bis 102
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
midterm 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Structes
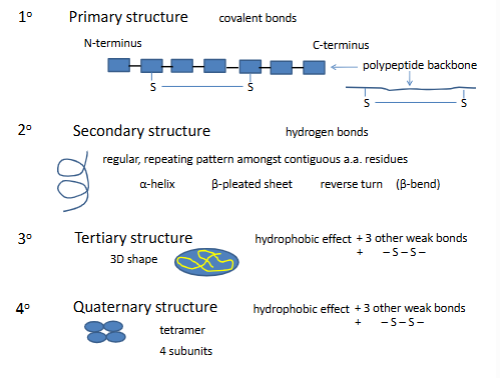
Primary structure
see if angiogenin destroys RNase (meaning there is enzyme activity)
in the x-ray, some x rays get deflected at different angles (dark sopts are where it is hit) comes up with 3d structure were all atoms are
helps determine second and tertiary struct
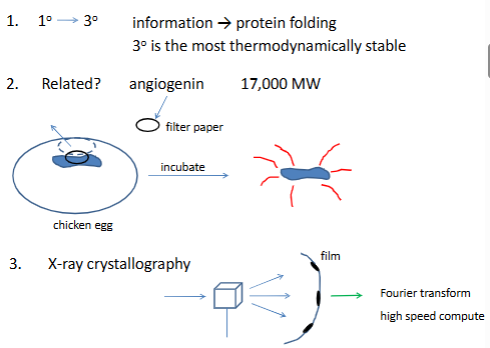
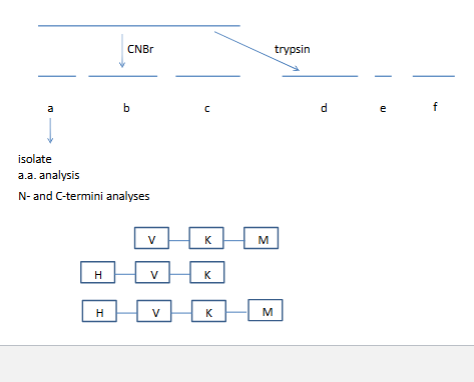
sequence a protein
stategy 1. generate small fragments
look for overlapping sequeces
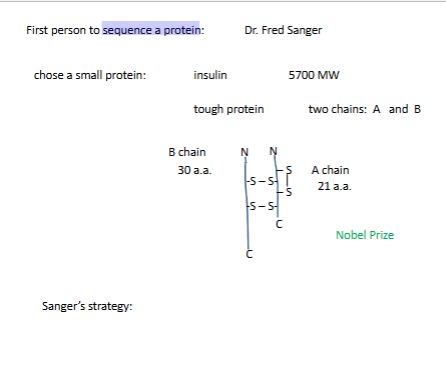
Tools that Sanger had
trypsin down K and down R
chumotryspin aromatic a.a down
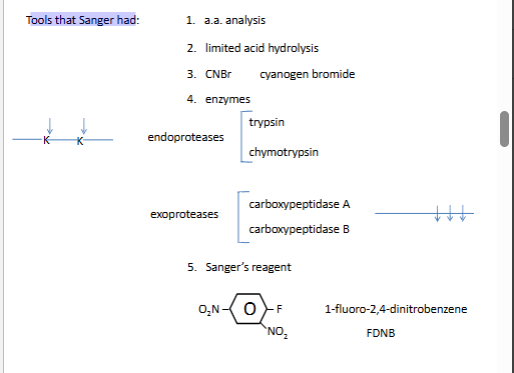
Sanger N-terminal chemistry
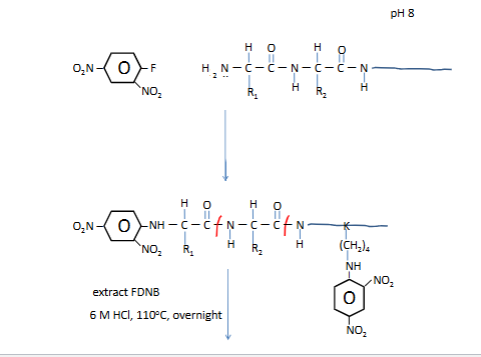
DNP is yellow
we need the yellow guy and run through stnadards to find who he is
