drivers ed exam 😬😬
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
if we ever get through this class.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
what does GDL stand for?
Graduated Drivers Licensing
What is GDL?
a 3 stage approach to ease new drivers into driving by providing practice and skill development under low risk conditions
How does GDL work?
it’s a process of incrementally increasing a new drivers privileges which has been shown to reduce teen crashes, injuries and deaths
what is stage 1 of GDL?
stage 1 is the learners permit stage. valid until you’re 18. have to drive with an adult over 21 or they have to have 5 years of experienced driving
what is stage 2 of GDL?
stage 2 is the provisional license stage. this means to hold the permit for a minimum of 6 months or until you’re 18. there can only be one passenger under 21 in the vehicle. You cannot drive by yourself between 1-5 AM. you also cannot have your phone while you drive
what is stage 3 of GDL?
stage 3 is the full unrestricted license stage. this is implied consent (if you get pulled over you must do a breathalyzer test and you might if you’re license if you don’t comply)
what are the common causes of collisions?
13% of crashes are vehicle failures, 34% are roadway factors and 90% are driver error/ human factors.
what are the three components of the highway transportation system (HTS)?
the three components are people, vehicles and roadways.
what are the characteristics of risk?
the characteristics are that you are at risk every time you are on the road, new drivers tend to underestimate the risks of the road, and there are always actions you can take to reduce risk.
what does IPDE stand for?
Identify any real risks, Predict wat they might do, Decide what to do and Execute your plan. (IPD mental skill and and E physical skill)
what is visual control zone?
system for managing the space around your vehicle.
what is the ideal zone for driving?
good pavement, light to moderate traffic and good weather
you should search how many seconds ahead of your path while driving?
12-15 seconds
a teen drivers chance of crashing is higher when driving at what times?
between 9pm and 6am
how long does it take to become a skilled driver?
5 years
what should you do before entering your car?
check around the outside of the vehicle and hold your key open for safety.
what equipment should you inspect before driving?
doors, windows, seats, mirrors, seatbelts, and air vents
what is the law for children seating?
children 12 or under must sit in the back seat
can you hold a cellphone and drive?
NO
what should you see when adjusting your mirrors?
you should see a vehicle first observed in the rear view, vehicle seen moving from rear view to left side mirror, vehicle seen in left side mirror, vehicle moving from left side into peripheral vision and vehicle fully visible in peripheral vison.
why should children be in the back seat
in the front airbags could hurt them
how close should your body be to the steering wheel?
12 inches between your chest and the wheel
where should your hands be while driving?
they should be at 9 and 3 or 8 and 4. they should remain on the steering wheel unless using universal hand signals. (hand up: right turn, hand down: stop and out to the side: left turn)
where should your feet be?
one foot on both pedals, other foot on the dead pedal
how often should you do pre driving checks?
every time you drive
where should the top of your head rest be?
level with the top of your head
what is traction?
the adhesion, friction or grip between the tires and the road surface
what affects traction?
the vehicles speed, tire condition and the road surface. (on the road: sewer covers, paint used for road markings, vinyl strips, tar, wet leaves, sand, loose gravel and mud)
what are the three natural laws of driving?
1. inertia: an object put in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an outside force. sharpness or turn of a curve, vehicle speed, vehicle size, hight, weight, roadway slope and roadway surface condition affect it.
2. gravity: the invisible force that keeps us on the ground. it affects a vehicles speed on hills, also makes stopping distance 4 times longer
3. the amount of energy needed to propel a vehicle. affected by the vehicles weight and speed and influence vehicle deceleration. (stopping distance 4 times longer)
where is the majority of the vehicles weight?
front, rear, sides or corners
what happens to the transfer of weight when a vehicle accelerates?
the rear contact patches increase while the front tires patch decreases
what happens when a vehicle starts to stop?
the front tires weight increases and the back tires weight decreases
what happens to the transfer of weight when you turn?
whatever side you’re turning to increases and opposing side decreases
what’s the proper backing up technique?
place your right hand on the back of the passenger seat, left hand on the wheel at 12:00 and accelerate slowly.
proper sequence for starting a car?
