Intro to MO and Diatomic Molecules
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
wavelength and frequency
inversely proportional
wavelength and energy relationship
The shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy
constructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a larger amplitude
destructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude
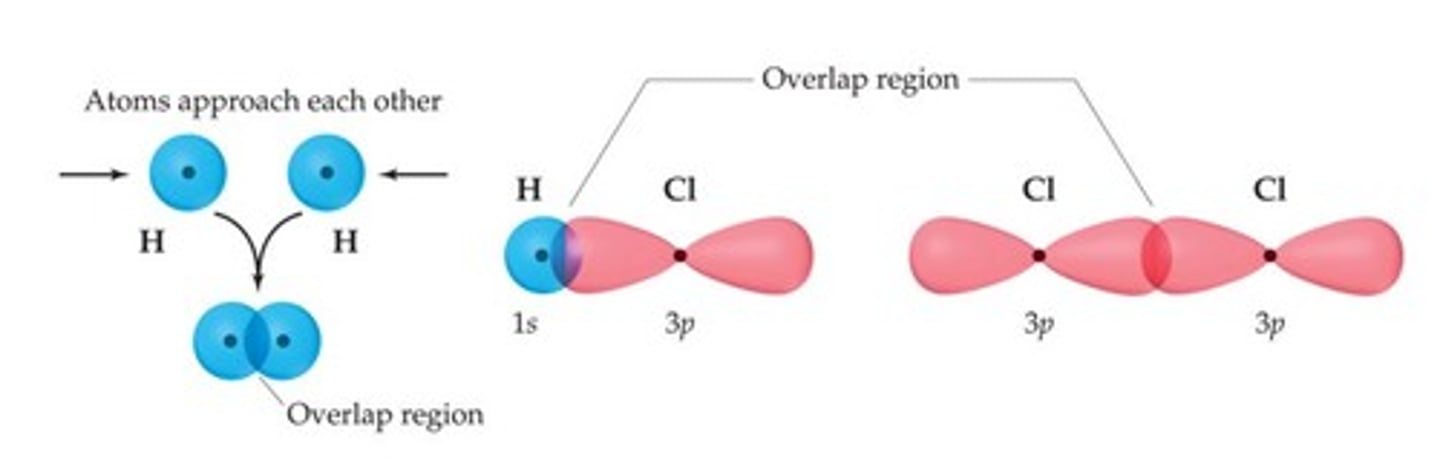
sigma bond
formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a bonding orbital
in-phase
constructive interference
stabilizing (lower energy)
Sigma antibonding orbital
formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a anti-bonding orbital around the axis
out-of-phase
destructive interference
high energy
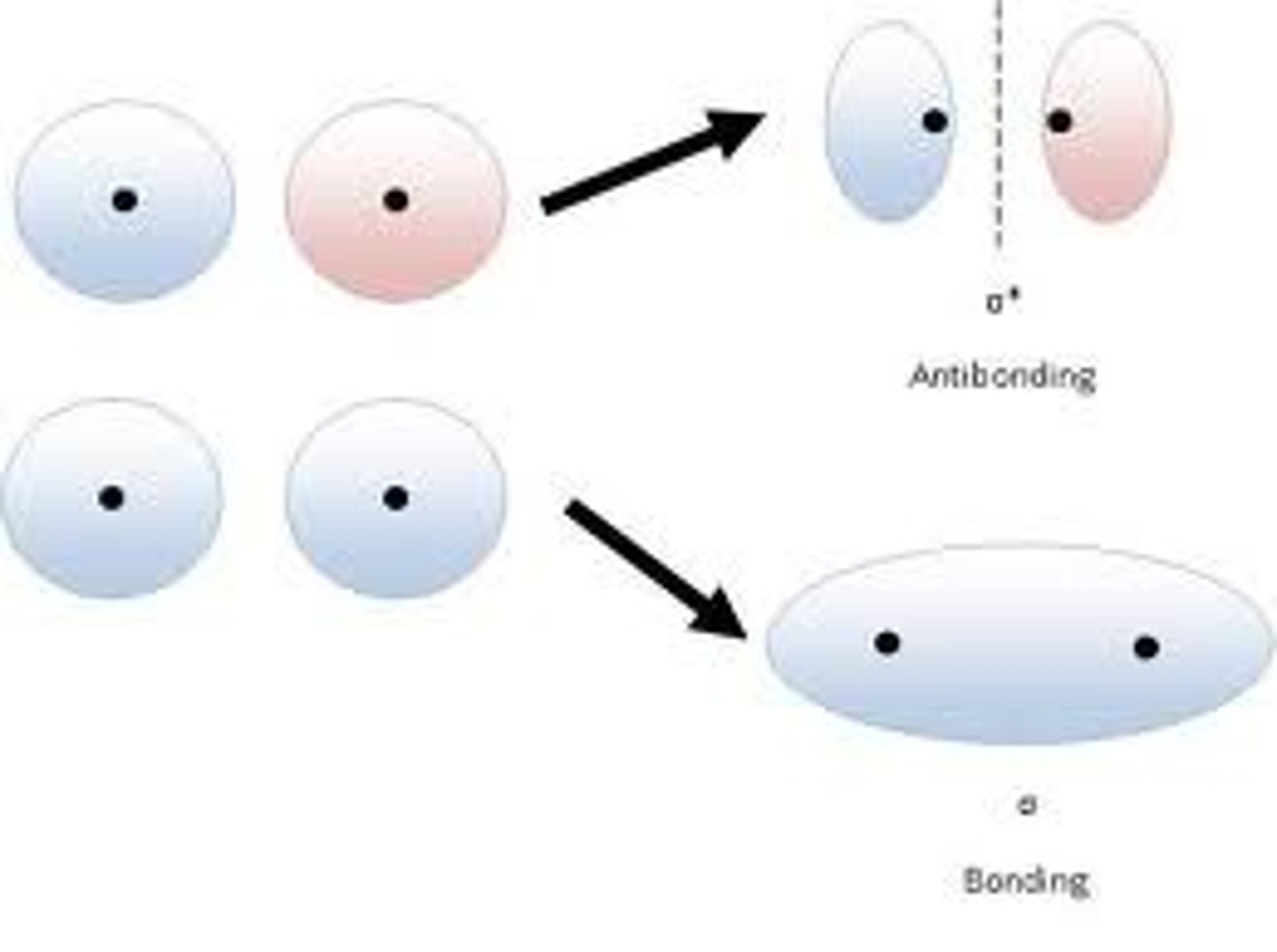
