General embryology and fertilization (Part 1)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Oral Histology
Branch of science that deals with the study of microscopic structures of oral/dental tissues. That deals with detailed histologic structures of the teeth and associated structures with emphasis on its development and clinical considerations.
Embryology
study of origin, growth and development and function of an organism from fertilization to birth
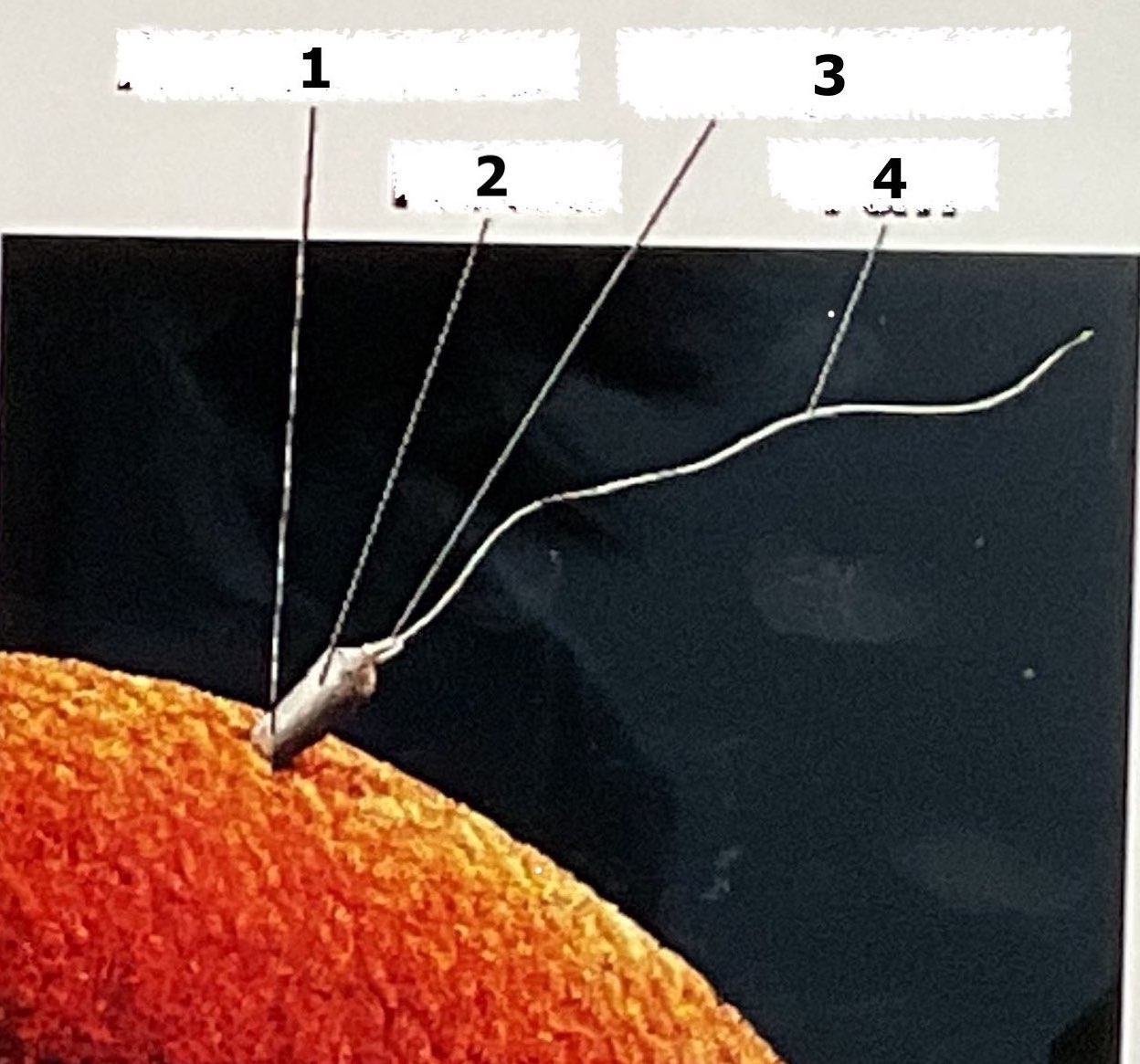
Acrosome, Head, Midpiece, Tail
Label each part

upper vagina
Spermatozoa are deposited in the _____ at insemination.
Insemination
Injection of semen into the vagina
Fertilization (4 weeks)
1st phase of prenatal life
Embryonic phase (5-8 weeks)
2nd phase of prenatal life
Fetal Phase (8 weeks to birth)
3rd phase of prenatal life
Embryonic Phase
What is the most vulnerable phase in prenatal life and the process of macrophogenesis?
Fertilization
What phase in prenatal life is the process of cellular proliferation and migration?
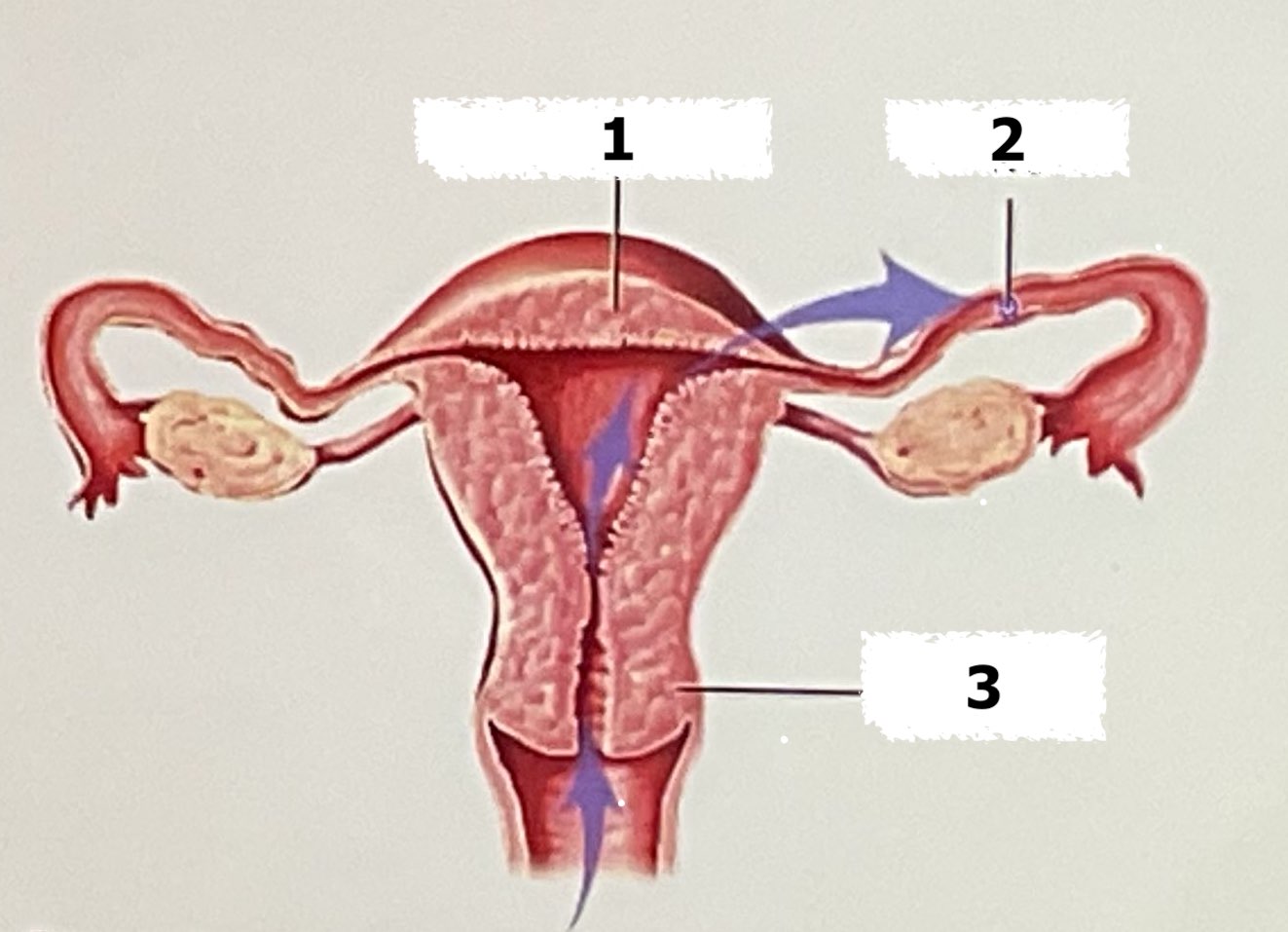
uterus, egg, cervix
Label each part
true
True or False
sperm travels through cervix into uterus searching for egg to fertilize
False, a minute fraction
True or False. If false write the correct answer
There is only 2 minute fraction of spermatozoa deposited in the female reproductive tract to reach the vicinity of the ovulated egg.