put your foot on the parking brake/pedal before staring the engine, make sure the parking brake is set, make sure the gear is in park, turn on the ignition, let the engine idle for 15-20 seconds, make sure no warning lights come on, turn on low beam headlights, drive at a moderate speed for the first few minutes so the vehicle can start.
proper sequence of events when stopping (parking) a vehicle?
stop with the wheels turned toward the roadway, keep foot on the brake pedal and seat the parking brake, shift gear to park, turn of accessories, close windows, turn of ignition, remove seatbelt, check mirrors for traffic, check rear seats, exit vehicle (dutch reach) and have key ready for safety, lock doors
4 types of acceleration?
1. idle acceleration: simply release pressure from the brake pedal can cause the vehicle to move slowly, forward or backward.
2. light acceleration: light acceleration is used to maintain slow forward motion and also to gradually increase speed with minimum vehicle weight shift
3. progressive acceleration: driver uses firm pressure on the accelerator to increase speed
4. thrust acceleration: a firm push or thrust of the accelerator increases acceleration, shifts more weight to the rear tires for traction, and can be used to pass other vehicles in high-speed traffic.
4 types of braking?
1. releasing the accelerator: stop forward propulsion, coasting
2. controlled (squeeze) braking: needs to be done with the right amount of pressure
3. threshold braking: apply sufficient brake (squeeze off) pressure to slow vehicle, avoids abrupt weight transfer.
4. trail braking (squeeze off) braking: smoothly and gradually reducing brake pedal pressure at the end of the braking maneuver
2 types of steering
1. hand to hand steering: both of your hands are always touching the wheel. the left hand works on the left hand side of the wheel and the right hand works on the right side of the wheel. one hand pushes up or pulls down the opposite hand slides up or down.
2. hand over hand steering: grasping the wheel with right hand between 2 and 3:00 positions and right hand between 9 and 10:00 positions. bottom hand releases the steering wheel and passes across forearm to grip the wheel on the far side.
hand to hand is recommended for 8 and 4 and 9 and 3 positions
where should you position your feet when driving?
right foot should be able to pivot between brake and pedal without getting stuck. left should should be on the dead pedal
what color are regulatory signs?
red, white and black
what color are warning signs?
yellow, lime and orange
what color are guide signs?
green, blue and brown
how are symbol signs read?
bottom up
what’s the traffic light pattern
green > yellow > red > green
what does a red light and flashing red light mean?
red light: stop prior to the pedestrian crosswalk or roadway edge line
flashing red light: you must stop but can go when it’s safe to do so
what does a yellow light and flashing yellow light mean?
yellow light: right of way is expiring. clear the intersection.
flashing yellow light: slow and proceed with caution (some type of intersection)
what does a sold yellow/white line mean?
you cannot cross
what does a dotted yellow/white line mean?
you can pass
what are the 4 different forms of communication?
intentions, presence, warning and feedback
an odd numbered interstate with a single or double digit number indicates a route that…
is north and south
who owns your drivers license and what rights do they have?
the state owns your drivers license and can take it away
what are three ways to show financial responsibility and which one is used the most?
maintain automobile liability insurance coverage, deposit money in the amount required by the state and deposit bonds or other security sufficient to meet the states requirements. insurance is used the most.
what is a certificate of title?
issued when a motor vehicle is purchased and demonstrates proof of ownership.
what is a vehicle registration certificate?
registered every 4 years. purpose is to show that the vehicle is registered
principals of right of way?
the purpose of them is to prevent conflicts and crashes caused by one driver failing to yield to the other
the right of way is either given or not given
to be given the right of way the driver should be driving in a lawful manner. all drivers should yield in order to prevent a collision though.
a driver is not given the right of way if they force it
regardless of who has to, the driver who can avoid the collision should yield the right of way.
when must you yield to others?
when pedestrians are crossing, you should yield to them, to the right of you at a stop sign gets the right of way, vehicles already on the road get the right of way, even if you have a green light yield to pedestrians you have to yield.
