4.3 & 4.4 Inhibitors, cofactors, coenzymes and prosthetic groups
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is an enzyme inhibitor?
a molecule that prevents enzymes from carrying out their normal functions of catalysis by binding to it to decrease its activity
True or false? a non-competitive inhibitor has a close structural resemblance to the substrate of an enzyme so it can fit into its active site
false - this is only true for competitive inhibitors
Fill in the blanks: a competitive inhibitor competes with the _____ molecule for the ____ ____
substrate, active site
Explain how a competitive inhibitor decreases the activity of an enzyme
it competes with the substrate molecules for the active site
after a successful collision, the inhibitor remains bound to active site blocking the substrate from entering
this reduces the number of substrate molecules binding to the active sites in a given time slowing down the rate of reaction
the inhibitor is then released
True or false? competitive inhibitors bind permanently to the active site so their effect is irreversible
false - they bind temporarily so have a reversible effect
True or false? competitive inhibitors change the Vmax of the enzyme
false
Why do competitive inhibitors not change the Vmax of an enzyme’s activity?
competitive inhibitors change the rate of reaction for a given substrate concentration, but if the substrate concentration is increased enough (so there is a very small concentration of inhibitors) then the Vmax can be reached
True or false? increasing the substrate concentration decreases the effect of a competitive inhibitor as it increases the changes of an enzyme-substrate collisions rather than an enzyme-inhibitor collision
true
True or false? non-competitive inhibitors have no structural resemblance to the substrates
true
What part of an enzyme do non-competitive inhibitors bind to?
allosteric site
Fill in the blanks: when a non-competitive inhibitors binds to the ____ site of the enzyme, it causes a ____ change in the ____ structure of the enzyme, also changing the configuration of the ___ ___. Therefore the active site is no longer complementary to the substrate so the enzyme cannot carry out its function and is ____.
allosteric, conformational, tertiary, active site, inhibited
Are the effects of a non-competitive inhibitor always reversible or irreversible?
either reversible or irreversible
Fill in the blanks: increasing the concentration of a non-competitive inhibitor ____ the enzyme concentration, ___ the rate of reaction
decreases, decreasing
Choose the correct words: in non-competitive inhibition, increasing the substrate concentration can/cannot reverse the inhibition as the bonding between the enzyme and inhibitor is usually temporary/permanent
cannot, permanent
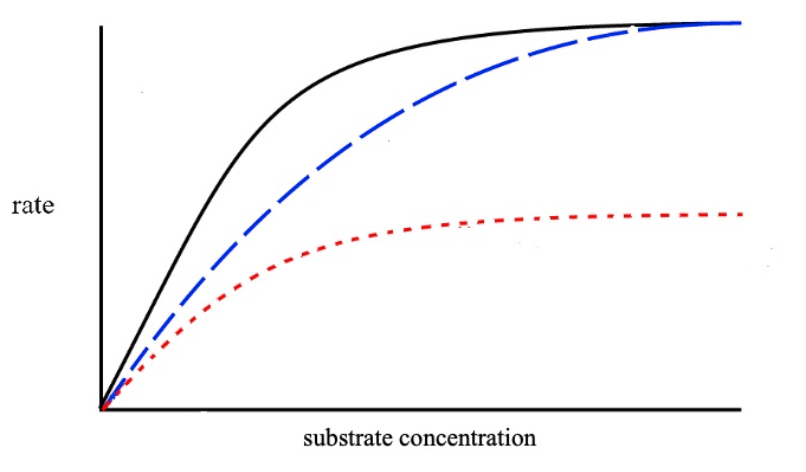
This graph shows the effect of enzyme inhibitors on rate of reaction. Which coloured line shows the effect of a non-competitive inhibitor?
orange

This graph shows the effect of enzyme inhibitors on rate of reaction. Which coloured line shows the effect of a competitive inhibitor?
blue

This graph shows the effect of enzyme inhibitors on rate of reaction. Which coloured line shows the effect of normal enzyme function without an inhibitor?
black
What is end-product inhibition?
when the end-product of a reaction (in a metabolic pathway) acts as an inhibitor to the first enzyme in that pathway
Why is end-product inhibition important for a cell?
it prevents excess product being made and resources being wasted
What is a metabolic pathway?
A series of catalysed reactions where the product of one enzyme-catalysed reaction becomes the substrate for the next reaction in the pathway, to produce a final product
Explain the link between inhibitors and the end-product of a metabolic pathway
The final product of a metabolic pathway can act as a non-competitive inhibitor to an earlier enzyme along the pathway, preventing any more of the final-product being produced. The inhibition is reversible allowing the product to be formed once again when the concentration of the product falls
Fill in the blanks: multi-enzyme complexes increase the (e)____ of metabolic reactions without increasing ___ ___ as the enzyme and substrate molecules are in the same area reducing ____ time
efficiency, substrate concentration, diffusion
What are allosteric enzymes?
enzyme’s whose activity can be altered by molecules acting at a site other than the active site which change the overall shape of the enzyme
What are the two types of regulatory molecule for allosteric enzymes?
allosteric activators and allosteric inhibitors
Explain how an allosteric activator works
When it binds to an enzyme at its allosteric site, the 3D shape of the active site changes so it is now complementary to and can bind to the substrate to catalyse the formation of the products. The enzyme remains activated until the allosteric activator leaves the allosteric site
True or false? enzyme inhibitors can cause disease, make poisons and form medicinal drugs
true
Choose the correct words: some enzymes, especially those involved in catalysing oxidation-reduction reactions, can only work if another small/large, protein/non-protein molecule is bound to them
small, non-protein
True or false? cofactors are organic ions
false - they are inorganic ions
What is the cofactor for amylase?
chloride ions
How can cofactors work?
transfer atoms between reactions in metabolic pathways
act as co-substrates, binding with the substrate or in the active site to allow the substrate to fit better
change the tertiary structure of the enzyme ‘s surface making the temporary bonds in the ESC easier to form
What is a prosthetic group?
a cofactor that is permanently bound to an enzyme
What bonds do prosthetic groups make with enzymes?
covalent
Give an example of an enzyme and its prosthetic group
carbonic anhydrase contains a zinc ion
What is the function of carbonic anhydrase?
found in red blood cells where is catalyses the interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid, which is important for carbon dioxide to be carried in the blood
Choose the correct word: coenzymes are inorganic/organic cofactors/prosthetic groups
organic, cofactors
True or false? coenzymes can be bound temporarily or permanently
true
What is one of the main functions of coenzymes?
to carry electrons or chemical groups between enzymes in a metabolic pathway
What are all coenzymes derived from?
water soluble vitamins
What large metabolic pathways are coenzymes often found in?
photosynthesis and respiration
What is the term describing enzymes that are produced in an inactive form?
inactive precursor enzymes
Why are some enzymes produced as inactive precursor enzymes?
to prevent damage to the cells producing them
Give an example of a group of enzymes which are produced in inactive precursor form
digestive enzymes
What 2 ways can inactive precursor enzymes be activated?
coenzyme or by certain environmental conditions
How does a cofactor cause the precursor activation of an enzyme?
it can change the shape of the enzyme’s tertiary structure, so the active site now has the correct 3D specific and complementary shape
What is the term to describe precursor enzymes before activation by a cofactor?
apoenzyme
What is the term to describe precursor enzymes after activation by a cofactor?
holoenzyme
How can a change in conditions, such as temperature or pH, activate a precursor enzyme?
it can cause a change in shape of the enzymes tertiary structure
What are precursor enzymes that are activated by changes in conditions called?
zymogens or proenzymes