Neuroanatomy Structures- Cedarville University
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
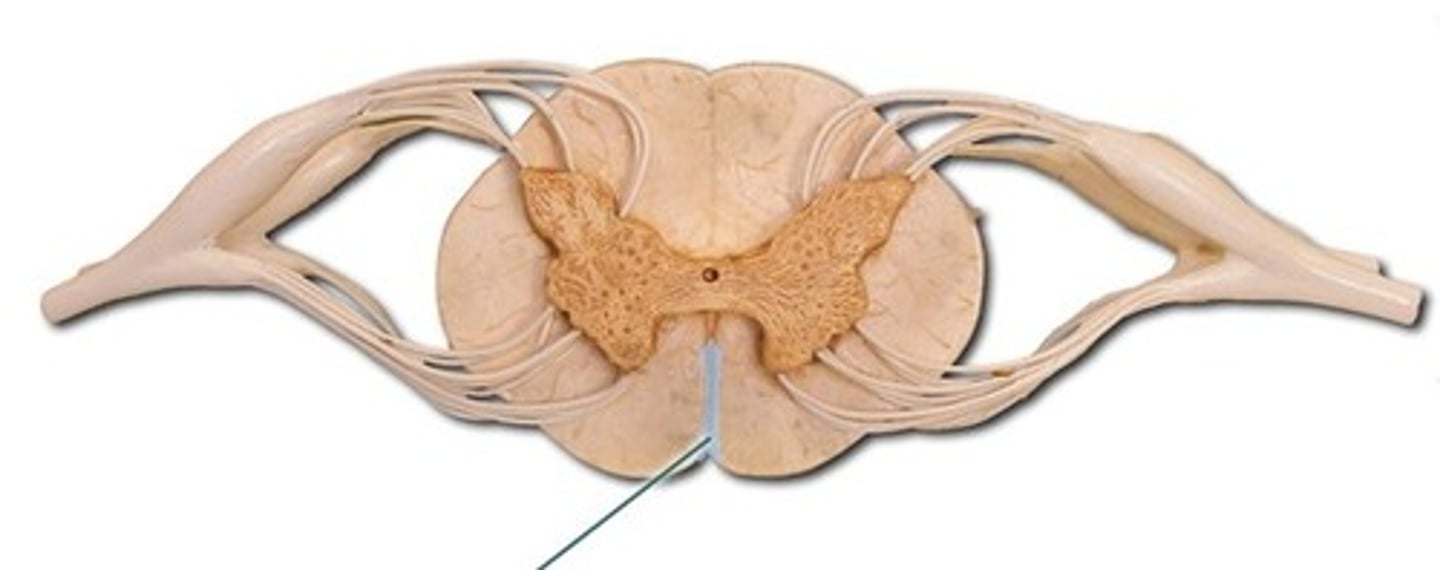
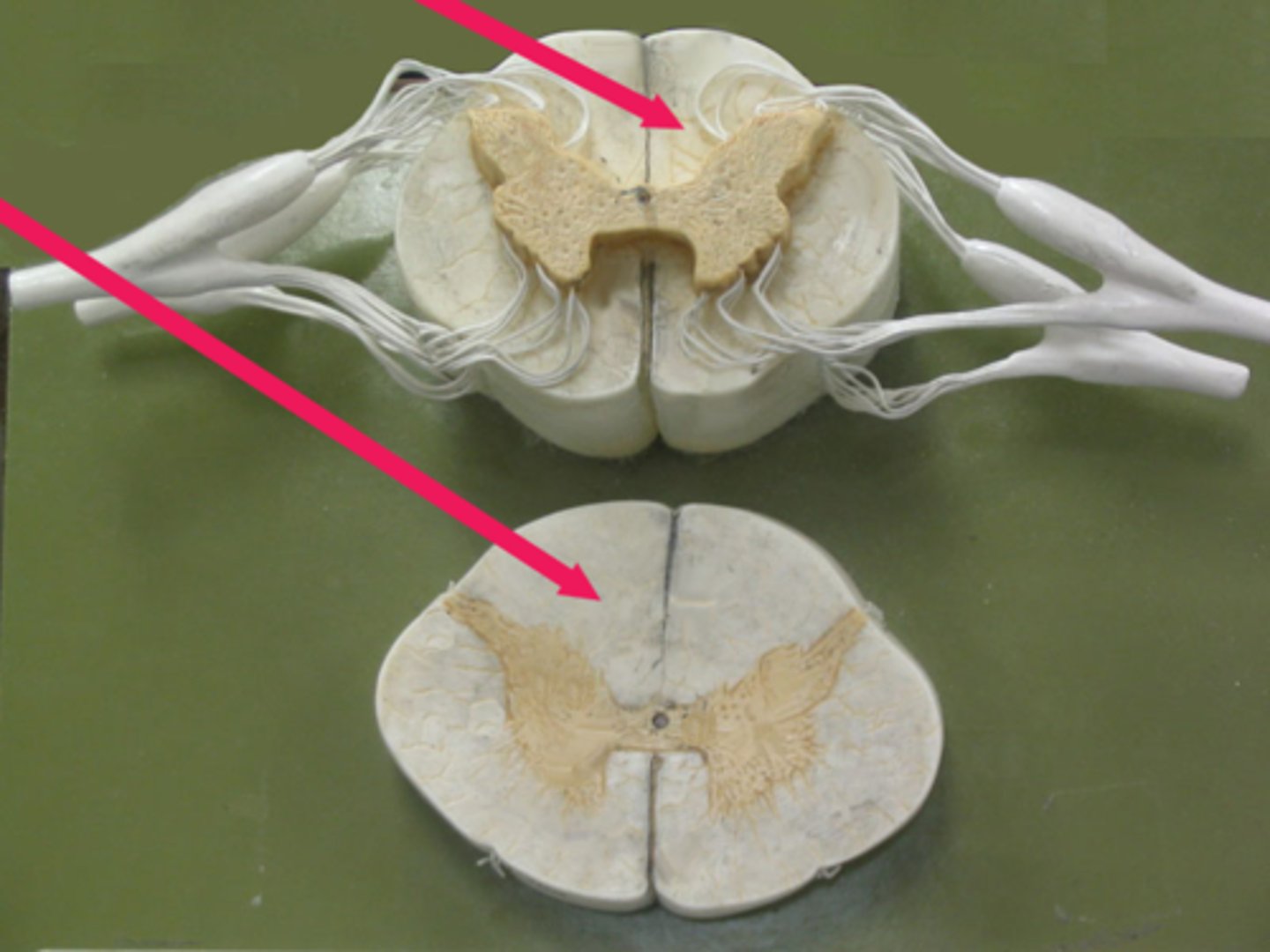
Anterior media fissure
spinal cord
arachnoid villi
structures that return cerebrospinal fluid to the venous blood in the dural sinuses
Arbor Vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
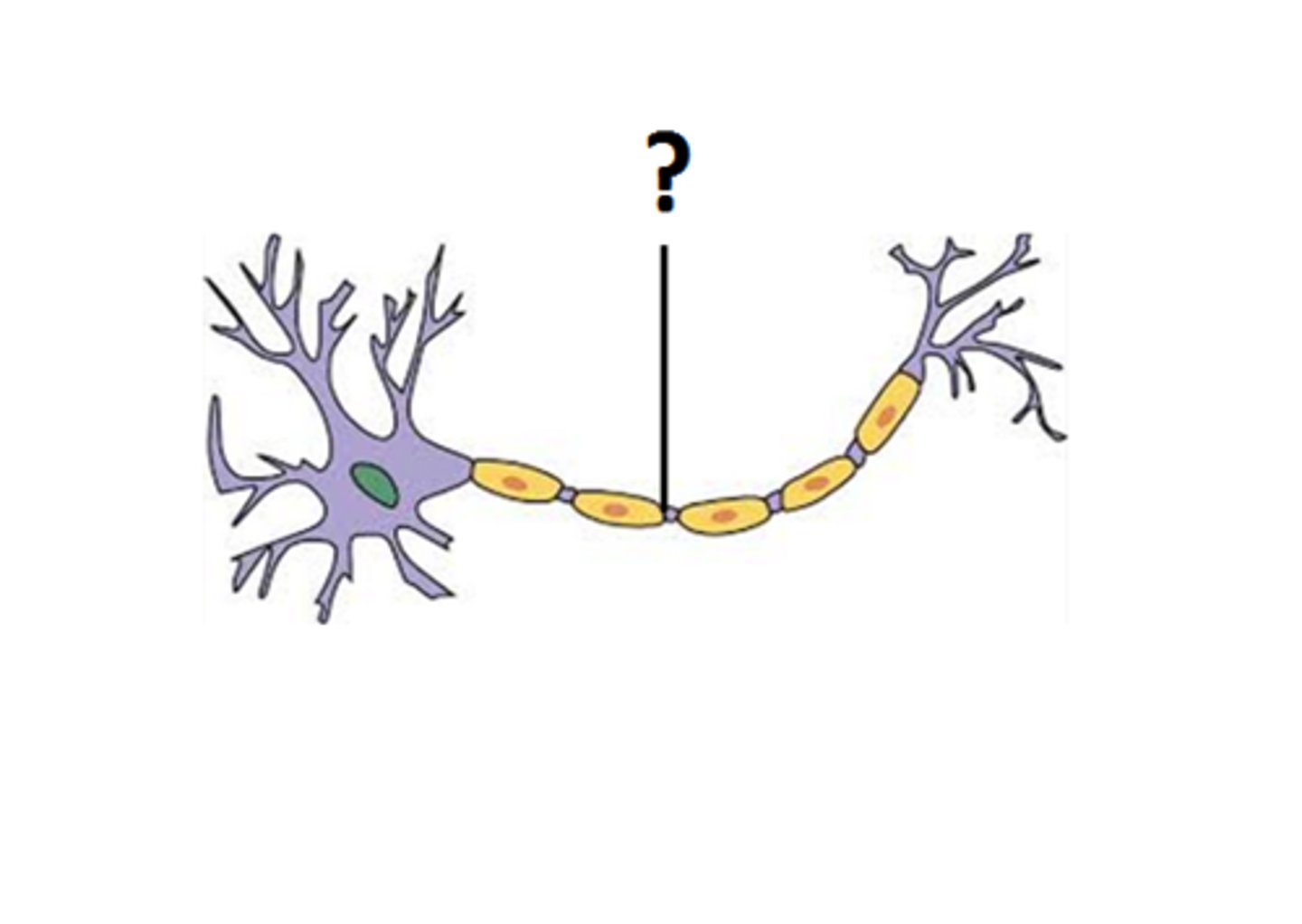
Soma
cell body
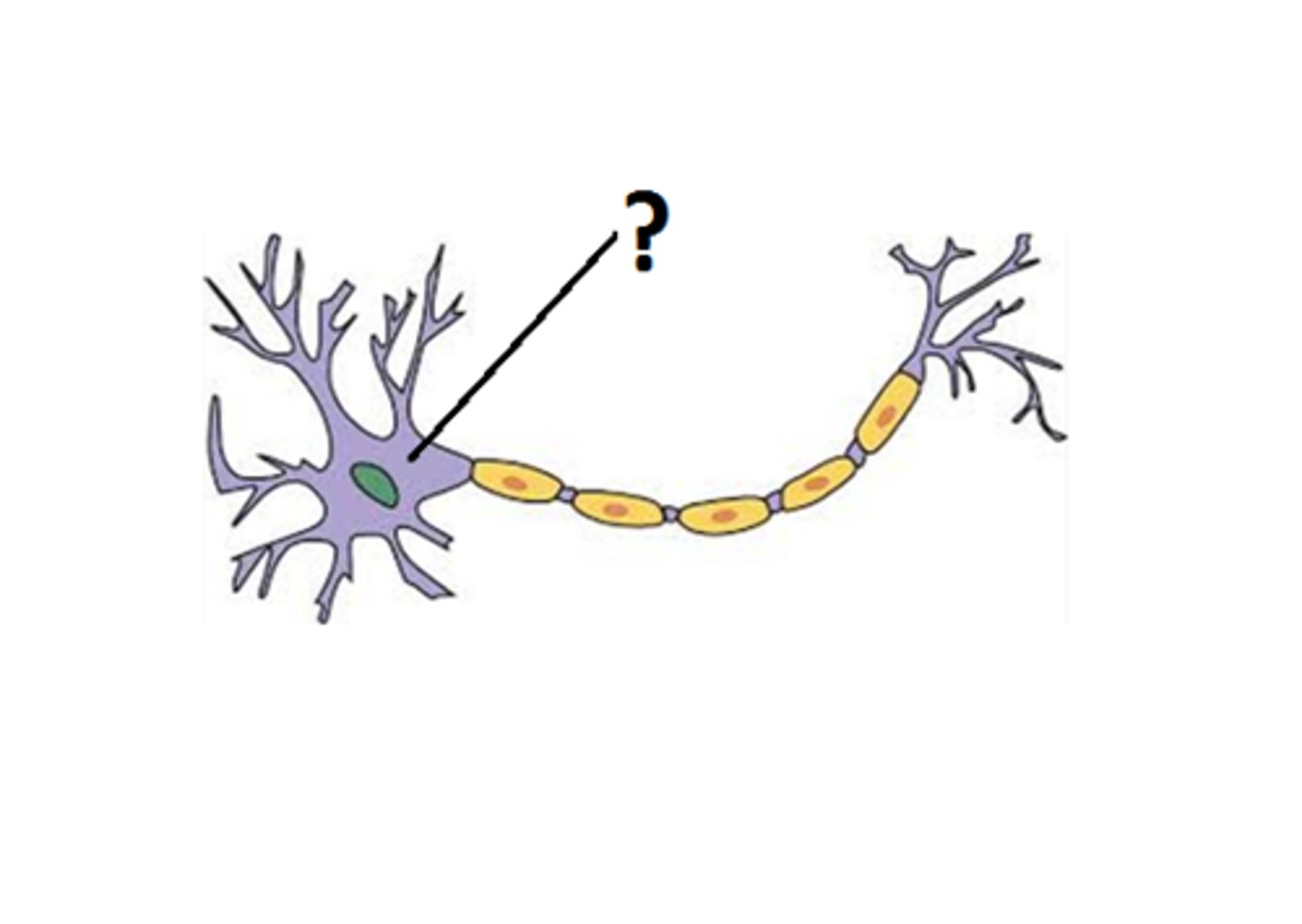
Dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
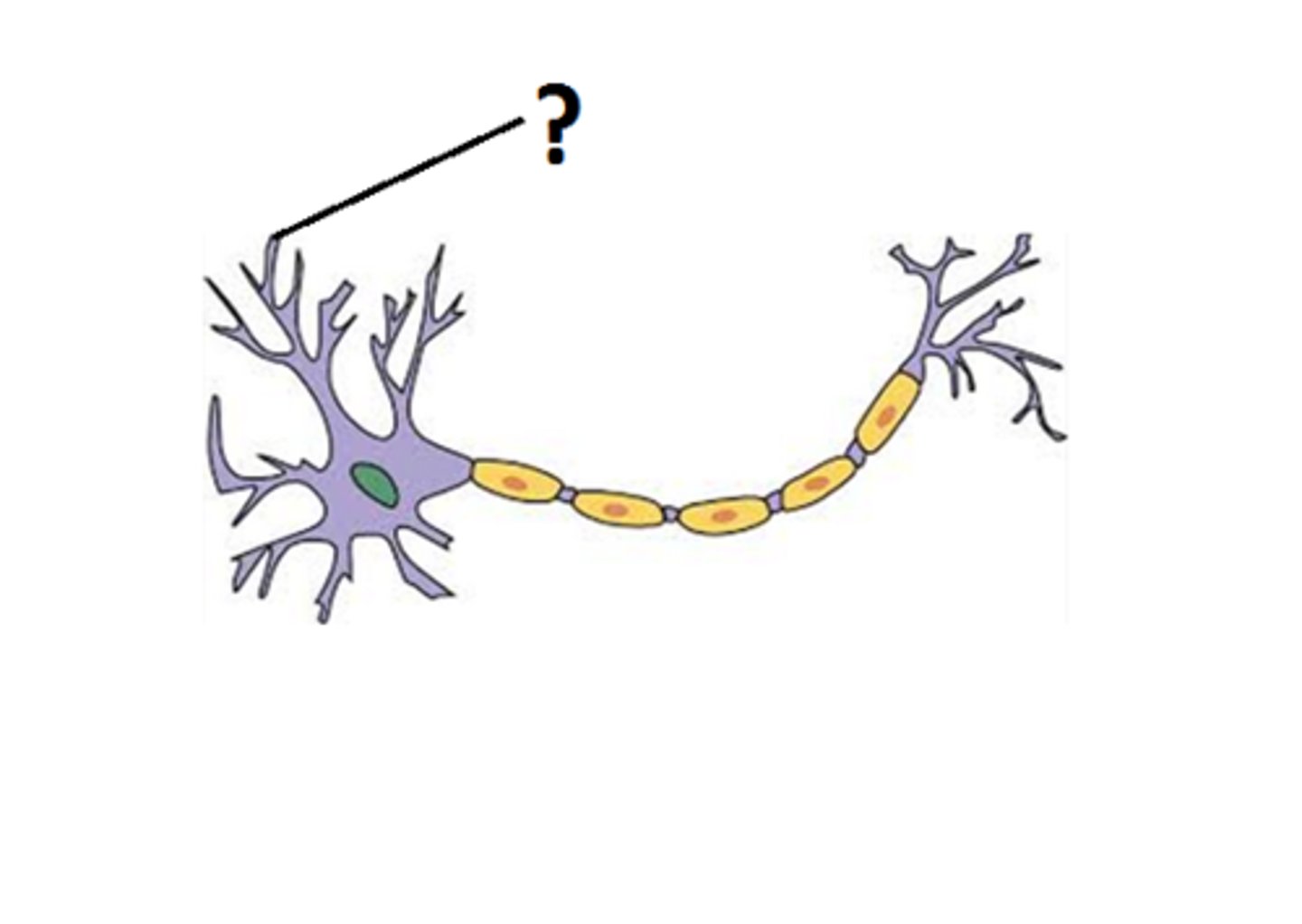
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
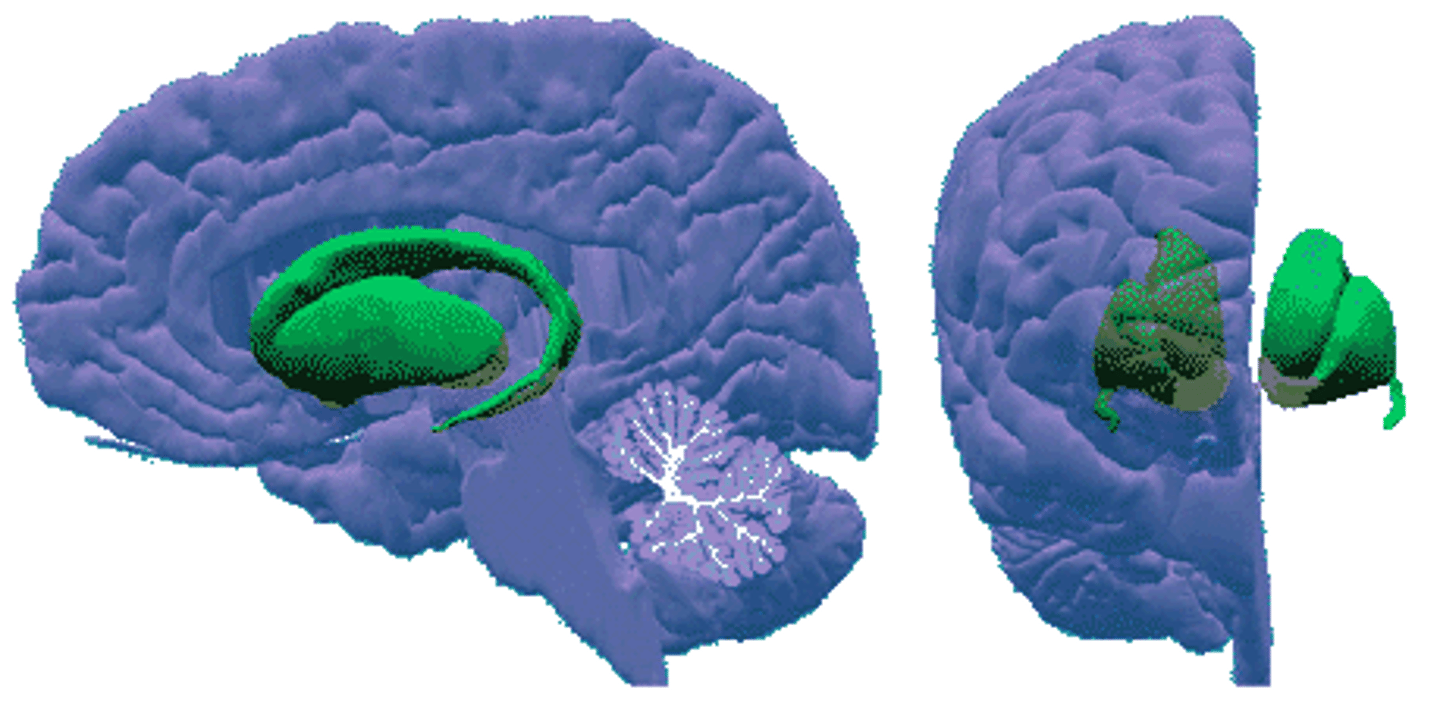
Basal Ganglia
a set of subcortical structures that directs intentional movements
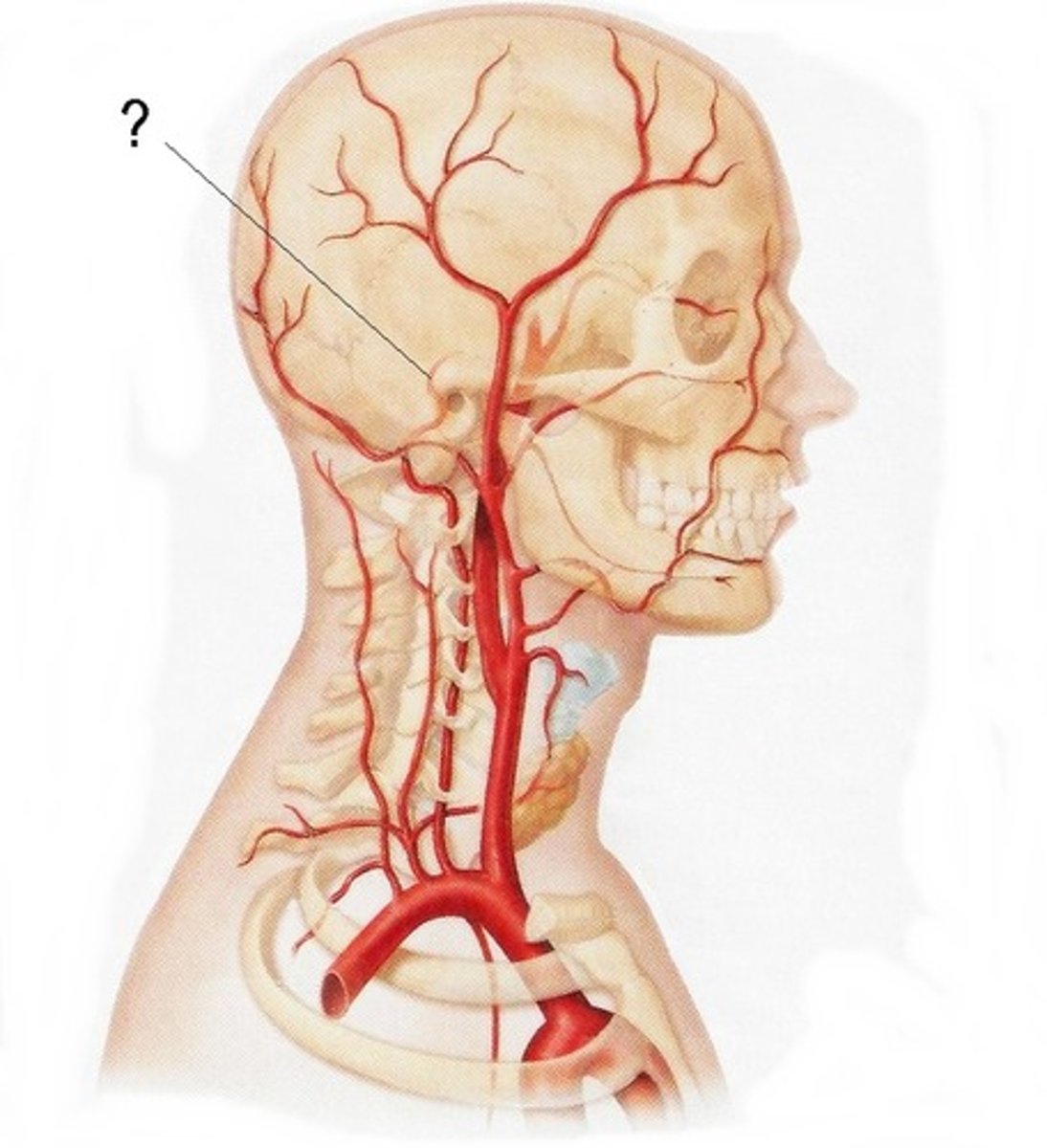
basilar artery
An artery, formed by the fusion of the vertebral arteries, that supplies blood to the brainstem and to the posterior cerebral arteries.
