National 5 Biology - Multicellular Organisms
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is the purpose of blood?
To transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and many other vital substances throughout the body
What are the main components of blood?
Plasma, white blood cells and platelets, and red blood cells
What is plasma?
The liquid part of blood that carries the other substances
What are white blood cells?
Cells that are part of the immune system and attack pathogens
What are the two main types of white blood cell?
Lymphocytes and phagocytes
How do lymphocytes attack pathogens?
They produce antibodies
How do phagocytes attack pathogens?
By engulfing and then digesting them
What is mitosis?
Cell division of normal body cells (also known as somatic cells)
What does mitosis result in?
Two genetically identical daughter cells
What is meant by the diploid chromosome complement?
That a cell contains two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis provides new cells for growth, repair of damaged tissues and replacement of dead or damaged cells. It also maintains the diploid chromosome complement
How is mitosis involved in growth?
The number of cells increases as the divisions take place, hence the organism grows
Why is it important for the diploid chromosome complement to be maintained?
To ensure that the daughter cells have all of the genetic material necessary to carry out their functions
What does a cell do in preparation for mitosis?
Chromosomes replicate, with each chromosome forming two identical chromatids joined at the centromere and becoming visible
What happens during mitosis, after the chromosomes become visible?
They line up at the equator of the cell
What happens during mitosis, after the chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell?
Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes, then contract
What happens during mitosis, after spindle fibres contract?
Pairs of chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
What happens during mitosis, after pairs of chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell?
Two new nuclear membranes form
What is the final stage of mitosis?
The cytoplasm divides and two genetically identical daughter cells are produced
Which cells in the body are diploid?
All of them except the s*x cells (gametes)
Which cells in the body are haploid?
Only the s*x cells (gametes)/sperm and egg
Which disease is caused by uncontrolled cell division?
Cancer
What are stem cells?
Unspecialised cells which can divide in order to self-renew and have the potential to become different types of cell
What are the two main types of stem cell?
Embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells
What is the main difference between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells can give rise to any type of cell within the body, but adult stem cells can only give rise to a limited number of related cell types specific to the tissue where they are found, such as bone marrow stem cells differentiating into various types of blood cells
What is the importance of the specialisation of cells?
Cells become specialised to give rise to a variety of cells, each with a particular function
State the hierarchy of organ systems.
Cells —→ tissues —→ organs —→ organ systems —→ organism
What is the nervous system made up of?
The central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which is made up of all other nerves extending from the CNS
What does the central nervous system (CNS) consist of?
The brain and spinal cord
What does the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consist of?
All nerves which extend from the CNS
What are neurons?
Nerve cells
What are the three main types of neuron?
Motor, inter, and sensory
What is the function of a sensory neuron?
To send an electrical impulse from a sense organ to the CNS
What is the function of an inter neuron?
To send an electrical impulse from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron, acting as a bridge between them
What is the function of a motor neuron?
To send an electrical impulse from the CNS to an effector
What is an effector?
A muscle or gland
How are messages passed along and between neurons?
Electrical impulses carry messages along neurons, and chemicals transfer these messages between neurons, at synapses
What is a synapse?
The minute gap between neurons which allows for communication
How do synapses work?
Electrical impulses cannot jump across the gap between the two neurons, so they are converted into a chemical called a neurotransmitter and they then diffuse across the gap
Why are reflexes useful?
They are rapid and protect the body from harm
Explain a reflex arc.

How is information passed along a neuron?
Electrical impulses
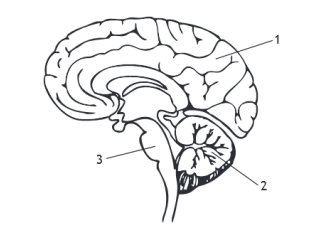
Identify each part of the brain.
1 = cerebrum, 2 = cerebellum, 3 = medulla
What is the function of the cerebrum?
To control conscious thought and reasoning
What is the function of the cerebellum?
To control balance and co-ordination
What is the function of the medulla?
To regulate breathing and heart rate
Which part of the brain is responsible for consciousness and reasoning?
