1.6 Cell cycle and cell division
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Where is GENETIC INFORMATION copies and pasted to ?
On to DAUGHTER CELLS
What is cell division necessary?
To increase the number o cells and to pass on genetic material to daughter cells
What is a CHROMOSOME?
.A long coiled section / threadlike structure of DNA,proteins and a small amount of RNA
.GENES run along the length of the chromosome
.It is only at the onset of CELL DIVSON that chromosomes become visible
What is a GENE?
A section of DNA that which encodes the Amino Acid sequence of a polypeptide
What happens to the DNA just before cell division begins?
.Each DNA molecule makes a copy of itself
.A single thread of DNA becomes two identical threads called CHROMATIDS (A) (2 copies of chromomes)
.They lie parallel along most of their length
.The chromatids are joined only is a specialised region called the CENTROMERE(B)
What is a CHROMATID?
One strand of a replicated chromosome
What is a CENTROMERE?
The structure on a chromosomes that links the two sister chromatids
How many chromosomes do HUMANS have?
46 chromosomes ( diploid) , 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes (haploid)
However is different in each species
What is a diploid number ?
The TOTAL NUMBER of chromosomes
What do GAMETES have instead of a diploid number?
.GAMETES ( SEX CELLS) have HALF the diploid number
.This is called HAPLOID ( humans gametes have 23 chromosomes )
Why do we have two copies of every gene in our body cells?
.We inherit one set of chromosomes from each parent
.Allows for genetic VARIATION
.Can act as backup or safety
What are different version of the same gene known as?
ALLELES
What is the SIGNIFICANCE OF MITOSIS in living organisms?
.Growth ( in plants increasing the number of cells and increasing length + size )
.Replacing worn out cells
.Repair damages tissue
.Asexual reproduction
What are the stages of the CELL CYCLE during MITOSIS ?
IPMAT= MITOSIS
. INTERPHASE - LONGEST STAGE (not part of mitosis)
.PROPHASE
.METAPHASE
.ANAPHASE
.TELOPHASE

What is INTERPHASE in mitosis ?
.Longest phase + metabolically active
. DNA replicates —> chromosomes becomes pair of chromatids
.Organelles replicate , eg mitochondria and chloroplasts—-> making new organelles
.other organelles increase in number
.Lots of ATP synthesis , ribosomal synthesis , protein synthesis occurs
.Cells increase in size (not growth)
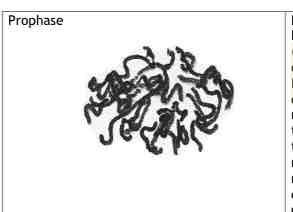
What happens during the stage of PROPHASE in mitosis ?
PROPHASE -
.Chromosomes condense (becomes shorter and thicker)
. become visible —-> can see them individually under light microscope
.centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell (only animal cells)
.Proteins Form the spindle fibres/ spindle apparatus
.Nucleolus disappears
.Nuclear membrane breaks down
.Pairs of chromatids are attached to the spindle fibres via their centromeres
What happens during the stage of METAPHASE in mitosis ?
.Pairs of chromatids align themselves along the centre of the EQUATOR of the cell
-The chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibres at the centromere
-Contraction of the spindle fibres draws the individual chromatids apart

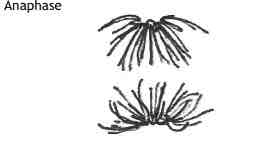
What happens during the stage of ANAPHASE in mitosis?
.A very rapid stage
.Spindle fibres contract
.Centromere splits
.One chromatid from each pair gets pulled to opposite poles of the cell ( CENTROMERE FIRST)
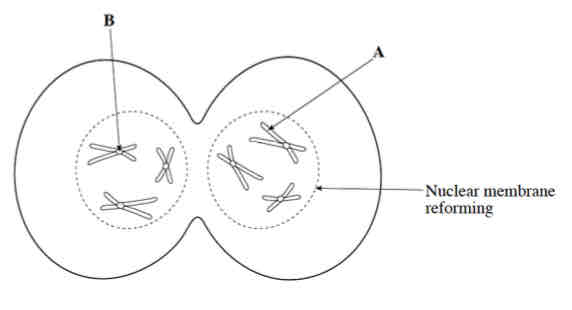
What happens during the stage of TELOPHASE in mitosis?