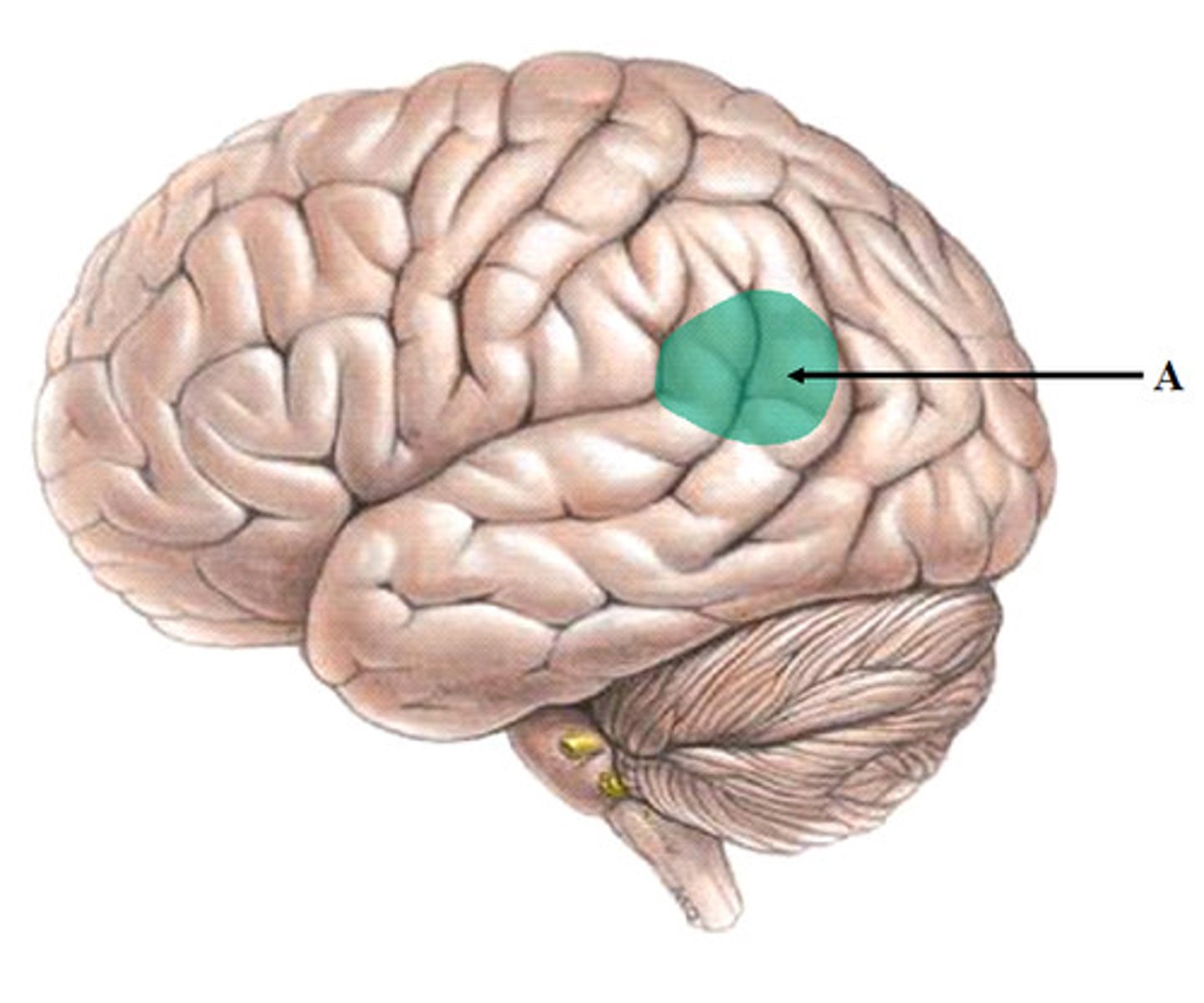
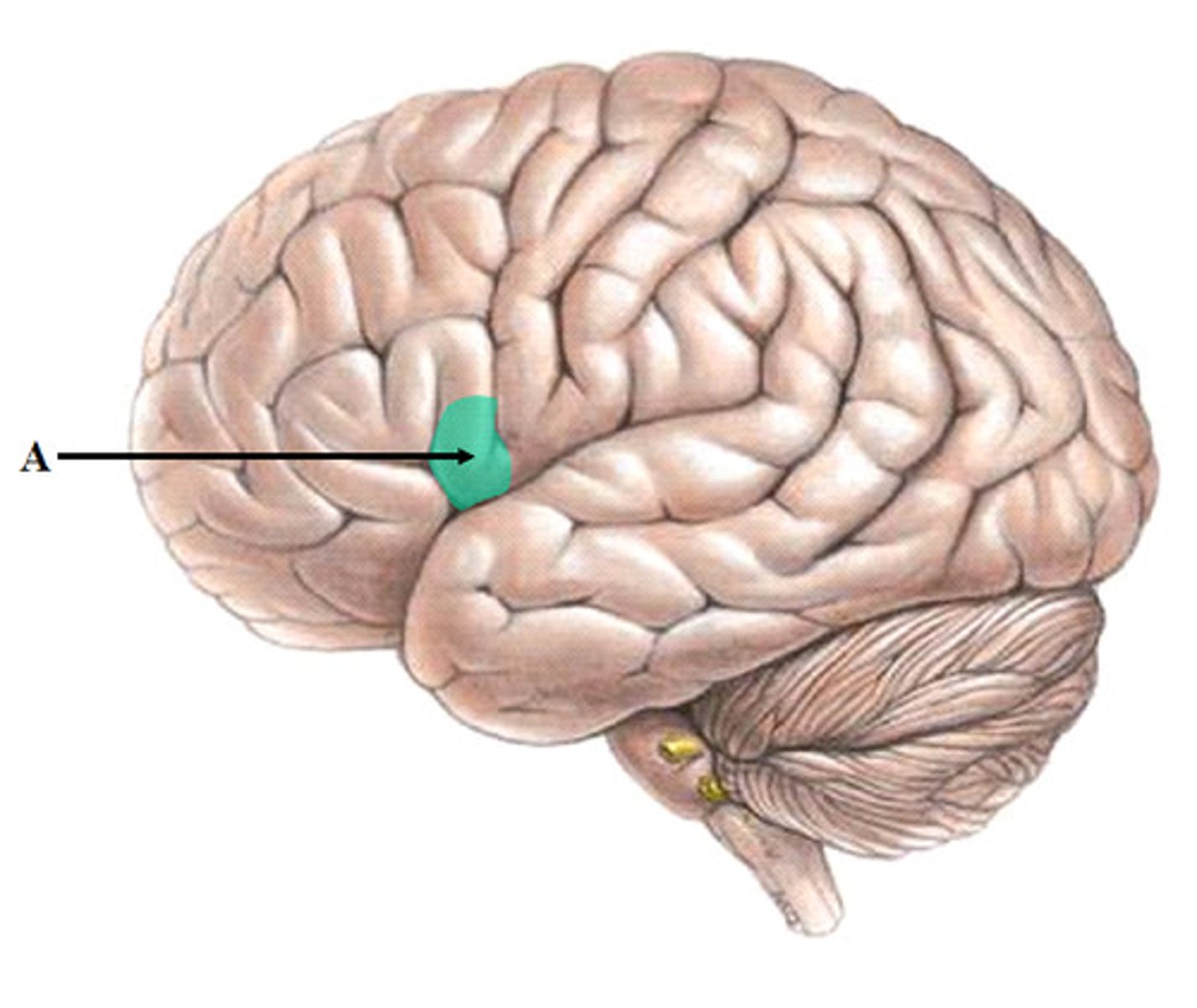
Brocas area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
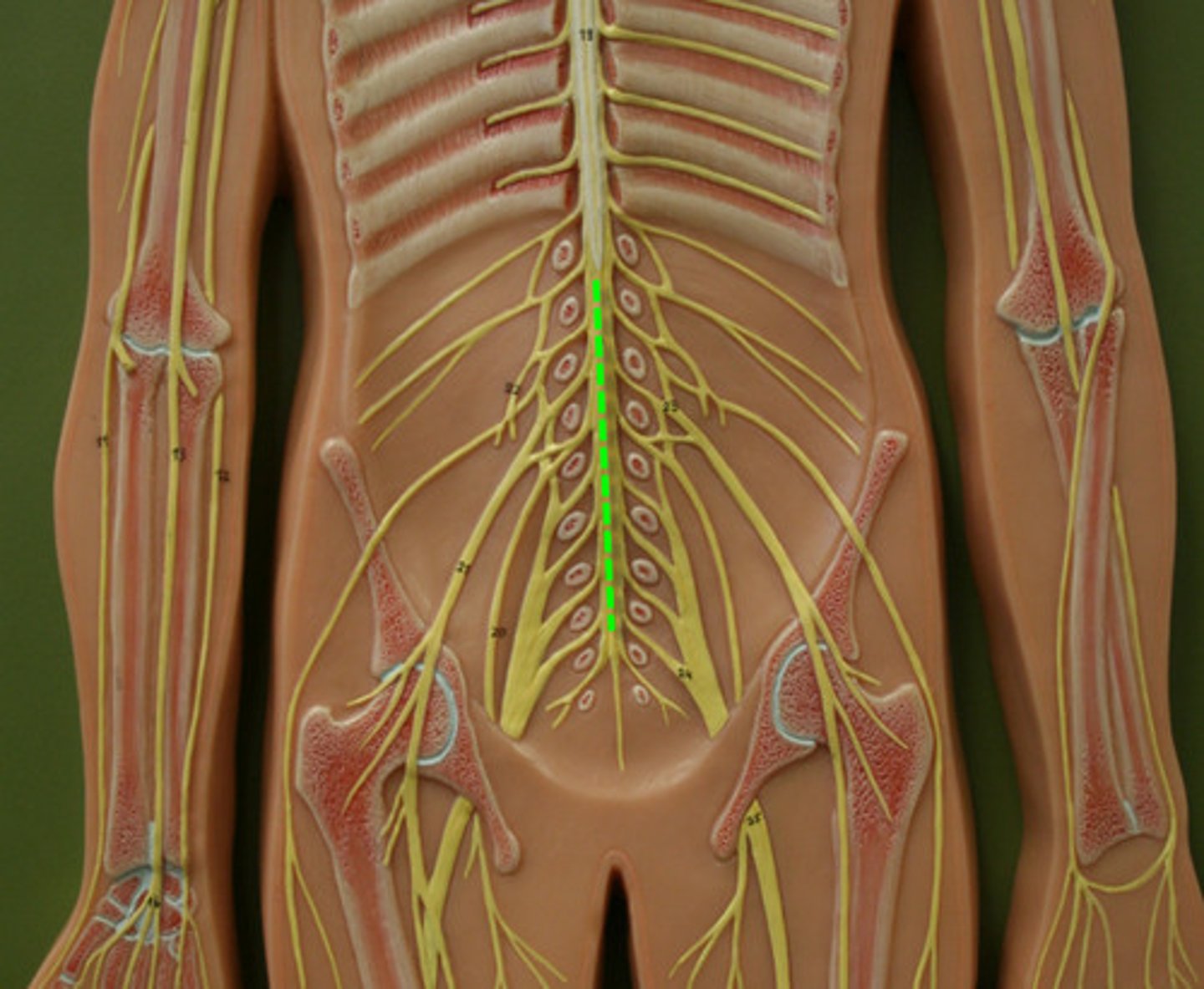
Cauda Equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
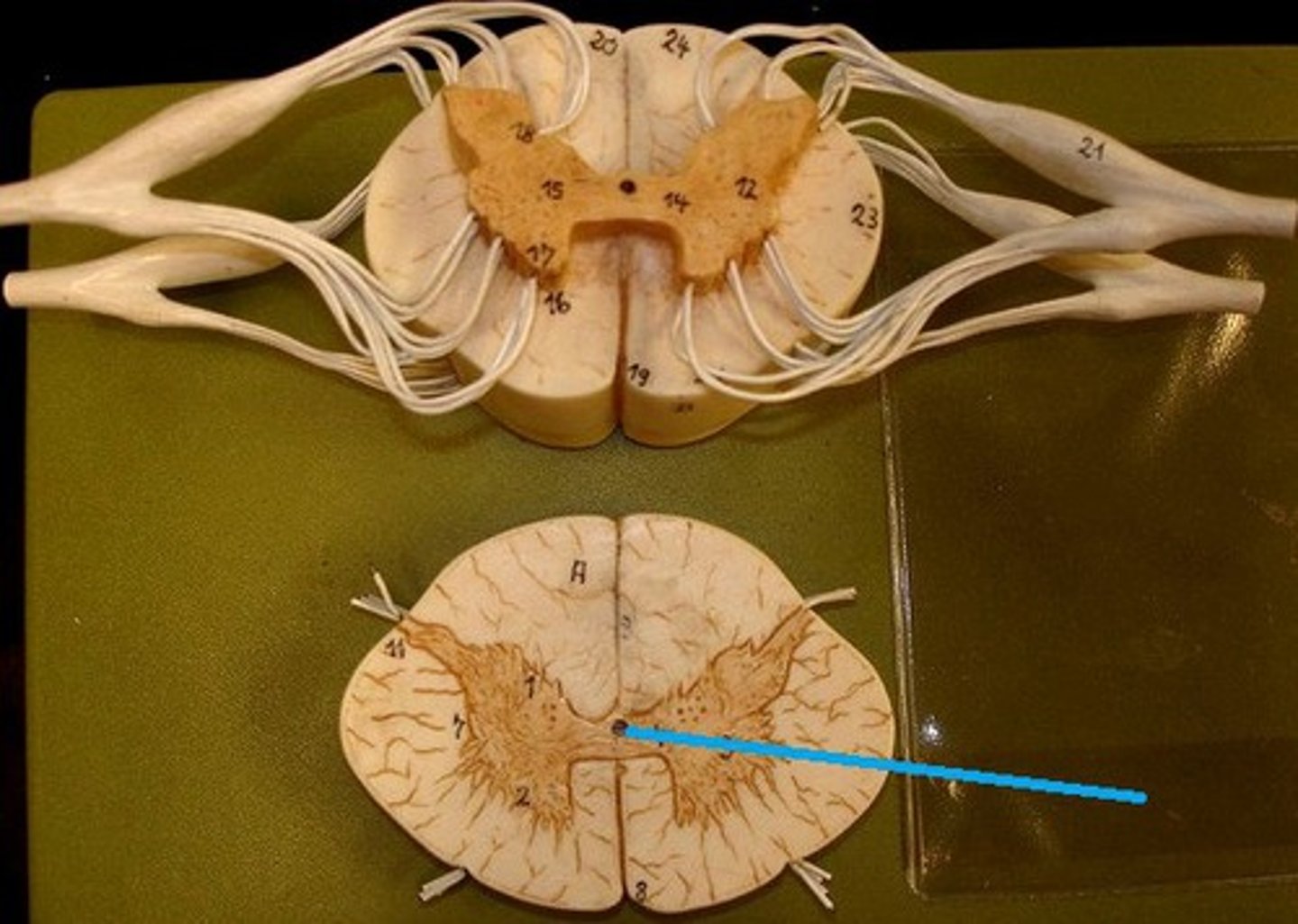
Central Canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata
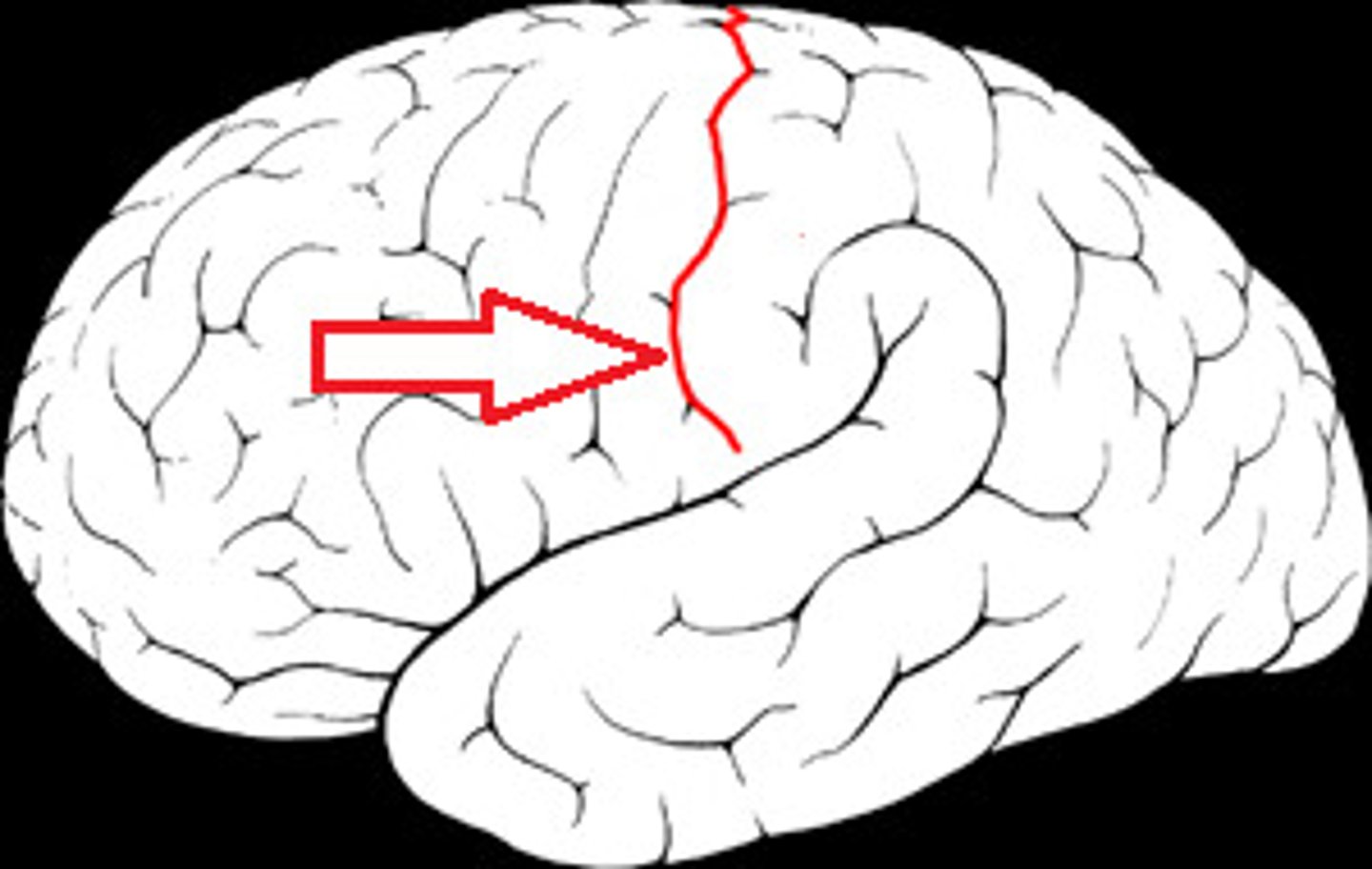
Central Sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
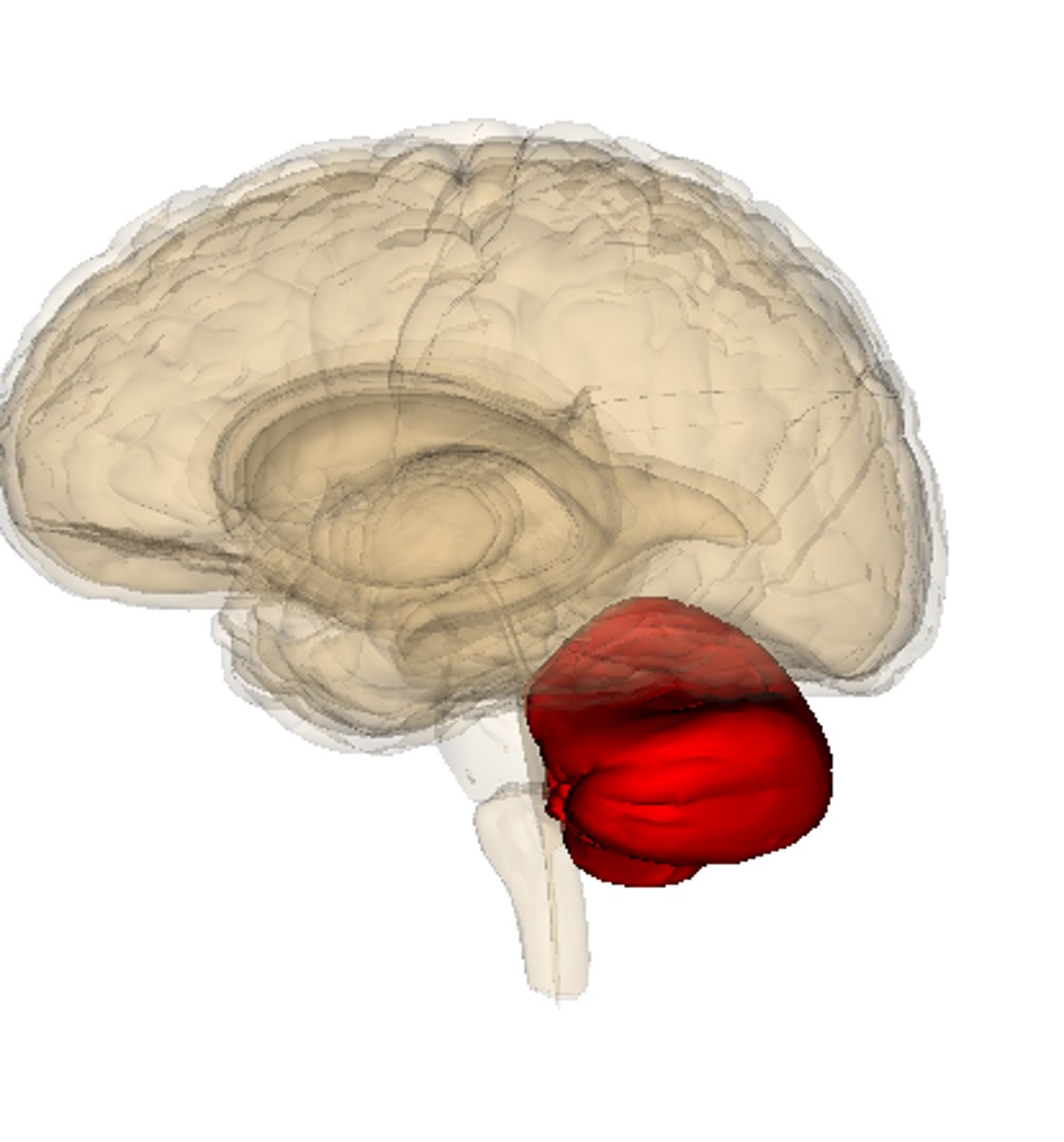
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
Cerebral Aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
Cerebral gray matter
dense matter. primarily in cerebral cortex. involved in function. associated with intelligence.
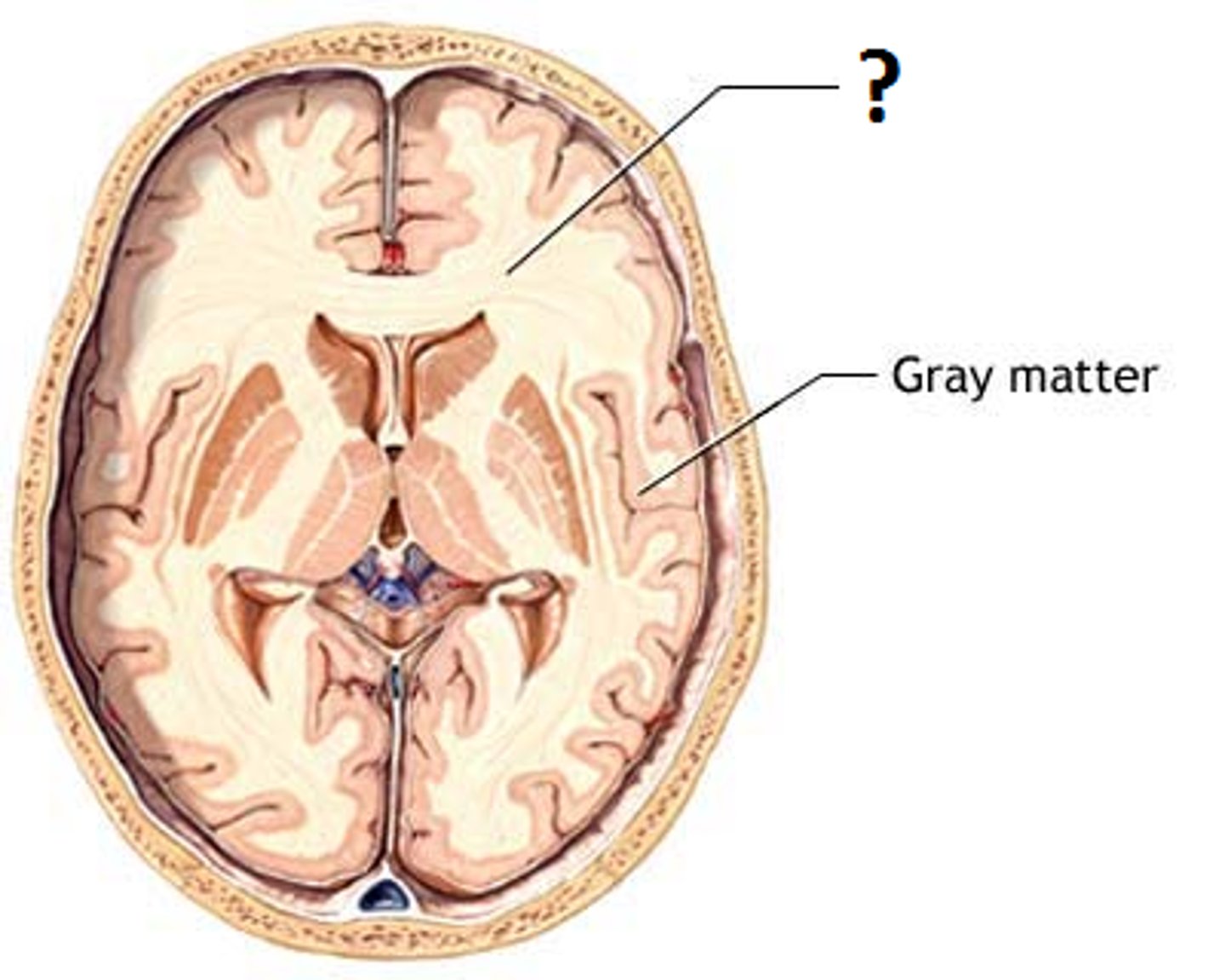
Cerebral White Matter
responsible for communication between cerebral areas and the cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers
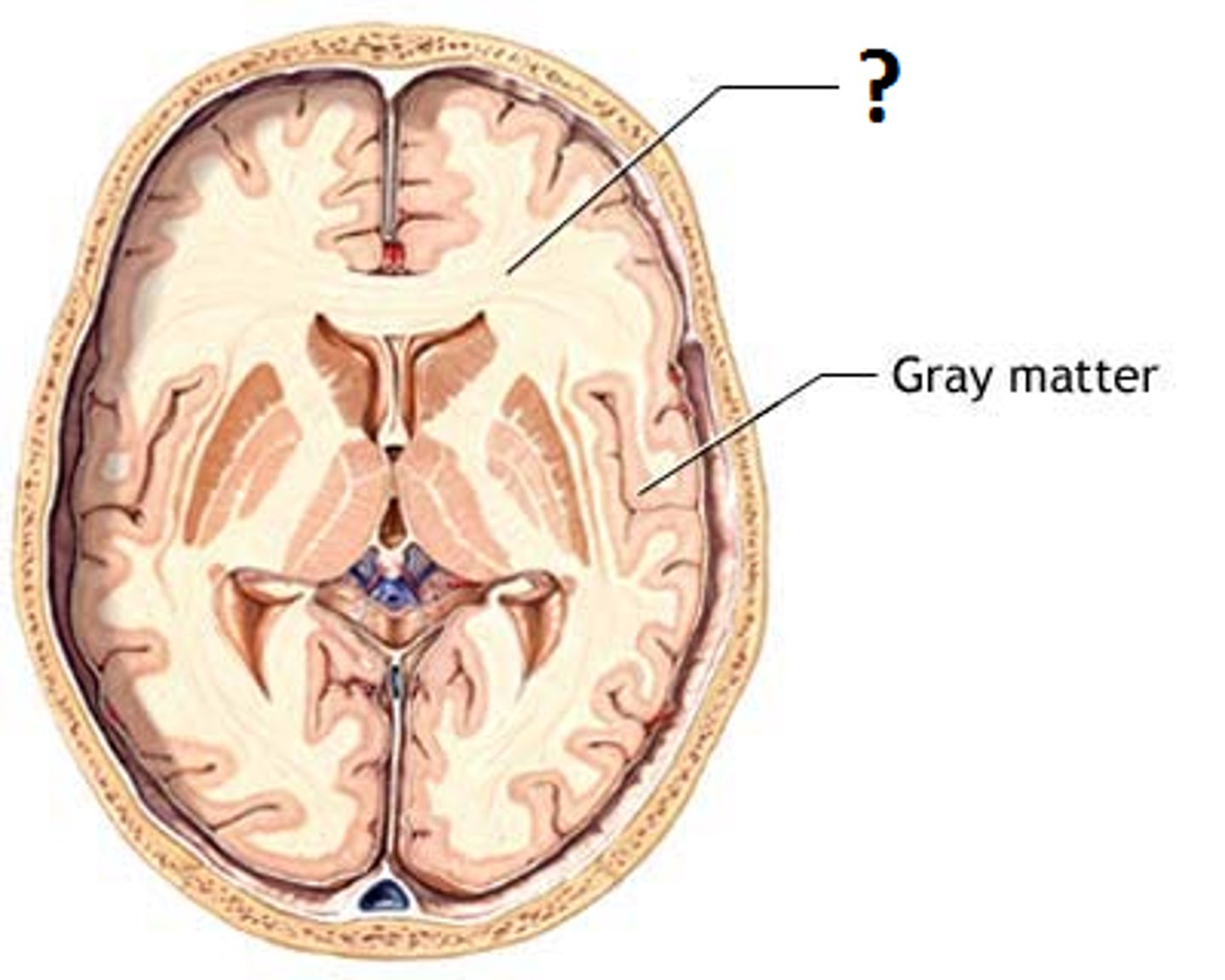