The cerebrum
Which part of the brain is responsible for balance and co-ordination?
The cerebellum
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating breathing and heart rate?
The medulla
What do endocrine glands do?
Release hormones into the bloodstream
What is a hormone?
A chemical messenger that travels in the bloodstream
What is the function of hormones?
To regulate and control a variety of functions within the body, such as metabolism, reproduction, and homeostasis
Explain why hormones only act on their target tissues.
A target tissue has cells with complementary receptor proteins for specific hormones so that only that tissue will be affected by those specific hormones
List five features of hormones.
They are made of protein, they travel in the bloodstream, they are released by endocrine glands, they only affect target tissues with complementary receptor proteins, and they can have a long term effect
Insulin has an effect on cells in the liver, explain why insulin does not affect cells in other organs.
Cells in other organs don’t have the complementary receptor proteins for insulin, only the cells in the liver do
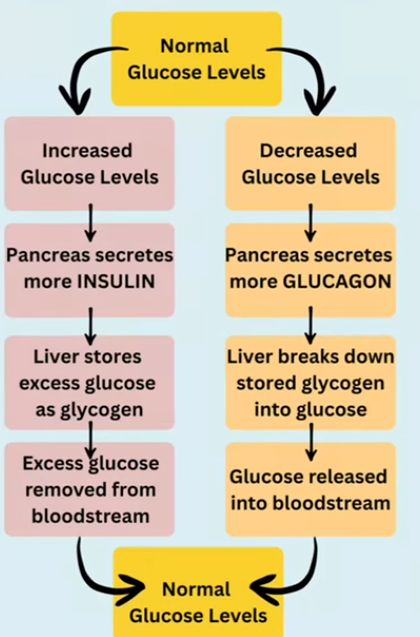
Describe how blood glucose is returned from low to normal levels in the human body.
The pancreas detects the low concentration of blood glucose and releases glucagon, which travels in the bloodstream to the liver. The liver then converts glycogen into glucose. Glucose is released into the bloodstream, returning blood glucose levels to normal
Describe how blood glucose is returned from high to normal levels in the human body.
The pancreas detects the high concentration of blood glucose and releases insulin, which travels in the bloodstream to the liver. The liver then converts excess glucose into glycogen, returning blood glucose levels to normal
Which hormone is released by the pancreas when blood glucose levels are too high?
Insulin
Which hormone is released by the pancreas when blood glucose levels are too low?
Glucagon
Which organ releases insulin and glucagon?
The pancreas
Which organ converts excess glucose into glycogen?
The liver
Name the chemical messengers carried from one part of the human body to another in the blood.
Hormone
Name the type of gland that releases hormones into the bloodstream.
Endocrine gland
Draw a flowchart to show the body’s way of regulating blood glucose.
What is a gamete?
A s*x cell
What are the human gametes?
Sperm for males and egg for females
Are gametes haploid or diploid?
Haploid
What happens during fertilisation?
When the nuclei of two haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote, which divides to form an embryo
Why do sperm cells have tails?
So they can swim towards the egg
Who do egg cells have food stores?
To provide food for the growing embryo
Where are eggs produced?
The ovaries
Where is sperm produced?
The testes
What are three plant organs?
Stems, roots, and leaves
What is the upper epidermis of a leaf?
The thin, transparent layer with no chloroplasts that allows light to pass through
What are palisade mesophyll cells?
Long cells that are tightly packed together and have many chloroplasts, making them the site of most photosynthesis within the leaf
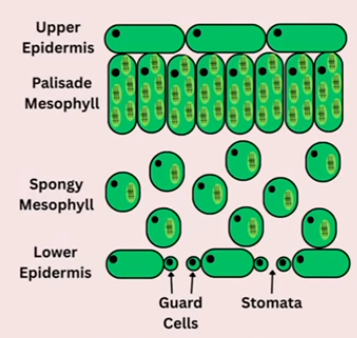
What are stomata?
Tiny pores on the underside of a leaf that allow for gases and water to diffuse in and out
Where on a leaf would you find stomata?
On the underside of the leaf