Adult Neurogenic Communication Disorders II Exam 1
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
symptoms
aphasia is not a disease; it’s a set of ______
etiologies of aphasia
stroke
tumor
TBI
degenerative diseases
infection
seizures
PPA
etc.
cognitive communication disorders
refer to difficulties with communication that arise from impairments in the cognitive processes that support language use
treatment
theories are important for ______ in clinical practice
different
two patients with the same lesion will show ________ symptoms
yes
people with aphasia will or will not show aided recovery after 1 year post-stroke?
types of aphasia
Broca’s
Wernicke’s
Global
Conduction
Anomic
Transcortical Motor
Transcortical Sensory
aphasia assessment
should result in the following:
diagnosis of a language disorder
description of the characteristics, severity, and functional impact of the language disorder
prognosis for change (in the individual or in relevant contexts)
recommendations for intervention, support, and community resources
referral for other assessments or services
outline of aphasia assessment
spontaneous recovery
assessment in general
evaluation of perceptual and motor skills
in-depth communication evaluation
differential diagnosis
test confounds
prognostic factors
mechanisms and bilingual aphasia
what is included in spontaneous recovery assessment?
mechanisms of language recovery
RH reorganization
there is an implication of residual LH language areas
recruitment of LH regions is not typically involved in language
reorientation of domain general networks not specifically dedicated to language
assessment in general
WHO ICF model
goals and general principles
flow
in-depth communication evaluation
includes comprehensive test batteries, tests of specific functions, and tests for other cognitive abilities
types of spontaneous recovery
acute
subacute
chronic
the first month
when is spontaneous recovery the greatest after a stroke?
spontaneous recovery
remission of language dysfunction without formal therapy
aided recovery
refers to the process of using external tools or support systems to help an individual recover or manage a condition, especially in the context of neurological or cognitive impairments
recovery in the acute phase
during the first 3 weeks
restoration of perfusion (normal glucose metabolism)
decrease of cerebral edema & disappearance of local inflammations
penumbra recovers over time
penumbra
zone around an irreversibly damaged core infarction
predictor of clinical progress
salvageable brain area
