Week 4 - Record Bases and Wax Rims
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What do occlusal wax rims allow you to do?
articulate master casts
Why do we mark our master casts?
to make guidelines for proper placement of the denture teeth
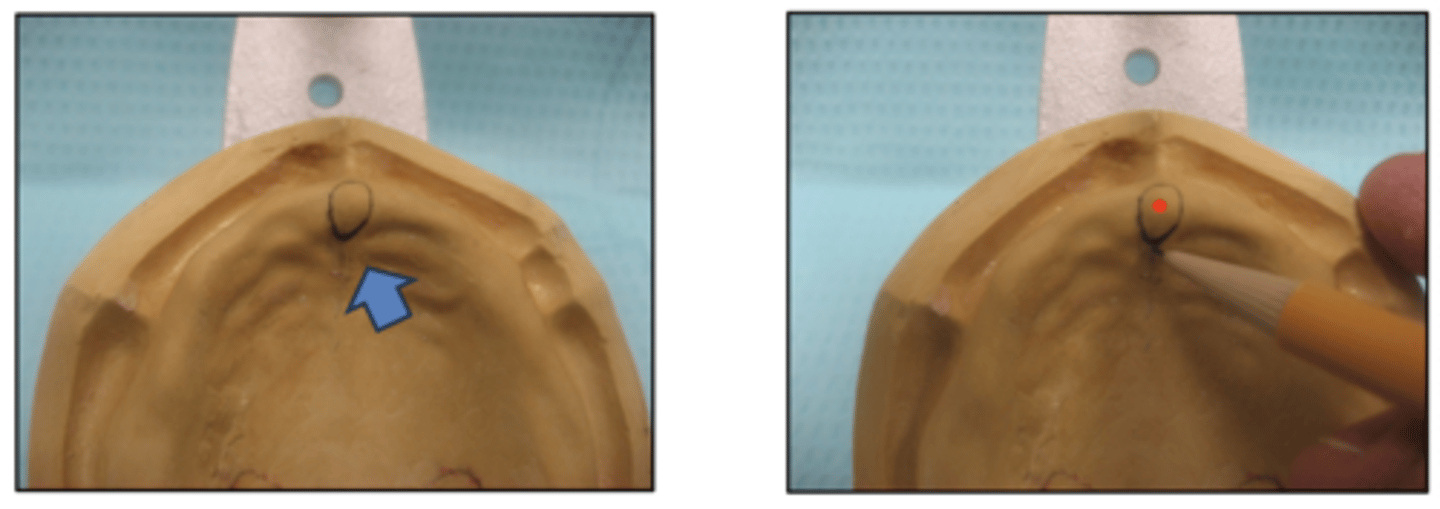
The incisive papilla is marked on the maxillary final cast to position which teeth?
Facial surface of maxillary central incisors
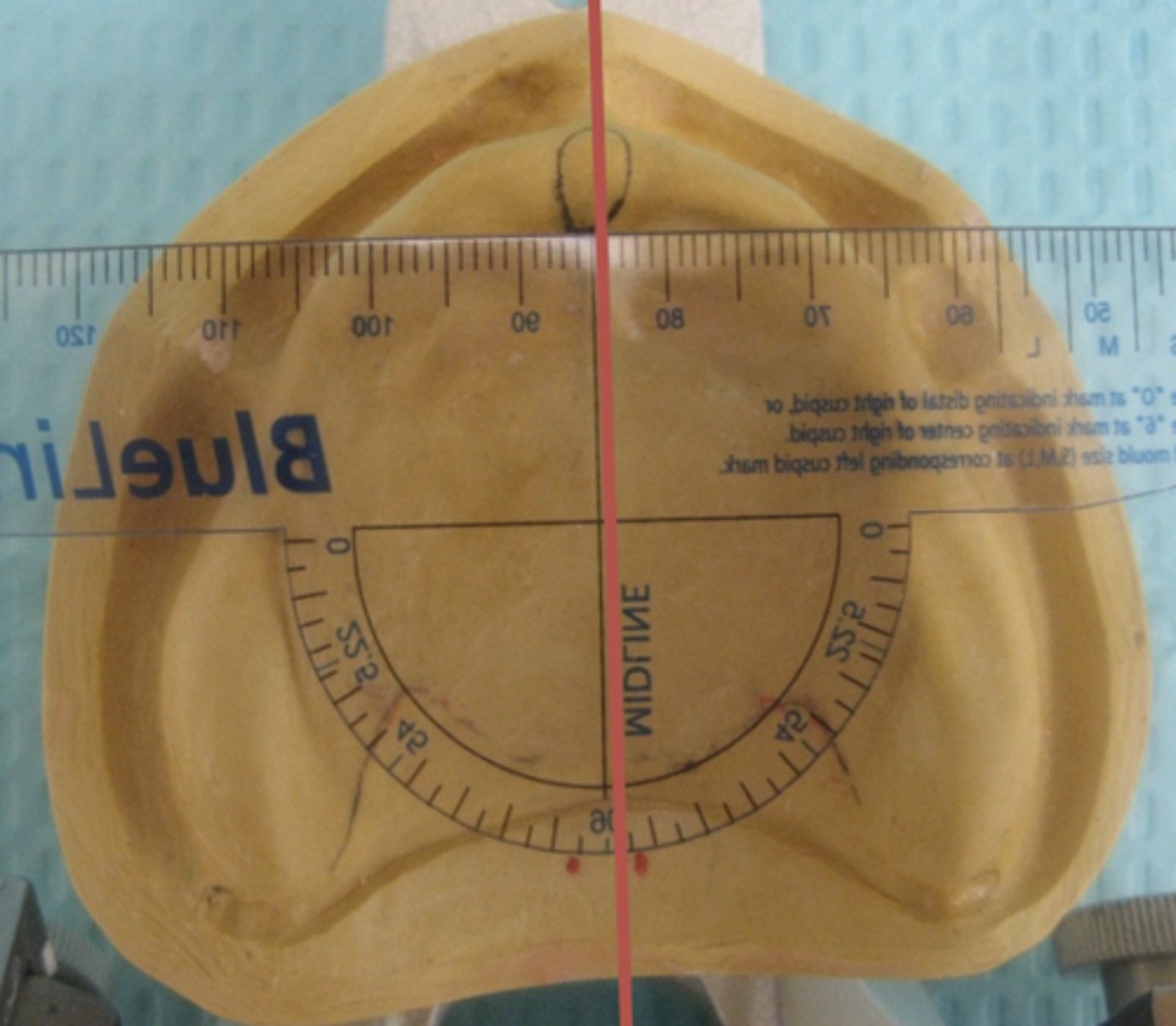
When placing the transparent ruler over the center of the incisive papilla, the front edge of the ruler should be perpendicular to what structure?
Mid-palatal suture
Where do you place a dot on each retromolar pad?
Place a dot anterior 2/3 of the height of each retromolar pad (make dots/reference points on side of casts while holding cast at eye level and look at it from the facial aspect)
Retromolar pads are marked in order to determine what?
height of posterior occlusal plane
After marking the retromolar pads, what are the second markings on the mandibular casts?
- Crest of the residual ridge
- Determine the bucco-lingual placement of posterior teeth
- The central fossae of the premolar and molar denture teeth are placed directly over the crests of the mandibular residual ridges
When we mark the ascending rami on the mandibular cast, what does this indicate for tooth placement?
