module 5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Last updated 10:35 PM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
niche
the role of an organism in an ecosystem
2
New cards
convection
when warm molecules go up, cool molecules go down
\-atmosphere: hot air rises and cool air goes down
\-hydrosphere; hot water rises and cool water goes down
\-atmosphere: hot air rises and cool air goes down
\-hydrosphere; hot water rises and cool water goes down
3
New cards
carbon sinks (what are the four main ones too)
store carbon
\-four main ones: organic molecules in dead organisms in biosphere
\-gas carbon dioxide in atmosphere
\-organic matter in soil
\-fossil fuel and sedimentary rock deposits in lithosphere
\-four main ones: organic molecules in dead organisms in biosphere
\-gas carbon dioxide in atmosphere
\-organic matter in soil
\-fossil fuel and sedimentary rock deposits in lithosphere
4
New cards
predator prey relationship
one species (predator) is preying on another species- the prey. This effects both populations, ex: fox and rabbit
5
New cards
food web
interlocking system of food chains
6
New cards
carbon cycle
a natural system to reuse carbon atoms.
\-carbon travels from the atmosphere to organisms on earth and then back to the atmosphere
\-carbon travels from the atmosphere to organisms on earth and then back to the atmosphere
7
New cards
symbiosis
interactions between two different organisms
\-mutualism, both benefit
\-commensalism, one benefit one neutral
\-paratism, one benefit one doesnt
\-mutualism, both benefit
\-commensalism, one benefit one neutral
\-paratism, one benefit one doesnt
8
New cards
bioaccumulation
increase in the concentration of a chemical in an organism overtime
9
New cards
photoautotrophs
an organism that photosynthesizes (green plants, cyanobacterium, algae)
10
New cards
observation
asking questions, qualitative observations (describes), quantitative observations (amounts).
\-leads to develop. of testable hypotheses
\-leads to develop. of testable hypotheses
11
New cards
experimentation
tests hypothesis by gathering data. can be modeled on natural or fake environments
12
New cards
modeling
helps understand changes over long periods of time or in large areas
\-mathematical formulas
\-lead to more hypotheses, experiments, data, and changes in models
\-improves ability to make predictions
\-mathematical formulas
\-lead to more hypotheses, experiments, data, and changes in models
\-improves ability to make predictions
13
New cards
demography
study of pop.
\-allows predictions to be made about how a pop. will change
\-allows predictions to be made about how a pop. will change
14
New cards
nitrogen cycle
cycle where nitrogen moves through atmosphere, soil, water, bacteria and organisms. in order to do this it must change forms
1. nitrogen fixation
2. nitrification
3. ammonification
4. denitrification
1. nitrogen fixation
2. nitrification
3. ammonification
4. denitrification
15
New cards
keystone species
if they don’t exist their ecosystem will collapse
16
New cards
earth’s system
biosphere- all parts where life exists
hydrosphere- all waters on earth’s surface like lakes and seas and sometimes clouds
atmosphere- gases that surround the earth
lithosphere- outer part of earth and the crust and upper mantel
hydrosphere- all waters on earth’s surface like lakes and seas and sometimes clouds
atmosphere- gases that surround the earth
lithosphere- outer part of earth and the crust and upper mantel
17
New cards
scavengers
the first level of decomposers
\-consumes decaying organisms left behind
vultures
\-consumes decaying organisms left behind
vultures

18
New cards
detrivore
\-second level of decomposers
feeds on dead decaying organisms
\-earth worms, dung beetles
feeds on dead decaying organisms
\-earth worms, dung beetles

19
New cards
saprotroph
\-3rd level of decomposers
\-decompose dead decaying matter into soil nutrients
\-fungi, protozoans
\-decompose dead decaying matter into soil nutrients
\-fungi, protozoans

