Routing in IPv4
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the Per-Router Control Plane?
individual routing algorithm components in each and every router interact in the control plane
What is the Routing Protocol Goal?
determine “good” paths (equivalently, routes), from sending hosts to receiving host, through network of routers
path - sequence of routers packets traverse from given initial source host to final destination host
“good” - least “cost”, “fastest”, “least congested”
routing - a “top-10” networking challenge
What is the Routing Algorithm Classification?

What is Dijkstra’s Link-State Routing Algorithm?
centralised - network topology, link costs known to all nodes
accomplished via “link state broadcast”
all nodes have same info
computes least cost paths from one node (“source”) to all other nodes
gives forwarding table for that node
iterative - after k iterations, know least cost path to k destinations
Why does Dijkstra’s Link-State Routing Algorithm work?
at each iteration, select the node with the smallest tentative distance (from the source) that hasn’t been processed
finalise the shortest path to this node, and update the tentative distances of its neighbours
once a node's shortest path is finalised, it cannot be improved later because
the shortest paths have the optimal substructure property (as long as the link costs are not negative)
optimal substructure property - any sub-portion of a shortest path starting from the source is itself a shortest path
What is the Internet Approach to making Routers Scalable?
aggregate routers into regions known as “autonomous systems” (AS) (a.k.a. “domains”)
intra-AS
inter-AS
What is Intra-AS (intra-domain)?
routing among routers within same AS (“network”)
all outers in AS must run same intradomain protocol
routers in different AS can run different intra-domain routing protocols
gateway router: at “edge” of its own AS, has link(s) to router(s) in other AS’es
What is Inter-AS (inter-domain)?
routing among AS’es
gateways perform inter-domain routing (as well as intra-domain routing)
What are Interconnected ASes?
forwarding table configured by intra- and inter-AS routing algorithms
intra-AS routing determine entries for destinations within AS
inter-AS & intra-AS determine entries for external destinations
What are the common Intra-AS Routing Protocols?
RIP - Routing Information Protocol [RFC 1723]
classic DV - DVs exchanged every 30 secs
no longer widely used
EIGRP - Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
DV based
formerly Cisco-proprietary for decades (became open in 2013 [RFC 7868])
OSPF - Open Shortest Path First [RFC 2328]
link-state routing
IS-IS protocol (ISO standard, not RFC standard) essentially same as OSPF
What is OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Routing?
“open” - publicly available
classic link-state
each router floods OSPF link-state advertisements (directly over IP rather than using TCP/UDP) to all other routers in entire AS
multiple link costs metrics possible: bandwidth, delay
each router has full topology, uses Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute forwarding table
security - all OSPF messages authenticated (to prevent malicious intrusion)
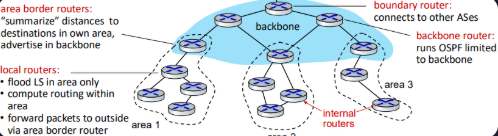
What is a Hierarchical OSPF?
two-level hierarchy - local area, backbone
link-state advertisements flooded only in area, or backbone
each node has detailed area topology; only knows direction to reach other destinations