Choroid Plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
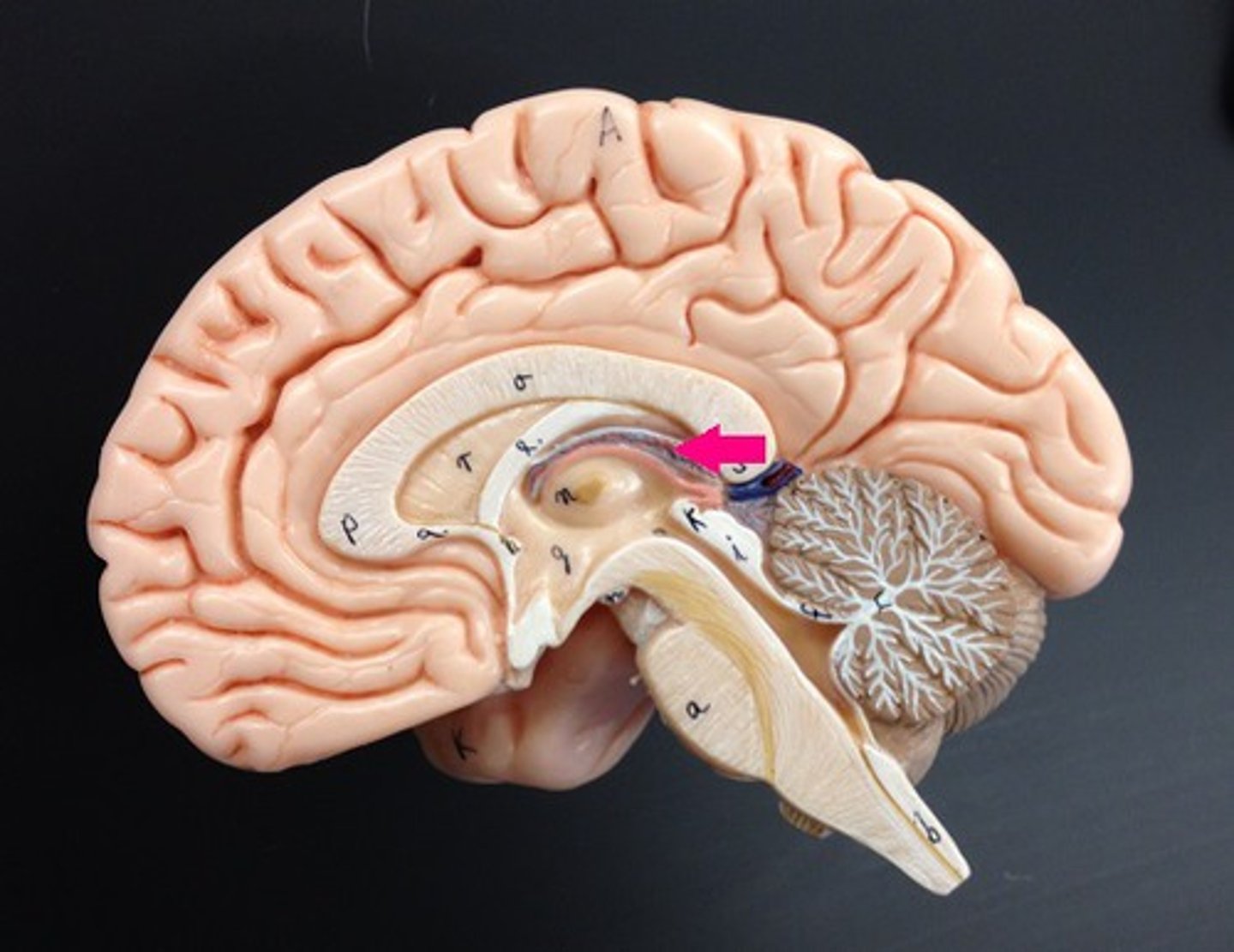
Commissures
connect corresponding gray areas of the two hemispheres
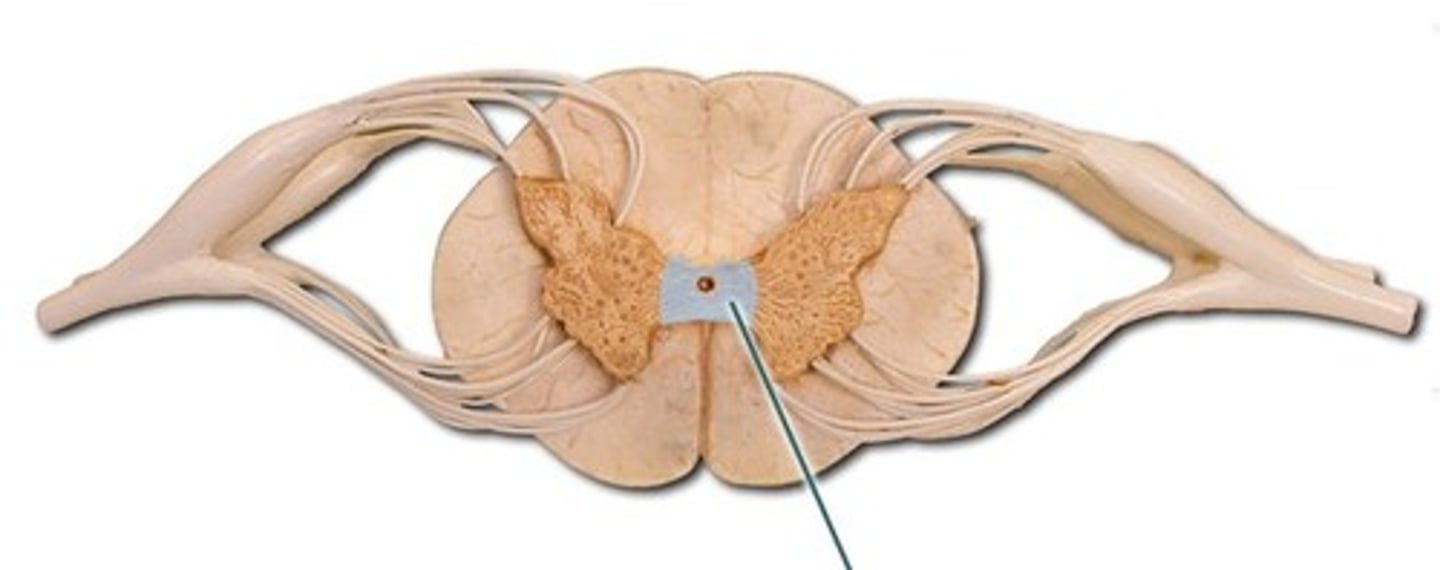
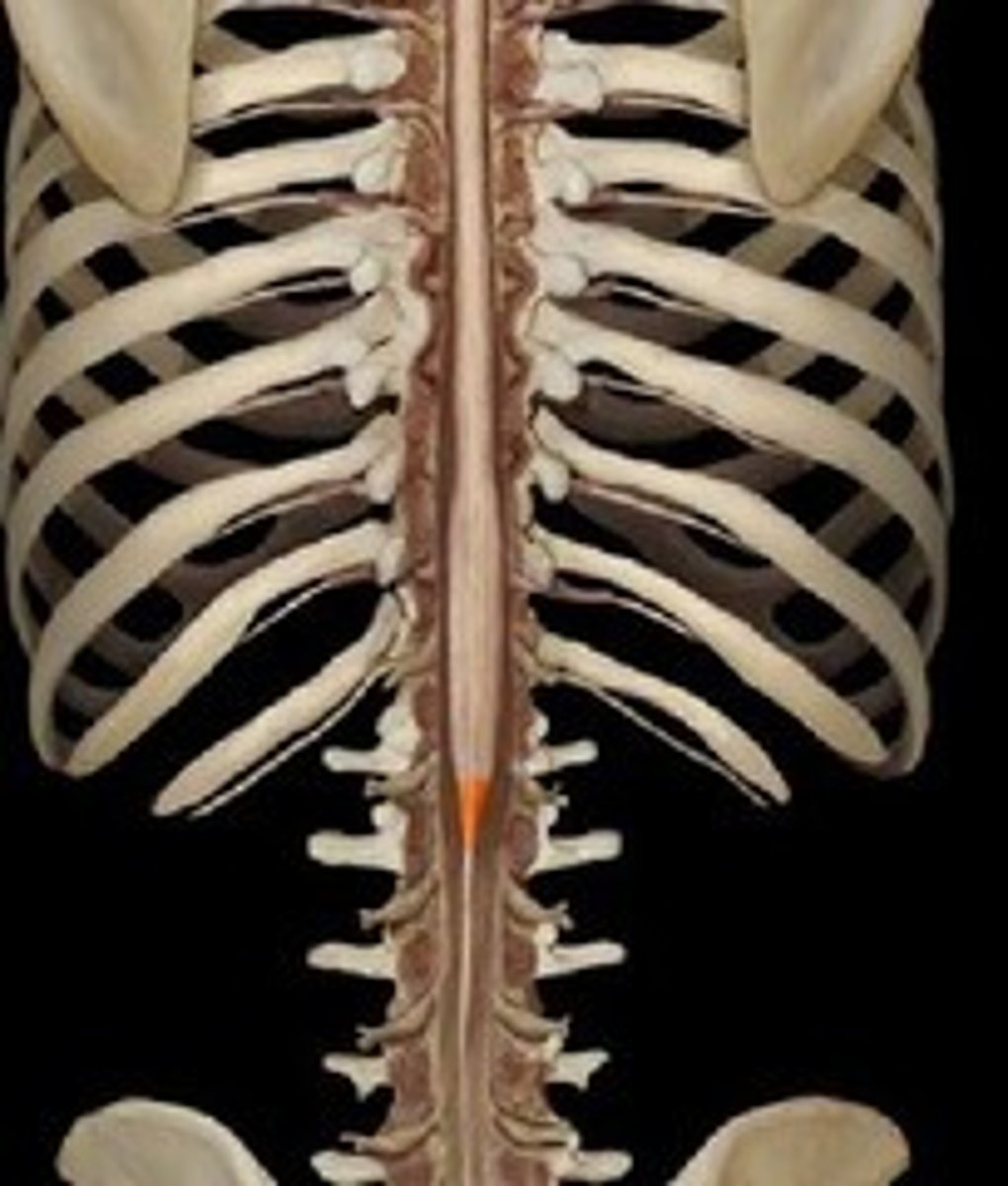
Conus Medullaris
end of spinal cord
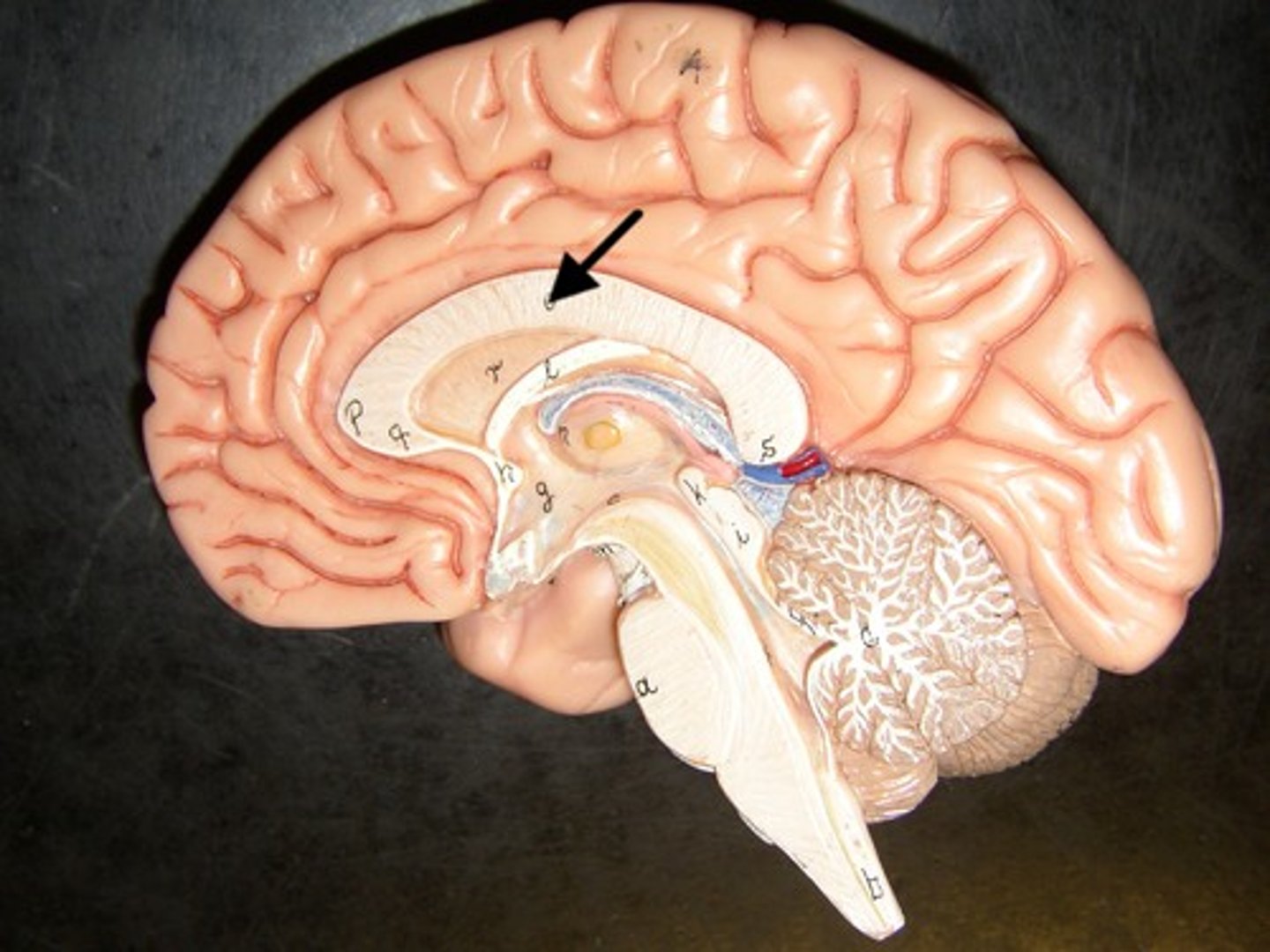
Corpus Callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
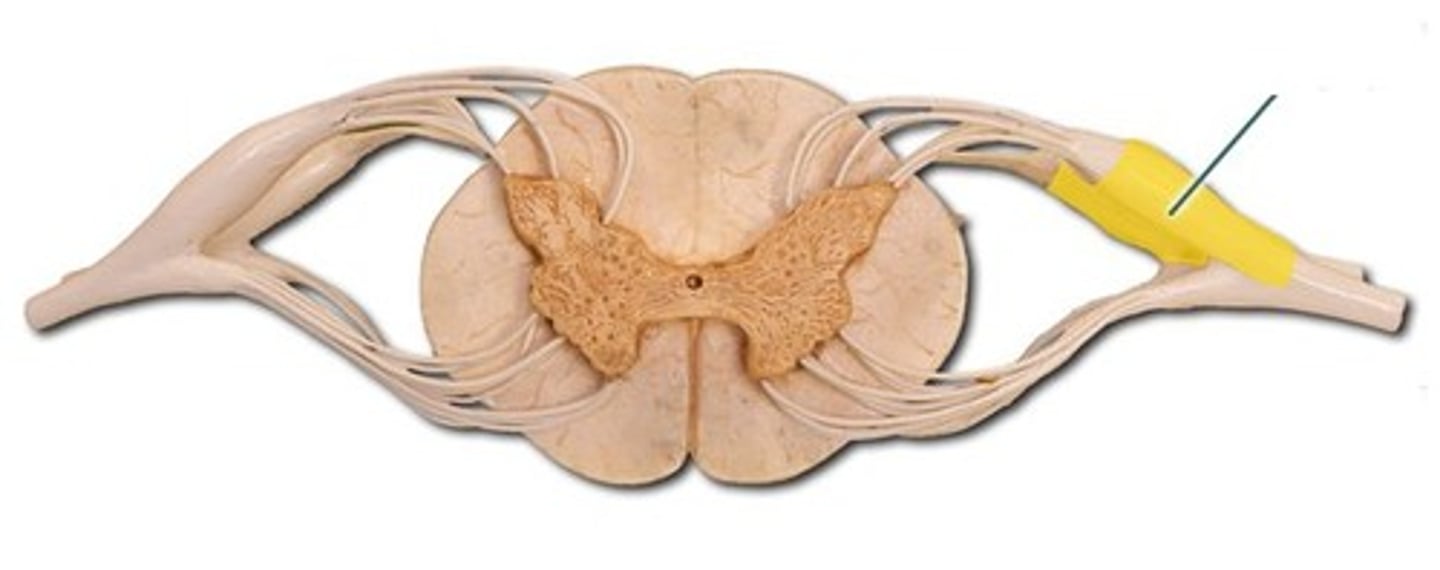
Dorsal Root Ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
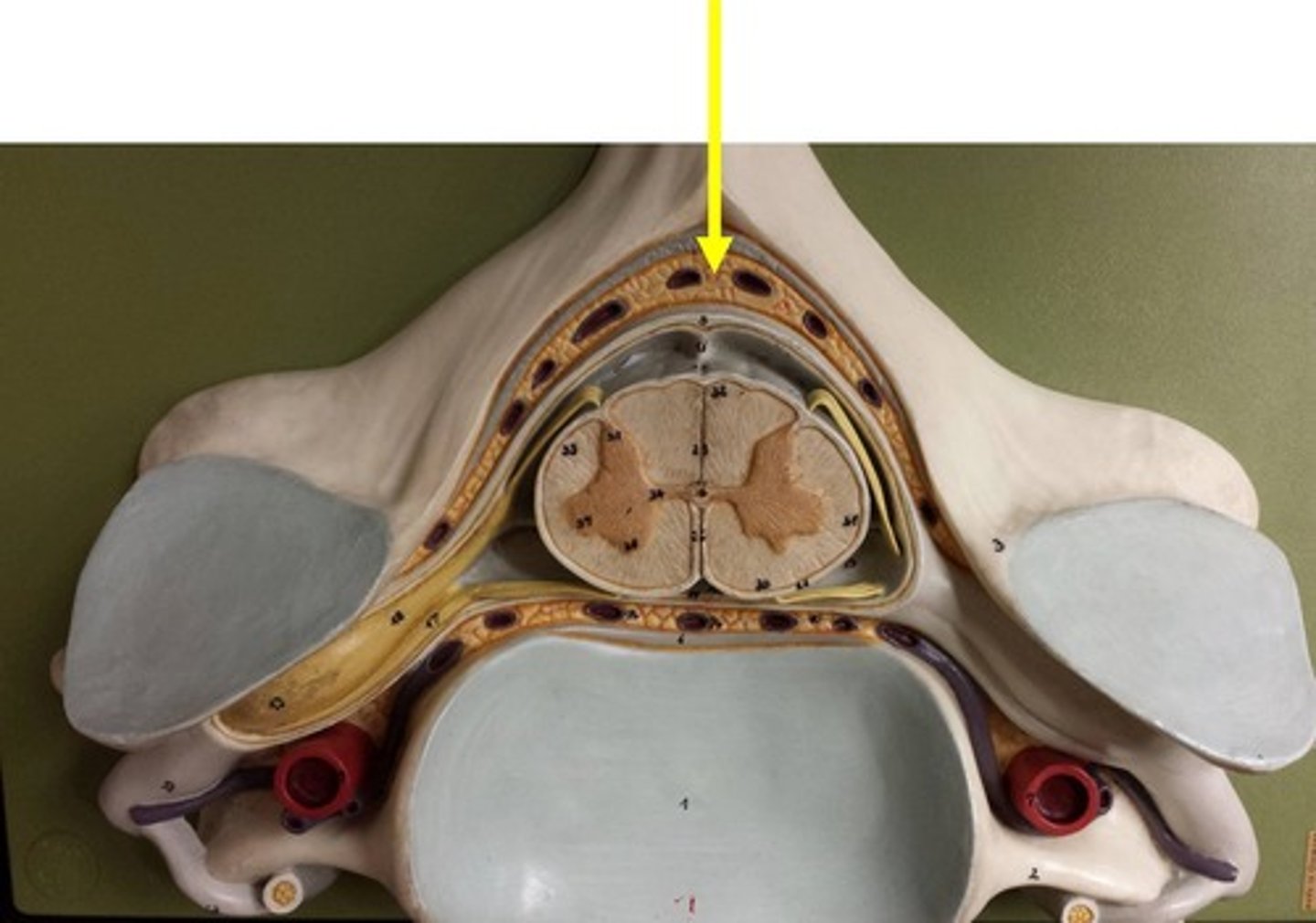
Epidural Space
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
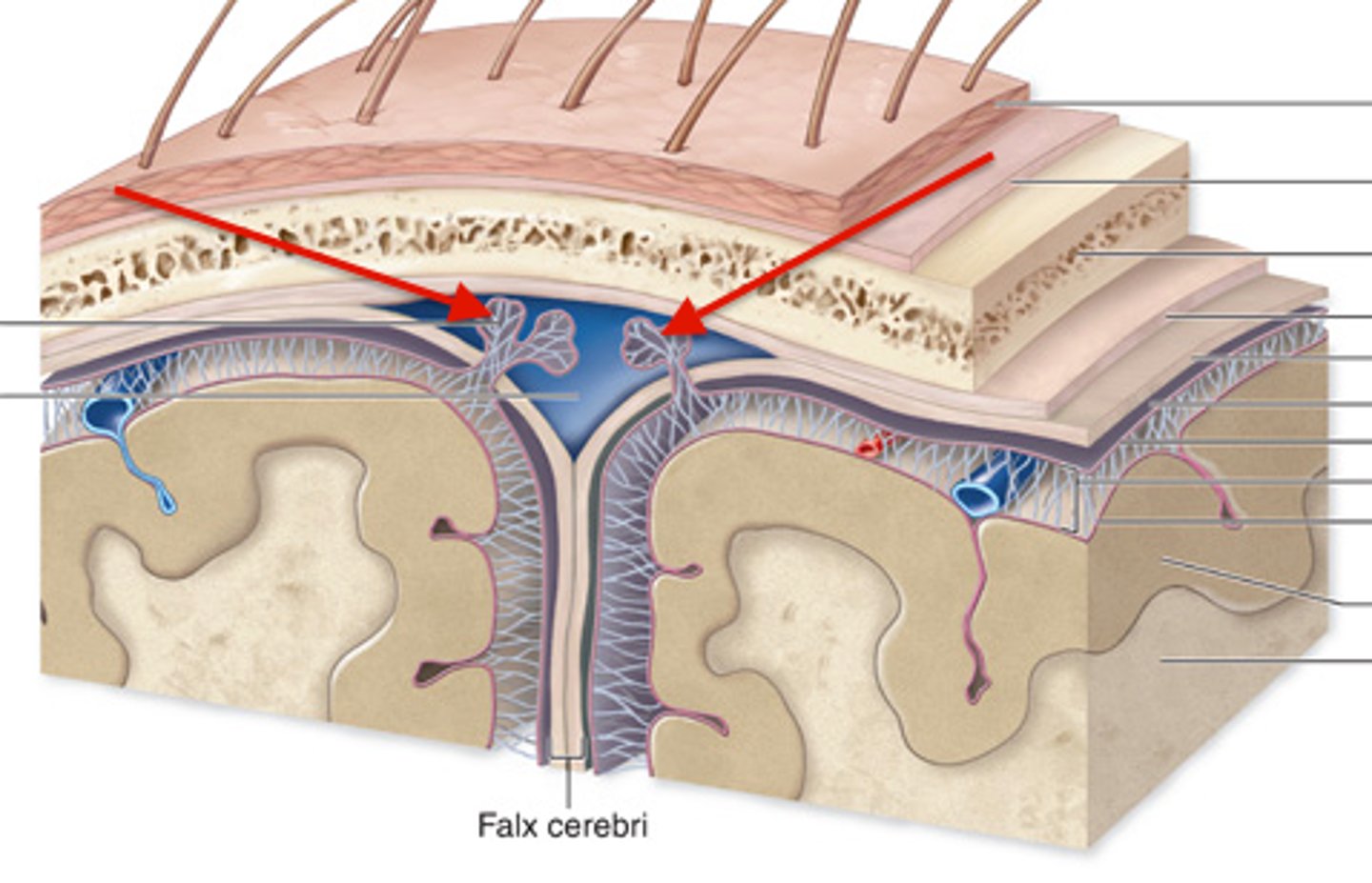
Falx Cerebri
separates the two cerebral hemispheres
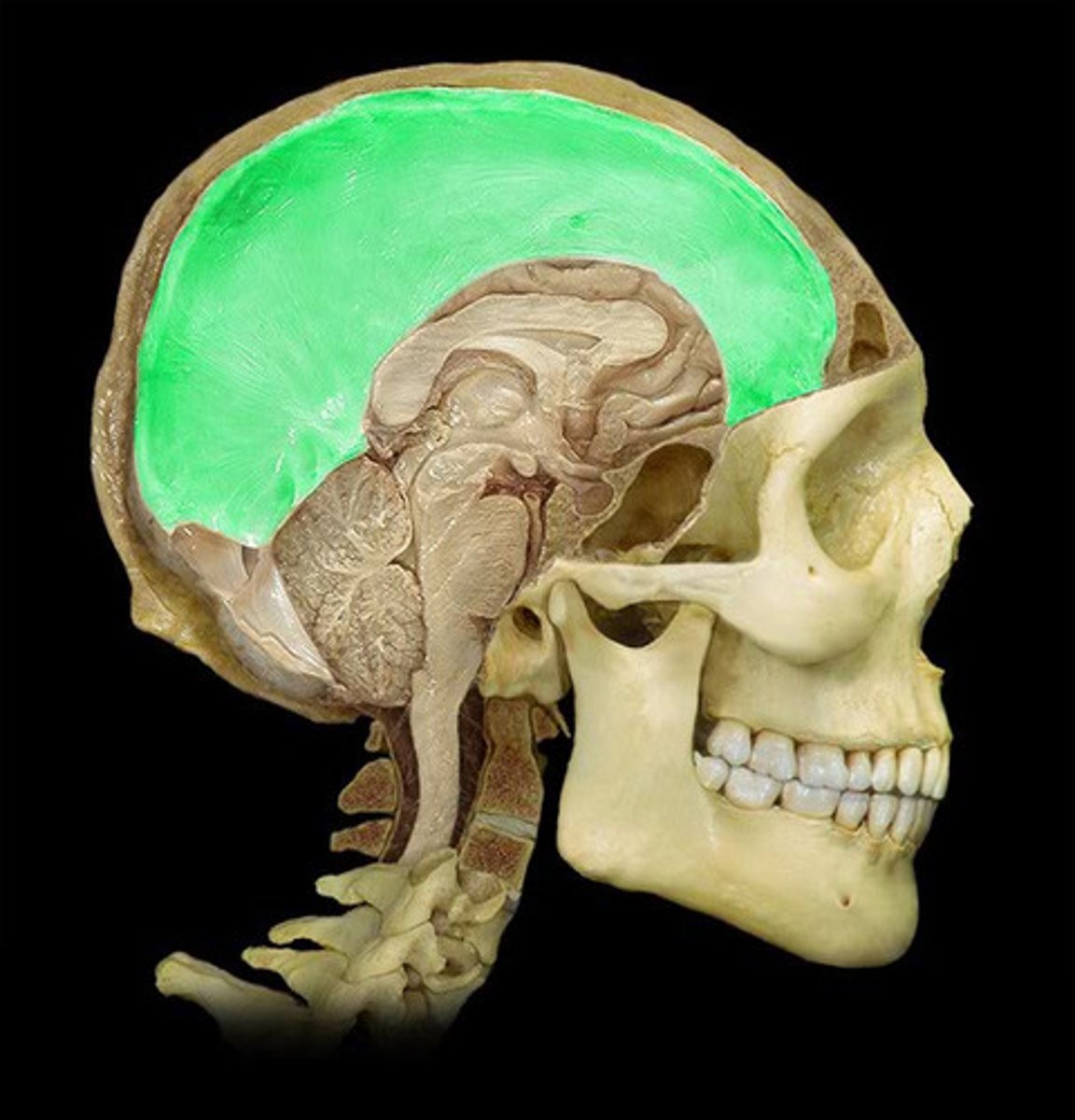
Falx Cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
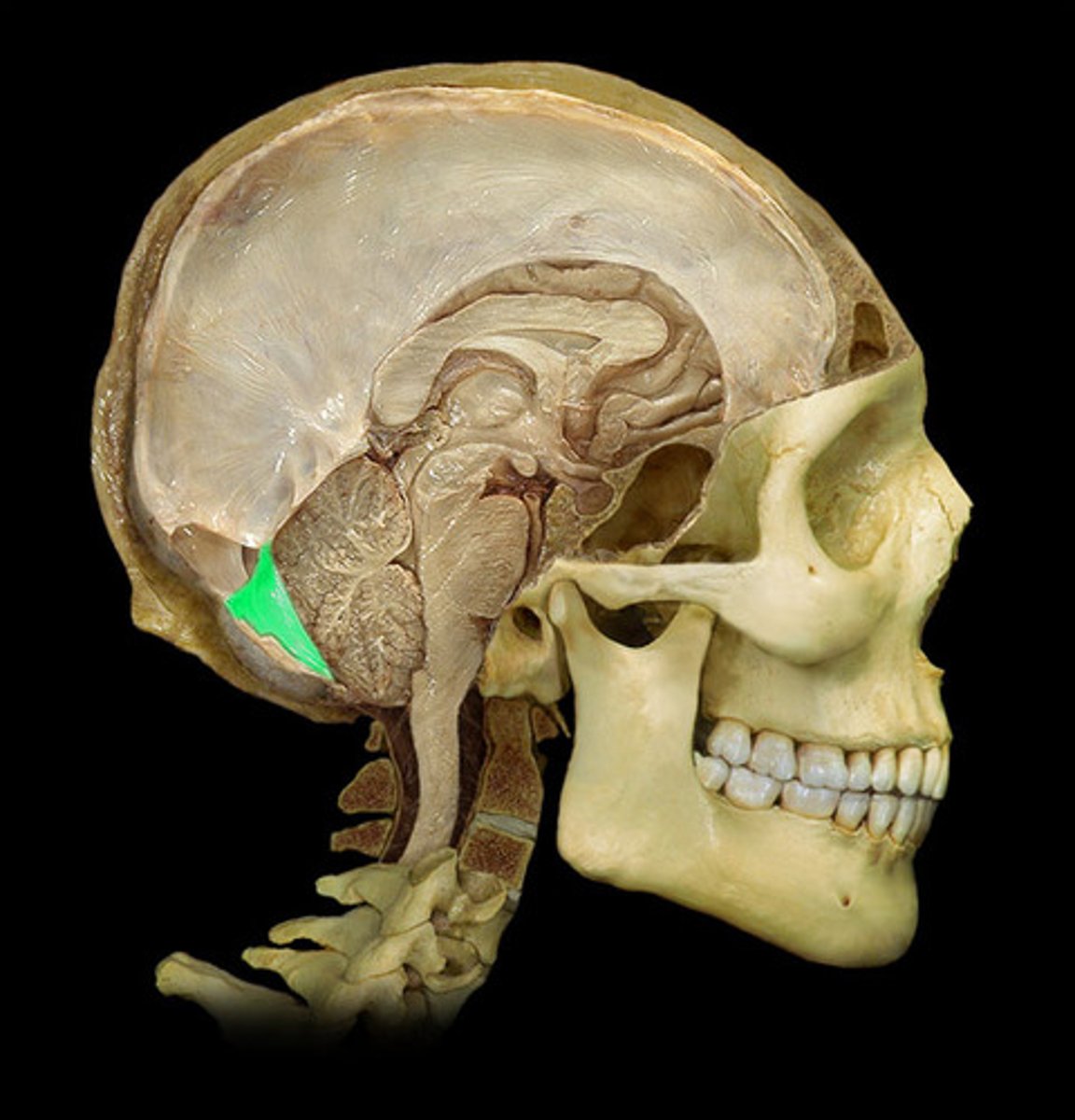
Filum Terminale
fibrous extension of the pia mater; anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
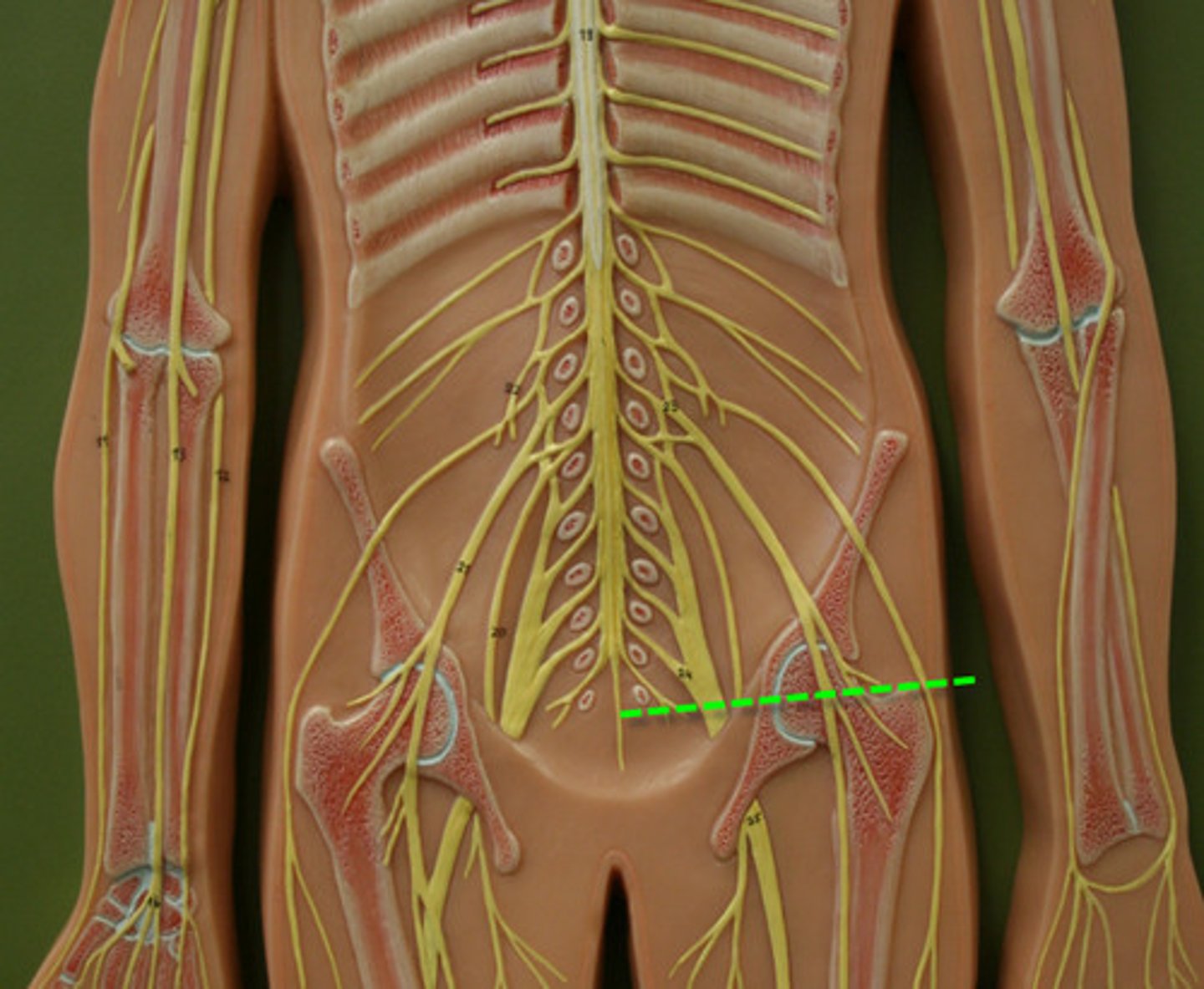