No tooth placed distal to this
Why do we mark the incisive papilla and the lines on the left and right land areas beneath the incisive papilla?
guideline for positioning facial surfaces of max. central incisors
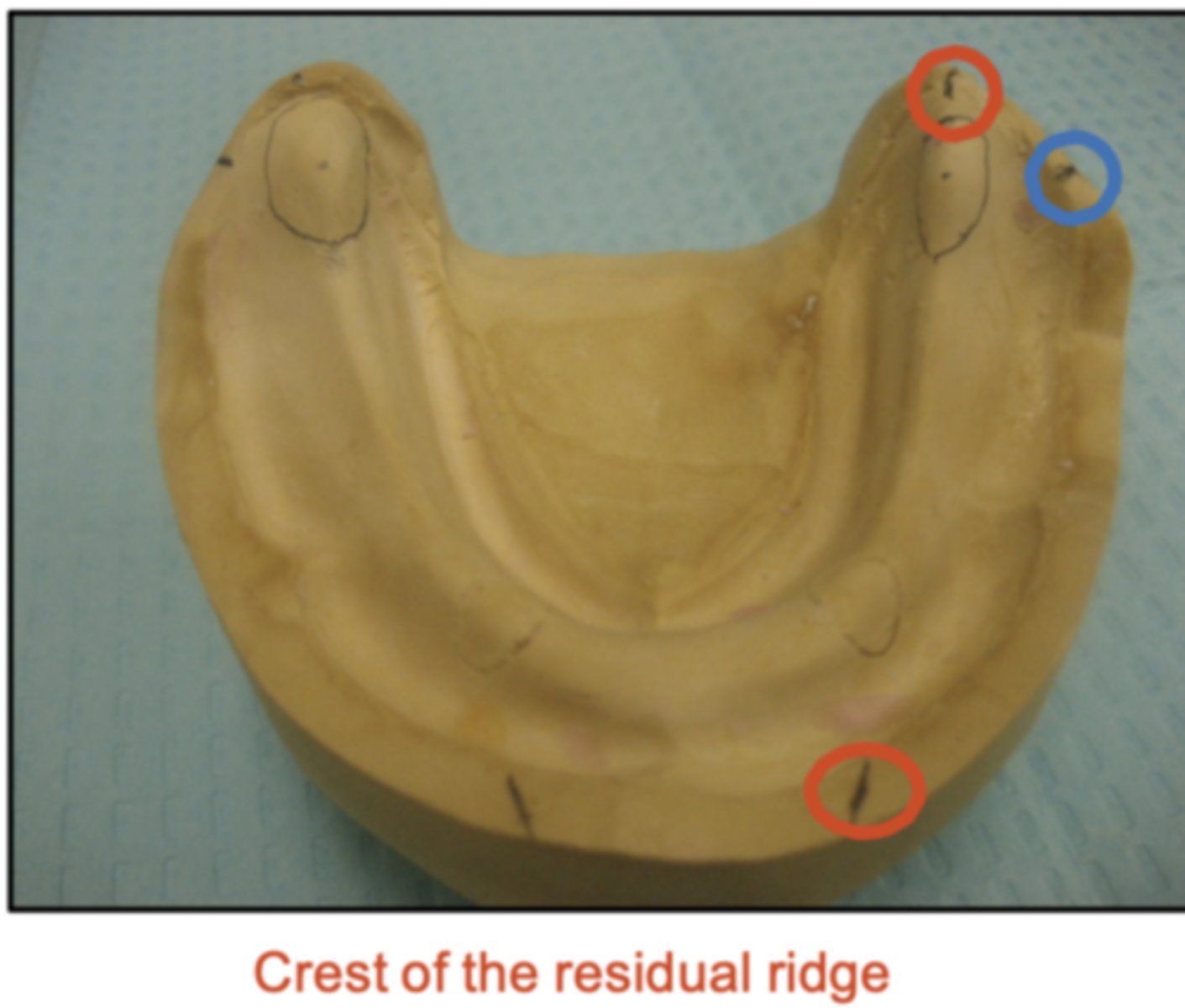
It is important that we mark the crest of the mandibular ridge correctly because, if we set teeth too buccally, what would happen?
Teeth/denture will lean outward and cause cheek biting
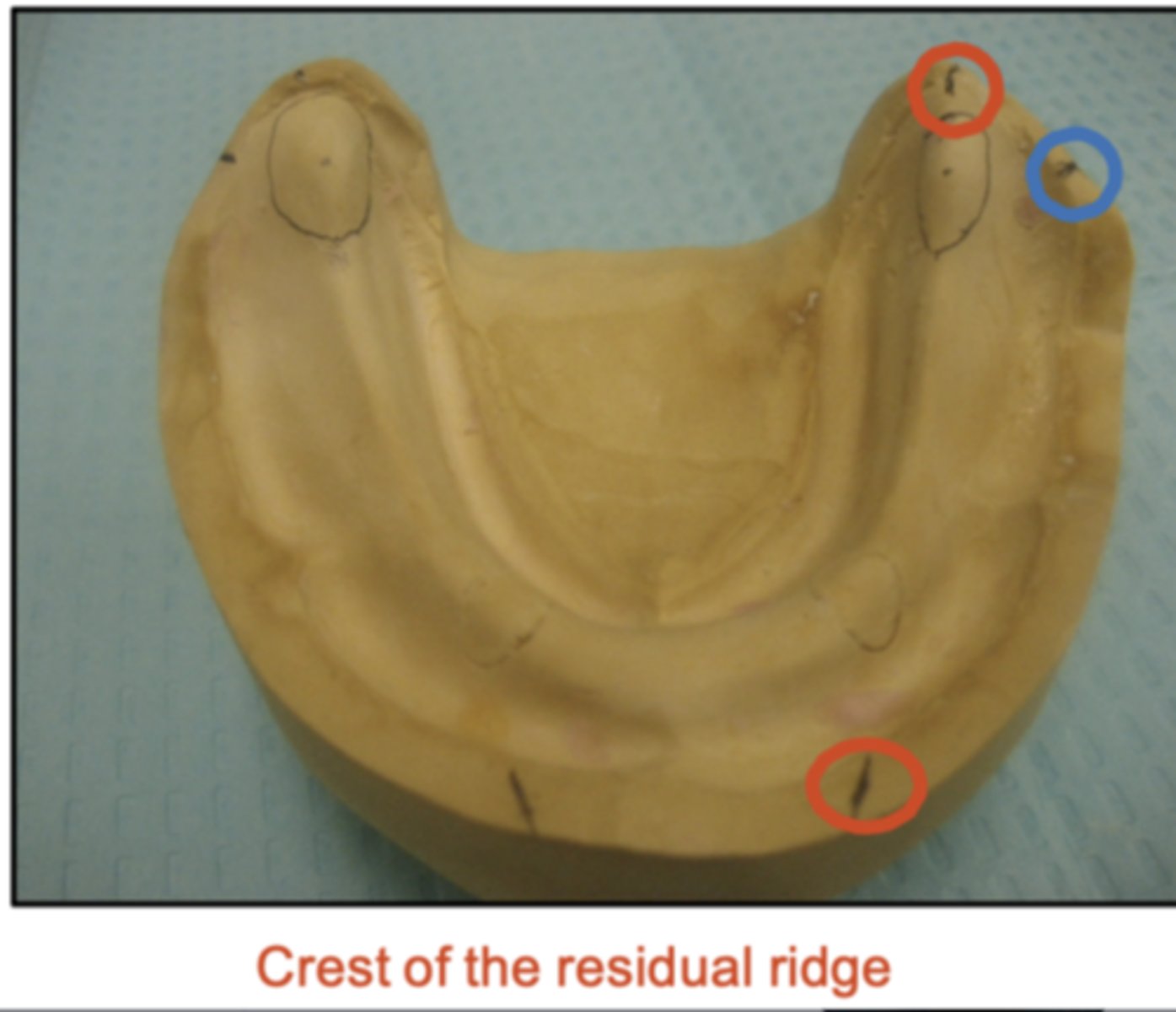
It is important that we mark the crest of the mandibular ridge correctly because, if we set teeth too lingually, what would happen?
