Lecture 1.1 (Central Dogma: Genomes, genes, mutations)
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Genetics
study of inherited traits and their variation and transmissions.
Genetics is the science of —. What does that mean?
hereditary; It is a precise explanation of biological structures and mechanisms that determine what is inherited and how.
Heredity
the way genes transmit biochemical, physical, and behavioral traits from parents to offspring
Traits
produced by an interaction between genes and their environment. Examples includes hairline, tendency to bald and how you clasp your hands
Certain difficult to define human characteristics might appear to be inherited if —
they affect shared family members
Genes
specific segments of DNA that serve as a functional unit of heredity by encoding a particular RNA or protein. Unit of inheritance.
Mendelian traits
predominantly caused by a single gene
Multifactorial (complex) traits)
determined by one or more genes and environmental factors
Mendelian or multifactorial- polydactyly? Hair color?
mendelian; multifactorial
Central dogma
DNA is transcribed to RNA. RNA codons are scanned by ribosomes and attract tRNAs that add amino acids. These amino acids are linked to form a polypeptide.
A protein chain grows from the — terminus to the — terminus
amino to carboxyl
Transcription
process by which DNA is copied into a single stranded RNA molecule
Translation
process by which RNA codons are scanned by ribosomes and attract tRNAs that add amino acids which link to form a polypeptide
Genome
complete set of genetic instructions characteristic of an organism. Includes both protein-encoding genes and other DNA sequences.
Genomics
field that analyzes and compares whole gnomes of different species
Genome annotation
process of marking all the genes in a genome and ascribing functions to each
Locus
site of gene within a genome.
—% of DNA is similar among humans
98.9
Approximate number of gene coding for proteins
21,000
Percentage of DNA sequence in exons
1.5%
Percentage of DNA in high copy-number repetitive elements
50%
Largest gene in human genome
DMD (duchenne’s muscular dystrophy) gene which is X-linked and is about 2.4 million bp long.
TTN gene
gene with the largest number of exons (363) and has the largest exon in the human genome (17,106 bp)
A human body contains about — cells and all cells except — contain the entire genome
50 trillion; RBCs
Most — cells within an individual contain the same genome
somatic
Different subsets of genes are — in cells of different —
expressed; tissues
Epigenetic mechanisms
heritable changes in gene expression that occur independently of DNA sequence. Allows for differentiation of distinctive cell types
Examples of epigenetic mechanisms
chromatin modifications and noncoding RNAs
Stem cells
less specialized cells that provide a reserve supply of cells. Important for tissue growth and/or regeneration
DNA structure and components
deoxyribonucleic acid. Components include phosphate, sugar, and base (A,T,C, or G)
Which base pairs pair with which? How many H-bonds in each pair?
adenine to thymine/uracil (2 h-bonds) and guanine to cytosine (3 H-bonds)
Nucleosomes
basic unit of chromosome packaging
Histones that make up nucleosomes
2 of each of the following- H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
Histone that is bound to linker DNA
H1
About — bp of DNA wraps around core histone proteins of nucleosome
147
Linker DNA
DNA which connects nucleosomes. Is variable in length.
Packaging of nucleosomes condenses DNA — -fold. Because of this, 2 m of DNA in a diploid human genome may be shortened to about — m
seven. 0.25
Higher order packaging may condense chromosomes further than just nucleosomes can, though the mechanisms are unknown. What two models are there for this though?
nucleosome supercoiling model and radial-scaffold model.
Centromeres
essential for spindle attachment during meiosis and mitosis (due to kinetochore formation). Carry passenger protein to daughter nuclei. Large stretches of tandem repeat DNA sequences
𝛂-satellite
170 bp sequence that is repeated 1,700 to 29,000 times (=300-5,000 kb of centromeric sequence). May be used as molecular probes to determine chromosome content in cells.
Telomeres
end “caps” of chromosomes. Essential for complete replication of chromosome ends and for pairing of homologous chromosomes in prophase of meiosis.
What is the tandem repetitive telomeric unit sequence (for both strands of telomere DNA)
TTAGGG and CCCTAA
Levels of genetics starting from smallest to largest
DNA→ genes→chromosomes→genomes→individuals→families→populations
Most expressed genes are found in the — region of chromatids while — regions are often not expressed
euchromatin; heterochromatin
Telomerase
protein responsible for extending telomeres. usually deactivated in most cells. often reactivated in cancer.
Individuals carry — alleles for most genes
two
Dominant allele
allele is expressed if individual carries one copy (heterozygous or homozygous)
Recessive allele
must be present on both chromosomes of a pair to be expressed (homozygous only)
Pedigrees
depict inheritance patterns between members of a family. Indicate which individuals have particular inherited traits.
