R & R exam 3
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
level of 11th and 12th rib
where are the kidney in relation to the ribs
T12-L3
where are the kidneys in relation to the vertebrae in SUPINE position
L1-L4
where are the kidneys in relation to the vertebrae in STANDING position
right
which kidney is slightly lower due to the liver
renal pelvis (pos), renal artery, renal vein (ant)
what is the order of vessels that enter the hilum from POSTERIOR to ANTERIOR
secures kidney to posterior abdominal wall
what is the function of the adipose tissue that surrounds the kidneys
retroperitoneal
A term describing the anatomical space BEHIND the PERITONEUM, where the kidneys are situated
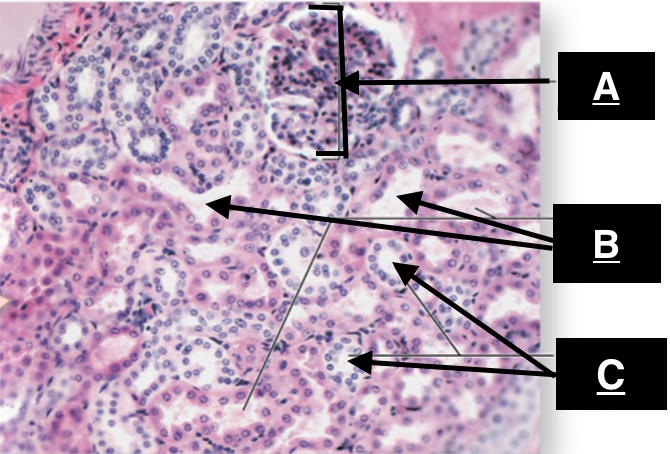
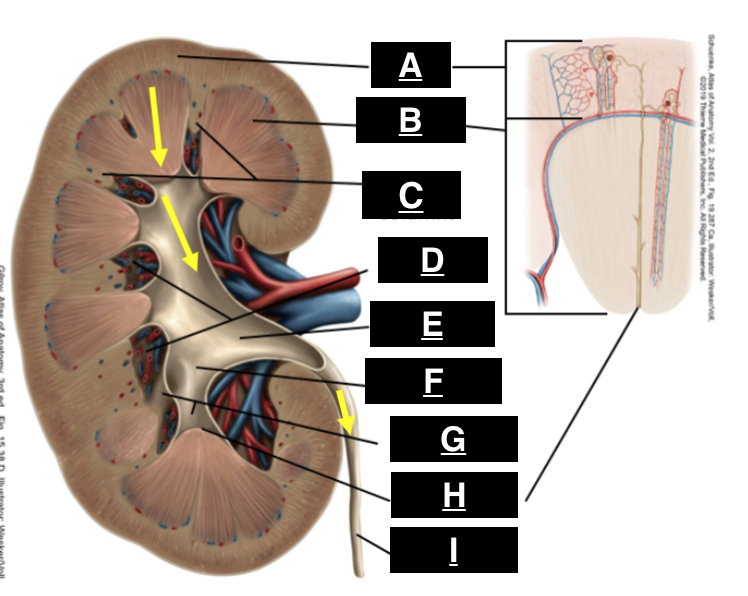
cortex
what is A
