system based on racial origins

Commercial Revolution
A dramatic change in the economy of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages. It is characterized by an increase in towns and trade, the use of banks and credit, and the establishment of guilds to regulate quality and price.
Potosi
a city in Bolivia: formerly a rich silver-mining center with the largest silver mountain
Absolutism
the acceptance of or belief in absolute principles in political, philosophical, ethical, or theological matters

Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.

Phillip II
King of Spain, 1556 - 1598; married to Queen Mary I of England; he was the most powerful monarch in Europe until 1588; controlled Spain, the Netherlands, the Spanish colonies in the New World, Portugal, Brazil, parts of Africa, parts of India, and the East Indies.

Peter the Great
(1672-1725) Russian tsar. He enthusiastically introduced Western languages and technologies to the Russian elite, moving the capital from Moscow to the new city of St. Petersburg.

Parliamentary monarchy
A government with a king or queen whose power is limited by the power of a parliament
Divine Rights
A belief of kings and monarchs that they have a God-given right to rule and that rebellion against them is a sin.
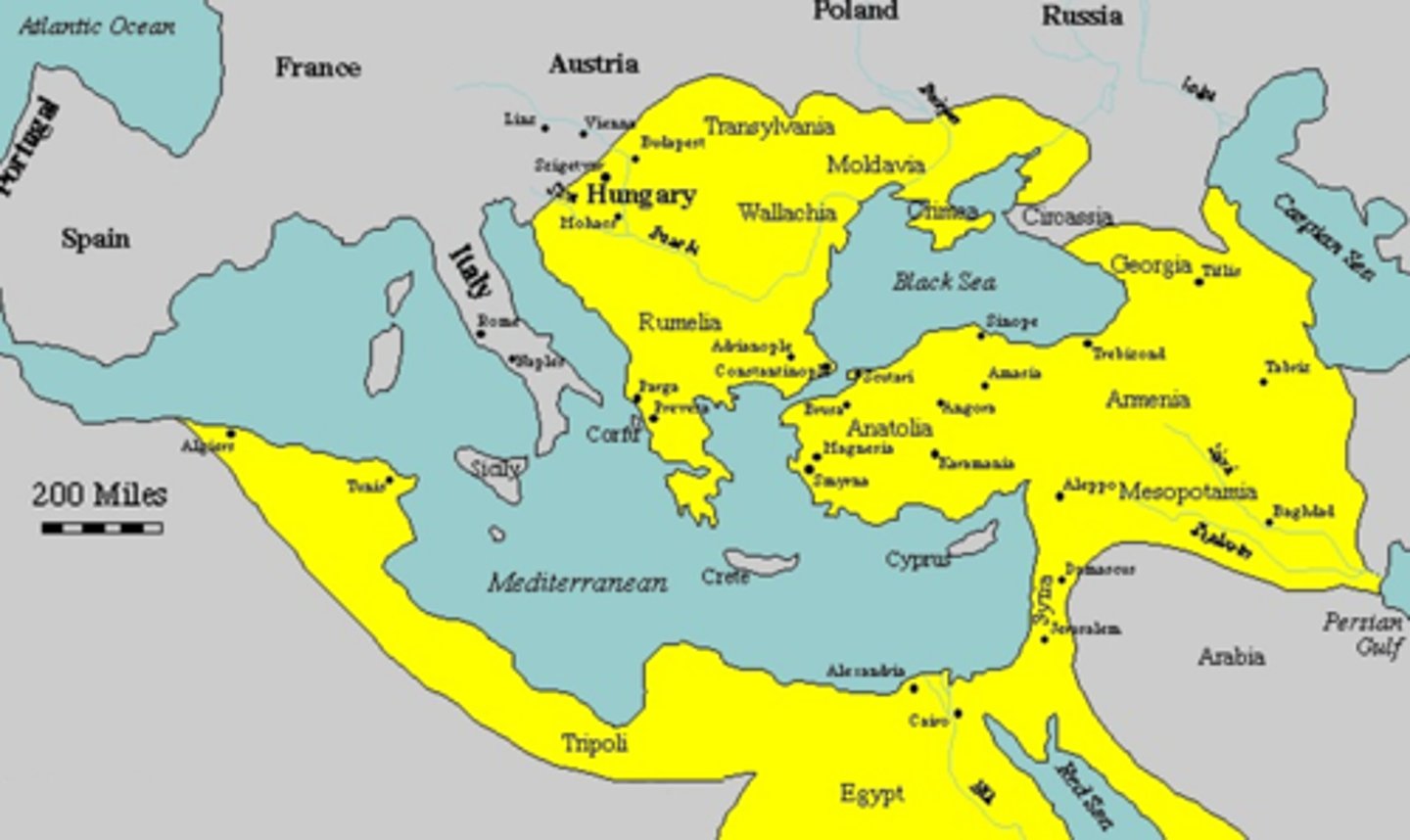
Ottomans
Turkic people who advanced from strongholds in Asia Minor during 1350s; conquered large part of Balkans; unified under Mehmed I; captured Constantinople in 1453; established empire from Balkans that included most of Arab world.
