PSY342 Exam 1
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
why study women's psychology, mortality/morbidity, heart disease, autoimmune disorders, cancer, menstruation/menopause + readings
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
health psychology
examine the influence and relationship between psychological factors (behavior, emotion, cognition, etc.) and health
what is the #1 major cause of death in men and women?
heart disease
what is a major issue in research?
women are majorly excluded from research
our understanding of diseases is majorly of male prevalence, presentation, course and treatment
female presentations are seen as atypical
there’s also less funding for research on diseases that more women are sick with
how do cultural forces impact the lower participation of women in exercise?
seeing sick/frail/thin/delicate women as attractive
attractive/modest female clothing sacrificing ease of movement (high heels, tight dresses, lonf skirts etc.)
safety concerns of women going out to exercise alone
what is the self-fulfilling prophecy seen with women and exercise?
expectations of women being weak → barrier to sports/exercise → women don’t exercise and are weak
title IX
a law passed in 1972 that bars sex discrimination
lead to an increase in women participation in sports/education
why are women excluded from research?
fear of hormones fucking up drug tests
researchers fearing that women will get pregnant during clinical trials
women’s health initiative (WHI)
a series of clinical studies done over 15 years by the national institute of health (NIH)
done to address major health issues in postmenopausal women
discovered the real impact of hormones (endogenous estrogen protects from heart disease, but exogenous estrogen raises heart disease and cancer rates)
what changes are suggested to change the second-class treatment women receive from the healthcare system?
practitioners need to learn to respect all patients
women need to be included in research
how do women in pain get treated by doctors?
doctors attribute their pain to hysterics and psychological causes
thought to be complaining
WOC are dismissed even more
gender and racial disparities in life expectancy
the average female life expectancy is longer than male
American Indian/Alaskan Native and Black life expectancy is lower than White expectancy, while Hispanic and Asian life expectancy is higher
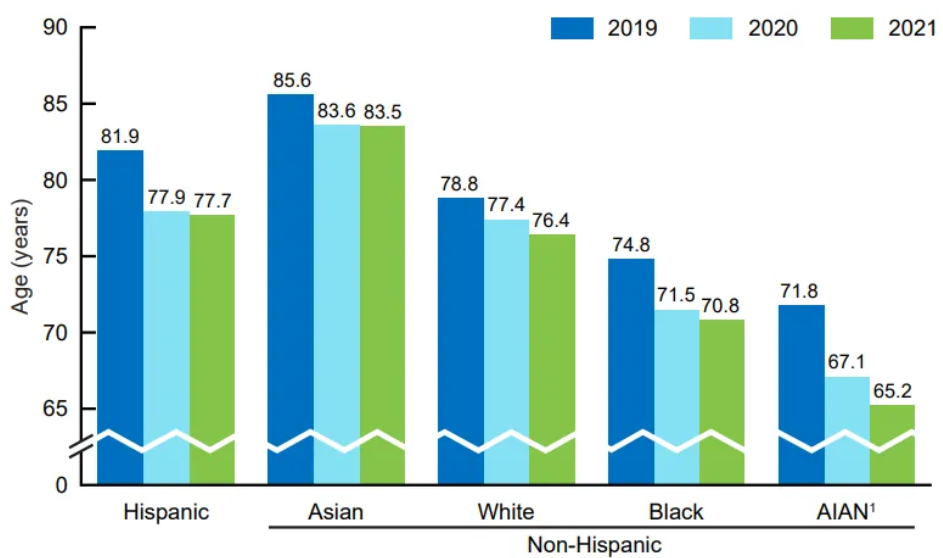
racial disparities in maternal mortality
American Indian/Alaskan Native maternal mortality is the highest
Black/Hispanic maternal mortality is higher than White
Asian maternal mortality is the lowest
morbidity
rates of people living with an illness
has been increasing over time, as less people are dying and living to older ages
women have higher morbidity rates than men
sex differences in morbidity
women perceive their subjective health (perception of one’s own health) as worse than men
women use healthcare more than men
boys use healthcare more than girls, but this reverses in adolescence
women have higher morbidity rates
biological explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
extra X chromosome gives females a chance to become recessive for a genetic disease
estrogen thought to be a protective factor
women thought to be more resistant to infections than men
however, they’re more vulnerable to autoimmune diseases
artifact explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
artifacts are factors that might cause a “fake” difference in health
healthcare providers respond to female patients different than male patients
who is more likely to be prescribed psychological drugs and why?