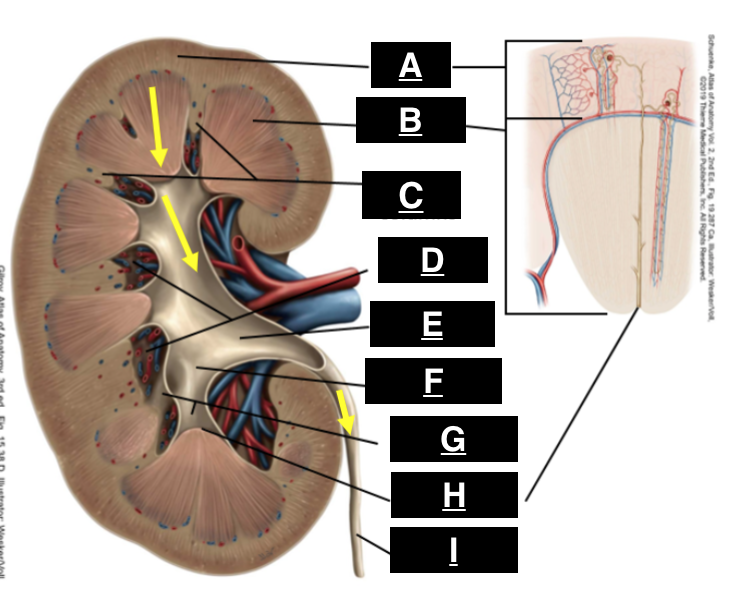
pyramid
what is B
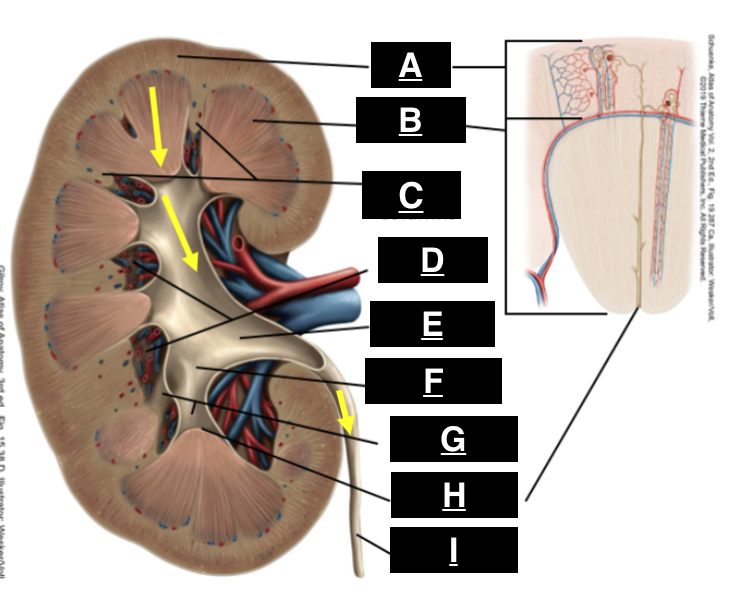
renal columns
what is C
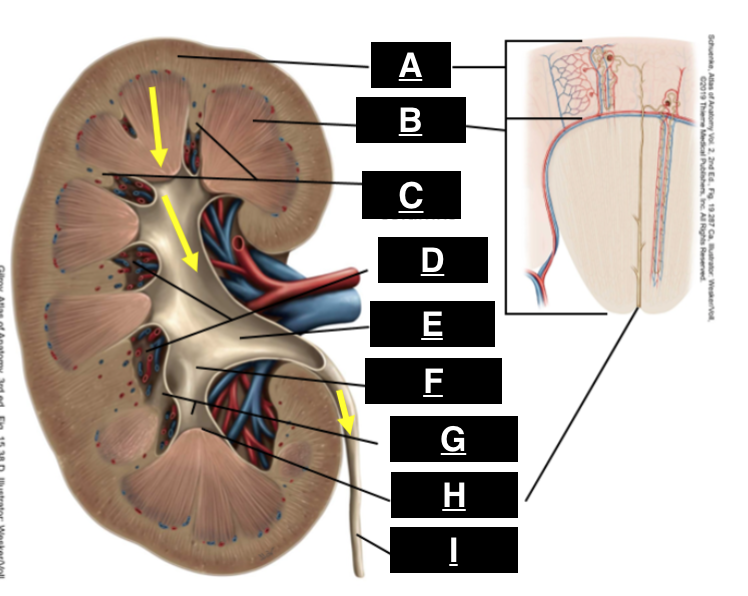
renal sinus
what is D
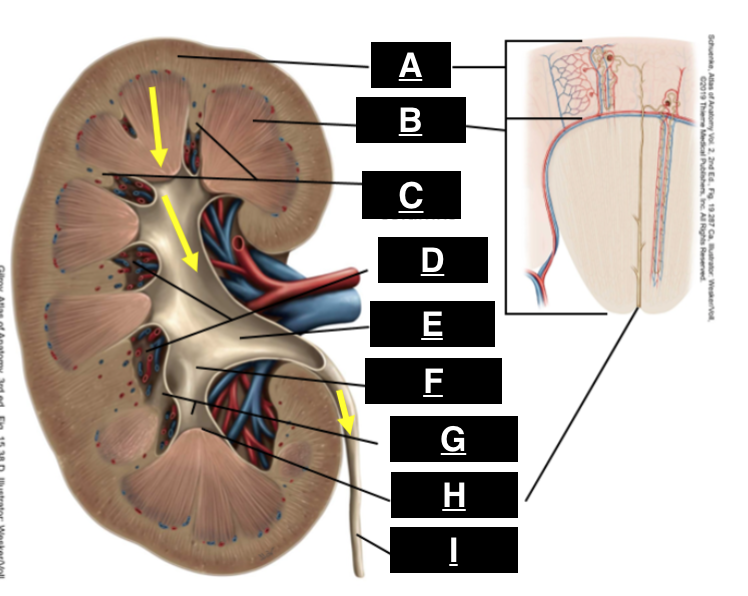
renal pelvis
what is E
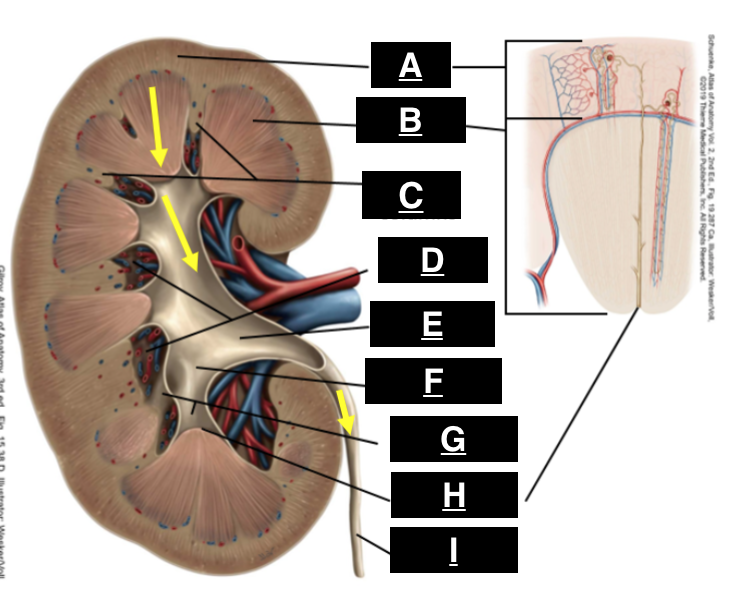
major calyx
what is F
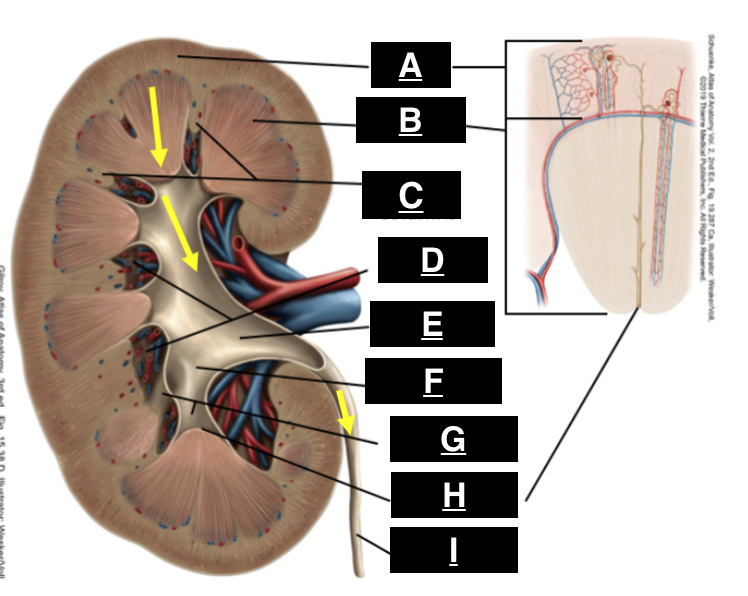
minor calyx
what is G
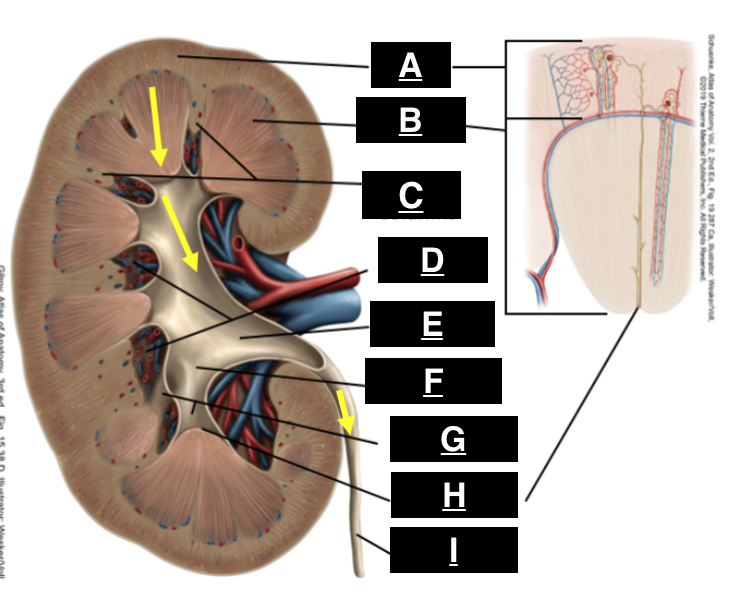