.Chromosomes unwind + become long + thin
.Spindle fibres break down
.Nucleolus reappears
.Nuclear membrane reforms

What is CYTOKINESIS in mitosis ?
ANIMAL CELLS - cytokinesis occurs by constriction of the centre of the parent cell from the outside inwards (cytokinesis means cytoplasm + cell membrane splitting)
PLANT CELLS - In plant cells, a cell plate forms across the equator of the parent cell from the centre outwards and a new cell wall is laid down.

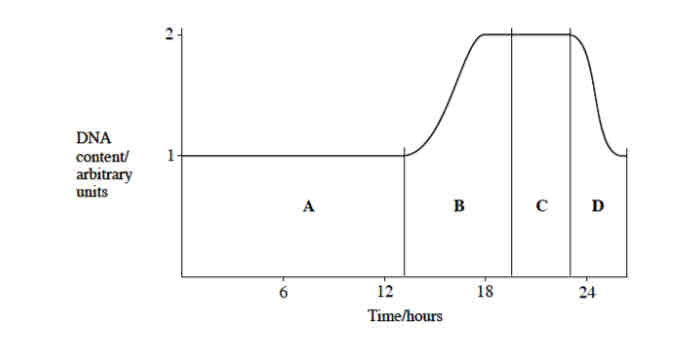
Does the number of chromosomes remain constant through the cell cycle?
The number of chromosomes remains constant throughout the cell cycle, but the amount
of DNA present in the cell changes. Look at the cell cycle and the table below
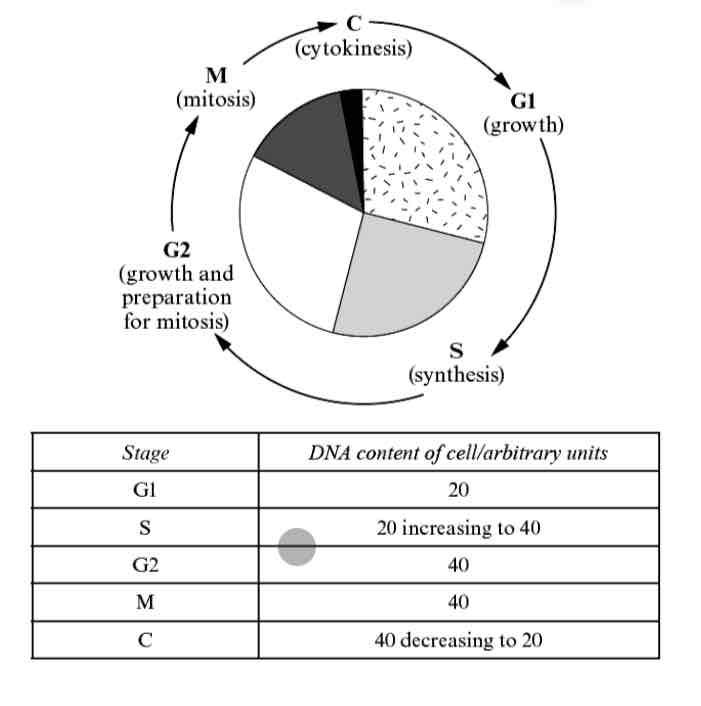
How do you interpretate the mitosis graph?
