Drug Treatment for Depression
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what is clinical depression also known as?
major depressive disorder
what type of disorder is clinical depression?
psychiatric, affective disorder
what is the second leading cause of disability in adults?
clinical depression (after cardiovascular disease)
what is the average age of onset for clinical depression?
mid to late 30s
what is the female to male ratio in clinical depression?
-2:1 (females are twice as likely as males)
-could be due to more female getting clinical diagnosis
what are the two sub-classes of clinical depression?
-endogenous (no obvious stress, chemical imbalance)
-reactive (identifiable stress trigger)
how is clinical depression diagnosed?
by continued, daily presence of symptoms for more than 2 weeks
what are the emotional symptoms of clinical depression?
-sadness or low mood
-loss of enjoyment in things previously pleasurable (anhedonia)
-low self esteem (hopelessness, worthlessness, guilt)
-suicidal thoughts
what are the biological symptoms of clinical depression?
-major change in weight (gain or loss)
-sleep disturbances (insomnia or excessive sleep)
-fatigue or loss of energy
-slowness of thought and action
how many symptoms are required for diagnosis of clinical depression?
at least 5 of the symptoms, on a daily basis over 2 weeks
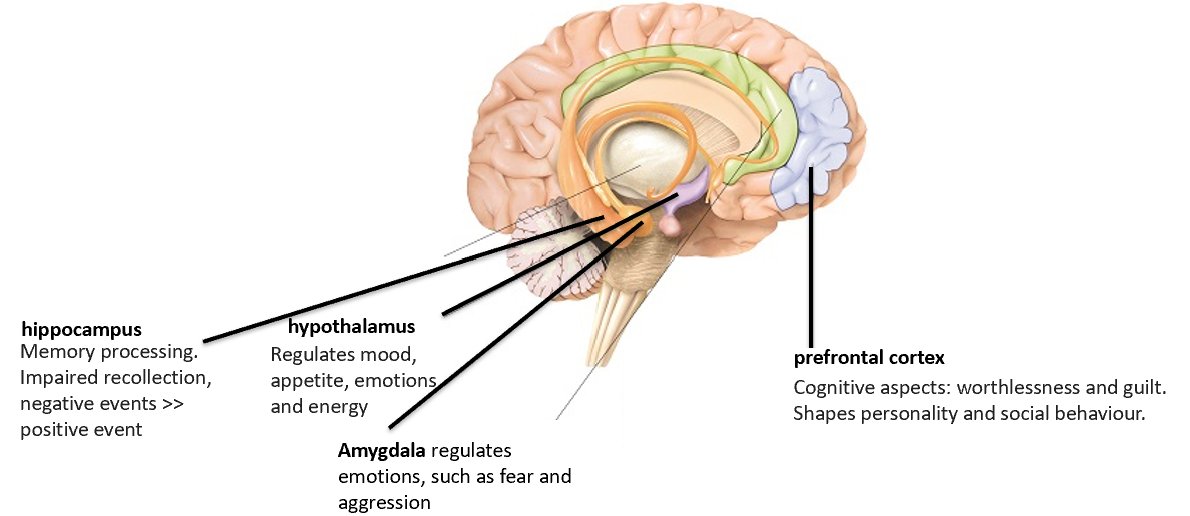
what brain regions are involved in depression?
-cortical and sub-cortical limbic regions including amygdala
-hippocampus
-hypothalamus
-prefrontal cortex
-anterior cingulate cortex
what is the role of the amygdala in depression?
regulates emotions such as fear and aggression
what is the role of the hippocampus in depression?
-memory processing
-impaired recollection with negative events recalled more than positive events
what is the role of the hypothalamus in depression?
regulates:
-mood
-appetite
-emotions
-energy
what is the role of the prefrontal cortex in depression?
cognitive aspects including worthlessness and guilt. shapes personality and social behaviour
what was the first antidepressant drug discovered?
iproniazid
how was iproniazid discovered?
