BIO 11.1 - 2ND LE
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
hypothesis
It is a tentative explanation to answer a question or problem.
hypothesis
This educated guess is made based on previous observations or from literature reviews. It is then tested, and the test results may confirm, deny, or cause a revision of the original hypothesis.
A testable hypothesis should have the following attributes:
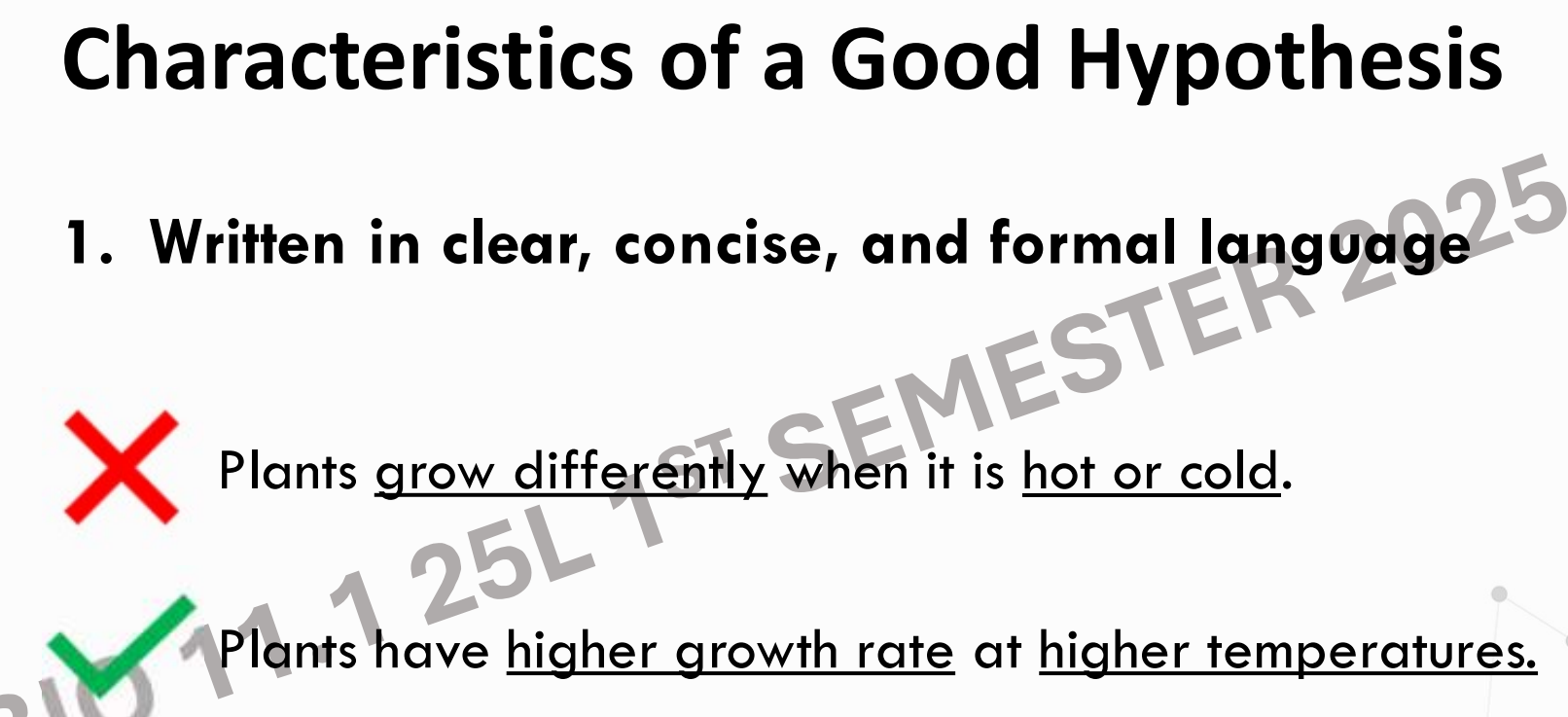
It is written in clear and concise language.
It predicts a tentative relationship between an independent (i.e. manipulated) and dependent (i.e. measured) variable.
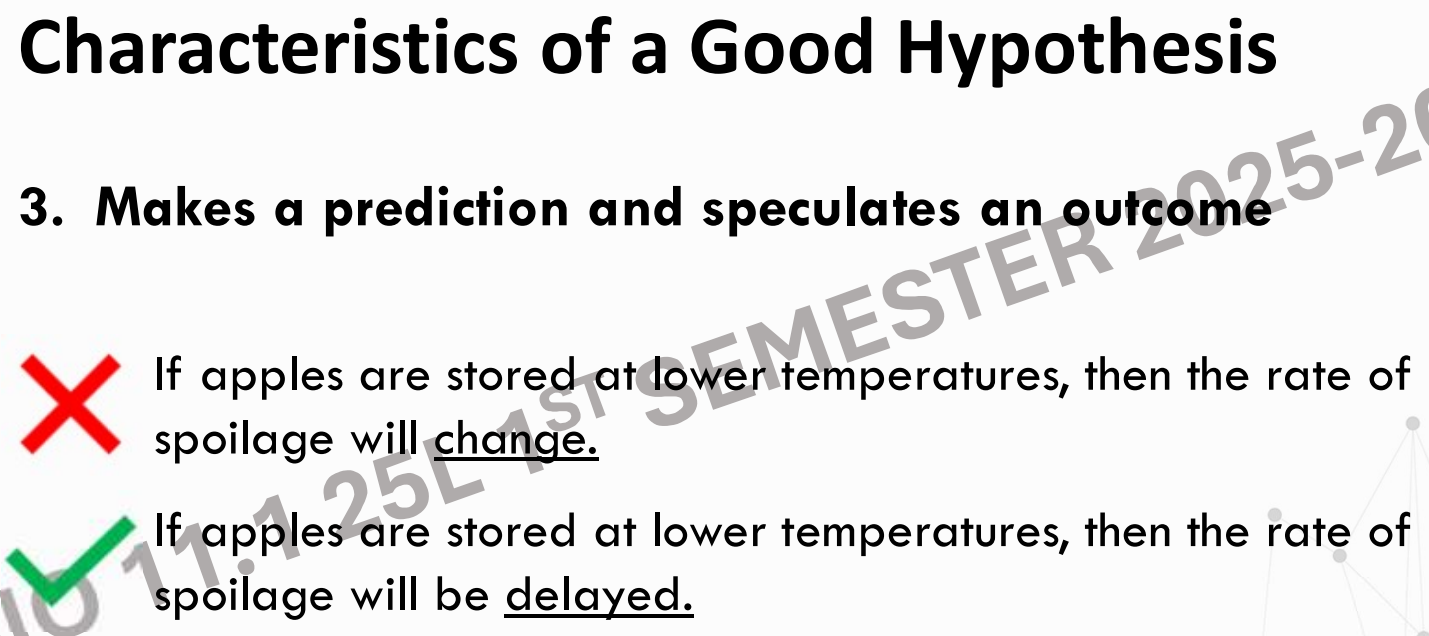
It makes a prediction and speculates an outcome.
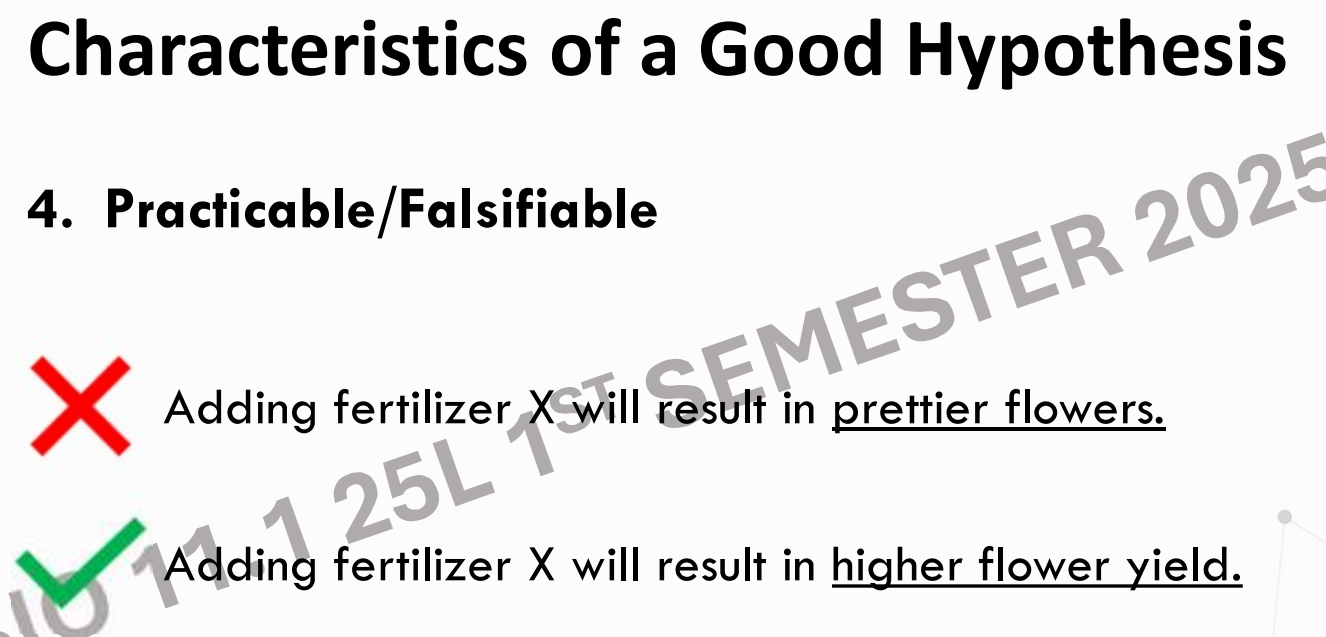
It is practicable or falsifiable.
The variables in question can be measured or an experiment can be designed to establish or disprove the hypothesis.
It leads to other hypotheses.
A testable hypothesis should have the following attributes:
__________________
__________________
__________________
__________________
__________________
mouse red blood cells (RBC); Rhoeo spathacea leaf cells
In this exercise, you will observe what happens to _______________ and ________________ when subjected to salt solutions of different concentrations.
Cell shrinkage/crenation
swelling
bursting
plasmolysis or withdrawal of the cell membrane from the cell wall.
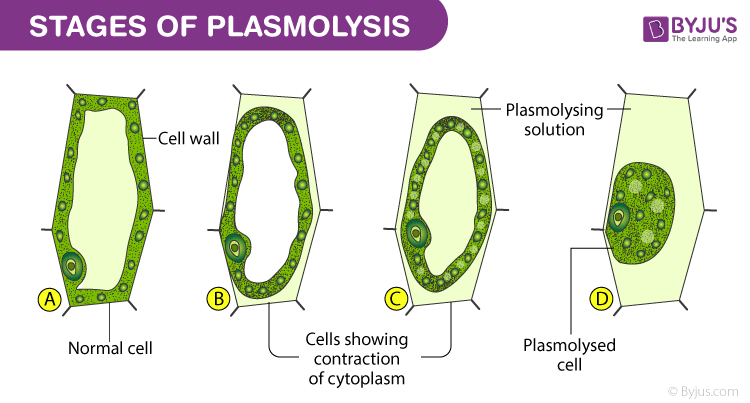
What are the possible morphological changes of the cells when subjects to a salt solution of different concentrations?
Its epidermal leaf cells are hexagonal.
What is the shape of R. spathacea’s epidermal leaf cells?
anthocyanin; large central vacuole; tonoplast
In R. spathacea’s epidermal leaf cells, the purple ____________ pigment is contained in the ___________, bounded by a membrane (__________).
If the Makahiya loses its sensory cells
then the leaves will not close when touched.
Hypothesis
Mouse red blood cells, Rhoeo spathacea leaf cells
Refer to this statement: "If the Makahiya loses its sensory cells, then the leaves will not close when touched."
What part of the statement is the premise?
What part of the statement is the prediction?
It refers to a tentative explanation to answer a question or problem.
What specimen/s will be used for exer 4’s activity?