.Time periods A and B represent INTERPHASE
.Time period C is MITOSIS
.Time period D is CYTOKINESES
.During time period B the DNA content of the cell has doubled —> due to replication
.During time period D the DNA content of the cell has halved after cytokinesis
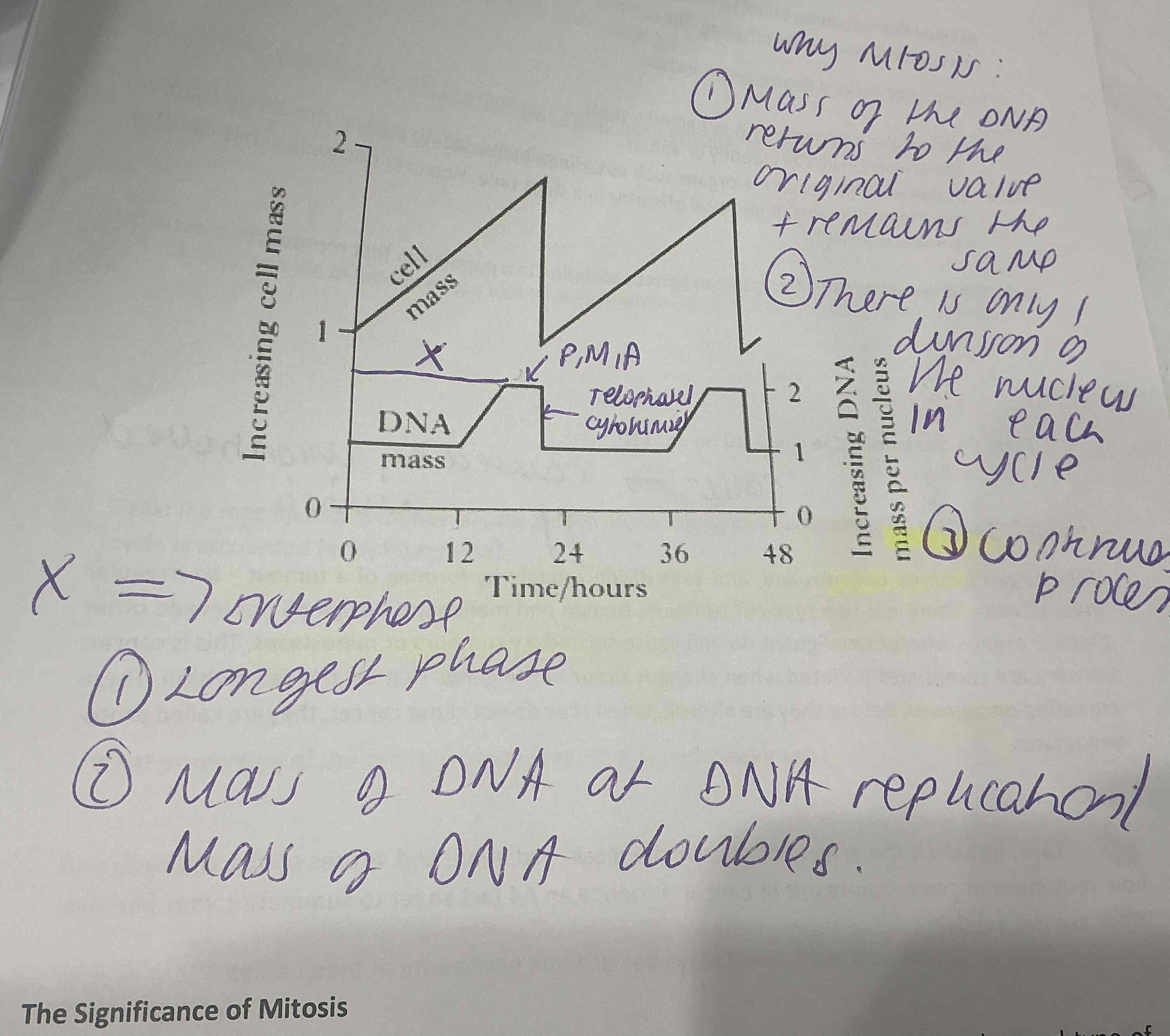
How do you interpret a mitosis graph with both cell mass and cell DNA
.X= Interphase ( longest phase , DNA mass doubles at replication
- Mass of the DNA returns to the original value + remains the same
- There is only 1 division of the nucleus in each cycle
-Is a continuous process
.Arrow of PMA= MITOSIS
.Telophase + CYTOKENISIS then occurs
Does asexual or sexual reproduction occur by MITOSIS?
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
-Offspring produces asexually are GENETICALLY IDENTICAL to the parent
What is 1 advantage and disadvantage of asexual Reproduction?
ADVANTAGE= the ability to increase in number quickly to take advantage of an ideal environment
DISADVANTAGE= lack of genetic variation, leading to an inability to adapt if the environment changes
How does Mitosis result in diploid daughter cells?
.DNA replicates once and is only follows by 1 cello division
What is the significance of mitosis in evolution ?