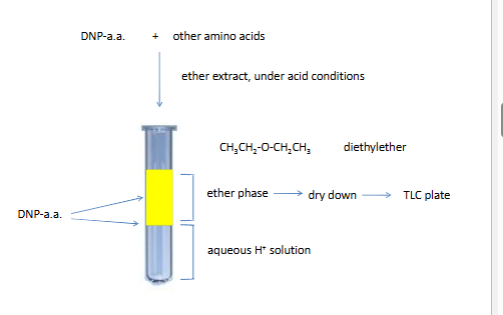
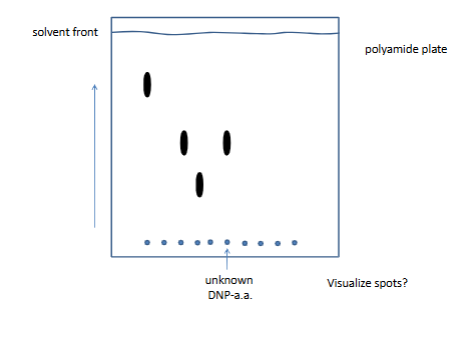
thin layer crmo togrsahy
arrow is polar solvent (polyamide plate)
plate si never homegenoues
nonpolar for the secon picture
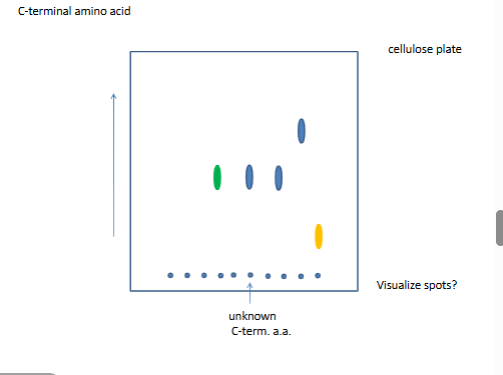
Overlapping sequences
trypsin cuts right hand side
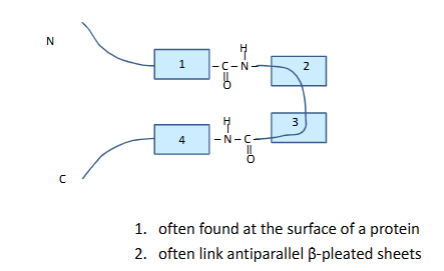
Secondary structure
reverse turn
one h bond holds reversre turn
many times its a proline not 2 though
cant have big guys or repusion
no di sulifde bonds
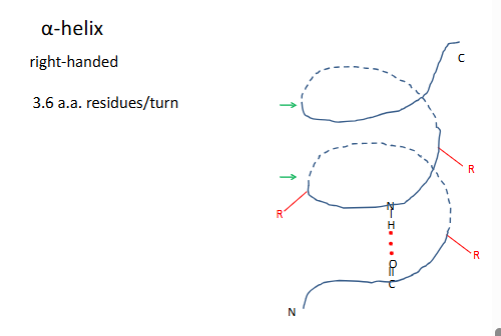
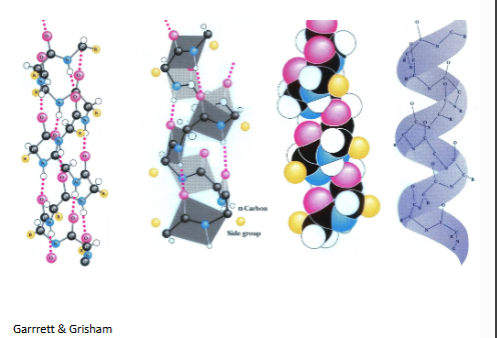
α-helix
most are right handded because most are made o l amino acids
rgroups on the outside are pointing down
residue 1h bond with residue 4
(-60,-50
# of h bonds=n-4 (n=residues)
avg length 10 aa residues
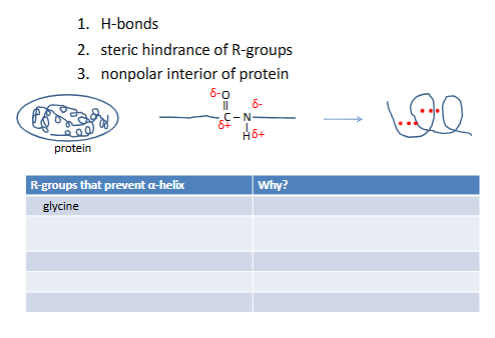
What causes an α-helix to form?