female patients, due to:
more psychological distress in females
doctors attributing women’s complaints to psychology
women requesting psychological drugs more
men being under-prescribed psychological drugs
smoking explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
men are more likely to smoke
smoking causes more damage to the lungs for women than men
women are less likely to quit smoking when they start
what is heavy alcohol use associated with?
a variety of diseases (heart disease, cancer, cirrhosis, etc.)
aggressive behavior leading to death
drunk driving, suicide, homicide, sexual assault
economic/social consequences (losing a job, losing a relationship, etc.)
physiological consequences
alcohol usage causes more damage to women’s livers
alcohol use explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
alcohol use is more diagnosed in men
antidepressant explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
men use more drugs than women at all ages (except antidepressants, tranquilizers, and sedatives)
women use those 3 drugs more often
obesity/overweight explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
obesity is a risk factor for heart disease and cancers, and predisposes one to other risk factors
the economic/social consequences of obesity are more damaging for women than men
e.g. higher risk of poverty
exercise explanations (gender differences in mortality/morbidity)
exercise is important in reducing risk of many diseases
women, especially WOC, are less likely to engage in physical activity than men at all ages
women are also more prone to gain weight during marriage, after childbirth, and during menopause
why do women survive better than men?
onset of disease: men tend to have earlier onset of diseases
women’s immune systems are better built and are more intense
women don’t die from sickness/illness as easily
medical gaslighting
term used by patients who felt their symptoms were inappropriately dismissed as minor or primarily psychological by doctors
experienced more by women, especially WOC
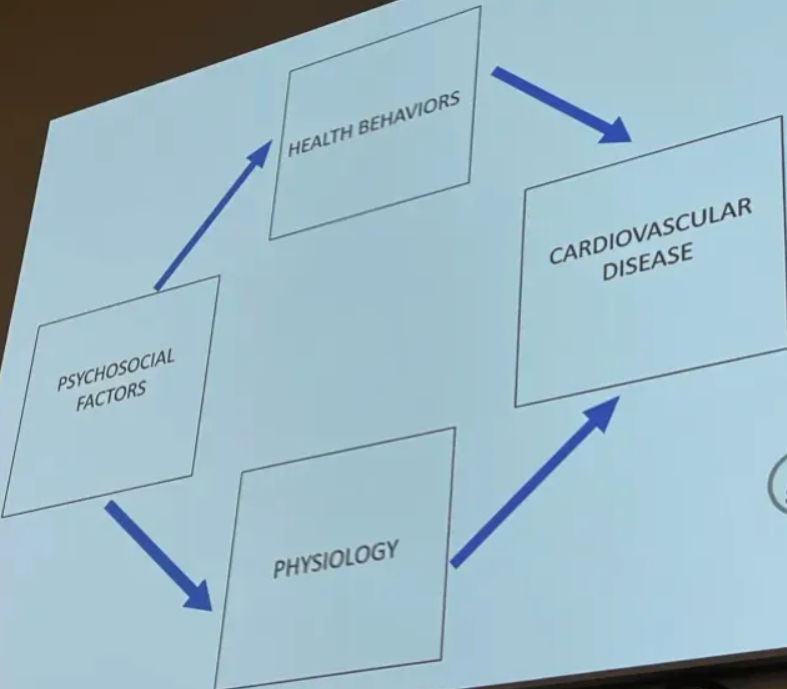
mediators
kind of middle “middle ground” factors that help explain the effect of one variable on an outcome
e.g. the mediators between psychological factors and cardiovascular disease are physiology and health behaviors
how does age affect heart disease?