-by chance (reverse drug discovery)
-chemists developing tuberculosis treatment found it destroyed bacteria in vitro but didn't cure tb
-however, patients went from lethargic and sad to better mood, increased appetite, and improved sleep
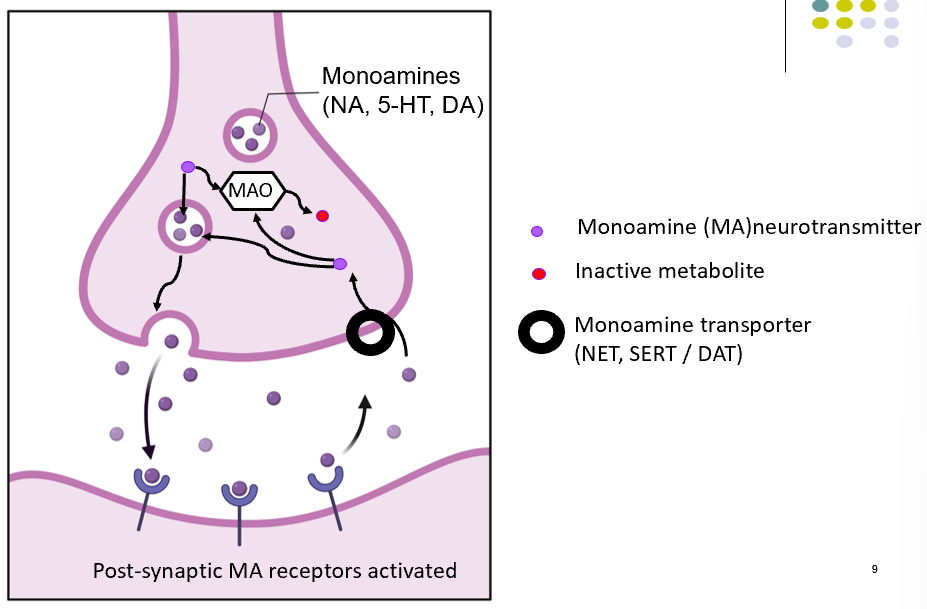
what enzyme does iproniazid block?
monoamine oxidase (mao), which breaks down monoamines
what are the three main monoamines affected by iproniazid?
serotonin, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine
what is reverse drug discovery?
-when a drug's therapeutic effect is discovered by observing its effects in patients
-rather than designing it for a specific target (disease → drug, instead of usual drug → disease direction)
what is the monoamine hypothesis of depression?
hypothesis by schildkraut (1965):
-decreased monoaminergic transmission is responsible for depression
-lower noradrenaline
-lower serotonin
-lower dopamine
-noradrenergic, serotonergic and dopaminergic pathways innervate forebrain areas and frontal cortex involved in mood / behaviour.
what are the three main monoamine neurotransmitters implicated in depression?
noradrenaline (na), serotonin (5-ht), and dopamine (da)
what evidence supports the monoamine hypothesis?
-reduced monoamine metabolites present in csf of depressed patients
-drugs that elevate na/5-ht/da improve mood in patients (through reduced reuptake or reduced intracellular breakdown)
-drugs that deplete monoamine stores (reserpine) cause depressive symptoms
what evidence contradicts the monoamine hypothesis?
-some drugs which elevate na/da/5-ht do not exhibit antidepressant activity (amphetamine, cocaine)
-monoamine levels increase rapidly with antidepressant drugs but clinical relief takes 2-4 weeks (lag)
how might the therapeutic lag be explained?