ischemic core
brain tissue destined to die
located within the penumbra
recovery in subacute phase
recovery that occurs up to 6 months after a stroke
neural plasticity
restoration of diaschisis
neural plasticity
ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization
includes sprouting and activation of silent synapses
sprouting
the growth of new dendrites at the level of the axons
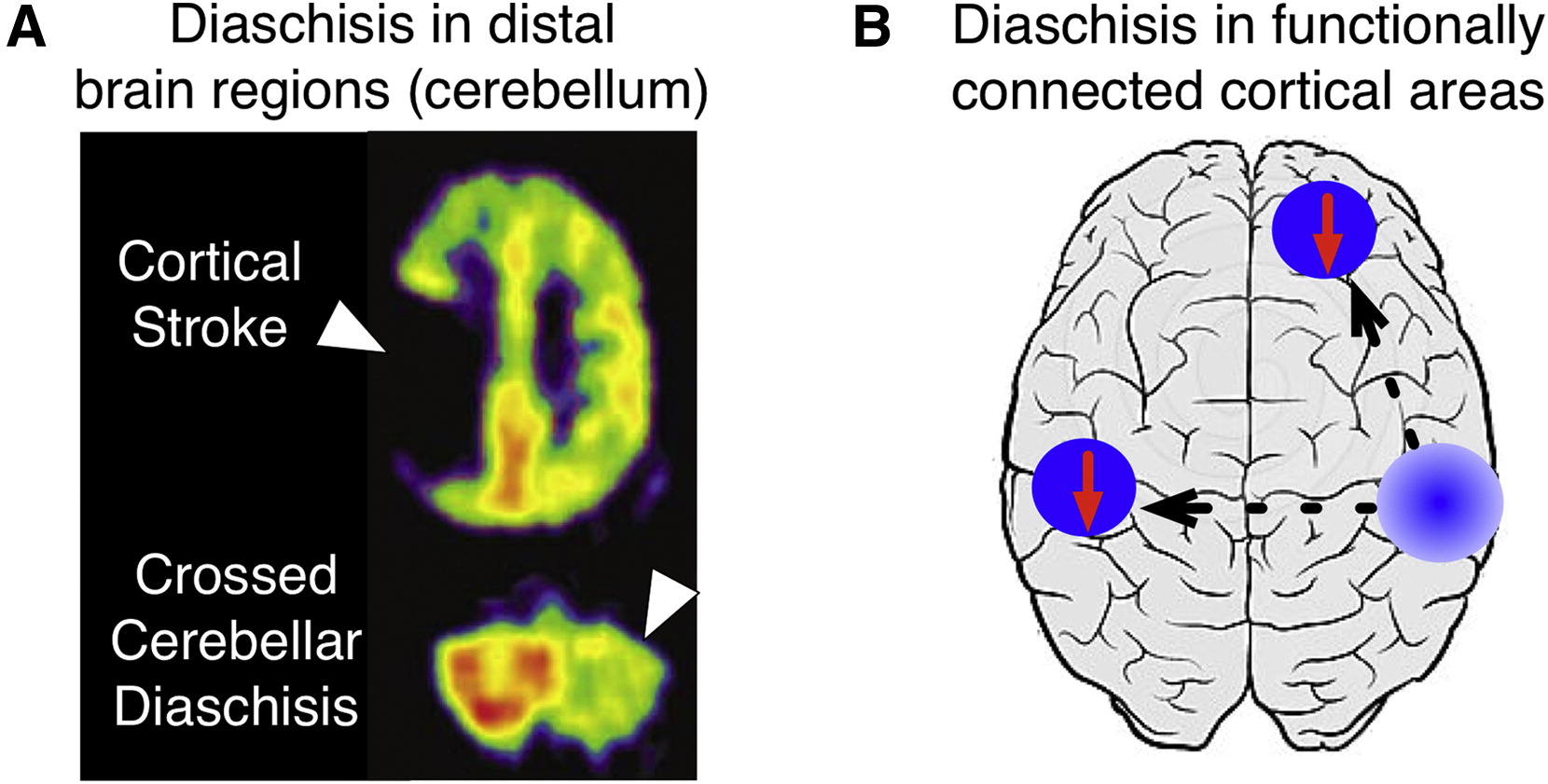
diaschisis
a sudden change of function in a portion connected to a distant but damaged brain area
positive correlation between the decrease in ______ and recovery
the breaking up of a pattern of brain activity by a localized injury that temporarily throws the whole activity out of function though destroying only part of a structure
chronic phase of recovery
after 6 months post-stroke
mainly therapy related
spontaneous recovery
steepest during the first month post onset
flattens out during 2nd and 3rd months but is still rising at 6 months (sometimes even longer)
typically a period of 6 months
types of insult
ischemic/occlusive stroke
hemorrhagic stroke
TBI
ischemic/occlusive stroke
greatest change occurs during 4-6 weeks post-stroke in an _______ stroke
hemorrhagic stroke
most difficult type of stroke to detect
most dangerous
little change initially (first month) but then recovery occurs quickly
TBI
stepwise improvement
reading
after a stroke, which comes back first?
reading or writing
listening
after a stroke, does listening or reading comprehension come back first?
comprehension
after a stroke, __________ comes back before expression does
patterns of recovery in bilingual aphasia
parallel
selective
successive
differential
antagonistic
etc.
parallel recovery
both languages recover at the same time
selective recovery
only one language recovers
successive recovery
one language comes back first, and the other comes back later
differential recovery
both languages comes back but to different degrees
antagonistic recovery
as one language recovers, the other worsens
selective aphasia
aphasia in only one language
WHO ICF model
Health Condition (disorder or disease)
Activities
Body Functions and Structures
Participation
Environmental Factors
Personal Factors
health condition
diagnosis, lesion location, and extent
body functions and structures
anatomical parts of the body such as organs, limbs, and their components
physiological functions of the body systems (including psychological functions)
examples include memory deficits, type and degree of impairment, neglect syndromes, rigidity, spasticity, weakness, etc.