the incidence of heart disease increases with age
this increase is greater for women in menopause
factors that affect cardiovascular health
family history
obesity (stronger impact on women than men)
smoking (stronger impact on women than men)
estrogen (cardio-protective factor)
estrogen impacts on women
estrogen is a protective factor of heart disease, but a risk factor for breast cancer
due to women in menopause getting heart disease more, women were prescribed estrogen pills
not until a study revealed that exogenous estrogen does nothing for heart disease and increases the risk for breast cancer did the pills get pulled off the shelves
psychosocial risks of heart disease
stress
high-damnd jobs, and especially if there’s work waiting for them at home, is the riskiest schedule to have
hostility
social isolation
depression
lower SES
has an inverse correlation with cardiovascular disease cross-culturally
men physiologically react higher to stress than women, which might explain the higher prevalence of heart disease in men
hostility
a stable tendency to become angry
raises risk of cardiovascular disease by the following:
health behaviors: more caffeine, tobacco, substance, and calorie consumption
physiology: high levels of stress hormones + higher reactivity to stressors
racial disparities in hypertension
in the US, black populations have more prevalence of hypertension
this isn’t seen in African populations, so it’s just the US being it’s racist thing
gender disparities in symptom/diagnosis of heart disease
symptoms
women have different symptoms of a heart attack than men
most common symptoms are extreme/unexplained fatigue, shortness of breath
results in:
women delaying seeking help during a heart attack
doctors delaying in examining women + less likely to refer them to the hospital
diagnosis:
a lot of tools used to diagnose CVD were originally designed for men and are not as effective in women
gender disparities in treatment of heart disease
men: most commonly treated surgically
due to:
women’s hearts being smaller in size and harder to operate on
depression is common in women following a heart attack, which makes surgery recovery harder
women: most commonly treated pharmacologically
cardiac rehabilitation
programs focused on promoting positive health behaviors following CVD
women are less likely to be referred to and stay in these programs
there are cardiac rehab programs specific to women
women are 3x less likely to die in these programs
autoimmune disorders
disorders where the immune system acannot differeniate between the self and non-self and attacks body’s own cells
e.g. multiple csclerosis, lupas, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
why are autoimmune disorders challenging?
difficult to diagnose properly
unpredictable and unique symptoms
autoimmune disorders are progressive + not curable
the treatment side-effects are hard to cope with
many people are unfamiliar/uninformed about them
etiology
study of the cause of the disease
epidemiology
study of the spread of the disease
gender disparity in autoimmune disorders
a lot of women have these disorders
they are thought to be caused by hormones or the menstrual cycle (women who have less pregnancies are more at risk for autoimmune disorders)
age of autoimune disorders
autoimmune disorders tend to strike in mid-life (30s-50s)
can lead to harmful stigmas about people with autoimmune disorders in their midlife not being able to perform
are autoimmune disorders genetic or environmental?
thought to have a genetic contribution that is triggered by environmental factors
stress can exacerbate autoimmune symptoms, as we know that stress suppresses the immune system
issues in patient/physician interaactions in autoimmune disorders
studies show providers often don’t cooperate with/believe/trust female patients and their complaints
the assumption that the provider is more knowledgeable is ineffective for getting a diagnosis
women who ask a lot of questions/complain a lot seen as uncooperative
how do autoimmune disorders impact work/family roles?
men:
more likely to return to the workforce
women:
experience higher divorce rates than men
how to autoimmune disorders affect body image/sexuality?
autoimmune symptoms affect pateint’s appearance and mobility
treatments often lead to weight gain
sexual dysfunction as a result of the disorder
how do poverty and stress affect autoimmune disorders?
conditions from being in poverty can exacerbate symptoms, such as:
stress from limited finances
uncontrollable events + daily hassles
unsanitary living/working conditions
less access to good healthcare
how does social support affect autoimmune disorders?
social support is good for:
mental health
practical help (taking care of responsibilities, transportation to appointments, etc.)
some social support groups exist for autoimmune disorders, but they are predominantly white and middle/upper class
excludes minorities
posiitve reappraisal
focusing on finding something positive within a bad situation
a strategy uadherence in autoimmune disorderssed by autoimmune disorder patients
adherence in autoimmune disorders
adherence is difficult in autoimmune disorders because of:
complex ass instructions
multiple prescribed medicines
many appointments/referraks
need to change to lifestyle
belief systems like fatalism can also make adherence harder
fatalism
a belief system that everything that happens to a person, good or bad, was meant to be
can made adherence to treatment of various diseases hard
cancer
the rapid and uncontrolled multiplication and spread of abnormal cells
theres many types of cancers and a lot of variability in how they interact/are caused
what is the most common type of cnacer among women?