Tonicity
Ability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by affecting water content
Osmolarity (or Osmotic Concentration)
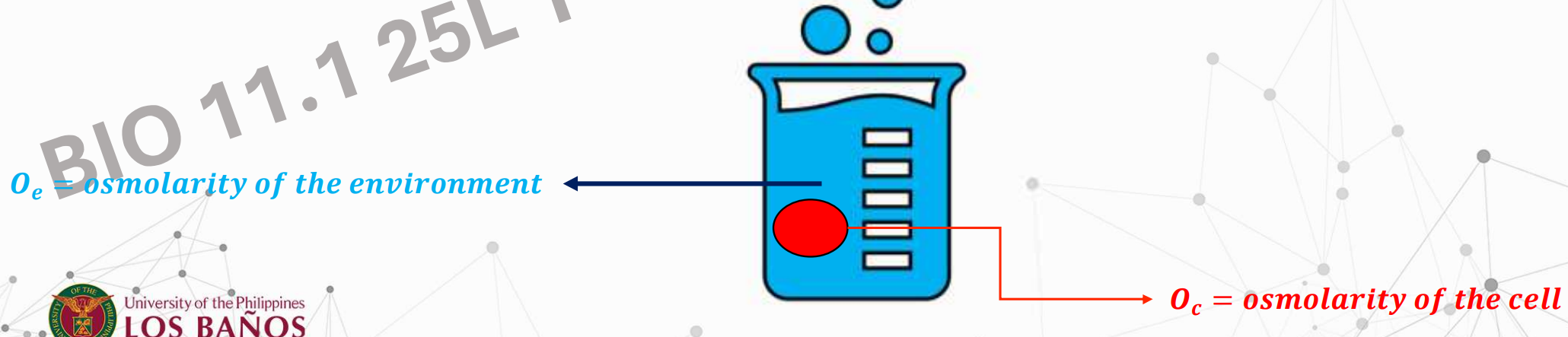
Concentration of particles (or osmoles) in a volume of solvent
Osmolarity (or Osmotic Concentration)

Usually used when there is a membrane involved that separates the particles and the solvent
Osmosis
Movement of solvent (H2O) across a membrane to an area with higher osmolarity
Hypertonic/Hyperosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Oe > Ocell
Hypertonic/Hyperosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Water will move out from the cell
Hypertonic/Hyperosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Volume of the cell decreases
shriveled
plasmolyzed