. Produces genetically identical daughter cells / offspring
.Therefore if the genome of an individual is adapted to a particular habitat , their offspring’s genome will also be adapted which increases their chances of survival
.Advantage = they can colonise habitats quickly
.Disadvantage = If a change in environment , the population will not be able to adapt as there is no genetic variation in the population
How do you calculate the mitosis index?
No of cells in prophase + metaphase + anaphase + telophase / Total number of cells X100
What is the SIGNIFICANCE of MEIOSIS?
.Gametes which are GENETICALLY DIFFERENT
.Therefore it creates genetic variation within a population
How does MITOSIS link to CANCER
.Cancers are the result of uncontrolled mitosis.
.Cancerous cells divide repeatedly, out of control, with the formation of a tumour.
. A tumour is an irregular mass of cells
.tumours prevent the normal function of body organs.
. Cancers are thought to be initiated when mutations (changes) occur in the genes that control cell division.
Where does MITOSIS occur?
PLANTS - meristems ( root shoot + tip)
ANIMALS - Somatic cells ( body cells ) , bone marrow , hair follicles , nails beds
As these are REGIONS OF GROWTH
Where does MEOSIS take place?
In the REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS of both
plants (Male- anther female - ovule pollen+ eggs) and
animals (ovary + testes )
What are the Products of MEOSIS?
.Gametes with HALF the normal chromosome number
.This is the HAPLOID number
.MEOSIS pReduces cells which have GENETIC VARIATION
.Plays an important role in brining about genetic variation in living organisms
What are the stage of the cell cycle during MEOSIS?
