Animal Biology Practical 2- Echinodermata & Chordata
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Asteroidea
________ arms are not sharply distinct from central disc
Ophiuroidea
_________ arms sharply distinct from central disc
Echinoidea
___________ body without arms
Holothuroidea
____________ body elongated in mouth to anus axis
Echinoidea
______________ body is globular with movable spines
Asteroidea
_______________ oral surface oriented toward ground
Holothuroidea
_____________ madreporite is internal
Echinoidea
___________ madreporite is aboral
Ophiuroidea
_____________ madreporite is oral
Crinoidea
_____________ madreporite is absent
Crinoidea
______________ mouth surrounded by branched tentacles
Echinoidea
___________ ossicles fused to form a hard test
Crinoidea
_______________ stalk present in most species
no cephalization, pentaradial symmetry, calcareous endoskeleton, water vascular system, most dioecious
Key characteristics for Phylum Echinodermata
complete
Phylum Echinodermata digestive system
none, metabolic waste diffused through tube feet
Phylum Echinodermata excretory system
most have separate sexes, external fertilization
Phylum Echinodermata reproductive system
Asteroidea
which class has tube feet with suckers
Asteroidea
which class is a carnivorous predator?
locomotion, prey capture, and respiration
Class Asteroidea tube feet (podia) function
filter & bring water into the water vascular system; regulate water pressure within water vascular system
Class Asteroidea Madreporite function
protection
Class Asteroidea Spines function
digestion; consumption of prey
Class Asteroidea cardiac stomach function
