Plant Taxonomy - Exam 3 (Strobilus, flower, fruit)
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Dehisces
Breaks open
Anthesis
Completely expanded flower
Receptacle
Attachment site of the four floral whorls. Involved in the dispersal of seeds.
Perianth
Composed of the calyx and corolla.
Tepal
Sepals and petals are undifferentiated. Found in lilies.
Calyx
First whorl. Made up of all the sepals.
Sepal
Leaf-like or petal-like appendages.
Color, pattern, texture, shape, and fragrance are variable, though mostly green and leaf-like.
Protect the immature flower.
May attract pollinators.
May have trichomes.
Trichomes
Fine hairs
Corolla
Second whorl. All of the petals.
Petals
Petal-like or leaf-like appendages.
Color, pattern, texture, shape, and fragrance are variable and abundant.
Protect the immature flower.
May attract pollinators, typically through nectaries.
May have trichomes.
Nectaries
Produce a sugary substance
Androecium
Third whorl. Male. All the stamens. May have trichomes.
Stamen
Microsporophyll
Anther and filament
Anther
Composed of pollen sacs.
Dehydrates and dehisces, releasing the pollen.
Filament
Thin stalk. Provides structural support and elevation for the anther.
Gynoecium
Fourth whorl. Female. Composed of all the carpels or pistils. May have trichomes.
Carpel
Modified leaf, the basic unit of the gynoecium
Pistil
Megasporophyll.
May be composed of one or more carpels that are modified leaves, folded lengthwise, with fused margins.
Stigma
Pad for pollen. Post commonly perched on the style, less commonly sessile on the ovary. May be simple or compound. May be free, partially free, or completely fused. Can be wet, usually sticky or dry, usually with papillae, short trichomes or long branching trichomes.
Style
Thin neck. An extension of the pistil. A perch and structural support for the stigma. May be simple or compound. May be free, partially fused, or completely fused.
Ovary
The largest portion of the pistil. Produces the ovules. Matures into a fruit.
Ovule
Single or up to thousands in a carpel. Matures into a seed.
Egg in angiosperms