Cerebral Lobes
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
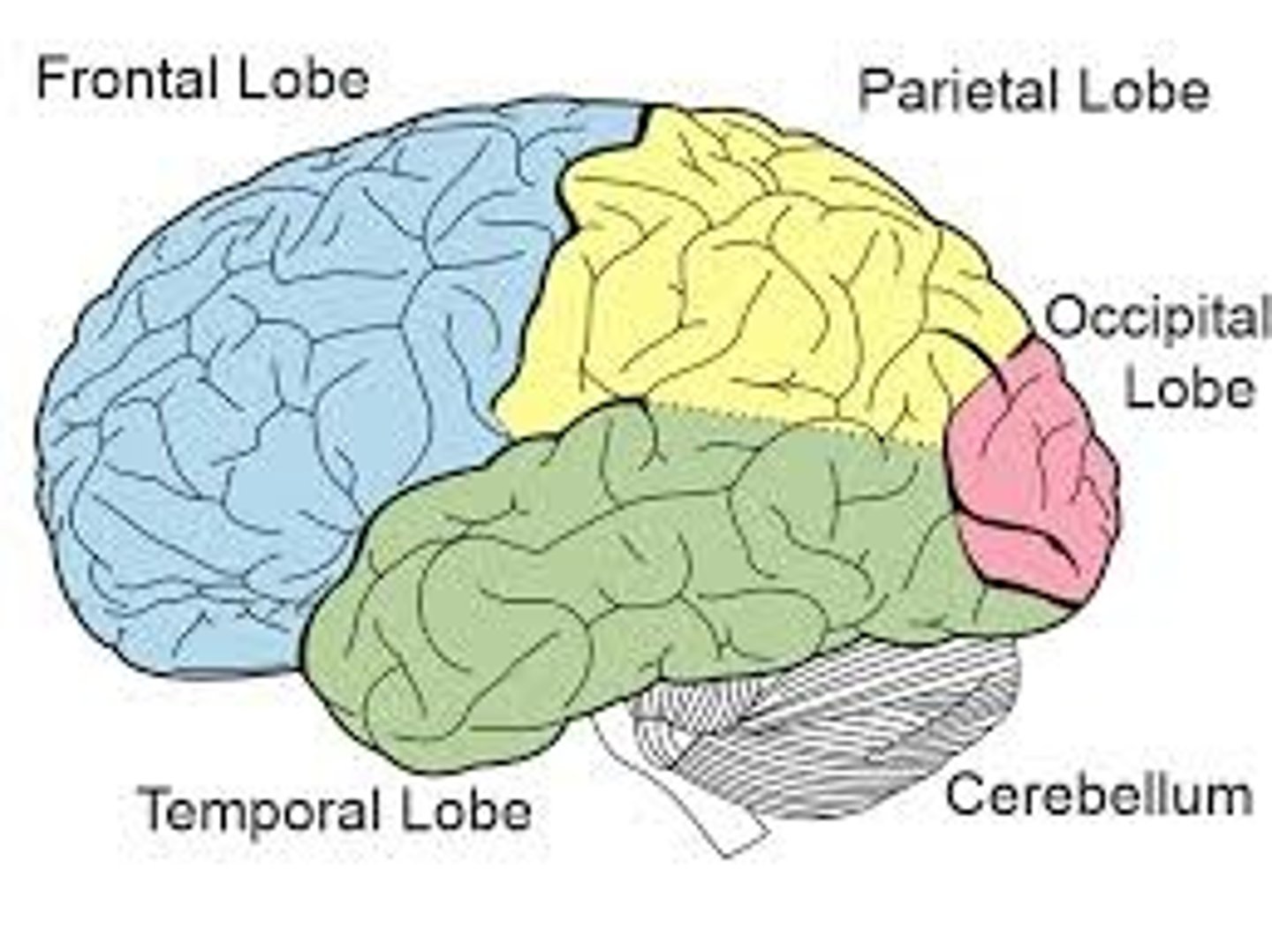
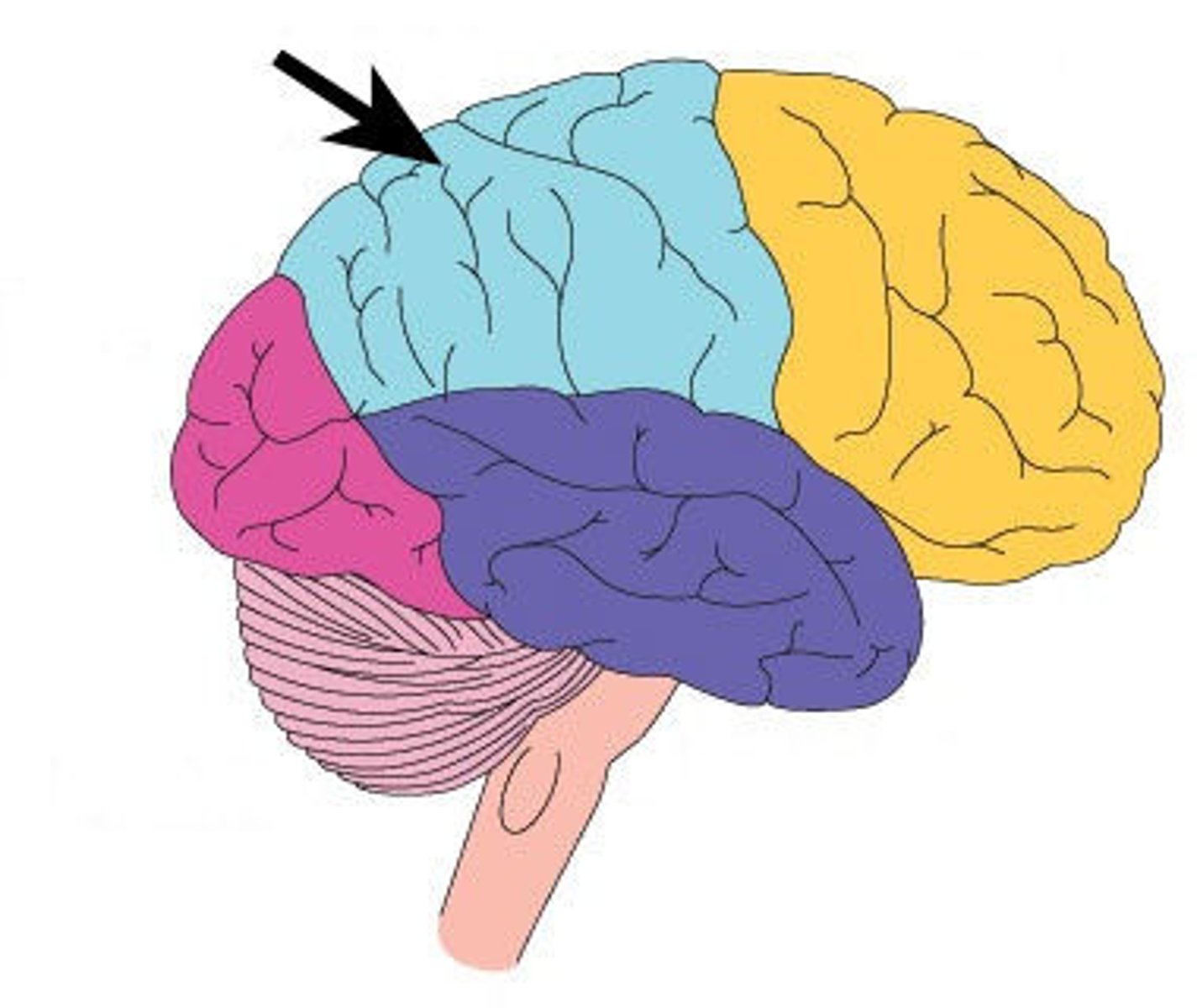
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
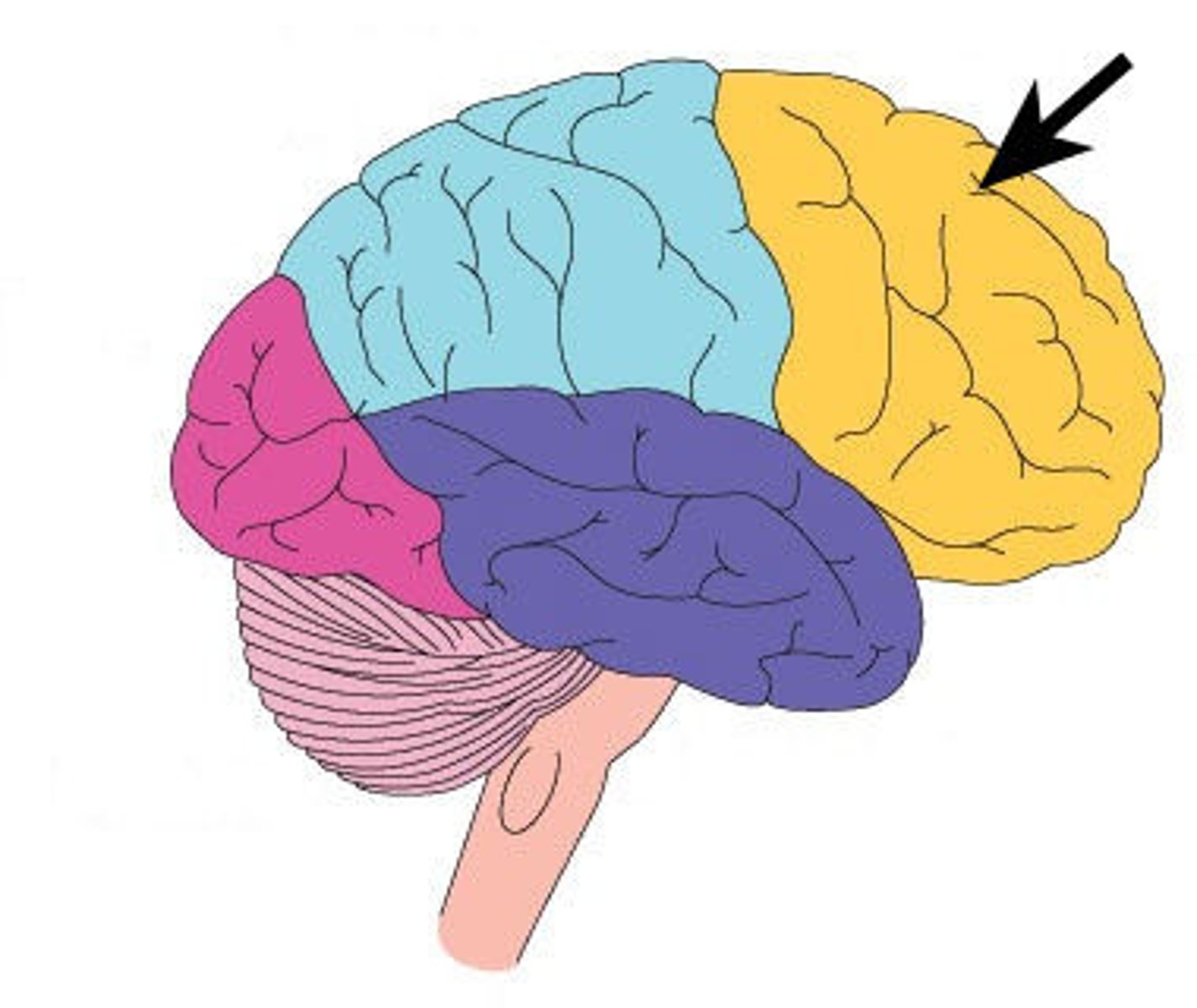
Parietal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
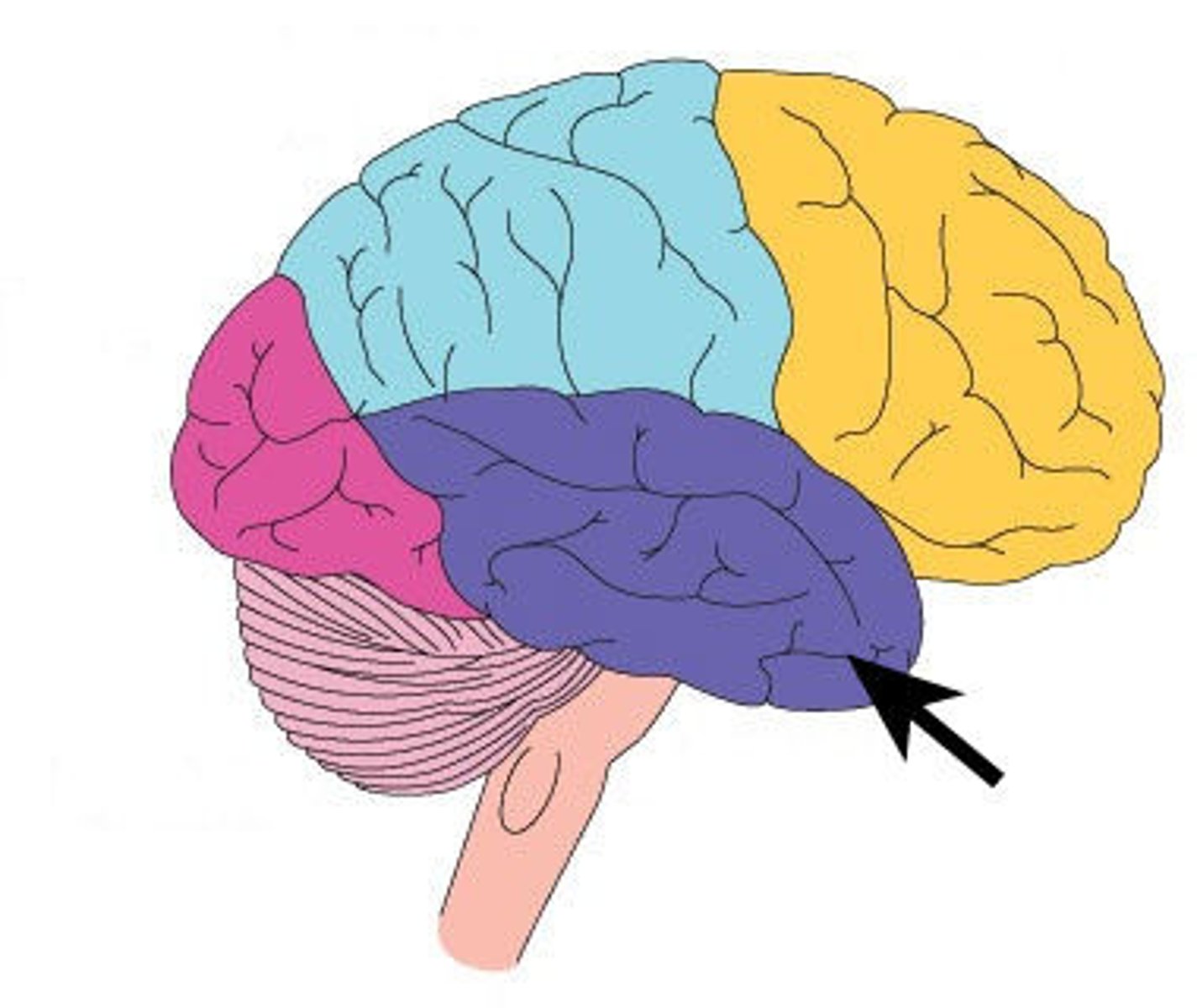
Occipital Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
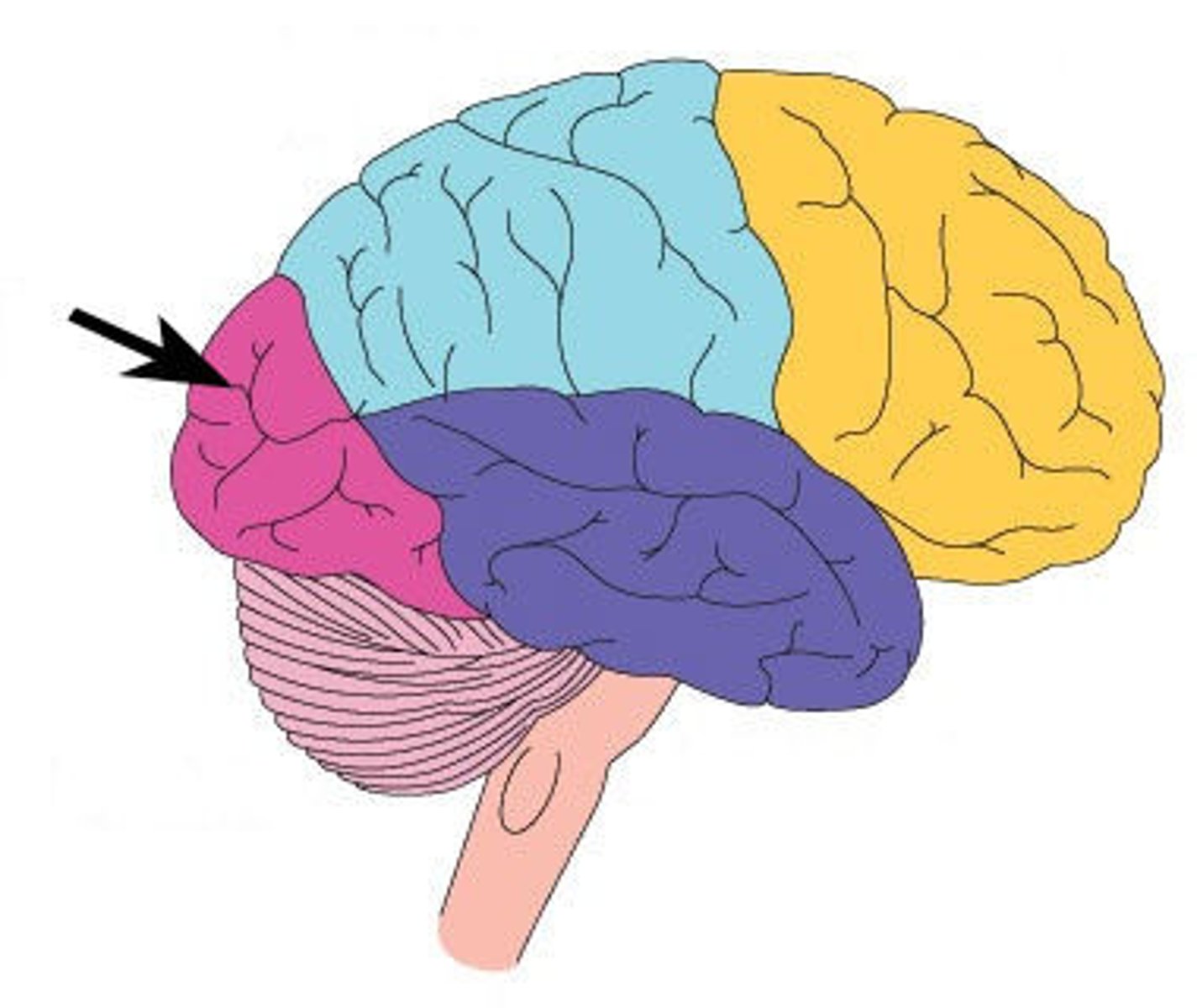
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
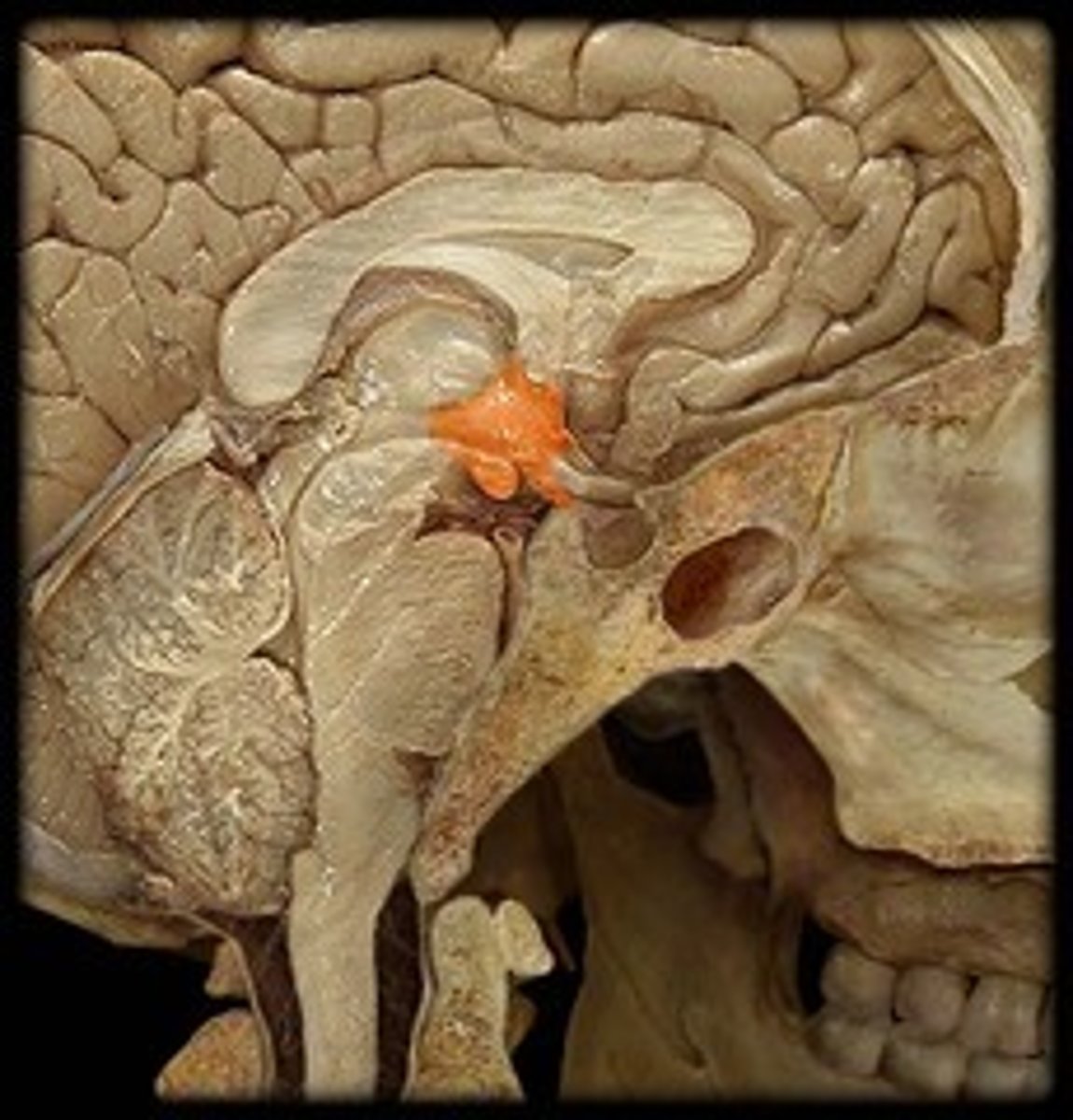
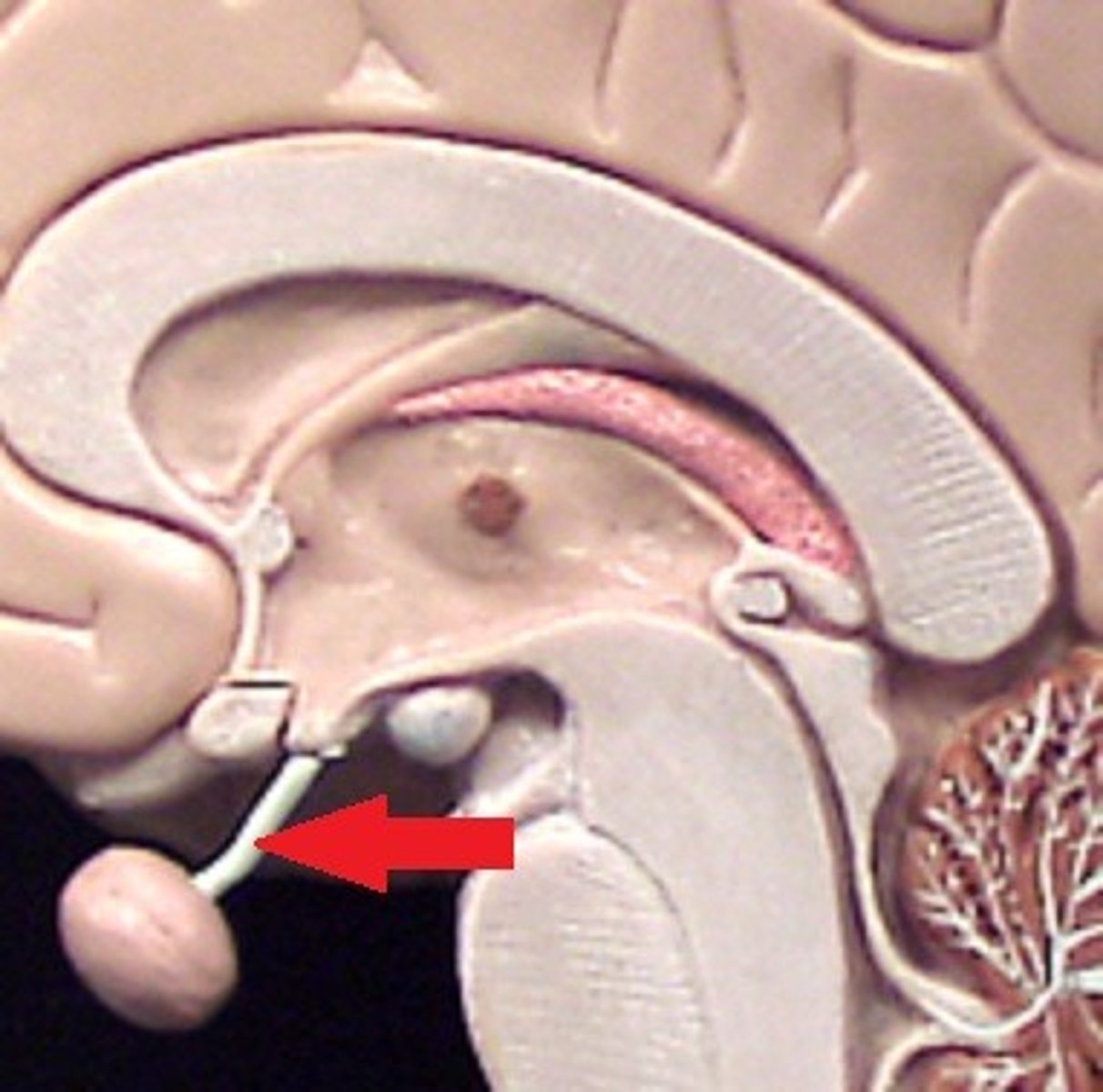
infundibulum of pituitary gland
A narrow stalk connecting the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland (endocrine system).
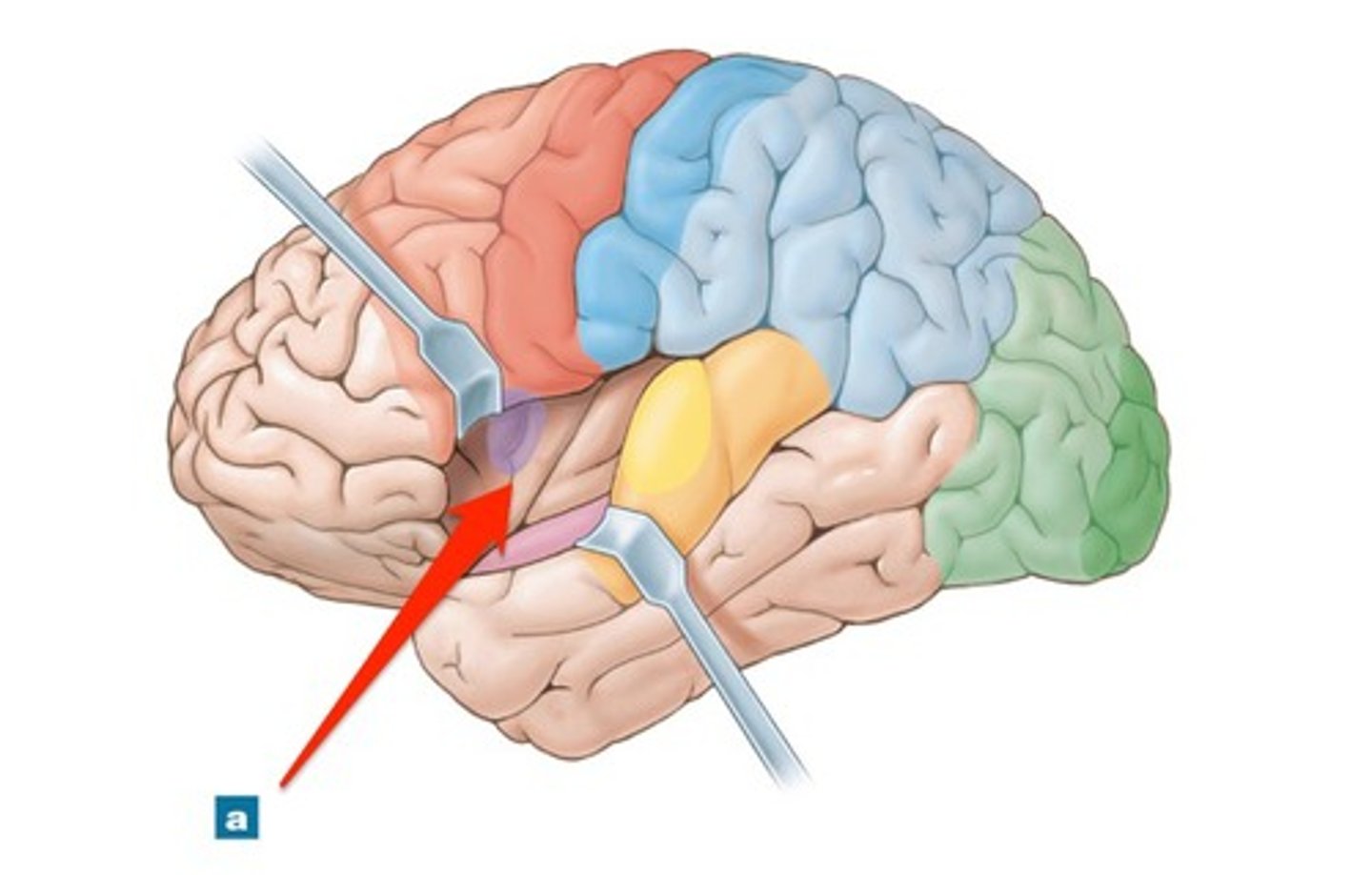
Insula
regions of cortex located at the junction of the frontal and temporal lobes
Interventricular Foramina
join lateral ventricles with third
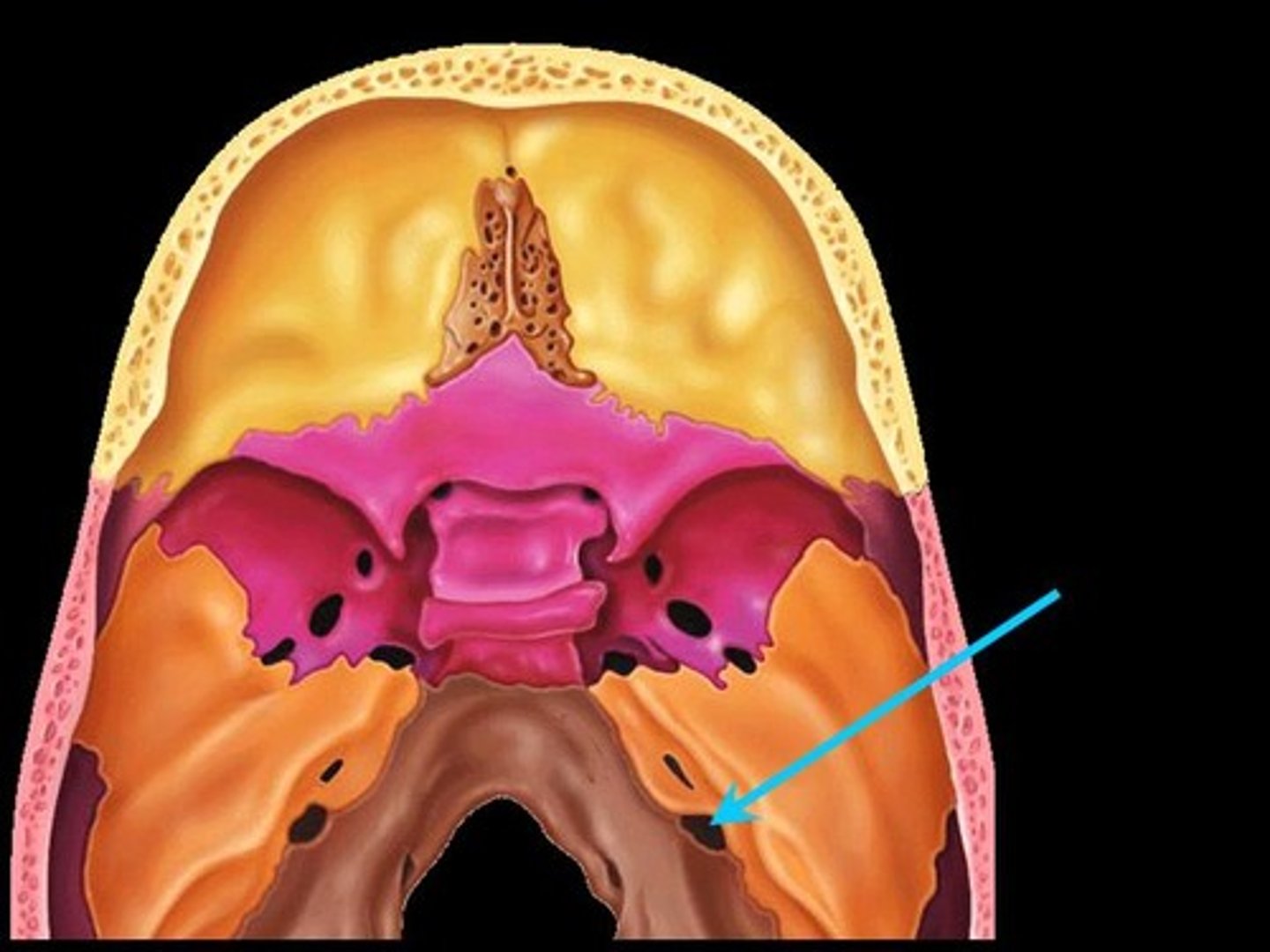
Jugular Foramen
Name this foramen.