Teeth/denture will tip too lingual and reduce space for tongue
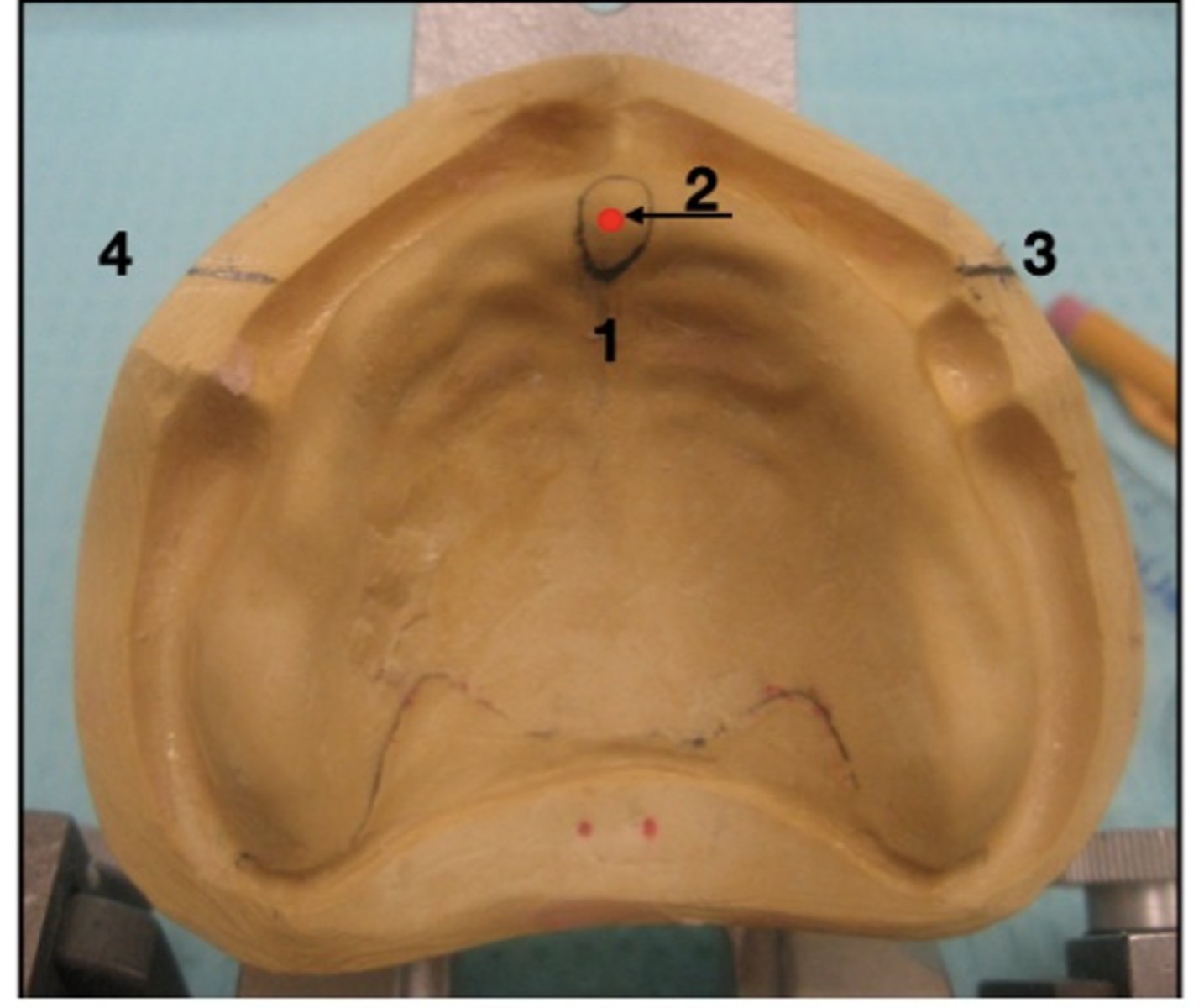
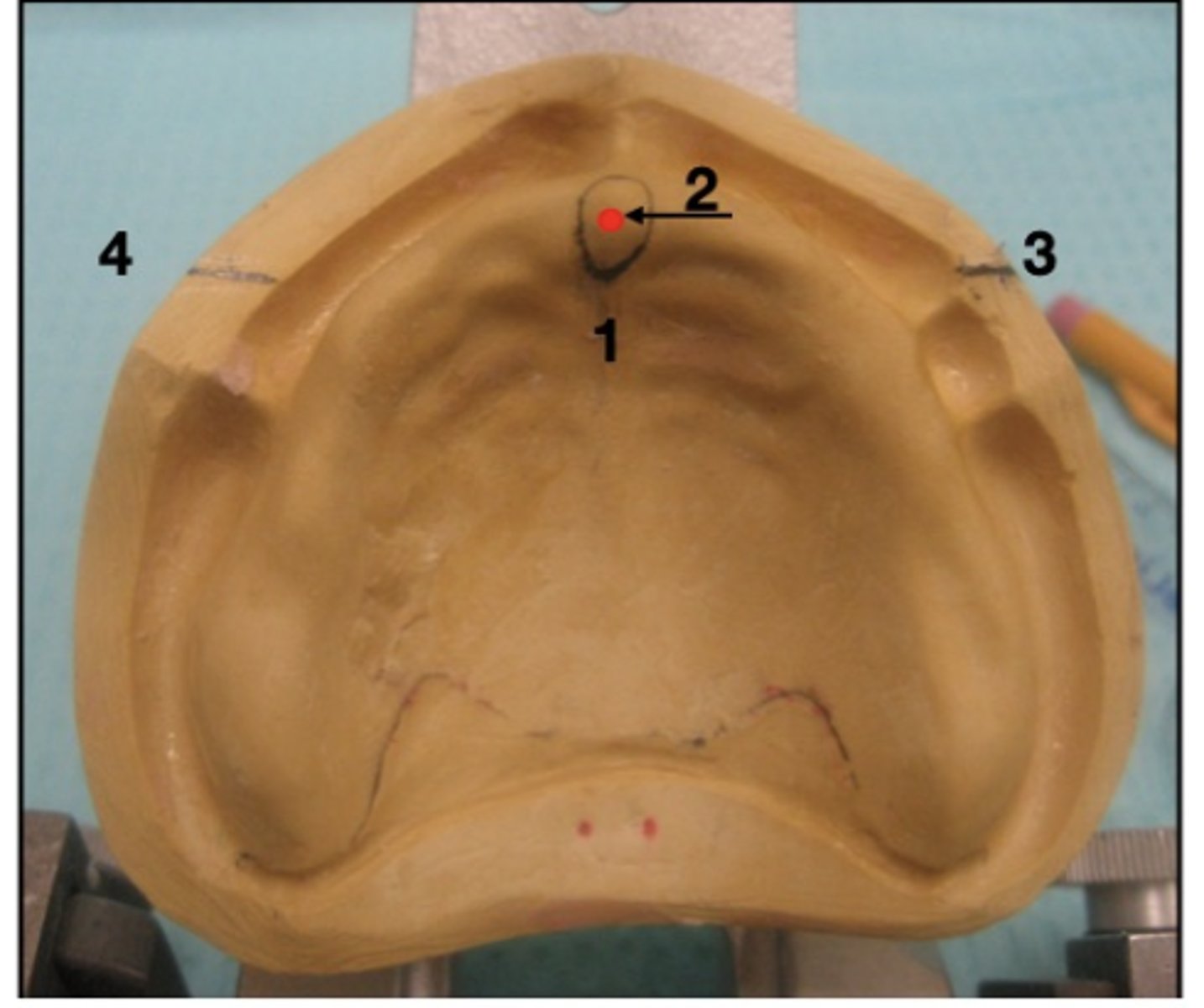
What is 1?