Mughals
muslim rulers over india, combined Hindu and Muslim, brought India to the peak of its political empire, had a single government with a common culture

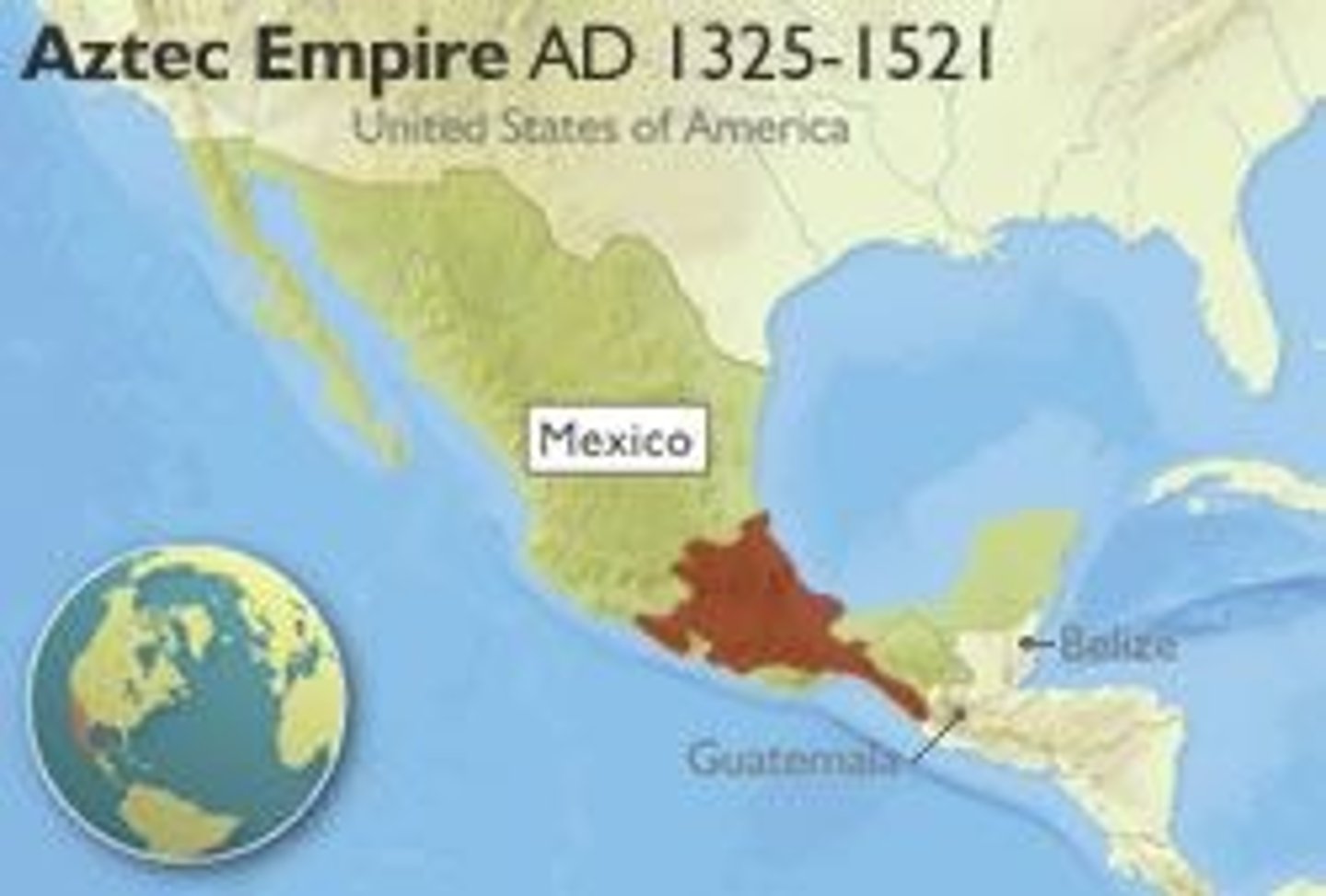
Aztecs
From their magnificent capital city, Tenochtitlan, this empire emerged as the dominant force in central Mexico, developing an intricate social, political, religious and commercial organization