activities
the execution of a task or action by an individual
examples include reading, writing, comprehension, following directions, talking on the phone, following a recipe, reading a newspaper, making appointments, etc.
participation
involvement of people in all areas of life
examples include working, going to church, leisure activities, occupation, family gatherings, going to the bank, etc.
environmental factors
physical, social, and attitudinal environment in which people live and conduct their lives
examples include who the patient lives with (home life), type of support they have, familial expectations, technology, societal awareness, social norms, etc.
personal factors
the particular background of an individual that are not part of a health condition or health states
examples include how many family members one has, methods of transportation, job, intelligence, cultural background, coping styles, socioeconomic status, etc.
formal assessment
any published quantification tool (psychometric properties such as standardization, reliability, validity)
informal assessment
process of creating and manipulating stimuli for making clinical decisions
gathering background information through record review, family interview, etc.
concomitant disorders with aphasia
anomia
agrammatism
auditory/visual deficits
motor speech disorders
depression
anxiety
goals
assessments should establish _____, and all domains of functioning/disability should be considered
assessment procedures
Case history
Observation
Screening
Formal tests
Qualitative and informal assessment
Caregiver assessment
screening
________ comes before the assessment tests
case history
contains information about health status and premorbid condition
includes medications, family history, goals, age, gender, education level, hobbies, cultural background, etc.
neurological exam
neck flexion
auscultation
palpation
neuro-ophthalmologic
assesses motor and sensory fx
cranial nerve fx
reflexes
higher cognitive fx (MMSE)
assessing structural level
angiography
computed tomography (CT)/CAT scan
MRI
assessing functional level
PET scan
fMRI
invasive assessments
angiography
CT
PET scan
noninvasive assessments
MRI
fMRI
bedside communication evaluation
provide nursing staff, physician, and family ways to enhance communication with the patient
better to use due to decreased attention and increased fatigue
highlight strengths and weaknesses during this period
less than 30 min.
guidelines for counseling and education
mini version of assessment batteries
screening tools
Aphasia Screening Test - 3
Quick Assessment for Aphasia
Inpatient Functional Comm. Interview
Shortened versions of WAB-R and BDAE-3
purpose of in-depth communication evaluation
obtains differential diagnosis
helps plan Tx
tests level of response, coping styles, motivation, etc.
serves as baseline data for Tx planning
background
consider educational, socio-economic, dialect/language, and cultural ________ when selecting a test
comprehensive batteries
assesses the number of linguistic skills and communication modalities
identifies the presence and type of aphasia
tests used to assess linguistic skills
Boston Naming Test
Northwestern Assessment of Verb and Sentences
aphasia
sudden onset
spontaneous recovery
may have hemiparesis
focal lesion
TBI
problems with orientation and memory
syntax, word finding, auditory comprehension, repetition
making up confabulatory stories
apraxia
effortful, trial/error, groping, dysprosody, articulatory inconsistency, difficulty initiating
psychiatric illnesses
disorientation, confabulation
gradual of symptoms in late adolescence
absence of observable brain damage
language problems such as excessive output, simplified syntax, decreased informativeness
pragmatic
age/education and ethnocultural background are important to take note of, especially when testing ______ skills
specific
prognosis should be for the improvement of ________ functions
biographical factors
Age
Gender
Education
Premorbid intelligence
Personality
Level of social support
most important determinants in prognostic factors for language recovery *
initial severity
etiology
site and extent of brain damage
superior temporal gyrus
problems with auditory comprehension = damage to the _____ ______ ____
standardized testing batteries
Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination
Western Aphasia Battery
Communication Activities of Daily Living
Assessment of Language-Related Functional Activities
Porch Index of Communicative Abilities