-glycine too flexible
roline wrong geo no h on N
-/- +/+ repulsion
W-W F-F steric hinderance
seerine mpefer h bond with h20
α-helix
dots are h bonds, in gray is the planes that are formed by the atoms), r groips are yellow
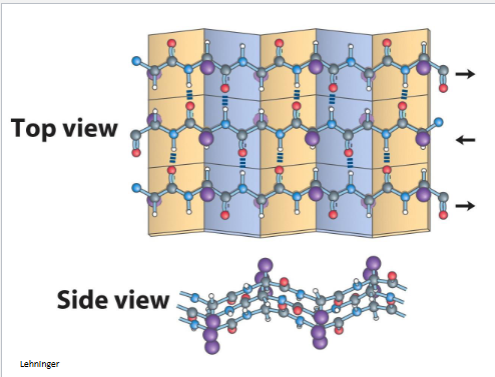
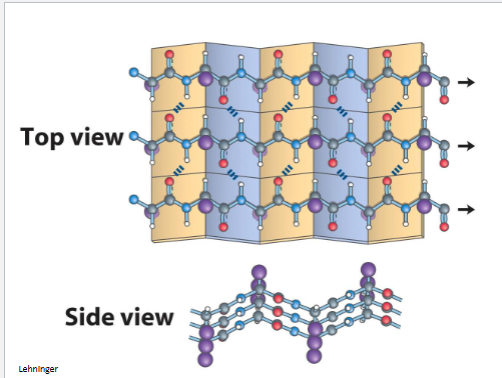
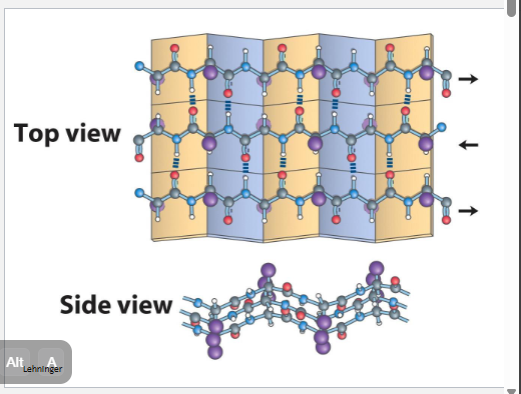
β-pleated sheea
serveral hydrogen bonds (how many depends on length) weaker if they are not in striaght line, both diagrams can make different mixture toghter
a helix stand by itslrf byt b can have family vin diseal
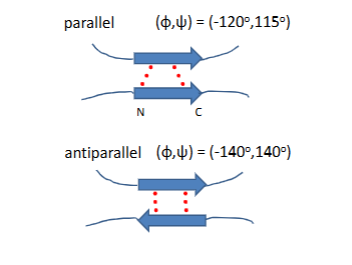
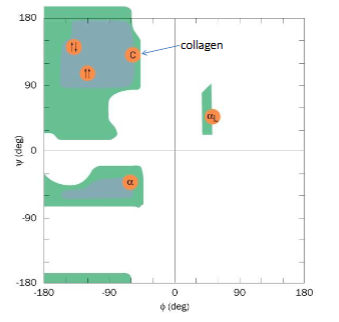
Ramachandran plot
organe is anti b pleated beta sheet
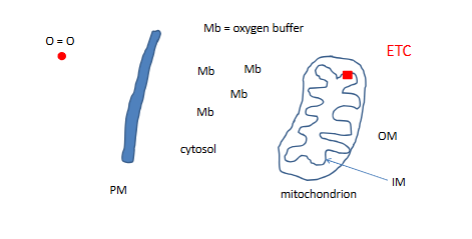
Myoglobin
this protien is sittign in muscles cells
etc is where o becomes water
mb has a tricky taks: how do yuo carry )2 without becoming oxdized
Mb 17000MW
the functional protein has heme ← protroporphin IX +Fe2+
apoprotein with out function
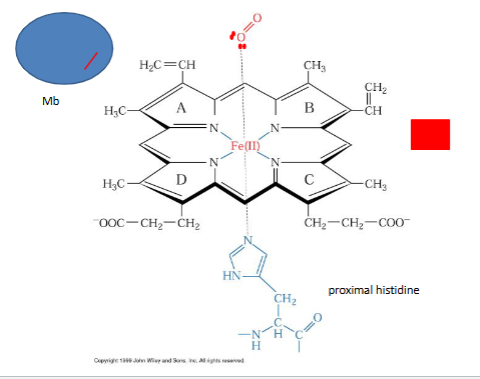
heme
letters are ring systems, iron i bound to N from cov. bonds, 5 covanletn bonds 4 ring and 1 from behind , amino acid is histdine base form
90-degree heme
all bottom arrows are illed
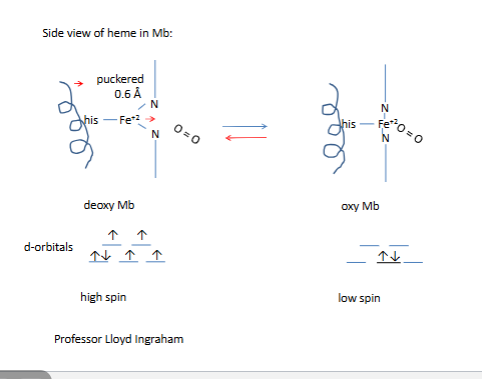
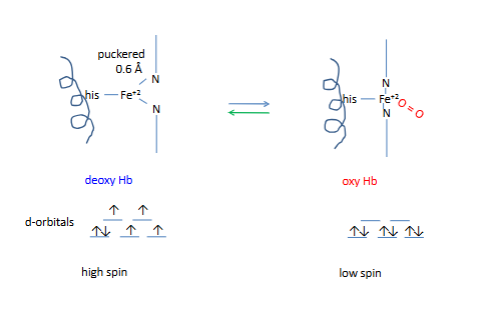
Side view of heme in Hb subunit (α or β
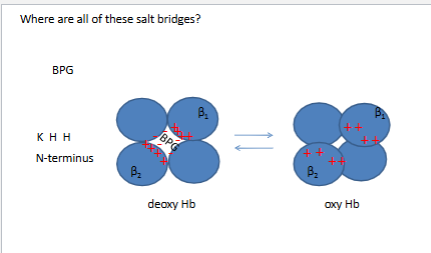
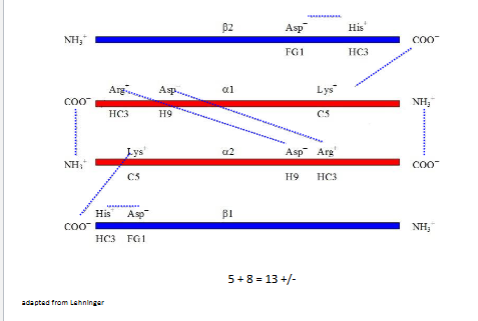
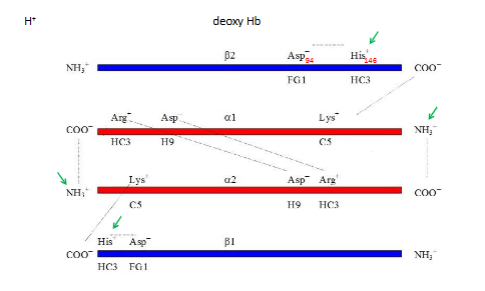
~13+/- on left (salt bridges)