that brought many of the region's city-states under their control by the 15th century, also known as Mexica
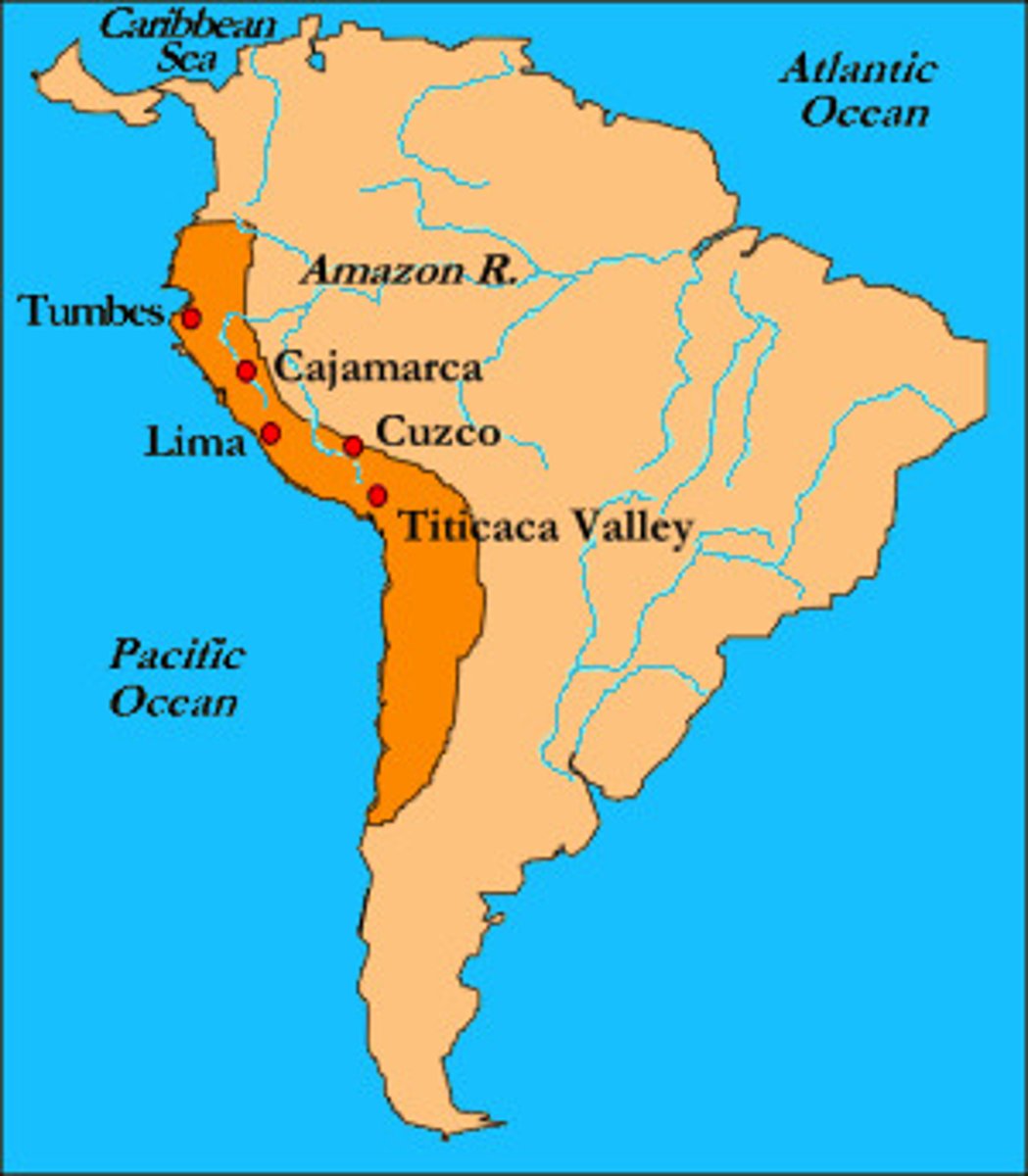
Incas
A Native American people who built a notable civilization in western South America in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The center of their empire was in present-day Peru. Francisco Pizarro of Spain conquered the empire.