(pedigree) male
square
(pedigree) female
circle
(pedigree) diseased
filled in
(pedigree) sex unspecified
diamond
(pedigree) deceased
line slashes through the individual
(pedigree) mating
lines between individuals
(pedigree) consanguineous mating (incest)
double lines between individuals
Population (biological definition)
a group of individuals that can have healthy offspring together
Population (genetic definition)
a large collection of alles, distinguished by their frequencies
Gene pool
sum of all alleles in a population
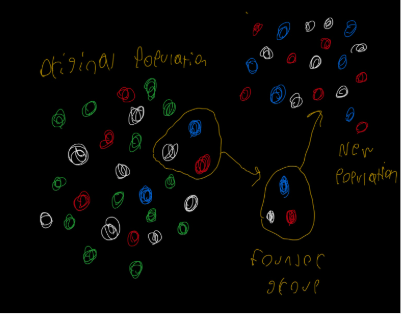
Founder effect
describes a reduction in genetic variations that results when a new colony is established by a small subset of a large original population. Accelerates genetic drift by perpetuating a subset of alleles from an original population to a new one.
Exons
expressing regions-coding regions of genes
Introns
intragenic regions- noncoding regions of genes
Allele
alternate form of single gene. Discrete units of inheritance.
Homozygous
when both alleles for a gene are the same
Heterozygous
when a gene has two different alleles
Mutation
permanent change in DNA sequence of a chromosome
Germline mutation
occur in sperm or egg and are passed on to next generation
Somatic mutation
occur spontaneously in non-sex cells after conception and are not inherited
t/f all mutations are deleterious
false, they may be positive negative or neutral
Spontaneous mutations
de novo or new mutations. Not caused by exposure to a mutagen. May be caused by errors in DNA replication of normal instability of DNA.
Mutagen
chemicals or radiation that may cause mutations in DNA
Carcinogen
any cancer causing agent. Many are mutagens.
Hot spot
regions in which mutations are more likely to occur. May be caused by short repetitive sequence or palindromes
How do short repetitive sequences result in mutations?
pairing of repeated may interfere with replication or repair enzymes
How can palindromic sequences result in mutations?
often associated with inerstions or deletions
A mutation change in a DNA sequence is — in a population ( —% of alleles) and typically affects the —
rare; less than 1%; phenotype
Polymorphism
means many forms. Change in a gene that is less rare (>1% alleles in a population) than a mutation and may not affect phenotype
Gene variant
term which may used for both mutation and polymorphism
Point/substitution mutation
refer to change of a single nucleotide in DNA
Transition mutation
changes a pyrimidine to a pyrimidine or purine to purine
Transversion mutation
changes a purine to pyrimidine or pyrimidine to purine
Silent mutation
mutation causes no change in amino acid. Due to multiple codons coding for the same amino acid. Aka synonymous mutation.
Nonsense mutation
point mutation in which a stop codon is generated (UAA, UAG, UGA)
Missense mutation
point mutation in which an amino acid is changed
Insertion or deletion mutation
mutation when 1 or more nucleotides are inserted or deleted from a DNA sequence
Frameshift mutation
occurs when an insertion or deletion alters the codon reading frame such that incorrect amino acids are incorporated into the protein. Frequently results in early stop codons.
How does a mutation in G551D CFTR cause cystic fibrosis?
it swaps a glycine amino acid for an aspartic acid which causes the protein channel it encodes to be blocked
InDels
insertion or deletion mutations. Insertion adds genetic material while deletions remove genetic material.
Deletions can be anywhere from — long to —
1 bp to an entire chromosome
Inversion
when a section of a chromosome is inverted
Translocation
break off a segment from one chromosome and attaches it to another
Lethal mutation
mutation which causes developing organism to die prematurely
Conditional mutation
produces phenotypic effects only under certain conditions.
Restrictive conditions
conditions that cause a conditional mutation to produce a phenotypic effect
Permissive conditions
conditions where a conditional mutation does not produce a phenotypic effect
Temperature sensitive mutation
conditional mutation which typically has a restrictive condition of high temperatures and a permissive condition of low temps
Loss-of-function mutation
reduces or abolishes gene activity. Most common mutation type. Usually recessive (usually one normal copy of gene is enough)
Null mutation
loss of function mutation which completely abolishes gene activity
Gain-of-function mutation
increases gene activity or makes it active in inappropriate conditions. Typically dominant
Dominant-negative mutation
mutant gene product interferes with normal product. Loss of function, but dominant.