20
New cards
heterotroph
depend on autotrophs for nutrition (other organisms)
\-consumers, decomposers
\-consumers, decomposers
21
New cards
autotroph
depends on itself for nutrition
\-photosynthetic, chemosynthetic
\-photosynthetic, chemosynthetic
22
New cards
exponential growth
keeps increasing
23
New cards
logistic growth
when the populations growth rate decreases as it approaches k (carrying capacity) which is caused by limiting factors
24
New cards
hydrologic cycle
cycle of water in earth-atmosphere system
1. evaporation
2. condensation
3. precipitation
4. collection
1. evaporation
2. condensation
3. precipitation
4. collection
25
New cards
pyramid of biomass
model of total living biomass/organic matter in each trophic level of an ecosystem
26
New cards
system
collection of elements or components that are organized for a common purpose.
27
New cards
herbivore effect
when an herbivore eats a specific type of plant and the plant populations density goes down
28
New cards
chemosynthesis
synthesis of organic compounds by bacteria/organisms using energy from chemicals without sunlight
29
New cards
population dispersion
\-clumped
\-uniform
\-random
\-one of the key 3 features of a population (dispersion, size, growth rate)
\-uniform
\-random
\-one of the key 3 features of a population (dispersion, size, growth rate)
30
New cards
greenhouse effect
way in which heat is trapped close to earth’s surface by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and water vapor (too much causes global warming)
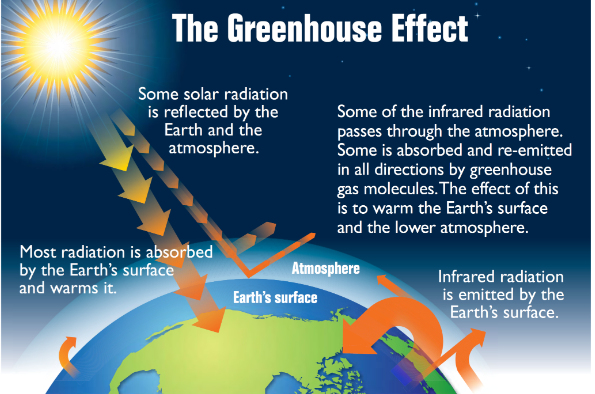
31
New cards
population growth rate factors
\-immigration
\-emmigration
\-birth rate (natality)
\-death rate (mortality)
\
\-emmigration
\-birth rate (natality)
\-death rate (mortality)
\
32
New cards
limiting factors
limits populations size and slows/stops it from growing
\-density dependant: disease, competition and predation
\-density independent: hurricanes, pollutants, food limitation
\-density dependant: disease, competition and predation
\-density independent: hurricanes, pollutants, food limitation
33
New cards
eutrophication
harmful algal blooms caused by when the environment is enriched with nutrients caused by too much fertilizer
34
New cards
runoff
\n The meandering stream of water from the mountains to the water bodies after precipitation
35
New cards
3 major climatic regions of earth
\-polar
\-temperate
\-tropical
\
\-temperate
\-tropical
\
36
New cards
realized niche
when an animal is forced to change it’s niche