incisive papilla
What are 3 and 4?
lower border of papilla (crest of anterior aspect of ridge)
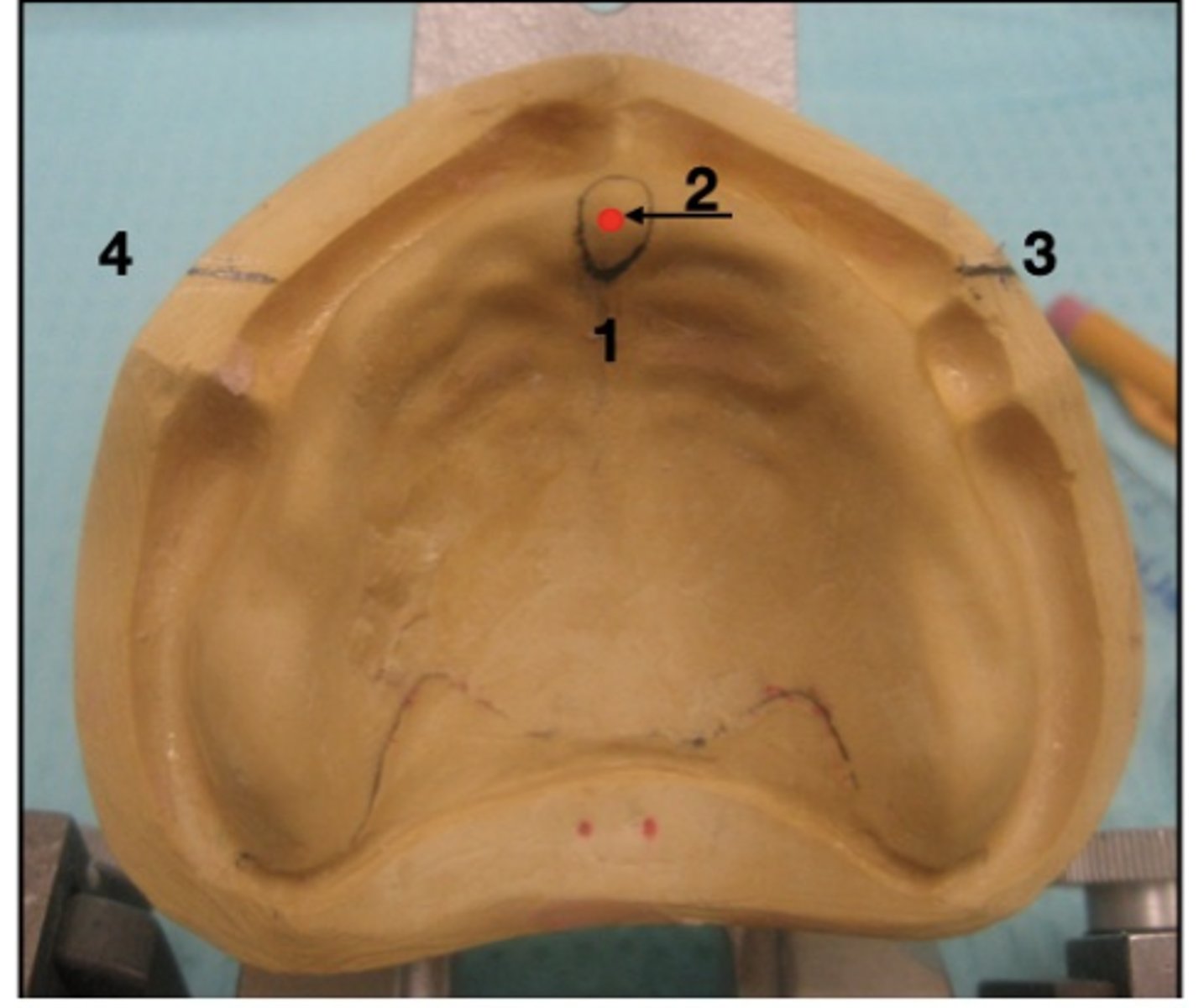
What is 2?
center of papilla
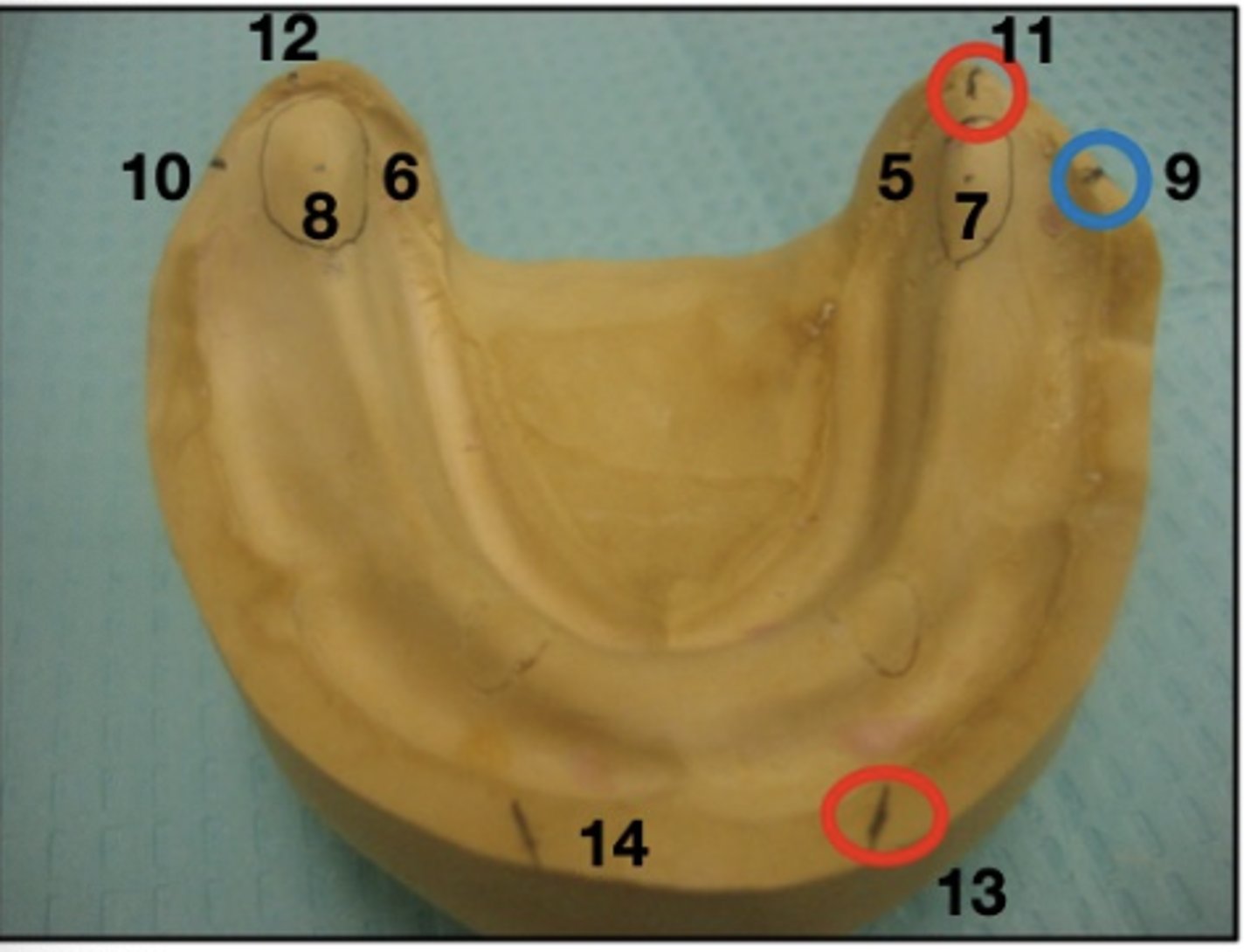
What are 5 and 6?