renal papilla
what is H
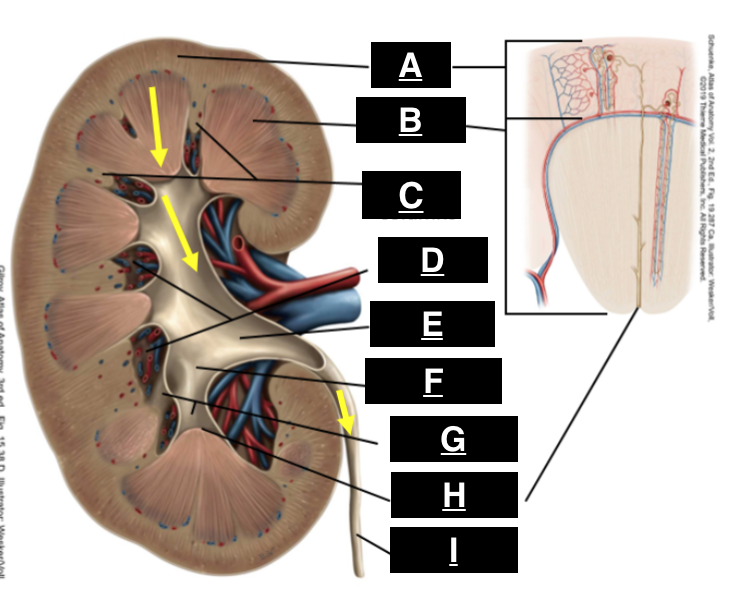
ureter
what is I
afferent arteriole
what is A
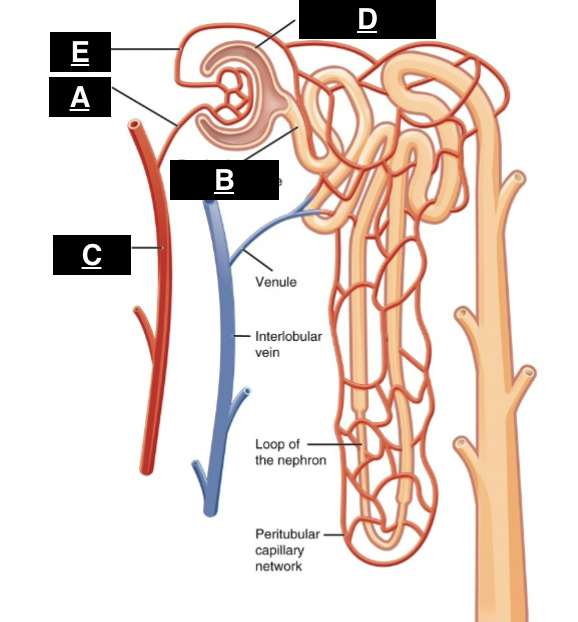
proximal convoluted tubule
what is B
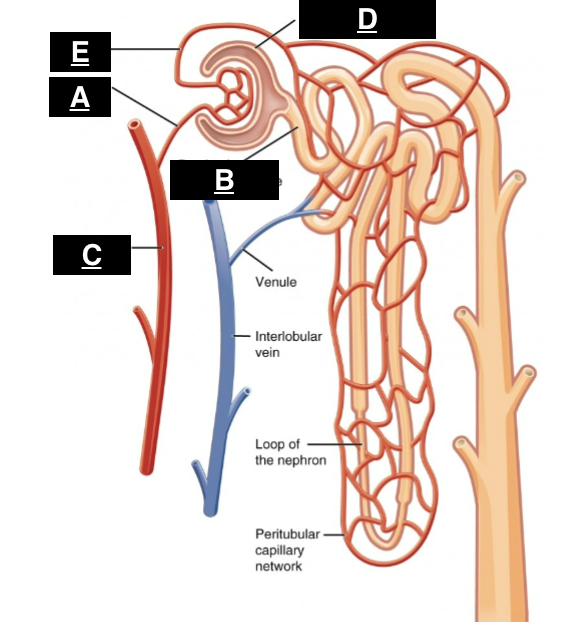
interlobular artery
what is C
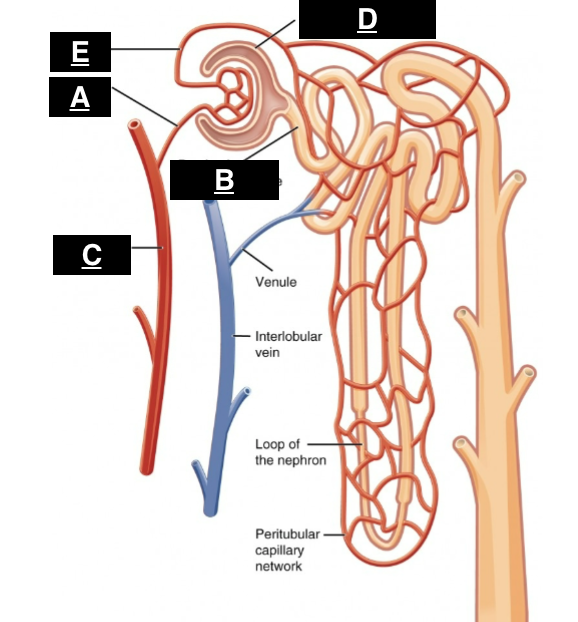
glomerular capsule
what is D
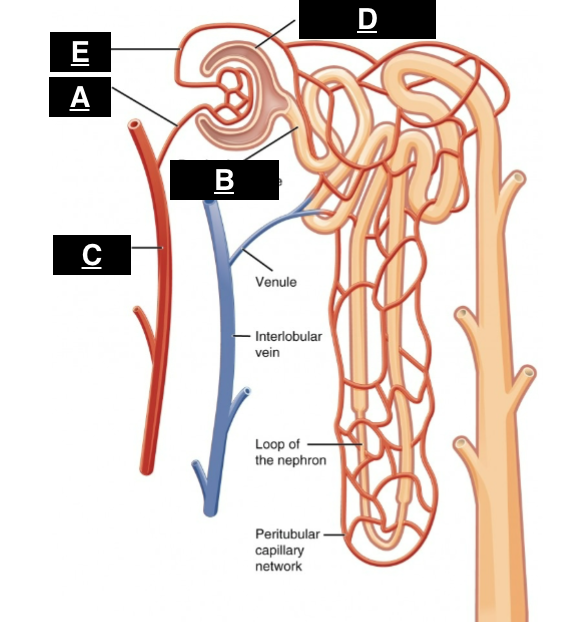
efferent arteriole