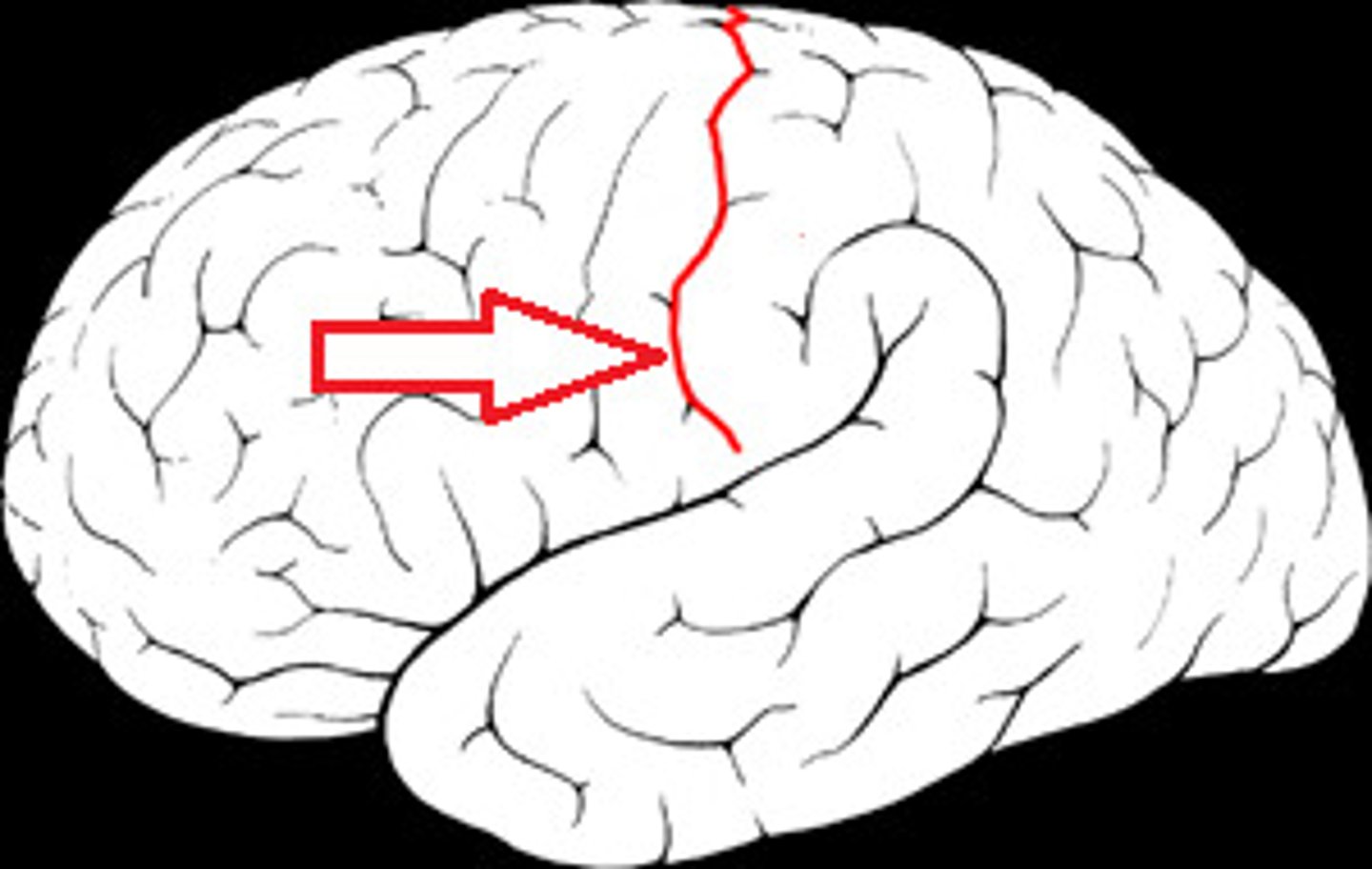
Lateral Sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
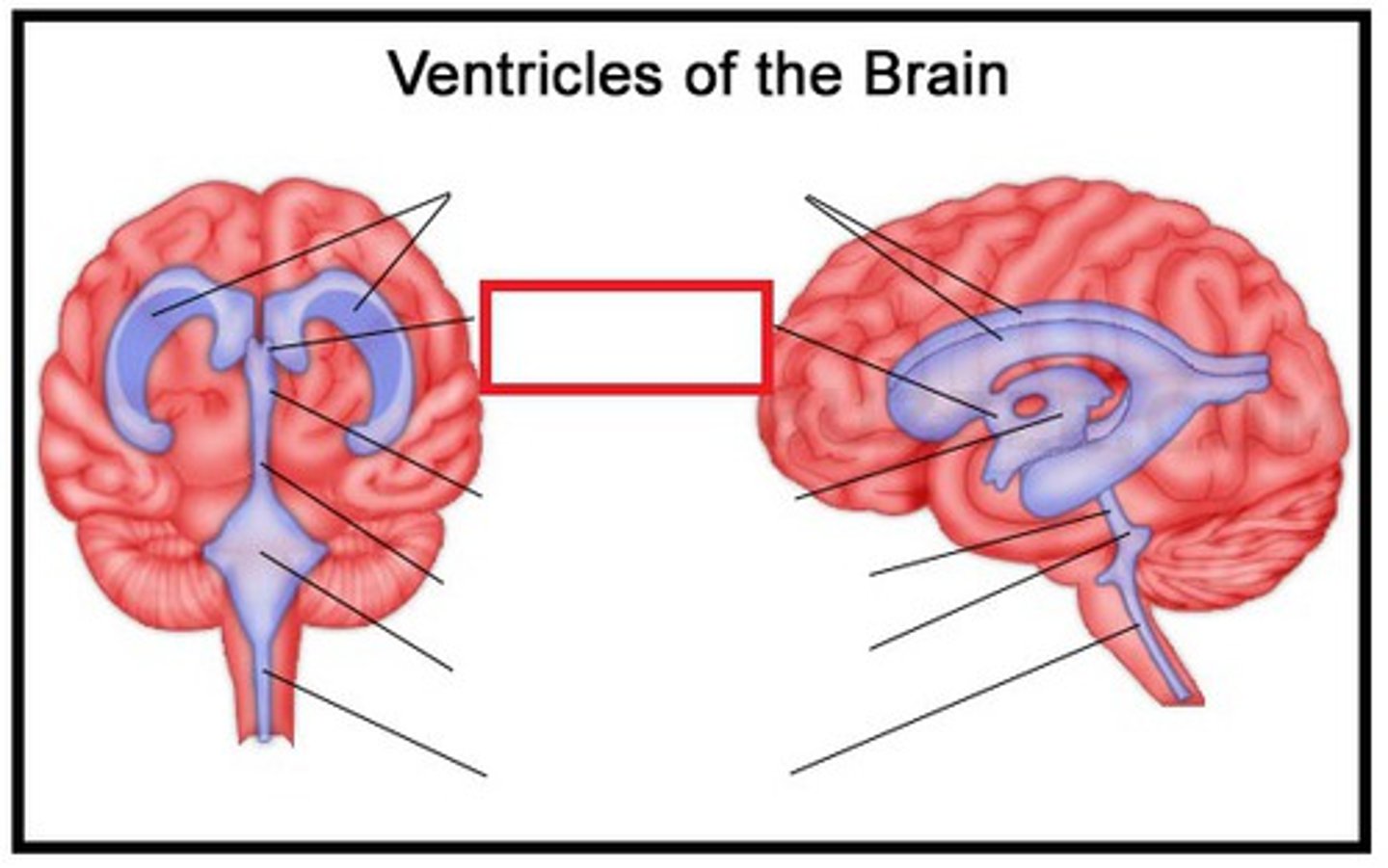
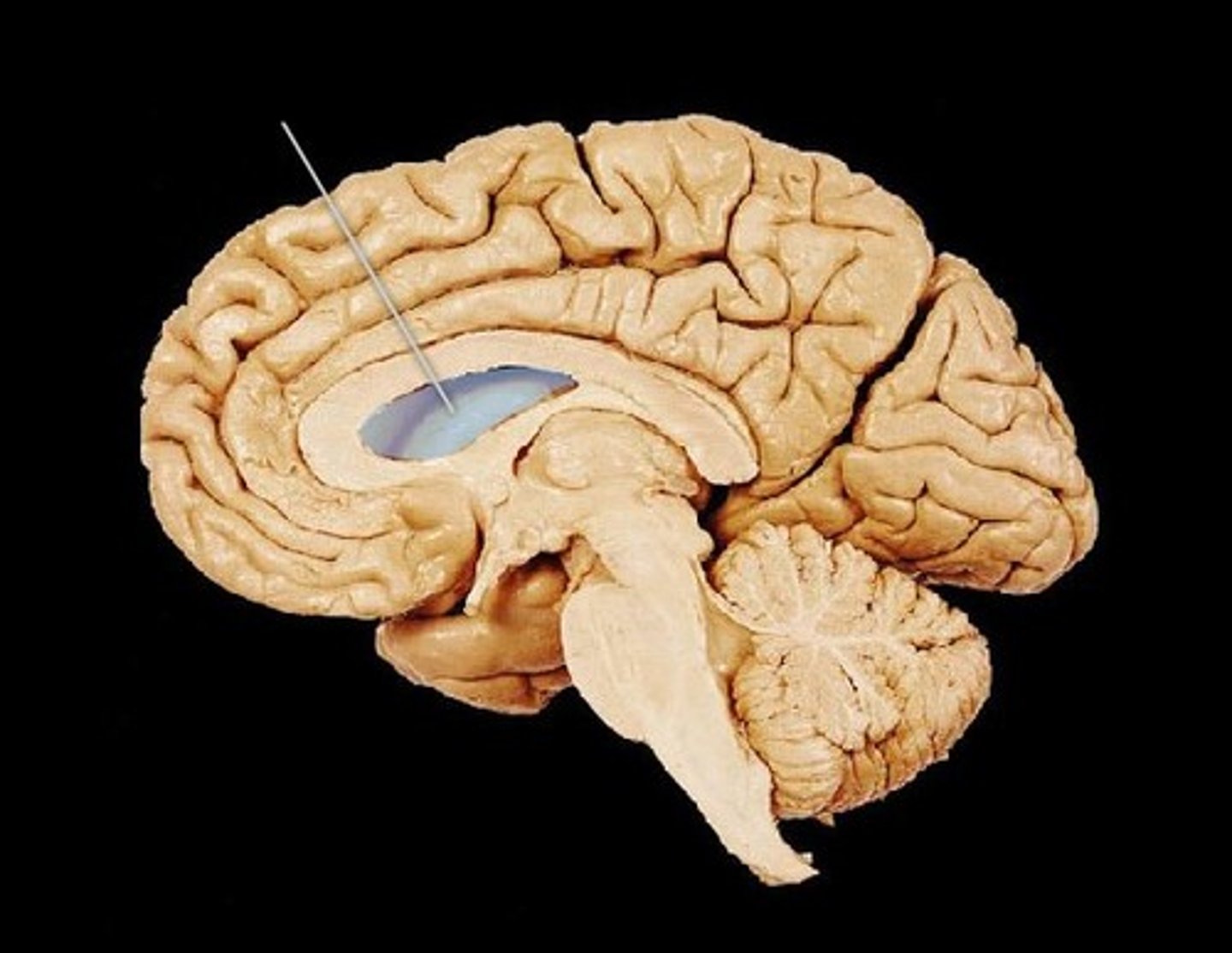
Lateral Ventricles
A set of paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres.
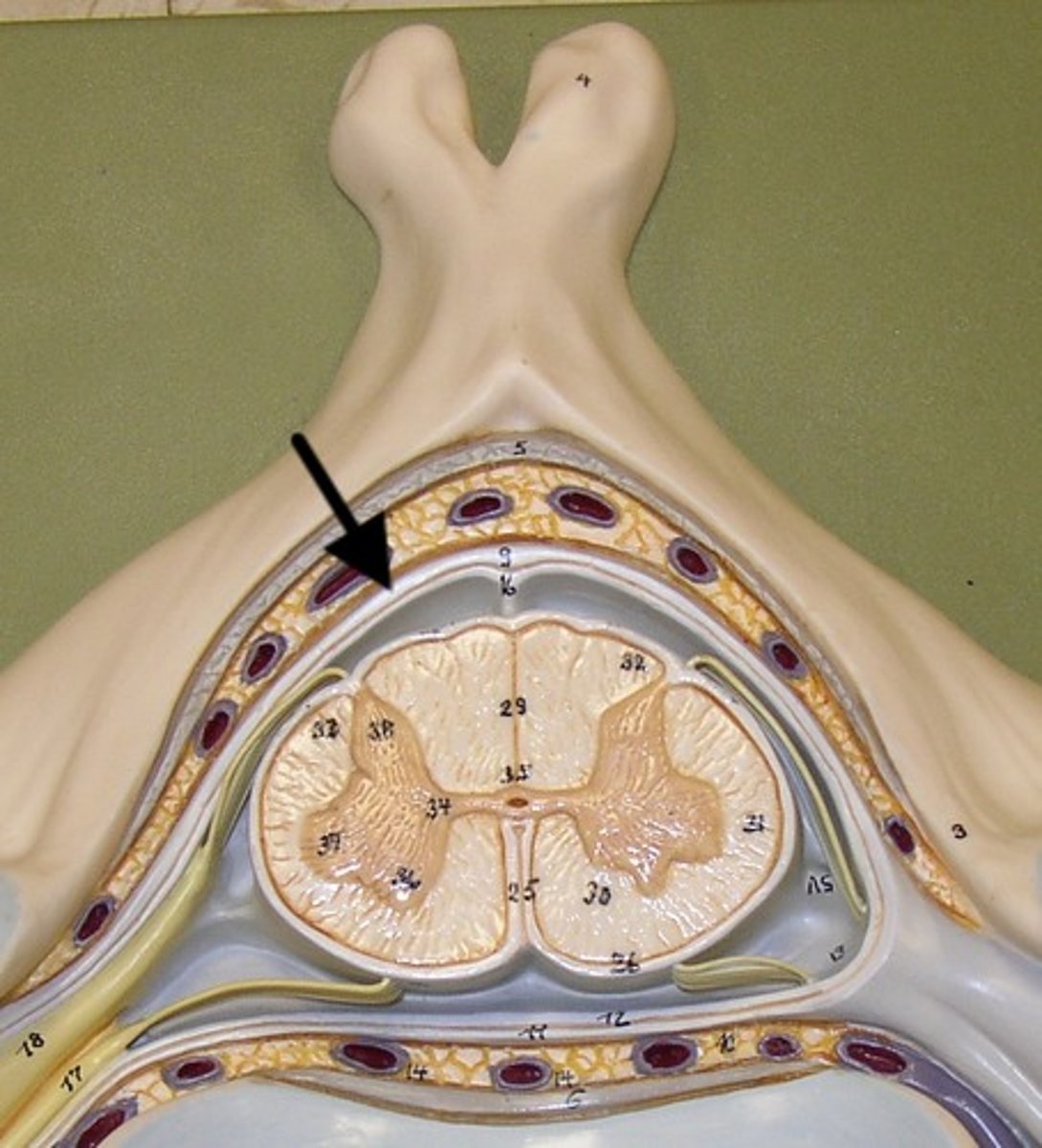
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
middle layer of the meninges
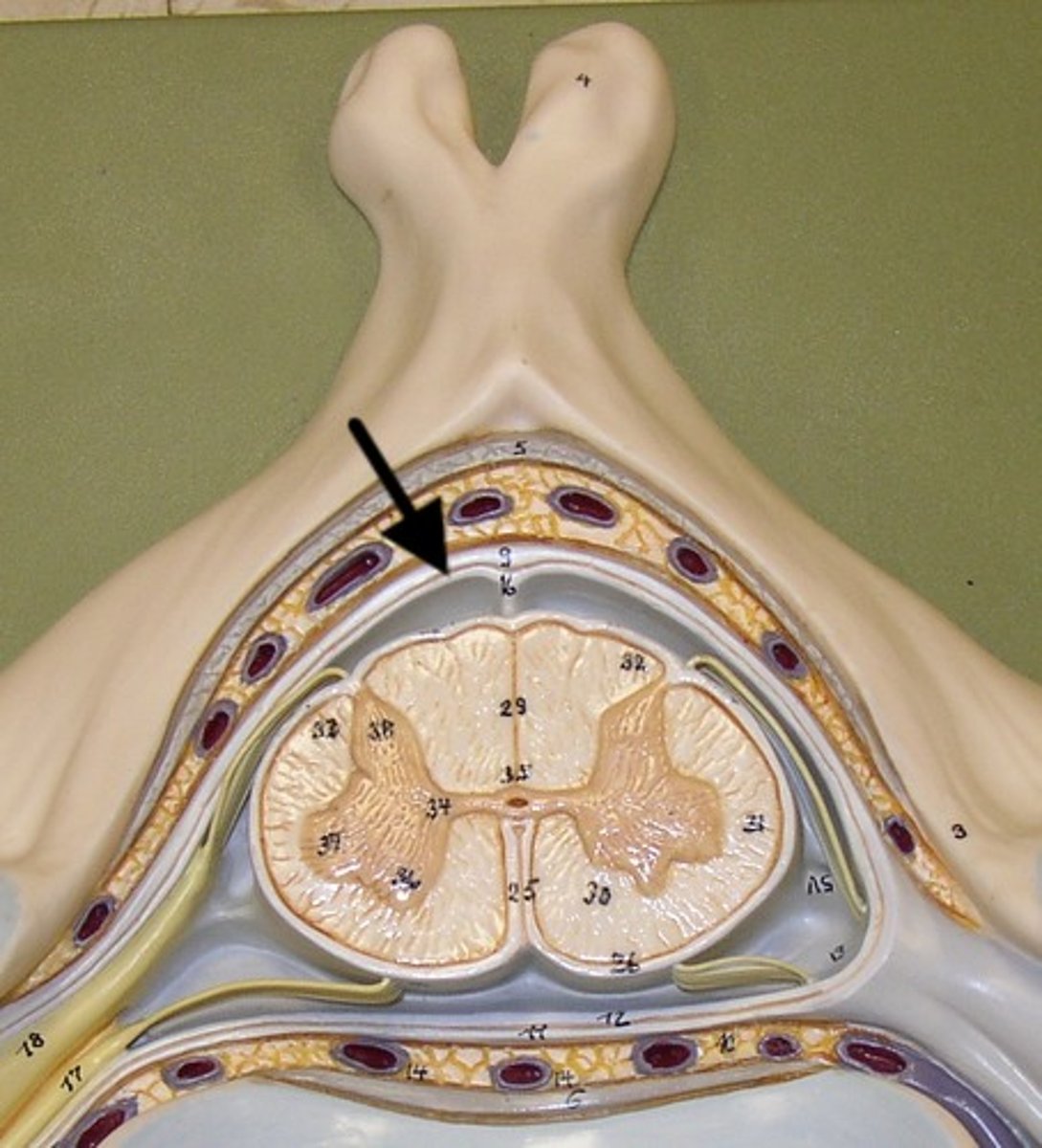
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
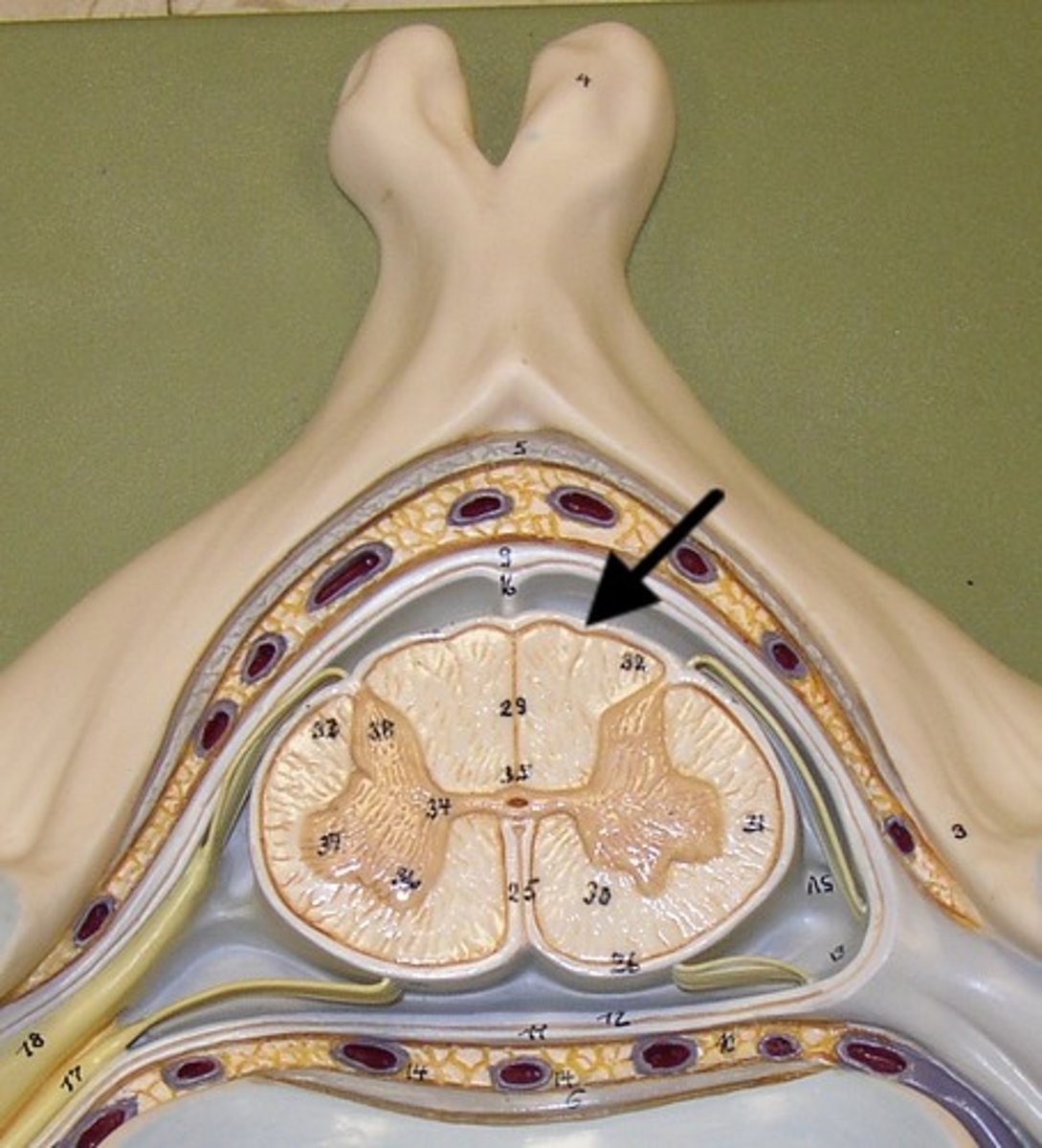
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
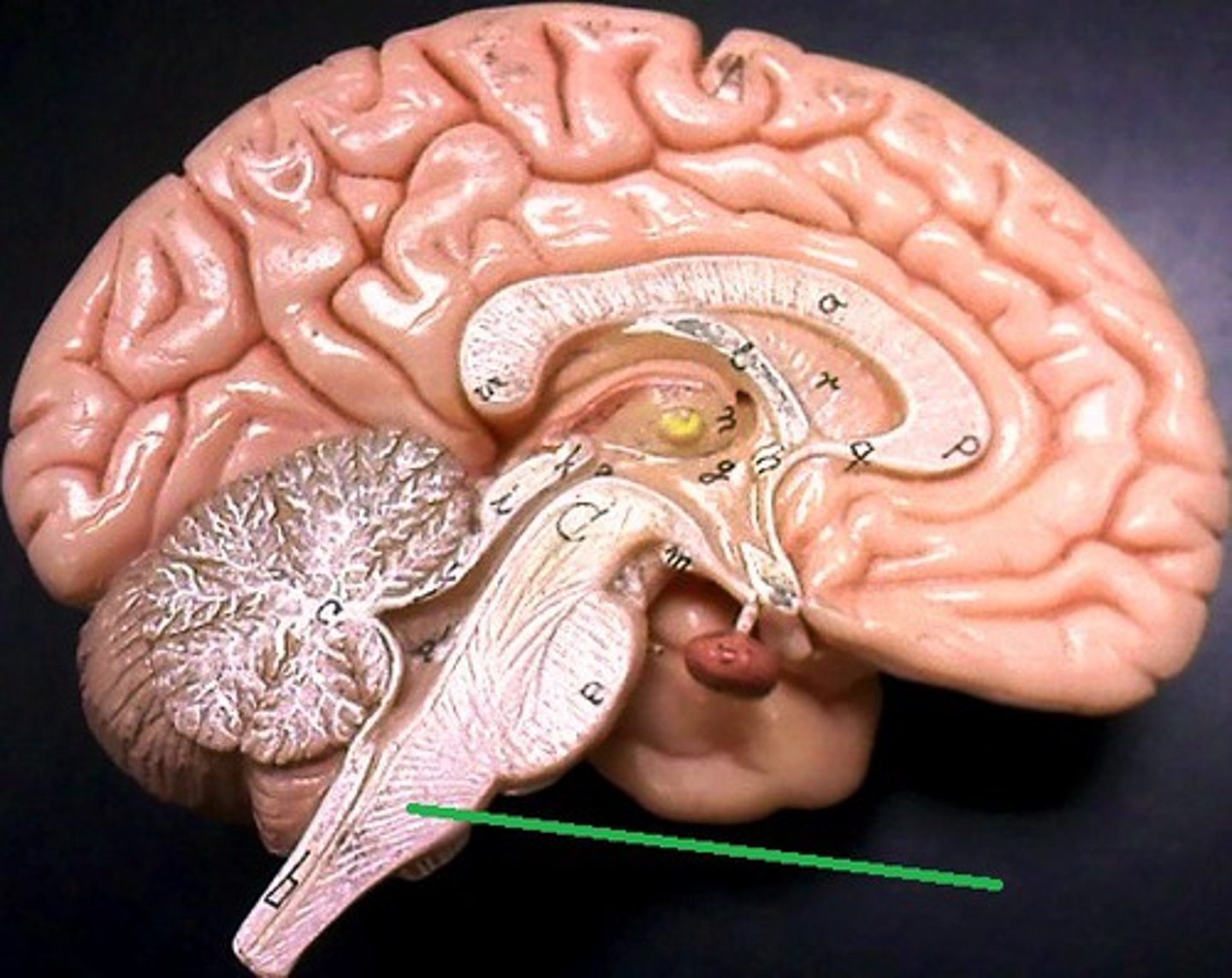
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
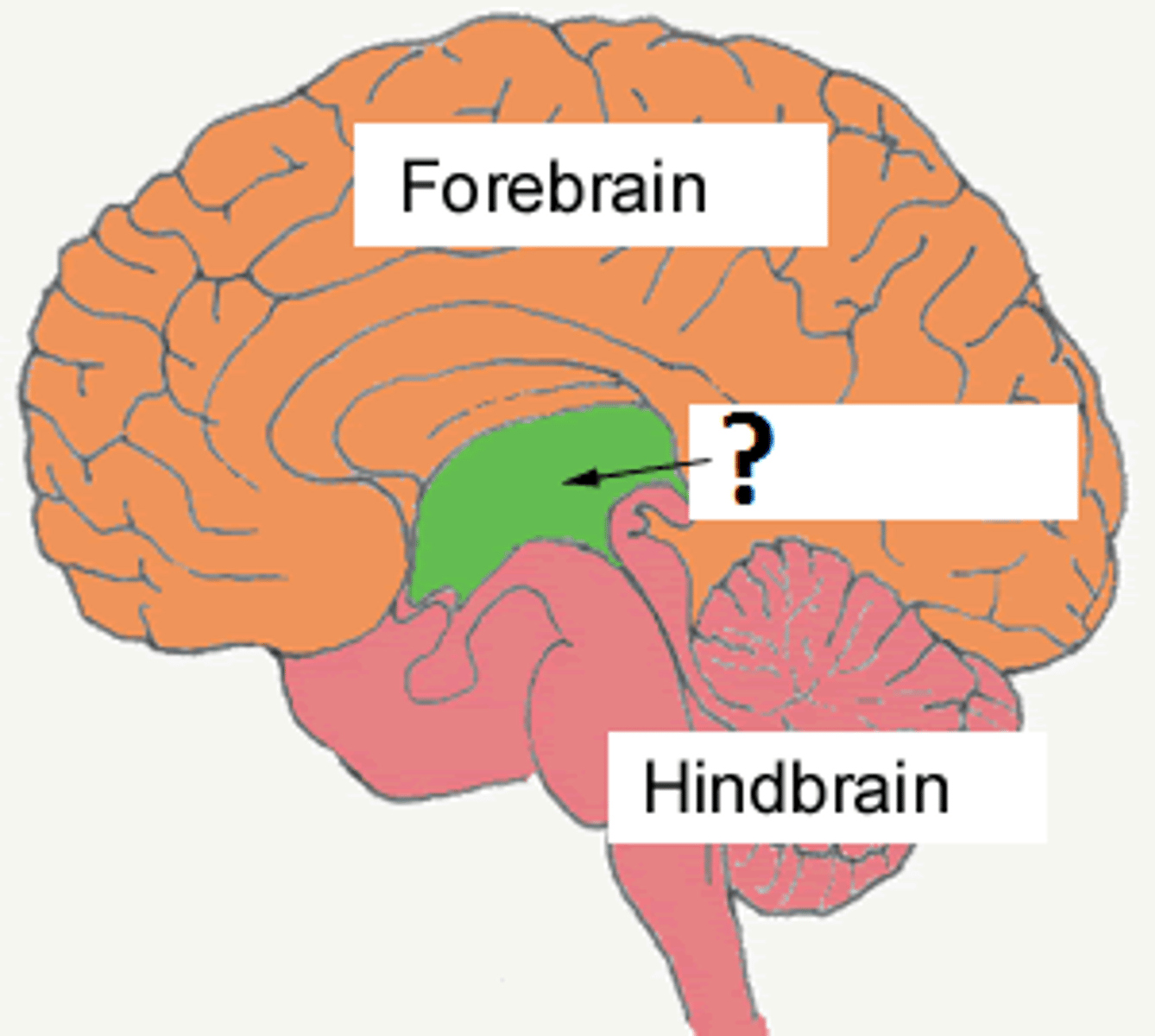
neural plexus
a network of intersecting nerves
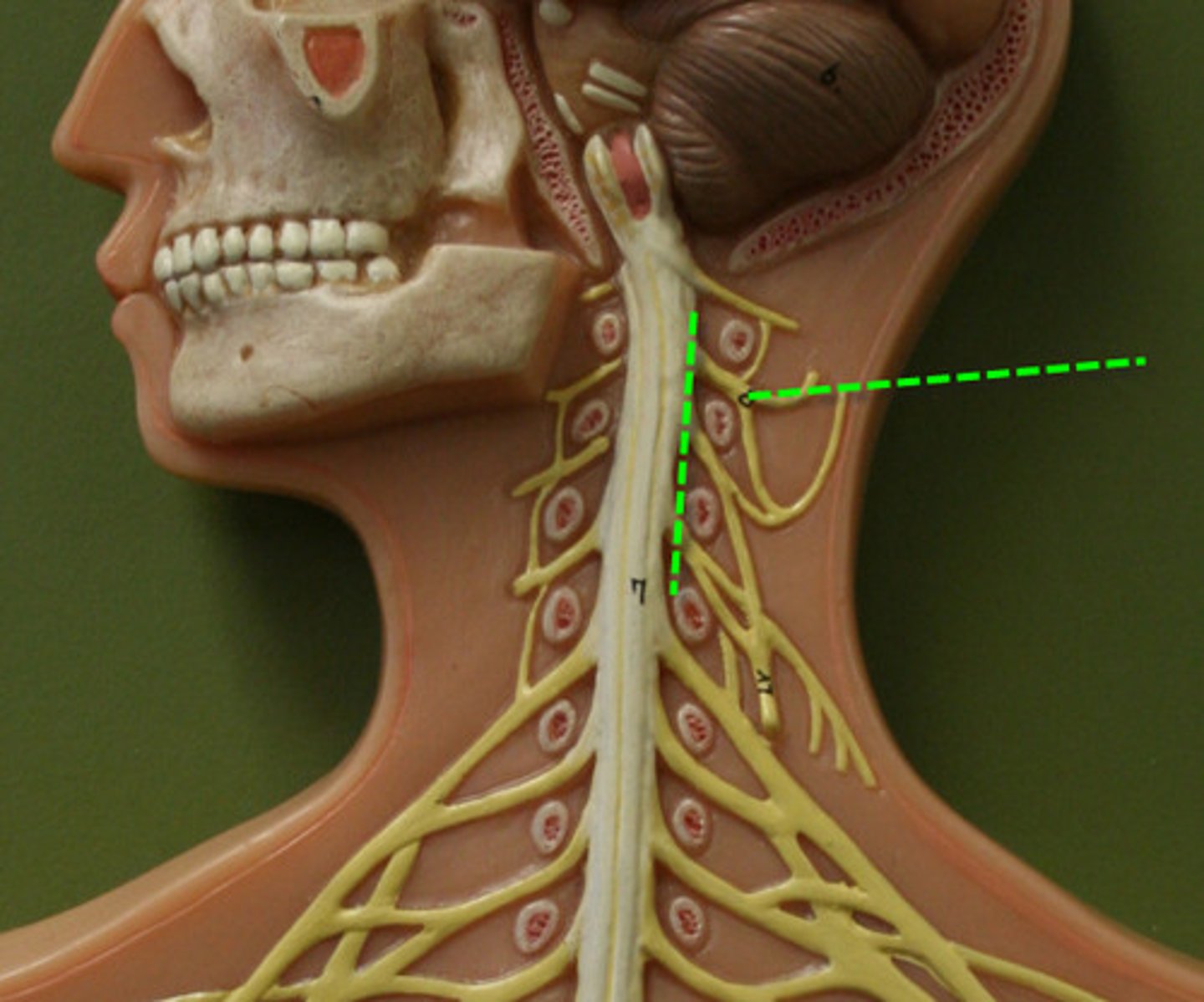
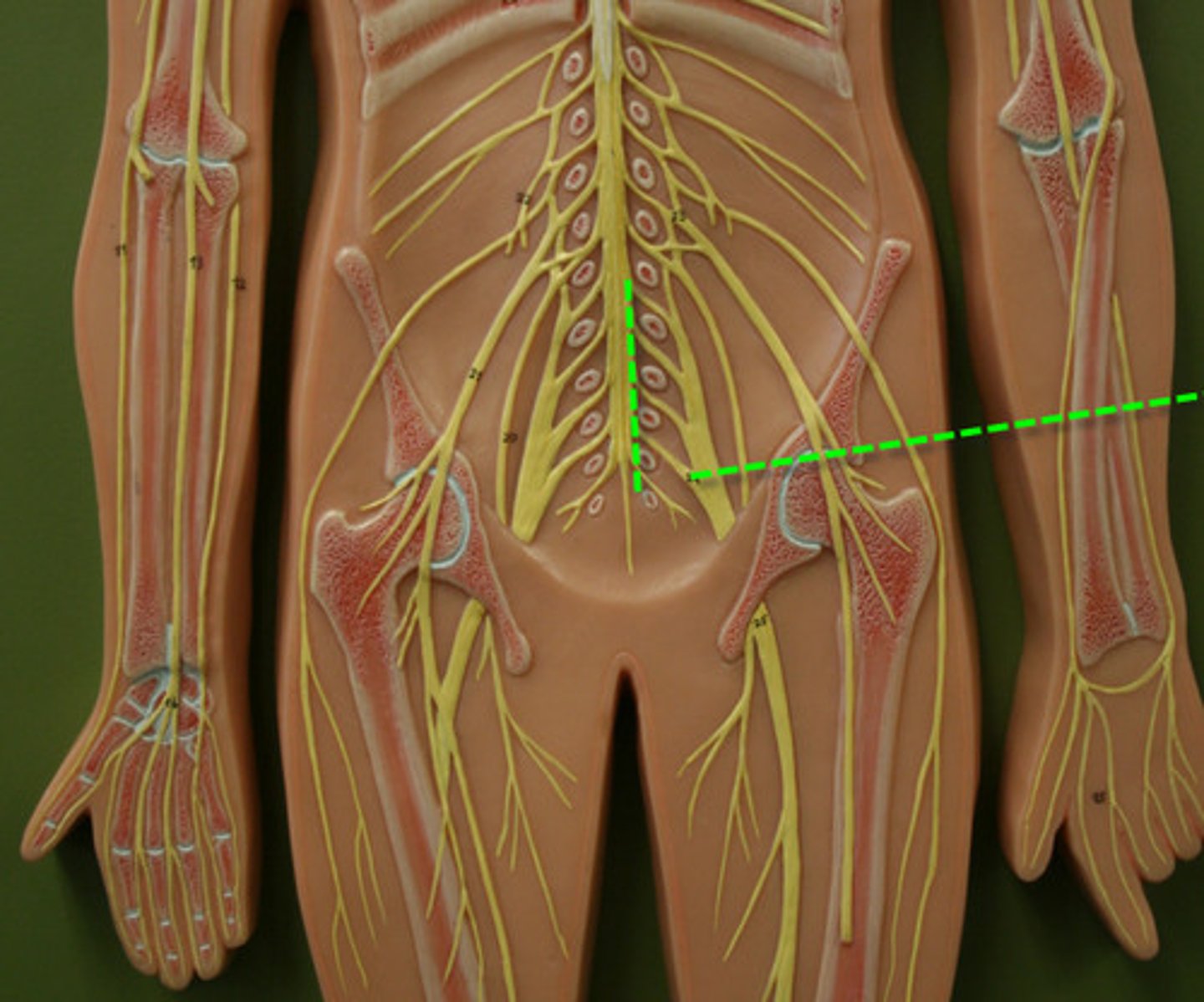
cervicle plexus
_______ consists of the ventral rami of spinal nerves C1-C5. It innervates the muscles of the neck and extends into the thoracic cavity where they control the diaphragm muscles.