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty was the ruling dynasty of China—then known as the Empire of the Great Ming—for 276 years following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
Tokugawa Shogunate
Unified daimyo (lords) to keep peace from 1600 to 1867 in Japan
Conquistadors
Early-sixteenth-century Spanish adventurers who conquered Mexico, Central America, and Peru. (Examples Cortez, Pizarro, Francisco.)
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange.
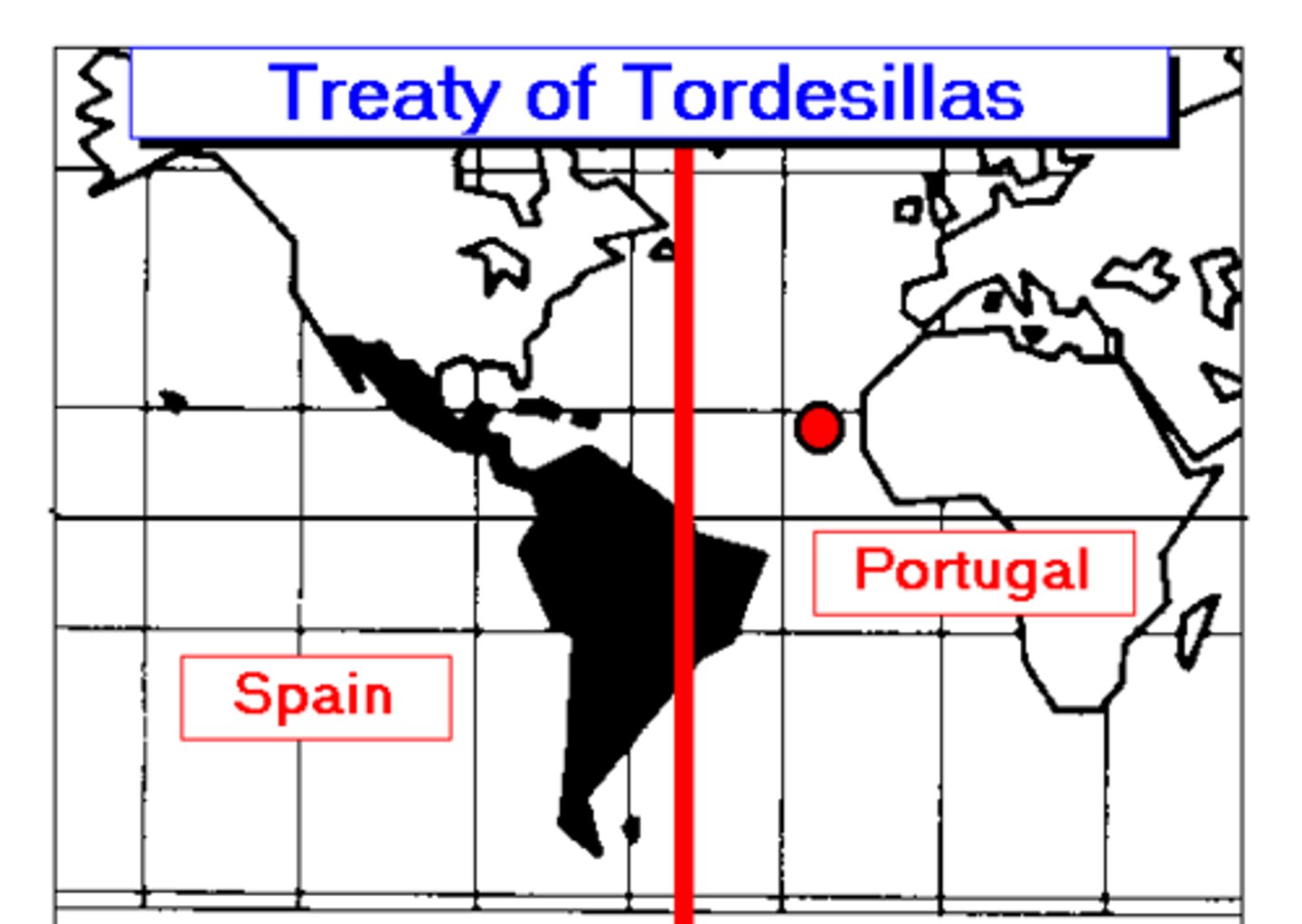
Treaty of Tordesillas
A treaty signed by Portugal and Spain to divide the new world.