what is E
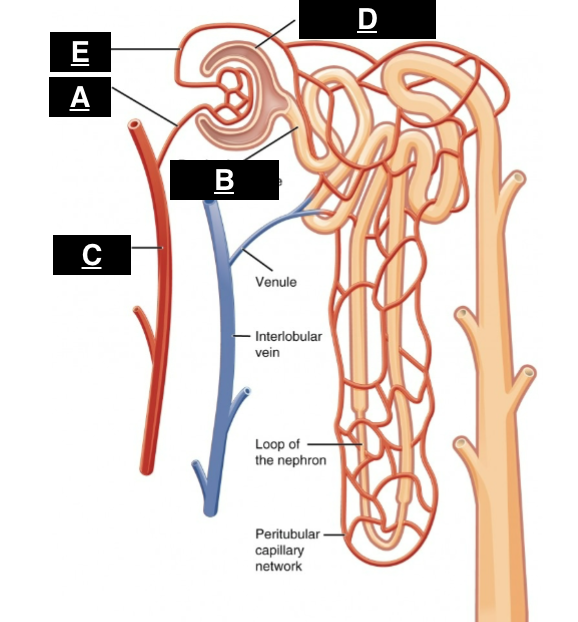
in the renal pyramids
where does urine enter the collecting ducts
renal papilla, minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, urethra
path of urine as it leaves the body
high
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) activity that leads to more concentrated urine
low
ADH activity that leads to more diluted urine.