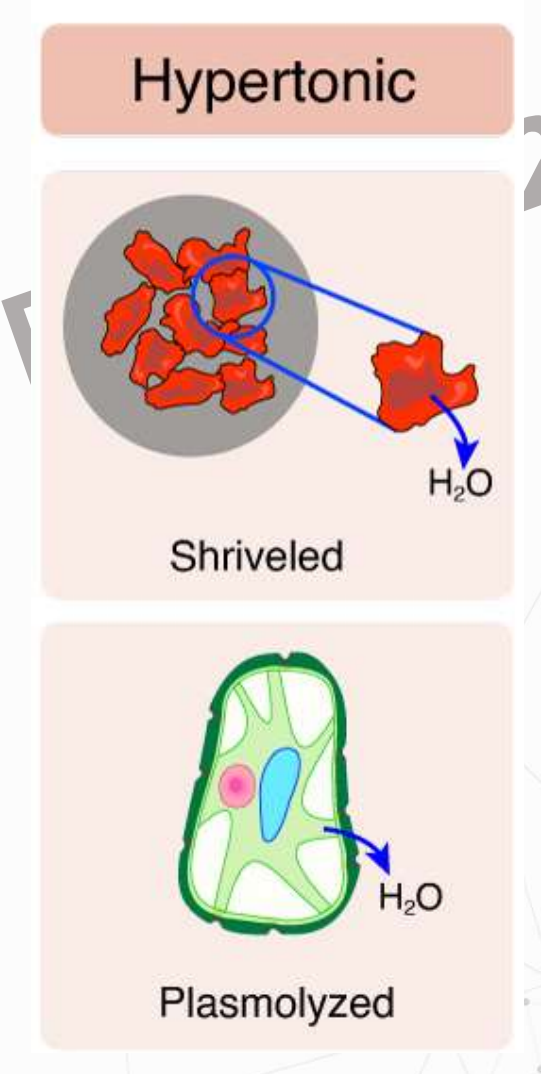
Tonicity Levels - Hypertonic/Hyperosmotic
Outcome:
Animal Cells – ____________
Plant cells - ____________
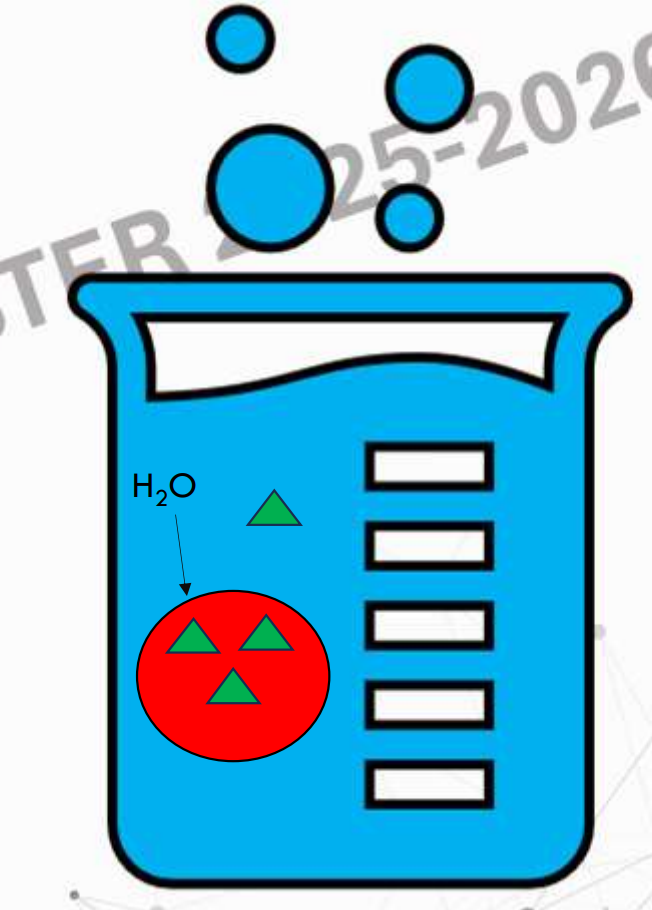
Isotonic/Isoosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Oe ≈ Ocell
Isotonic/Isoosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Net movement of water is zero
Isotonic/Isoosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Net movement of water is zero
normal
flaccid


Tonicity Levels - Isotonic/Isoosmotic
Outcome:
Animal Cells – __________
Plant cells - ___________
Hypotonic/Hypoosmotic
Tonicity Levels
Oe < Ocell
Hypotonic/Hypoosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Water will move into the cell
Hypotonic/Hypoosmotic

Tonicity Levels
Volume of the cell increases
Lysed (or will burst)
turgid (normal)

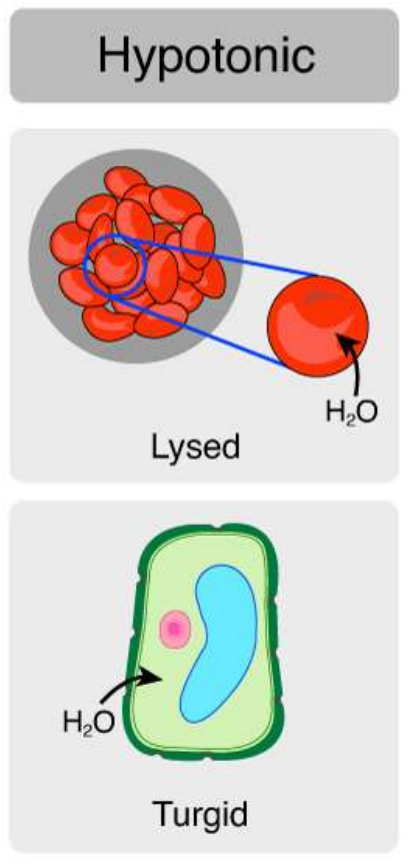
Tonicity Levels - Hypotonic/Hypoosmotic
Outcome:
Animal Cells – ____________
Plant cells – ____________
simulacra
Many complex phenomena are more readily understood if their presentation can be simplified. This simplification may involve the use of a model which may be mathematical, a series of diagrams on paper or a working physical system. Although close estimations, models are generally regarded in __________ (i.e. empirical reflection of reality).
technological viewpoint
scientific viewpoint
A model may be defined in two ways.
In the _____________, it may be anything used as a guide in testing a new design, such as small-scale version of a bridge or airplane.
A model, in the ______________, may also be a design or structure representative of some system.
The scientific viewpoint of a model.
It aims to synthesize a structure-function relation based on universally accepted knowledge and understanding.
scientific viewpoint
In biology, which definition of a model is generally more useful?
technologically-limited; small; large
There are several uses of a model.
First, a model may simplify the study of some _____________ system which are either too ______ (e.g. cellular components) or too ______ (e.g. solar system).
visualize; understand; analyze
There are several uses of a model.
Secondly, it may serve to better v_________, u_________, and a__________ concepts, principles and systems.
Hence, models could be tangible or intangible.
For example, one can clearly recognize some properties of and processes in the cell through the aid of a model.
False
“Hence, models could be tangible or intangible.“
True or False?
Models are often only tangible.
broad concept; specific