each controls one tube foot by pushing water into or pulling water out of it
Class Asteroidea ampullae function
reproduction
Class Asteroidea gonad function
extracellular digestion
Class Asteroidea tube pyloric ceca (digestive glands) function
Ophiuroidea
Which class has 5 arms used for locomotion?
Ophiuroidea
Which class has tube feet suckers NOT used for locomotion?
Echinoidea
__________ move via coordinated effort of their tube feet, powered by their water vascular system
locomotion
Class Echinoidea tube feet (podia) function
chewing food
Class Echinoidea aristotle's lantern function
protection; can assist with locomotion
Class Echinoidea spines function
Crinoidea
Which class has five flexible branched arms?
1. notochord
2. dorsal nerve chord
3. pharyngeal slits or pouches
4. endostyle or thyroid glabd
5. post-anal tail
5 structures only found in Phylum Chordata
gills, lungs, and/or skin
phylum Chordata respiratory system
closed
phylum Chordata circulatory system
complete
phylum Chordata digestive tract
metabolic waste removed via kidneys
phylum Chordata excretory system
sexes are usually seperate, most produce sexually
phylum Chordata reproductive system
sessile filter-feeders
most urochordates are ____________________.
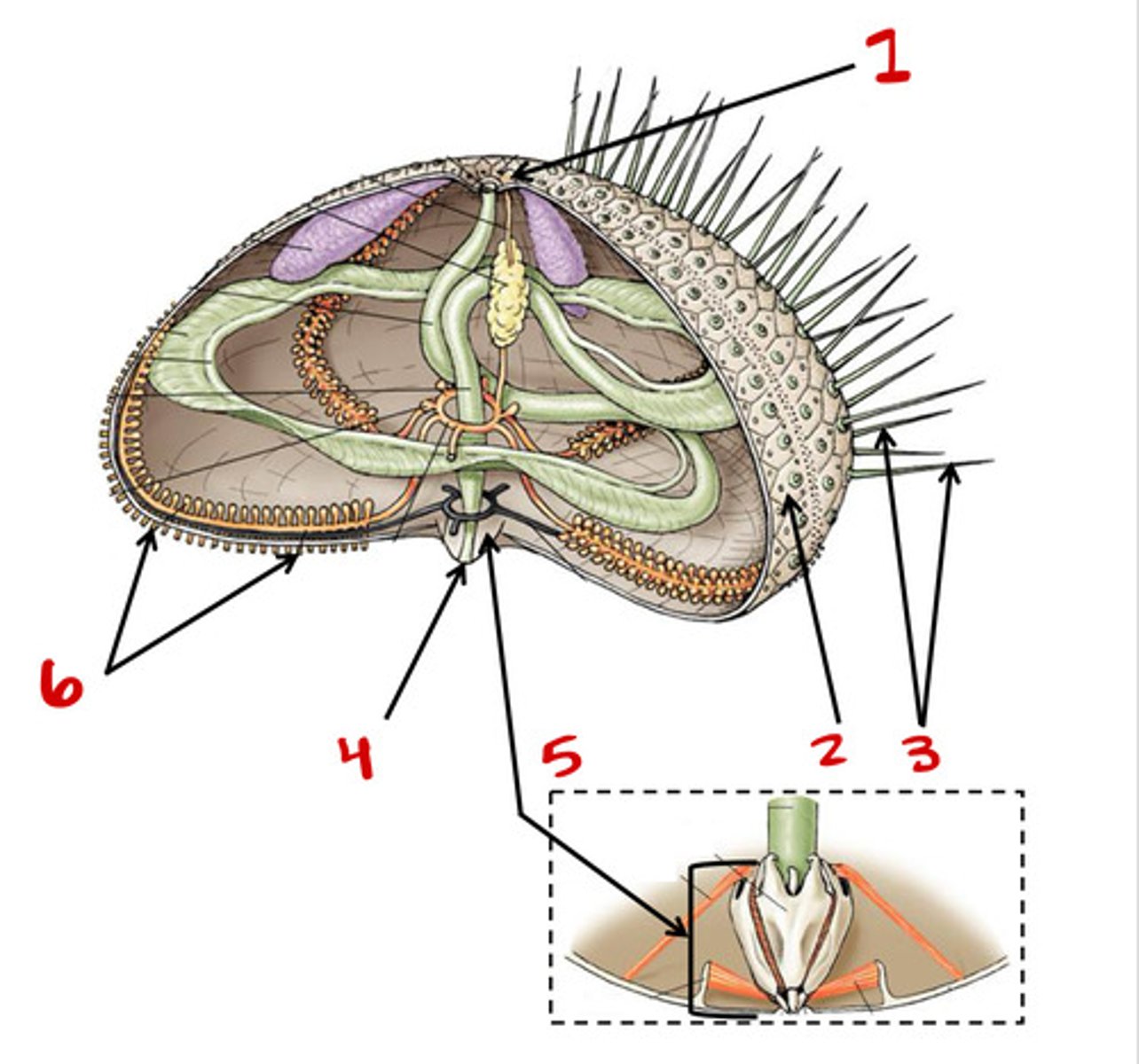
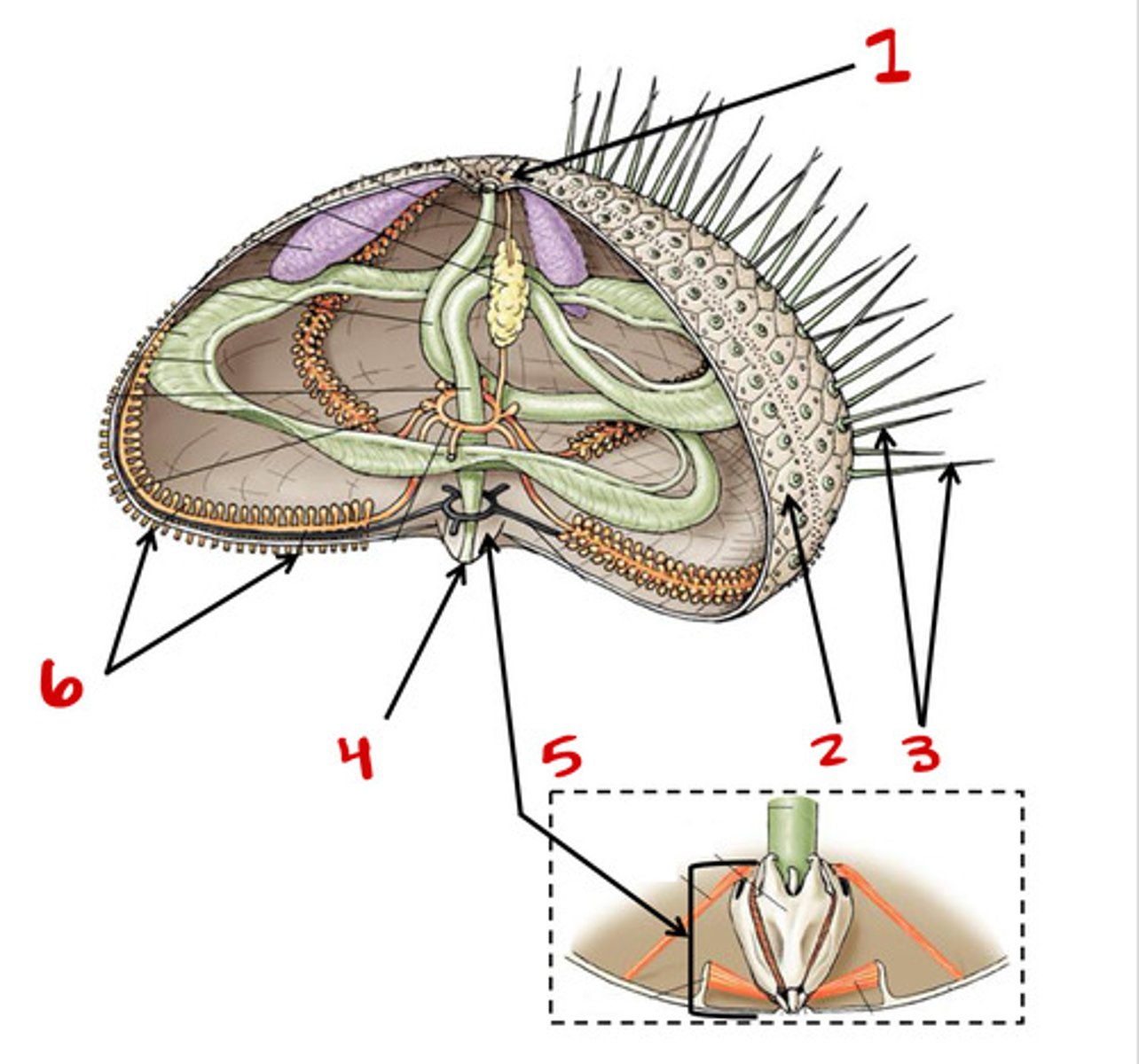
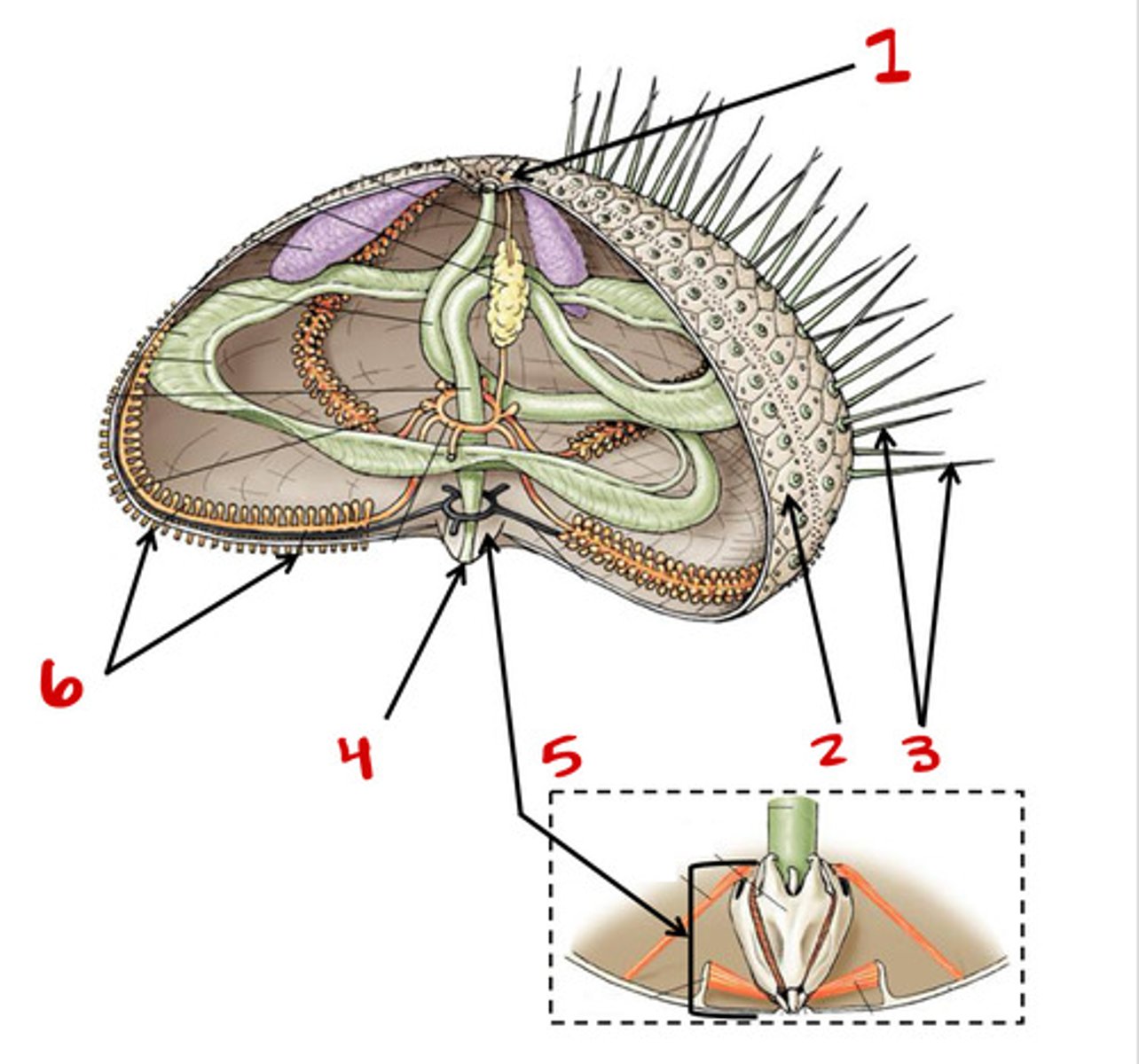
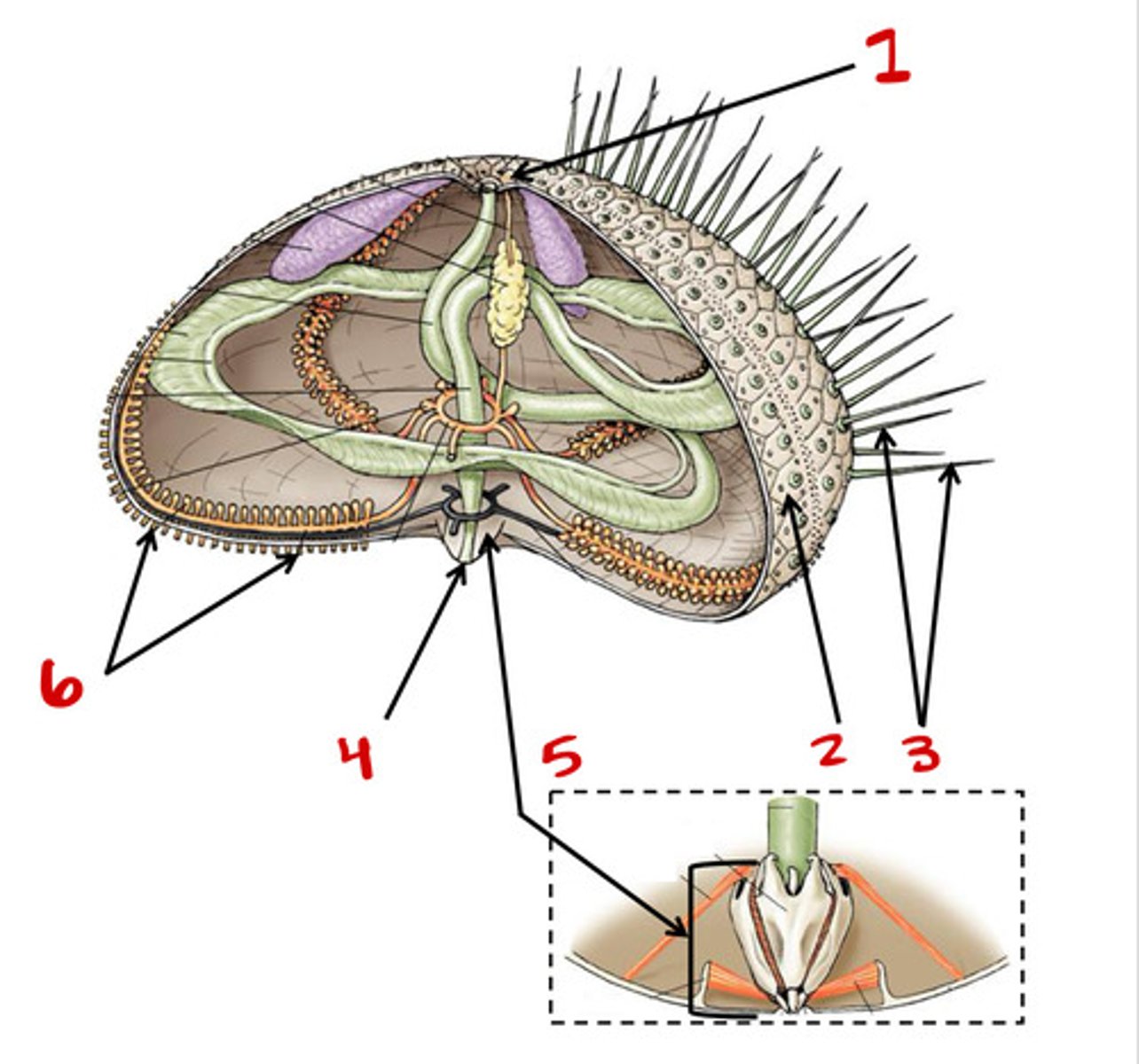
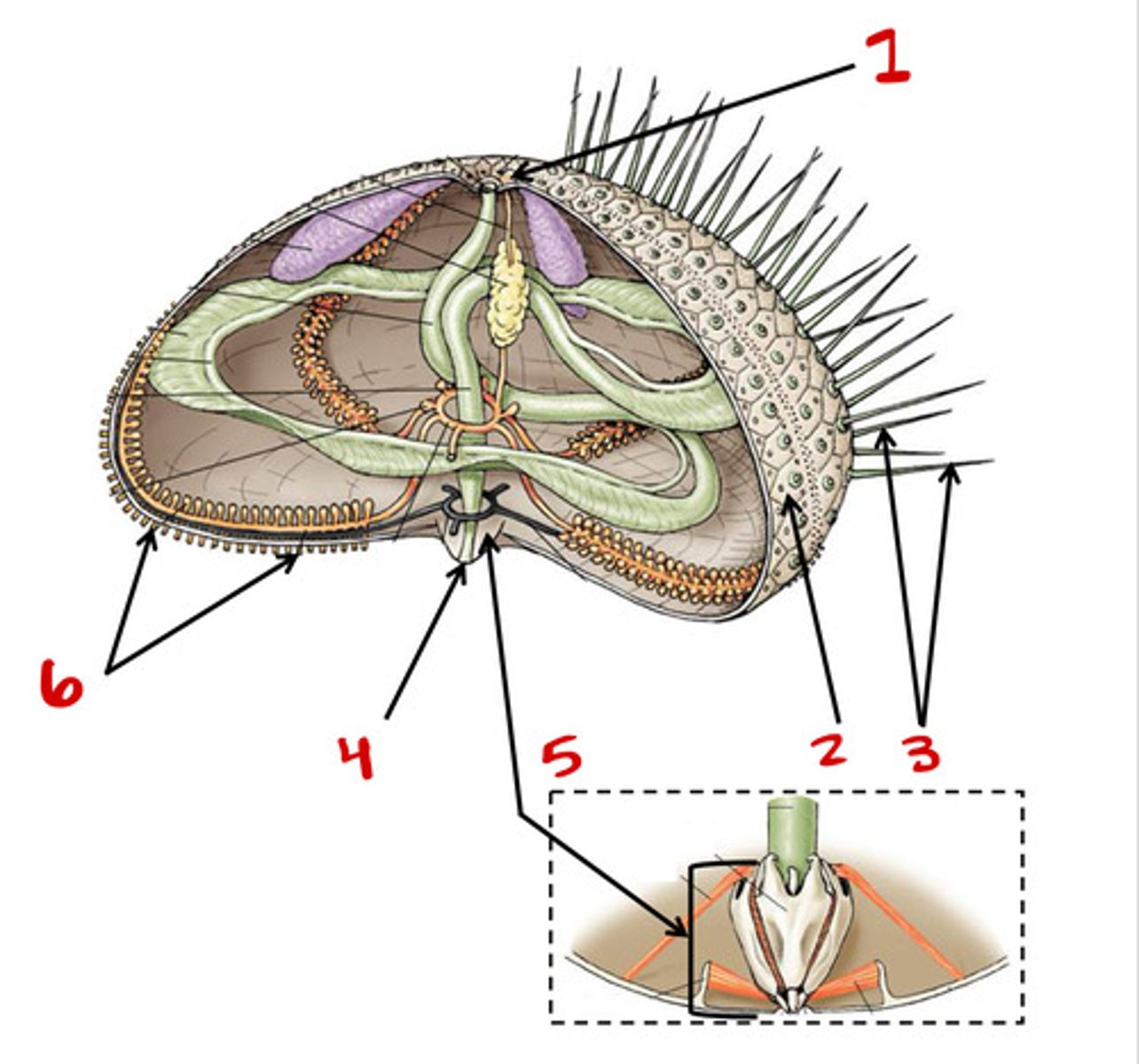
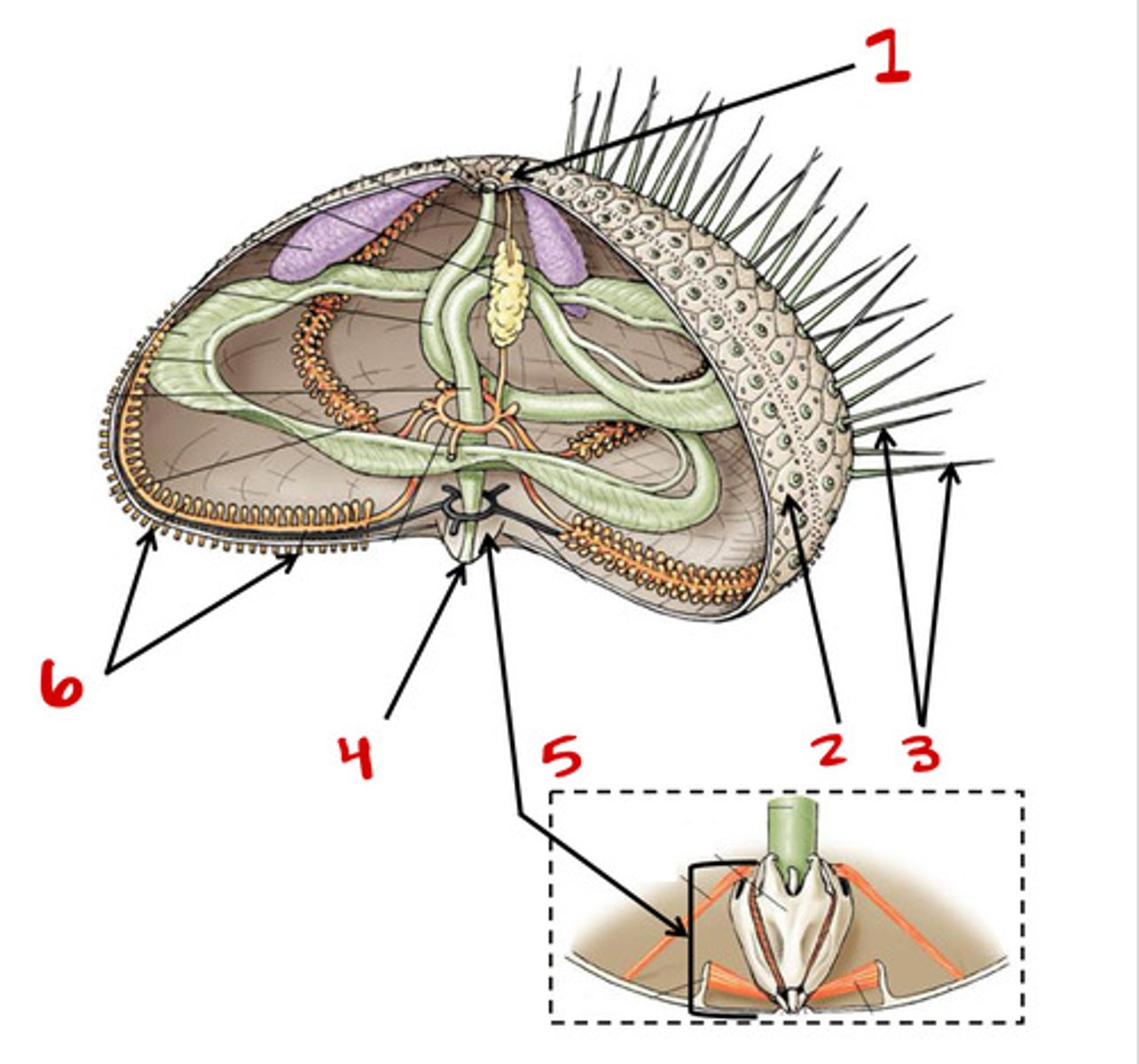
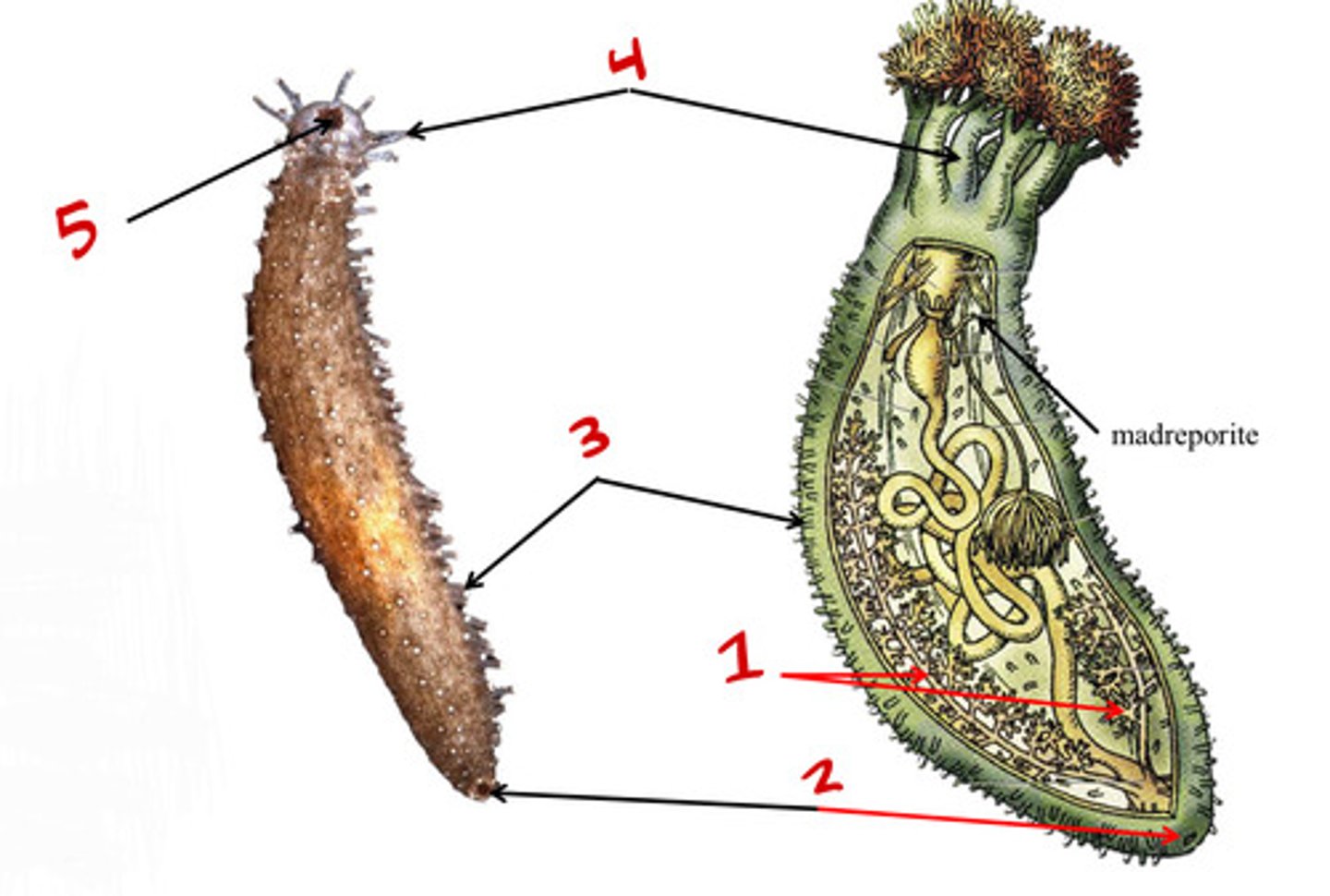
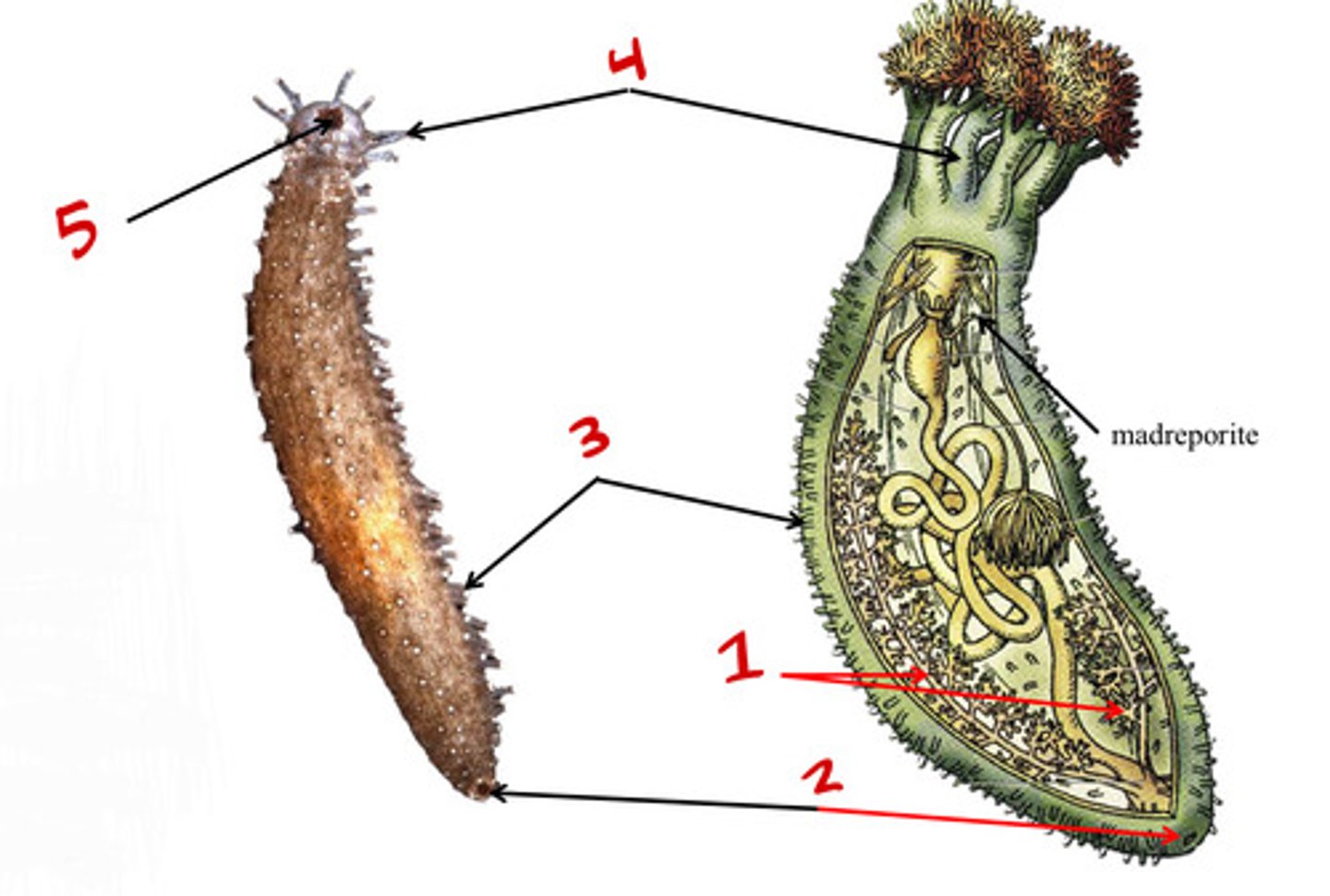
Madreporite
1
Test
2
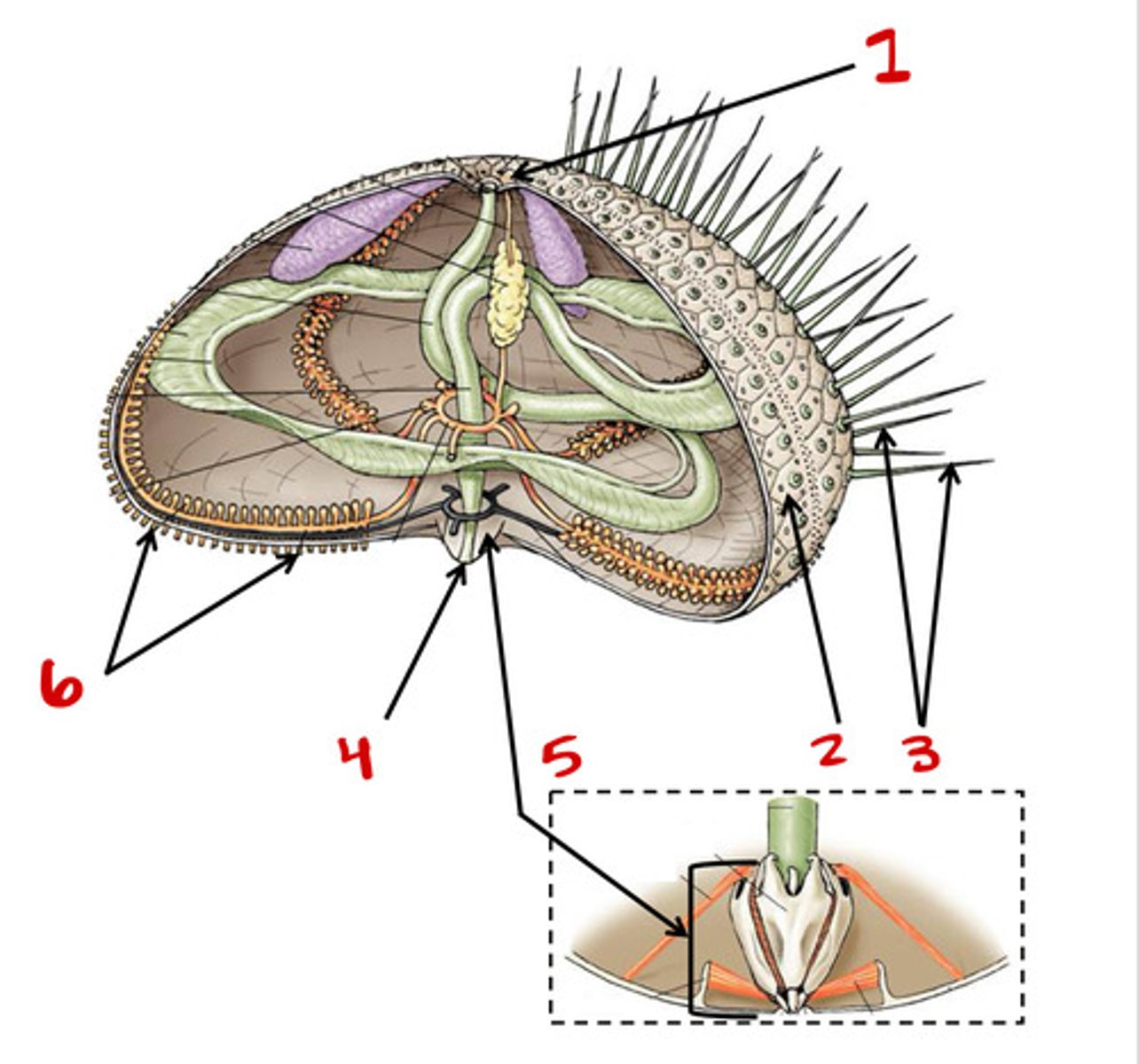
Tube feet
6
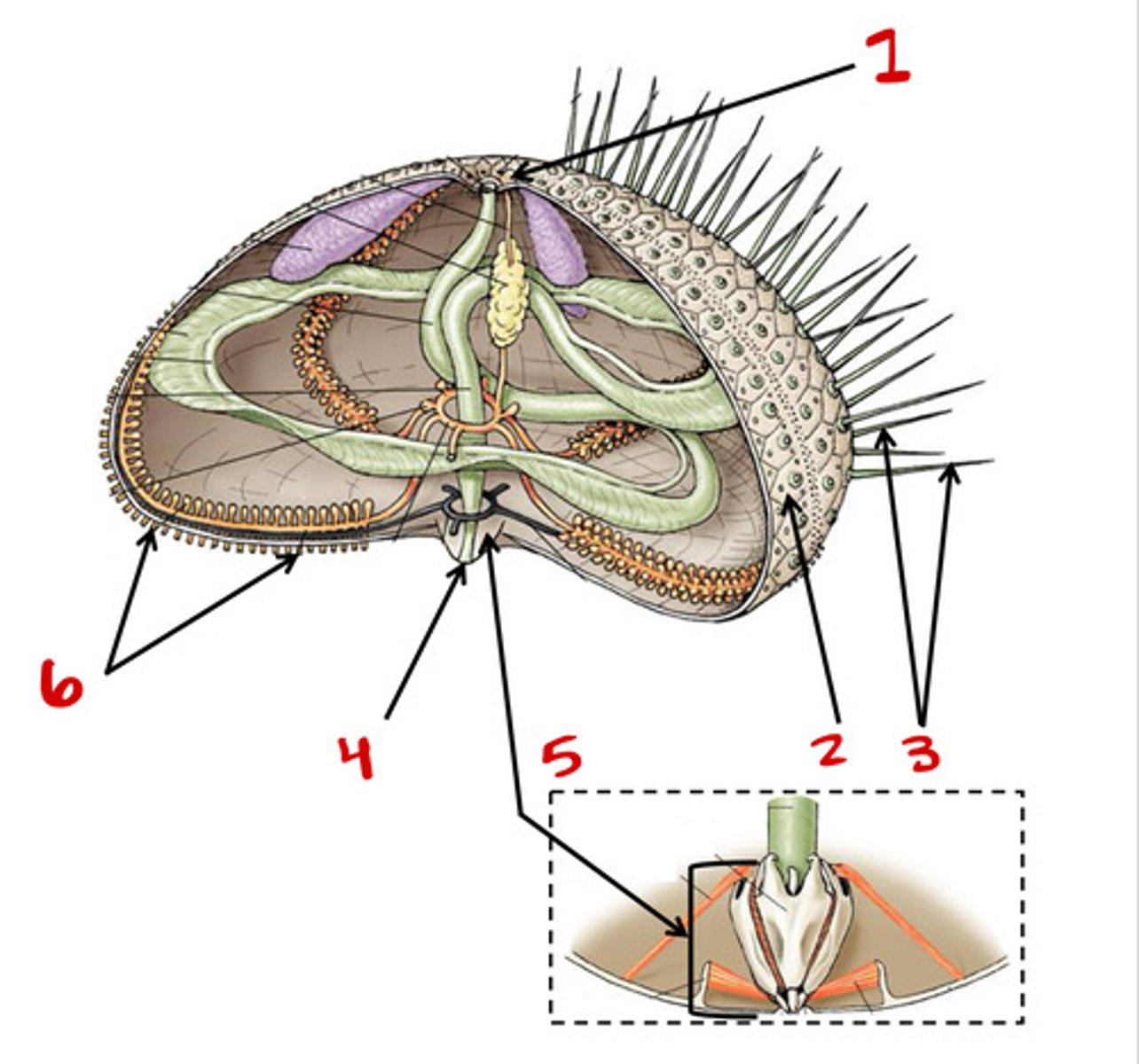
Spines
3
Bottom
Where is the oral surface?