IPMAT= Meosis 1
PMAT = Meiosis 2
.INTERPHASE (Not part of meiosis, is the longest stage)
.PROPHASE 1
.METAPHASE 1
.ANAPHASE 1
.TELOPHASE 1
.PROPHASE 2
.METAPHASE 2
.ANAPHASE 2
.TELOPHASE 2
.CYTOKINESIS
What are homologous chromosomes ?
2 chromosomes determining the same characteristics
(one from mother, one from father) Both with the same gene
What happens during INTERPHASE in MEOSIS?
.Longest phase + metabolically active
. DNA replicates —> chromosomes becomes pair of chromatids
.Organelles replicate , eg mitochondria and chloroplasts—-> making new organelles
.other organelles increase in number
.Lots of ATP synthesis , ribosomal synthesis , protein synthesis occurs
.Cells increase in size (not growth)
What happens during PROPHASE 1 of meiosis
.Chromosomes condense (becomes shorter and thicker)
. become visible —-> can see them individually under light microscope
. HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES link together forming BIVALENT ( Connected by chiasmata ) —> CROSSING OVER can take place EXCHANGING ALLELES BETWEEN HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES
.centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell (only animal cells)
.Proteins Form the spindle fibres/ spindle apparatus
.Nucleolus disappears
.Nuclear membrane breaks down
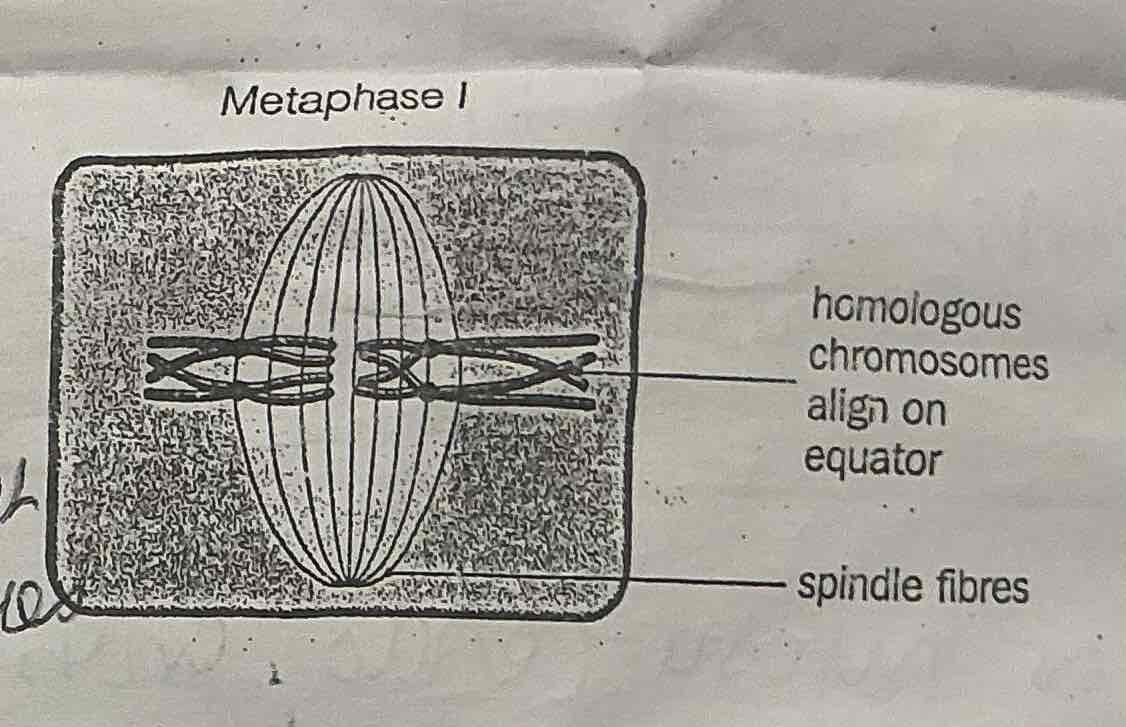
What happens during METAPHASE 1 of MEOSIS ?
. The homologous pairs of CHROMOSOMES align along the equator of the cell
.INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT of homologous chromosomes in metaphase 1 is a source of GENETIC VARIATION
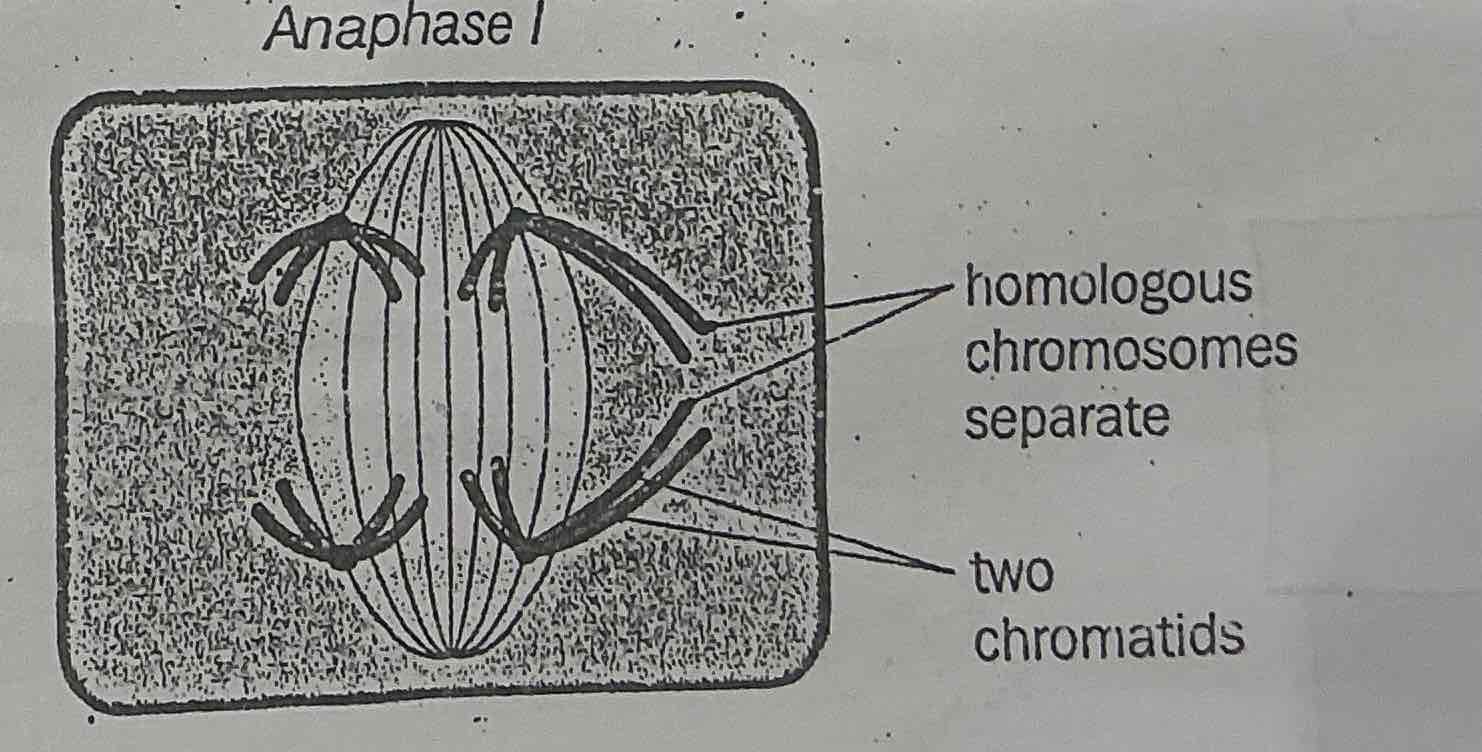
What happens during ANAPHASE 1 of MEOSIS?