chemical hazard and mechanical obstacles
The route of sperm transportation in the female reproductive may be difficult due to?
True
True or False
Chemical hazard is a strong acid secretion
bacteriostatic medium
The natural acidity of the upper vagina act as __________.
bacteriostatic
a state of suspended growth of bacterio
4.3 to 7.2
Vaginal pH can rise up to?
seminal fluid
What acts as an effective buffer (barrier/cushion) against acidity within 8 seconds of insemination?
200 to 300 milion
Number of spermatozoa contained in an ejaculation of semen of a human?
30 minutes
How many minutes can the spermatozoa take to reach the uterine tube?
true
True or False
from the upper vagina, some spermatozoa are transported extremely rapidly up the female reproductive tract
swimming movement
Spermatozoa moves with what kind of movement?
seminal fluid
some component/s of ______ stimulates CONTRACTIONS of upper vagina which may help propel spermatozoa into the cervical canal
false
True or False
hormonally induced does not change the time of ovulation which reduce the viscosity of the mucus and allow better penetration of spermatozoa
oral cavity
what does oral stomodium/stomatodium mean?
development of the tooth
what does odontogenesis mean?
hard tissues and soft tissues
Tissues in the mouth
hard tissue
enamel, dentin, cementum is an example of what kind of tissue?
soft tissue
pulp is an example of what kind of tissue?
upper uterine tube
where does fertilization occur?
zygote
the union of male and female gametes forms a _______?
mechanical obstacles
This is an example of chemical hazards or mechanical obstacles of spermatozoa?
Crooked and compressed cervical canal
Narrowed uterine tube
Occluded by disease
utero-tubal junction
acts as a valve that prevents the passage of spermatozoa into the uterine tube
true
True or False?
SLOW PHASE OF SPERM TRANSPORT is where the spermatozoa enter the cervix, and they lodge in numerous irregular crypts (pit) that line the cervical canal
True
True or False?
ONCE IN THE CERVICAL CRYPTS – spermatozoa is slowly released into the uterine cavity
True
True or False?
ONCE IN THE UTERINE TUBES - spermatozoas continues their upward path by combination of “muscular contractions and ciliary currents to the tube”and swimming of spermatozoa
upper end of the uterine tube
It is when the swimming activity of the spermatozoa is very prominent
positive rheotactic response
the gentle current where spermatozoa orient themselves to move against
true
True or False
ONCE THROUGH THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT – spermatozoas penetrate the membrane surrounding the egg also known as CAPACITATION
thick mucus
what fills the cervical canal
spasmodic contractions
orgasm of females causes ______ of the smooth muscles of the uterus
human follicular fluid
It is said to possess sperm attracting property
capacitation of spermatozoa
process in which the spermatozoon, after it reaches the ampulla of the fallopian tube, undergoes a series of changes which leads to its ability to fertilize ovum
5 IMPORTANT COMPONENTS OF FERTILIZATION
1 Initial membrane contact between egg and sperm 2 Entry of sperm cell into the egg
2 Entry of sperm cell into the egg
3 Prevention of polyspermy by the egg