37
New cards
fundamental niche
the conditions which an animal can survive and reproduce

38
New cards
biomagnification
concentrations of toxins in an organism that came from ingestion of other organisms
39
New cards
phosphorus cycle
cycle of transformation and relocation of phosphorus in soil, water and living/dead organisms/material
\-weathering
\-absorption by plants
\-absorption by animals
\-return through envrionment by decomposition
(no atmosphere)
\-weathering
\-absorption by plants
\-absorption by animals
\-return through envrionment by decomposition
(no atmosphere)
40
New cards
system
\-has 2+ interacting parts
\-has 3 components: input, processing, and output
\-there are two types: negative and positive feedback loop
\-has 3 components: input, processing, and output
\-there are two types: negative and positive feedback loop
41
New cards
negative feedback loop
brings back stability
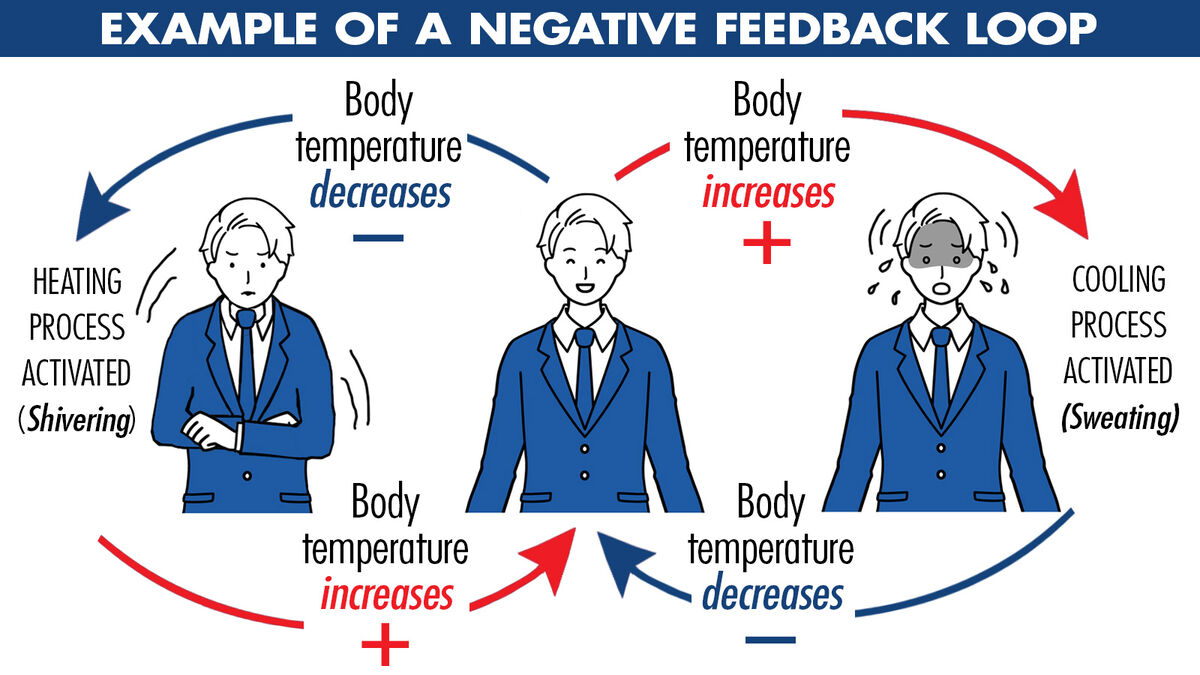
42
New cards
positive feedback loop
reinforces what’s happening
43
New cards
invasive species
\-not native
\-cause harm
\-pests
\-harm human resources
\-cause harm
\-pests
\-harm human resources
44
New cards
population density
\-The measure of a pop. per unit area/volume
\-larger animals have lower population density due to needing more resources
(# of individuals) divided by (amount of space occupied) = population density
\-larger animals have lower population density due to needing more resources
(# of individuals) divided by (amount of space occupied) = population density
45
New cards
density dependent factors
biotic factors in the environment that increase with population size
\-disease
\-competition
\-parasites
\-disease
\-competition
\-parasites
46
New cards
density independent factors
abiotic factors in the environment that affect the environment despite it’s density
\-temperature
\-weather
\-temperature
\-weather
47
New cards
classes of organisms
\-generalists (broad choice of food), opposum
\-specialist (narrow range of food), koala
\-specialist (narrow range of food), koala
48
New cards
primary succession
**-pioneer stage**
1. exposed bare rock, there’s no soil to start
2. elements like wind and water create a bit of soil
3. lichens start to grow and chemically weather rock to make more soil
4. mosses and herbs start growing so insects, worms and birds come
**-intermediate stage**
1. moss and it’s community die/decompose, making more soil
2. bigger herbs and small shrubs start growing
3. big insects, small herbivores, carnivores, and large birds come.
4. more soil forms due to decomposition.
**-Climax**
1. Maximum decomposition, huge amount of top soil
2. Due to the canopies of large trees top predators start to live there
3. This all leads to a climax community
1. exposed bare rock, there’s no soil to start
2. elements like wind and water create a bit of soil
3. lichens start to grow and chemically weather rock to make more soil
4. mosses and herbs start growing so insects, worms and birds come
**-intermediate stage**
1. moss and it’s community die/decompose, making more soil
2. bigger herbs and small shrubs start growing
3. big insects, small herbivores, carnivores, and large birds come.
4. more soil forms due to decomposition.
**-Climax**
1. Maximum decomposition, huge amount of top soil
2. Due to the canopies of large trees top predators start to live there
3. This all leads to a climax community
49
New cards
Climax community
all the species an ecosystem can support in a balanced state
50
New cards
Secondary succession
* **pioneer stage**
\-soil is already presents, seeds are already in soil.
\-water comes and seeds sprout out
\-insects and worms come in
\-small birds visit
\-mosses and ferns grow abundantly.
* **Intermediate stage**
1. more herbs start growing
2. small herbivores and carnivores start to live there
3. biggger herbivores and carnivores come
4. more shrubs and small trees grow
* **Climax**
1. ecosystem flourishes
2. large trees shrubs and animals come to live there
3. climax community
\
\-soil is already presents, seeds are already in soil.
\-water comes and seeds sprout out
\-insects and worms come in
\-small birds visit
\-mosses and ferns grow abundantly.
* **Intermediate stage**
1. more herbs start growing
2. small herbivores and carnivores start to live there
3. biggger herbivores and carnivores come
4. more shrubs and small trees grow
* **Climax**
1. ecosystem flourishes
2. large trees shrubs and animals come to live there
3. climax community
\
51