.A very rapid stage
.Spindle fibres contract
.The chromosomes in each BIVALENT separates and are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
.The random arrangement of homologous pairs at metaphase means that EACH POLE HAS A RANSOM MIXTURE OF PATERNAL AND MATERNAL CHROMOSOMES.
(The centromere does not split and chromatids are not pulled apart. The chromosomes remain intact at this stage.)
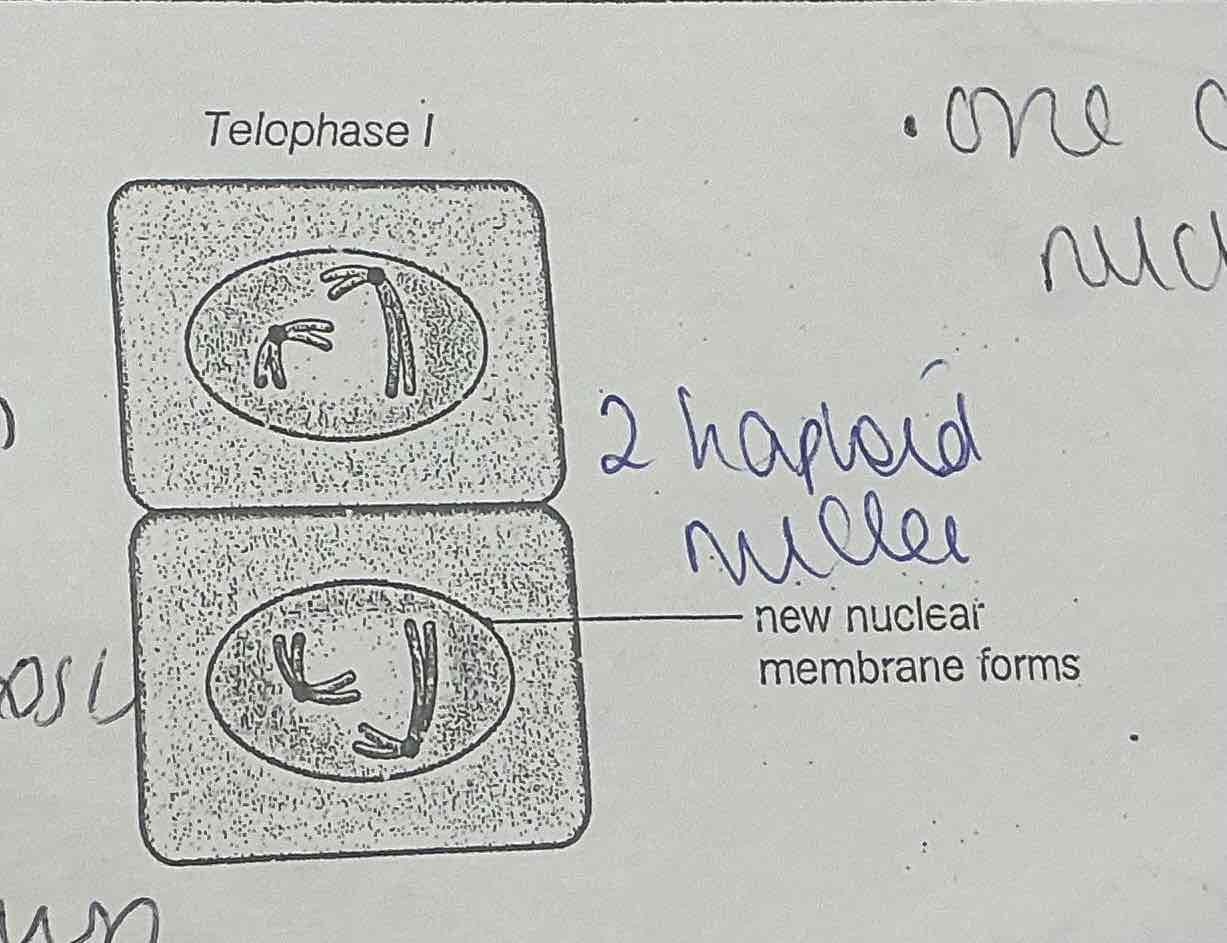
What happens during TELOPHASE 1 in MEOSIS?