Top
Where is the aboral surface
Echinoidea
Class
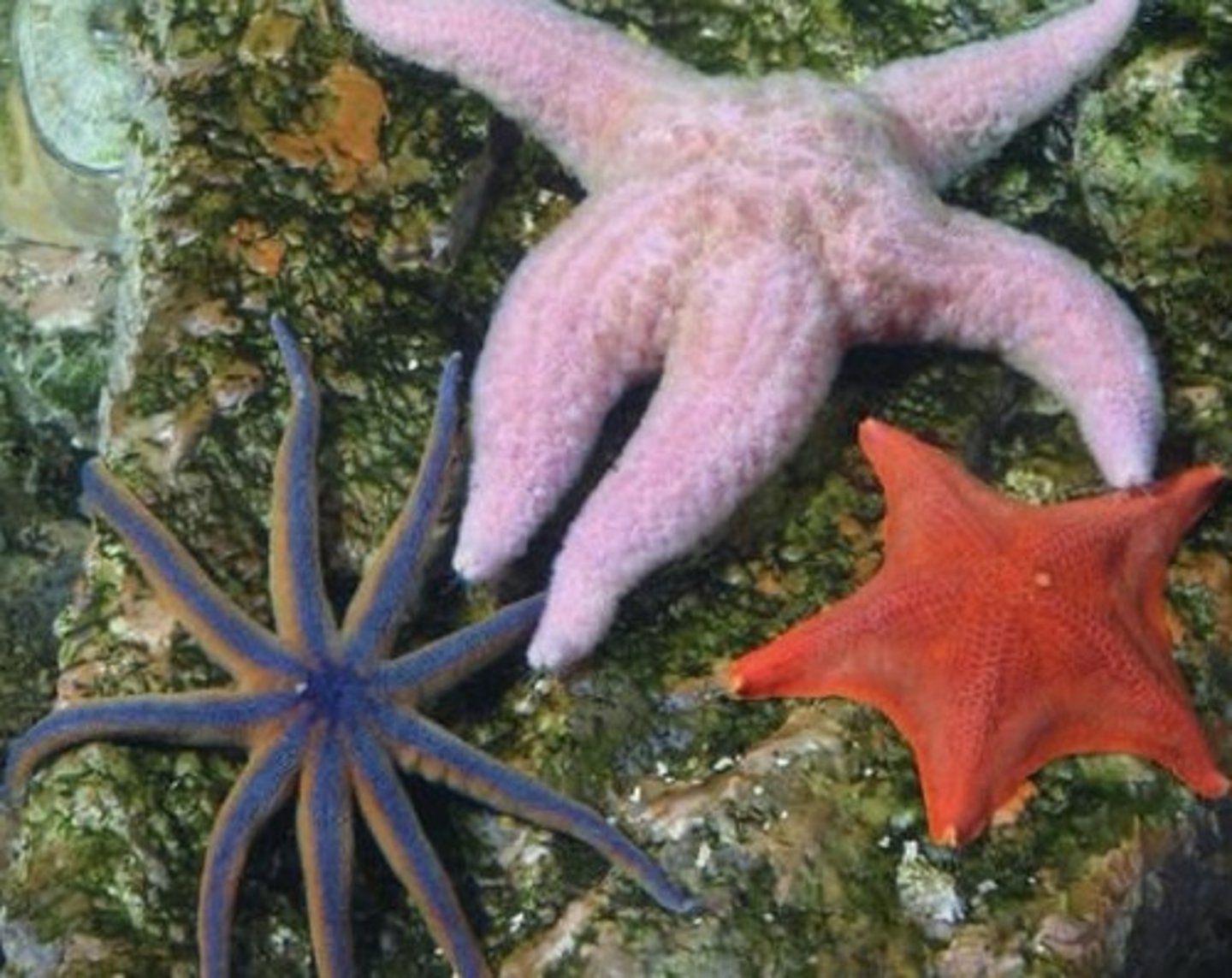
Asteroidea
Class
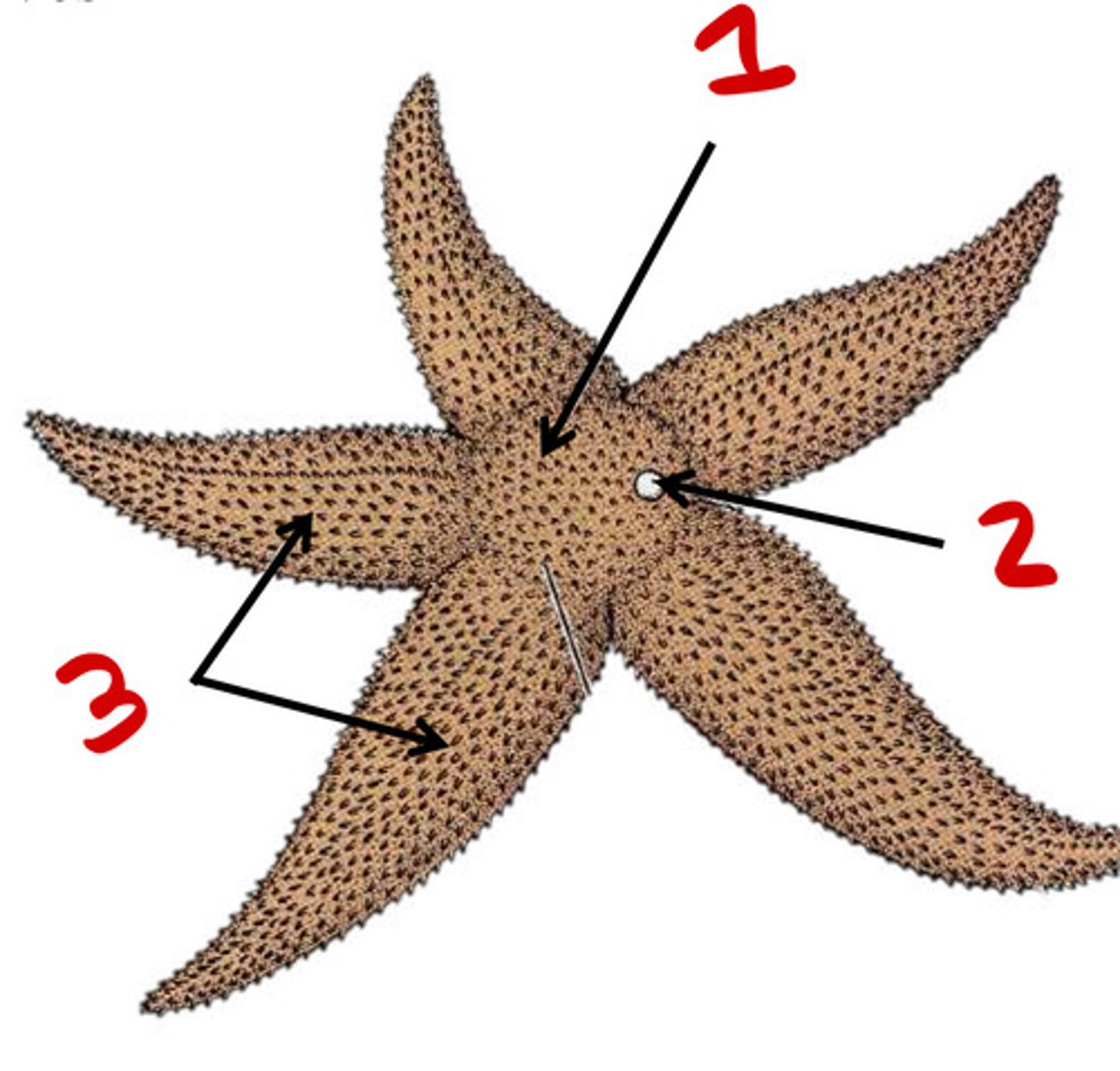
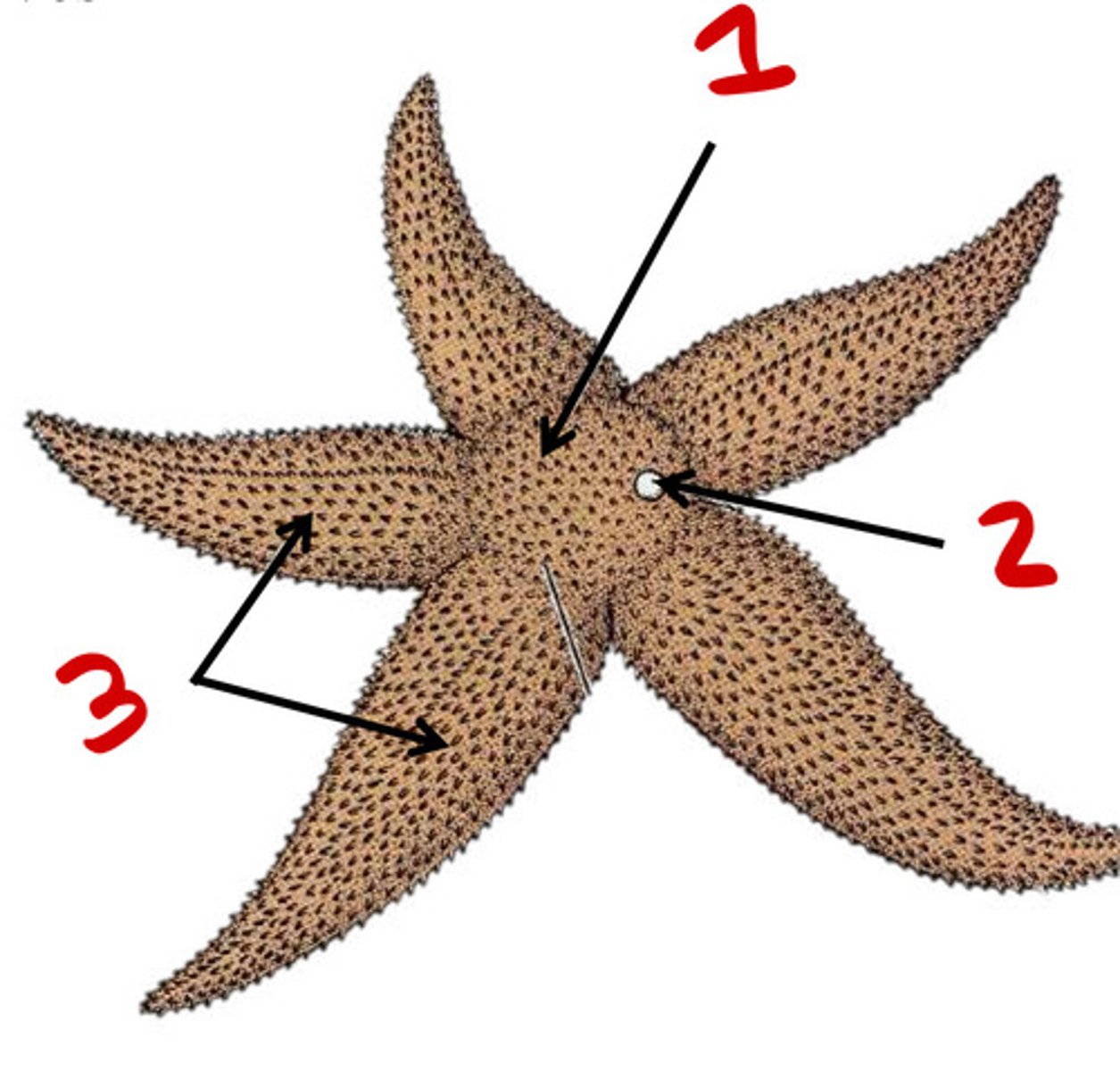
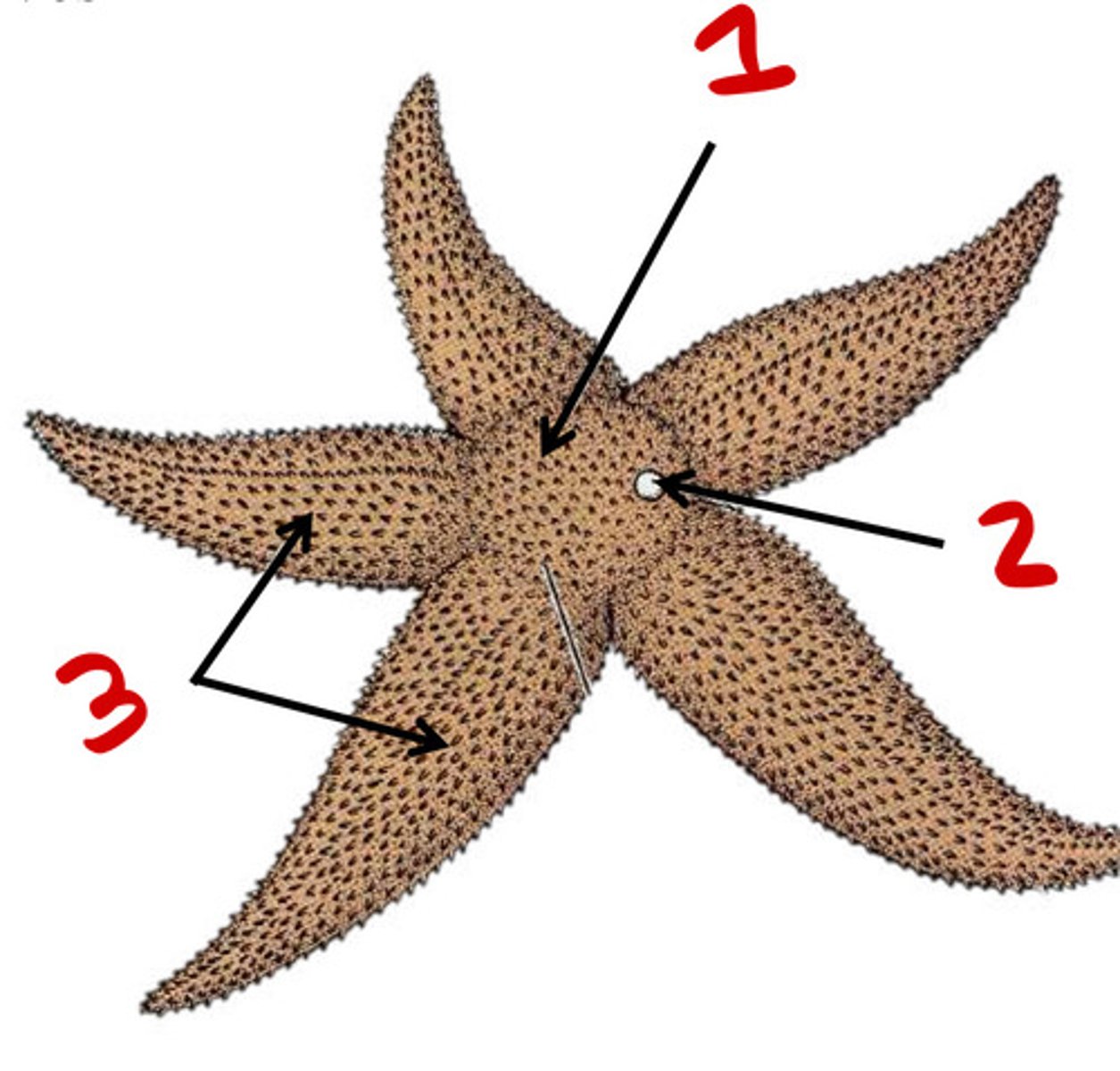
Central disc
1
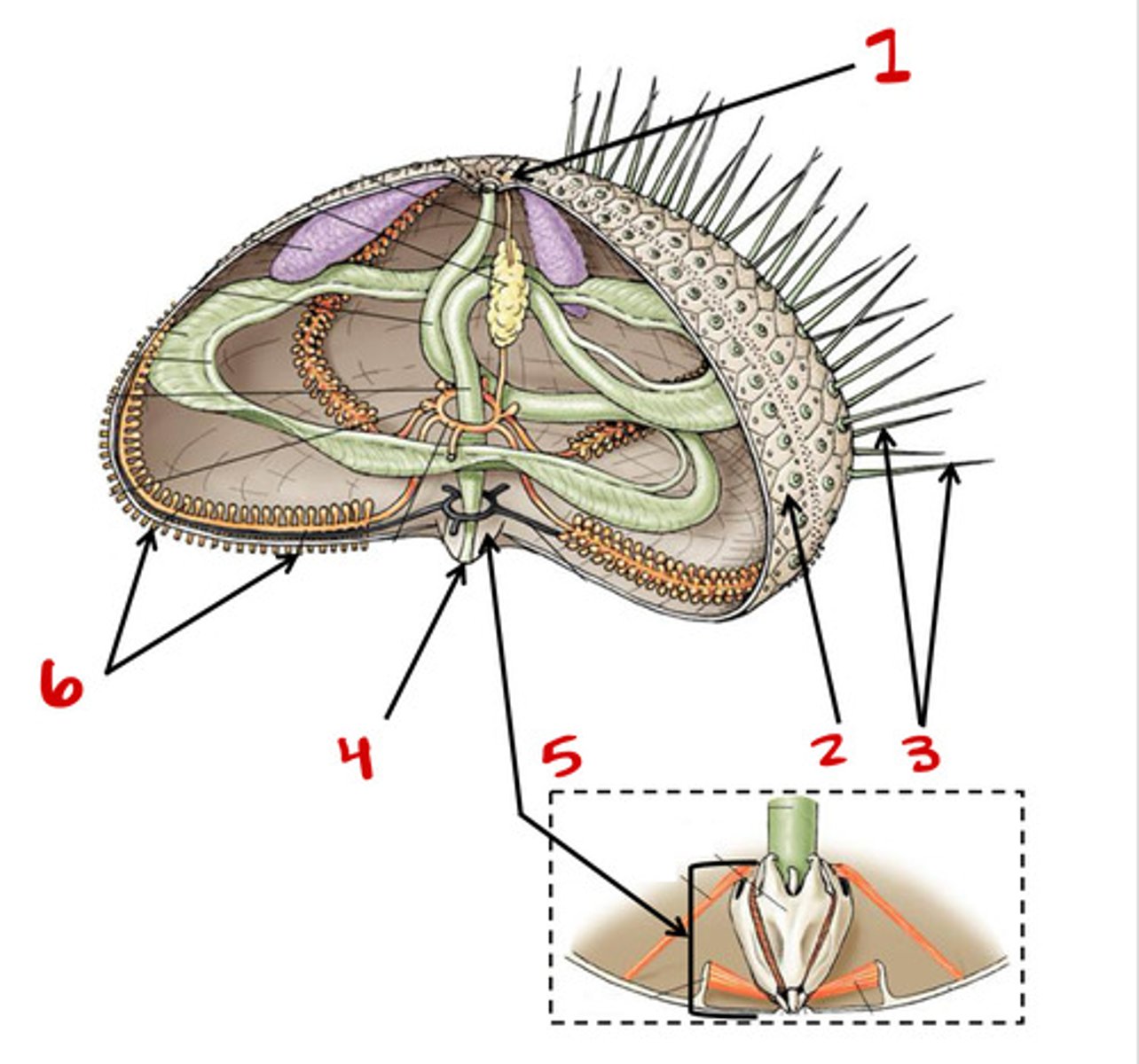
Aristotles lantern
5
Madreporite