BUN and creatinine
waste products measured to assess kidney function
Na, K, Cl, CO2
solutes regulated by kidneys
tubules
where does resorption and secretion occur
reabsorption
transfer from TUBULE to BLOOD
secretion
transfer from BLOOD to TUBULE
glomerulus
where does filtration occur
juxtamedullary nephron
nephron with loop of henle that extends deep into medulla, functions to CONCENTRATE URINE
inner medullary collecting tubule
major site of water regulation
proximal tubule
ONLY site of glucose reabsorption
proximal tubule
major site of reabsorption
proximal tubule
major site of water reabsorption
descending loop
where does water reabsorption occur in LOOP OF HENLE
ascending loop
where solutes are reabsorbed using active transport in the loop of Henle
medullary concentration gradient
increasing concentration of solutes in the renal medulla that facilitates water reabsorption
PCT dysfunction, SGLT2 (Na/glu transporter) blockade, hyperglycemia
potential causes of glucose in urine
loop of henle
creates medullary concentration gradient that allows for conc. of urine
ascending loop
where do loop diuretics act
ascending loop
main site of Mg reabsorption
solute reabsorbed via active transport
what happens as filtrate travels up ASCENDING loop
water reabsorbed
what happens as filtrate travels down DESCENDING loop
distal tubule
site of fine tuning reabsorption
distal tubule
where do thiazide diuretic act
cortical collecting duct
major site of K secretion
cortical collecting duct
where does aldosterone act
principal/light cells
REABSORB Na (ENaC) and SECRETE K (ROMK) in cortical collecting duct
ENaC
SODIUM channel responsible for REABSORPTION in PRINCIPAL cells of cortical collecting duct
ROMK
POTASSIUM channel responsible for SECRETION in PRINCIPAL cells of cortical collecting duct
intercalated/dark cells
control pH through H+ SECRETION and HCO3- REABSORPTION in the cortical collecting duct
cortical collecting duct
major site of regulation of Na, K, and H+
Na
what is reabsorbed at cortical collecting duct
K and H+
what is secreted at cortical collecting duct
aldosterone
hormone that increase Na REABSORPTION and K SECRETION
increased K and H+ secretion
side effects of aldosterone
medullary collecting duct
site of antidiuretic hormone control
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
inserts aquaporin channels in medullary collecting duct to promote WATER REABSORPTION
intracellular fluid
where is the majority of total body water located?
aquaporins
specialized water channel proteins that facilitate water transport across cell membranes, particularly in the kidneys.
Na
major solute in extracellular fluid
K
major solute in intracellular fluid
efferent arteriole
blood vessel that EXITS the glomerulus
afferent arteriole
blood vessel that ARRIVES at the glomerulus
efferent arteriole
orgin of blood in capillaries wrapped around the tubules?
macula densa
specialized cells in the DCT that help regulate blood pressure and GFR.
fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane, podocyte filtration slits
layers of filtration barrier
water, glucose, electrolytes (Na, K ect), amino acids
what passes through a healthy filtration barrier
large proteins and cells
what CANNOT pass through a healthy filtration barrier
protein or blood in urine
what indicates injured/diseased filtration barrier?
decreases
what happens to GFR if hydrostatic pressure in BOWMANS SPACE INCREASES
decreases
what happens to GFR if hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries DECREASES (hypotention)
increases
what happens to GFR if EFFERENT arteriole is vasoCONSTRICTED
decreases
what happens to GFR if AFFERENT arteriorlie is vasCONSTRICTED
renal blood flow (RBF)
the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time, affecting GFR and kidney function.
renal plasma flow (RPF)
the volume of plasma that passes through the kidneys per unit time, a crucial metric in assessing kidney function.
GFR decreases
what happens if RBF decreases
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
the rate at which blood is filtered through the glomeruli of the kidneys, affecting fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
125ml/min
normal GFR
most water is reabsobed
why is GFR NOT equal to urine output
BP (pressure), BV (volume), arteriole resistance, barrier integrity, hormone signal
determinants of GFR
juxtaglomerular apparatus
what structure is outlined by the yellow box
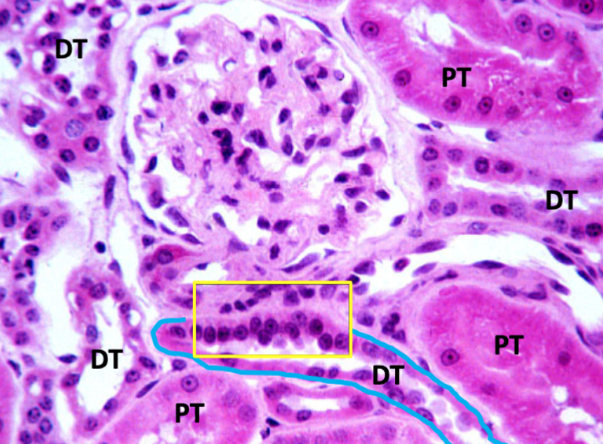
macula densa
senses NaCl levels in distal tubule and regulates blood pressure and GFR.