Where are all of these salt bridges?
5 salt brdiges in the central cavity of the molecule at the end of the channel
Other salt bridges of deoxy Hb
CO2
bottom forms new+/ -
-0 to Nh is carbamate
carbmate+ H
binding co2 is alllosteric not binfin whereo2 binds but inderctly affect O2
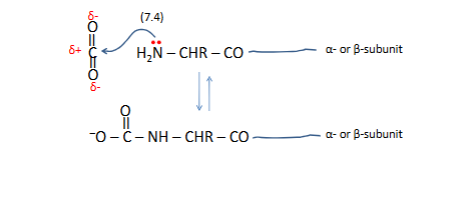
Wherre do protones binds
where is ther net bindin of H+ at these sites
1 dramtic changes in pka oxy Hb →← deoxy HB
more H+ in tissues
Ph= pka +log b/a
7.6=6.2 +log b/a
hence no salt bridge
virtually no + charge on H
r is too far away coulomb’s Law
for tissue 7.2=7.7+logb/a
a=1/1.316=76%

What environmental factors affect a pKa
2 which xharge is thermo favored
what will lead to the lower energy
up to accpmlish thiw
which charge is thermo favored
pka down to accomplisjed
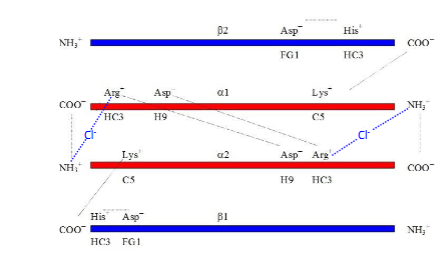
Cl-
pka up
dr ani
urea know struct, it forms h bonds
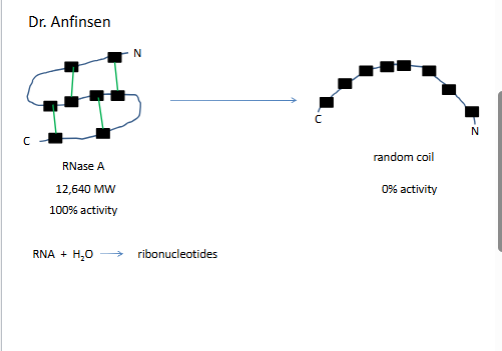
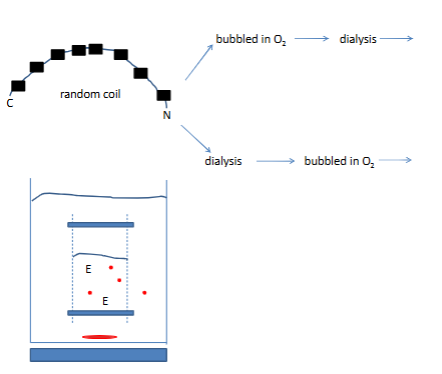
top 1% activity 1/105
→ trace amounts mercapteothanol 10gr 4C
bottom 95% actvitvit
red dots are urea, at time zeor no urea so net flow is out
con.1. all info is in the 1
3 is the ost thermo stbale
disuslfide bonds prodive strngth but weak bonds are more important

in viv they are syntg as inactive precursors
proinsulin (took pic)
What if all of the RNase A was not completely denatured?
amino acids→synthesice RNase A
Kinetics of protein folding
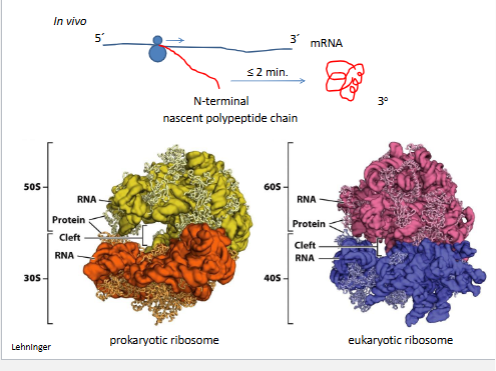
How then does protein folding occur?