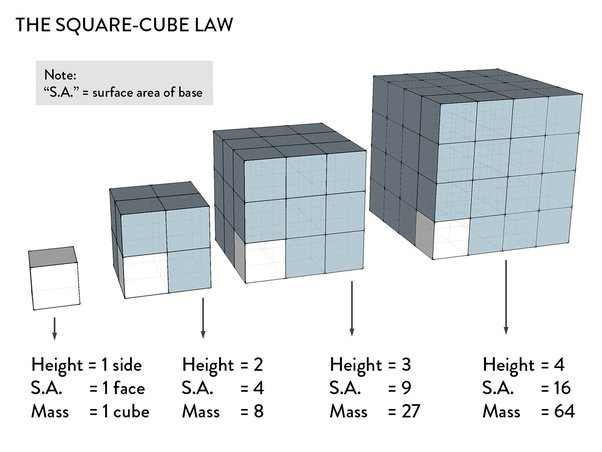
There are several uses of a model.
Thirdly, a model represents a __________ and thus may act as a springboard for further investigation of more _________ problems.
Building and disputing scientific models is a fundamental scientific undertaking.
True
True or False?
a model represents a broad concept and thus may act as a springboard for further investigation of more specific problems.
hypothesis
There are several uses of a model.
Finally, a __________ may be formulated and tested using the same scientific model.
Thus, a scientific model provides a logical framework of analysis.
False
“Finally, a hypothesis may be formulated and tested using the same scientific model.“
True or False?
A hypothesis cannot be formulated and testing used the same scientific model due to its various considerations and factors.
It's the selective/semi- permeability of the cell membrane. When it comes into contact with a solute-rich or solute-poor solution, instead of diffusing the solutes themselves into or out of the cell, osmosis occurs to move the solvent (in this case, water).
What is the property of the cell membrane we investigated during the last exer (Exercise 4 – Formulating Testable Hypothesis)?
osmosis
The movement of solvent molecules (i.e. water) across the cell membrane that caused the changes in the cell size and shape is the phenomenon known as ___________.
diffusion
Osmosis is simply __________ (the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to low concentration) across a semi-permeable membrane.
osmotic concentration; moles per liter (mol/L);
Here are a few more concepts related to osmosis.
First, ____________ refers to the number of dissolved particles, such as molecules and ions.
It is usually expressed as ____________.
Thus, in the previous exercise, the osmotic concentrations of the salt solution where you subjected the cells were 0.07 M, 0.15 M and 0.30 M for the RBCs and 0.01 M and 0.30 M for the R. spathacea leaf cells.
hyperosmotic or hypertonic;
hypoosmotic or hypotonic;
isoosmotic or isotonic;
shape; size
Here are a few more concepts related to osmosis.
Secondly, the medium to which cells are exposed to can be described as hyper-, hypo- or isoosmotic.
A medium is _____________ relative to a cell if it has a higher osmotic concentration than the cell.
Conversely, a medium is _____________ relative to a cell if it has a lower osmotic concentration.
An _____________ medium is one that has the same osmotic concentration as the cell.
Hence, you observed changes in cell ______ and ______ as a dynamic response of these cells to varying osmotic concentrations.
dialyzing membrane
The use of biological models, therefore, becomes an essential and integral part of studying cells.
For example, it is particularly helpful in the analysis of the properties of the cell membrane.
In this part of the exercise, you will use an artificial membrane, the ___________, as a model to investigate the cell membrane and its properties.
dialyzing membrane
This artificial membrane has microscopic pores that allow the passage of substances. This membrane of variable pore sizes can be sourced from laboratory suppliers in the form of dialysis tubings.