4 Completion of meiosis by the egg
5 Formation and fusion of male and female pronuclei leading to the first cleavage division
removed from the female reproductive tract
what happens to spermatozoa that are not directly involved in fertilization?
swept through the cervix and into the vagina
what happens to sperm in the uterine cavity after sperm transport?
ingested by phagocytosis
what happens to sperm in the uterine tube after sperm transport?
corona radiata
layer that is very important in egg transport
without this later ovum makes little progess
true
True or False
the freshly ovulated egg surrounded by corona radiata, lies free in the peritoneal cavity
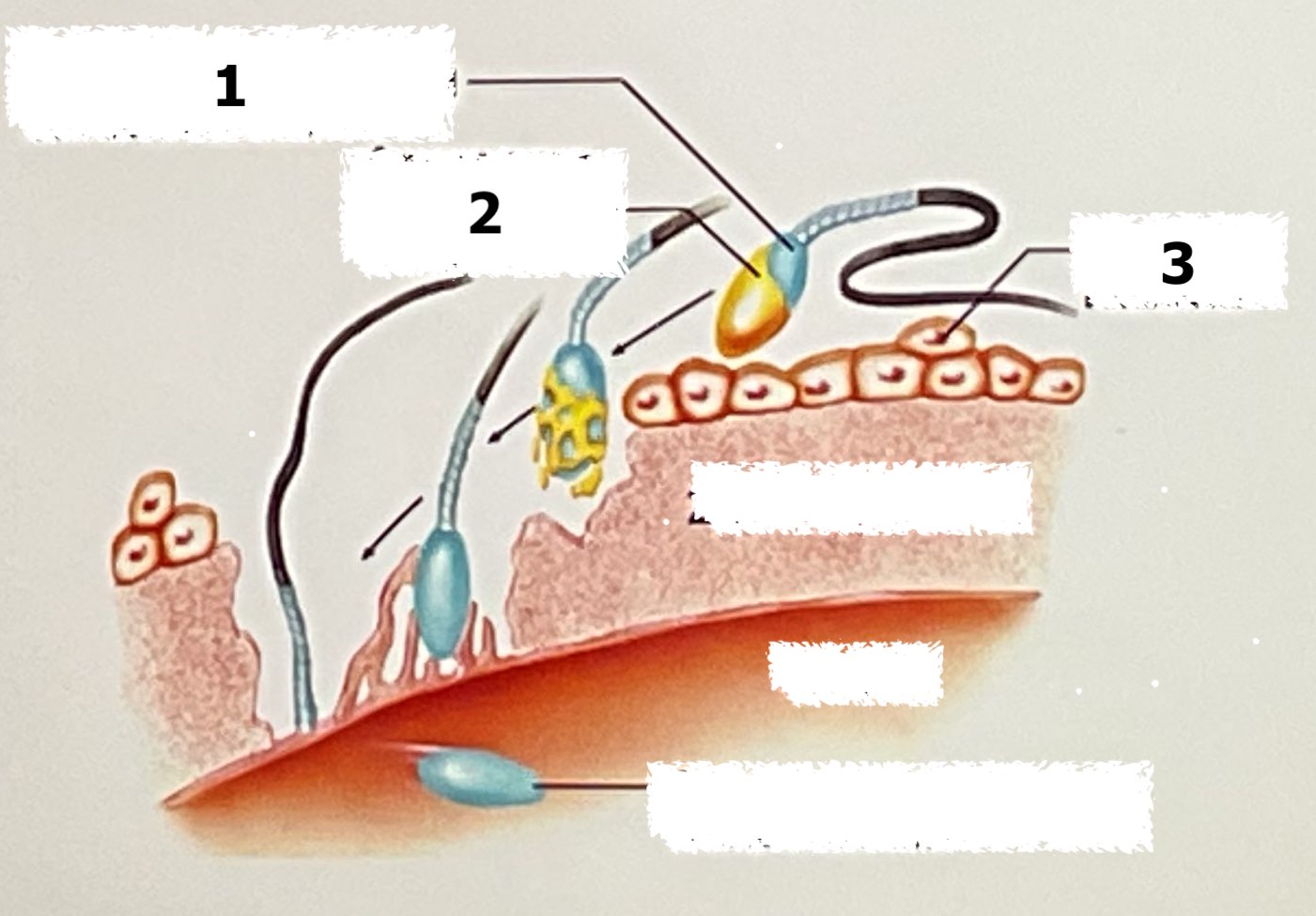
nucleus containing chromosomes, autosome containing enzymes, corona radiata
label each part (number 1-3)
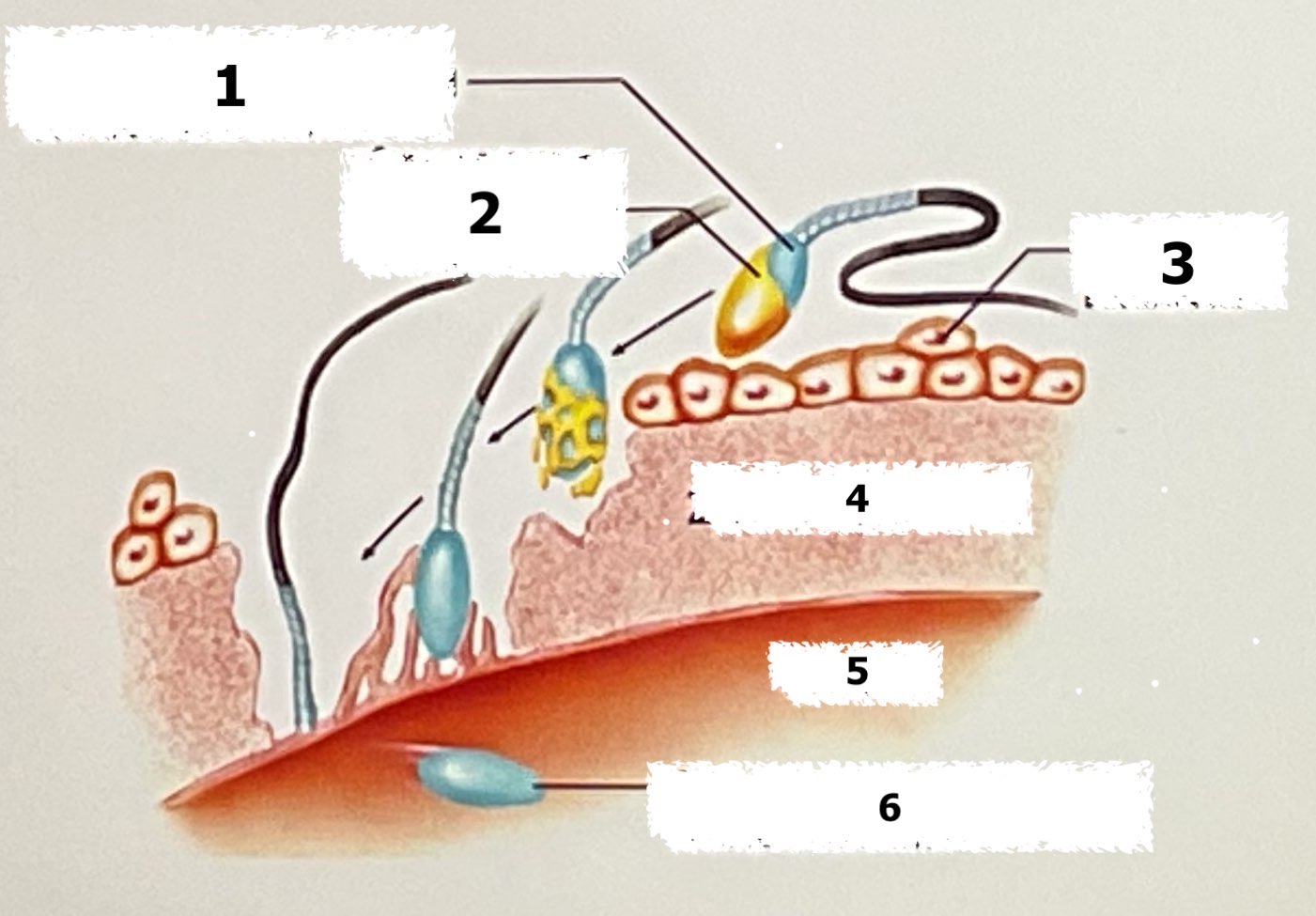
zona pellucida, ovum, sperm cell nucleus inside ovum
label each part (number 4-6)
3 days
it takes _ days for an unfertilized egg to pass through the uterine tube
true
True or False
pregnancy can still occur in the absence of female orgasm
fertilization
phenomenon in the field of biology
process
fertilization is _____ not a single event
false, depression of metabolic activity
True or False, if false write the correct answer
When free from the ovary, the ovum undergoes changes such as:
aging or deterioration
cytoplasm becomes coarsely granular
elevation of metabolic activity
limited viability
ovum and spermatozoa have ______ once they are in the female reproductive tract
24 hours
Ovulates eggs must be fertilized within __ hours
overripe and non-viable
If not being fertilized within 24 hrs what happens to the egg?
1 or 2 days
How many days does the fertilizing power of sperm last?
epididymis, ductus deferens
when it comes to the viability of ova and spermatozoa:
in _______ and ______ spermatozoa remains non motile
gametes
mature male and female germ cells that are capable of functioning in fertilization
corona radiata, zona pellucida
PENETRATION OF CORONA RADIATA
spermatozoa penetrates the cells of _______ and the _______ before they can contact the plasma membrane of the egg
hyaluronidase
sperm derived enzyme that facilitates penetration of CR by dissolving extracellular matrix around the cells
sperm receptors
PASSAGE THROUGH ZONA PELLUCIDA:
where specific molecules on the sperm head bind to (when it reaches zona pellucida)
acrosome, capacitation
PASSAGE THROUGH ZONA PELLUCIDA:
________ reaction results from further contact with the sperm head
________ is its pre requisite
Lytic enzymes stored within the acrosome are released
Causes change in plasma membrane of the sperm that allows it to fuse egg cell membrane
pervitalline space
ONCE THROUGH THE ZONA PELLUCIDA:
spermatozoon enters the fluid filled _____
between the zona and plplasma membrane
Fertilization cone
WHEN SPERM MAKES CONTACT WITH THE EGG:
Cytoplasm of the egg bulges out in elevated process. What comes up?
retracts, ovum, penetration
plasma membrane of the egg and sperm fuse together, then the fertilization cone _______
- Carrying the sperm head into the ____
- Completes the phase of ______
muscular contractions
ciliary currents
What propels spermatozoa on its upward path inside the UTERINE TUBE?