New cards
ammonia/ammonification
a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen NH3
* nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas into ammonia
* in ammonification organic compounds in plant/animal matter are broken down, released as ammonia
* nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas into ammonia
* in ammonification organic compounds in plant/animal matter are broken down, released as ammonia
52
New cards
dentrification
the conversion of nitrates (NO3) into nitrogen gas (N2)
* reduces the amount of nitrogen that plants and animals can use
* can remove nitrogen from water and release into the atmosphere as N2
* reduces the amount of nitrogen that plants and animals can use
* can remove nitrogen from water and release into the atmosphere as N2
53
New cards
Nitrate/nitrification
ion made up of nitrogen and oxygen (NO3)
* add ammonia and oxygen to make nitrates
* plants convert nitrates to ammonia to make DNA and ammino acids
* add ammonia and oxygen to make nitrates
* plants convert nitrates to ammonia to make DNA and ammino acids
54
New cards
Nitrifying bacteria
Convert ammonia to nitrites or nitrates
* two types:
1. ammonia nitrifying bacteria, which add oxygen and ammonia (NH3) to make nitrites (NO2)
2. nitrite nitrifying bacteria which add oxygen to nitrites (NO2) and make nitrates (NO3)
* this is the nitrification step of the nitrogen cycle
* two types:
1. ammonia nitrifying bacteria, which add oxygen and ammonia (NH3) to make nitrites (NO2)
2. nitrite nitrifying bacteria which add oxygen to nitrites (NO2) and make nitrates (NO3)
* this is the nitrification step of the nitrogen cycle
55
New cards
nitrite
* NO2
* made up of nitrogen and oxygen
* nitrifying bacteria combine oxygen and ammonia to make nitrites
* made up of nitrogen and oxygen
* nitrifying bacteria combine oxygen and ammonia to make nitrites
56
New cards
nitrogen fixing bacteria
convert N2 into ammonia NH3
57
New cards
importance of biodiversity
* genetic diversity
* protect freshwater resources
* fast recovery from natural disasters
* maintains balance in ecosystems
* sustainability and growth
* provision of food security
* adaption to different habitats
* provision of biological resources
* promote soil formation and protection
* maintains food chain in nature
* protect freshwater resources
* fast recovery from natural disasters
* maintains balance in ecosystems
* sustainability and growth
* provision of food security
* adaption to different habitats
* provision of biological resources
* promote soil formation and protection
* maintains food chain in nature
58
New cards
benefits of biodiversity
increases stability and resilience of ecosystems
benefits agriculture
benefits economy through tourism
provides rich environment with medicine
benefits agriculture
benefits economy through tourism
provides rich environment with medicine
59
New cards
conserving biodiversity
* halt human induced extinctions
* recover species populations
* stop unsustainable wildlife exploitation and trade
* protect habitats
* recognize indigenous people land and water rights
* transition to sustainable practices in agriculture, fishing, forestry
* recover species populations
* stop unsustainable wildlife exploitation and trade
* protect habitats
* recognize indigenous people land and water rights
* transition to sustainable practices in agriculture, fishing, forestry
60
New cards
biodiversity problems
1. massive destruction of natural spaces
2. catastrophic loss of species and diversity of life
3. unsustainable production in consumption of nature’s resources
61
New cards
biodiversity
variety of life on earth at all its levels
62
New cards
weather vs climate
weather: short term atmosphere pattern that can change quickly (minutes, hours)
climate: long term weather pattern that changes over time (years)
climate: long term weather pattern that changes over time (years)
63
New cards
phases of logistic population growth
3rd; plateua phase
* no growth
* limiting factors balance the populations capacity to increase
* population reaches k of environment
* no growth
* limiting factors balance the populations capacity to increase
* population reaches k of environment

64
New cards
whats competitive exclusion
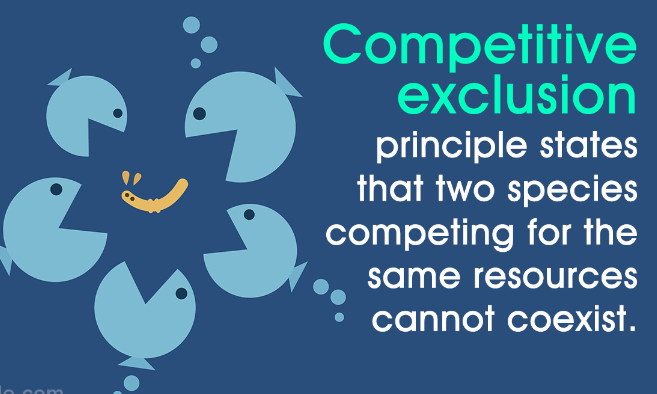
65
New cards
gross primary productivity
net primary productivity
net primary productivity

66
New cards
interspecific competition
between different species
67
New cards
intraspecific competition
same species