MO Diagram for H2
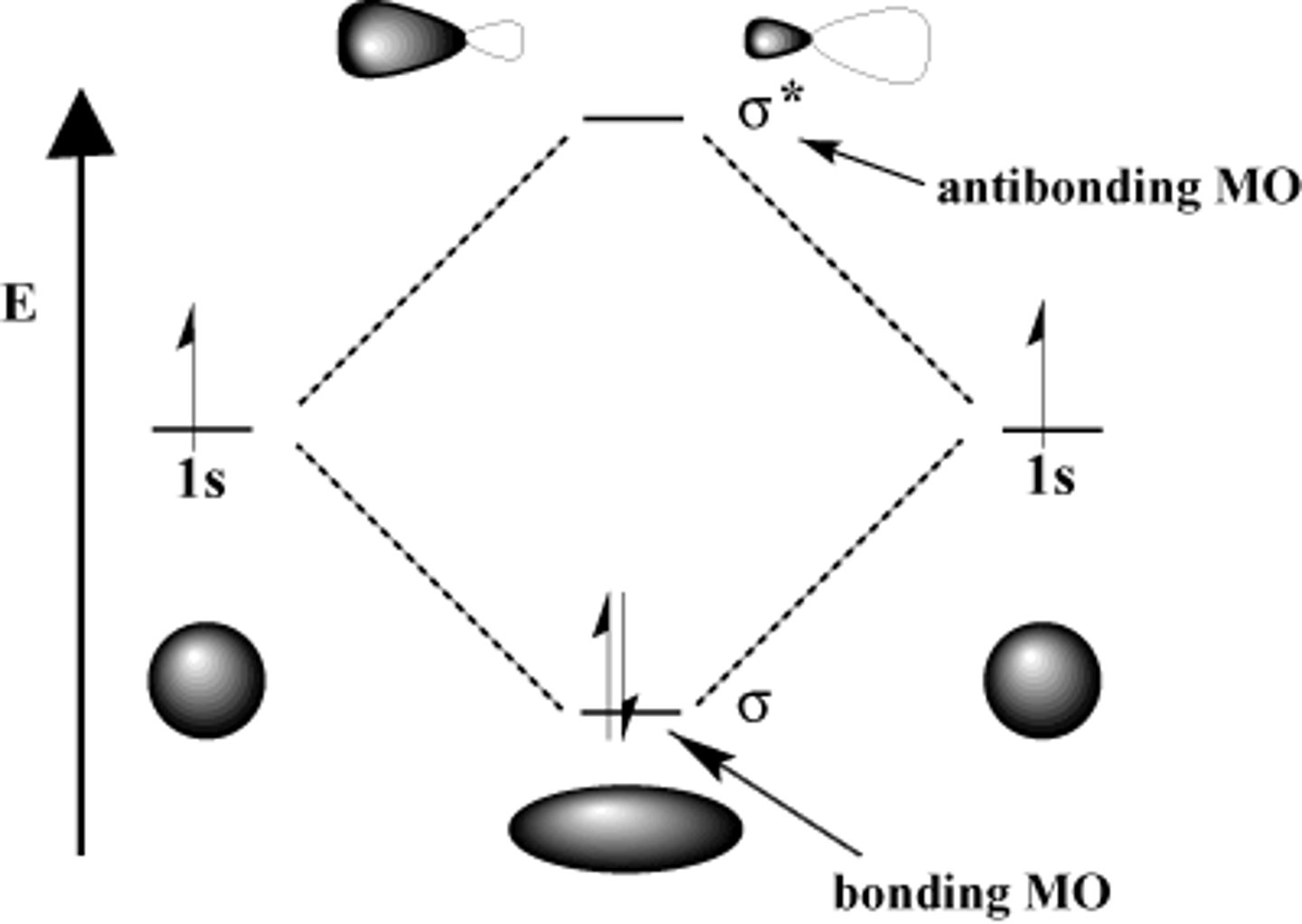
pi bond
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap above and below axis
in-phase
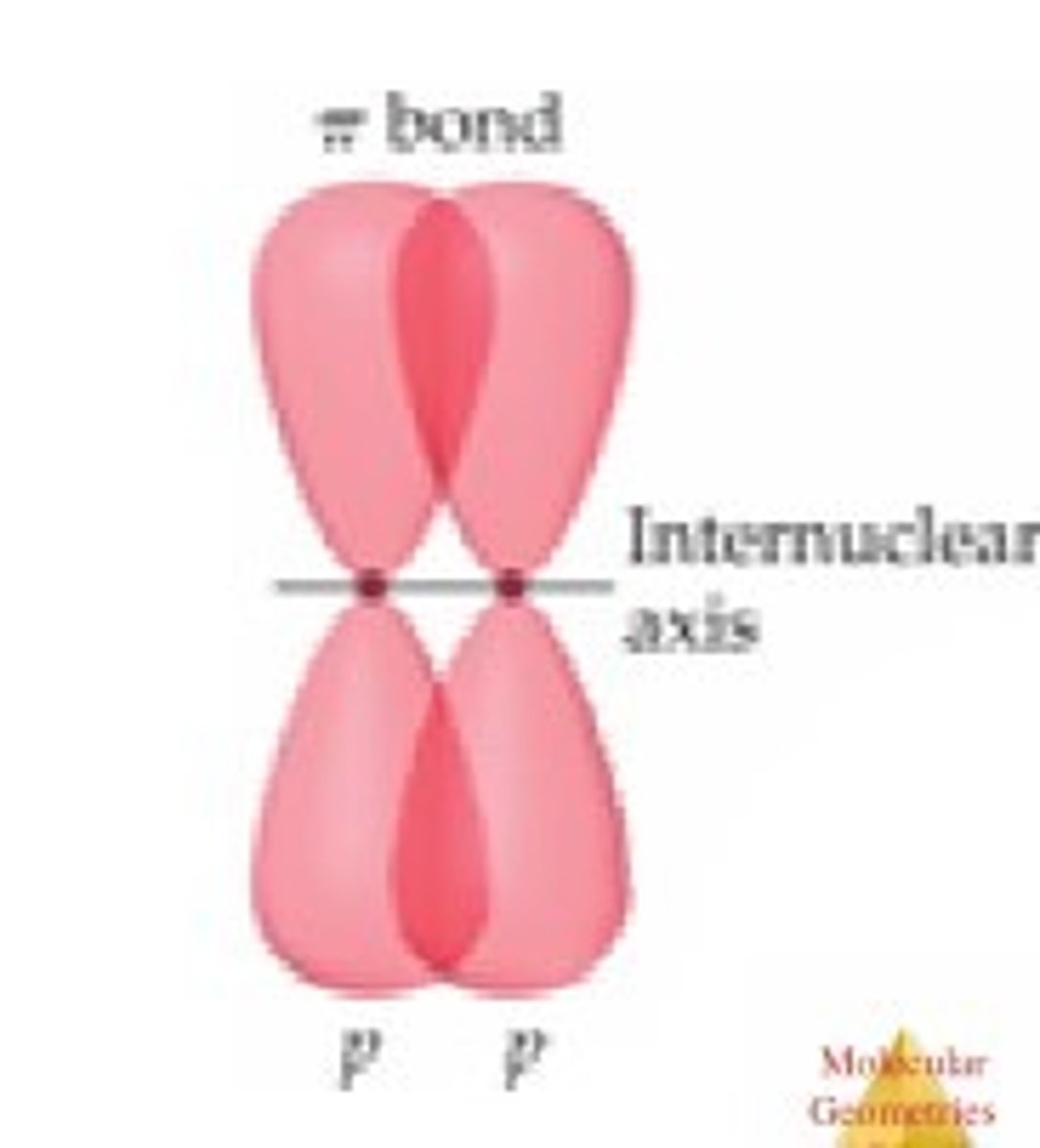
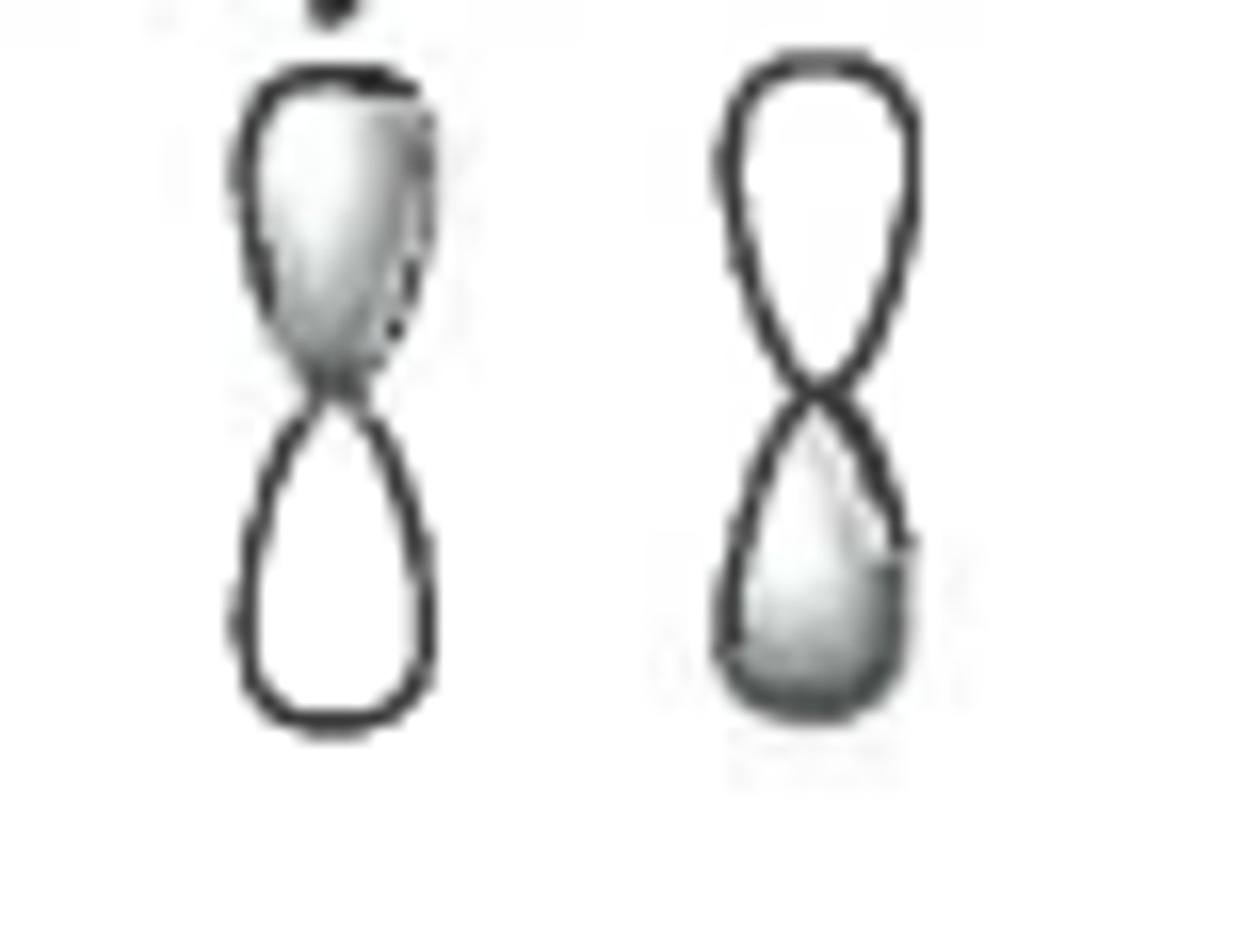
pi* antibonding molecular orbital
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap above and below axis
out-of-phase

MO diagram