retromolar pads (oval lines)
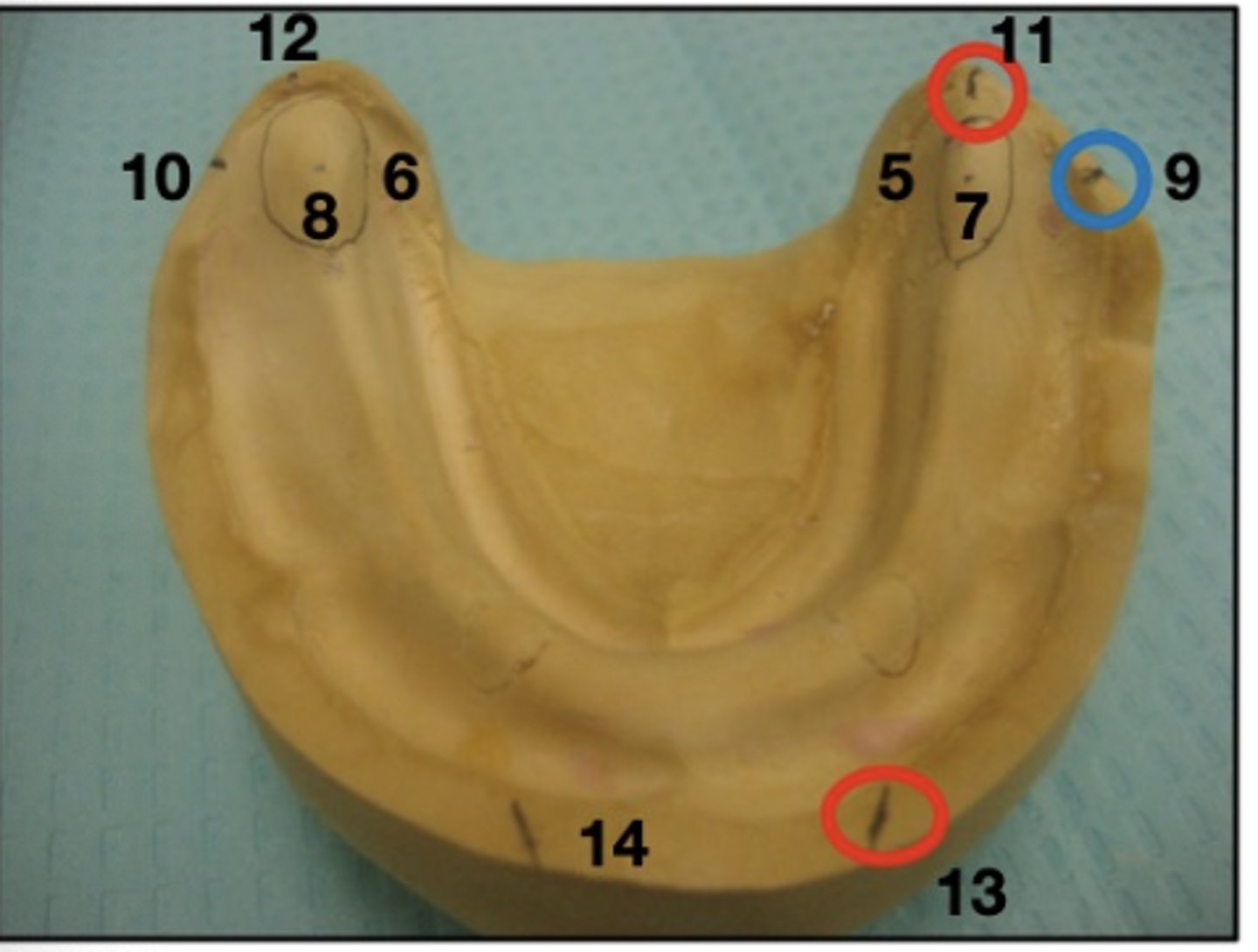
What are 7 and 8?
ant. 2/3 of retromolar pads
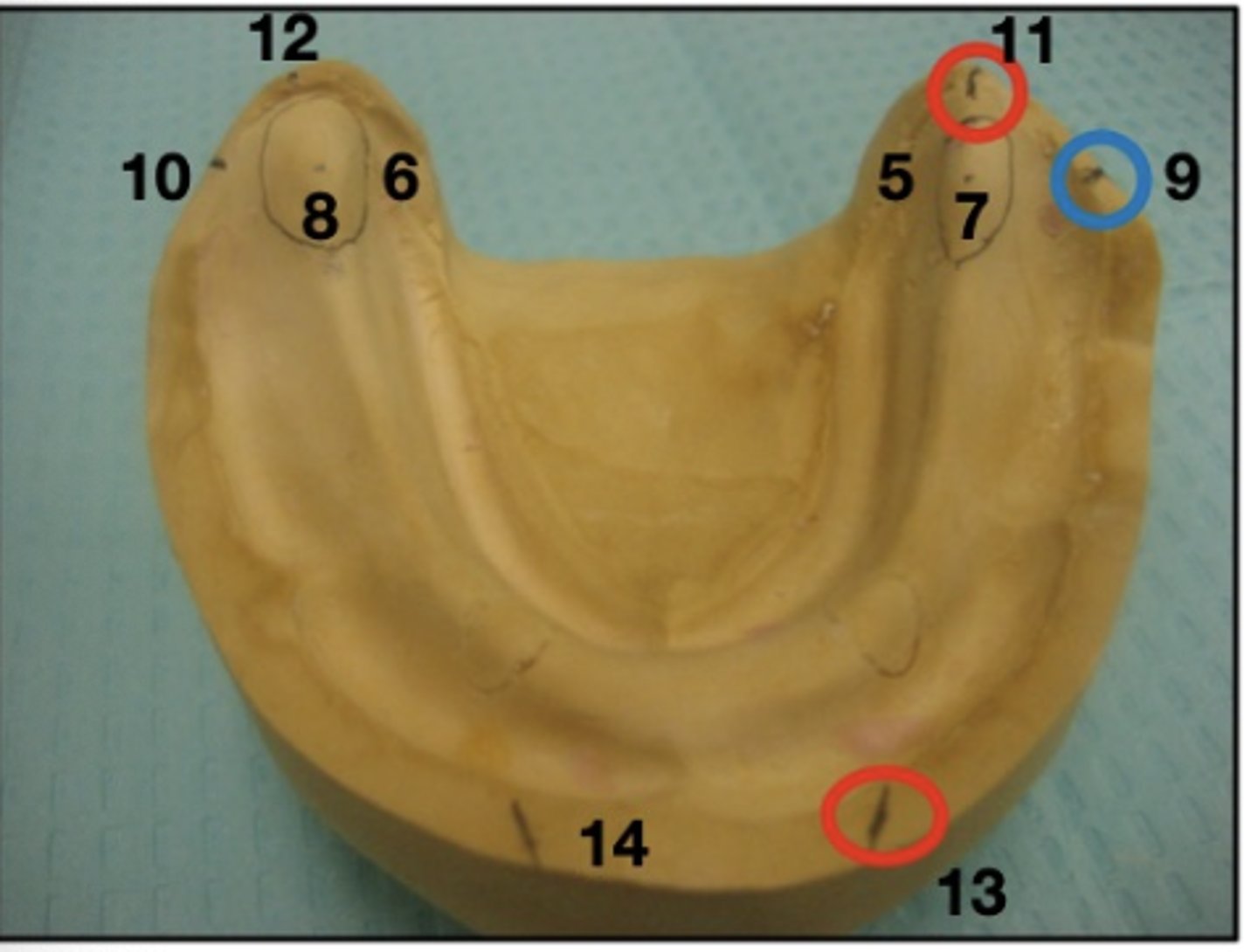
What are 9 and 10?