2
Mouth
1
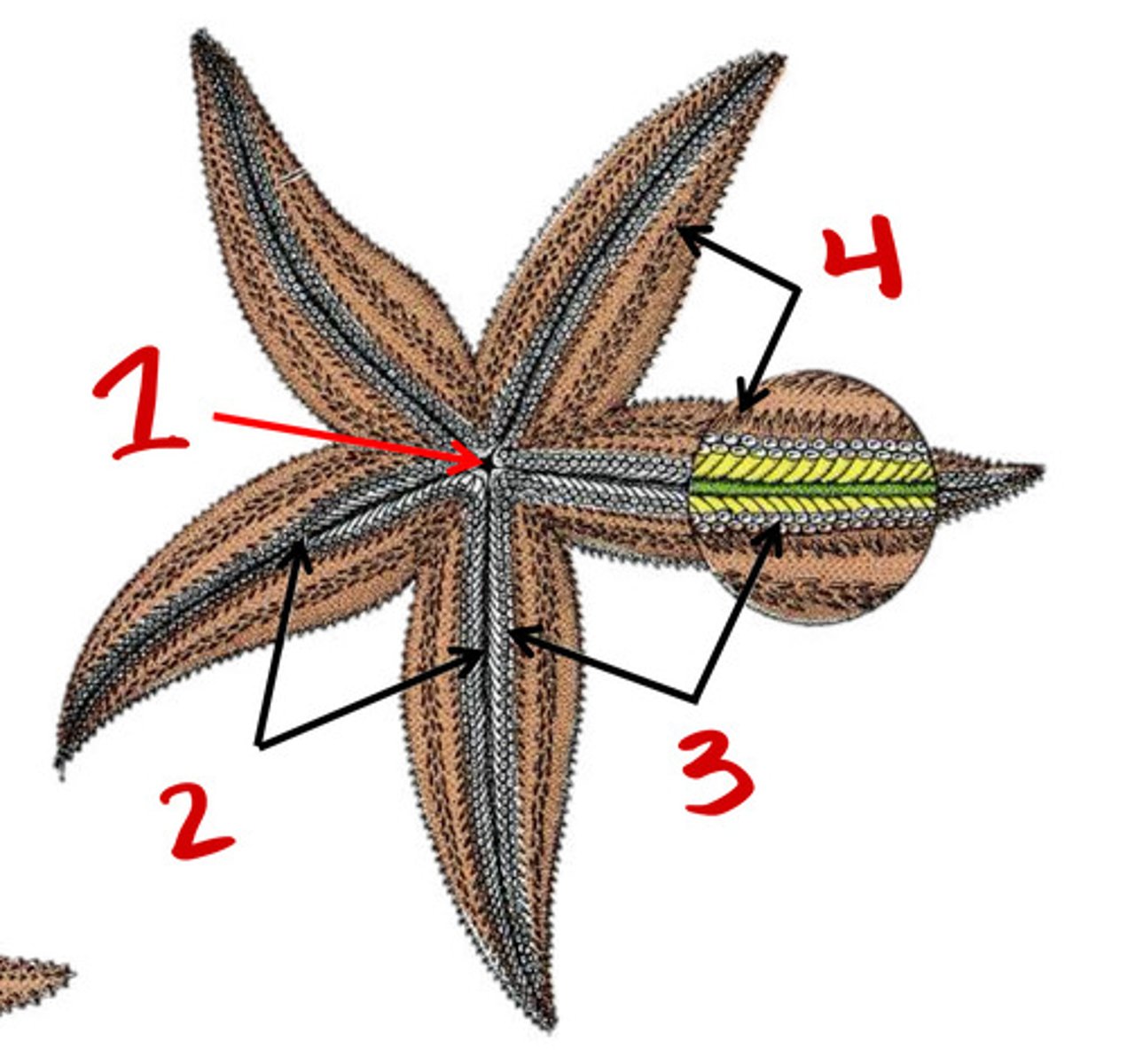
ambulacral groove
2
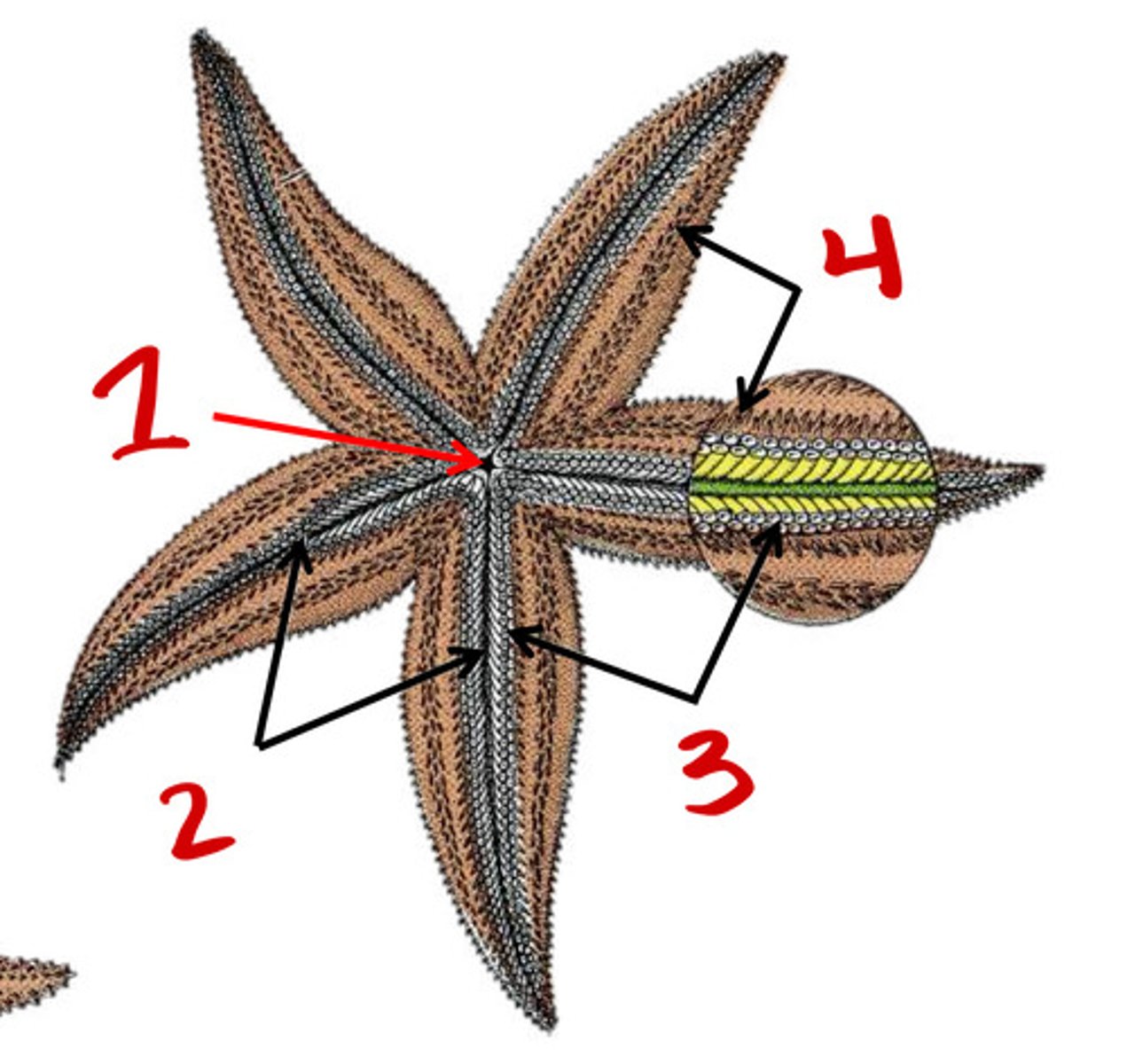
Tubefeet
3
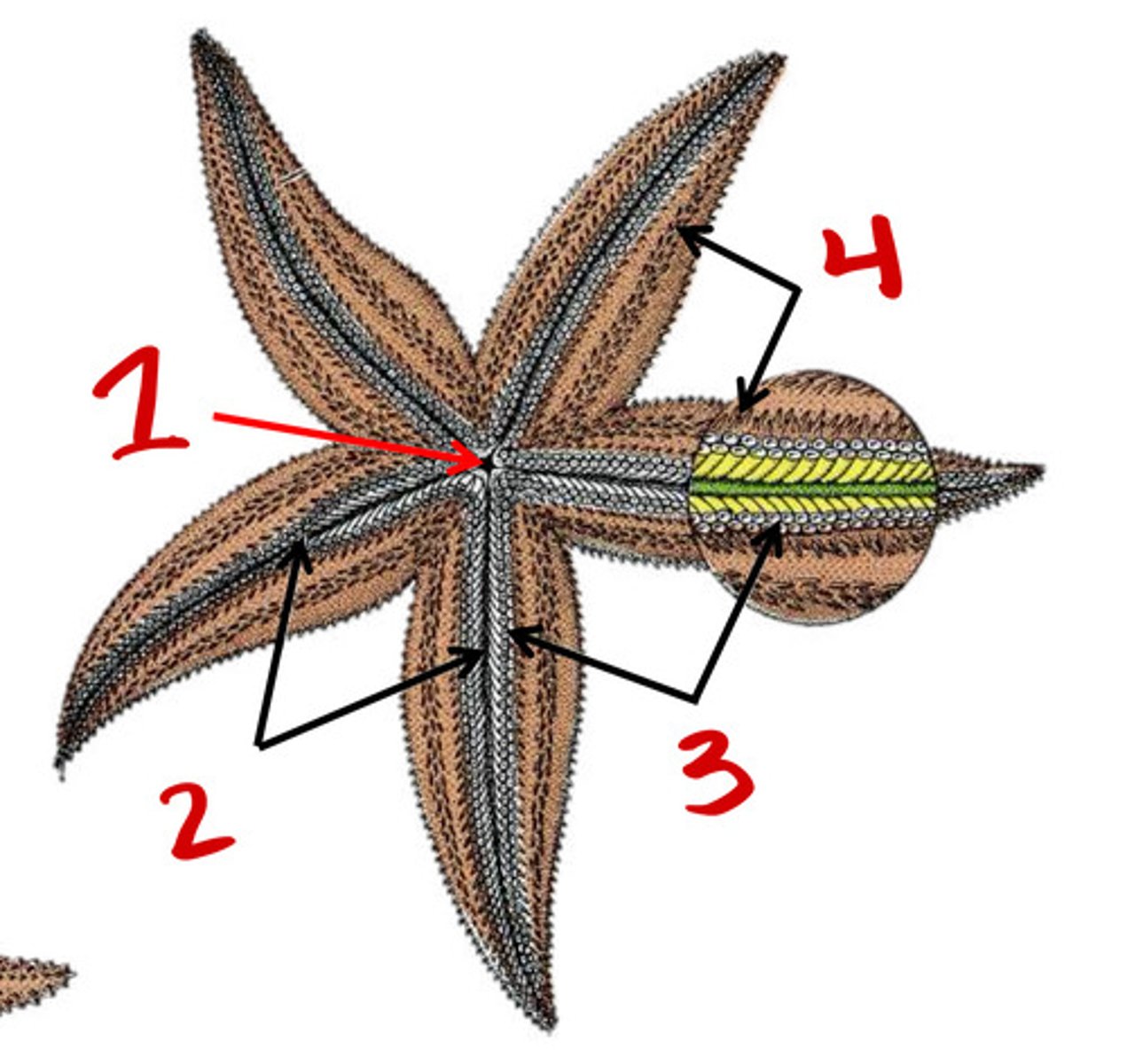
Spines
4
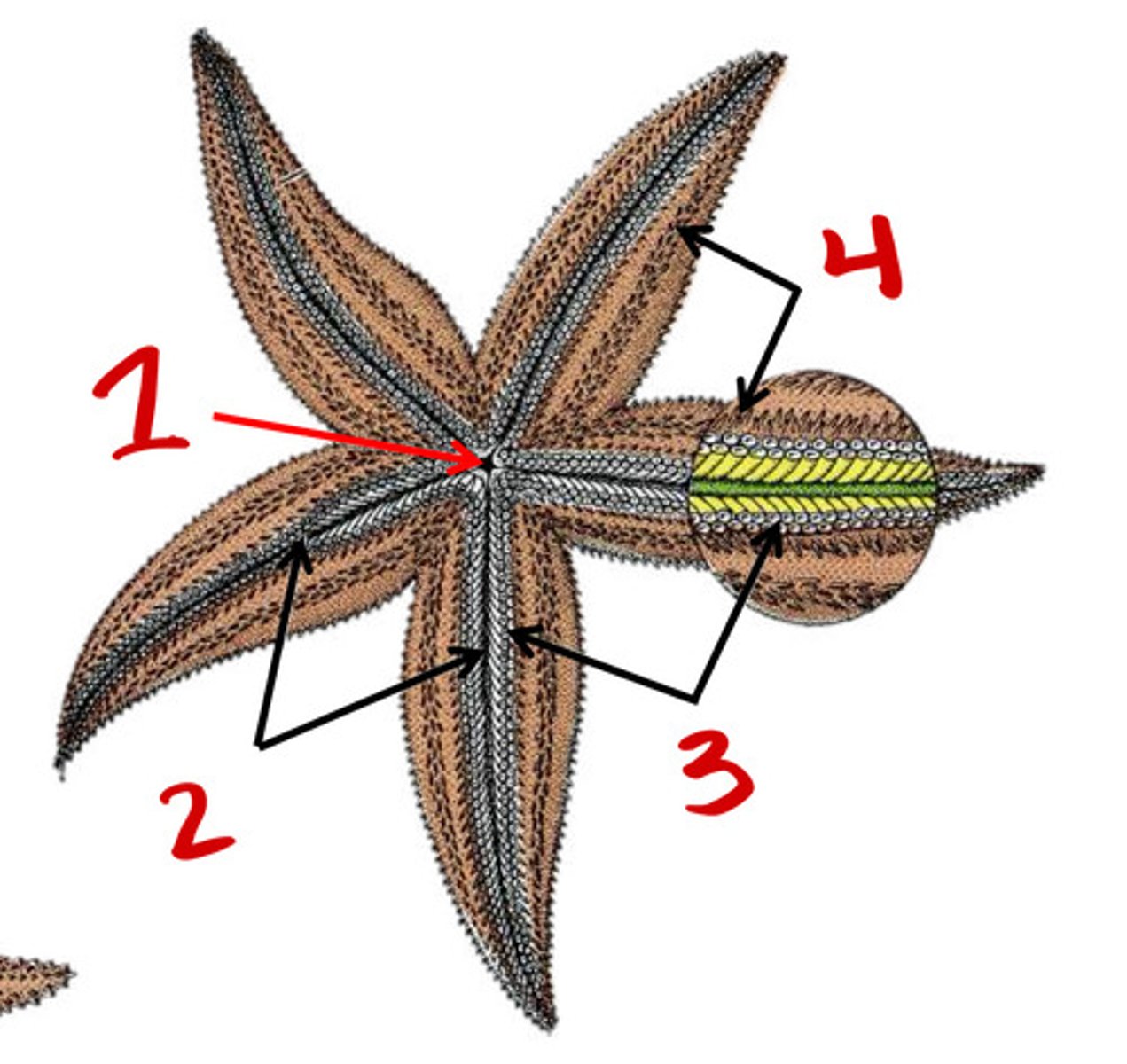
Respiratory tree
1
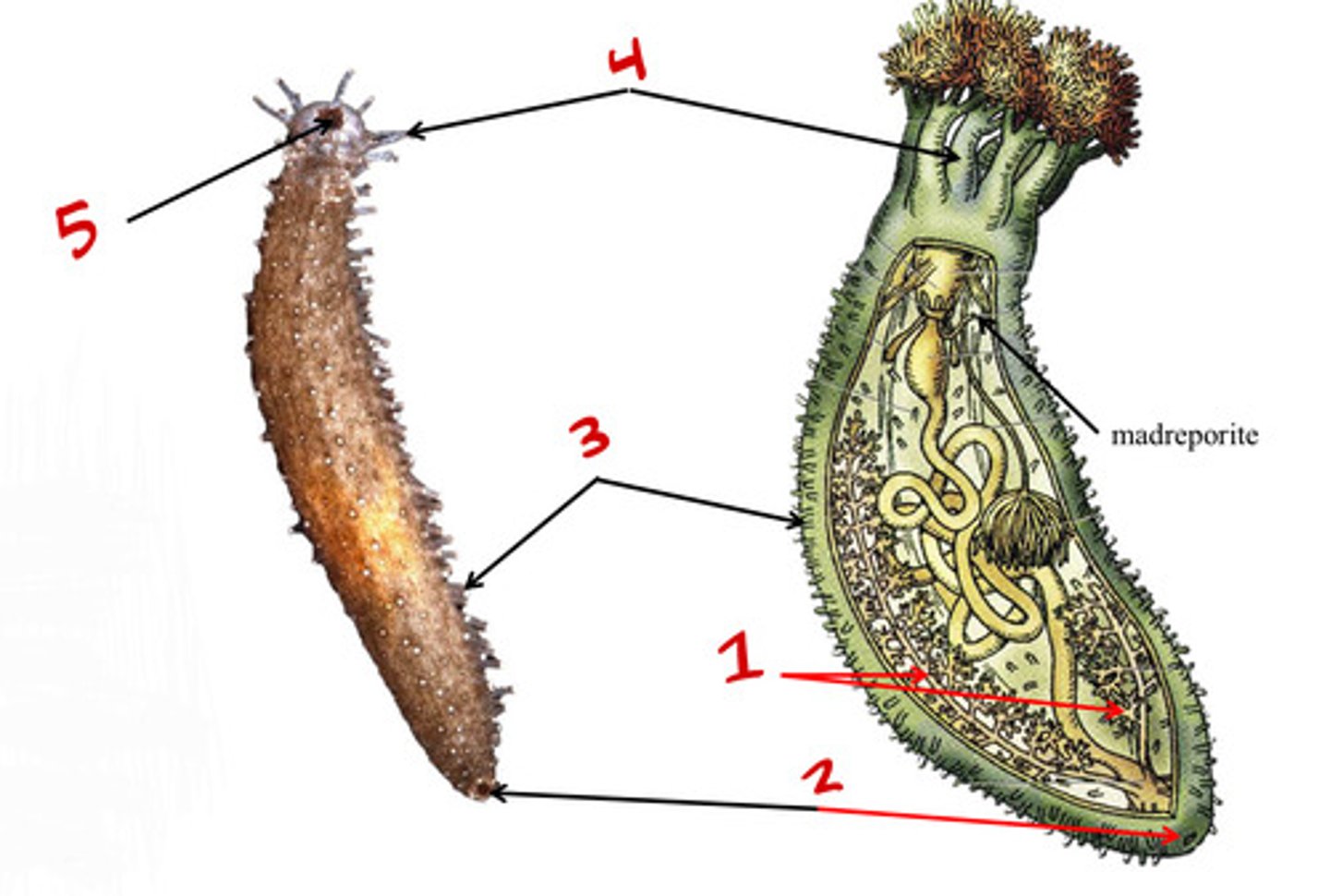
Anus
2
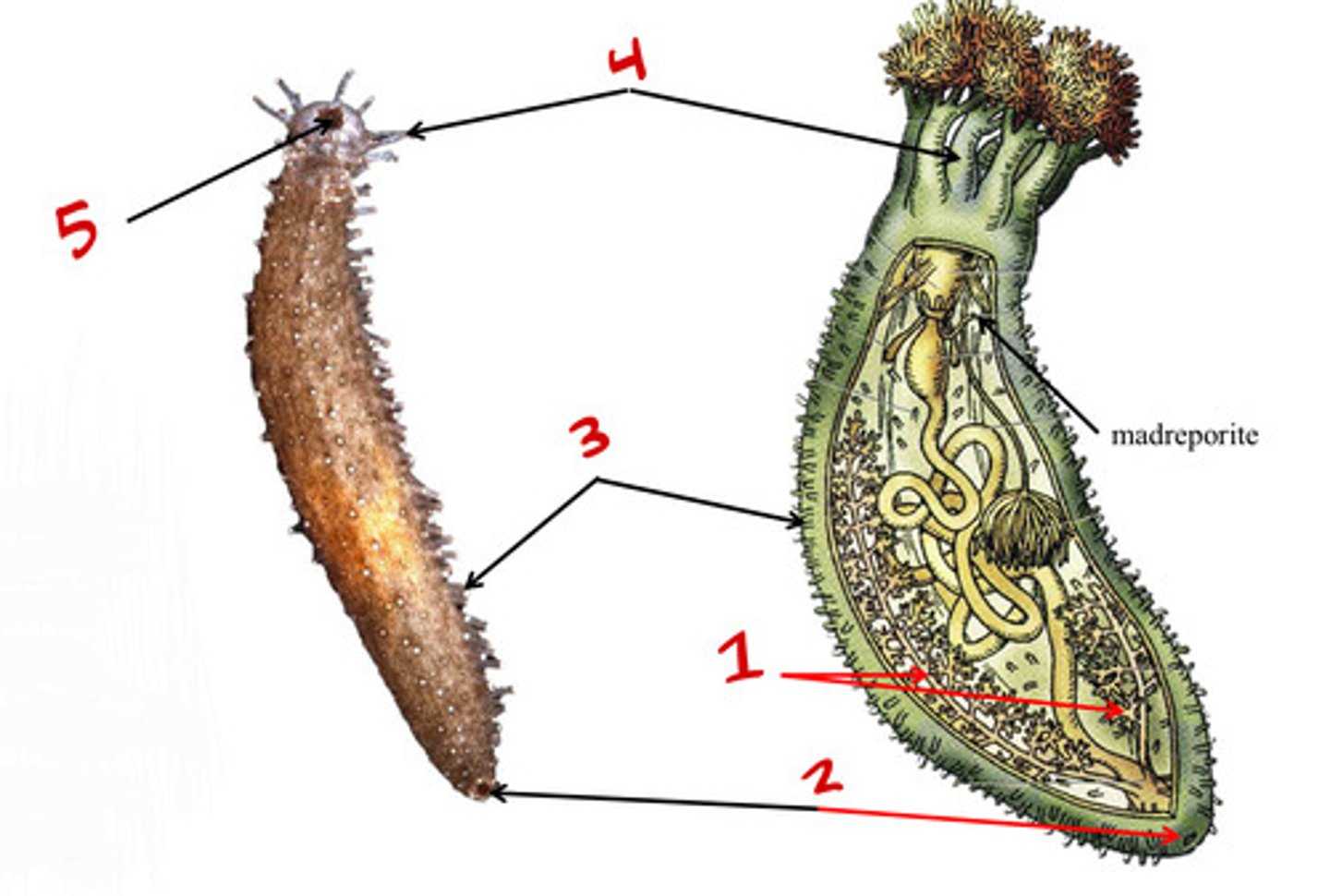