Female gamete. After fertilization, matures into an embryo.
Monocotyledon whorls
Most commonly in threes or multiples of 3
Dicotyledon whorls
Most commonly in 4s or 5s or in their multiples.
Complete flower
All floral whorls are present
Perfect flower
Both male and female parts are present and functional
Synecious
A perfect form. Every flower on the plant is perfect
Incomplete flower
One or more floral whorl is absent or nonfunctional
Imperfect flower
Either male or female parts are absent or nonfunctional.
Staminate flower
Androecium is present and functional, gynoecium is absent or nonfunctional
Pistillate
Gynoecium is present and functional, androecium is absent or nonfunctional
Imperfect forms
Monoecious and dioecious
Monoecious
Staminate and pistillate flowers are borne separately but on the same plant
Dioecious
Staminate and pistillate flowers are born on different plants
Actinomorphic
Regular symmetry. Ray shaped. Radially symmetric.
Zygomorphic
Irregular. Bilaterally symmetric.
Free
Floral whorls or parts are distinct (unattached)
Fused
Floral whorls or parts are fused
Connate
Same floral parts are fused. Ex.: petal-petal
Adnate
Different floral parts are fused. Ex. Stamen-petal
Perianth
Nonreproductive parts of a flower. Usually sepals (calyx) and petals (corolla)
Asepalous
Sepals absent. The least common form of an incomplete flower that is missing a perianth part.
Aposepalous
Polysepalous. Sepals free.
Synsepalous
Gamosepalous. Sepals fused.
Apetalous
Petals absent. The most common form of an incomplete flower that is missing a perianth.
Apopetalous
Polypetalous or choripetalous. Petals free.
Blade
Flattened portion of a petal or leaf.
Petal blade attachment
Sessile
Claw
Sessile petal
The blade is directly attached to the receptacle or hypanthium
Petal claw
The blade is attached to the receptacle or hypanthium by a narrow stalk-like claw
Hypanthium
The fusion of the bases of all of the filaments, petals, and sepals. Form a disk, bowl, or urn-shaped structure
Sympetalous
Gamopetalous. Petals are fused.
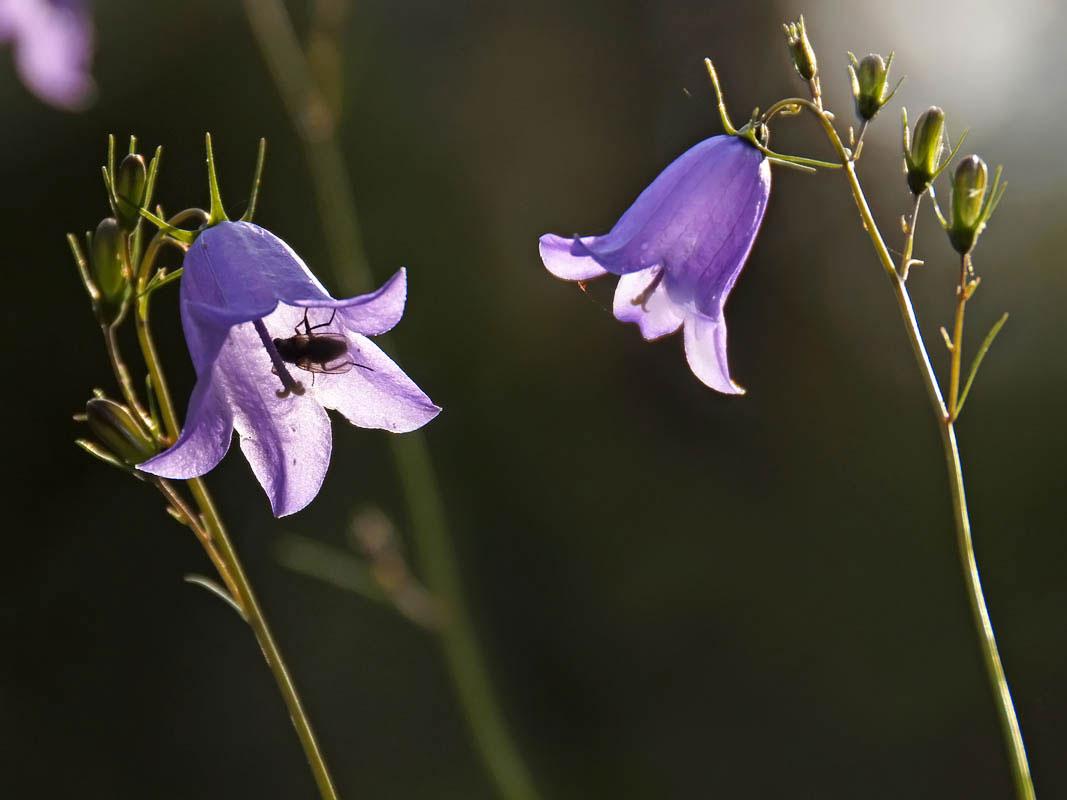
Campanulate corolla
Bell