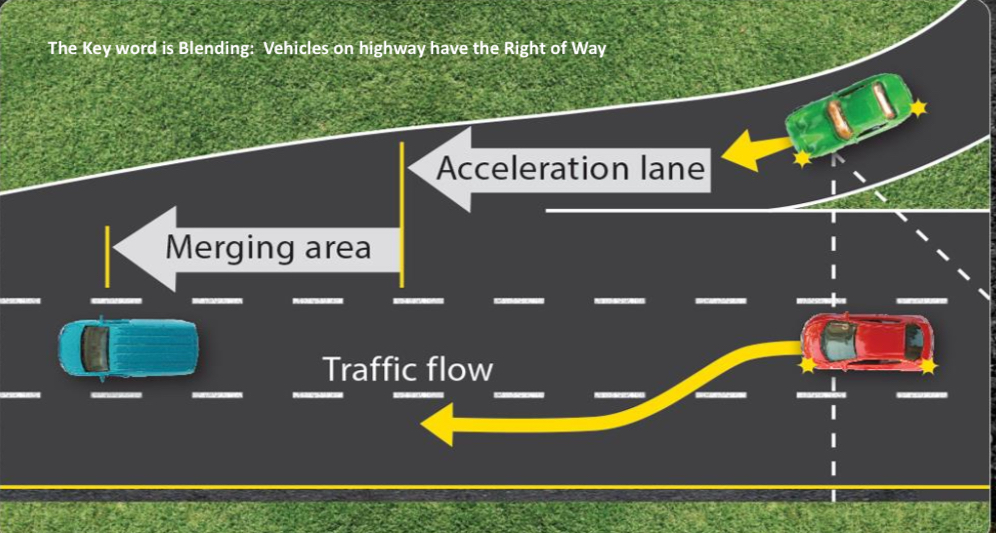
who should yield in the freeway merge?
people in the acceleration lane
who should yield on a round about?
the vehicles entering
when should you yield with a school bus?
if you’re about to go onto the road, if you’re across the road on a double yellow or a dotted yellow, if there’s a barrier you don’t have to yield.
what’s the difference between aggressive driving, road rage and reckless driving?
aggressive driving is depicted as behaviors that indicate an aggressive mindset but are not necessarily directed toward another specific driver. road rage is depicted as behaviors that are directed at specific vehicles or occupants with malicious intentions. reckless driving is described as improper driving example: going 20-25 miles over in a school zone.
when do you apply to be an organ donor?
when you apply for a permit.
what lane do you pass a vehicle in?
the right.
the three types of vision and what do they do?
1. central vision: provides the greatest amount of detail of objects and conditions and is the primary visual function used in targeting.
2. fringe vision: used to judge depth and position
3. peripheral vision(side vision): encompasses central and fringe vision as the broadest type of vision. detects presence, color, and motion which warns drivers about potential objects in your way.
how do you visually search?
look for vehicles, pedestrians, animals and other objects that could move
search for any changes in the road ahead.
search intersection and interchanges, where potential for conflict increases
identify conditions that can influence traction
search any areas from which hazards could suddenly appear
observe the behavior of other road users.
quickly direct your attention from objects and conditions that do not affect your line of travel
what are the 2 components of the selective search program?
1. direct your search; know what to look for
2. classifying information; organize the information in your brain
a what should a good visual search clear?
vehicles, people, animals and other objects that may be in the road by the time you reach them
warning signs of potentially hazardous conditions
traffic signals that require you to act
what is the smith system?
aim high in steering
get the big picture
keep your eyes moving
leave yourself an out
make sure they see you
3 parts of braking distance?
perception distance + reaction distance = total braking distance
how to use the 3-4 second rule
pick an object on the road and as soon as the car in front of you passes it, count the seconds until you pass it.
how do you increase the 3-4 second rule?
the faster you go, the larger distance you’re traveling. you do not change the 3-4 seconds but just apply it faster.
what is closing probability?
the chance that a vehicle and another road user will move closer together as they move along projected paths of travel.
what are wolfpacks?
wolfpacks are when drivers are in traffic. they are clusters of vehicles that drive close together. they driver faster and closer together. you should increase your following distance.
what is the basic speed law?
speed limits are posted on black and white signs. the assumed speed is 25 MPH unless posted on one of these signs.