Height of occlusal plane (at level of ant. 2/3 of retromolar pads)
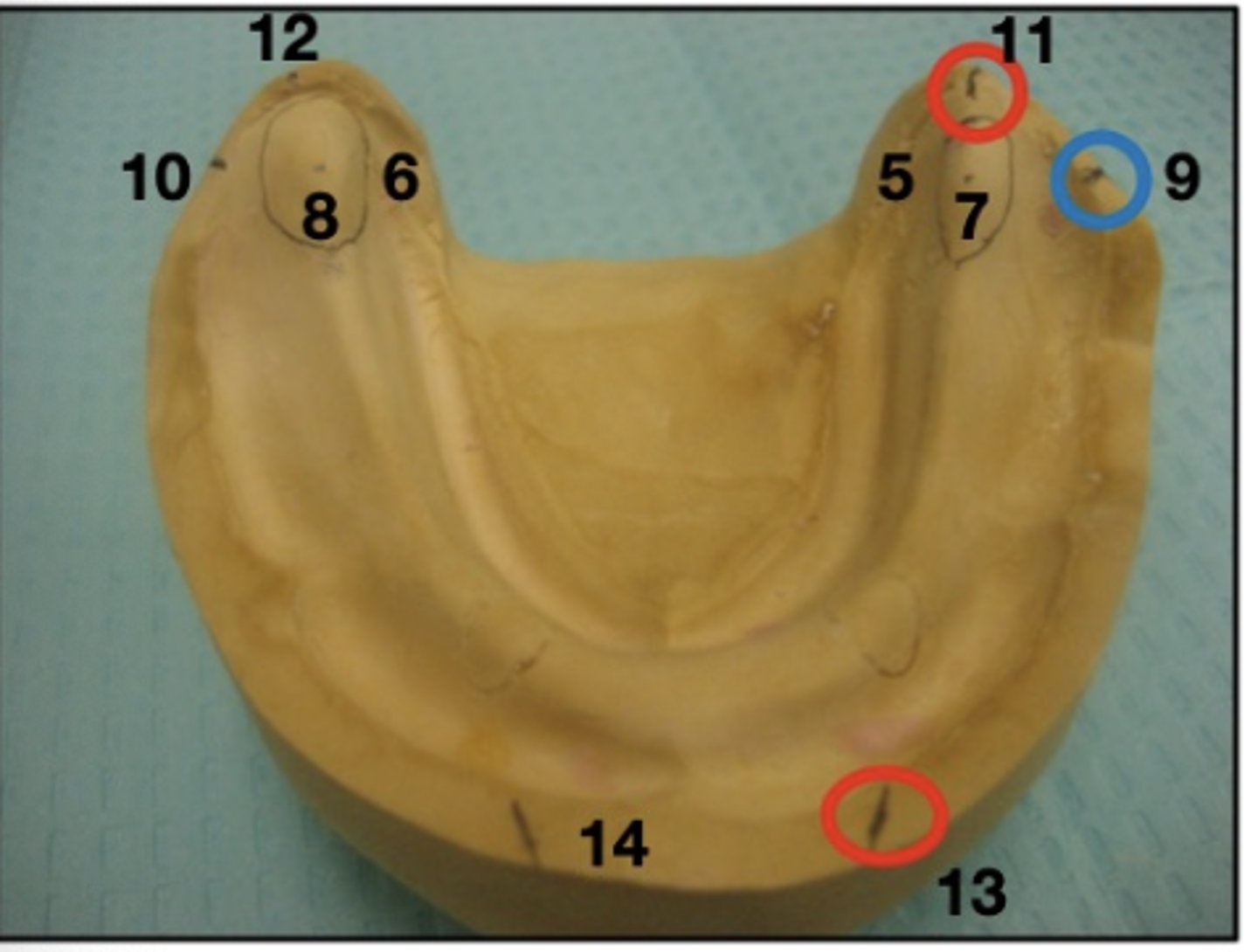
What are 11 and 12?
crest of residual ridge (posterior)
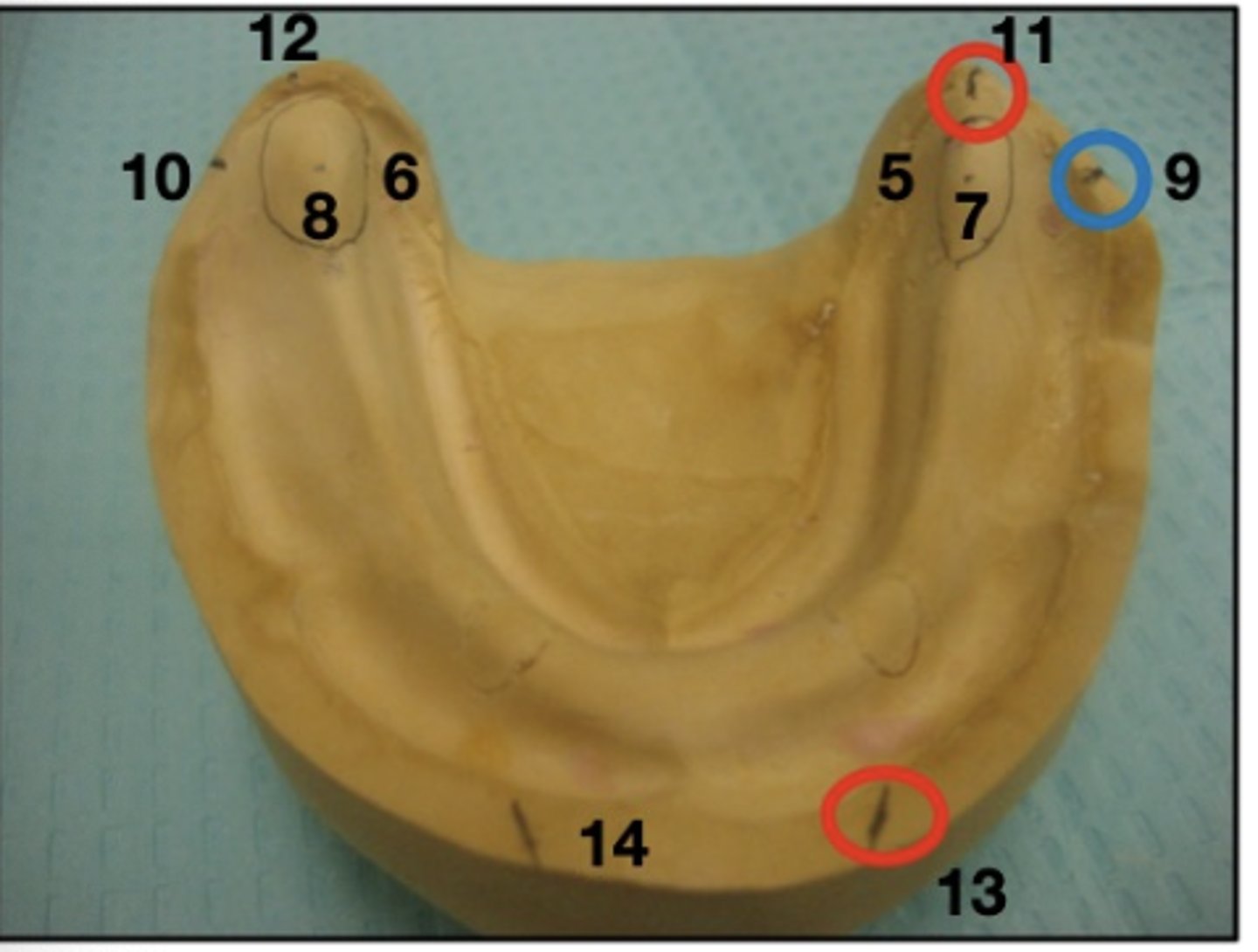
What are 13 and 14?
