biology - osmosis and diffusion
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is osmosis?
its the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from higher water concentration to lower water concentration
when does osmosis happen?
when the total concentrations of all dissolved substances inside and outside the cell are different
it can only occur if the membrane is partially permeable
how does osmosis work?
water will move across the membrane from the dilute solution to the concentrated one
why is osmosis important?
its important for moving water from cell to cell, for example in plant roots
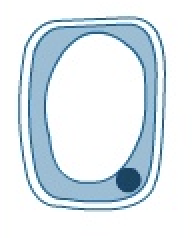
what happens when a cell is placed in a dilute solution or water?
it absorbs water by osmosis then becomes turgid
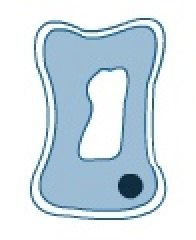
what happens when a cell is placed in a concentrated solution?
it loses water by osmosis and becomes flaccid
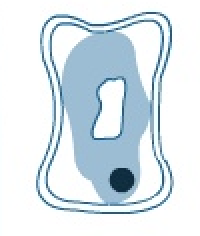
what happens when a cell is placed concentrated solution for longer time?
eventually the cell contents shrink so much that the membrane and cytoplasm split away from the cell wall
and gaps appear between the wall and membrane
a cell like this is called plasmolysed
design a practical to investigate the effects of osmosis
we can use onion epidermis cells
add a drop of concentrated sucrose solution one one slide, then a drop of distilled water on a second slide
then take two small squares of inner epidermis from an onion layer
and transfer one to the sucrose solution then one to the water
a drop of the correct solution is added to the top of each specimen then followed by a cover slip
after being examined through a microscope for several minutes
the specimen in water will show turgid cells
and the cells in the sucrose solution will gradually plasmolyse
what will happen to a cell if you replace a concentrated solution with distilled water
they will gradually recover from their plasmolysed condition until they are fully turgid again
what is diffusion?
its the net movement of particles (molecules or ions) from a region of high to low concentration
when / how does diffusion happen?
for example: if the cell is making carbon dioxide by respiration, the concentration of carbon dioxide inside the cell will be higher than outside.
over time, more molecules will move from inside to outside then move in the other direction
why is there is a greater diffusion of molecules from the more dilute solution than the more concentration
for example, in a sucrose and water solution the water molecules are able to pass through the partially permeable membrane, but the sucrose molecules cannot as they are too large
so if the solution is more dilute, there will be a greater diffusion of water molecules compared to a more concentrated solution
describe the uptake of water by roots
so water can enter the root hair cell by osmosis
what is water potential?
it is how free the water molecules are to move
the more concentrated the solution is, the lower its water potential will be
what is the rate of diffusion affected by?
surface area to volume ratio. a larger surface area compared to the volume will increase the rate
temperature. the rate is greater at higher temperatures, since a higher temperature provides the particles with more kinetic energy
diffusion happens quicker if theres a steep concentration gradient
design a practical for diffusion
take a block of agar jelly which has been dyed purple and cut it up into three smaller cubes of different sizes next, you carefully drop all the cubes into the beaker of diluted hydrochloric acid. when a cube turns completely colorless, you should record it.
what are the materials needed for a practical demonstrating diffusion + safety?
petri dish, hydrochloric acid, small knife and agar jelly
wear gloves and eye protection to avoid skin contact with the acid, and keep all chairs out of the way