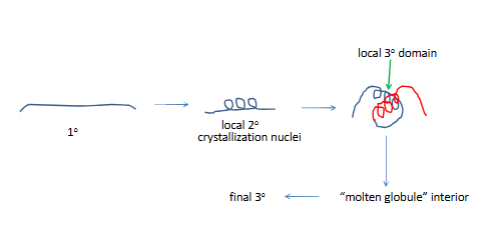
How then does protein folding occur?
no one path to fnial 3 struct
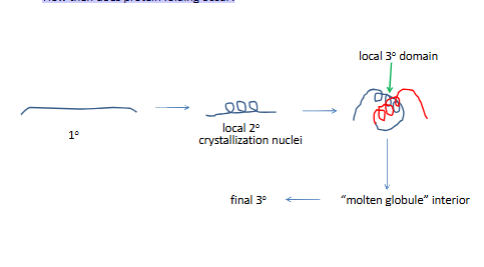
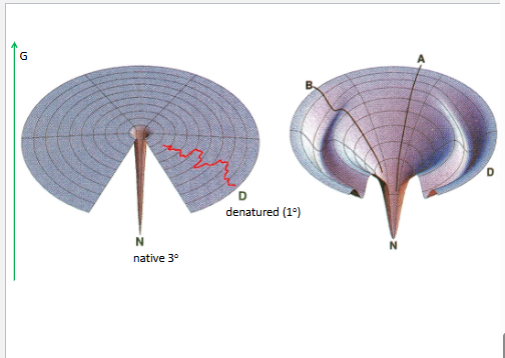
right is order collpased
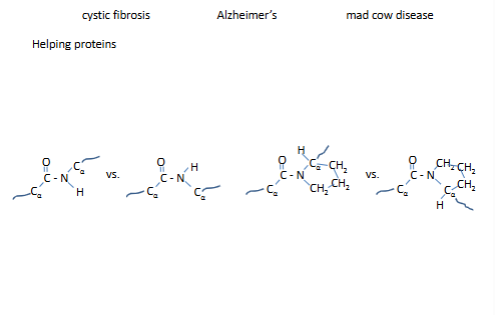
Several diseases are associated with improper protein folding:
protein disulfuide isomerase
catalyzes disulfide reaction in the ER
proline race mase
trans 1000 cis 1
trans 4 csi 1
← proloene racemarse
chaperionins proten complexes that allo phobi interactions a second chance
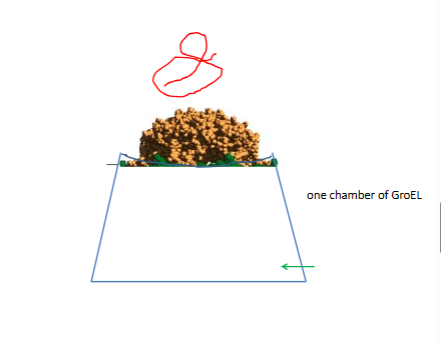
inerior holds 90000mw
red is incorreclty folded
interior loines with bydrophobic residues
bottom atp hydrolysis
lid off then gren ort
protien does not fild faster
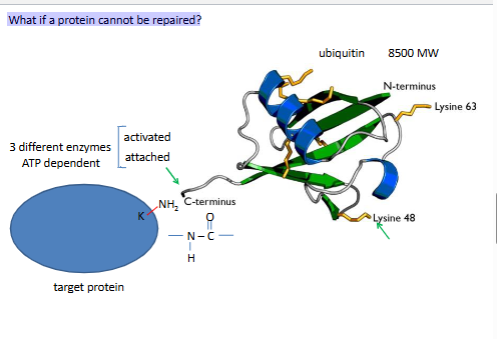
What if a protein cannot be repaired?