minute fraction
Only a ______ of spermatozoa will ever reach the ovulated egg
motility of spermatozoa
When it comes to the viability of ova and spermatozoa
__________ only aroused when, at the moment of ejaculation, are mixed with secretions of seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands
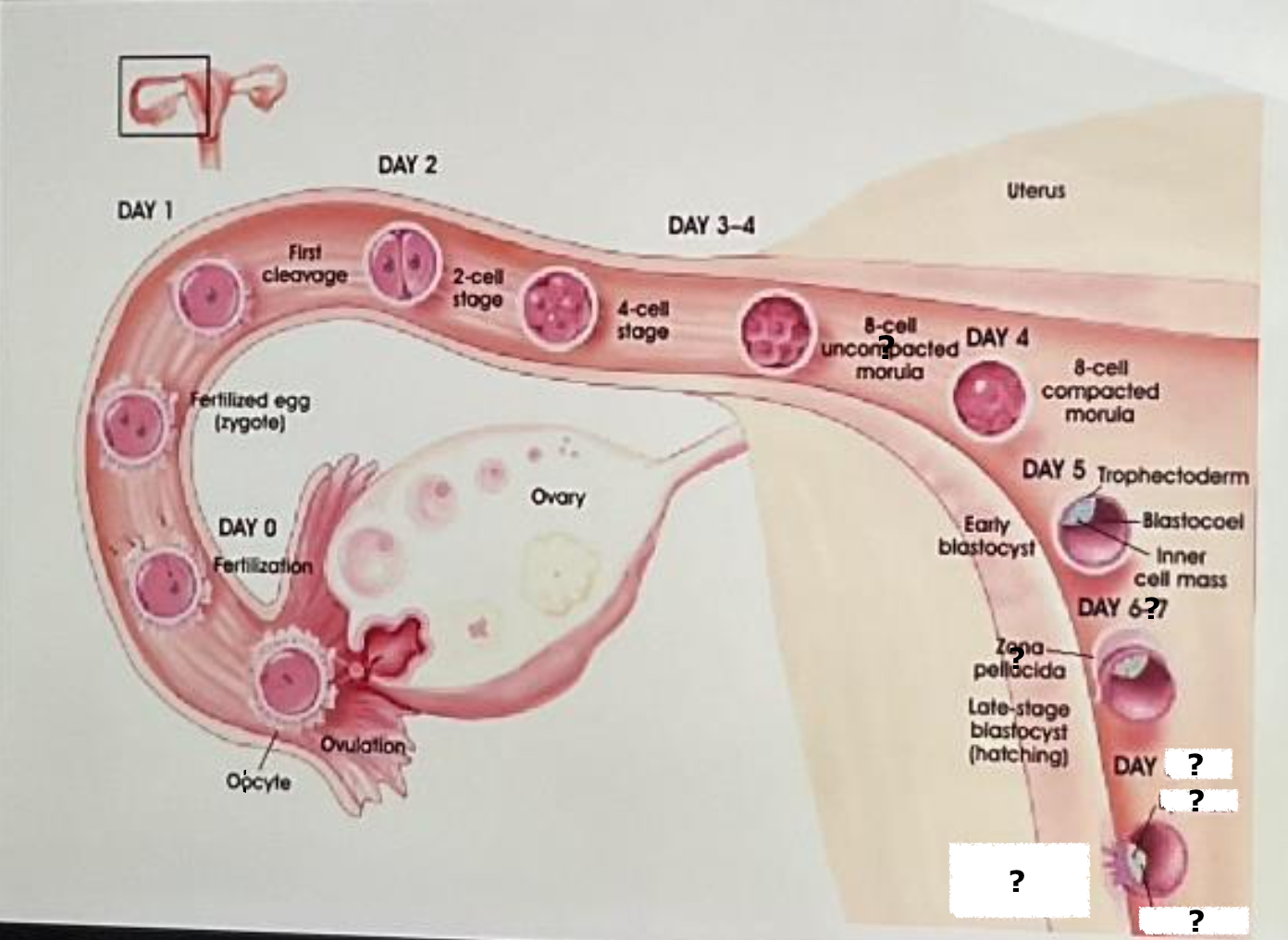
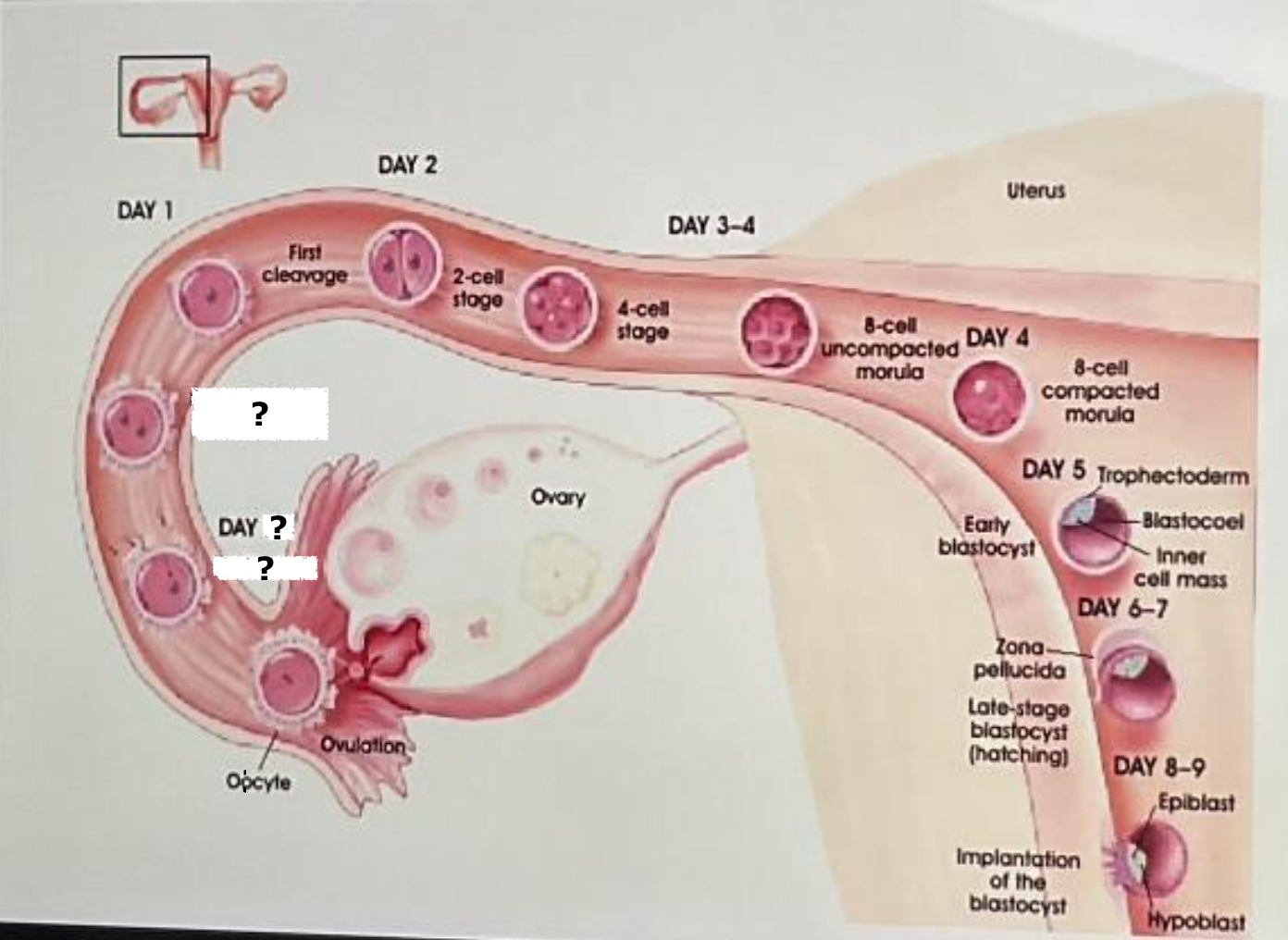
ovary
ovulation
oocyte
label
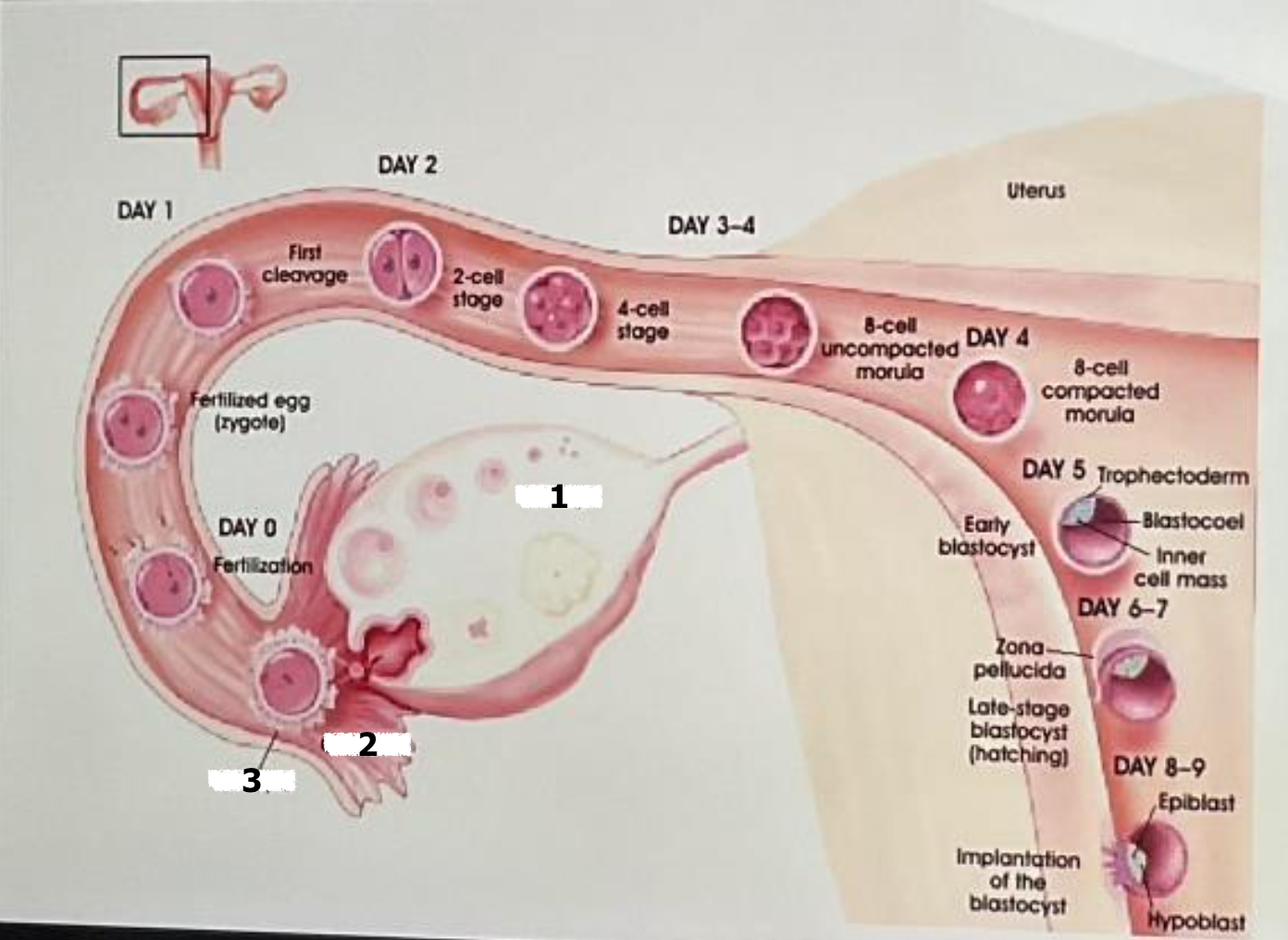
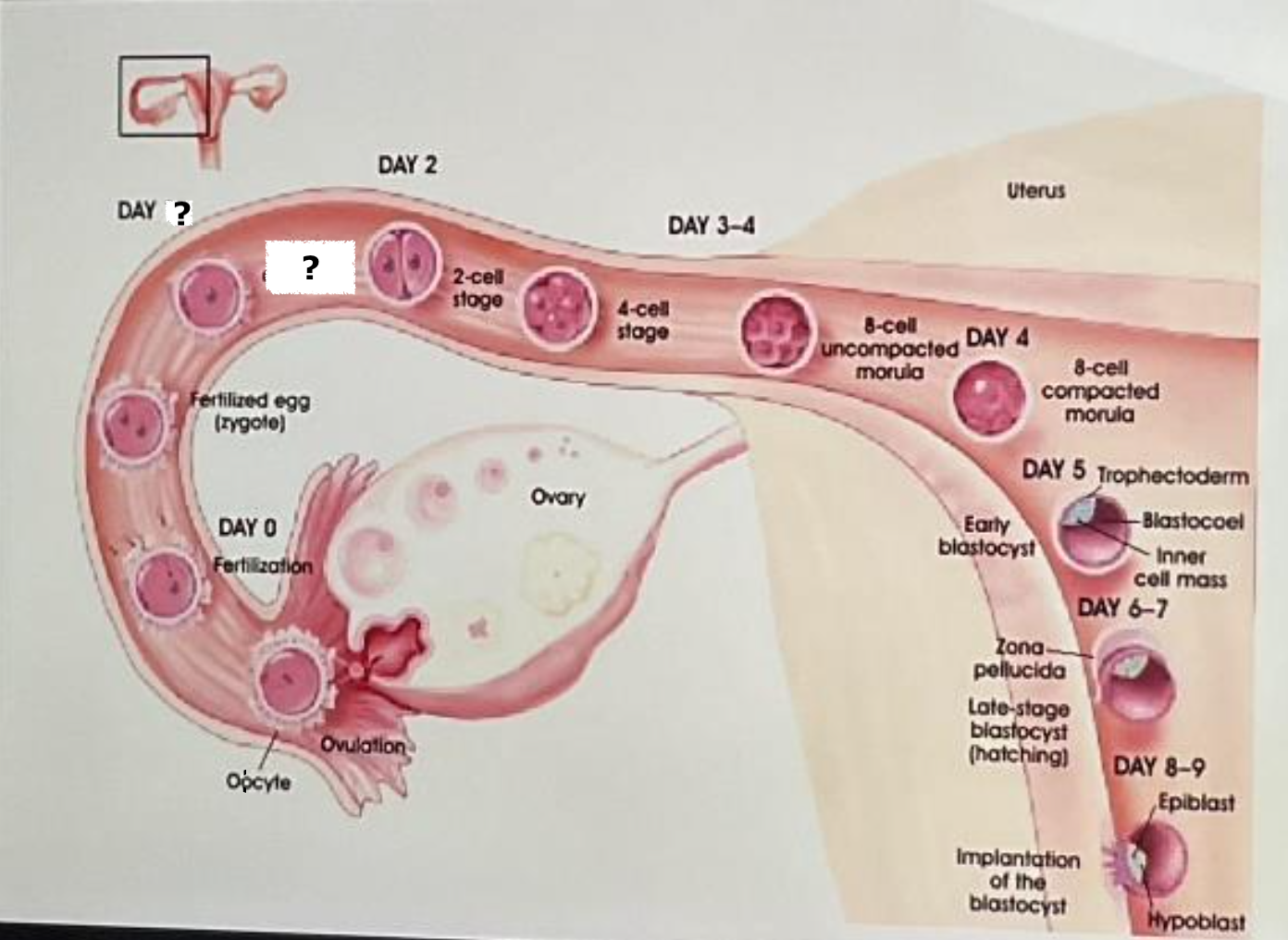
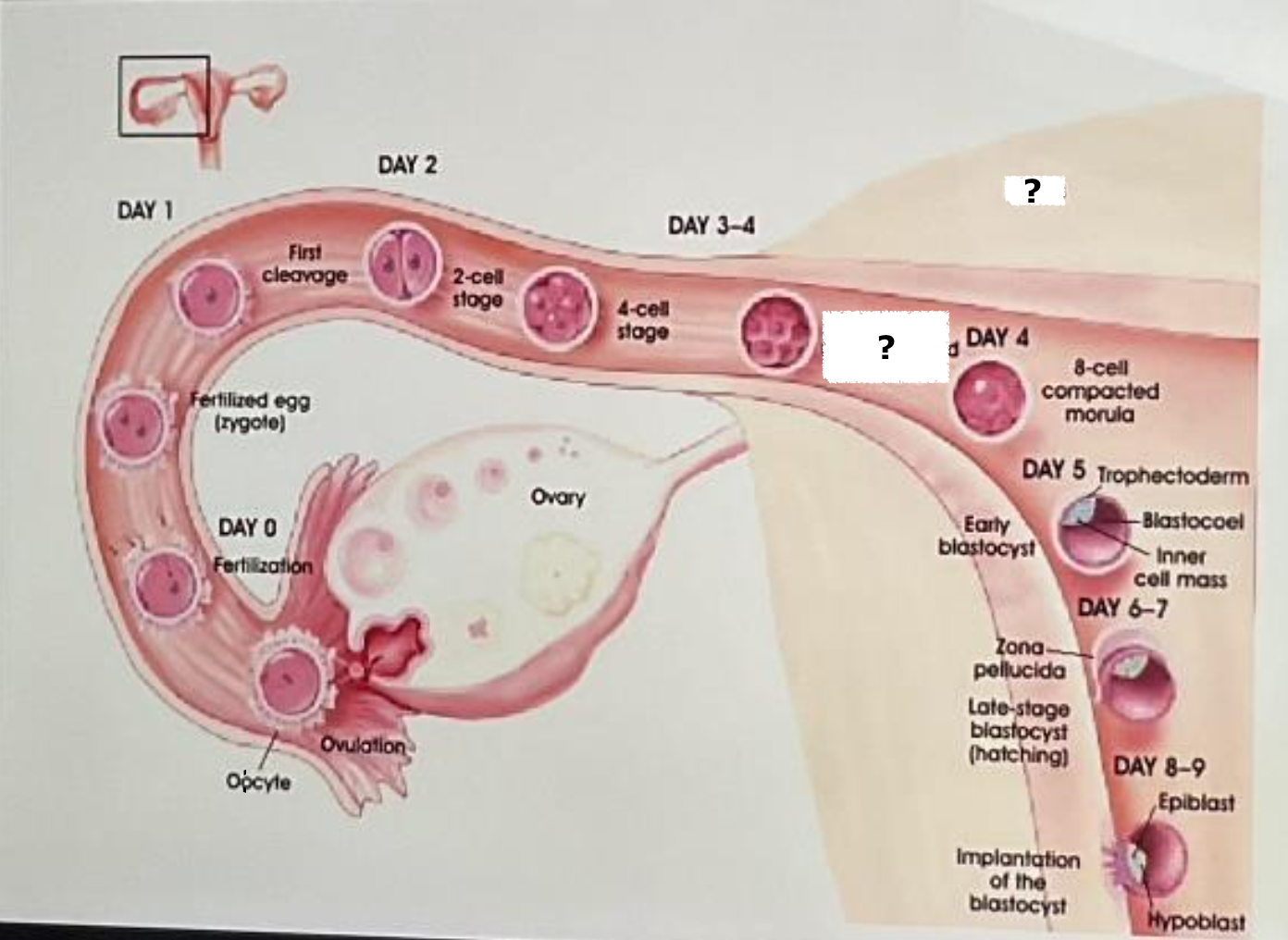