the quick increases in monoamines may produce secondary neuroplastic changes on a longer timescale (gene changes)
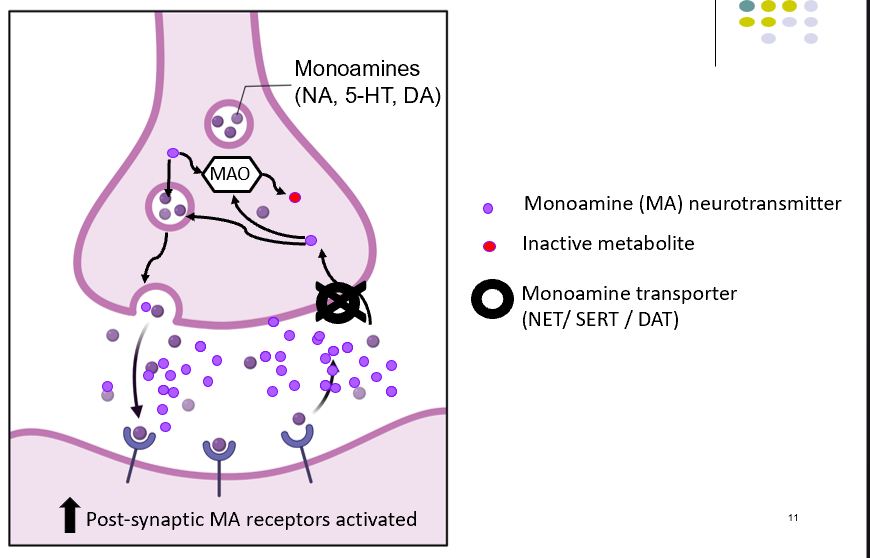
monoamine transmission diagram
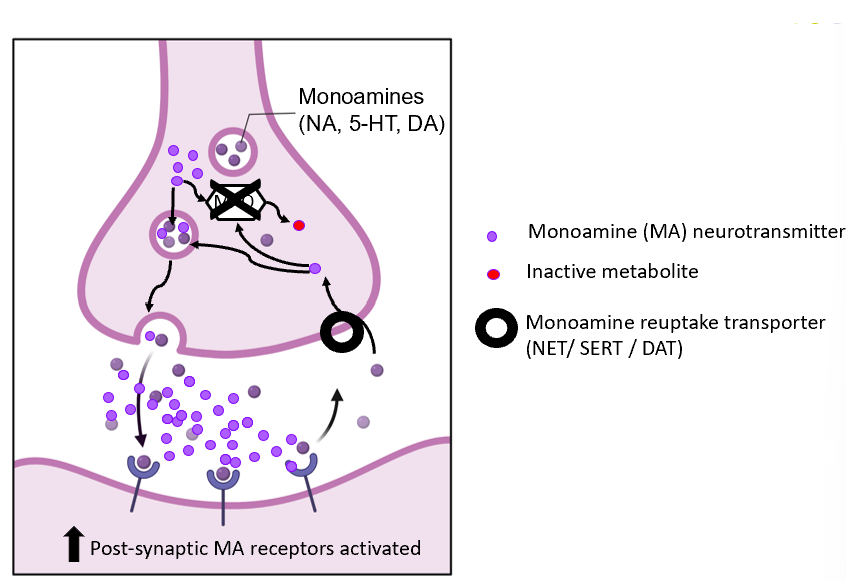
what is phenelzine
-monoamine oxidase inhibitor
phenelzine mechanism
-MAOI’s inhibitors block breakdown
-allowing build up of MA for subsequent release
phenelzine synapse diagram
what must patients on MAOI need to do
avoid tyramine rich foods:
-mature cheese
-chianti
-yeast
-fermented soya bean
to prevent hypertensive crisis
when are MAOIs prescribed
-prescribed by psychiatrists when all other types failed
what is amitriptyline
tricyclic antidepressants
TCA mechanism
-block reuptake transporters
-allowing build up of MA in synaptic cleft
TCA structure diagram
what are TCA used for more
-chronic pain conditions
-increase NA/5-HT levels in spinal cord; reduce ascending pain transmission
what line of treatment is TCA
-not first line of treatment
-dangerous CV side effects
what is venlafaxine
-serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor
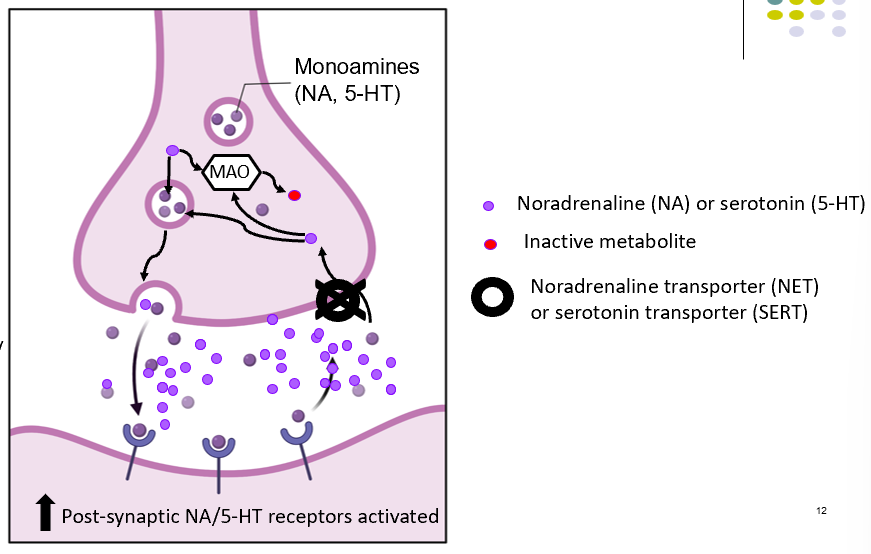
SNRI’s mechanism
-selectively block and reuptake of NA and 5-HT
SNRI’s side effects
-panic attacks
-high bp
-less commonly used than SSRI’S
SNRI synapse diagram
what is fluoxetine
-selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