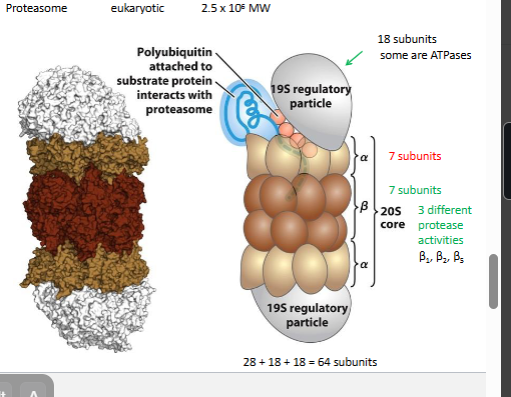
ubiquitin proteasome
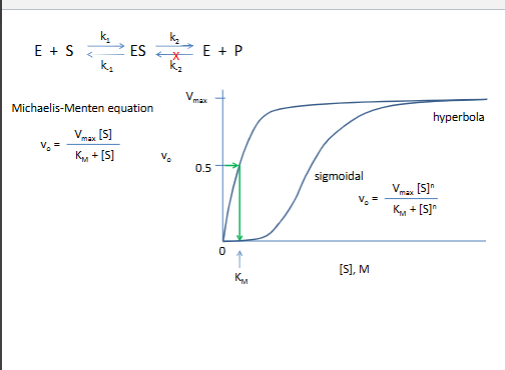
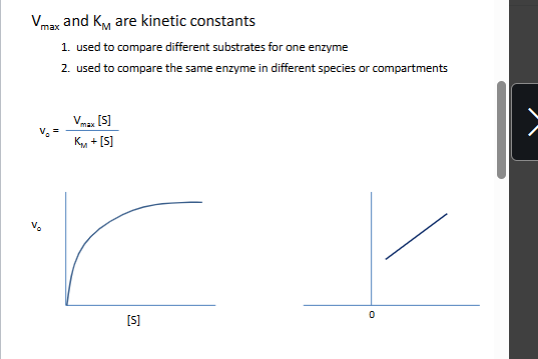
MM equation
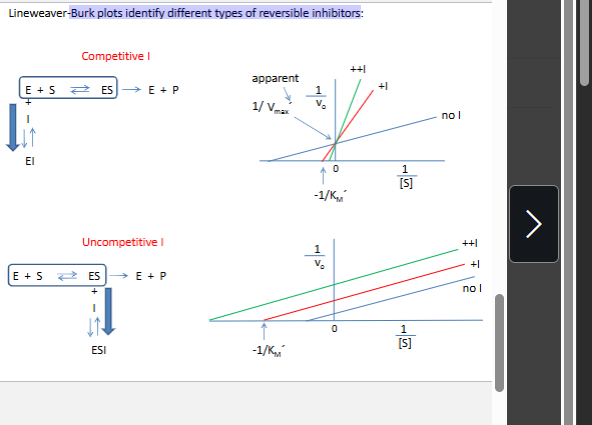
Burk plots identify different types of reversible inhibitors:
Active site participants:
Binding?
all 20 aa res idues
cofactors mg2+,Zn2+, Fe2+, Mn2+
coezemzmes : NAD FMN lipoic acid biotin
Catalysis?
NU attckers C S K H H2O
gen acid cat. (dono pro at actvit site) - 7 inozable group can do this (in prtonated form)
gen bas cat - 7 inozable group can do this argine
cofactos
coenzymes
ph affects
all above
struct of enzymes
substrates (any chargees care about ph)
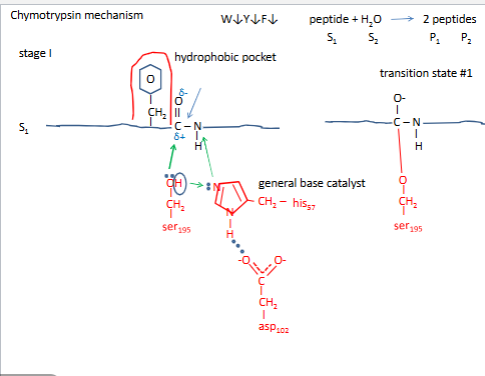
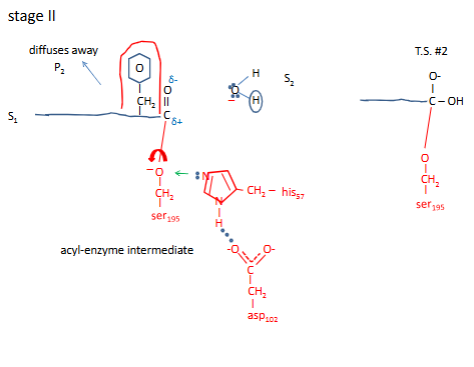
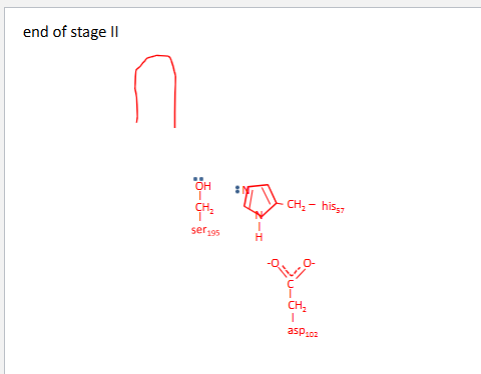