crest of residual ridge (anterior)
What does this line mark?
Where the ascending rami begins
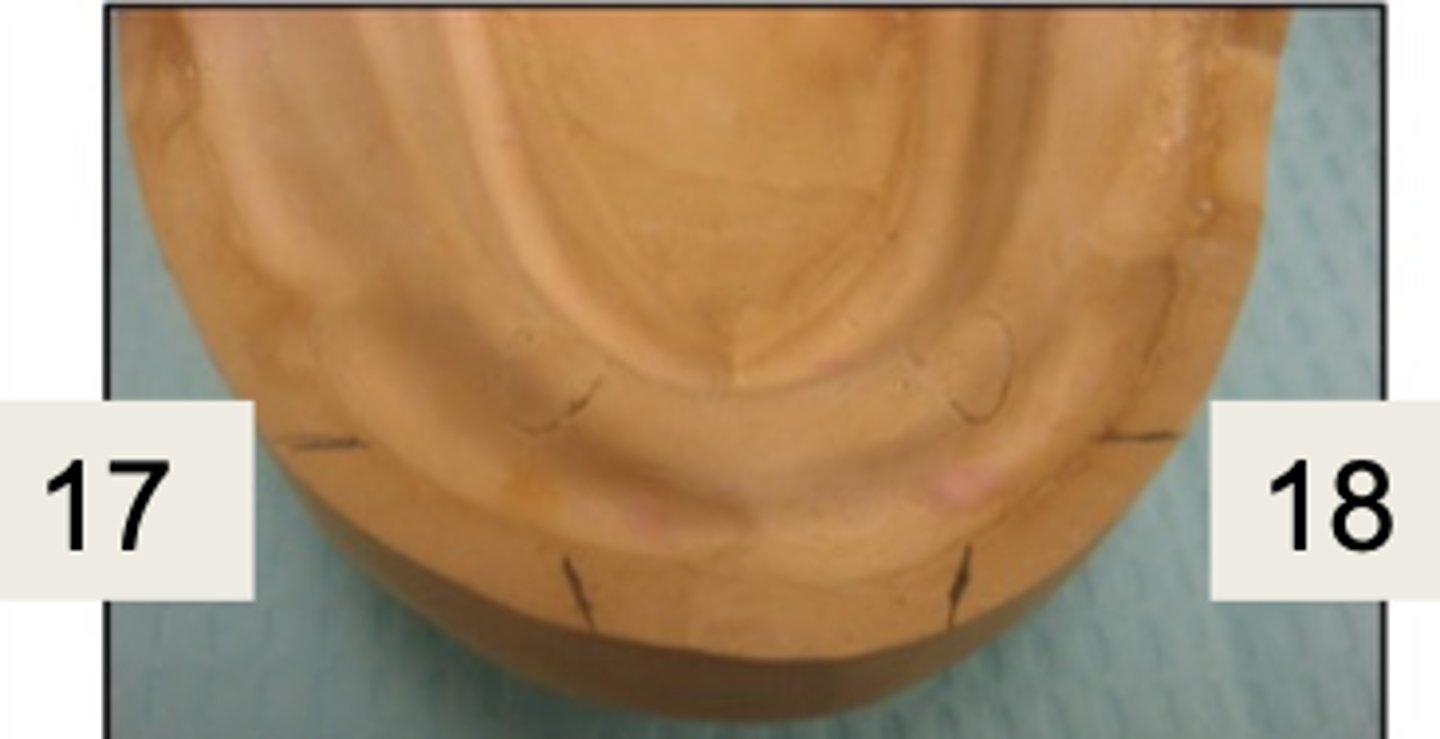

What are 17 and 18?
anterior ridge crest
Where are there undercuts on the maxillary arch clinically?
left and right undercuts in the anterior area and above both tuberosities posteriorly
Where are there undercuts on the mandibular arch clinically?
labial aspect of the mandible and in both retromylohyoid areas
What should you coat on the impression cast before placing the triad?
Vaseline
Ideal border molder determines the proper ________, ________, and ________ of the final complete denture
- Height
- Width
- Contour
For this project, we will assume that our impression are perfect. Therefore, the triad material should completely fill the entire __________ of your final edentulous casts.
Peripheral rolls
When fabricating the maxillary record paces, be sure that the material completely fills the ___________ areas and is straight across the posterior aspect of the cast.
Hamilar notch
On the back portion of the maxillary triad, how wide anterio-posteriorly should this area be?
10 mm
With a Vaselined finger, thin the back edge
of the record base to about one-half of its
original thickness. What does thinning the back edge of the triad on the maxilla do?
minimize acrylic shrinkage
What is the reccomended curing time of the triads?
2 minutes cure on the casts > take off casts and flip > 6 minute cure
What bur can you use to smooth and round-off all of the peripheral edges of both record bases?
Pineapple acrylic bur
For the maxillary posterior area, how much space is allowed without having to remake?
no more than 2 mm
What does thinning the anterior aspect of the record base do?
Makes room for teeth set-up (this should be done before adding wax)
What is a key feature of the anterior portion of the maxillary wax rims?
