Topic 5 - Energy Changes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is an exothermic reaction?
An exothermic reaction is one which transfers energy to the surroundings. This results in a rise of temperature.
What are some examples of exothermic reactions?
Combustion - Burning fuels
Neutralisation - Acid + Alkali
What is the reaction profile for an exothermic reaction?
See Image:
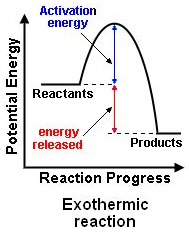
What is an endothermic reaction?
An endothermic reaction is one which takes in energy from the surroundings. This results in a fall of temperature.
What are some examples of endothermic reactions?
Citric acid + Sodium hydrogencarbonate
Thermal Decomposition
What is the reaction profile for an endothermic reaction?
See Image:
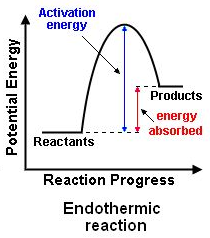
Required Practical: How can energy transfer be measured?
Measure the amount of energy released in a neutralisation reaction:
Put 25cm³ of chosen acid in a polystyrene cup.
Place a thermometer in the cup.
Measure the start temperature.
Get a chosen metal or carbonate.
Add the metal/carbonate and stir.
Take the highest/lowest temperature in the reaction.
Repeat steps with other metals/carbonates.
What reaction is bond breaking and bond forming?
Bond Breaking - Endothermic
Bond Forming - Exothermic
What is the format of a bond energy calculation?
You are given a reaction: H-H + Cl-Cl → H-Cl H-Cl
You are given the bond energies: H-H: 436 Cl-Cl: 242 H-Cl: 431
First find the energy needed to break the bonds:
(1 x H-H) + (1 x Cl-Cl) = 436 + 242 = 678
Then find the energy released by forming new bonds:
(2 x H-Cl) = 2 × 431 = 862
Then use (Overall = energy required - energy released) to find the overall energy change:
678 - 862 = -184 kJ/mol
If it is negative it is exothermic.
If it is positive it is endothermic.
Explain chemical reactions in a cell?
It is a system made up of two different electrodes in contact with an electrolyte. The two electrodes are metals that conduct and the electrolyte is a liquid that contains ions which react with the electrodes.
The chemical reaction between the electrodes and the electrolyte set up a charge difference between the electrodes. If the electrodes are then connected by a wire, the charge s able to flow and electricity is produced.
The type of electrodes affect the voltage. A higher difference in reactivity creates a higher voltage.
A battery is formed by connecting two or more cells together in series.
Explain a non-rechargeable cell?
Explained: The chemicals are used up and are irreversible. Once one reactant is used up no electricity is produced.
Examples: Alkaline Batteries.
Advantages: Cheap.
Disadvantages: They need replacing, They need to be recycled.
Explain a rechargeable cell?
Explained: They produce electricity in the same way as non-rechargeable cells. The reaction is reversed when connected to an external electric current.
Examples: Lithium-Ion Cells.
Advantages: The reaction can be reversed to produce electricity again, Used multiple times.
Disadvantages: They need to take time to be recharged, They lose electricity after each recharge cycle.
Explain a fuel cell?
Explained: A cell that uses fuel, oxygen and energy from the reaction to produce electrical charge. It uses a redox reaction to produce a product.
Examples: Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cells.
Advantages: They produce electricity for as long as you provide hydrogen, They stay the same efficiency over time.
Disadvantages: Hydrogen is explosive and hard to store, It produces a relatively low amount of electricity.