Tube feet
3
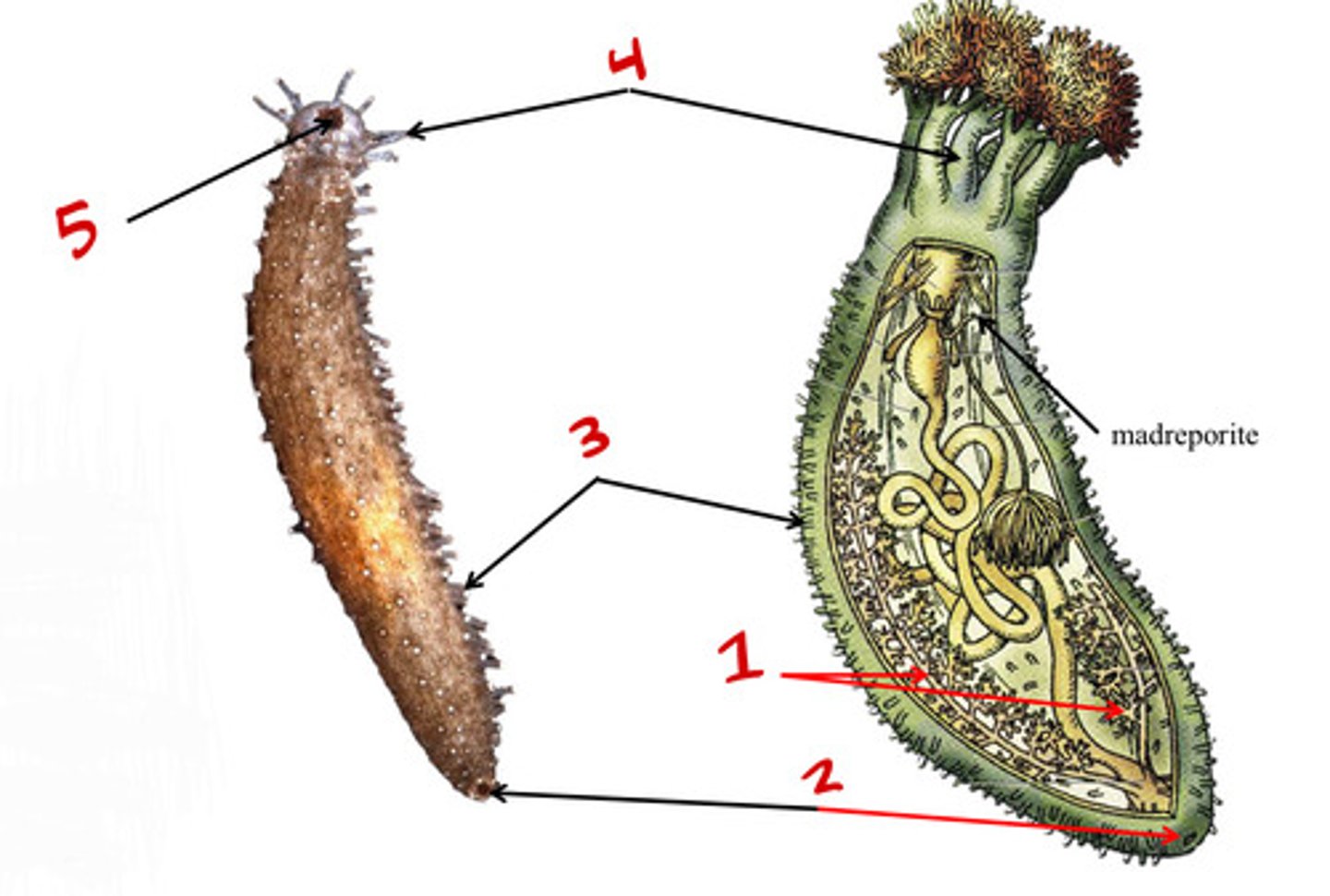
Mouth
4
Arms
3
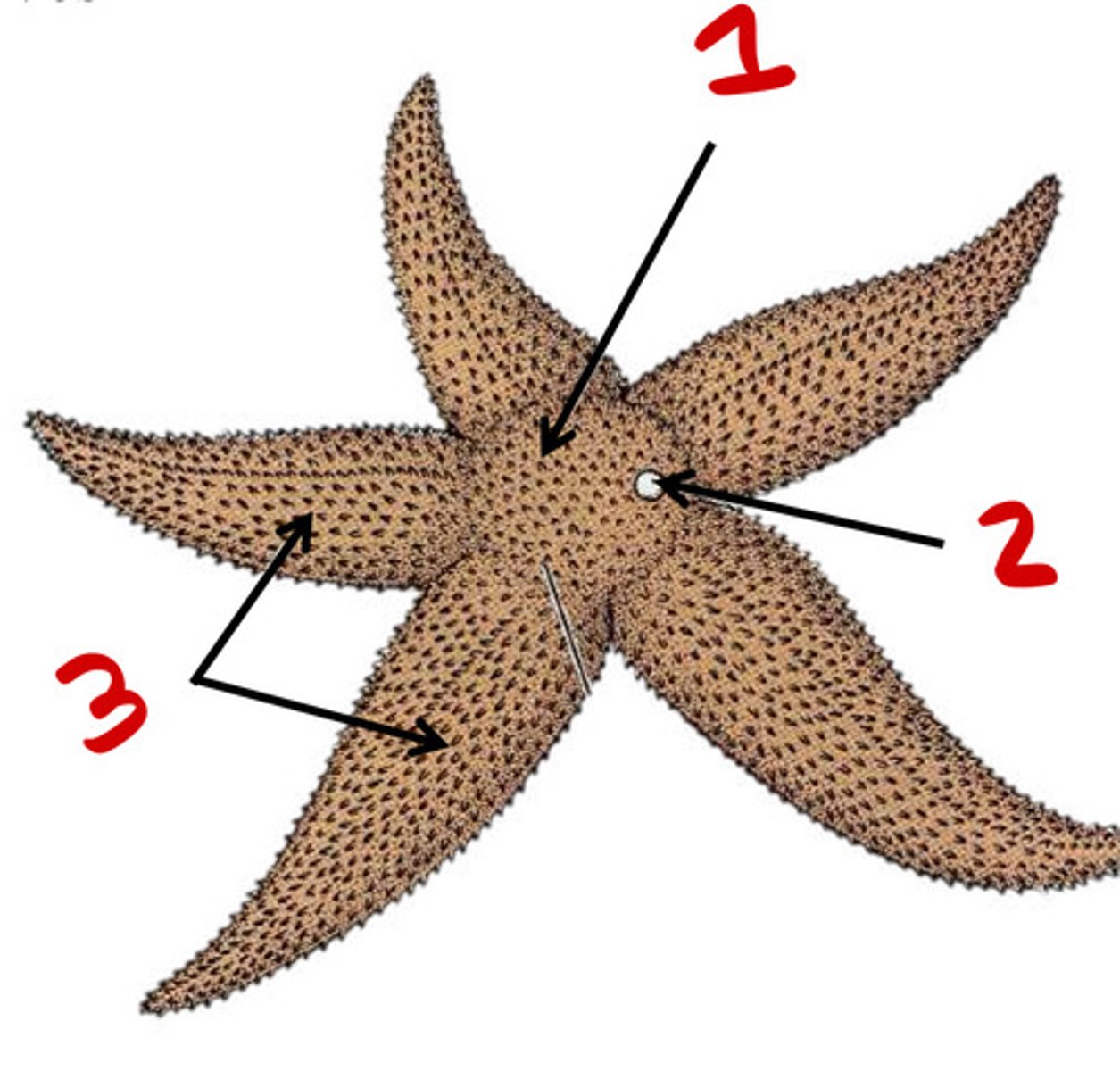
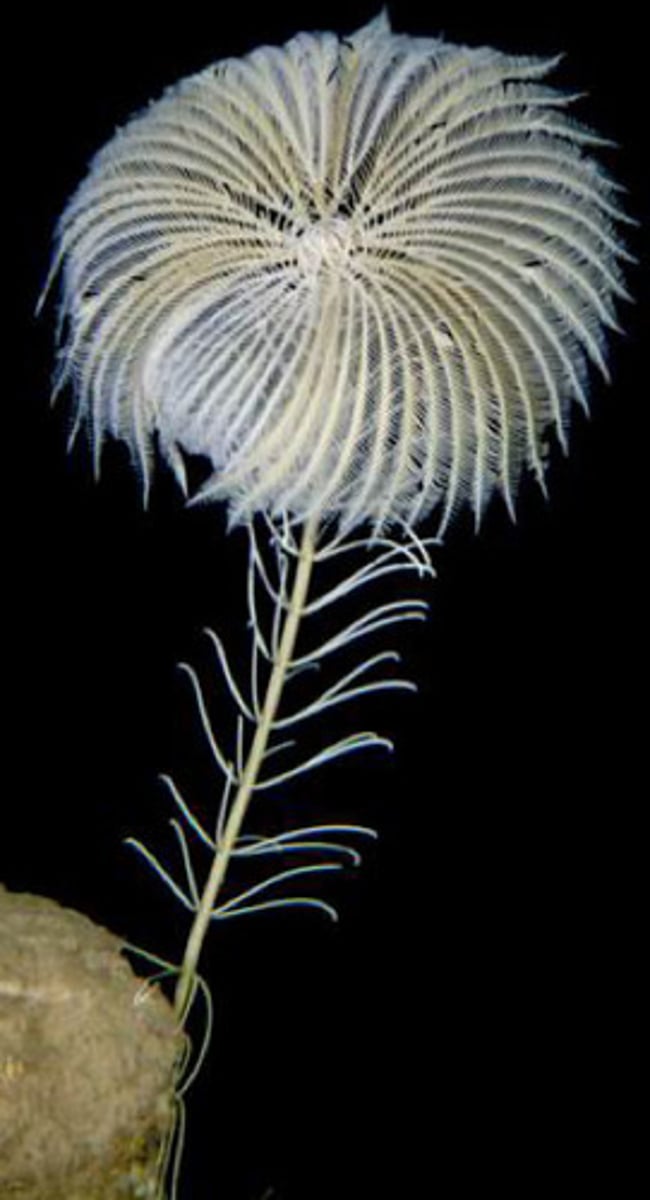
Crinoidea
Class

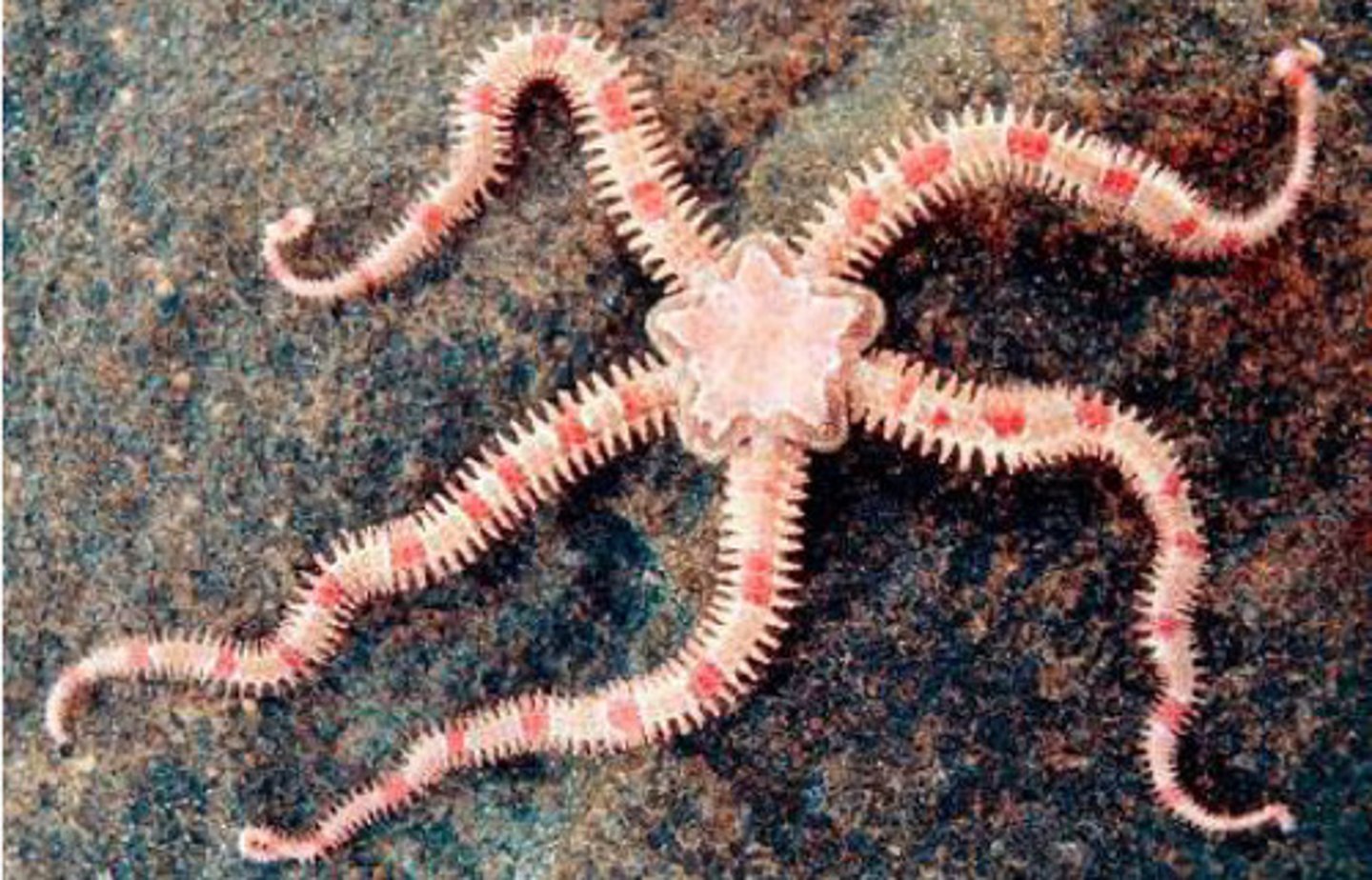
Ophuroidea
Class

Holothuroidea
Class
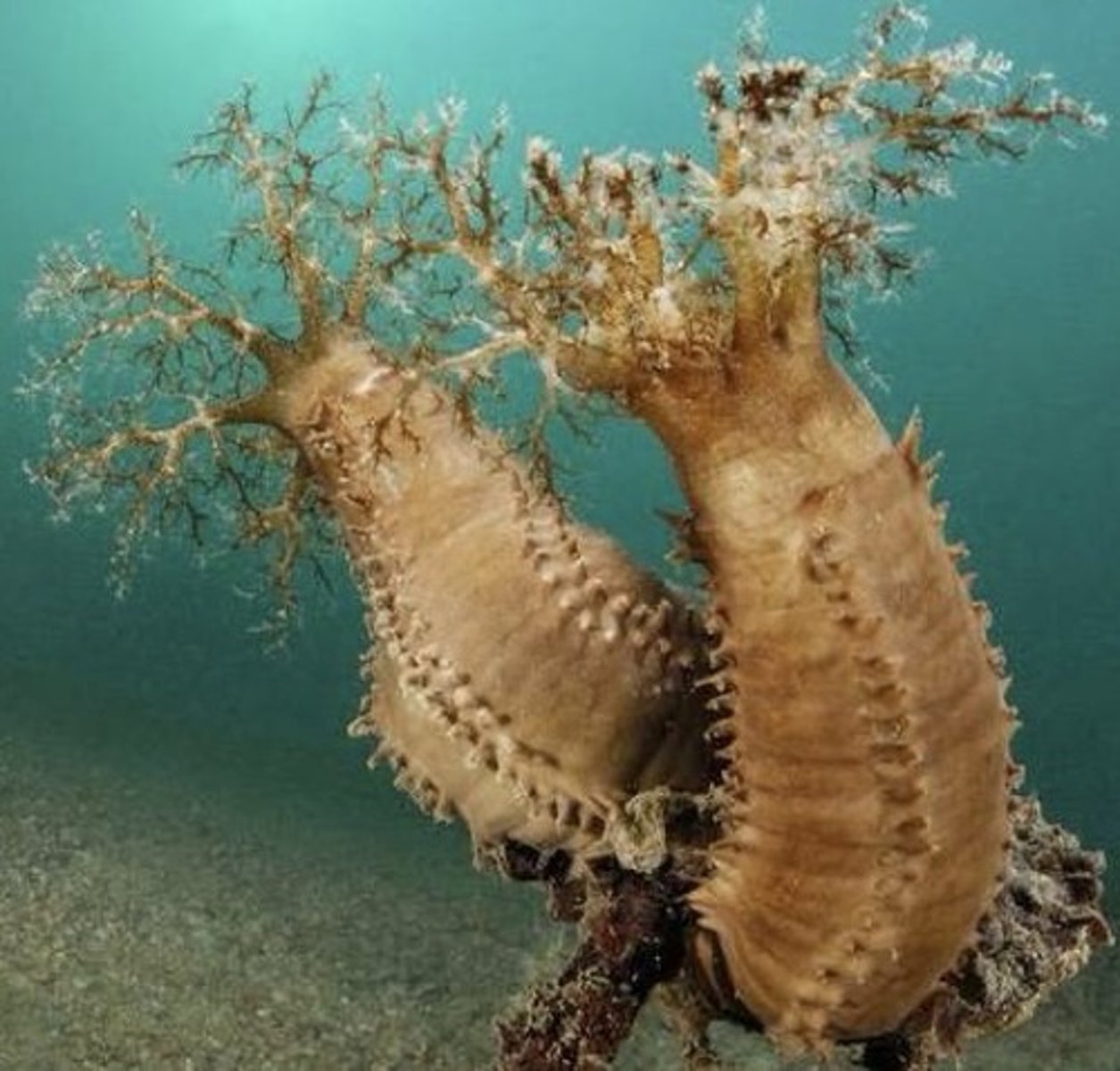

Asteroidea
Class