MARKS THE END OF THE FIRST MEIOTIC DIVISION
.Chromosomes DO NOT unwind and become thin , they remain their condensed form
.The spindle fibres break down
.The nucleolus reappears
.The nuclear membrane reforms
.Is now one cell with 2 haploid nuclei
IN ANIMLA CELLS CYTOKENISIS NEXT BUT MEIOSIS 2 FOLLOWS IMMEDIATELY AFTER
PROPHASE 2
.Chromosomes condense (short + thick)
.Chromosomes become visible again - under light microscope
.Spindle fibres begin to develop
.Nuclear membrane breaks down
What happens during METAPHASE 2 of MEOSIS?
.The chromosomes line up separately on the spindle fibres at the equator
.Each chromosome is attached to the spindle by its CENTROMERE
.IN MEOSIS 2 CENTRIOLES MOVE FROM EAST —→ WEST
.IN MEOSIS 1 CENTRIOLES MOVE FROM NORTH—> SOUTH
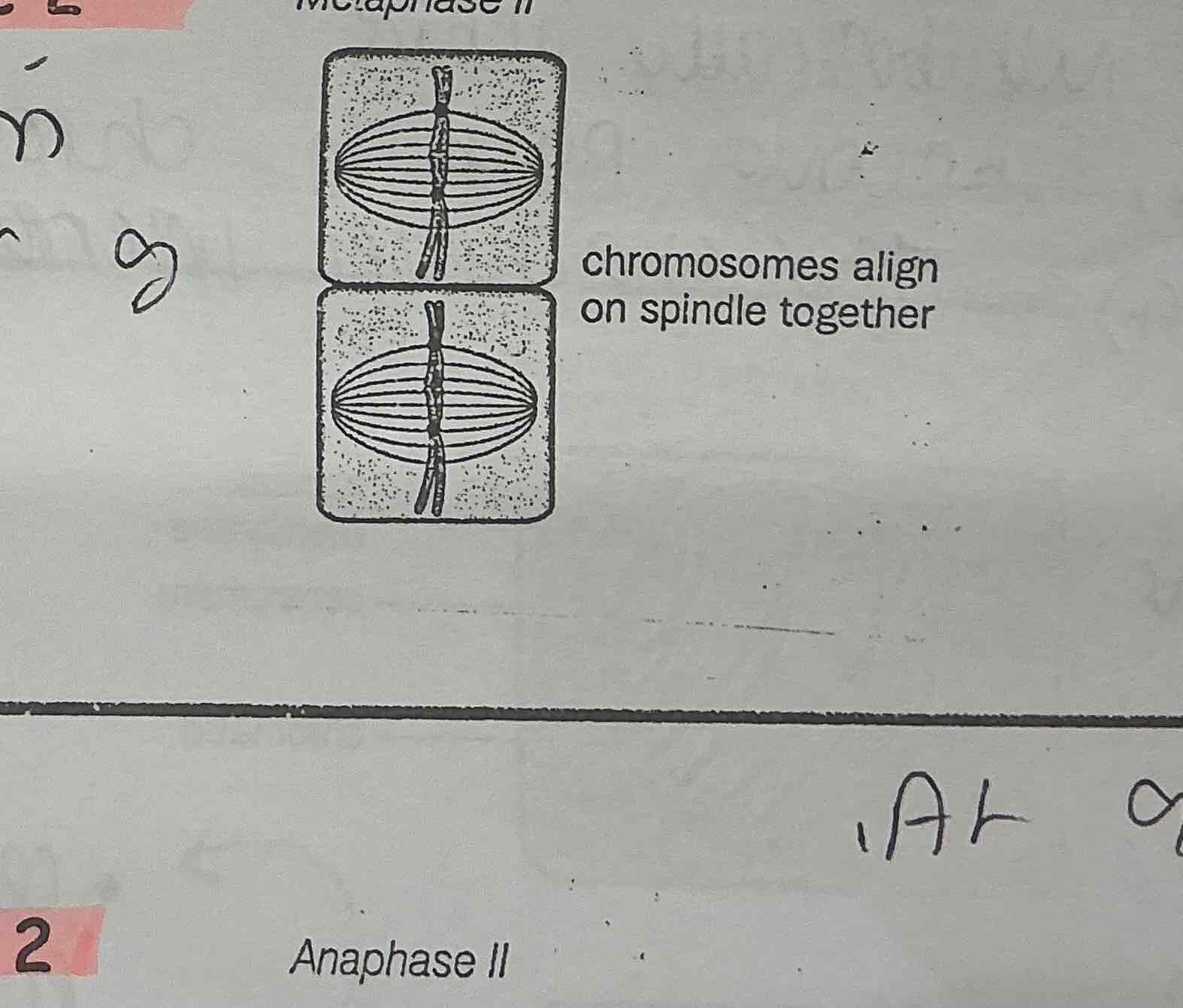
What happens during ANAPHASE 2 of MEOSIS?
.Spindle fibres contract
.Centromere splits
.Chromatids are pulled to opposite poles ( centromere first)
.At 90 deg to how it happened before

What happens during TELOPHASE 2 of MEOSIS?
.Chromosomes unwind and become ling and thin again
.The spindle disappears
.The nucleolus reappears
.The nuclear membrane reforms
CYTOKINESIS TAKES PLACE AFTER
.Ends with 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells , each with genetic variation
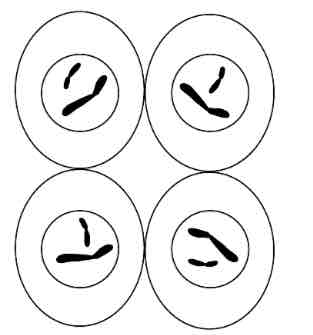
Why does MEOSIS produce haploids gametes / half the number of chromosomes?
Because the DNA only replicates once , but is followed by 2 divisions of the cell
Why is it important that gametes are haploid / why is important that gametes are produces by meiosis and not mitosis ?