fertilization
day 0
fertilized egg (zygote)
label and insert the day
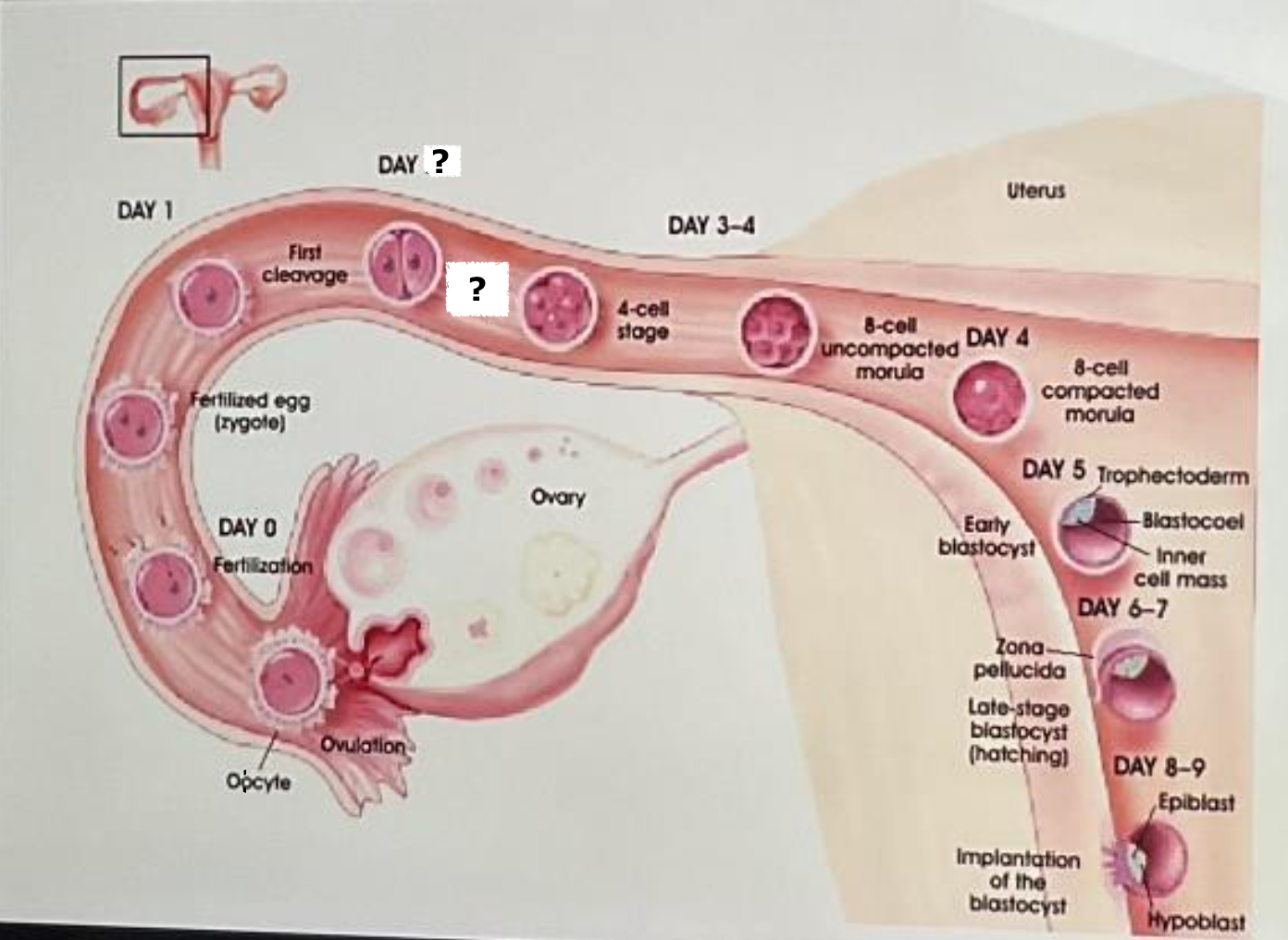
day 1
first cleavage
label and insert the day
day 2
2 cell stage
label and insert the day
day 3-4
4 cell stage
label and insert the day