breast cancer
which cancer is responsible for the most deaths?
lung cancer
which health behaviors would cause a reduction in 50% of cancer deaths?
stopping the use of tobacco
limiting exposure to second-hand smoke
limiting heavy alcohol use
nutrition-related health behaviors related to cancer
obesity increases risk
unhealthy/poor diet includes ovarian hormones, which could be a mediator to getting cancer
staurated/animal fat is a risk factor
meanwhile., omega 3 fats/fiber are protective of cancer
natural killer cells
cells in the body that control tumor growth
high stress + insufficient social support = lower levels of these cells
greater emotional support = higher levels of these cells
what is the hormone theory of cancer?
this theory states that the total number of ovulatory cycles a woman has determines her risk for breast cancer
because every cycle, the breast tissue is flooded by ovarian hormones
evidence for this theory is the following women have higher incidences of breast cancer:
women whos tart menstruating earlier
women who enter menopause later
women who have few/no children
what are the 2 genes that contribute to breast cancer?
BRCA1 and BRCA2
these 2 genes contribute to the genetic factor of cancer, but only 10% of people with these genes actually develop breast cancer
suggests that the environment plays a big role
human papillomavirus (HPV)
a virus that causes cervical cancer
gender disparity in cancer incidence
women were always at a lower risk of getting and dying of cancer
gender differences in lifestyle/behavior contributing to cancer
work and stress (women have second shift at home
discrimination (ssexism for women)
risky behavior (men more likely to engage in this)
sunscreen (more women use)
eating patterns (men eat more high fat, women eat more vegetables/fruits)
culture
shared understandings of food, activities, values, attitudes, etc.
culture impacts health behaviors and risk factors
gender disparities in poverty
women are more likely to live below the poverty line than men
affects their access to medical care and other high-cost things
racial differences in health behaviors health behaviors affecting cancer
white women tend to use more alcohol
Native American + white women smoke more
African-American and white women consume more fat
white women c
how does immigration affect cancer risk?
immigrants who come to America adopt American diets which is hella unhealthy and bad
e.g. latin-american/Asian women have healthier diets before adopting America’s
how does poverty affect cancer rates?
lower paying jobs associated with exposure to carcinogens
lower access to good medical care
less education associated with more obesity, less exercise, and more smoking
some reasons why heart disease is different for women?
heart attack symptoms more subtle (women less likely to experience straight up chest pain)
women have many different types of heart disease
women patients take longer to get to the hospital
everyday stress affect women’s hearts more
doctors are less likely to dicuss women’s heart risks
tools don’t work as well in women (e.g. implanted defibrillators)
why do women delay seeking shelp for their heart attack symptoms?
obscure symptoms (not straight up chest pain)
belief that women aren’t as vulnerable to heart attacks as men
women having heart attacks later in life
social gradient
the trend of mortality/morbidity increasing as social status decreases
what were 3 health strategies valued by women in that one reading we did about how women are treated with heart disease?
supporting give and take in relational connections
being listened to = good
identifying/acknowledging unique health-promoting behaviors
providers dismissed how maintaining housework could be beneficial for patients
focusing on empowerment
being dismissed in the health care system reinforced sex discrimination women face
zon’t zo it
according to the readings, what were some of the theories for the sex discrepancy in autoimmune disorders?