.Because upon fertilisation the diploid number of chromosomes are restored
.To prevent the number of chromosomes doubling in each generation ( which is what would happen if they were produced by mitosis)
Why do ANT MALES only have 1 chromosome?
. Ant males are HAPLOID because they develop from UNFERTILISED EGGS.They inherent their entire genome from their mother so only has one set of chromosomes (haploid)
How does MEOSIS produce cells that are genetically different
1.Crossing over between non - identical sister chromatids in PHROPHASE 1
1.Independent assortment of bivalent/homologous chromosomes in metaphase 1 (or independent assortment of chromatid pairs in Metaphase 2
3.The random fertilisation between 2 genetically different haploid gametes
4.MUTATION
Where does MEOSIS occur ?
ANIMALS= sperm + eggs (
PLANTS = Anther/Ovary
BOTH REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
Annotate a graph of MEOSIS

What is the differences between MITOSIS AND MEOSIS?
.MITOSIS has 1 division resulting in 2 daughter cells
. MEIOSIS has 2 division resulting in 4 daughter cells
.MITOSIS number of chromosomes is unchanged
. MEOSIS number of chromosomes is halved
.MITOSIS homologous chromosomes not associate in pairs .
MEOSIS homologous chromosomes pair up to form BIVALENTS
.MITOSIS crossing over does not occur
.MEOSIS crossing over occurs and chiasmata form
.MITOSIS daughter cells are genetically identical
.MEOSIS daughter cells are genetically different
.MITOSIS chromosome number in daughter cell is 46
.MEOSIS chromosome number is daughter cell is 23
.MITOSIS no independent assortment
.MEOSIS there is independent assortment