Punnet Squares n Stuff
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
dominant traits
Traits that always show in a person even if only one gene of the pair is inherited for the trait
recessive traits
traits that typically do not show in a person unless both genes for the trait are inherited
representation of dominant vs recessive traits
Capital letters vs lowercase letters
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism, informally known as "characters", ex: eye color
allele
An alternative form of a gene, informally known as a "trait"
who was the father of genetics and what did he do?
Gregor Mendel, studied patterns of inheritance by experimenting with pea plants
why did Mendel use garden peas?
Short Generation Time, Lots of Pure Bred, Easy to change the crosses
Genes
distinct hereditary factors that determine traits--smt physical
homozygotes
Organisms containing two identical copies of the same gene on corresponding chromosomes.
sex linked crosses
traits are carried on the sex chromosomes; notated with X and Y with traits as superscripts, either the X or Y won't have a superscript because
Why are X-linked recessive traits more likely to occur in males?
Men will have one X and one Y, therefore, if the X is recessive, that's all you need. The Y automatically won't be able to combat anything because the trait will only appear on one chromosomes. Women, on the other hand, have two X's, so in order for the recessive trait to be expressed, you also need the other X chromosomes to be recessive, and the probability of this happening is lower.
pleiotrophy
The ability of a single gene to have multiple effects on the body (ex: sickle cell anemia, results can include blindness, liver failure, heart attack, etc)
Why does pleiotropy occur?
1) the expression of a single gene can affect cell function in more than one way
2) a gene may be expressed in different cell types in a multicellular organism
3) a gene may be expressed at different stages of development
incomplete dominance
Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another, causing the traits to blend (ex: snapdragon color: red + white = pink)
Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed (ex: red + white = red and white stripes)

polygenic inheritance
occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait, produces a bell curve graph when you plot the number of individuals
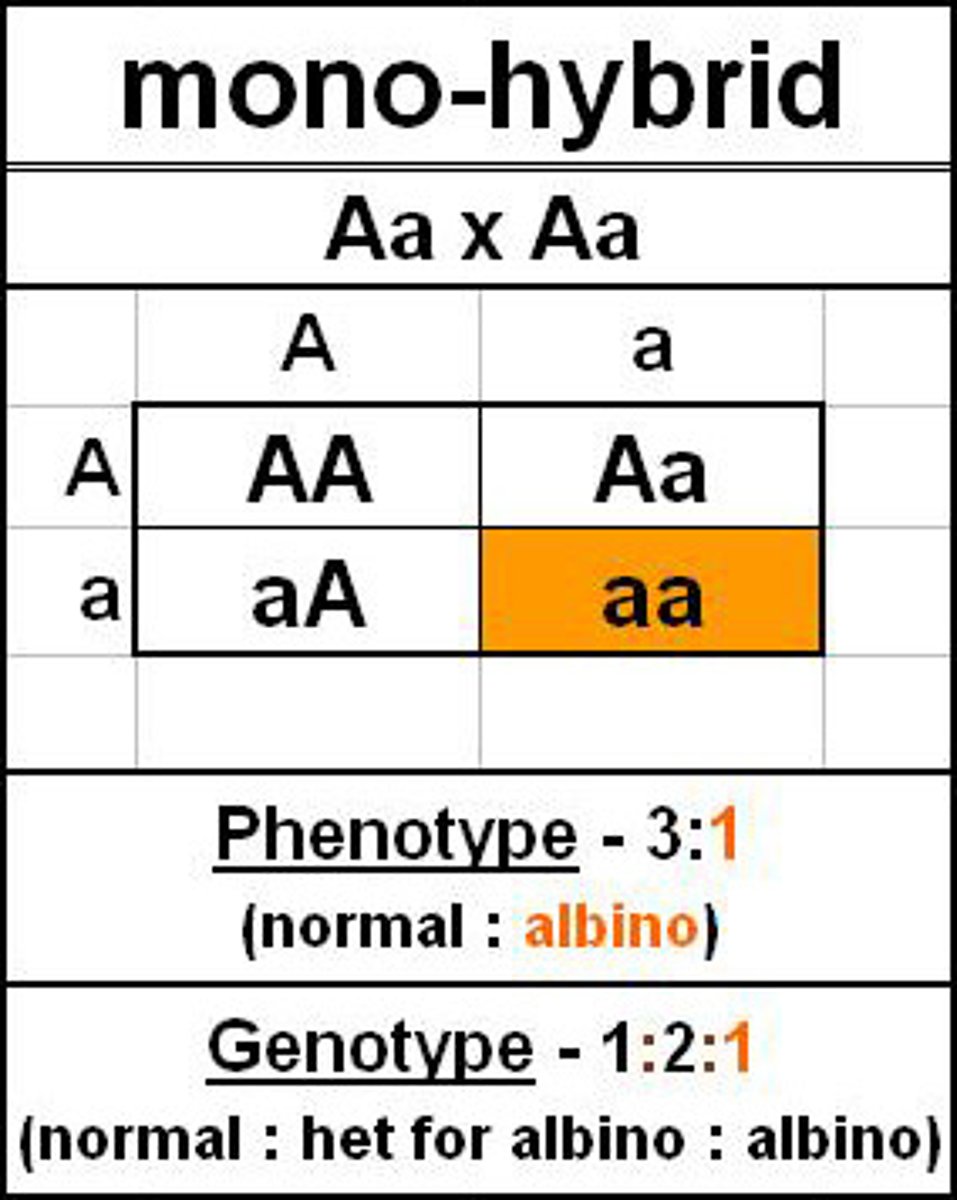
monohybird cross Aa (draw the punnett square)
a hybrid that is heterozygous with respect to a specified gene.