what is the basic speed limit?
the basic speed limit is 25 MPH
when do you pass someone?
you should pass when no opposing cars are coming at you and when there’s not a solid yellow line. any other time is legal
what should you evaluate before you pass someone?
is the road ahead clear?
how far away is an approaching vehicle?
how fast is it approaching?
is it possible an oncoming vehicle I cannot see is approaching?
can i see far enough ahead?
how long will i take to pass and return to my lane?
can i communicate to the driver i’m passing what i’m doing?
is there an intersection, road or driveway that allows road users to enter the road i’m on before i finish passing?
am i being passed or about to be passed?
when should you turn your blinker on?
100 feet MINIMUM before you turn (one telephone pole before)
how do you safely change lanes?
ask yourself; is anyone already in the lane i want to move into? will any vehicle near me attempt to move into that lane? is anyone rapidly approaching from behind?
search ahead, to the sides, and behind your vehicle to identify a safe gap in traffic
signal your intention to move right or left
recheck your blind spots in the direction of your lane change
when you have enough space, gently steer into the new lane and adjust your speed if necessary.
once you are safely in new lane, cancel turn signal and recheck speed and position.
common mistakes new drivers make
the driver does not signal to communicate the change of lanes
the driver moves toward or into the new lane prematurely
the driver decreases speed
the driver turns the wheel more than necessary
the driver moves into the lane in a position too close to the vehicle ahead
the driver doesn’t turn off their turn signal
how to reverse direction
1.go around the block (safest)
2. make a u turn (most dangerous)
3. make a three point turn
4. make a two point turn
what are reference points?
a point to help you not park too close or too far from the curb
how do you use reference points?
aim tp position your vehicle 12 inches or closer to the curb
what are the advantages and disadvantages of parking at an angle?
advantages:
one way streets
allow parking to be on both sides
disadvantages:
exiting requires travelling in same direction as when the driver approached the parking
what are the advantages and disadvantages of parking perpendicular?
advantages:
perpendicular parking to the left allows a greater line of sight
disadvantages:
you have to have proper vehicle positioning
need more room to maneuver than angled spots
what are the advantages and disadvantages of parallel parking?
advantages:
its like a slow lane change but in reverse
disadvantages:
there is not enough curb to allow you to pull in front
rear wheels do not steer
how do you park uphill?
use your parking brake for any hill
position your vehicle so the curbside wheels are parallel to and 6 inches away from the curb
move forward and very slowly and turn the steering wheel sharply away from the curb
shift to neutral and allow your vehicle to slowly roll backward until the front tire rests against the curb
set the parking brake and then shift to park
how do you park without a curb?
you park with the same guidelines but position your wheels parallel to the road edge
how do you park downhill with a curb?
position your vehicle so the curbside wheels are parallel to and 6 inches away from the curb
move forward and turn wheel sharply toward the curb
stop your vehicle when the front curbside tire first touches the curb
set parking brake and park.
where are the blind spots on large trucks?
wherever you cannot see the truck driver, they cannot see you. always assume that a truck driver cannot see you

why should you never drive beside a truck?
they cannot see you.
where do you go if your car gets stuck on a railroad crossing?
run to a point where you are not in the line of the train or in a line where debris can hit you
bicycle safety
don’t use bicycle lanes
use dutch reach technique
motorcycle safety
they stop quicker
you should increase your following distance
farm machinery safety
they are slow moving vehicles

parts of the freeway
multiple lanes of traffic moving in the same direction
medians and other physical barrier to separate traffic traveling in opposite directions
wide,paved shoulders
relatively open lines of sight
risk reducing engineer standards
what is highway hypnosis?
when driving for long periods of time drivers can exhibit trance like states. occurs when drivers don’t have enough rest to stay alert
what is velocitation?
when drivers have been driving for so long that they become used to their vehicles speed and sounds
law for making a right on red
you can
3 rules for passing on the right in rhode island
In Rhode Island, you can only overtake and pass on the right under specific conditions: when the vehicle ahead is making or about to make a left turn, on a one-way street, or on a roadway with traffic restricted to one direction and sufficient width for two or more lanes.