Chymotrypsin mechanism
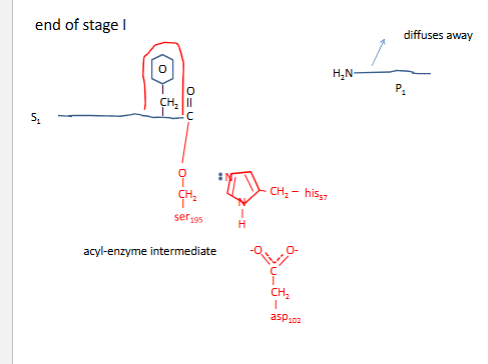
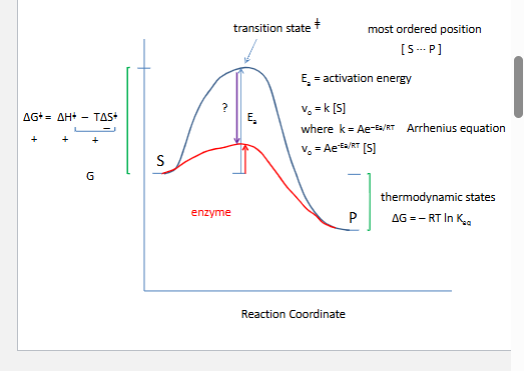
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
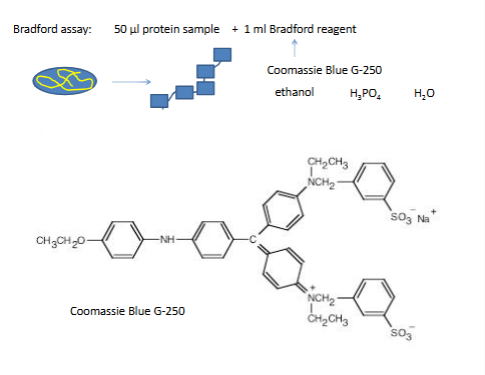
Bradford assay
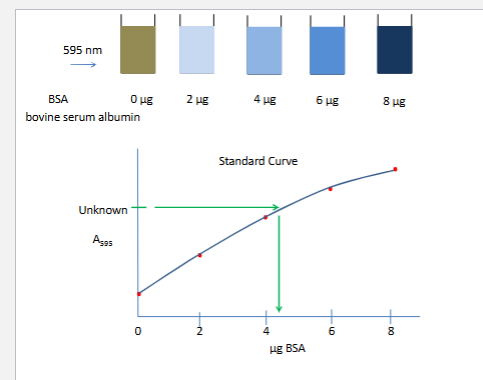

1 enzyme Z assy
bradford protein assay
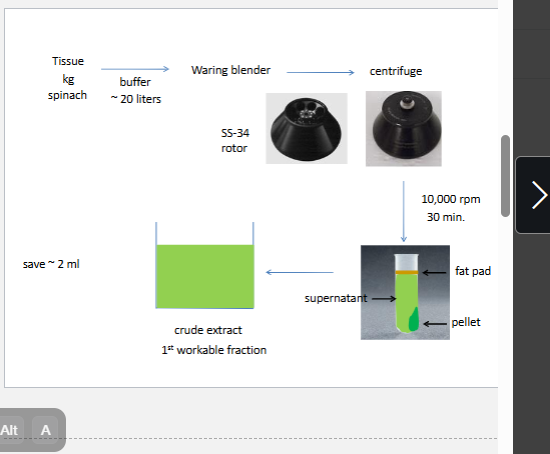
need to reduce te vol
2 need to remove nucleic acids and cho polymers (if kept in they will bind to everything)
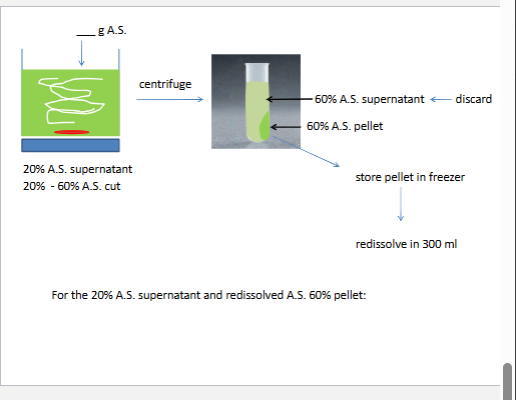
we will do two NH42 si4 cuts cuts refer to precipate
0%-100% saturation ~4.2M at 4*C
the first cut removes nucleic acids and CHO polymers
th second cut reduces the voulume and safty the enzyme
at best givs 2x purfication
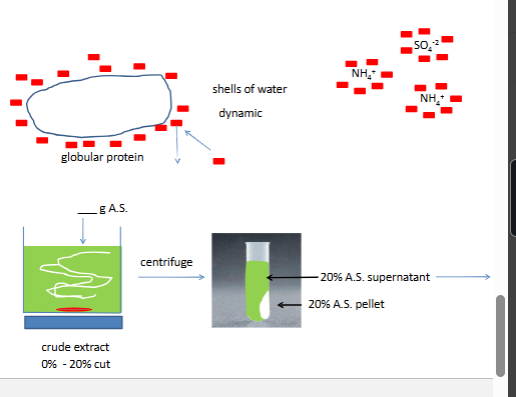
how does ammonium sulfate fractionation work