X chromosome has more genes related to autoimmune functioning
women have smart af immune systems to fight antigens without killing a fetus
placenta makes powerful anti-inflammatory hormones
sedentary lifestyles cause this
complex interactions of all of these combined
what is the relationship between age and cancer?
as one gets older, the risk fo contracting most cancers increases
health behaviors performed early in life can increase or decrease this risk
what is the relationship between depression and cancer?
depression + symptoms are common in people with cancer
a lot of MDD criteria and cancer treatment side-effects overlap, making diagnosing hard in patients with cancer
depression can lower adherence to treatment
in what 3 parts of life is anxiety common for people with cancer?
when waiting for test results/to receive a diagnosis
when in active cancer treatment
when a person with cancer is in remission
how do women adjust to life after finishing cancer treatment?
after around 2 years, women who completed treatment have similar quality of life as to people who didn’t experience cancer
yippie
common physical symptoms of cancer/treatment?
fatigue (recall the coined term “cancer fatigue”")
insomnia
physical pain (especially after surgery)
sexual-reproductive concerns of cancer
cancer treatments can cause women to enter menopause early/become infertile
poses concerns about having children, especially since cancer in younger women has been on the rise
social effect/influences on cancer
cancer declines the amount of social relationships women have
women get good social support during the beginning stages of cancer, but that support deteriorates over time
and we know social loneliness is a risk factor and not good
a cancer diagnosis affects not only the patient but everyone in her close circle
benefit finding (post-traumatic growth)
phenomenon of people who experience cancer to find positive things during their diagnosis/treatment
e.g. being more grateful, finding relationships to be more meaningful/pleasurable, etc.
what are the most adaptive ways of coping with cancer?
problem-focused coping: focusing on the problem itself
accepting the reality of one’s situation (not avoiding/denying diagnosis)
expressing cancer-related emotions
pap smear
a preventative screening tool for cervical cancer
mammogram
a preventative screening x-ray of the breasts for breast cancer
what are the 3 stages of prevention as described by Dr. Iris Granek?
primary prevention
health behaviors, vaccinations, preventative meds like folic acid supplements for pregnant women
secondary presentation
early detection via screening
tertiary prevention
preventing further negative effects of the disease
arrythmias
irregular heartbeats
stroke is a risk factor for this
a type of heart disease
stroke
a type of heart disease where there’s a blood clog in the brain, preventing circulation in the brain
2 types:
embolic stroke: which is a clog
hemorrhagic stroke: a weakness in the blood vessel
coronary heart disease (CHD)
type of heart disease where there’s a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, leading to shitty circulation of stuff to the cardiac muscle and surrounding tissue
what are the risk factors in the female body of heart disease?
smaller blood vessels
caregiver responsibilities delaying prevention/treatment for heart disease
what is the #1 cancer killer in men and women?
lung cancer
what is the most prevalent form of cancer among women?
breast cancer
gender disparities in heart attack diagnoses and deaths
men:
have higher prevalence of heart attacks (diagnosed)
women:
have lower prevalence of heart attacks (diagnosed)
more likely to die from a heart attack
due to being diagnosed older
what does the reading Psychology, men, and cancer suggest to reduce population-level differences?
population-level differences call for population-level interventions
also, making sure these interventions are gender non-specific
e.g. societal ban on smoking indoors to reduce lung cancer
menarche
the onset of menstruation in female bodies
usually around 12-13 years of age on average
what is a recent trend we’ve been seeing around the world regarding menstruation?
the age of menarche, amount of people with irregular cycles, and development of secondary sex characteristics (e.g. breasts) is decreasing
a substantial # of girl bodies are starting to menstruate before 11
especially for WOC and girls of lower SES
what are some of the reasons for the trend of earlier menarche happening around the world?
exposure to hormonal disruptors (from poor diet, BPA/chemicals in plastic, etc.)
rising obesity rates
exposure to sexualized stimuli
stress (chronic, discrimination, trauma, abuse, etc.)
how does early menarche impact attitudes of the person menstruating?
insufficient preparation for starting their period + having an earlier menarche → girls having more negative attitudes towards their periods → leads to more physical symptoms during menstruation
PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
there is no consensus on how to define PMS, what its causes are, what the treatments are, or whether it really exists
the idea of “PMS” is separate from physical symptoms of abnormal menstruation, such as dysmenorrhea and endometriosis
dysmenorrhea
painful menstruation; NOT PMS!
endometriosis
chronic disease where endometrium (uterus tissue) is found outside the womb
associated with very painful menstruation
no definitive etiology (cause)
how do studies define PMS?
negative emotions, behaviors, and sometimes physical symptoms happening only during the luteal phase