cell membrane
We are well aware that it is the boundary separating the inside of the cell from its surrounding.
cell membrane; 8 nm
The _____________ has been shown to be ____ thick and presumed that its formation may have been one of the earliest events in the evolutionary origins of the cell.
lipids; lipids; phospholipids; hydrophilic; hydrophobic
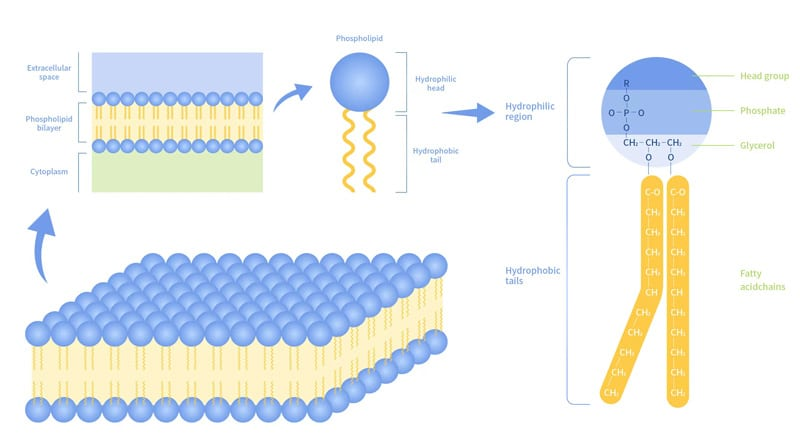
The cell membrane is made up of several kinds of molecules, mostly ________. These _______, mainly ___________, contain both a _________ head (polar) and a ___________ tail (non-polar). In addition, protein and carbohydrates are part of the membrane and play key roles in several membrane processes.
Ernst Overton; selectively permeable envelope
The first account of the semi-permeability of the cell membrane is in the 1890s when ____________ identified a _________________ around cells that has a lipid nature with cholesterol and lecithins.
Irving Langmuir; lipid monolayers; polar; non-polar
It was _____________ in 1917 who studied the behavior of _____________.
He determined that in one molecule thick of oil film, which is spread upon the surface of the water, the hydrophilic groups (the _____ heads) are down in the water and the hydrophobic chains (the ______ tails) are on the surface.
Gorter; Grendel
The lipid monolayer model was then proposed to be a bimolecular lipid leaflet model in 1925 by __________ and ___________.
Davson; Danielli
In 1935, ________ and _________ developed the protein-lipid sandwich model which suggested that membranes contain this protein sheets.
These models inferred the membrane to have lipids and proteins, and is a bilayer.
electron microscopy; Robertson; trilayer appearance
With the advent of ____________, ________ in 1957 proposed the unit membrane model, noting its ____________. The three layers include the polar head of the lipid chains together with the associated proteins of the two apposed lipid monolayers.
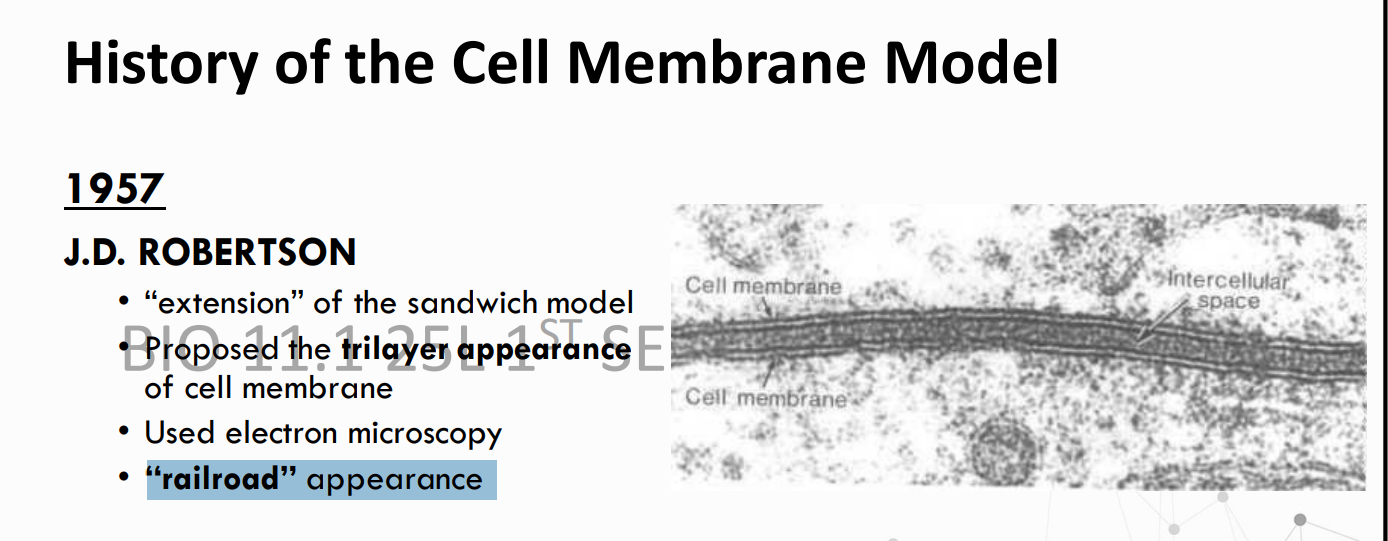
He stated that the cell membrane had a “railroad“ appearance
Davson-Danielli; Robertson
However, __________ and __________ models cannot explain how globular proteins can form thin protein sheets and allow transport of substances. Such challenges and difficulties show the dynamism of developing biological models as they may be revised and improved through time.
Mueller; Rudin
In 1966, _________ and _________ recognized that the membrane consists of bimolecular lipid layers that exhibit fluidity and self-healing.
This augmented our understanding of not just the components but also the essential properties exhibited by the cell membrane.
Singer; Nicolson
In 1972, ________ and ________ proposed the fluid-mosaic membrane model of the membrane.
Fluid – Different components can freely and independently move; membrane can flex and bend
Mosaic – components are arranged randomly
Why is the fluid mosaic model considered fluid and mosaic?
fluid-mosaic membrane model of the membrane by Singer and Nicolson (1972)
At present, it is the widely accepted model for the structure of the cell membrane.
fluidity; mosaicity
integral; peripheral; lipid-anchored
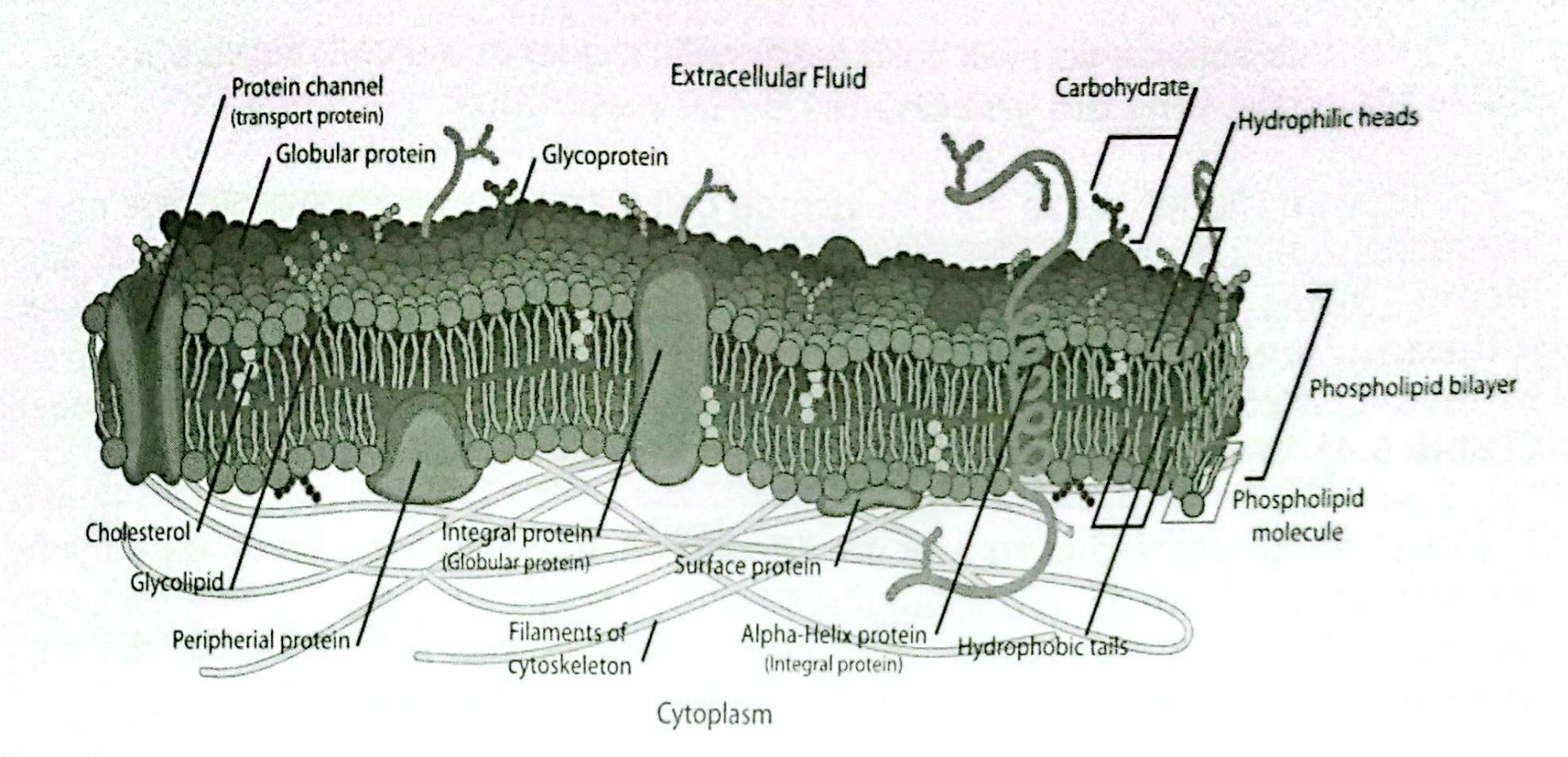
The fluid-mosaic membrane model has two main features — _________ as exhibited by the lipid bilayer and _________ due to embedded proteins.
The integration of globular proteins in the membrane rather than as coated thin sheets makes it more acceptable.
In addition, membrane proteins could be _______, __________, or ___________.
extracellular matrix; cytoskeletal
The fluid-mosaic membrane model’s first revision was made in 1976 which included the interactions of ___________ and certain __________ elements with the membrane.
These affect the mobility and distribution of transmembrane proteins.
domains; lipid rafts; cytoskeletal fencing
crowd; fluctuate
In 2014, an updated version of the fluid-mosaic membrane model incorporated information on membrane _________, _________ and ______________ that were unknown in the 1970s.
It proposes that membrane components "_______" together into non-random, non-uniform domains and the composition of such domains may _________.
Phospholipids
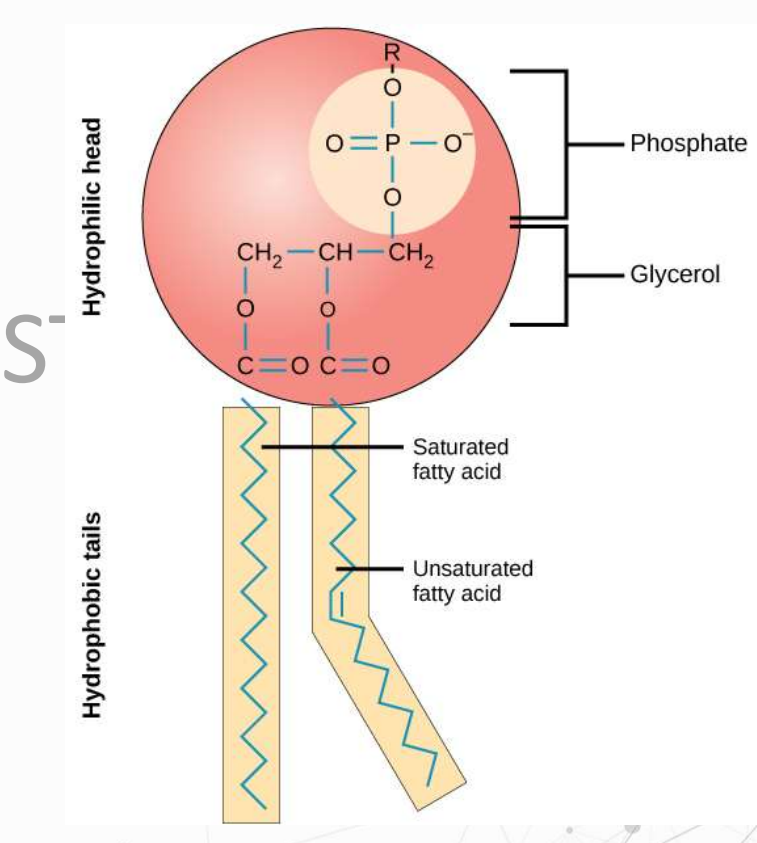
lipid with a polar head and two hydrophobic tails; head is a phosphate group hence the name
Phospholipids