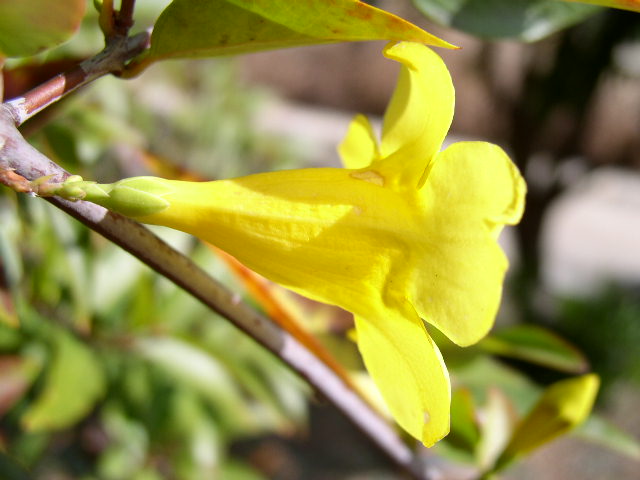
Funnelform corolla

Rotate corolla
Salverform corolla

Tubular corolla
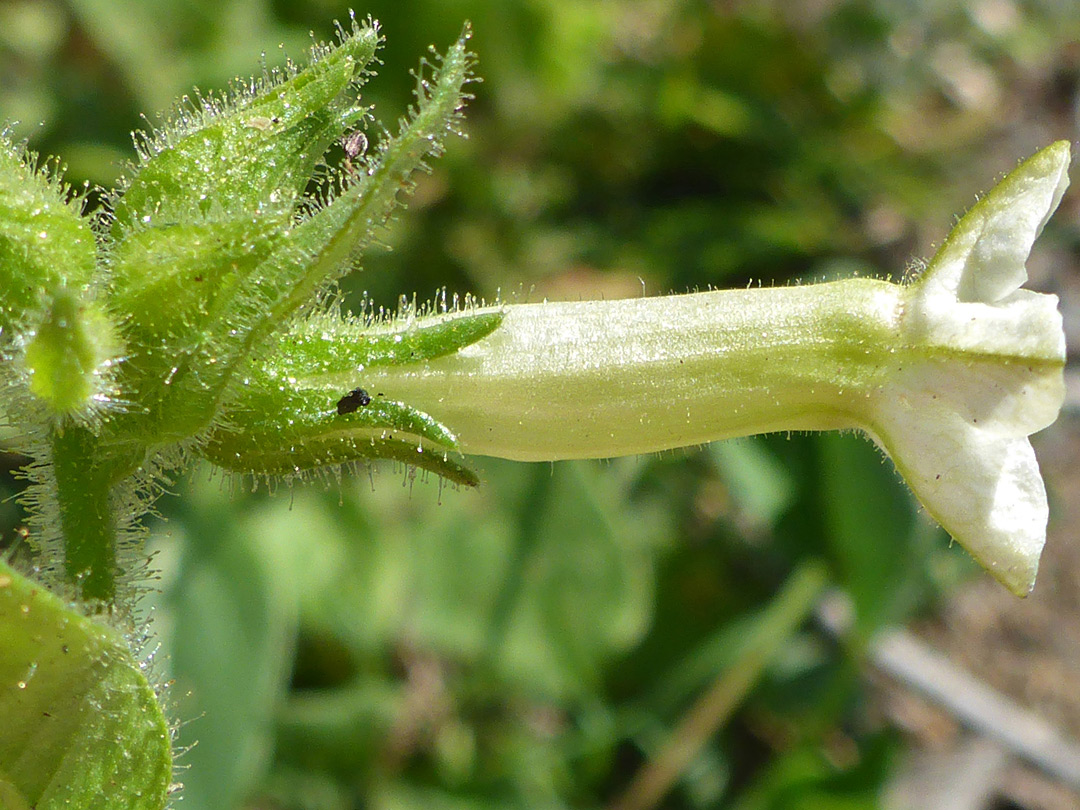

Urceolate corolla
Urn

Bilabiate corolla
Two lipped

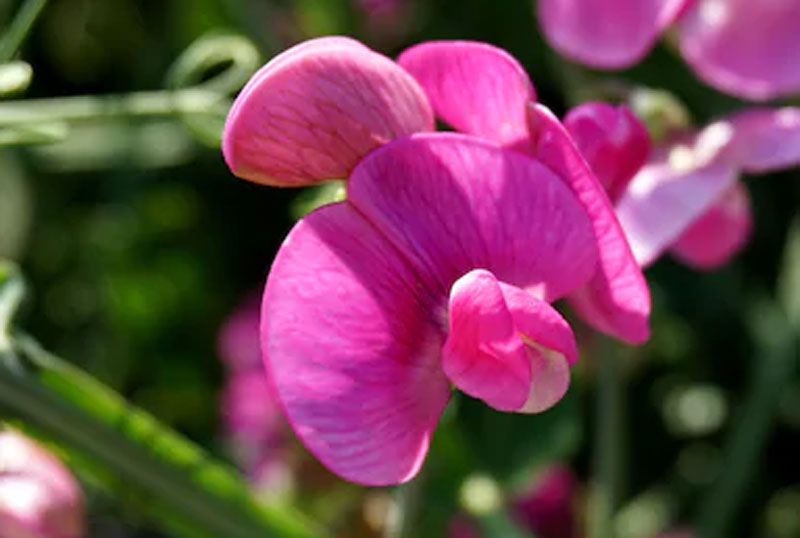
Papilionaceous
Butterfly

Tetradynamous
The stamens are two different lengths, four of one length and two of another length
Connate
Stamens are fused, most commonly the filaments, less commonly the anthers, as in Asteraceae
Monodelphous
Filaments of all the stamens are fused into a cylinder (hibiscus)
Diadelphous
Filaments of the stamens are fused into two separate bunches
Polyadelphous
Filaments of the stamens are fused into many separate bunches
Syngenesious
Anthers of the stamens are fused (shooting star flowers)
Adnate
Stamens that are fused to other floral parts
Epipetalous
Filaments of the stamens that are fused to the petals
Staminodes
Sterile stamens that may be variously modified
Alternate stamen position
Attached to the receptacle BETWEEN the petals
Opposite stamen position
Attached to the receptacle IN FRONT of the petals
Included stamens
Stamens shorter than or do not extend beyond the length of the corolla
Exerted stamen length
Stamens are longer than or extend beyond the length of the corolla
Distinct pistil
pistils are free from one another
Monocarpous
A gynecium with one pistil or carpel
Simple pistil
A pistil with one carpel. Results in a single ovary with one locule. Ex. drupes
Apocarpous
A gynoecium with multiple pistils or carpels, all free. Multiple simple pistils. Ex. strawberry
Connate pistil
Pistils are fused to one another
Syncarpous
A gynoecium with multiple pistils or carpels, all fused.