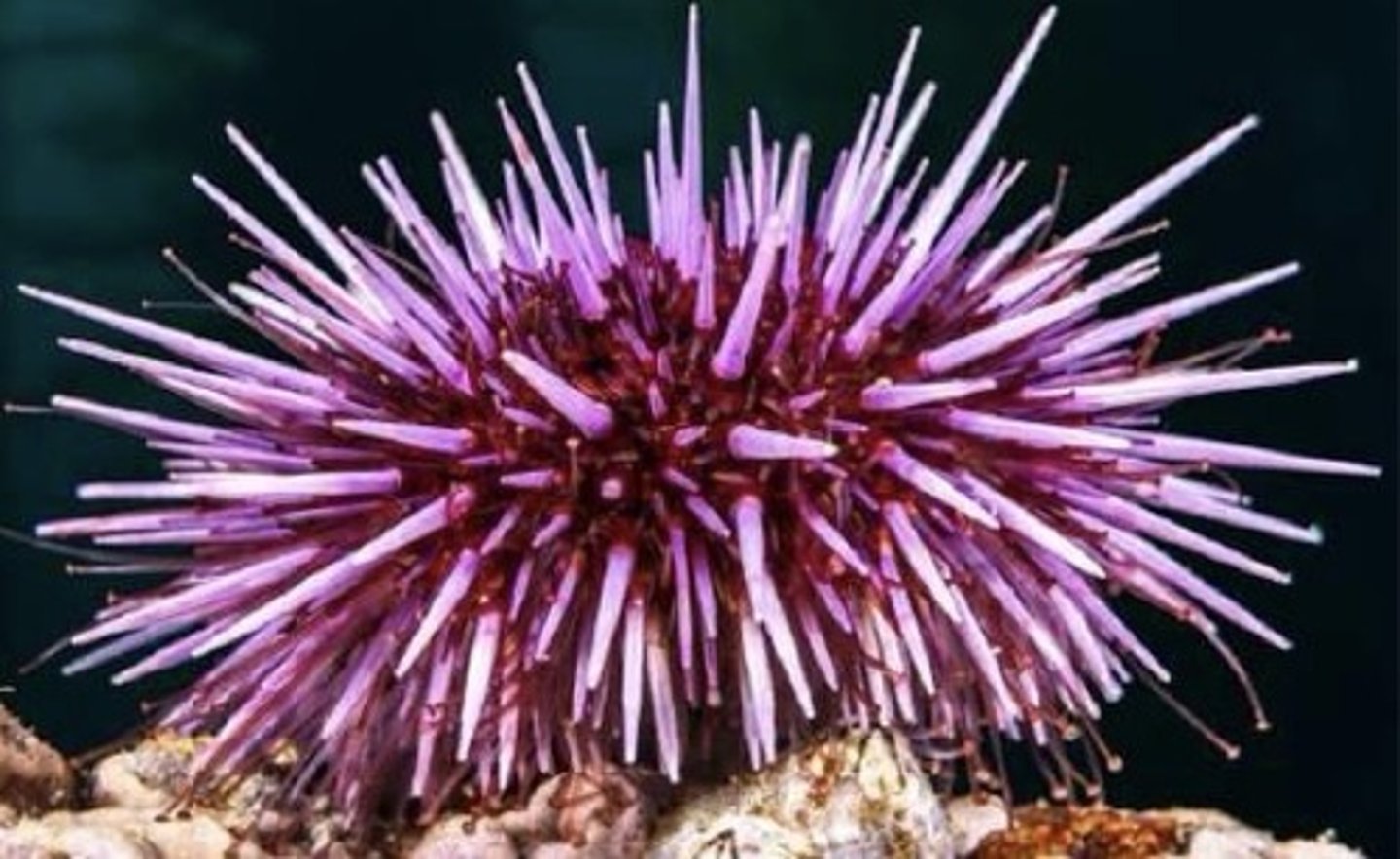
Echinoidea
Class

Endocyte
2
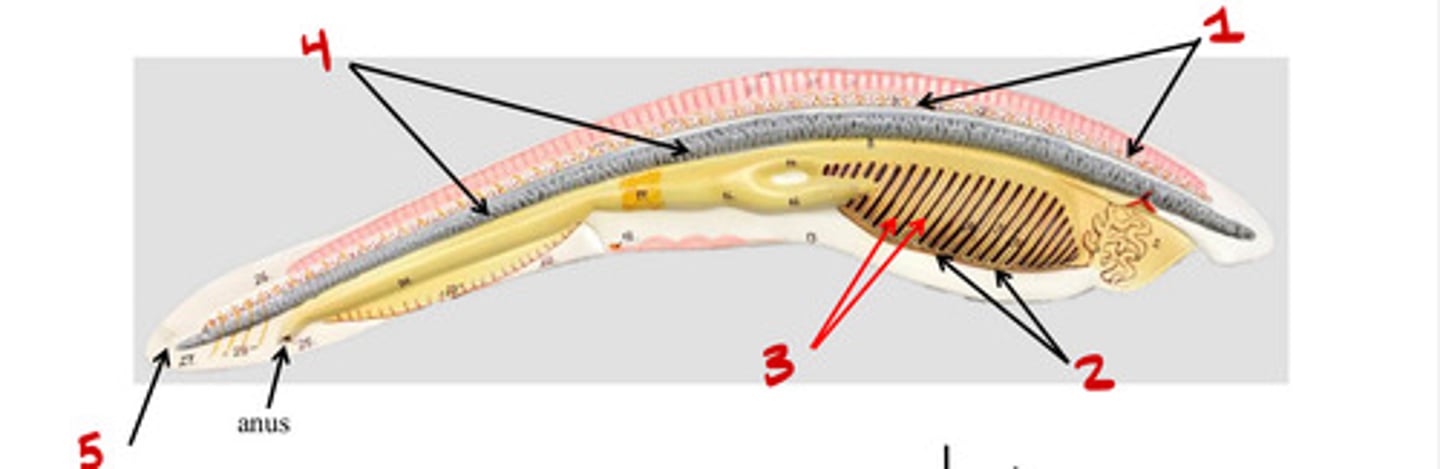
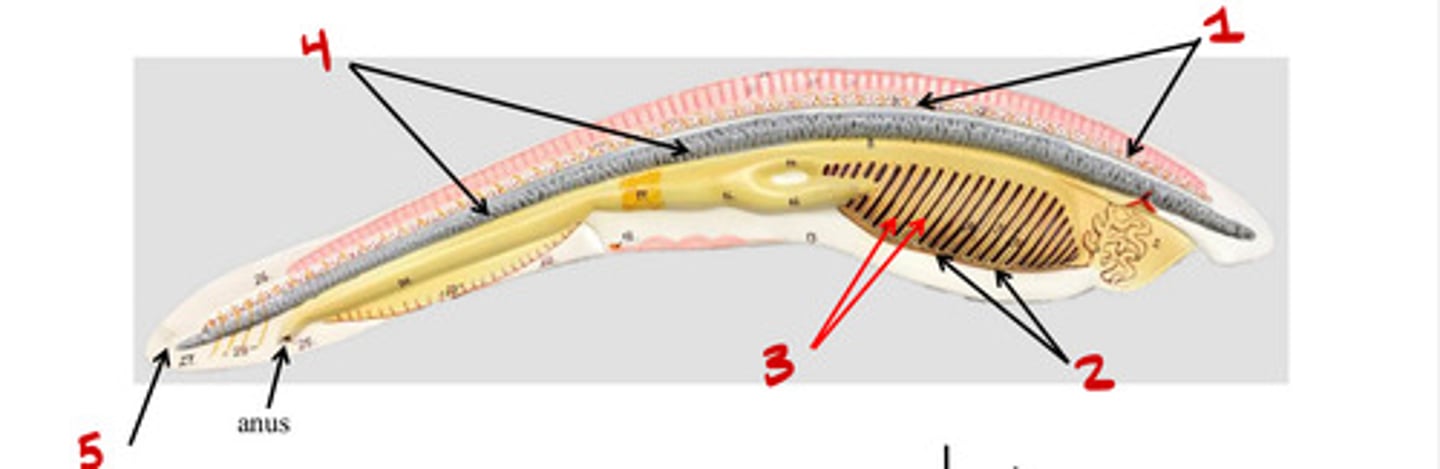
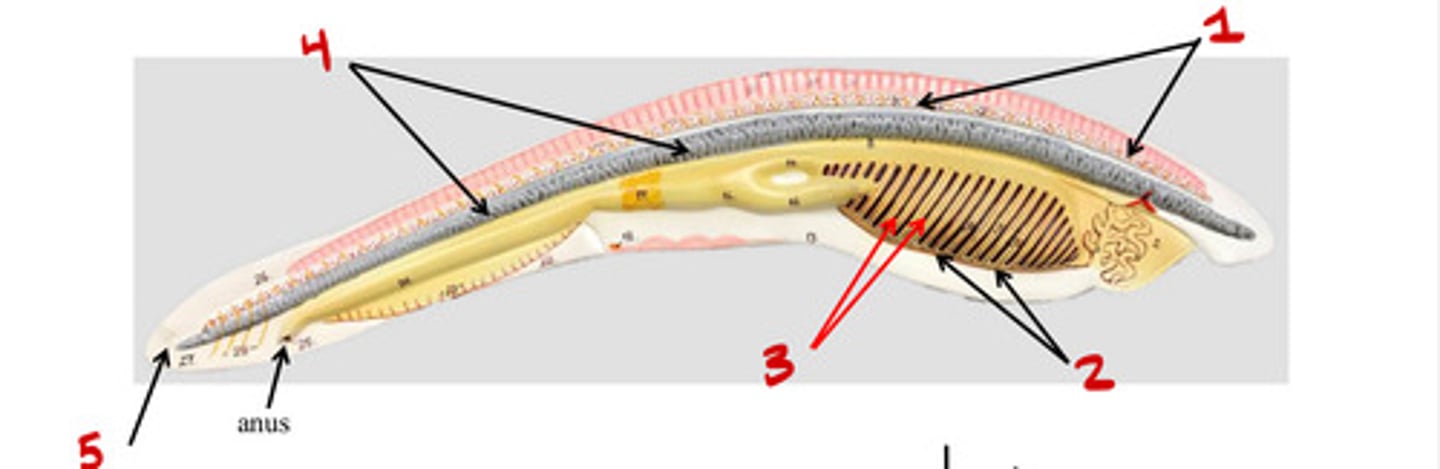
Dorsal nerve chord
1
Tentacles
4
Pharyngeal slits
3
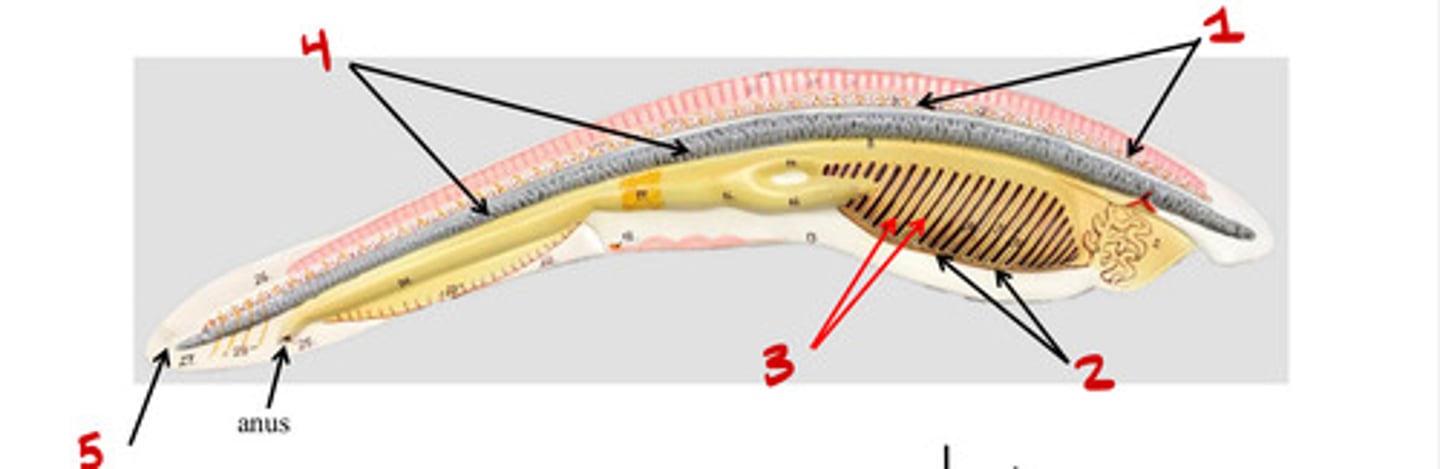
Mouth
5
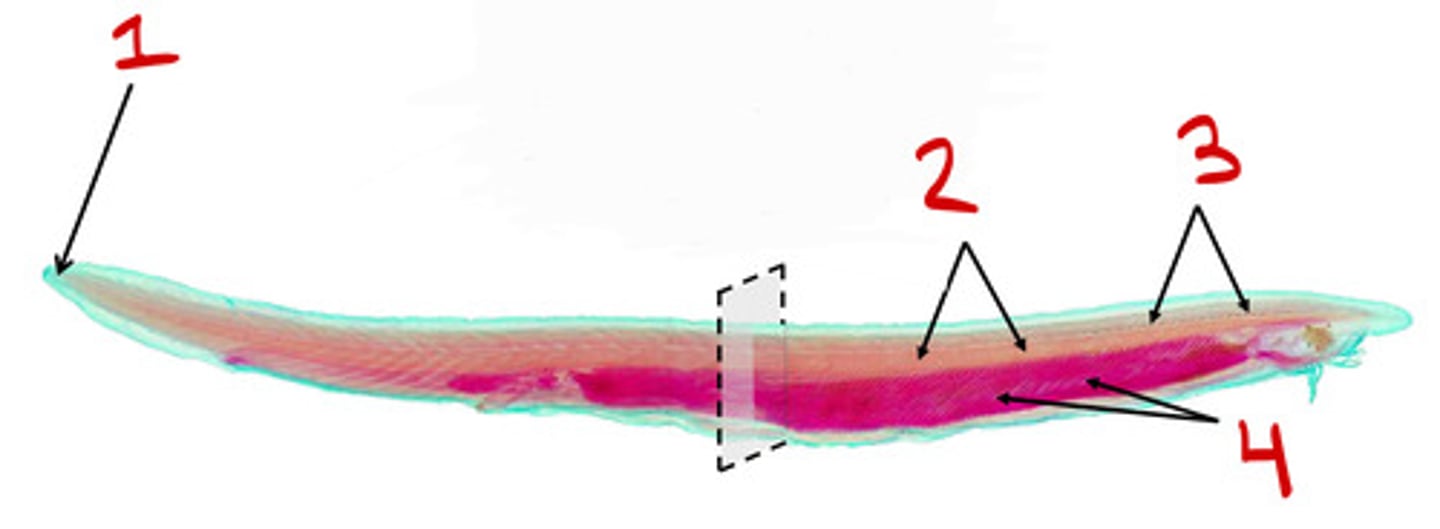