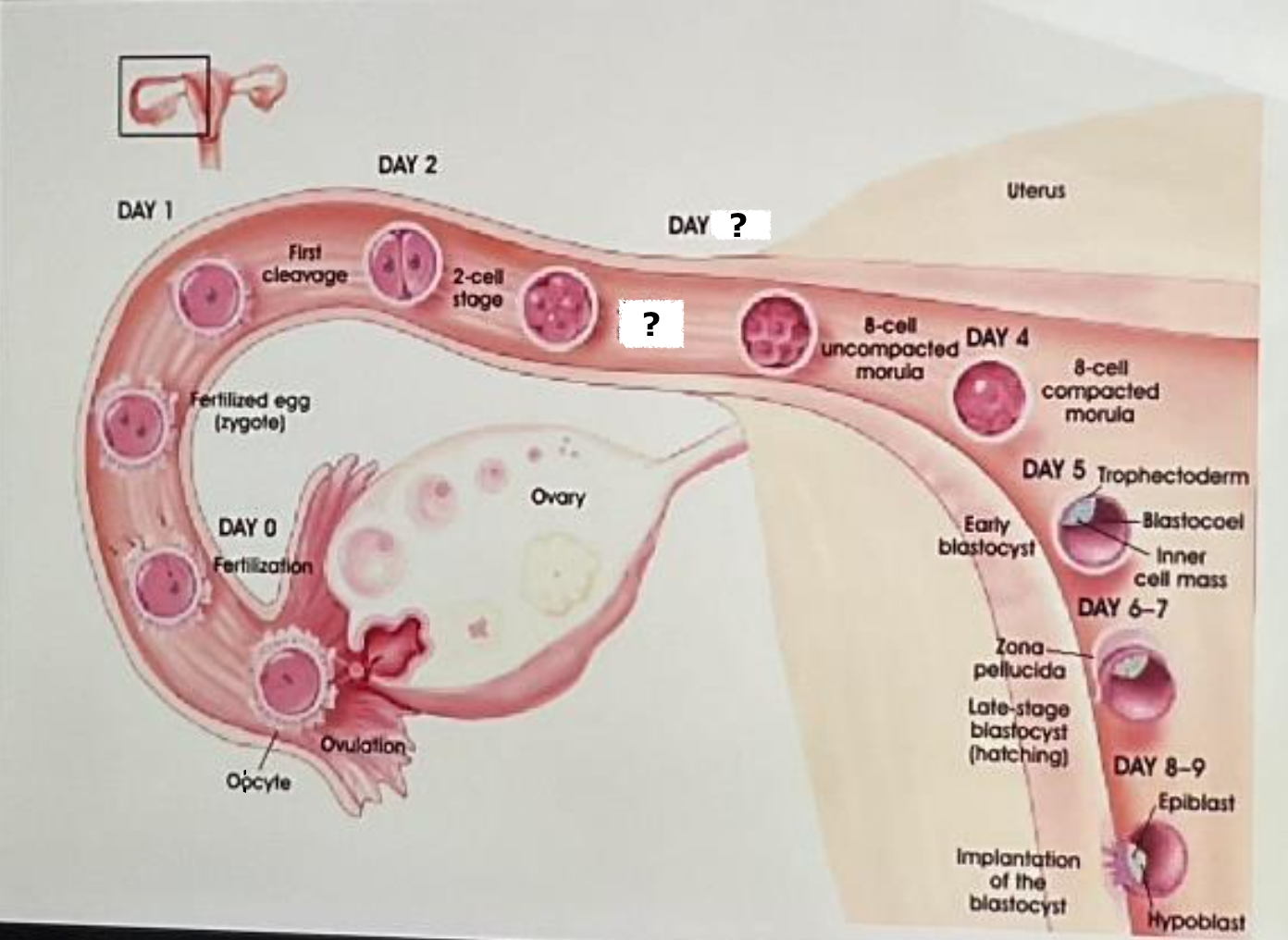
uterus
8 cell uncompacted morula
label
day 4
8 cell compacted morula
label and insert the day
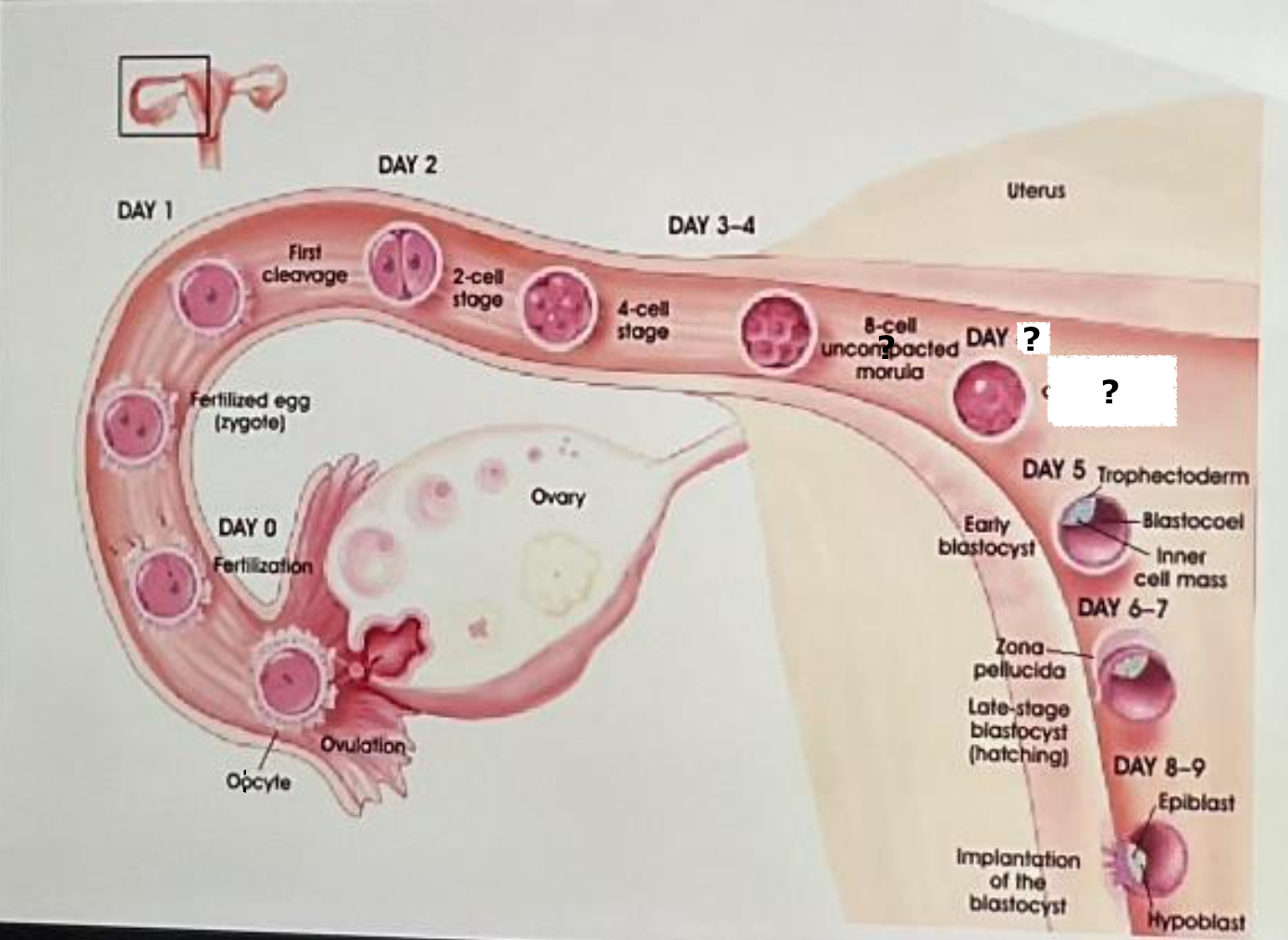
day 5, trophectoderm, blastocoel, inner cell mass, early blastocyst
label and insert the day