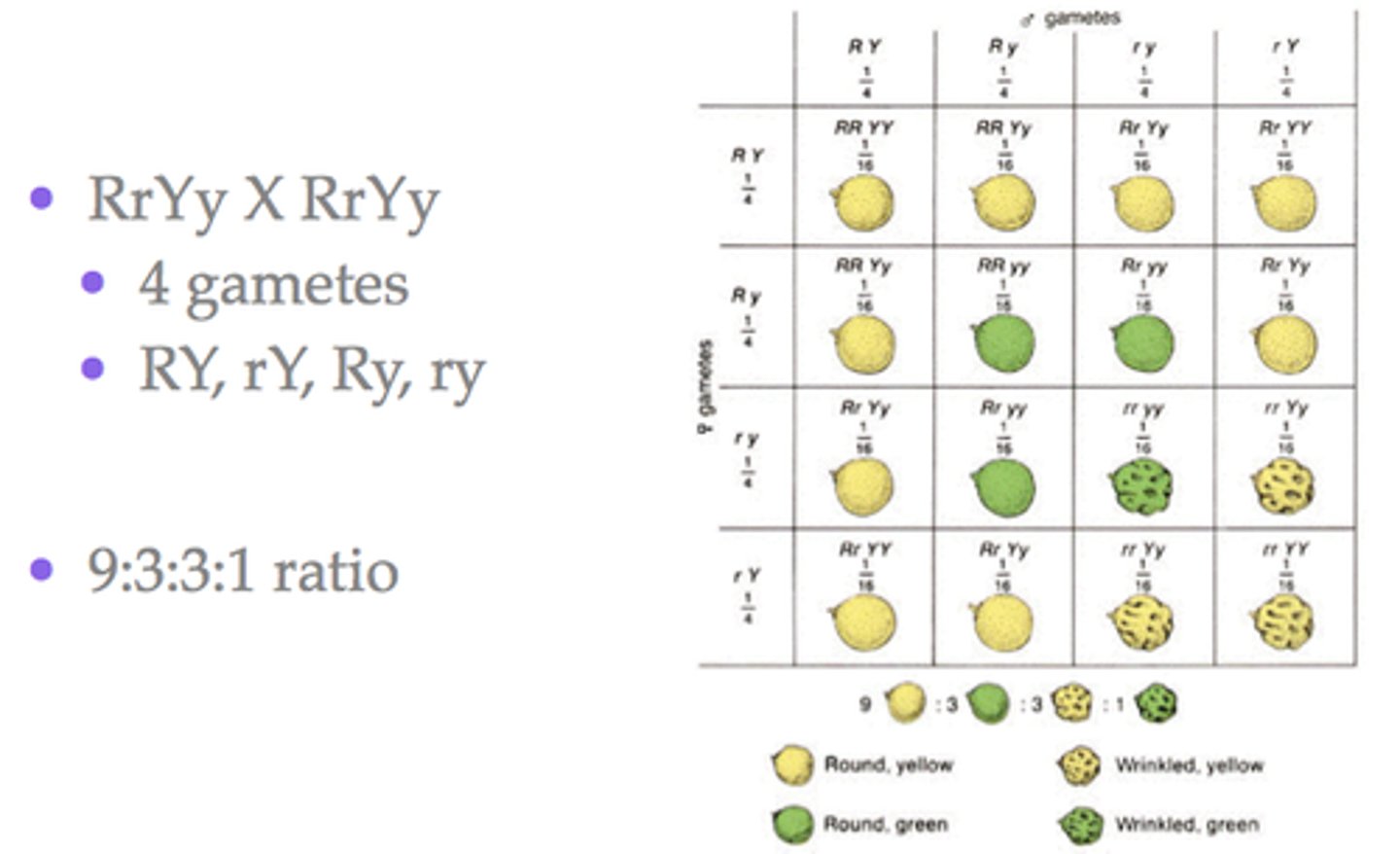
dihybrid cross RrYy (draw the punnett square)
a hybrid that is heterozygous for alleles of two different genes.
quantitative traits
phenotype determined by multiple genes
locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.