Cephalochordata
Subphylum
Dorsal nerve chord
1
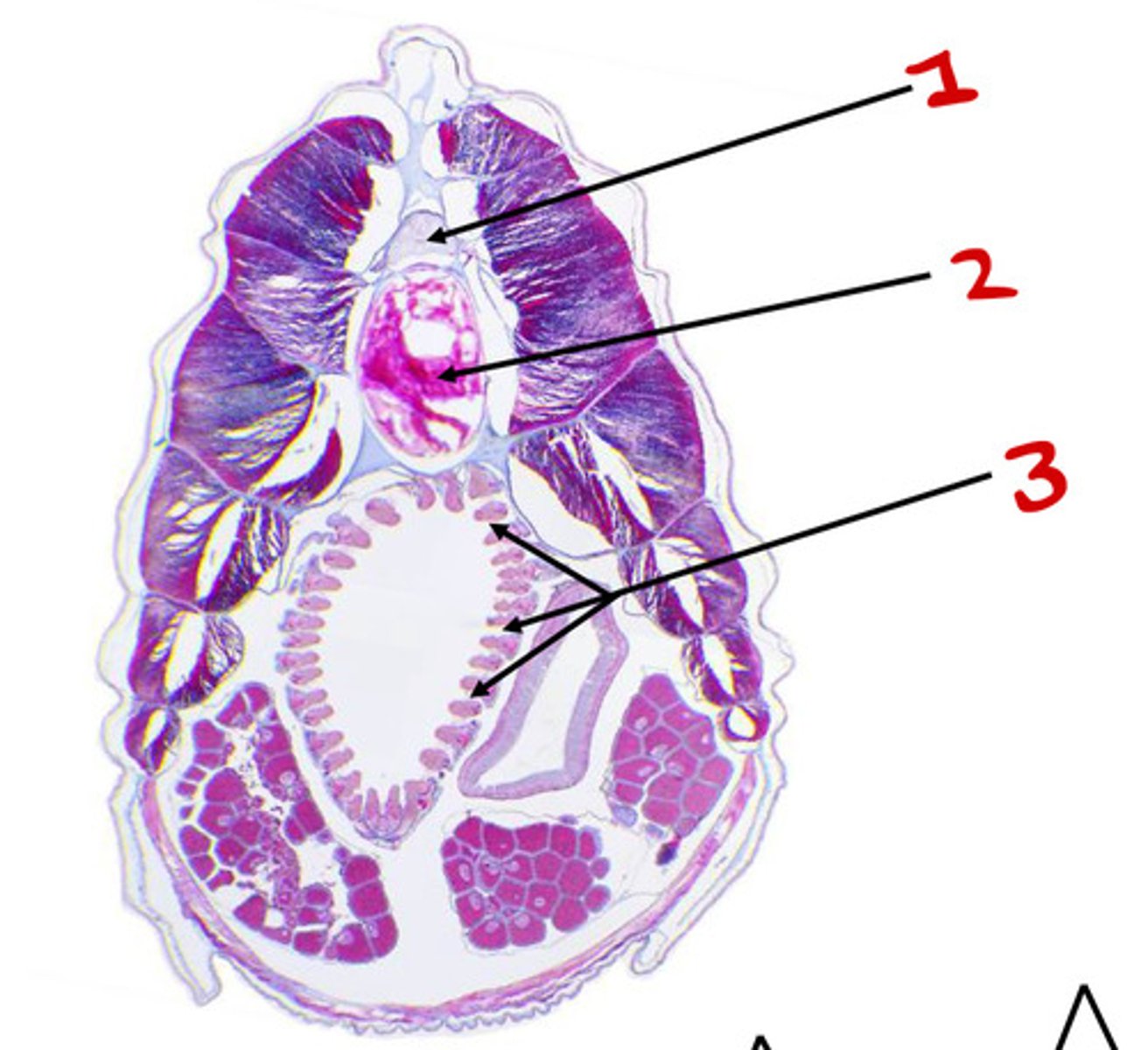
Notochord
2
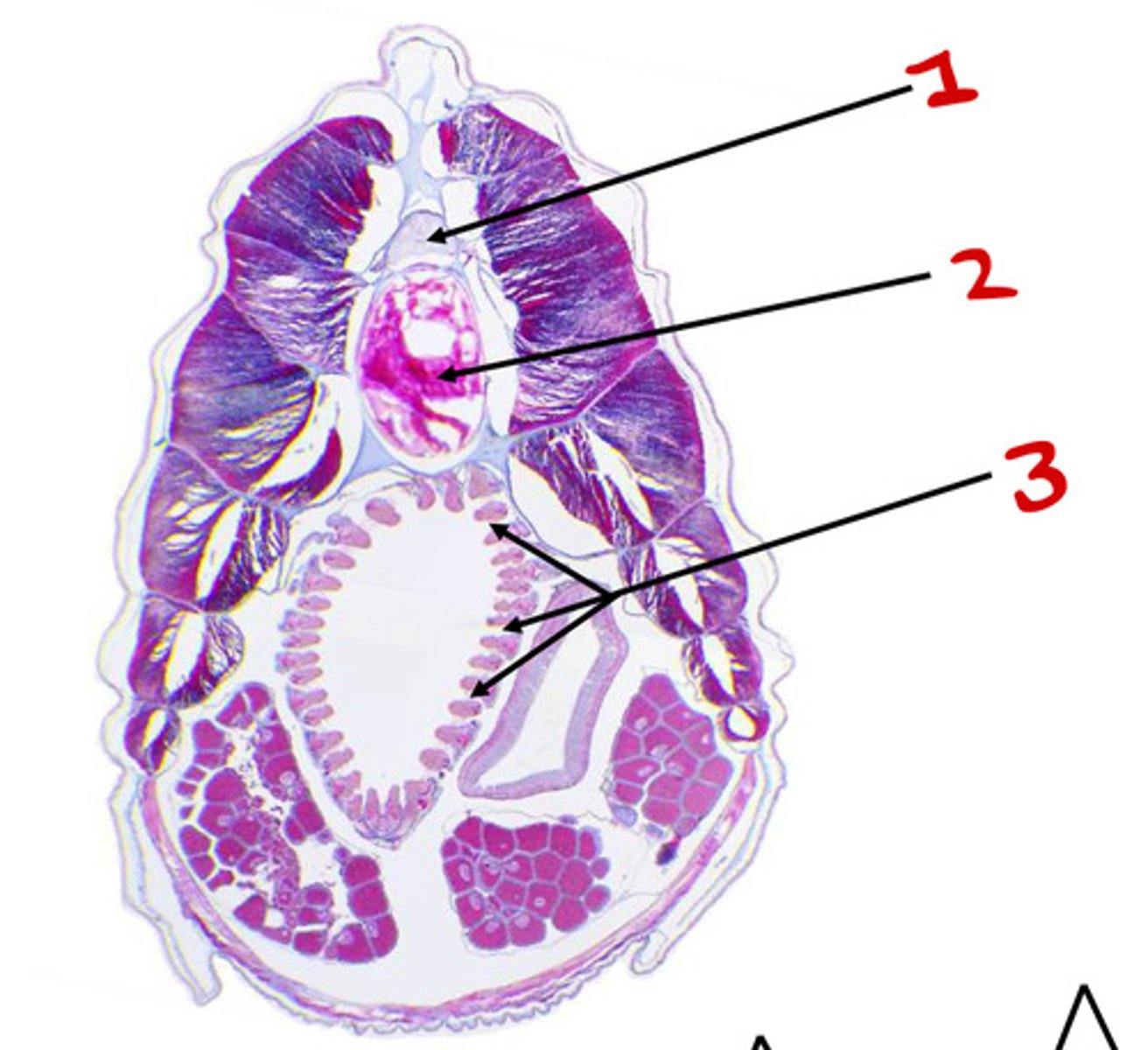
pharyngeal slits
3
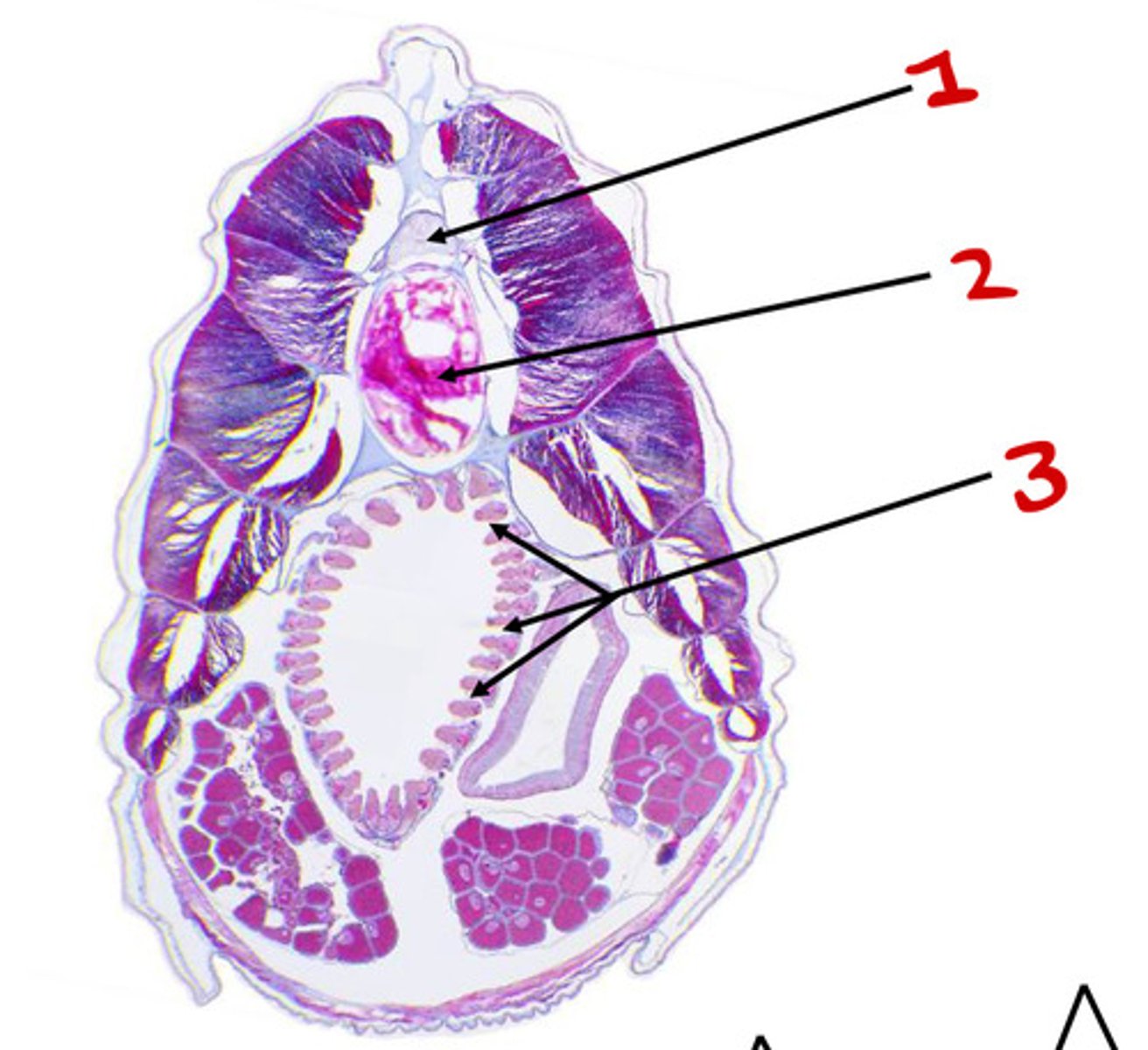
Notochord
4
Tail
5
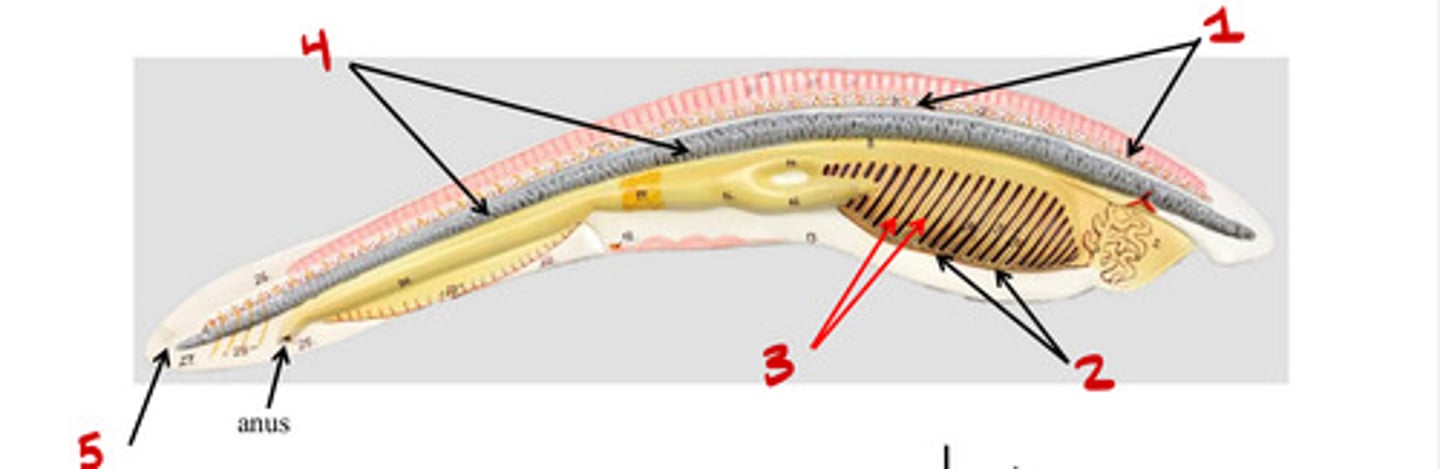
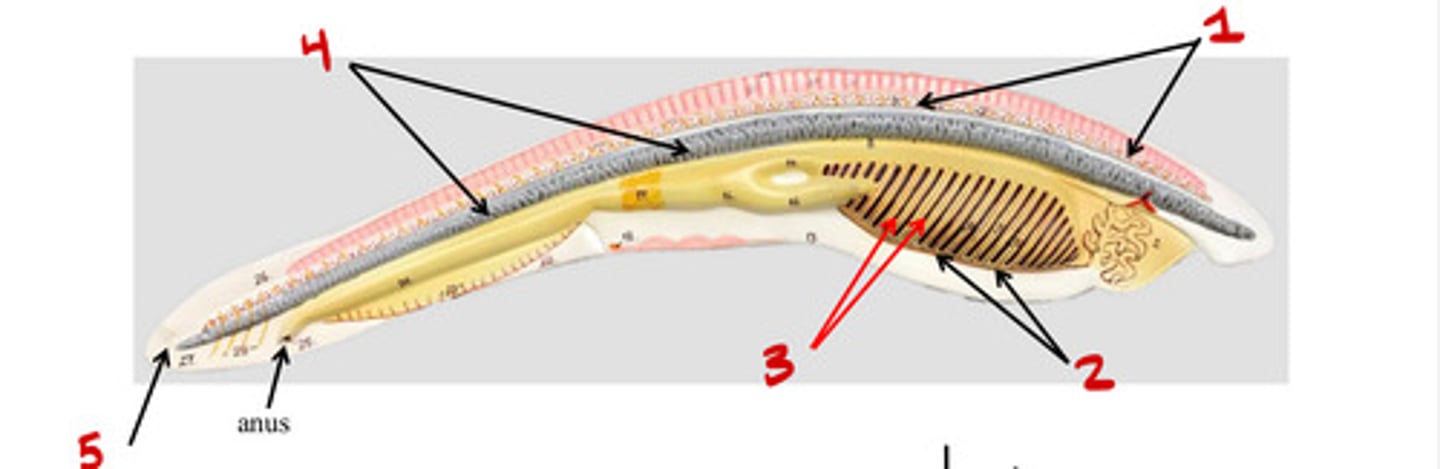