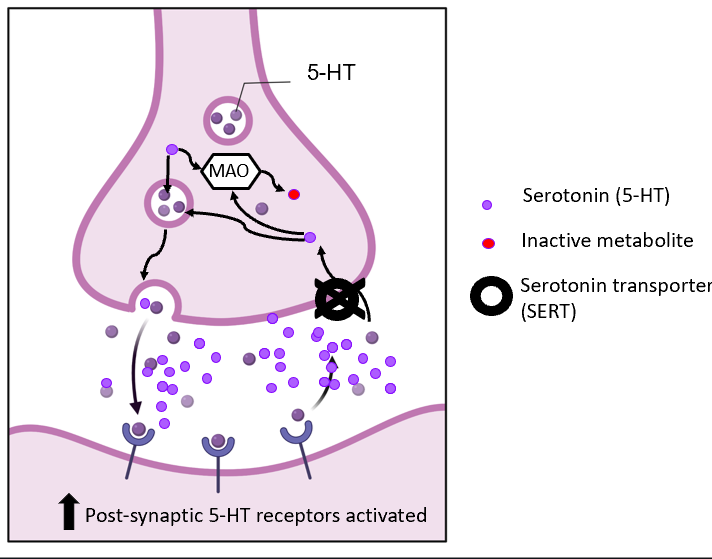
SSRI’s mechnaism
-selectively block reuptake of 5HT
how often is SSRIs prescribed
most prescribed class of anti-depressants
SSRI’s synapse diagram
what is reboxetine
-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor
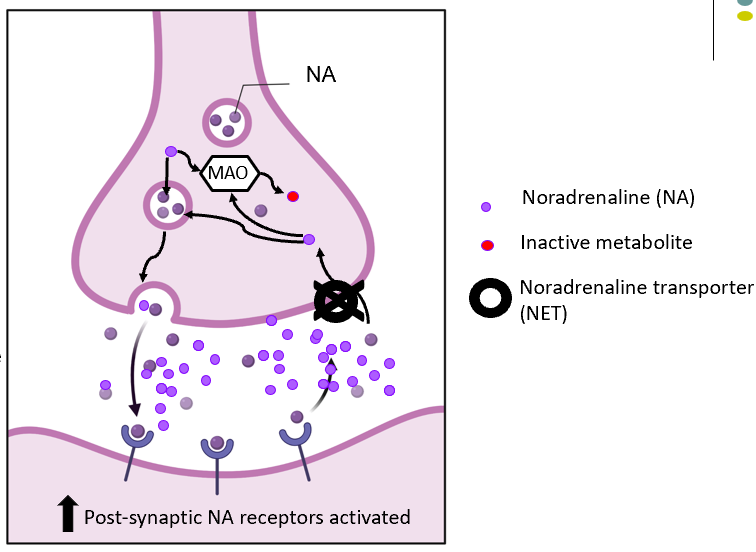
NRI’S mechnaism
-selectively block reuptake of NA
NRI’s synapse diagram
when are NRI’s prescribed
when SSRI’s are ineffective
what hypothesis are all current antidepressants based on?
the monoamine hypothesis
what is the clinical efficacy of antidepressants?
all have similar clinical efficacy, but 30-40% of patients don't improve
what factors determine the choice of antidepressant?
patient's treatment history, patient's suicide risk, and adverse effect profile
what are the main problems with the monoamine theory of depression?
-some drugs that elevate monoamines don't work as antidepressants (amphetamine, cocaine)
-therapeutic lag of 2-4 weeks despite rapid monoamine elevation
-30-40% of patients don't respond to monoamine-based treatments
challenges when looking for new anti-depressants
-difficult to cross bbb
-we dont fully understand basis of disease; hard to model and rationally design drugs
-animal models for drug testing are not good
-dont understand the disease: poor construct validity
-symptoms cant be replicated in animals; poor face vadility