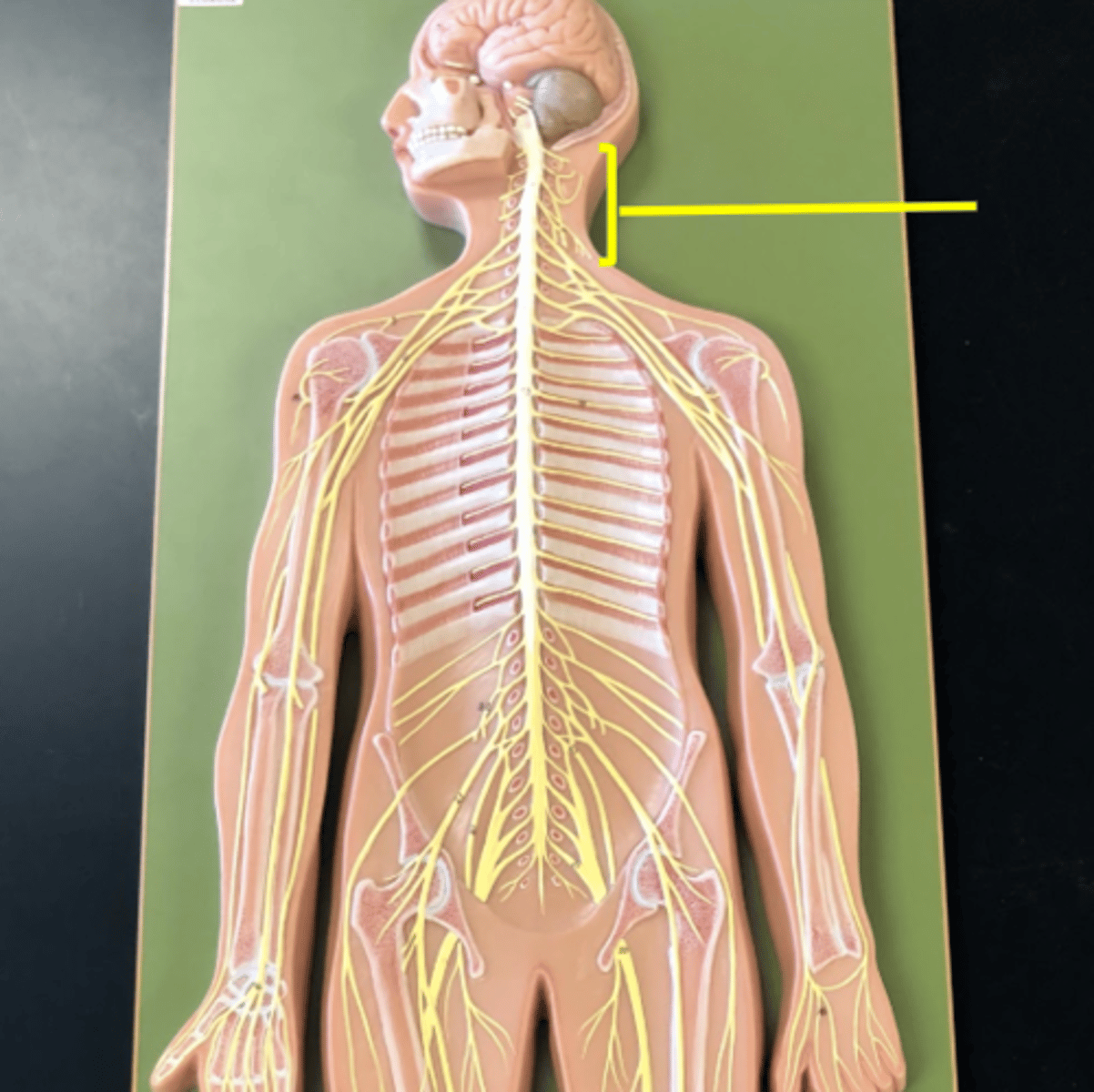
brachial plexus
C5-T1
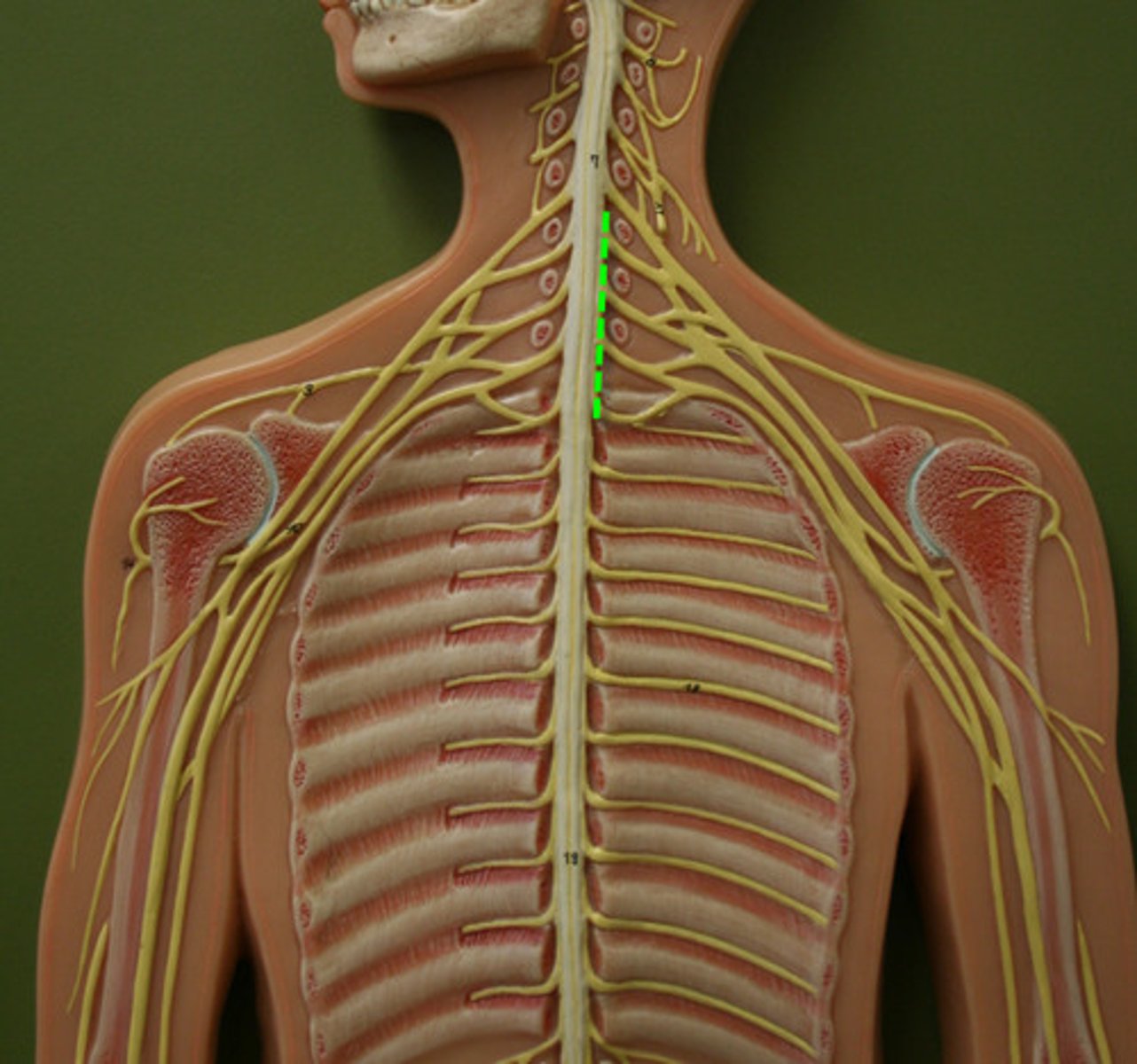
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
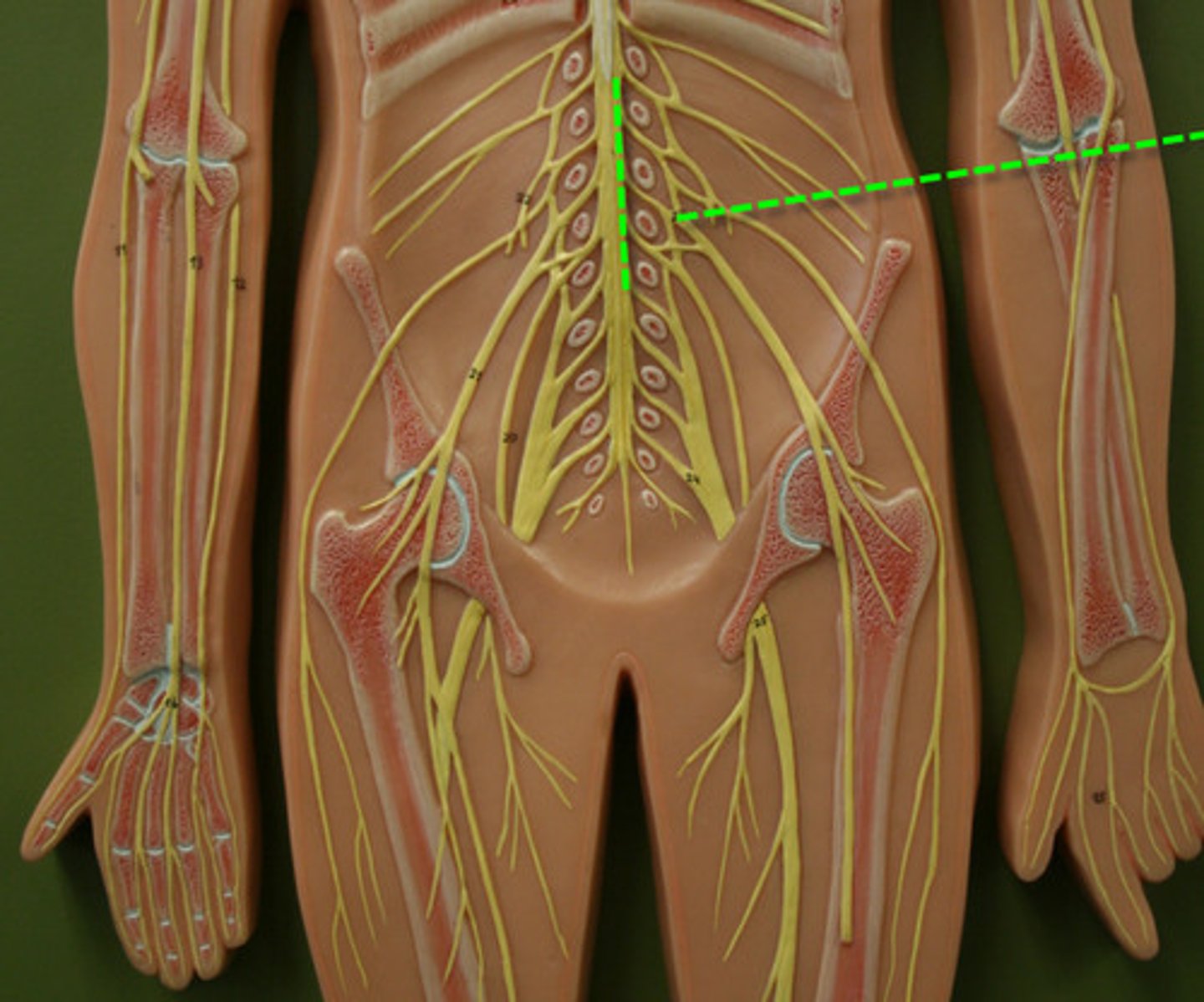
sacral plexus
Arises from L4-S4
- Serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, and perineum
olfactory bulb
a brain structure located above the nasal cavity beneath the frontal lobes
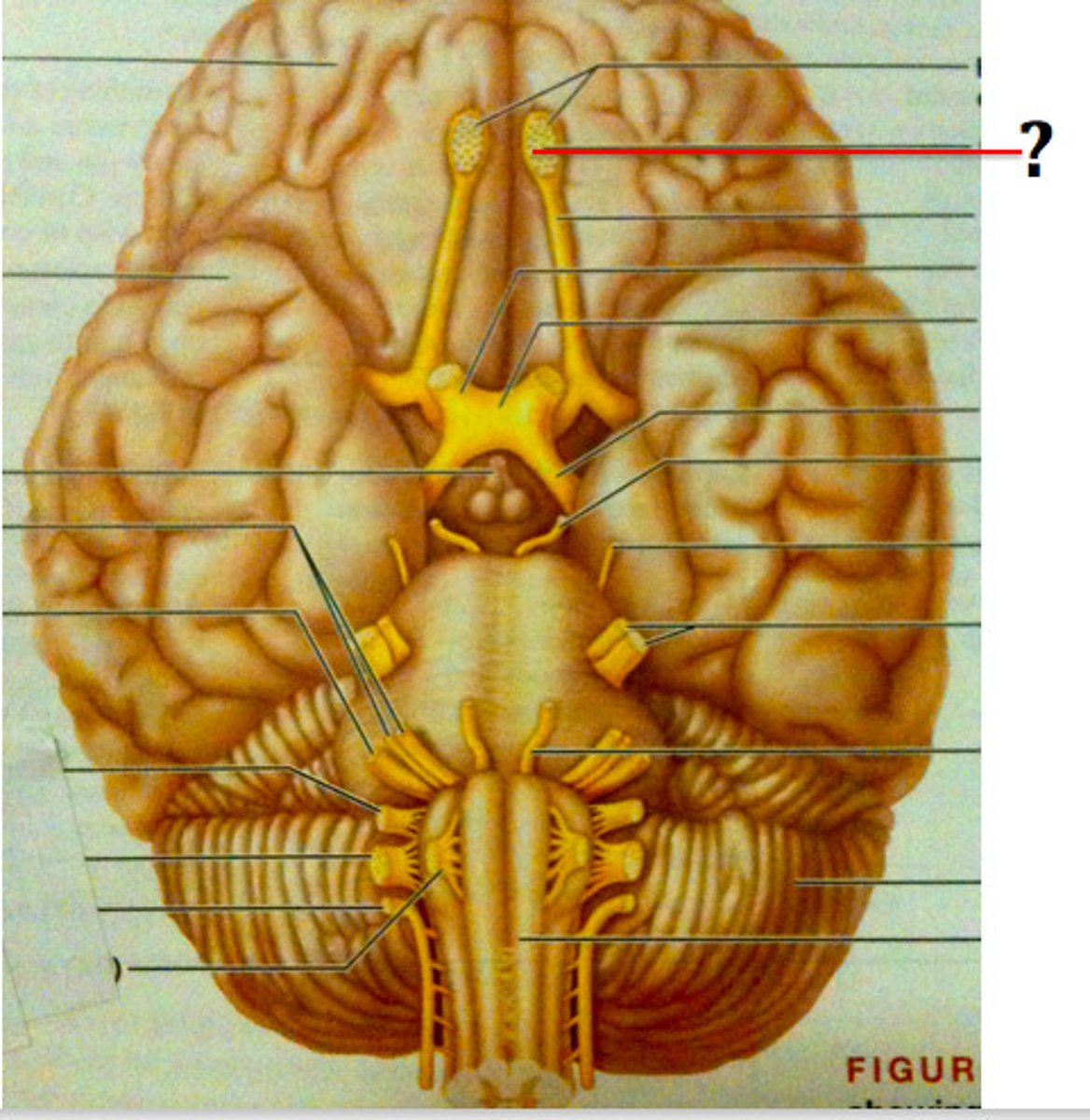
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
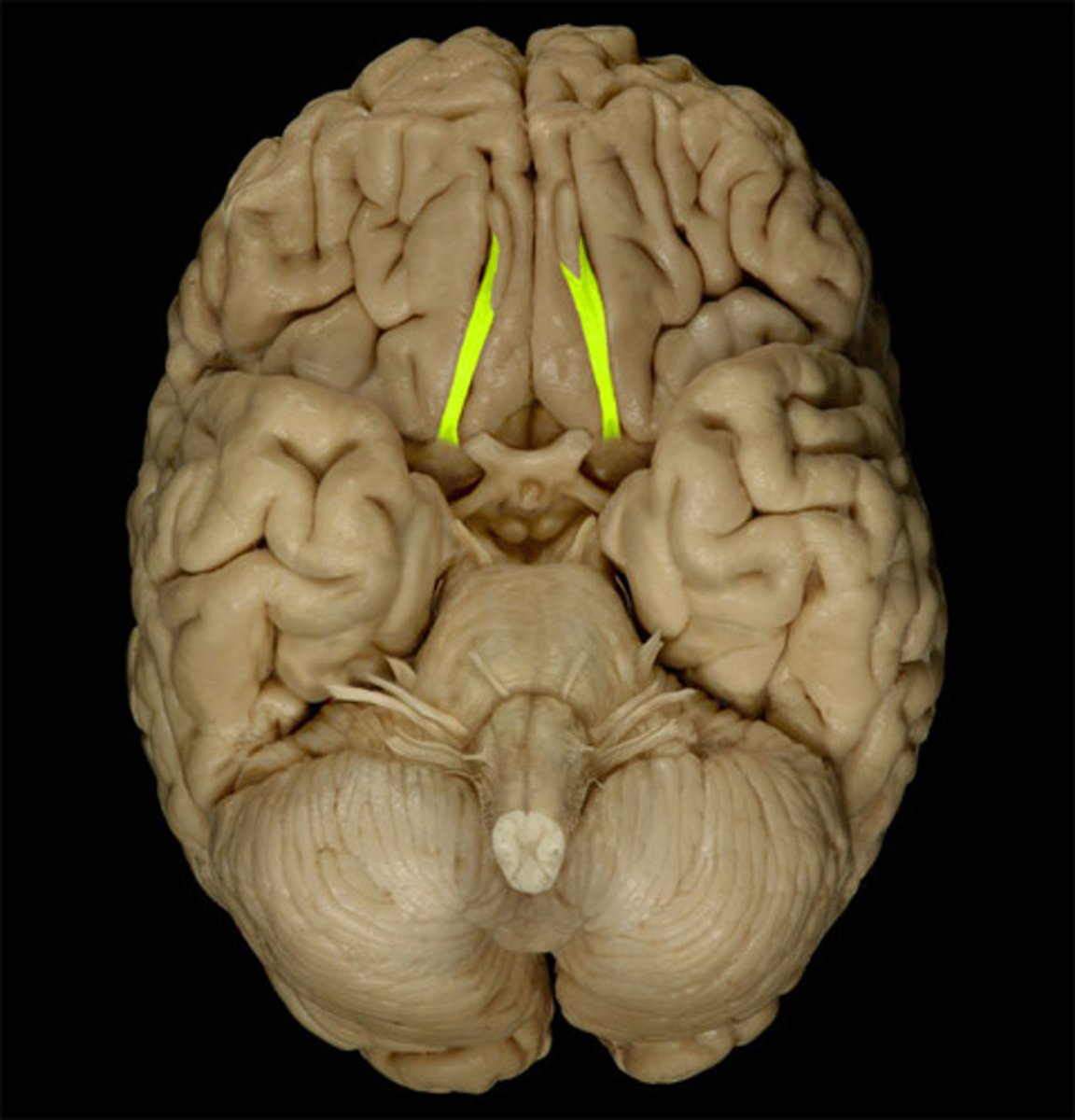
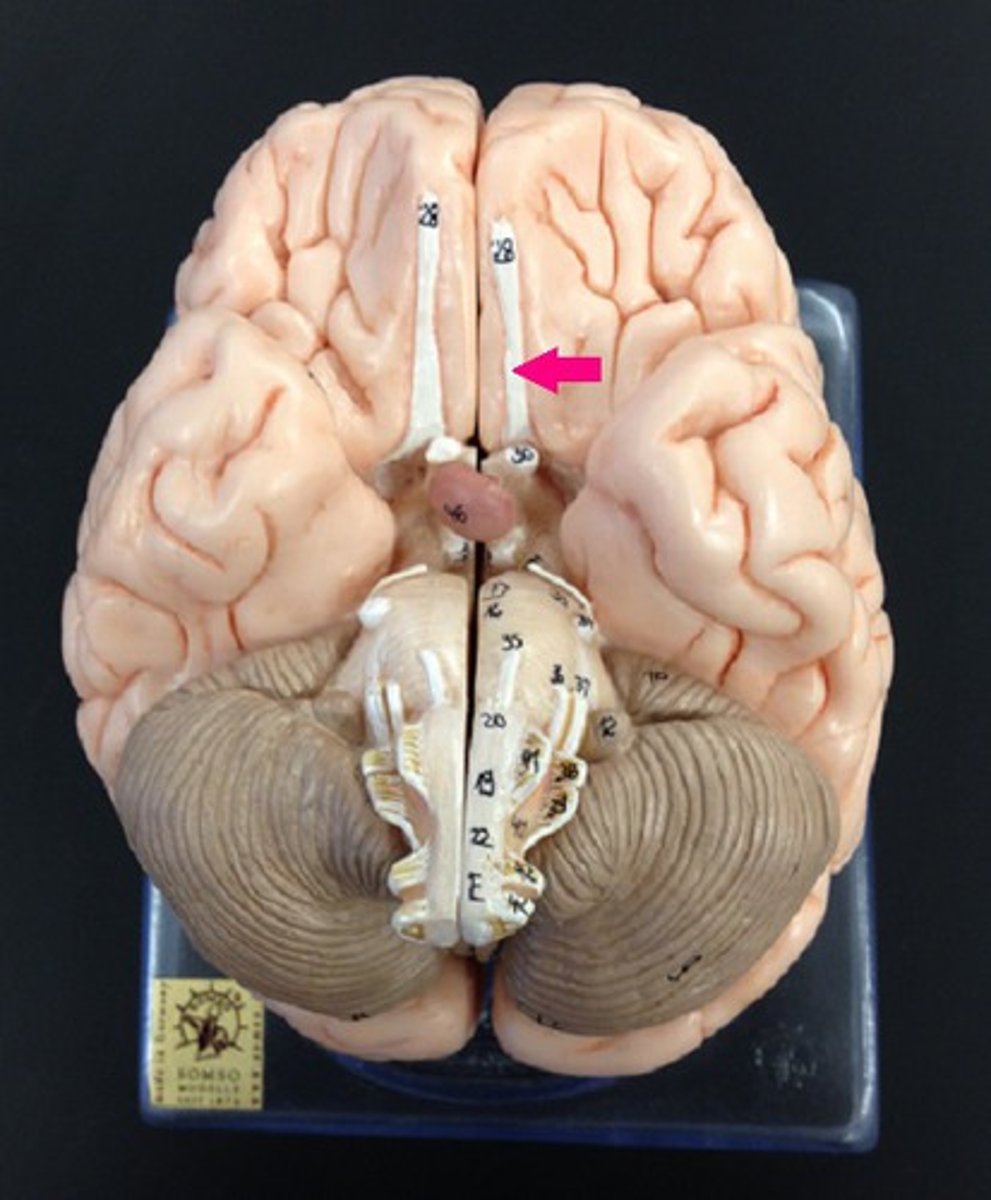
Olfactory Tract
the path along which the olfactory receptors send their electrical messages to the brain.