Main lipid component of the cell membrane
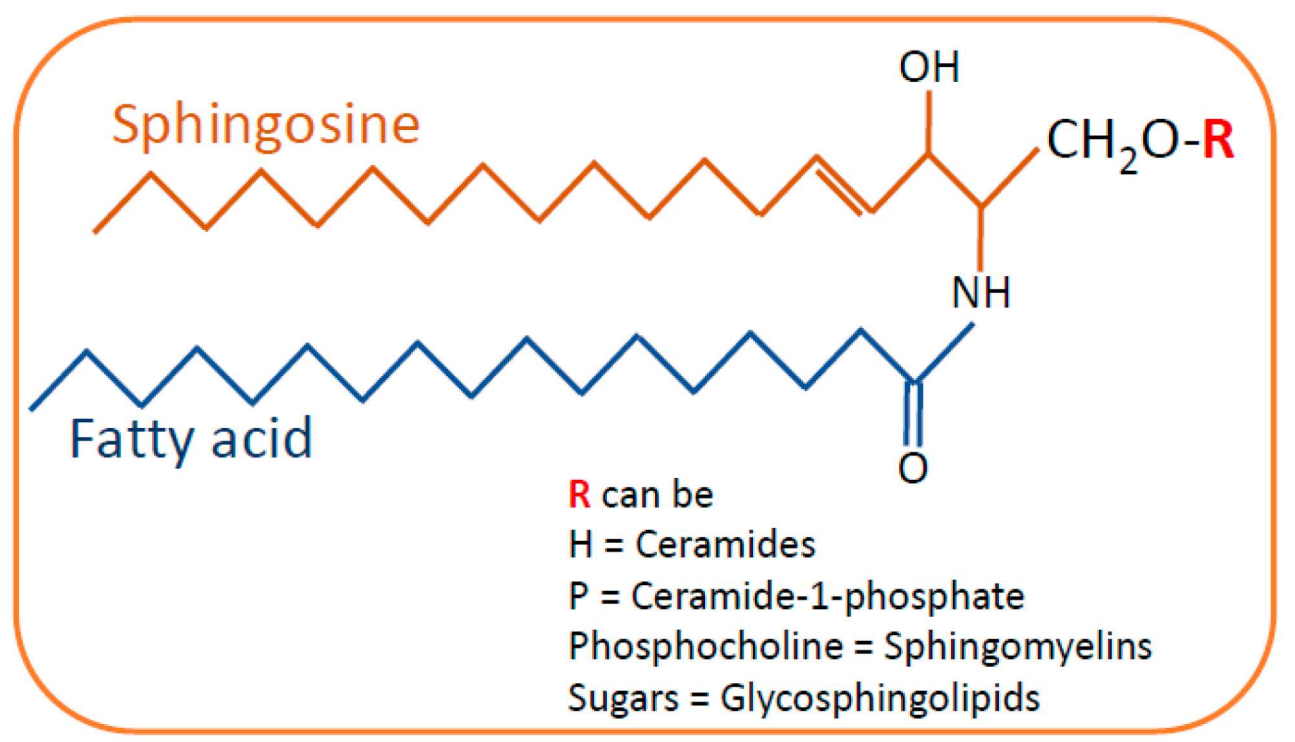
Sphingolipids
lipid with a polar head and two hydrophobic tails; head is a sphingosine group hence the name; fewer in number than phospholipids
Cholesterol
small 4-ringed non-polar substance inserted in the lipid bilayer;
Cholesterol
A steroid that can control fluidity of the cell membrane
Proteins

large macromolecules that can be peripheral (only on the surface) or integral (embedded on the membrane)
Monotopic
Polytopic

_____________ – partially embedded protein
_____________ – fully embedded protein
peripheral proteins

Proteins found only on the surface
integral proteins

Proteins embedded in the membrane
Carbohydrates
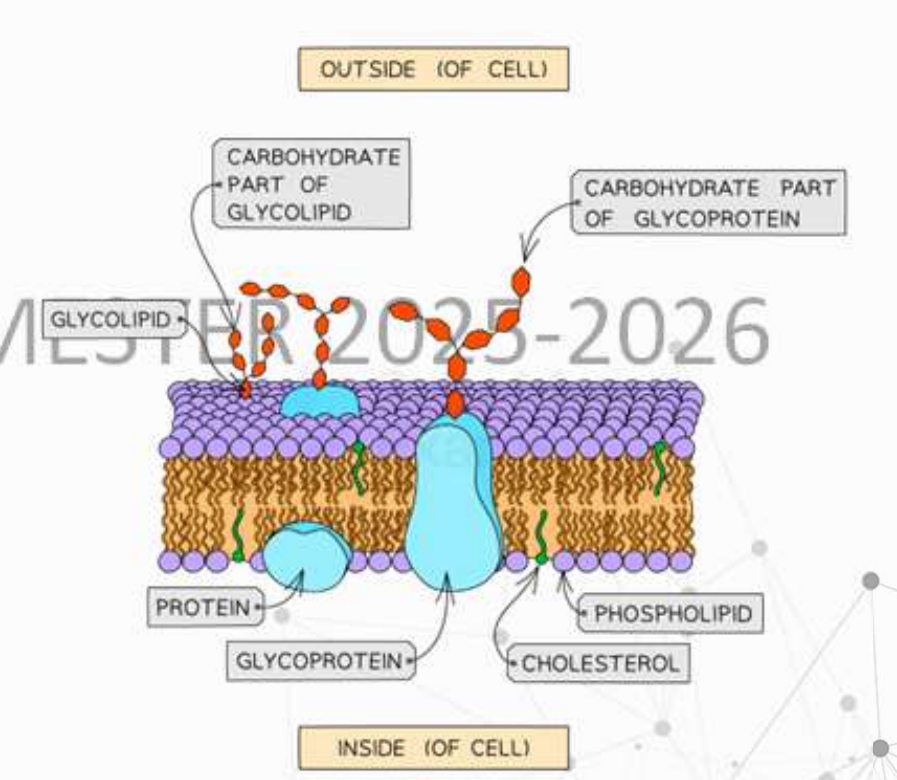
can be attached to proteins forming glycoproteins and to lipids forming glycolipids
glycoproteins, glycolipids