Compound pistil
A pistil with multiple carpels, all fused. Results in a single ovary with multiple locules. Ex. orange.
Locule
Carpel
Hypogynous
Low. Superior ovary. Other floral parts are attached BELOW the ovary
Periogynous
Middle. Half-inferior ovary. Other floral whorls attached halfway up the ovary.
Epigynous
Upon. Inferior ovary. Other floral whorls attached above the ovary.
Ovule attachment
Attachment of the ovules to the ovary. Due to the formation of the carpels or carpel
Marginal ovule placement
A single locule from one carpel. Ovules attached in two rows at the two margins of the fused carpel. (Legume pod)
Axile
Two to many locules from two to many carpels divided by septa. Ovules attached along the central axis formed from the fused margins of the carpels. (Okra)
Parietal
One locule, from two to many carpels, NOT divided by septa. Ovules attached along the fused margins of the carpels, no axis formed due to the absence of septa. (Spiny melon)
Free central
One locule, from two to many carpels, not divided by septa, with a free central axis. Ovules attached along the fused free central axis of carpels, no septa. (Kiwi)
Apical ovule placement
Ovules attached at the TOP of the ovary
Basal ovule placement
Ovules attached at the BOTTOM of the ovary
Solitary flower
A single flower
Sessile
Flower is attached directly to the stem
Pedicellate
Flower is attached to the stem by a stalk
Inflorescence
Groups or clusters of up to thousands of flowers
Peduncle
The stalk that attaches the inflorescence to the stem
Rachis
The main axis of the inflorescence, an extension of the peduncle
Pedicel
The stalk that attaches the flower to the rachis