Hernan Cortes
a Spanish Conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire
Francisco Pizzaro
Spanish conquistador who conquered the Inca's
Japan's Closed Country policy
As a result of Europeans entering and converting thousands to Christianity, the Shogun expelled or eliminated European entrance to the country
Primogeniture
right of inheritance belongs exclusively to the eldest son
Omani-European Rivalry
A trade rivalry between the Muslim Omani of the Middle East and the European traders.
trading post empire
16th Century. Built initially by the portuguese, these were used to control the trade routes by forcing merchant vessels to call at fortified trading sites and pay duties there.
Manila Galleons
Heavily armed, fast ships that brought luxury goods from China to Mexico and carried silver from Mexico to China.

Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation that directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.
Bartholomew Dias
led the Portuguese closer to discovering a water route to Asia

Jacques Cartier
French explorer who explored the St. Lawrence river and laid claim to the region for France
Samuel Champlain
French explorer who founded Quebec, the first permanent French settlement in North America
Maize
An early form of corn grown by Native Americans
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.
African Diaspora
the forced removal of Africans from their homeland to serve as slaves in the Americas
Asante
African kingdom on the Gold Coast that expanded rapidly after 1680. A major participant in the Atlantic economy, trading gold, slaves, and ivory.
Kongo
Central African kingdom in the 1400s that engaged in warfare and slavery
Price Revolution
increase in prices in 16th century-inflation-increased demand for goods-influx of gold and silver
Syncretism
a blending of beliefs and practices from different religions into one faith
Polygyny
a form of marriage in which men have more than one wife
Santeria
Cuban religion that combines Catholic and West African beliefs
Viceroy
Governor of a country or province who rules as the representative of his or her king or sovereign; think Spanish colonies.
Audiencias
advisory groups to viceroys in Spanish America
Dahomey
West African kingdom that became strong through its rulers' exploitation of the slave trade.
Ndongo
Angolan kingdom that reached its peak during the reign of Queen Nzinga (r. 1623-1663).
Maratha Empire
The Maratha or Mahratta Confederacy was a South Asian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. An excellent example of yet another rebellion against imperial power (the Mughals) in this time period
Pugachev Rebellion
Eugene Pugachev, a Cossack soldier, led a huge serf uprising in southwestern Russia; eventually captured and executed
William of Orange
Dutch prince invited to be king of England after The Glorious Revolution. Constitutional monarch
Metacom's War
Native Americans battle New England colonies; large percentage of native americans died
Pueblo Revolt
Native American revolt against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years; Spain began to take an accommodating approach to Natives after the revolt
Maroon Wars
Conflicts between the Jamaica Maroon settlements and the British after the British gained control of the island from the Spanish.
Gloucester County Rebellion
Indentured servants and slaves rebelled in this early resistance to slavery in colonial America.
Mehmed II
Ottoman sultan called the "Conqueror"; responsible for conquest of Constantinople in 1453; destroyed what remained of Byzantine Empire. Tolerant of Jews and Christians
Akbar
Mughal emperor known for religious tolerance. grandson of Babur who created a strong central government
Roxelana
Suleyman's wife. Power-hungry. Tricked into killing son (and heir) and best friend
Qing Empire
Empire established in China by Manchus who overthrew the Ming Empire in 1644. The last emperor of this dynasty was overthrown in 1911 by nationalists.
Manchus
Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644, which was the last of China's imperial dynasties.
Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
Ivan the Terrible
Confirmed power of tsarist autocracy by attacking the authority of the boyars; continued policy of expansion; established contacts with western European commerce and culture.
Timars
administrative and tax collecting grants handed out by the sultan. Charged with administrative duties upon collecting.
Boyar
landowning noble in Russia under the tsars
Sephardic Jews
Jews whose traditions originated in Spain and Portugal
Ashkenazi Jews
Jews whose traditions originated in central and eastern Europe
Sulieman the Magnificent
Ottoman Turk leader who modernized the army and conquered many new lands, and extended the Ottoman empire in the mid 16th century