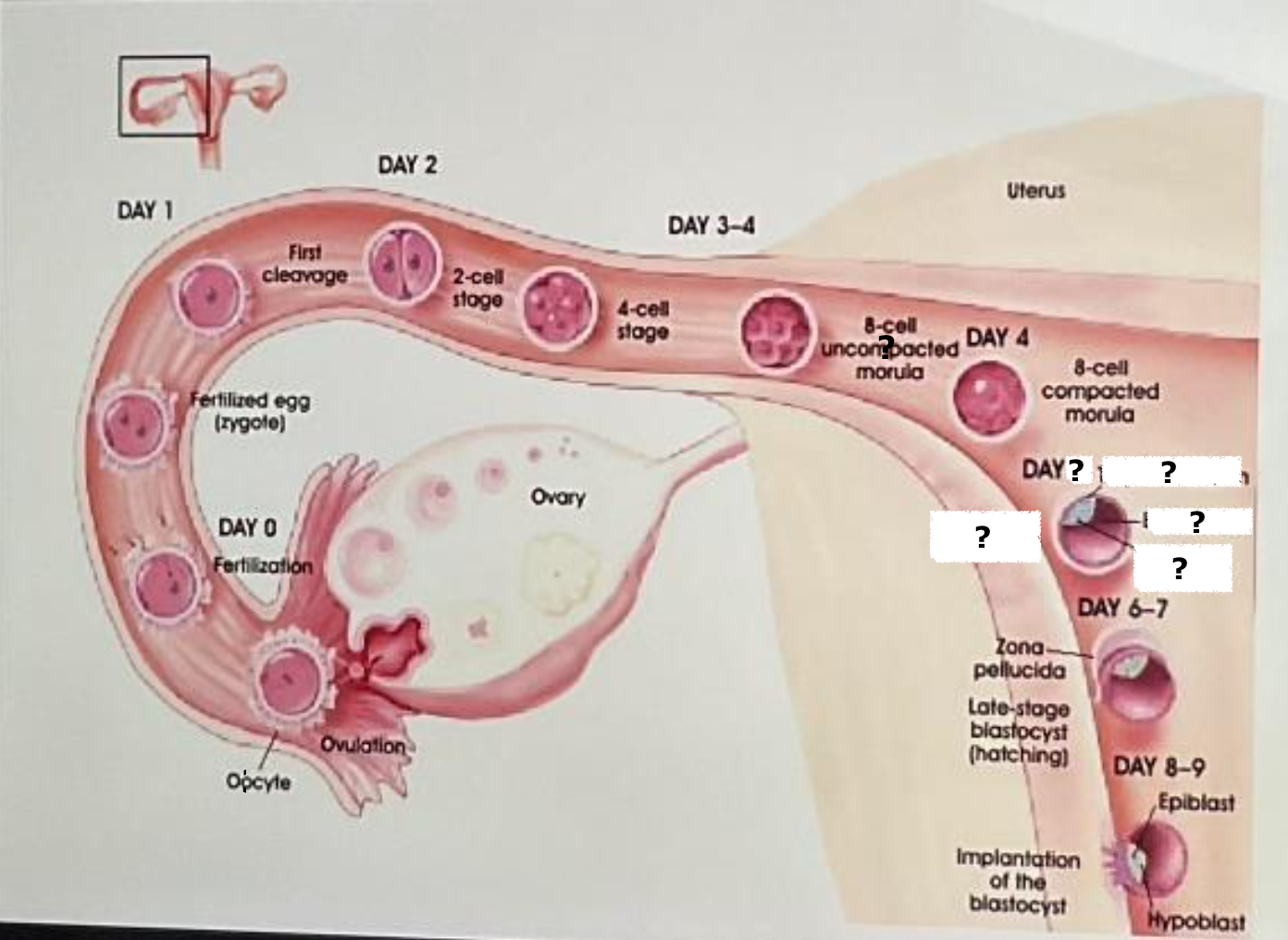
days 6-7
zona pellucida
late stage blastocyst (hatching)
label and insert the day
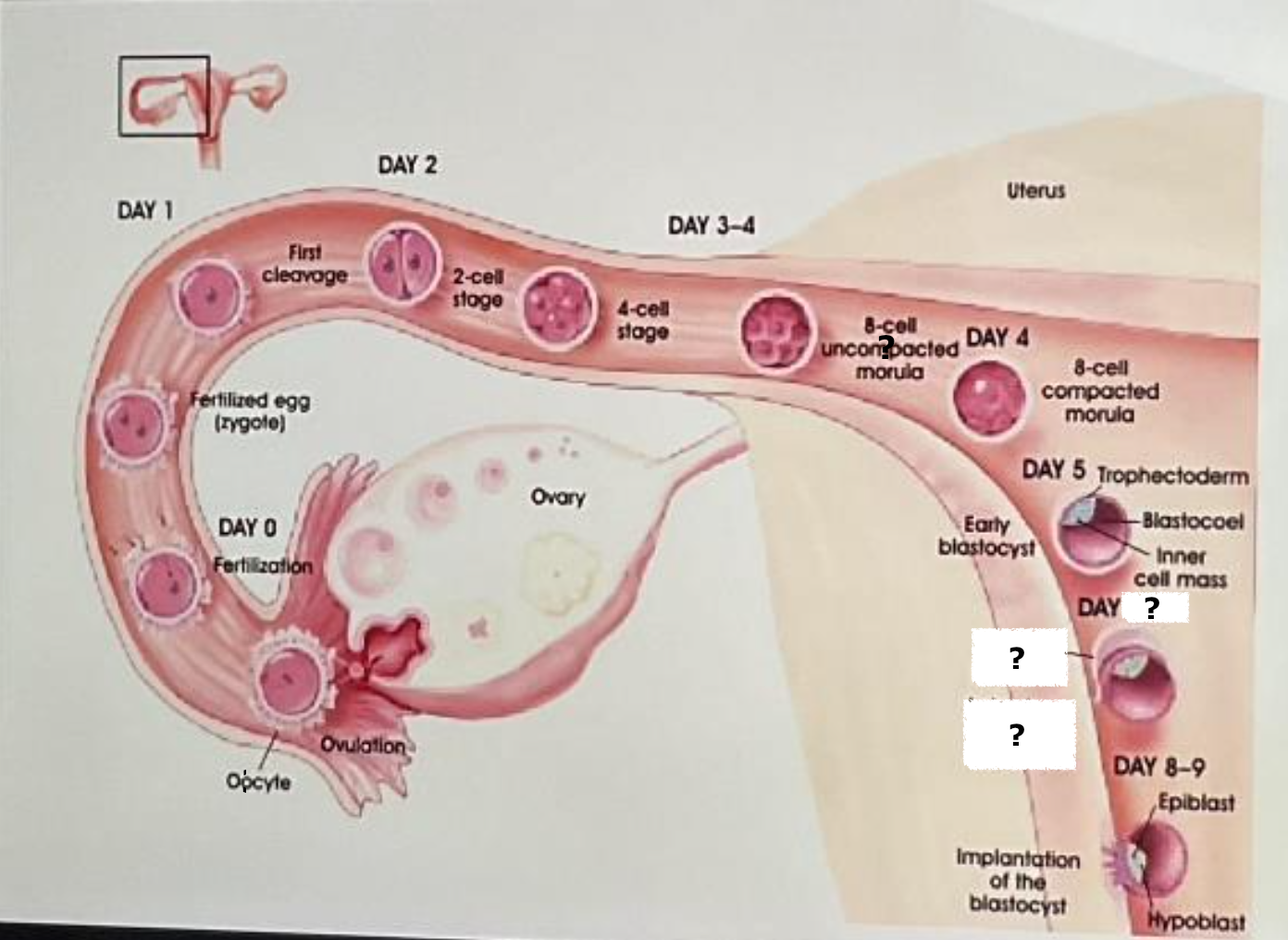
day 8-9, epiblast, hypoblast, implantation of the blastocyst
label and insert the day