adenosine release/ decrease GFR
response of MACULA DENSA if NaCl is HIGH
prostaglandin (PEG2) release/ increase GFR
response of MACULA DENSA if NaCl is LOW
adenosine
vasoCONSTRICTOR of AFFERENT arteriole released by MACULA DENSA
prostaglandin/PEG2
vasoDILATOR of AFFERENT arteriole released by MACULA DENSA
Renin
Hormone released by JUXTAGLOMERULAR cells in response to LOW blood pressure, leading to increased production of angiotensin II.
RAAS
A hormonal system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance, initiated by the release of renin from the kidneys.
low BP
what causes juxtaglomerular GRANULAR cells to signal RENIN release
low NaCl
what causes MACULA DENSA to signal RENIN release
low-level angiotensin II
causes vasoCONSTRICTION of EFFERENT arteriole INCREASING GFR
aldosterone
hormone produced by adrenal glands that promotes Na RETENTION INCREASING BP and blood volume
NSAIDs
block prostaglandin mediated vasodilation and renin release, DECREASES GFR
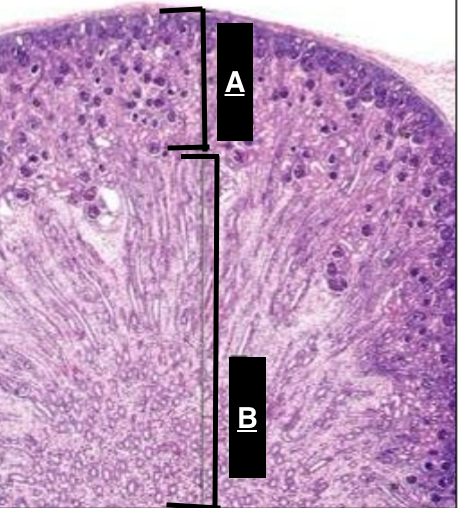
cortex
Identify A
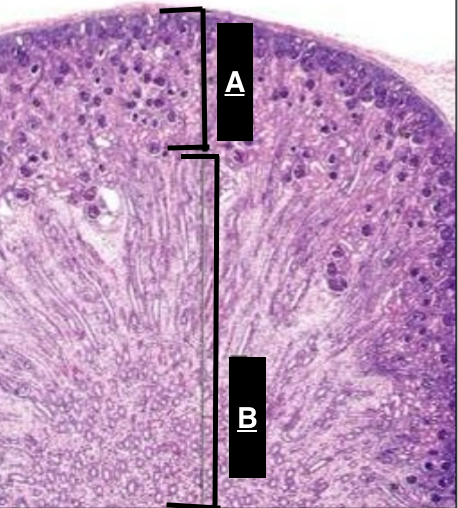
medulla
Identify B
renal corpuscle
Identify A
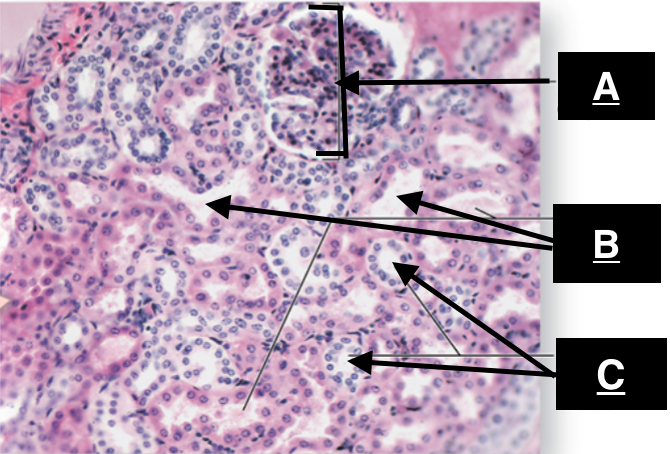
proximal convoluted tubule
identify B