optic chiasm
the point in the brain where the visual field information from each eye "crosses over" to the appropriate side of the brain for processing
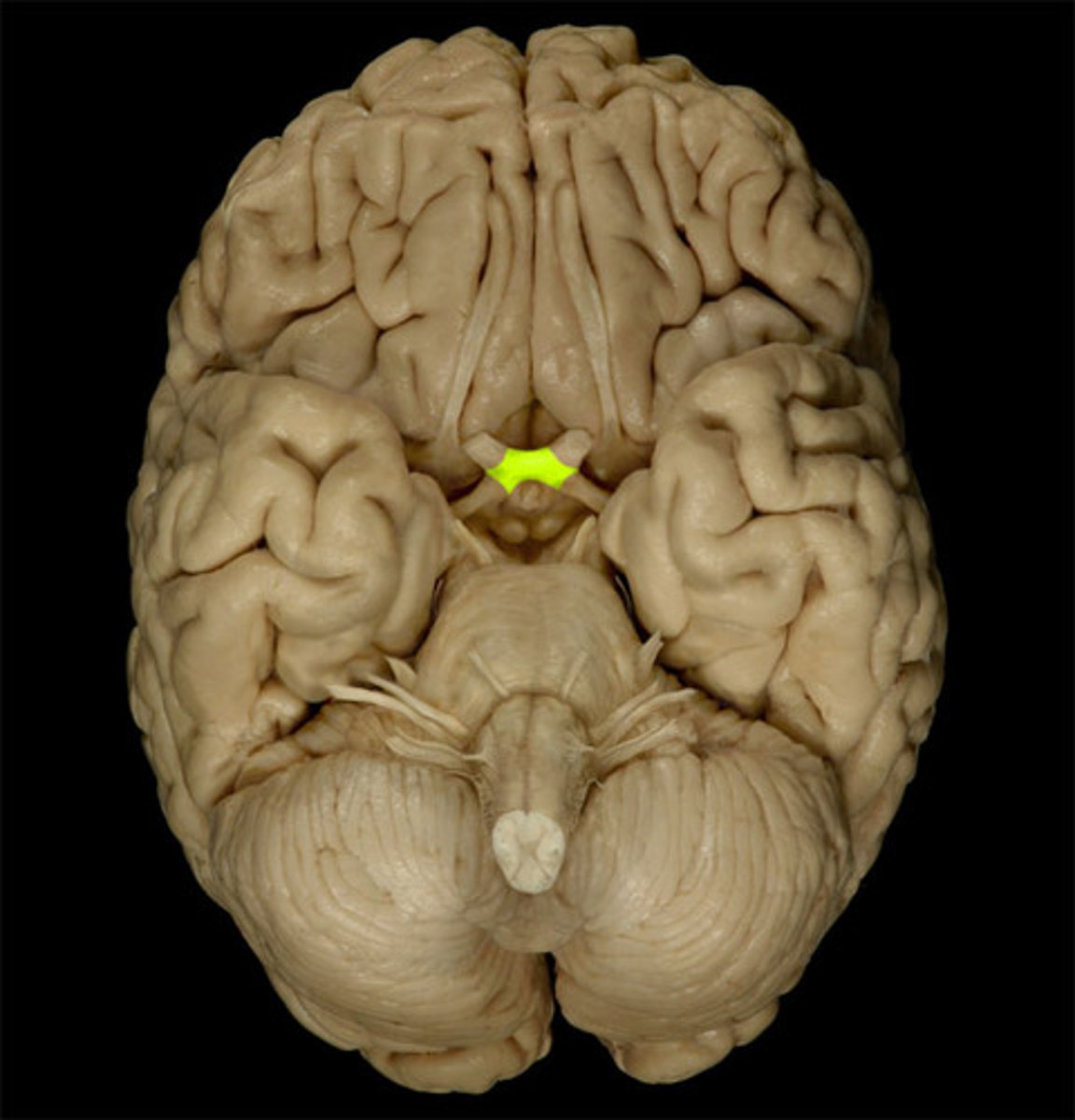
Optic Nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
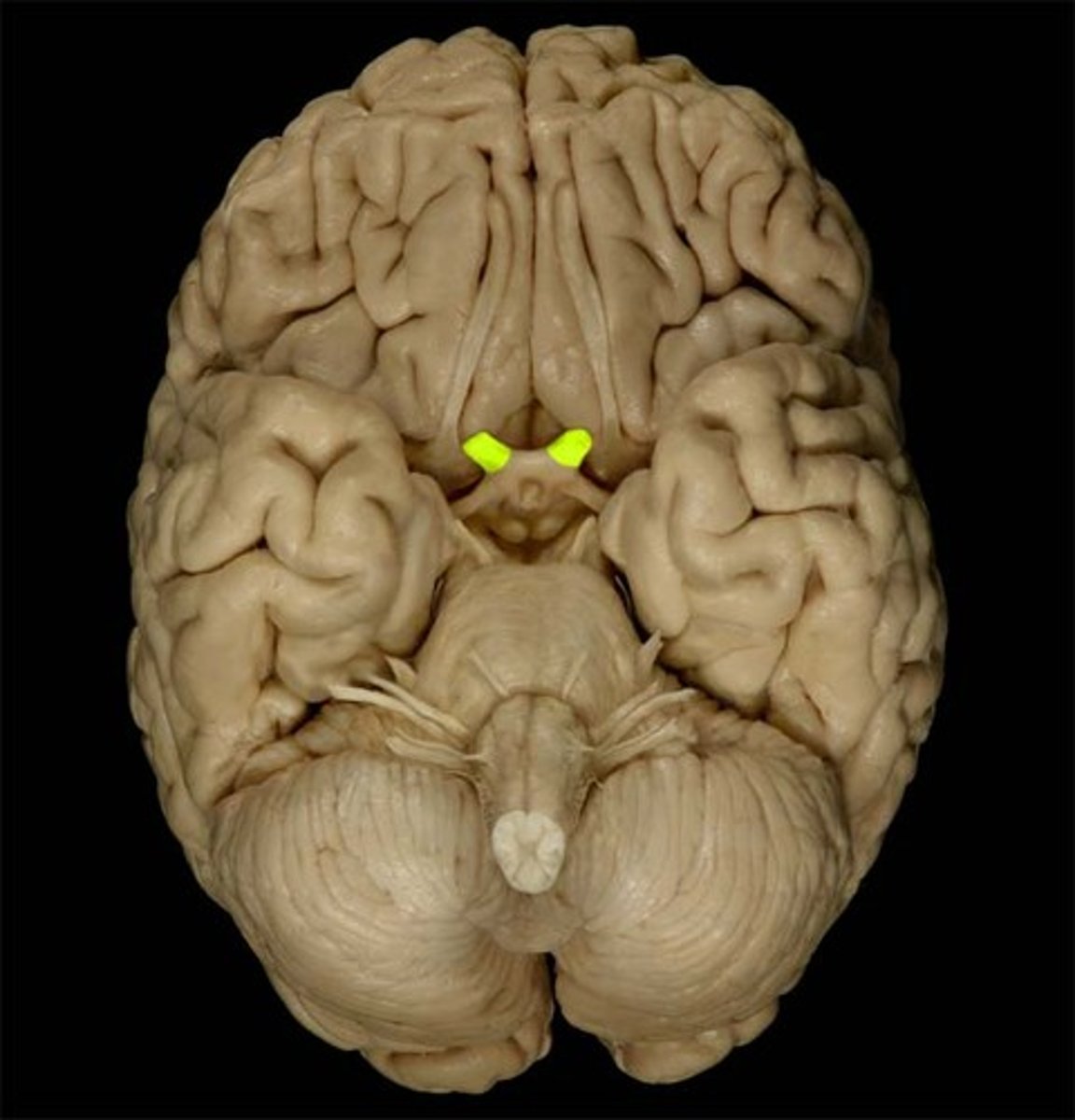
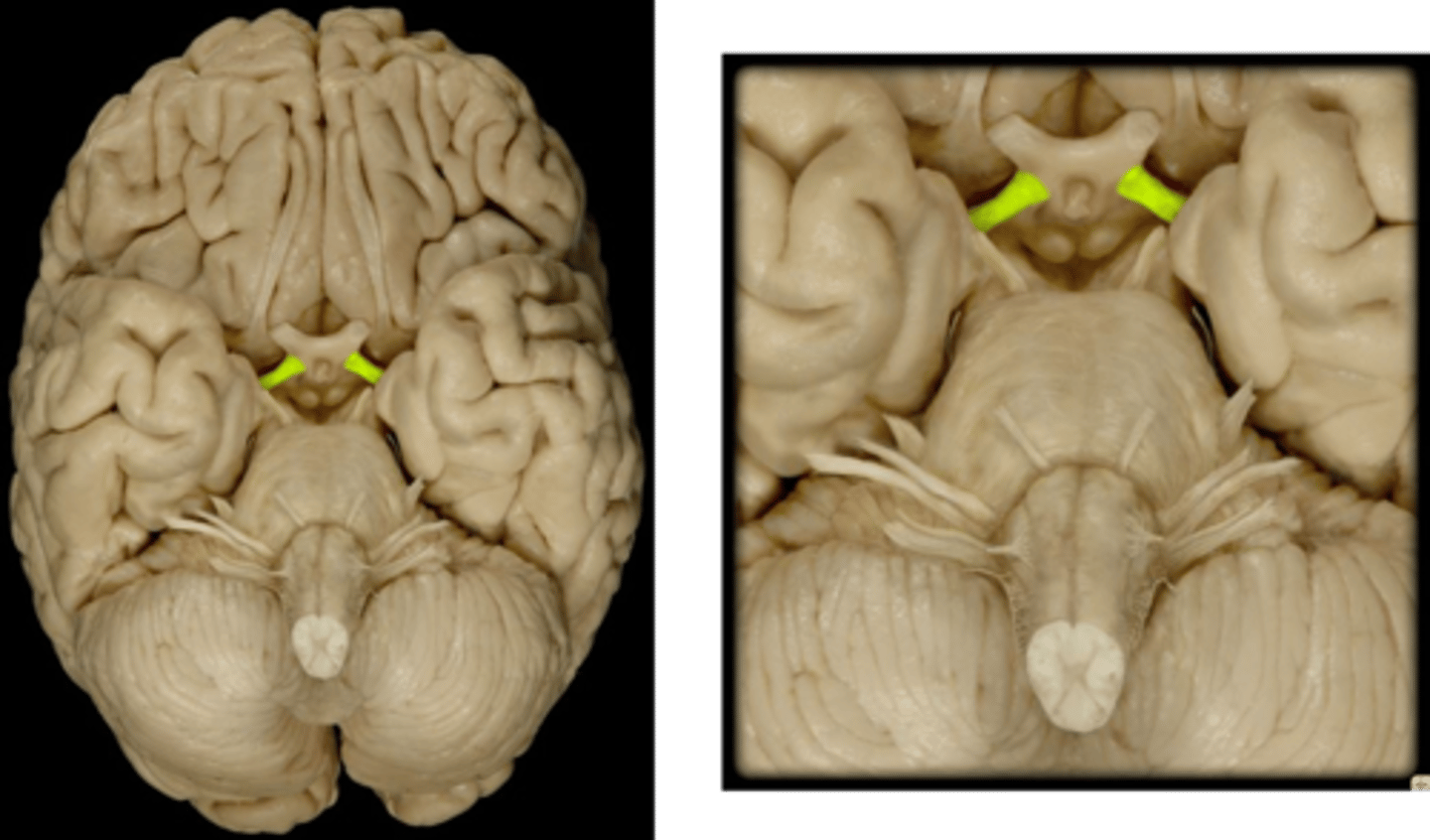
Optic Tract
How information from the optic nerve travels to the thalamus.
Pineal Gland
secretes melatonin
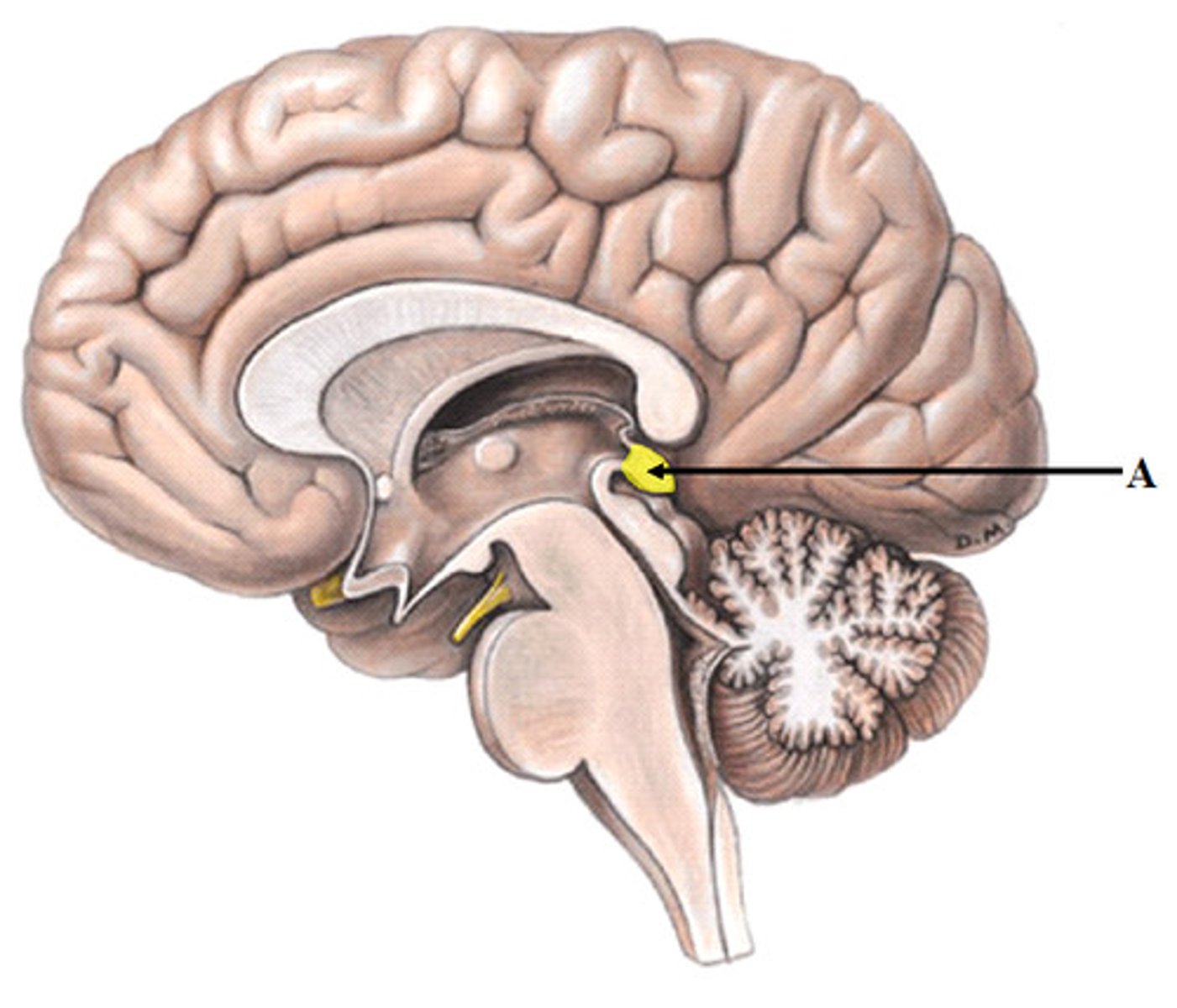
Pituitary Gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
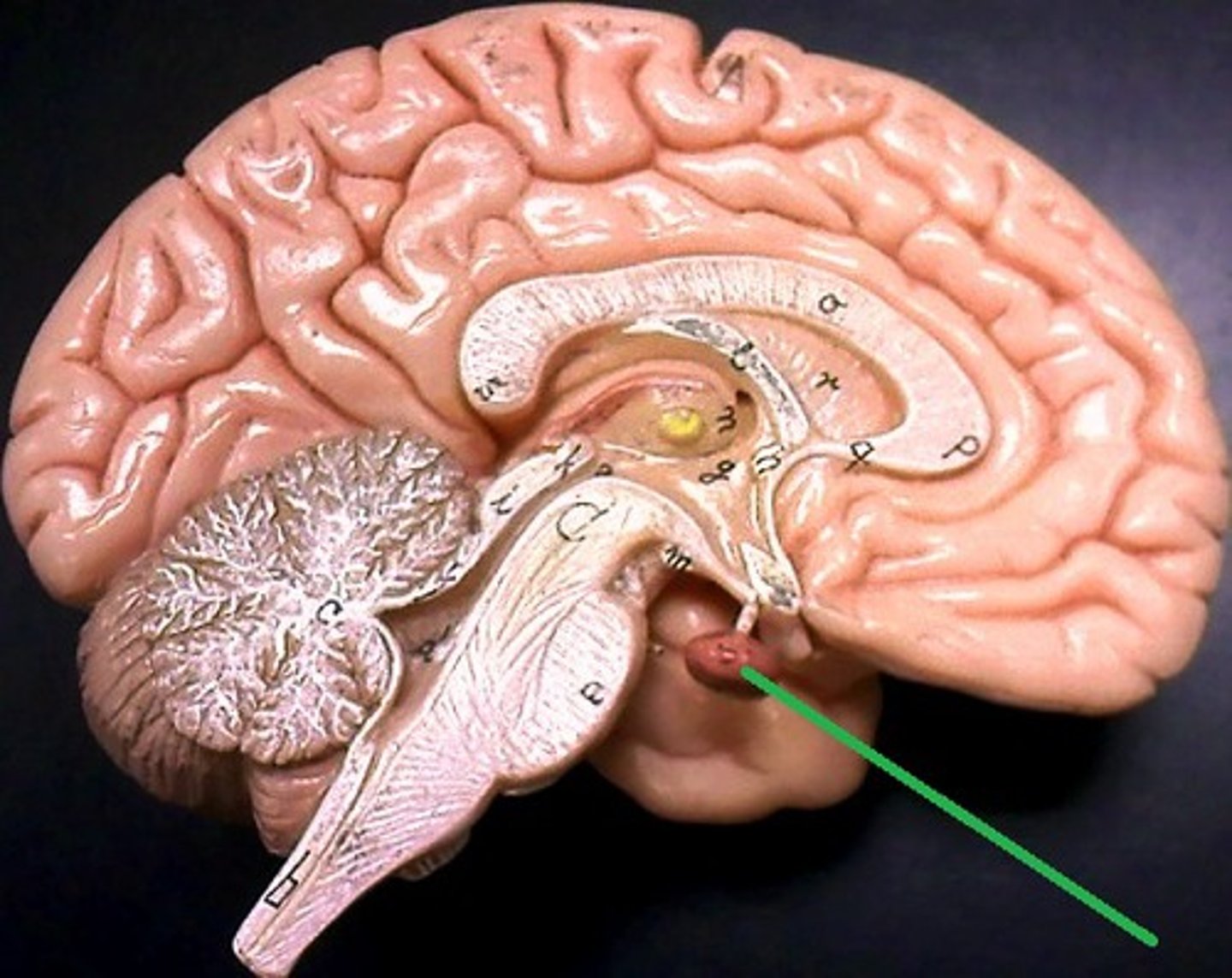
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
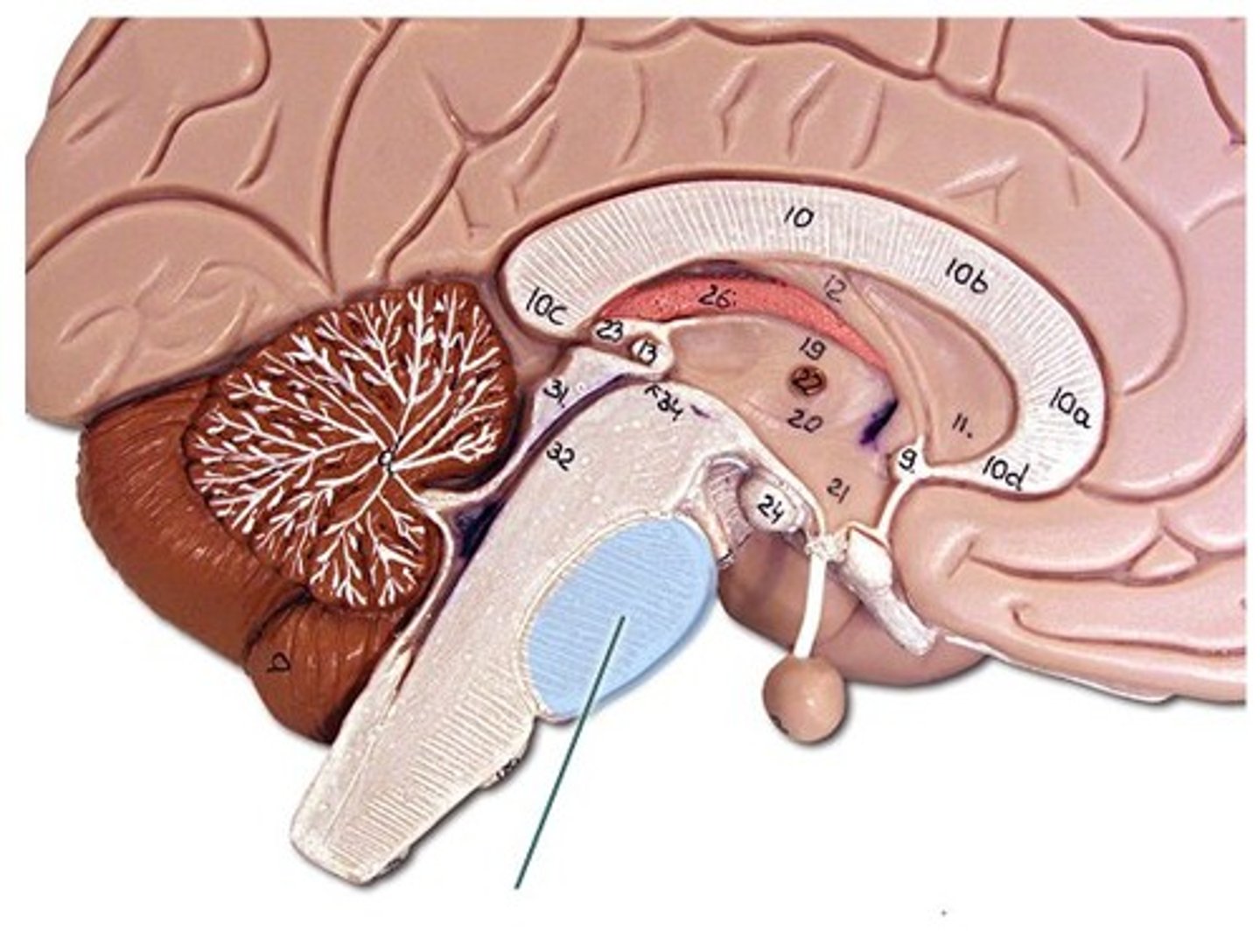
Posterior White Columns
lie between posterior gray horns and posterior median sulcus
postcentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
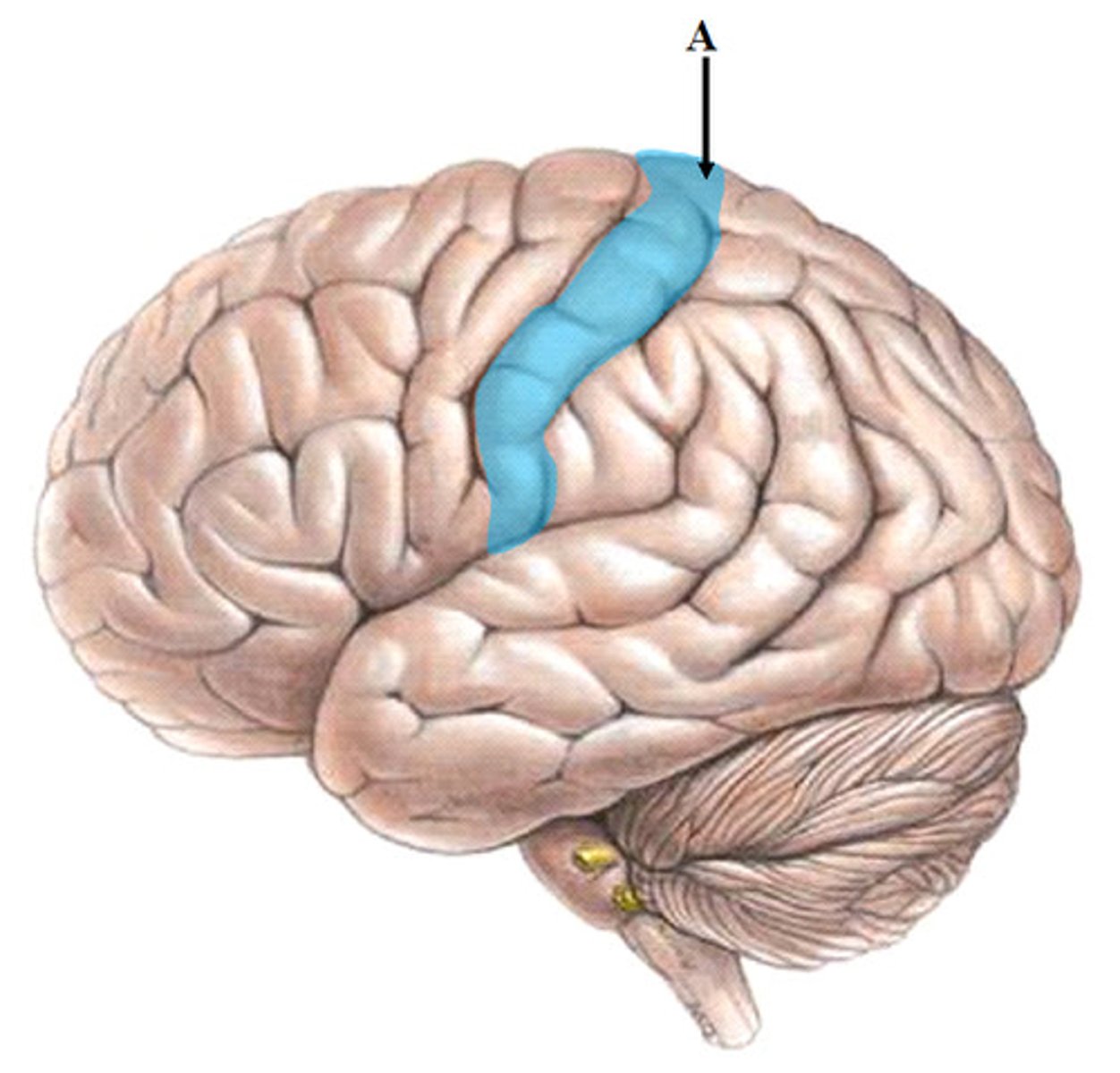
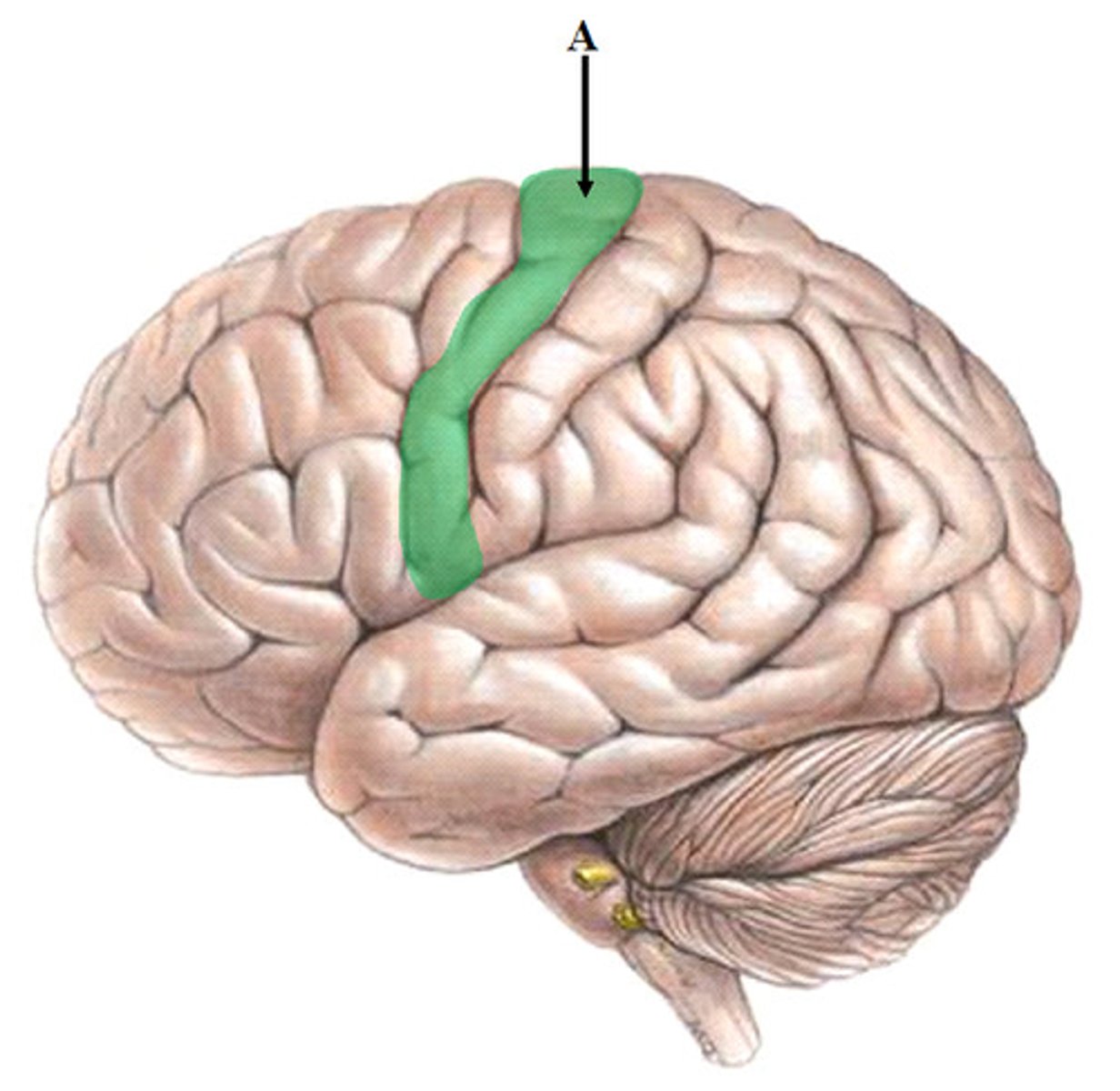
precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
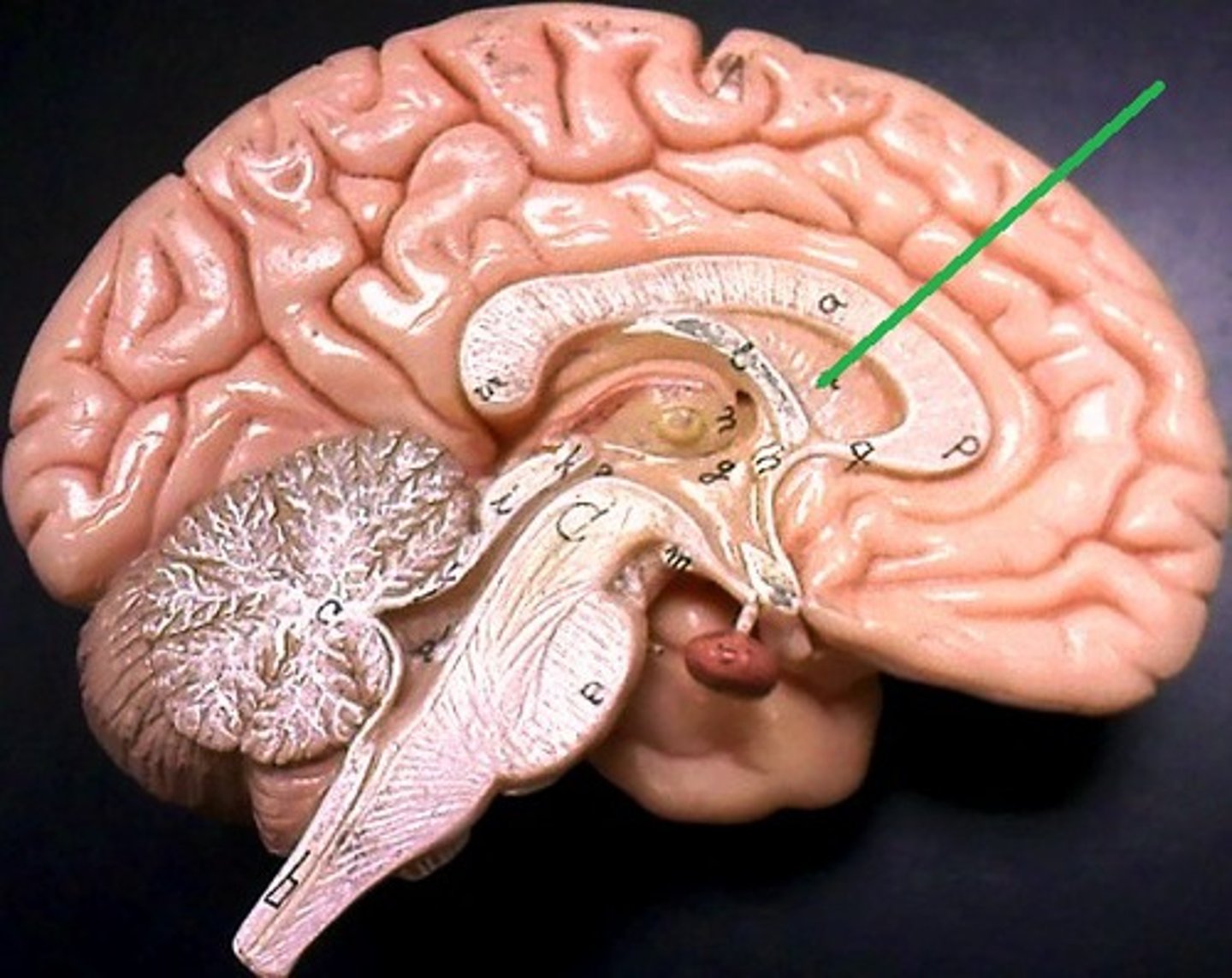