What do you call carbohydrates attached to proteins and those attached to lipids?
Cytoskeleton
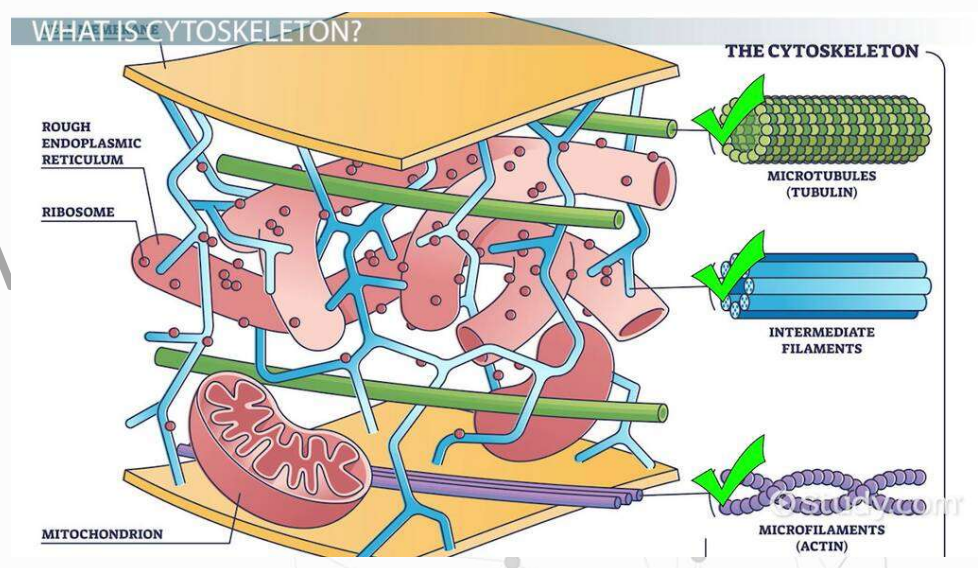
skeletal framework that holds the shape of the cell; made of numerous small proteins
Extracellular matrix
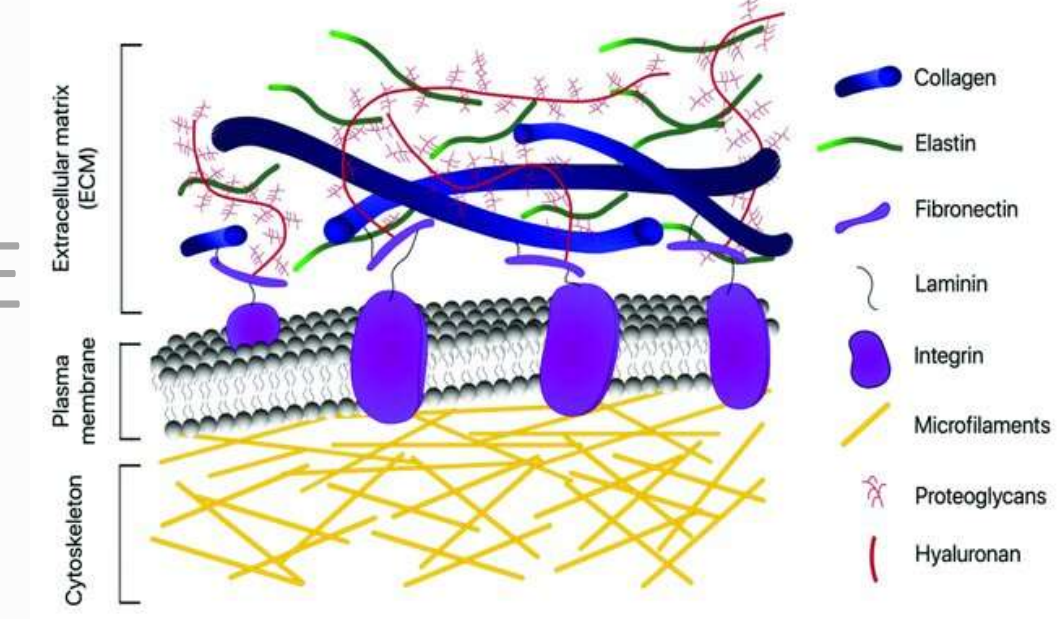
a mixture of substances released by the cell (e.g. polysaccharides) and a variety of proteins; can have fibers
metabolism
In your cells, there are numerous chemical reactions (both breakdown and synthesis) continuously providing the cell with products such as energy and organic materials that are needed to maintain its living state. The sum of these reactions is called ___________.
proteins; lipids
The _________ and __________ of the cell membrane that we investigated earlier are products of metabolism.
Enzymes

____________ are vital components of these metabolic pathways. They are proteins that catalyze or speed up chemical reactions.
Enzymes
Provides alternative pathways with lower activation energy
Oxidoreductases
catalyze redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions; transfer of electrons
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Transferases
transport of one functional group from one molecule to another
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Hydrolases
cleave covalent bonds by addition of water (hydrolysis)
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Lyases
creates or reduces double bonds by addition of small molecules including H2O, CO2 , or NH3
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Isomerases
rearranges the structure and shape of a molecule
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Ligases
attaches molecules together
Oxidoreductases
Transferases
Hydrolases
Lyases
Isomerases
Ligases
Simple Enzyme
Types of Enzymes
Consist entirely of proteins
Simple Enzyme
Types of Enzymes
No other components needed to perform a certain function
Conjugate Enzyme (Holoenzyme)

Types of Enzymes
Consist of other components other than proteins
Apoenzyme – protein portion
Cofactor – non-protein portion
Apoenzyme
Cofactor

Types of Enzymes
Conjugate Enzyme (Holoenzyme)
Consist of other components other than proteins
___________ – protein portion
___________ – non-protein portion
Activators
Types of Enzymes - TYPES OF COFACTORS
cations that are temporarily bound to enzymes
Prosthetic groups
Types of Enzymes - TYPES OF COFACTORS
organic groups permanently bound to the enzyme
Coenzyme
Types of Enzymes - TYPES OF COFACTORS
organic molecules (e.g. vitamins) which are NOT permanently bound to the enzyme, but combine with the enzyme substrate complex temporarily
substrate; enzyme
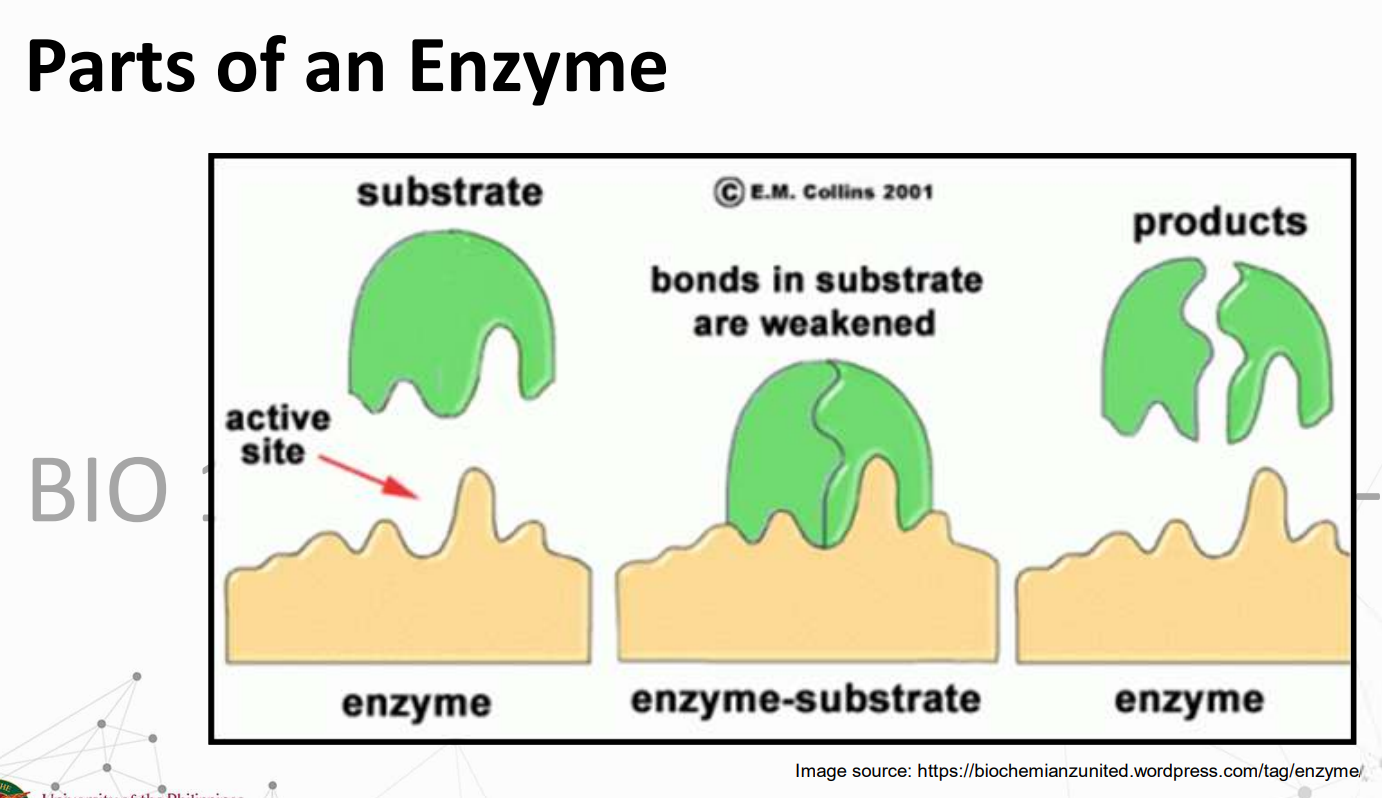
A __________ binds to the active site of the _________ and gets converted into products. The products then leave the active site and may bind a different enzyme in another chemical reaction
lock and key
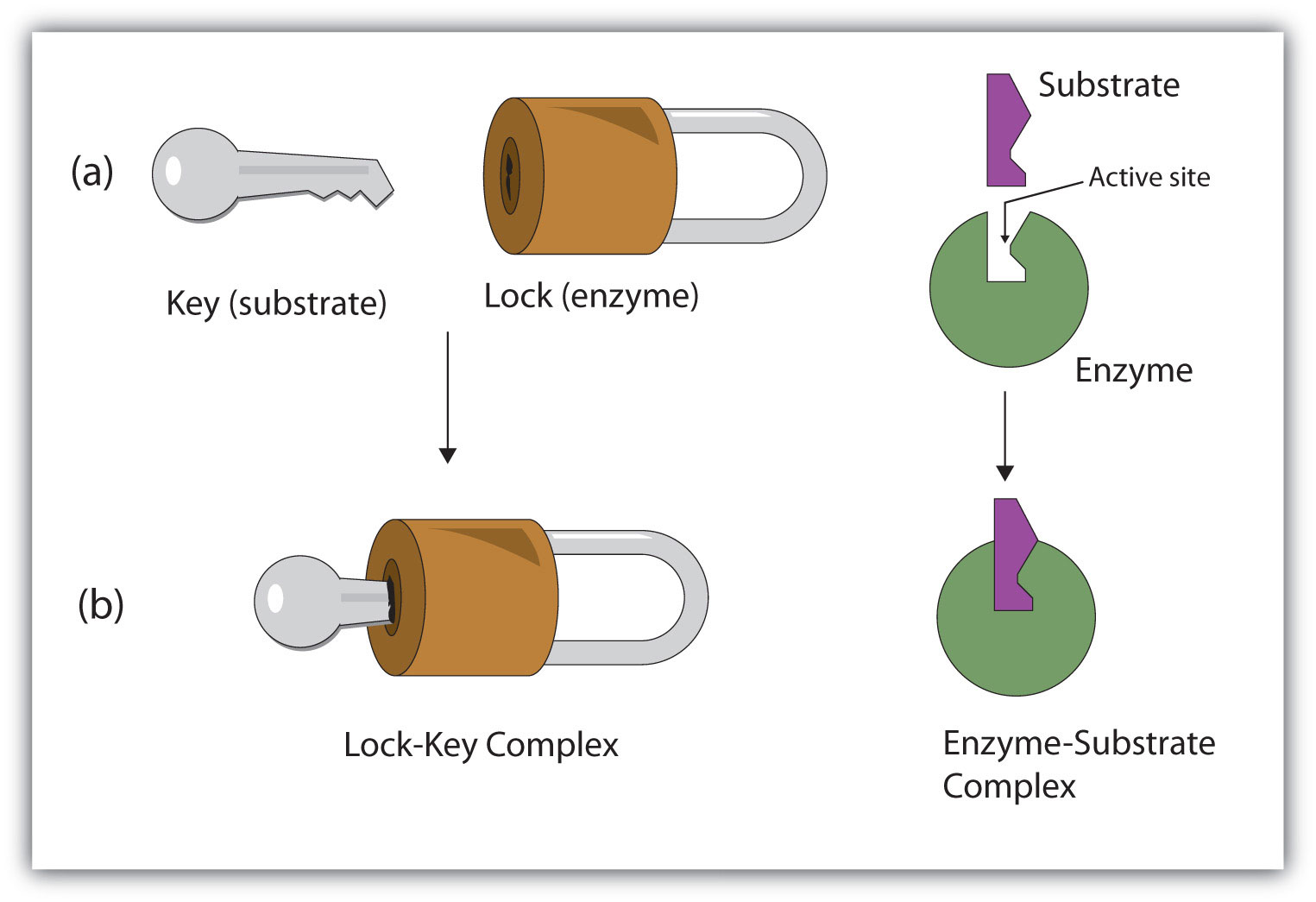
The "__________" model was first proposed in 1894. In this model, an enzyme's active site is a specific shape, and only the substrate will fit into it.
Fischer

Who postulated the Lock and Key Model for Enzymes?