Energy level diagram for showing the relative energies and electron occupancy of the MOs for a molecule
rules for MO diagram
1. Number of electrons in MO = number of electrons in two starting atoms
2. Number of orbitals in MO = number of orbitals in two starting atoms
3. Total energy of orbitals in MO = energy of starting atoms
diatomic molecule
A molecule consisting of two atoms
Diatomic MO pattern
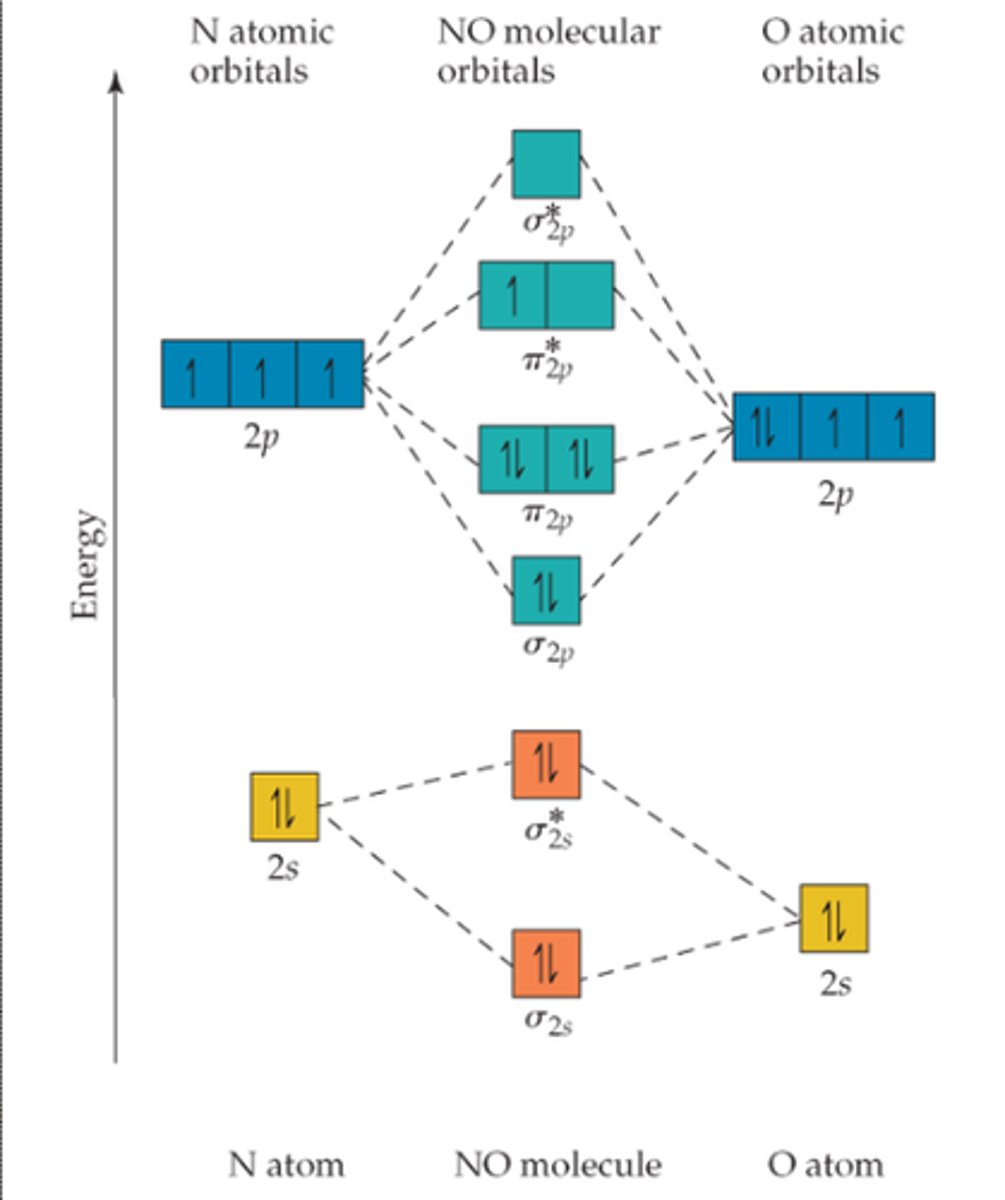
bond order
the number of shared electron pairs between two atoms
bond order equation
(# bonding electrons - # antibonding electrons)/2
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired
paramagnetic
Atom or substance containing unpaired electrons and is consequently attracted by a magnet.
Which is shorter (sigma or pi bond)?
pi bond