Organic 1b Topic 5
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Other Carbonyl Functionalities
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound:
The C=C bond is electrophilic
The C=O bond is electrophilic
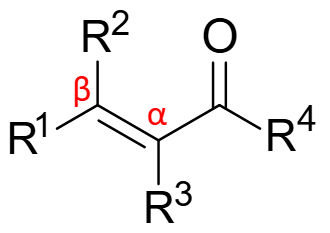
α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are …
ambident electrophiles
What is an ambident electrophile?
A species which is electrophilic at more than one point and can react through different sites depending on the reaction conditions
What are the conditions for two double bonds in a diene to be conjugated?
double bonds must be separated from each other by a single bond
the π-MOs in each double bond must be able to overlap
Conjugated dienes tend to generate new … which can be viewed as new …
MOs, frontier orbitals
What are the two manners in which a nucleophile can add to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound?
1,2 addition and 1,4 addition
The β-carbon of the alkene acts as a …
soft electrophile
The carbonyl carbon acts as a …
hard electrophile
1,2 addition results in addition to the …
carbonyl carbon
1,2 addition can be effected by a …
hard nucleoohile
Why do hard nucleophiles attack the carbonyl carbon preferentially?
Hard nucleophiles are smaller and more able to attack the congested/sterically hindered carbonyl group.
1,4 addition results in addition to the …
β-carbon of the alkene
1,4 addition can be effected by a …
soft nucleophile
Why do soft nucleophiles attack the β-carbon of the alkene preferentially?
Soft nucleophiles are larger and less charged, so it is easier for them to attack the less sterically hindered carbon. The MO of the alkene functional group is more diffuse on this carbon.
Examples of hard nucleophiles include:
hydroxide ion
fluoride ion
cyanide ion
Grignard reagents
Examples of soft nucleophiles include:
sulfur-based nucleophiles (RS-, RSH)
secondary amines
benzene
alkene
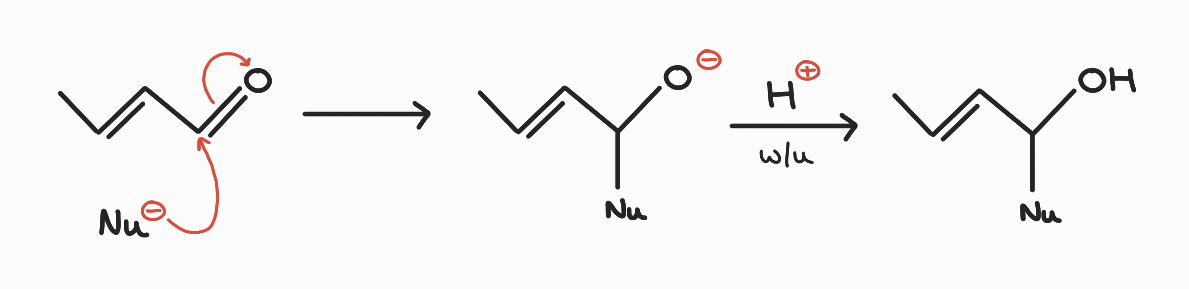
1,2 addition mechanism:
Nucleophile attacks at carbonyl carbon. Negative charge accommodated on carbonyl oxygen. Acidic work-up neutralises negative charge to produce alcohol functionality.
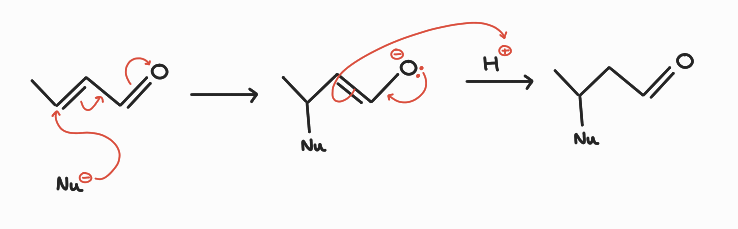
1,4 addition mechanism:
Nucleophile attacks at the alkene carbon. Movement of electrons through π system. Negative charge accommodated on carbonyl oxygen. Addition of a proton across the new double bond, carbonyl double bond regenerated.
Hard nucleophiles and electrophiles are …
small, highly polarised species
Soft nucleophiles and electrophiles are …
larger, more diffuse species
The cyanide anion can react with … to form …
aldehydes and ketones, cyanohydrins
The cyanohydrin is formed via the rapid and reversible … reaction and is the … product
1,2 addition, kinetic
Conjugate addition of the cyanide anion is … because the nucleophile attacks at the β-carbon
slower
1,4 addition of the cyanide anion affords the … product, which is more stable due to the retention of the … bond
thermodynamic, C=O
Performing the reaction with the cyanide anion under kinetic conditions promotes … and achieves … addition
irreversibility, 1,2P
Performing the reaction with the cyanide anion under thermodynamic conditions achieves … addition
1,4
Organolithium reagents and Grignard reagents are … nucleophiles
hardO
Organocuprate and zinc reagents are … nucleophiles
soft
Organocuprates are synthesised …
in situ
Organocuprates are formed by reacting the appropriate organolithium or Grignard reagent with …
Cu(I)Br
Acetals are readily … under … to the corresponding alcohol and aldehyde or ketone
hydrolysed, acidic conditions
The presence of an aldehyde or ketone can present a … as they are reactive …
chemoselectivity problem, electrophiles
Acetals can be used as a …
protecting group
Imines are formed by the … of a … with an …
condensation, primary amine, aldehyde or ketone
The reaction to form an imine requires the addition of a … catalyst
mild acid
… conditions are needed to produce an imine
dehydrating
Imines are … electrophilic than aldehydes or ketones
less
Imines react similarly to carbonyls, with … conditions
more forcing
Imines can be protonated to generate … ions which are more …
iminium, electrophilic
Why is the nucleophilic substitution of alkyl halides with amines problematic?
It can often result in overalkylation as the amine afforded by the first substitution is more nucleophilic than the starting material.
Imines can be used to produce amines in a process called …
reductive amination
The reducing agent used to reduce imines is called …
sodium triacetoxyborohydride (Na(OAc)3BH)
The reaction of an … with an … to form an amide is very slow
ester, amine
In order to produce an amide, an … must be generated in situ from the acid before the amine is added
activated ester
To convert a carboxylic acid to an acid chloride, add …
thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
To convert a carboxylic acid to a thioester, add …
coenzyme A