Cephalochordata
Subphylum
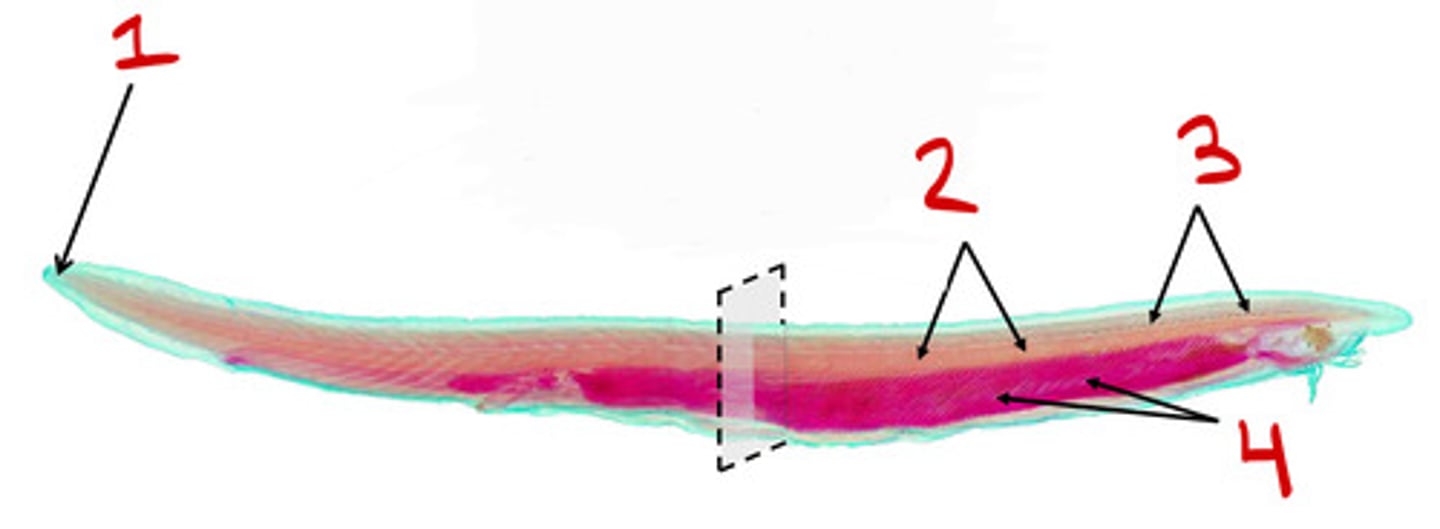
Tail
1
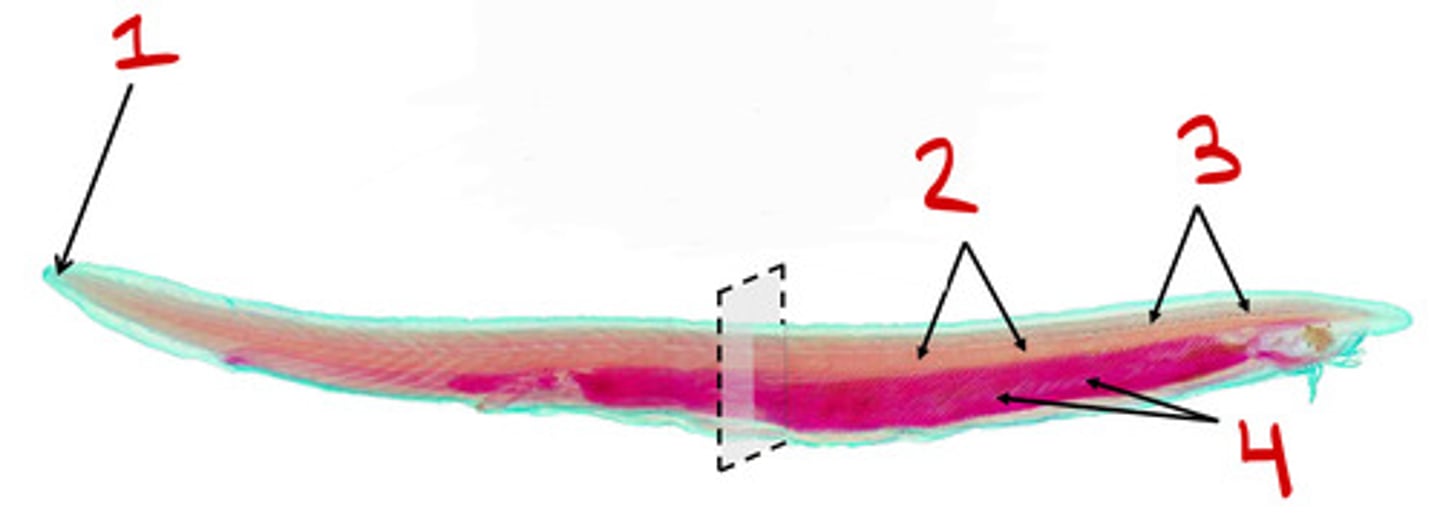
Notochord
2
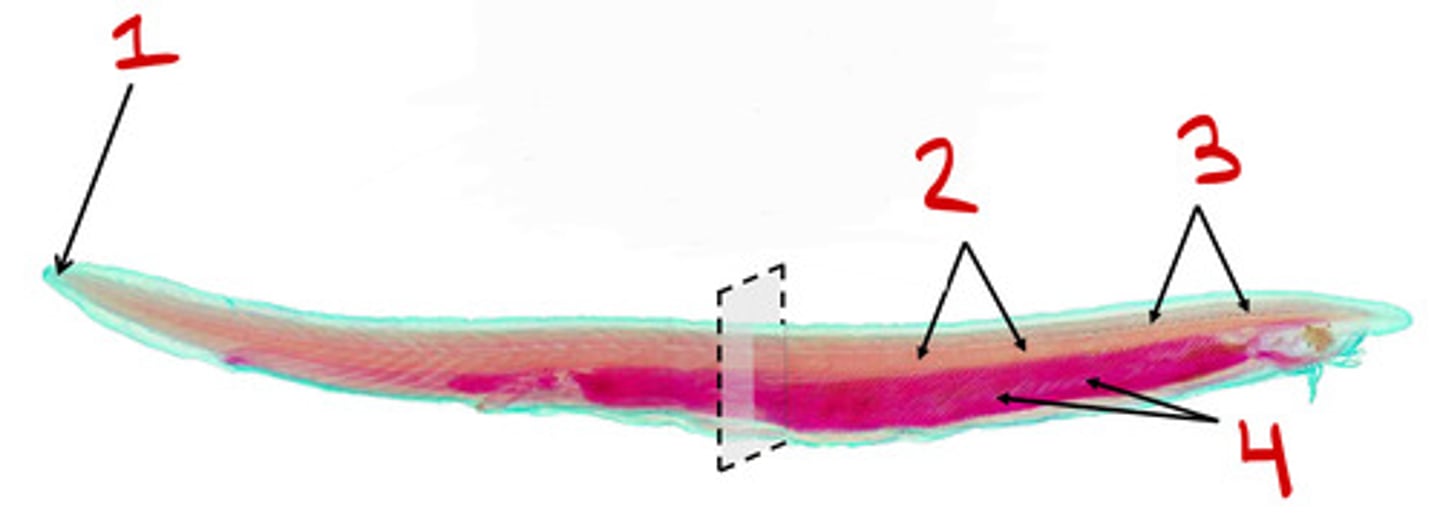
Urochordata
Subphylum
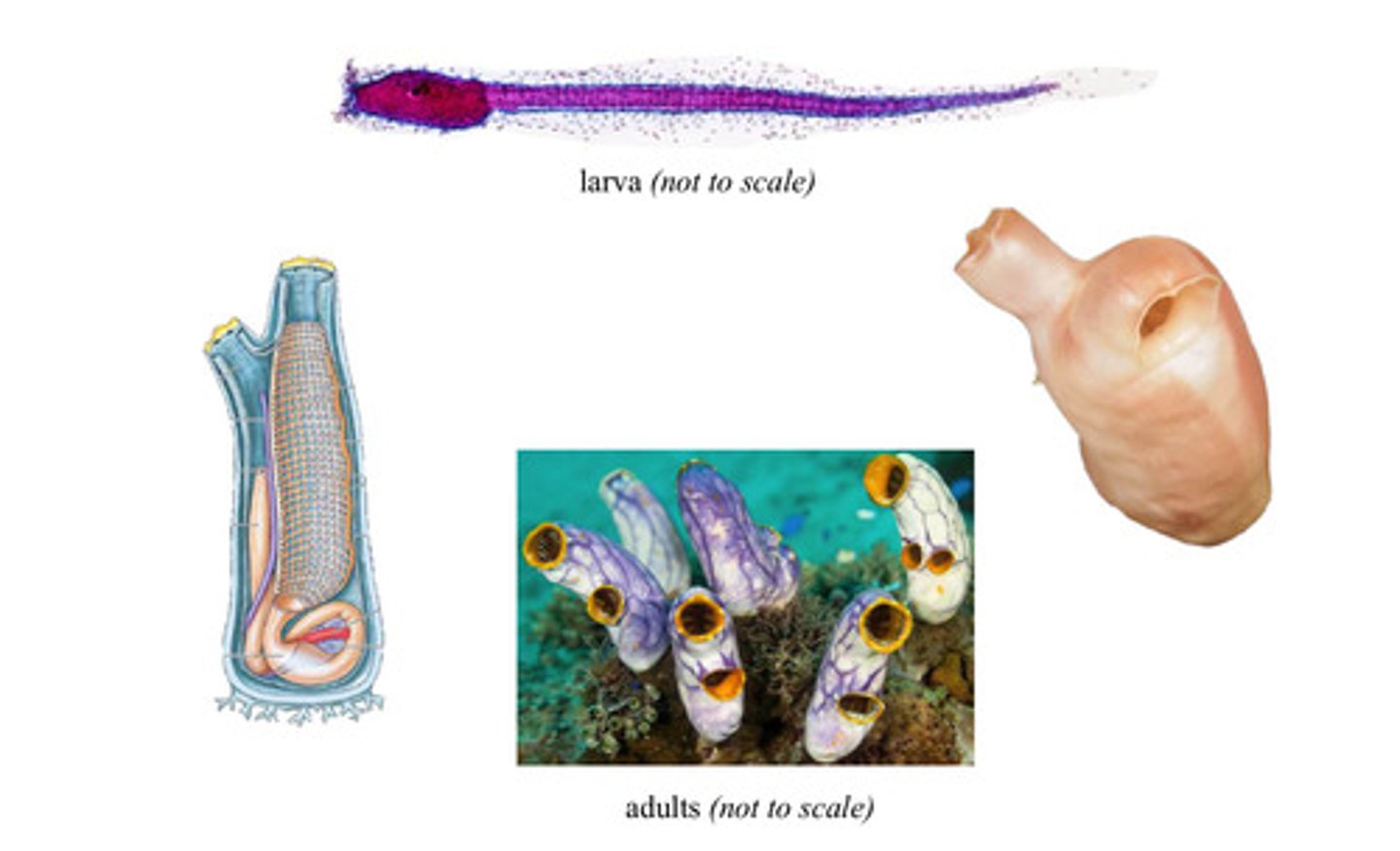
Pharyngeal slits
4
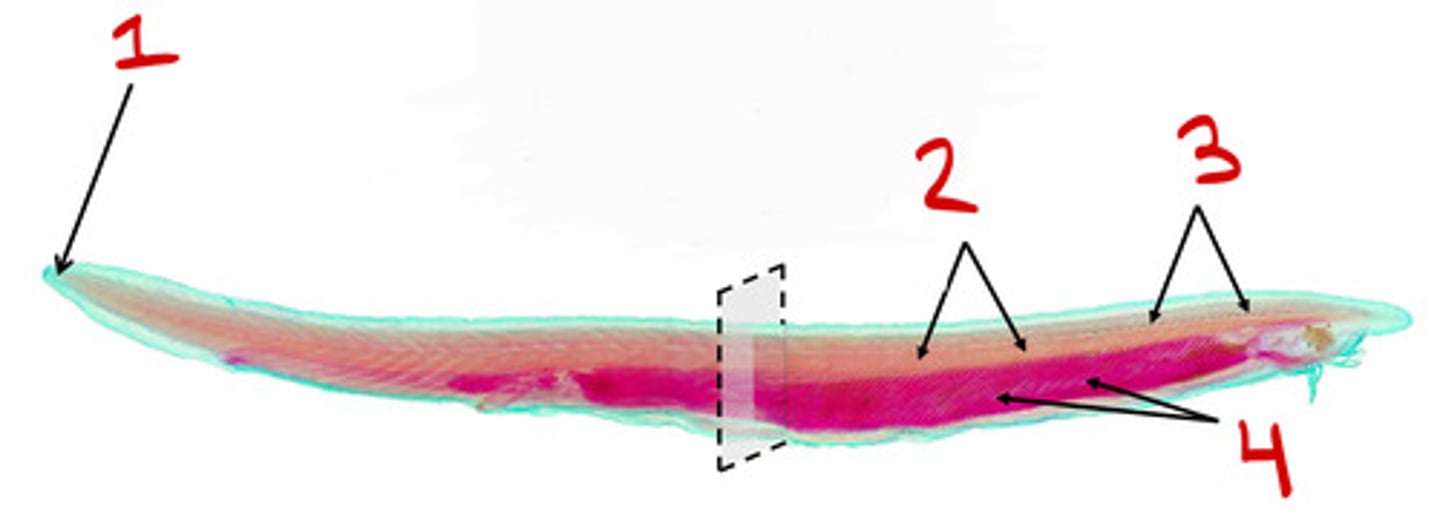
Dorsal nerve chord
3