anterior inclination
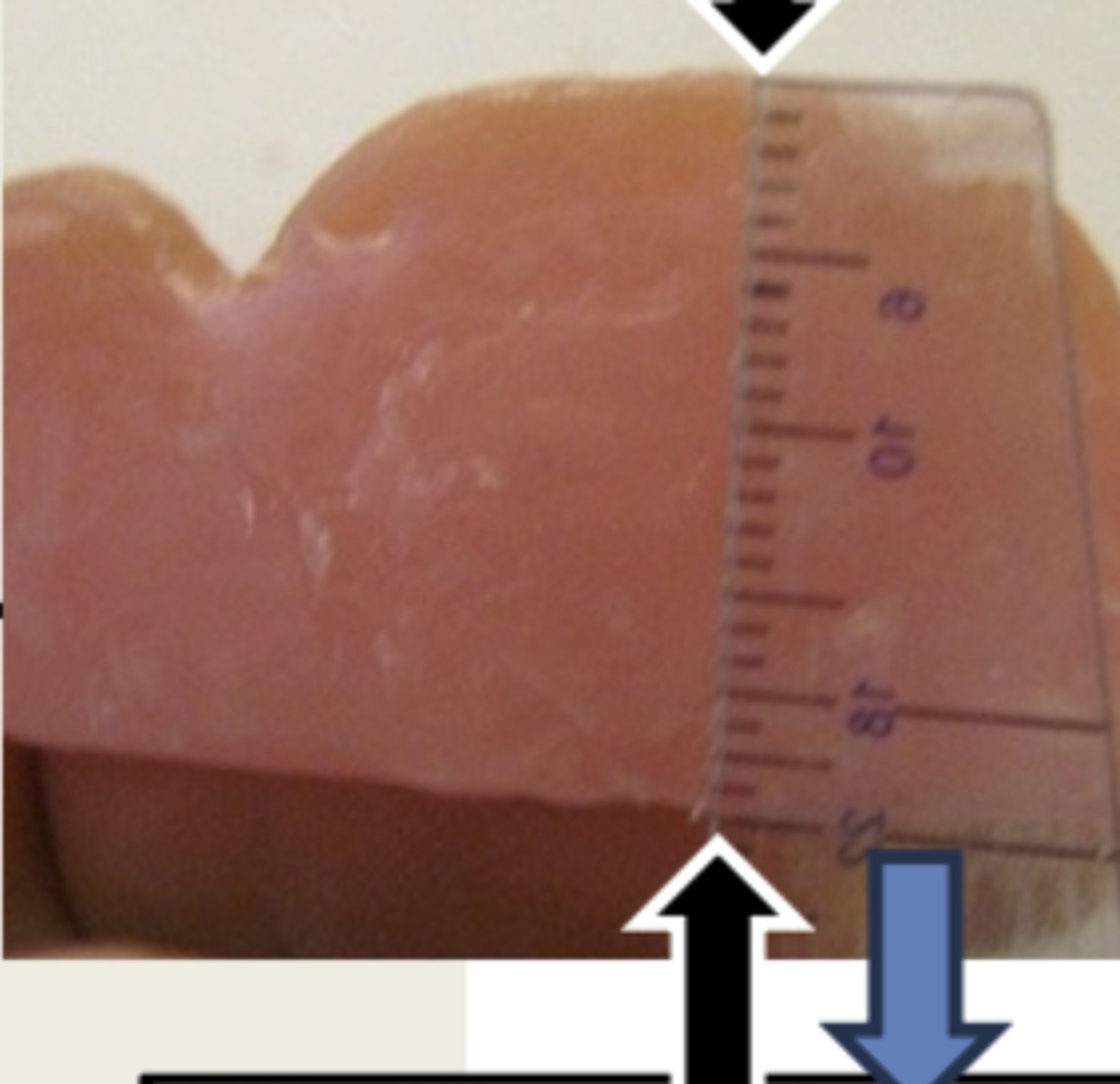
What is the measurement at the area of the lateral incisors for the maxillary wax rim?
22 mm
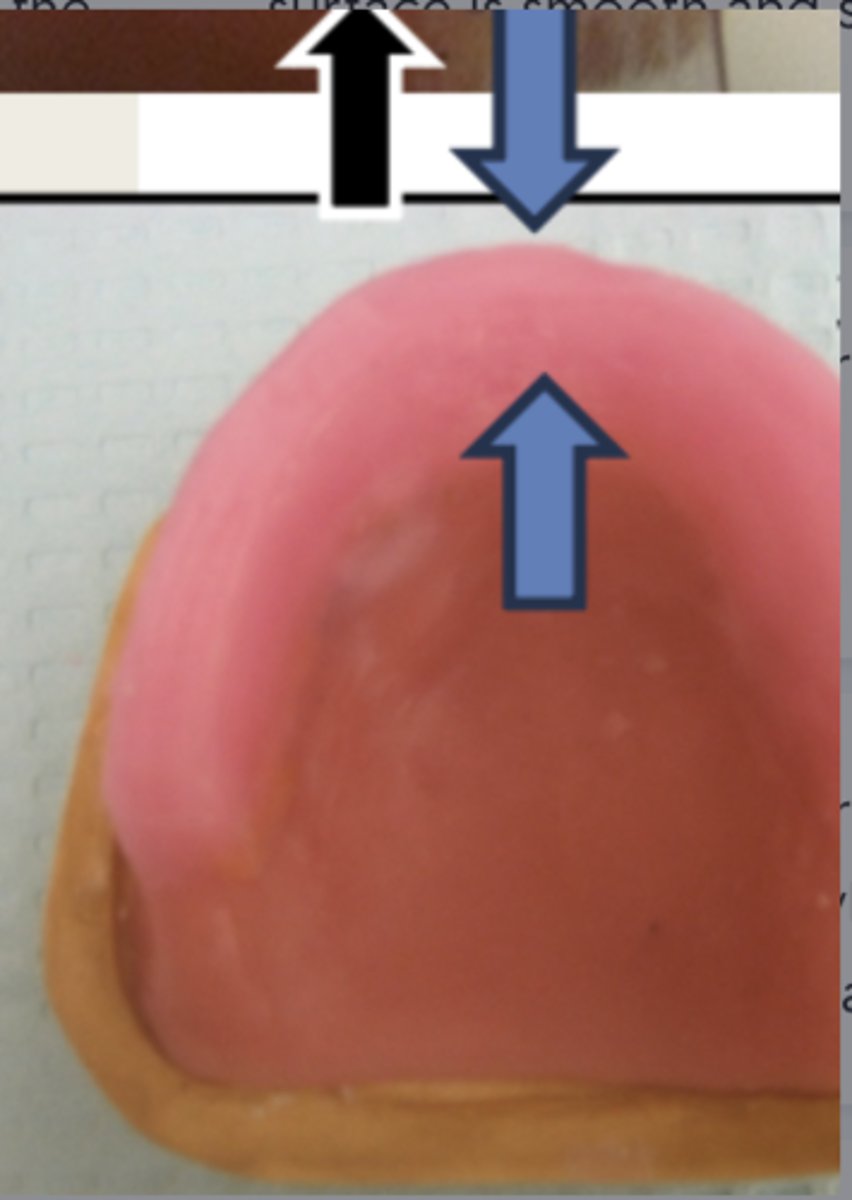
How wide is the incisal plane at the anterior portion of the maxillary wax rim?
3 mm (flat and smooth)
The buccal surface of the maxillary wax rim should be smooth and sloping towards what?
peripheral roll
The lingual surface of the maxillary wax rim should be smooth and sloping towards what?
palate
Where should the posterior maxillary wax rim be located over?
Over the crest of the maxillary ridges
For the fabrication of the maxillary posterior wax rim, it should have a lingual wax smooth and sloping towards the ________
Midline
What should the posterior maxillary wax rim be parallel to?
maxillary mean foundation plane
How wide should the maxillary wax rims be in the bicuspid areas?
5 mm
How wide should the maxillary wax rims be in the molar areas?
10 mm
Where should you cut the posterior ends of the maxillary wax rim?
Where you expect the junction of the first and second molars to be - put about a 45 degree angle on this cut
How high is the anterior mandibular wax rim?
18 mm
How wide is the anterior mandibular wax rim?
3 mm
What is a key feature of the mandibular wax rim?
flat and straight anterior portion
How wide is the occlusal surface of the mandibular wax rims in the bicuspid area?
5 mm
How wide is the occlusal surface of the mandibular wax rims in the molar area?
10 mm
The facial and lingual walls of the mandibular wax rim are flat with a slight flare as they feather toward the _________
Peripheral rolls
What is the occlusal plane of the mandibular wax rim parallel to?
mean foundation plane
Is there a buccal inclination of the mandibular wax rim?
No