comp for water
1 enzyme Z assy and bradprotein essay calcualte specific activity fold purfication and % yeild
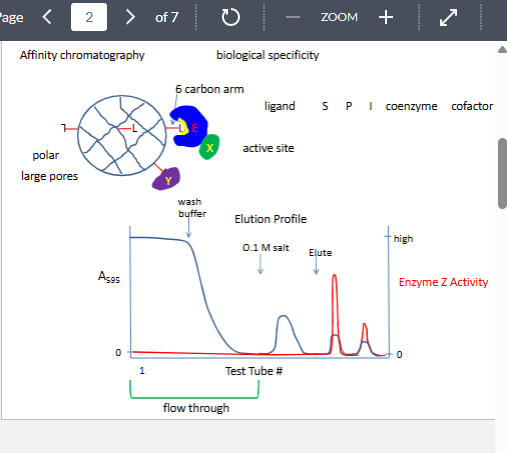
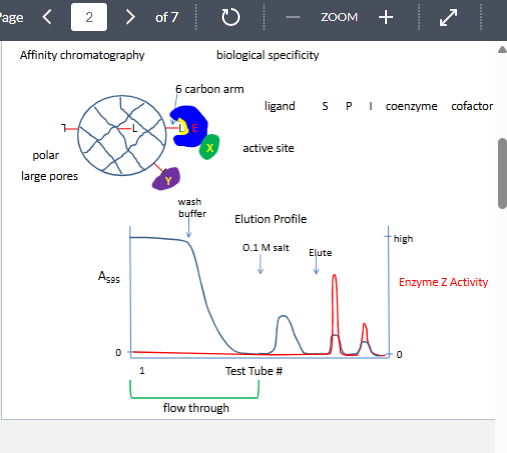
affinity chromatography
only technique that can separt biologically active form from denautre from
can give 2000x purficatipn
why might it not work
lignd presented to the enzyme inthe wrong confoguration
enzyme has two substrate and the other substart must bind first
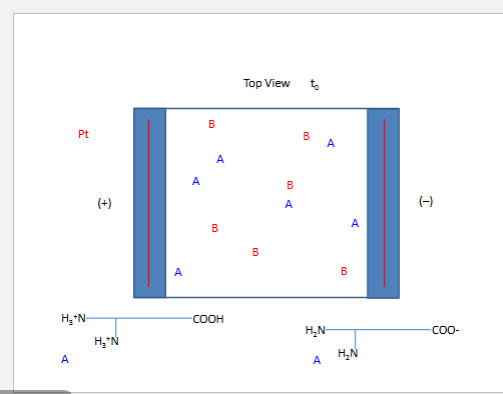
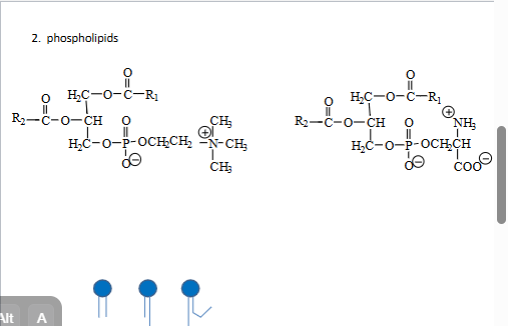
2. phospholipids
phosphodiester 4 amine
phosphatidylcholine PC
phosphatidlyserine PS
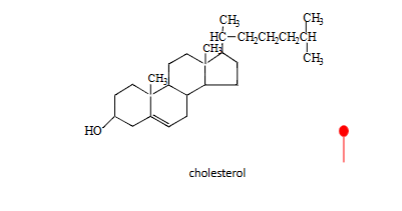
terpenoids
SDS fatty acids lyoplipids
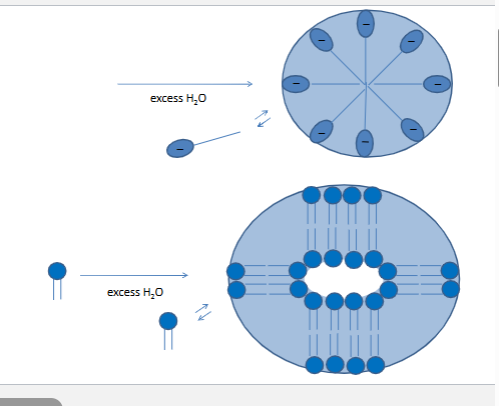
facilitated diffusion
steropsefcific
saturable