septum pellucidum
thin membrane that separates lateral ventricles
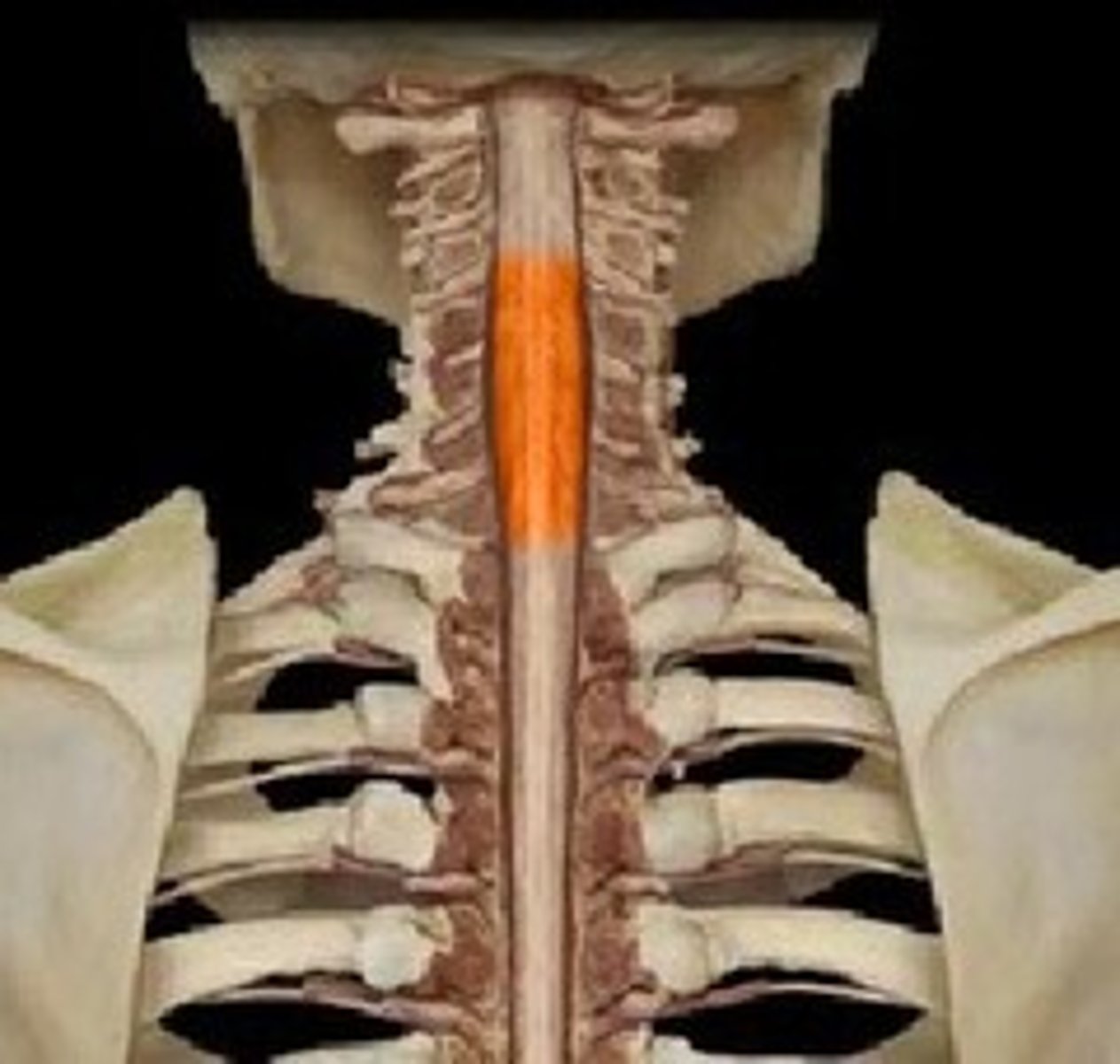
cervical spinal enlargement
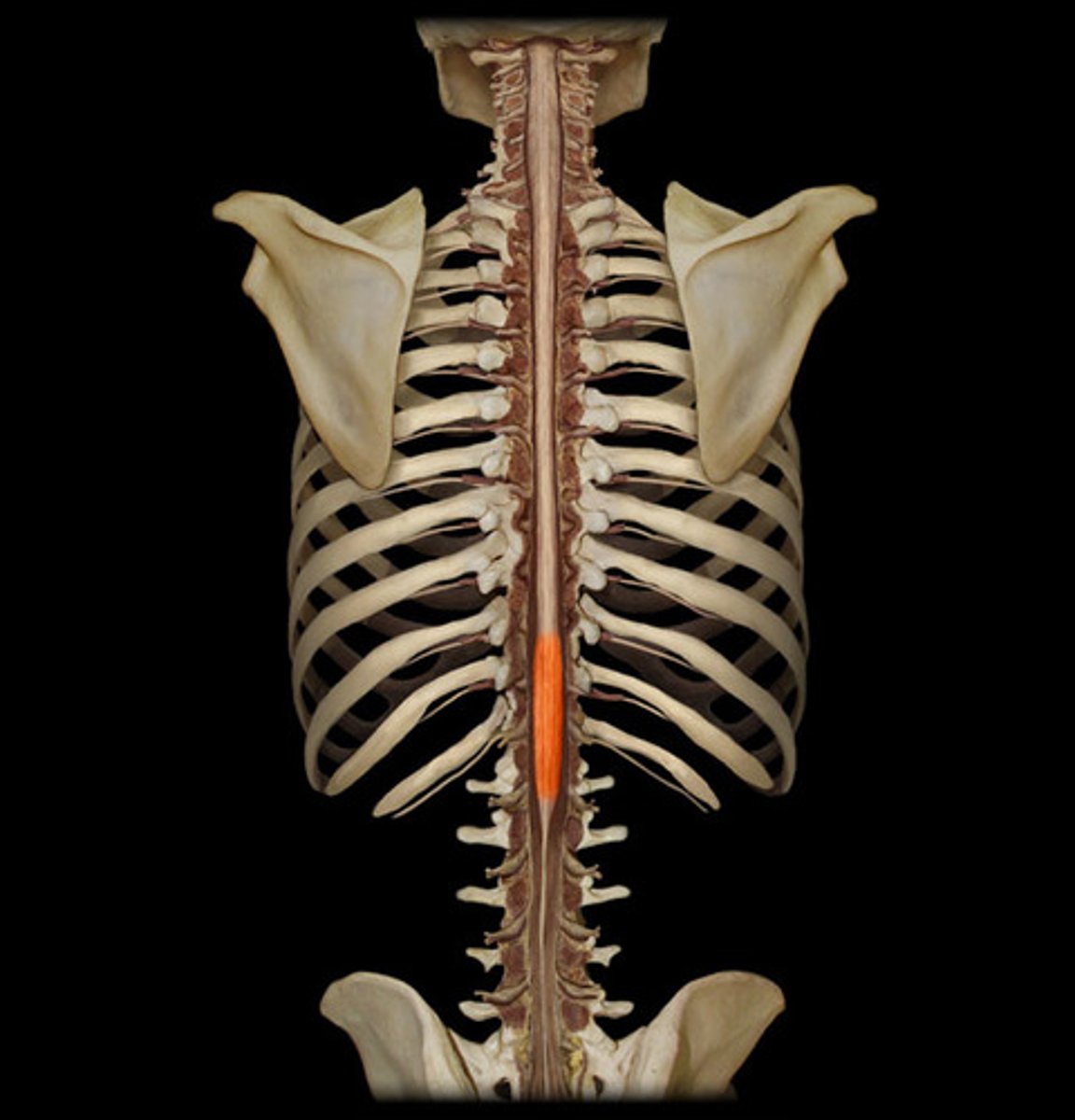
Lumbosacral spinal enlargement
Spinal Nerve
a peripheral nerve attached to the spinal cord
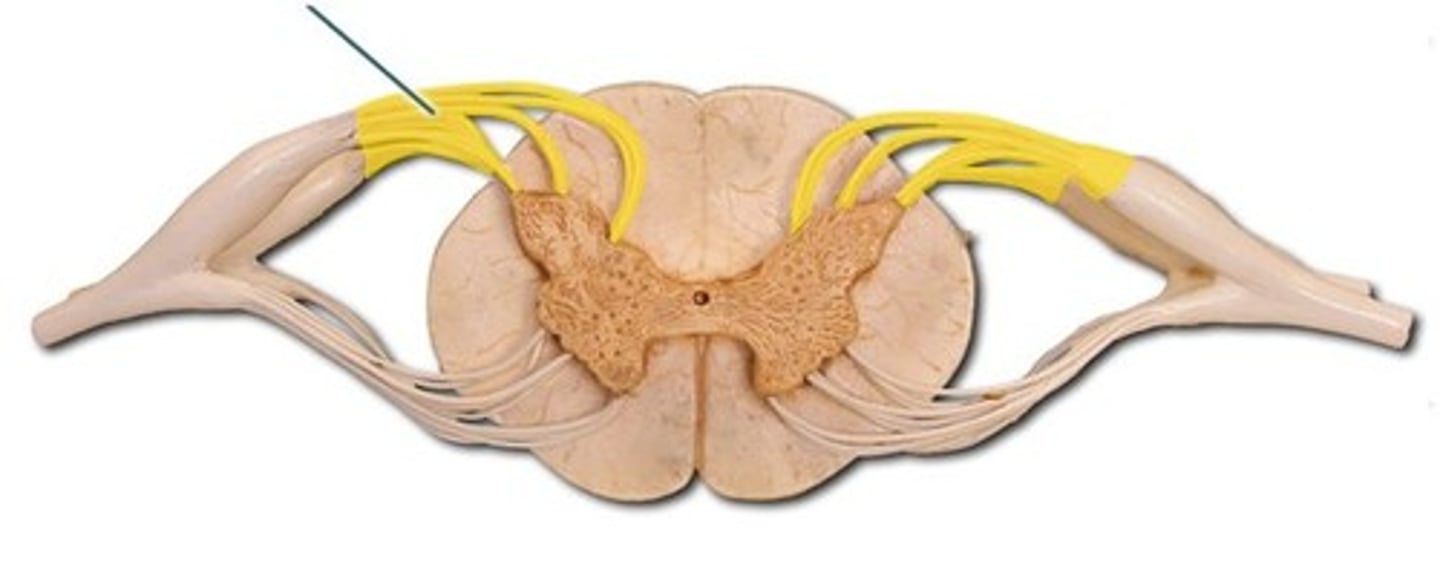
Spinal Rootlets
Thin bundles of afferent and efferent fibers/axons
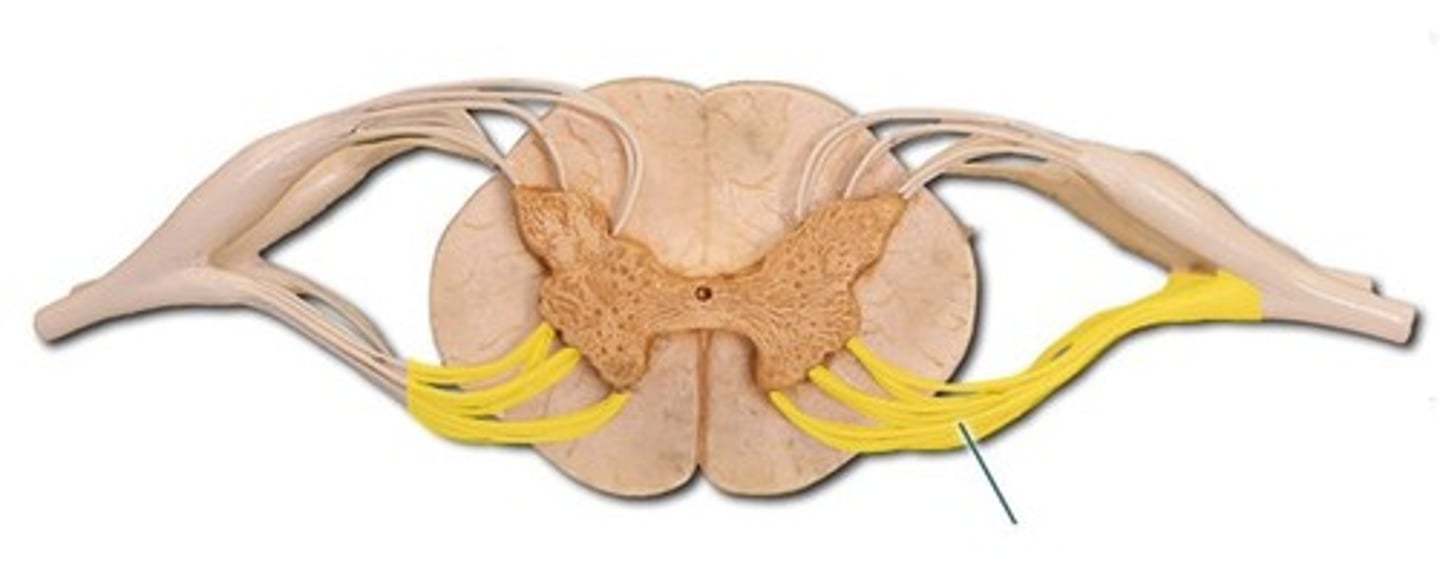
Subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
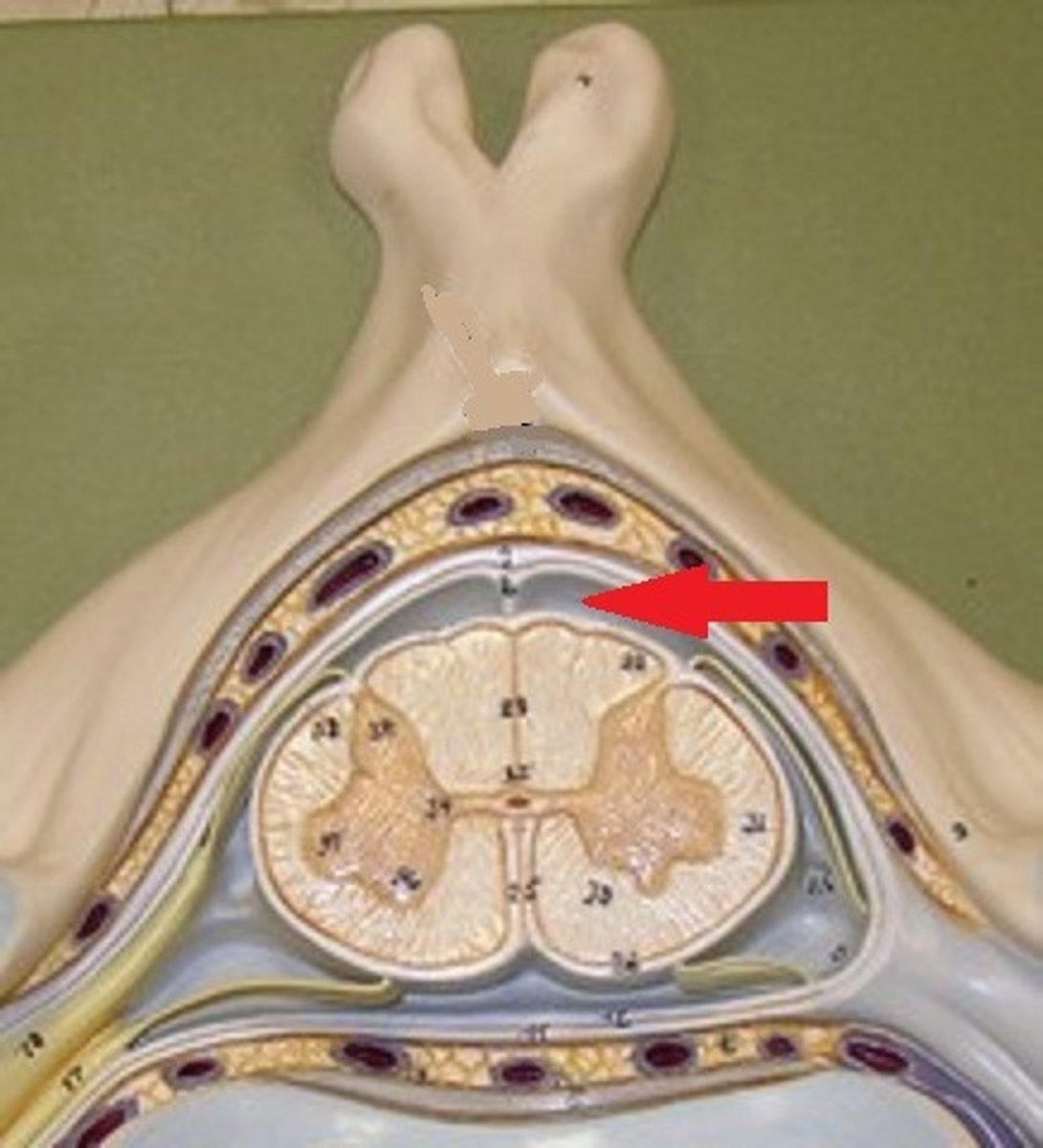
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
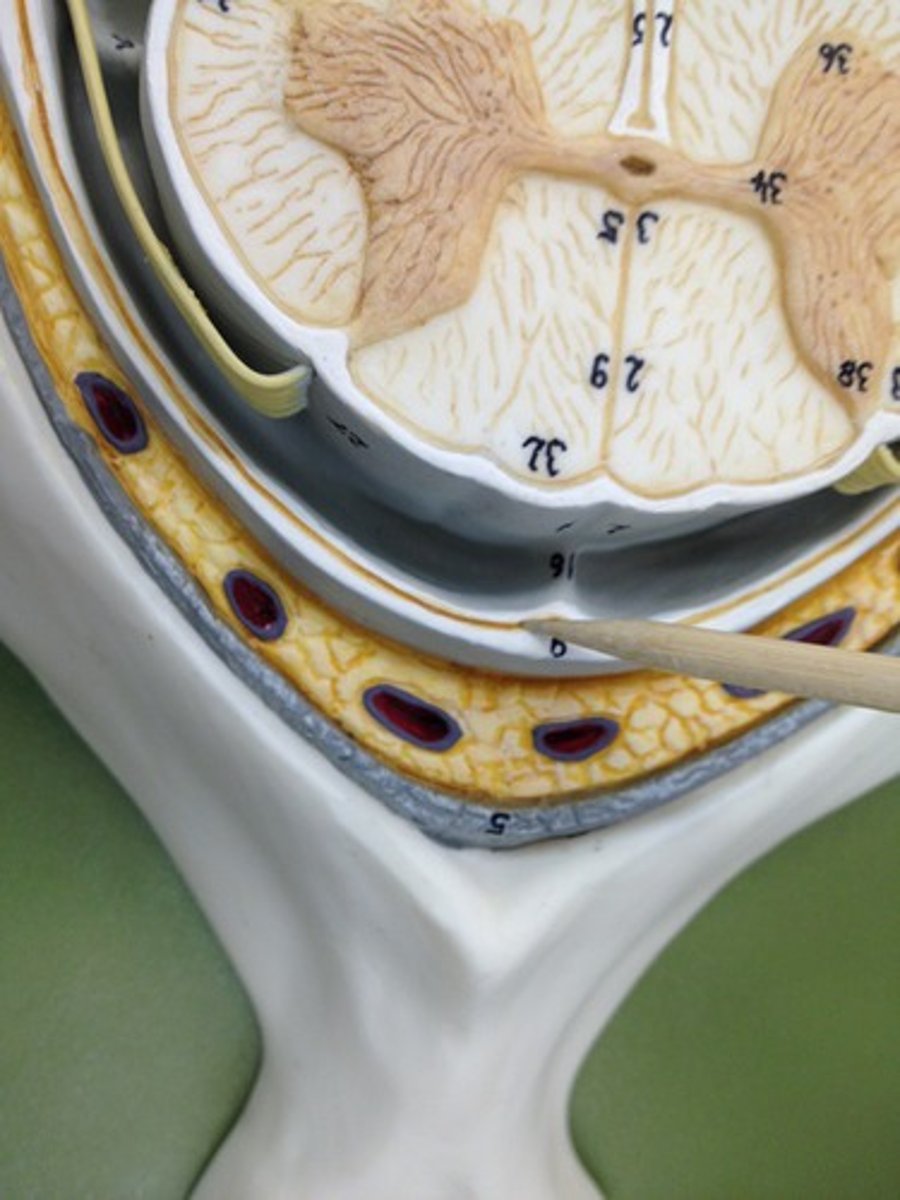
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
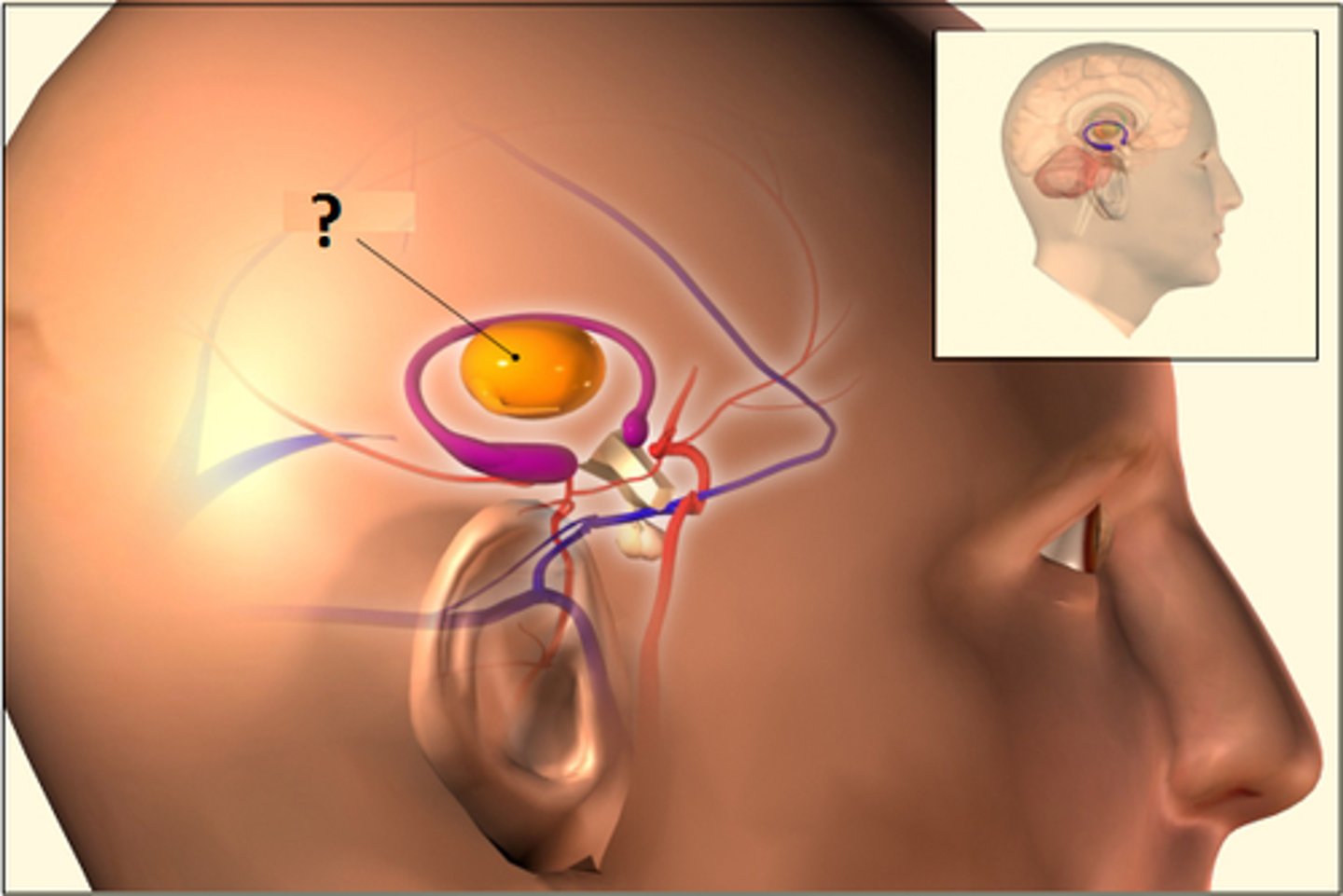
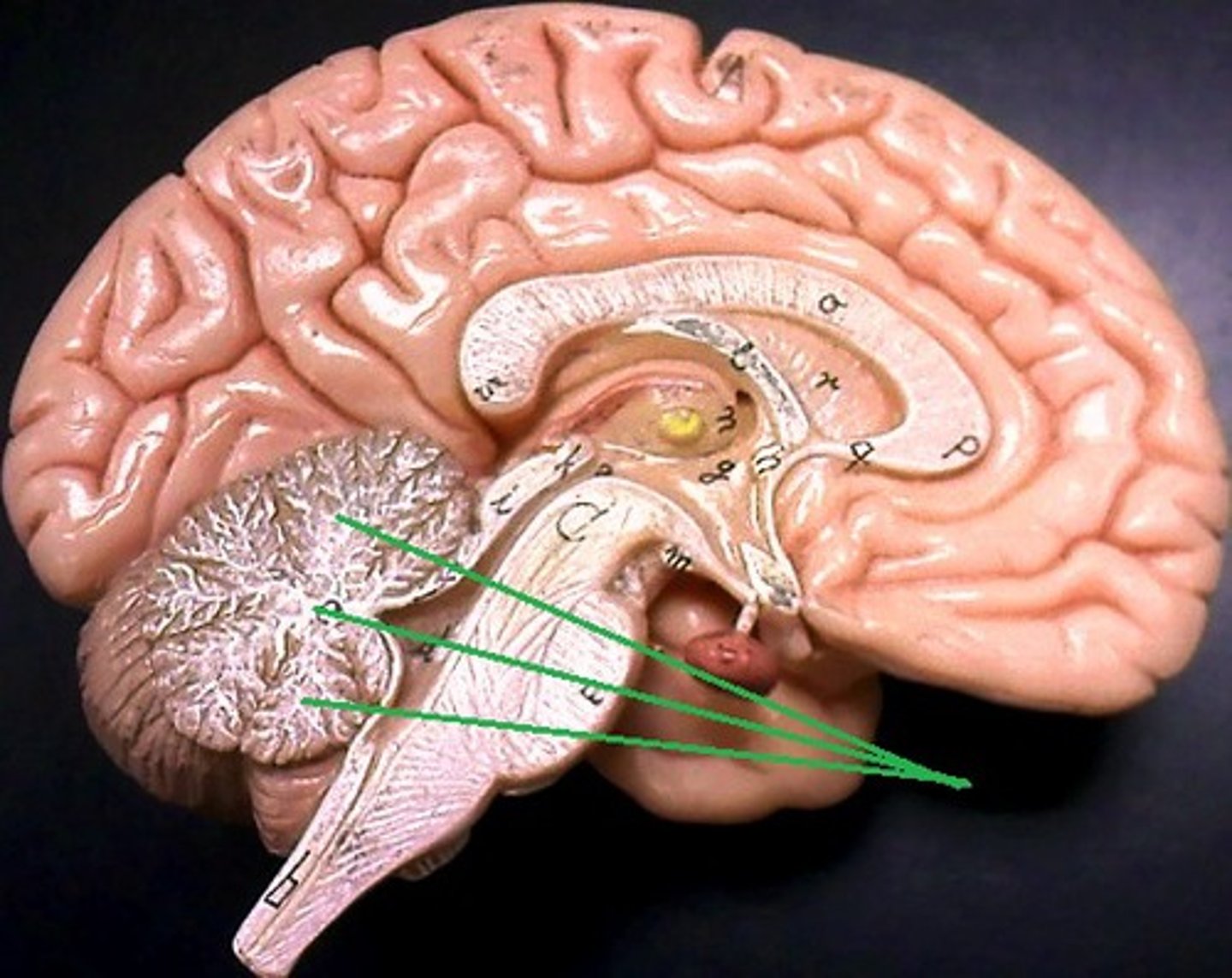
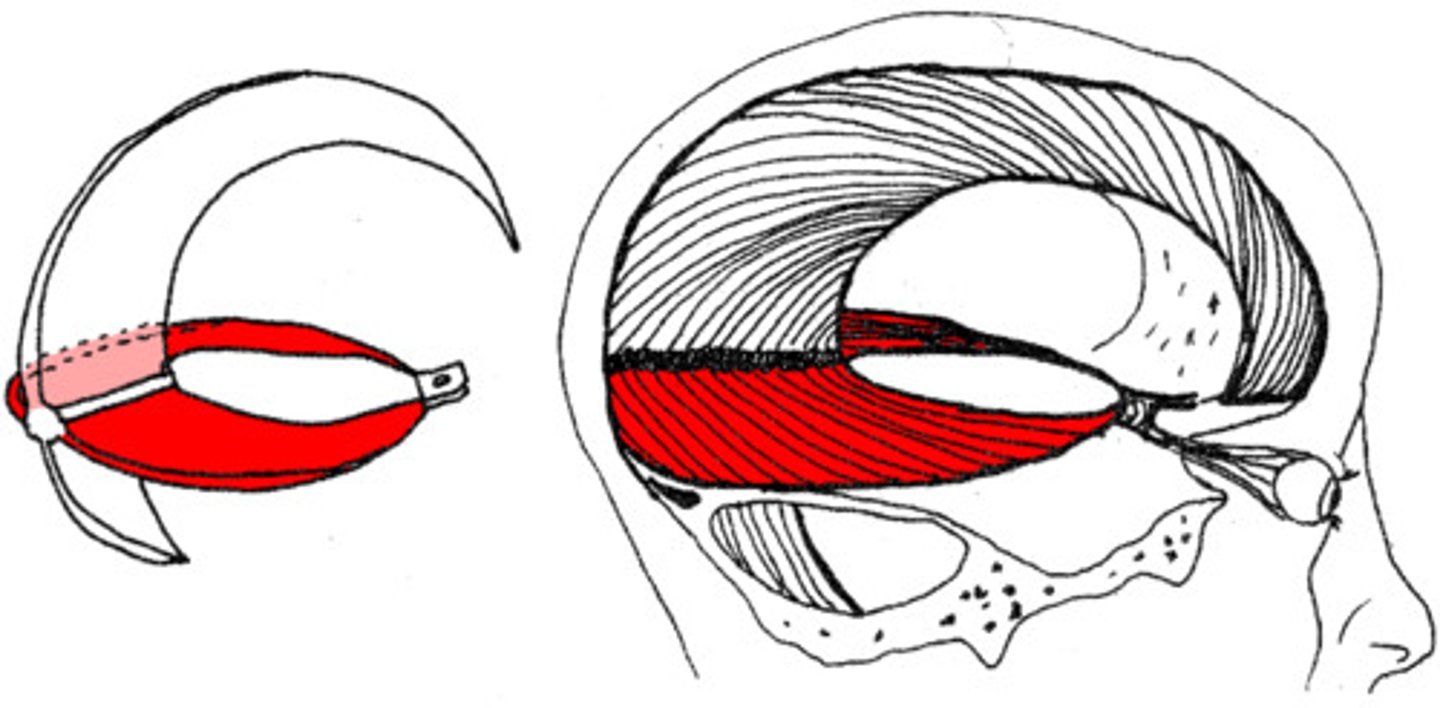
Tentorium Cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
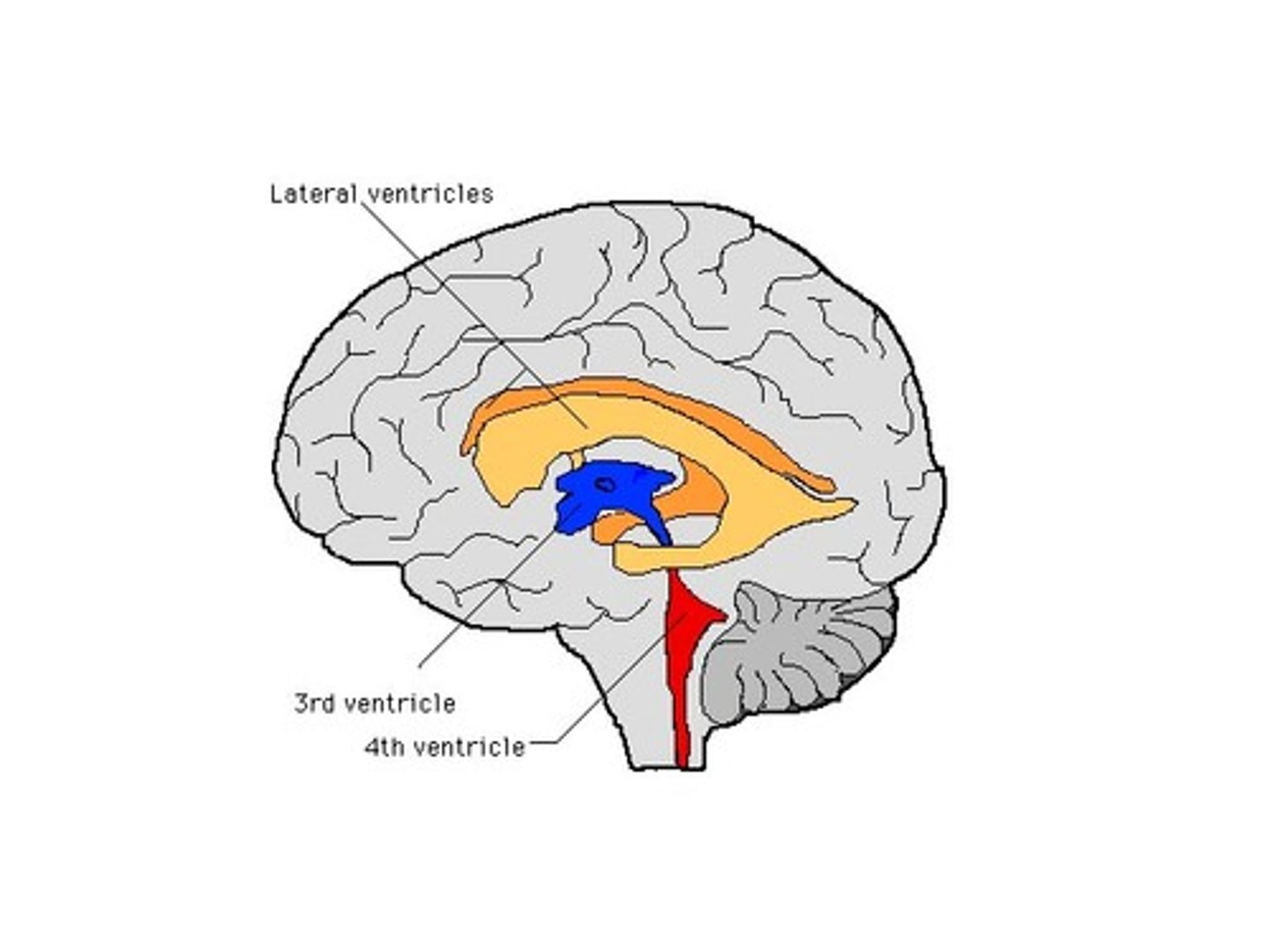
Ventricals of the brain
Wernicke's area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe