WCUI echo exit interview questions
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
MVA P 1/2 T severe
>220 ms
Mitral stenosis:
Mean PG Mild
< 5 mmHg
Mitral stenosis:
Mean PG Moderate
5-10 mmHg
Mitral stenosis:
Mean PG Severe
> 10 mmHg
Mitral stenosis:
Max PG Normal
<20 mmHg
Mitral stenosis:
Max PG Moderate
20-40 mmHg
Mitral stenosis:
Max PG Severe
>40mmHg
Mitral Valve area ( MVA )
Normal
4.0–6.0 cm²
Mitral Valve area ( MVA )
<1.0 cm²
Aortic Stenosis AVA:
normal valve
3-5 cm²
Aortic Stenosis AVA:
Severe valve
<1.0 cm²
Continuity Equation for AVA
= 0.785 x LVOTᵈ² x LVOT VTI / AOV VTI
Aortic Regurgitation P 1/2 T:
Mild
>500 ms
Aortic Regurgitation P 1/2 T:
Severe
<200 ms
PASP/RVSP equation
4×(TR Vmax sq)+RAP
Normal PASP/RVSP
≤ 35 mmHg
Severe PASP/RVSP
> 70 mmHg
IVC ≤ 2.1 cm AND collapses >50% with sniff
RAP = 3 mmHg
IVC ≤ 2.1 cm AND collapses <50% with sniff
RAP = 8 mmHg
IVC > 2.1 cm AND collapses <50% with sniff
RAP = 15 mmHg
Simplified Bernoulli Equation
ΔP=4×(V)sq
ΔP = pressure gradient (mmHg)
V = peak velocity (m/s)
4 parameters for Diastolic Function
1) Avg E/e = >14
2) Septal e' velocity = <7
3)TR velocity = 2.8
4) LA volume index = >34
Aortic Stenosis:
Mean PG Mild
<20 mmHg
Aortic Stenosis:
Mean PG Severe
>40 mmHg
LVOTO PW
walk down PW Mid LV to AOV
significant LVOTO
> 30 mmHg
HOCM
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
LVOTO
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction
dynamic LVOT obstruction due to
Septal bulging into LVOT
SAM (systolic anterior motion) of the mitral valve.
is the dynamic obstruction it creates.
LVOTO
is the disease
HOCM
4 characteristics of LVOTO/ HOCM
1) IVS thickness
2)SAM- systolic anterior motion of MV
3) Mid-systolic notching of the AOV
4) Dagger-shaped waveform through LVOT
E/e' ( TDI ) normal
<10
E:A normal
>0.8
LA volume index normal
16-34 mL/m sq
Deceleration Time ( DT )
140-240 ms
3 stages of Coronary Arteries & Myocardial Damage
1) Ischemia
2)Injury
3) Infraction
myocardial infarction
1) LV/RV failure
2)Heart wall rupture
3) Papillary Dysfunction
4) Mitral Regurgitation
STEMI
ST elevation MI, real-time ongoing death of heart tissue due to ischemia
ST segment elevation
NON STEMI
ST segment depression or inverted
S-A-L-I
1) septal
2) Anterior
3) Lateral
4) Inferior
LAD coronary artery
Anterior wall
LCX coronary artery
Lateral
RCA coronary artery
Interior wall
Cardiac tamponade Symptoms
1) CP
2)Cough
3) Fatigue
4)Cold extremities
Beck's Triad
1) Hypotension
2) Distant/muffled heart sound
3) Elevated venous pressure
Hypokinetic
Reduced contraction
Wall thickens/moves inward, but less than normal.
Example: ischemia, stunned myocardium.
Akinetic
No contraction
Wall does not thicken or move inward during systole.
Example: infarcted/scarred myocardium.
Dyskinetic
Dyskinetic
Paradoxical/outward motion during systole.
Instead of contracting in, the wall bulges out.
Example: ventricular aneurysm after MI.
GLS Hypokinetic
less negative
GLS Akinetic
close to zero
GLS Dyskinetic
positive
GLS normal
> -18%
Shunt flows
Left to Right
Causing Right ventricular overload ( RVVO )
ASD Echo findings secondary findings
1) IVC Dilation
2) Right Atrial Enlargement
3) Tricuspid Hypertension
ASD (Atrial Septal Defect)
a hole in the interatrial septum that allows blood to flow between the left atrium (LA) and right atrium (RA).
PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale)
A PFO is a small, flap-like opening in the atrial septum that fails to close after birth.
PFO Right to Left Shunt
expect embolism.
Bubble study
Valsalva
VSD (Ventricular Septal Defect)
A VSD is a hole in the interventricular septum that allows blood to flow between the left and right ventricles.
VSD secondary findings
1) Left Atrial Enlargement
2) IVC Dilatation
3) Pulmonary Artery Dilation
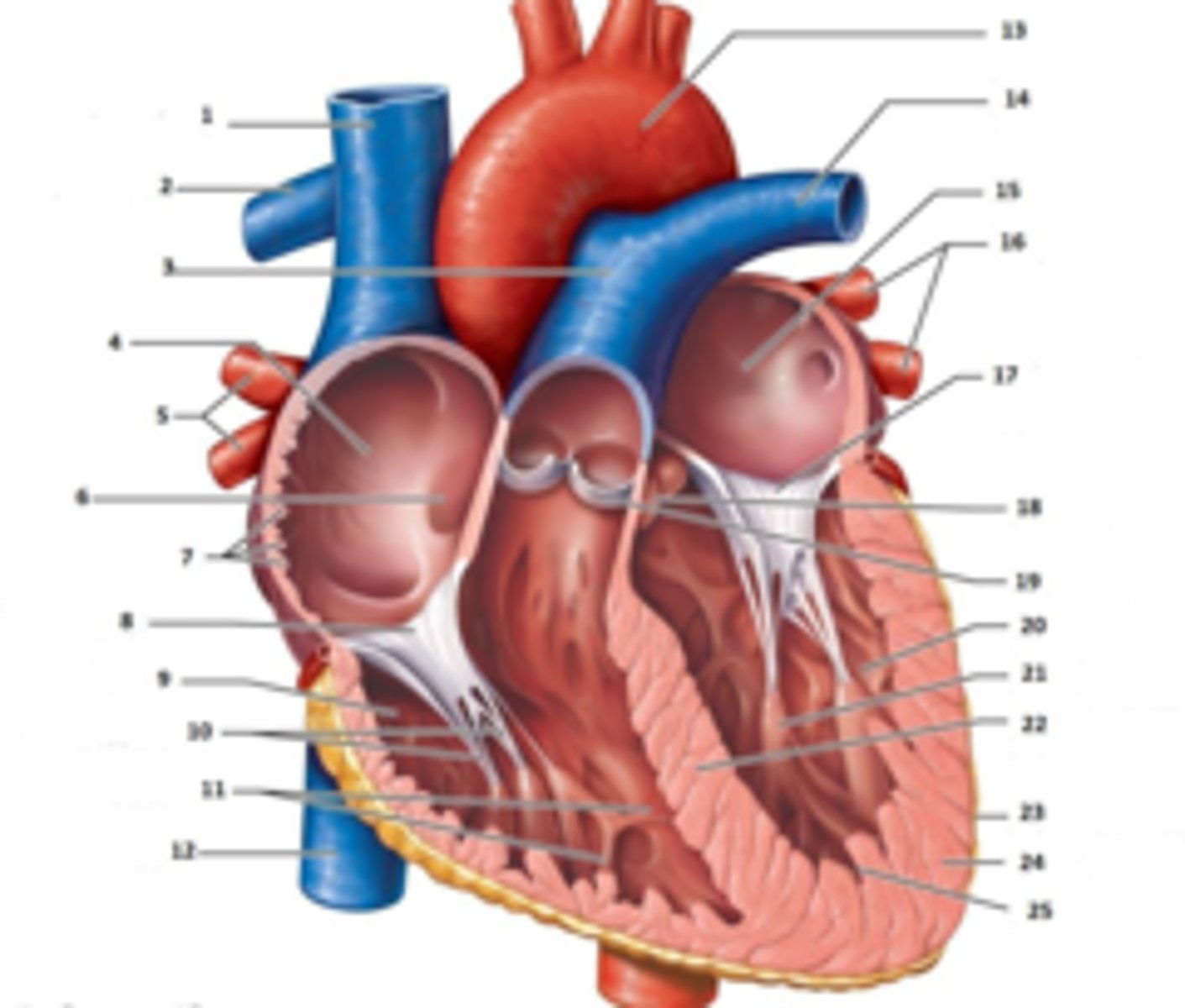
IAS
6
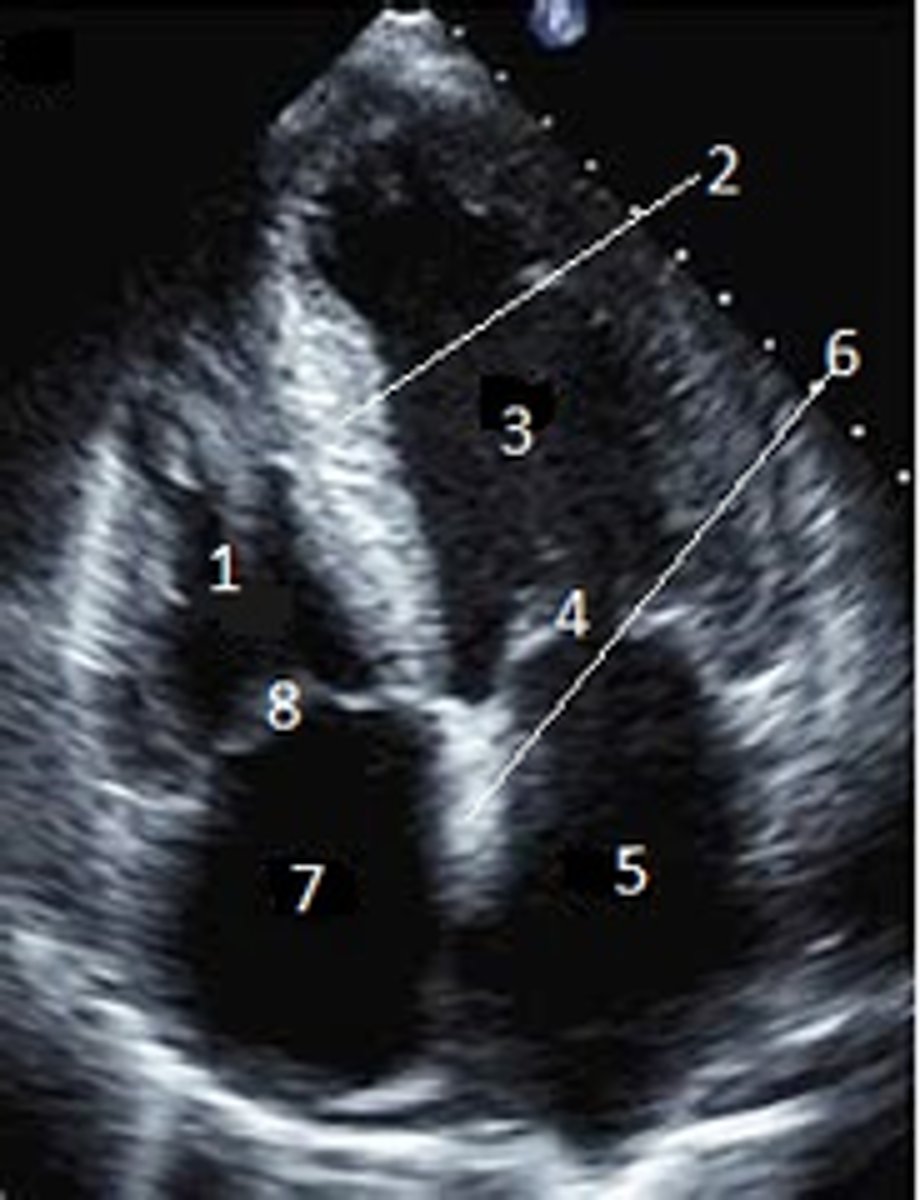
Superior Vena Cava
What is #1
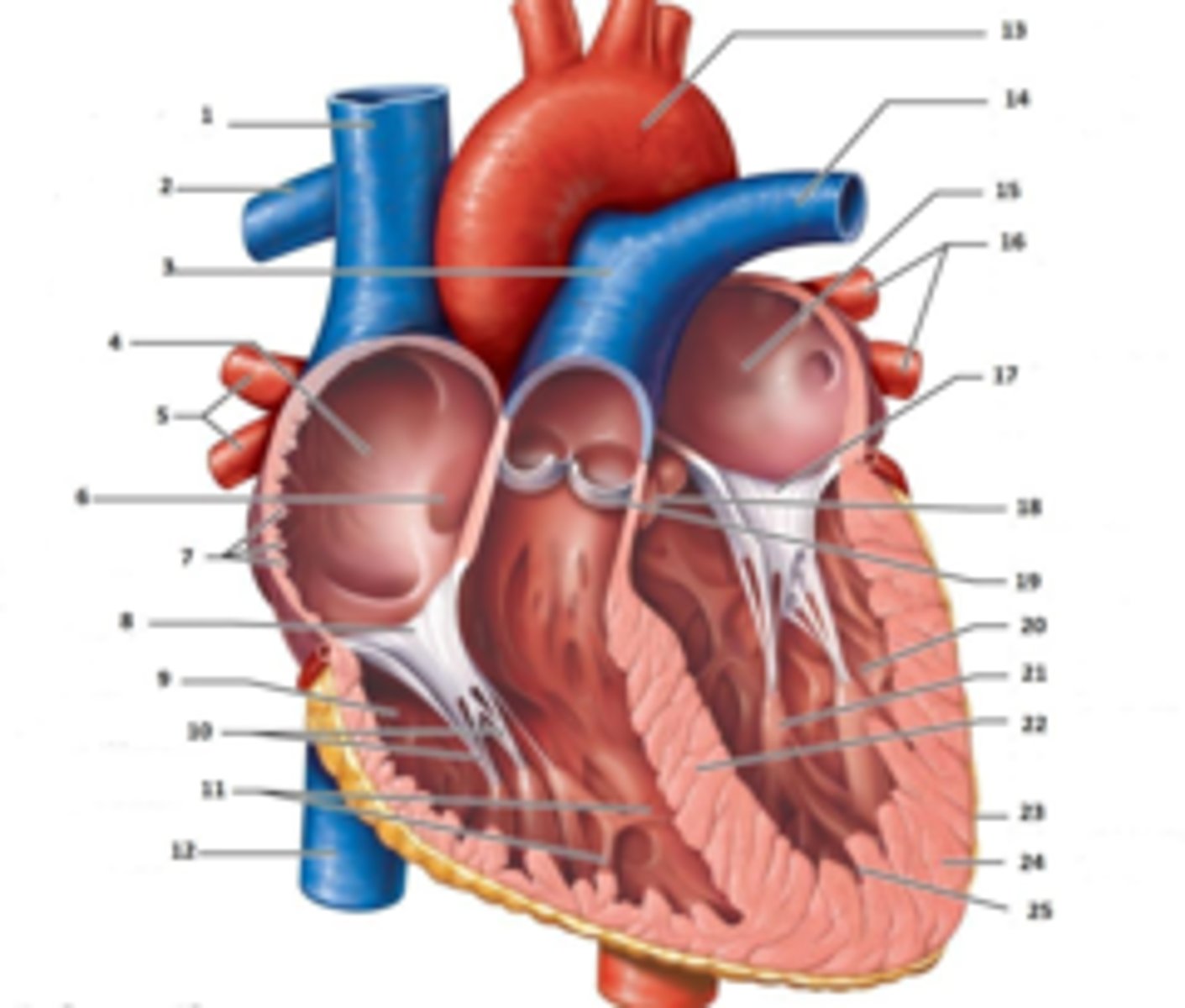
RT Pulmonary Artery
What is #2
Pulmonary Trunk
What is #3
RT Atrium
What is #4
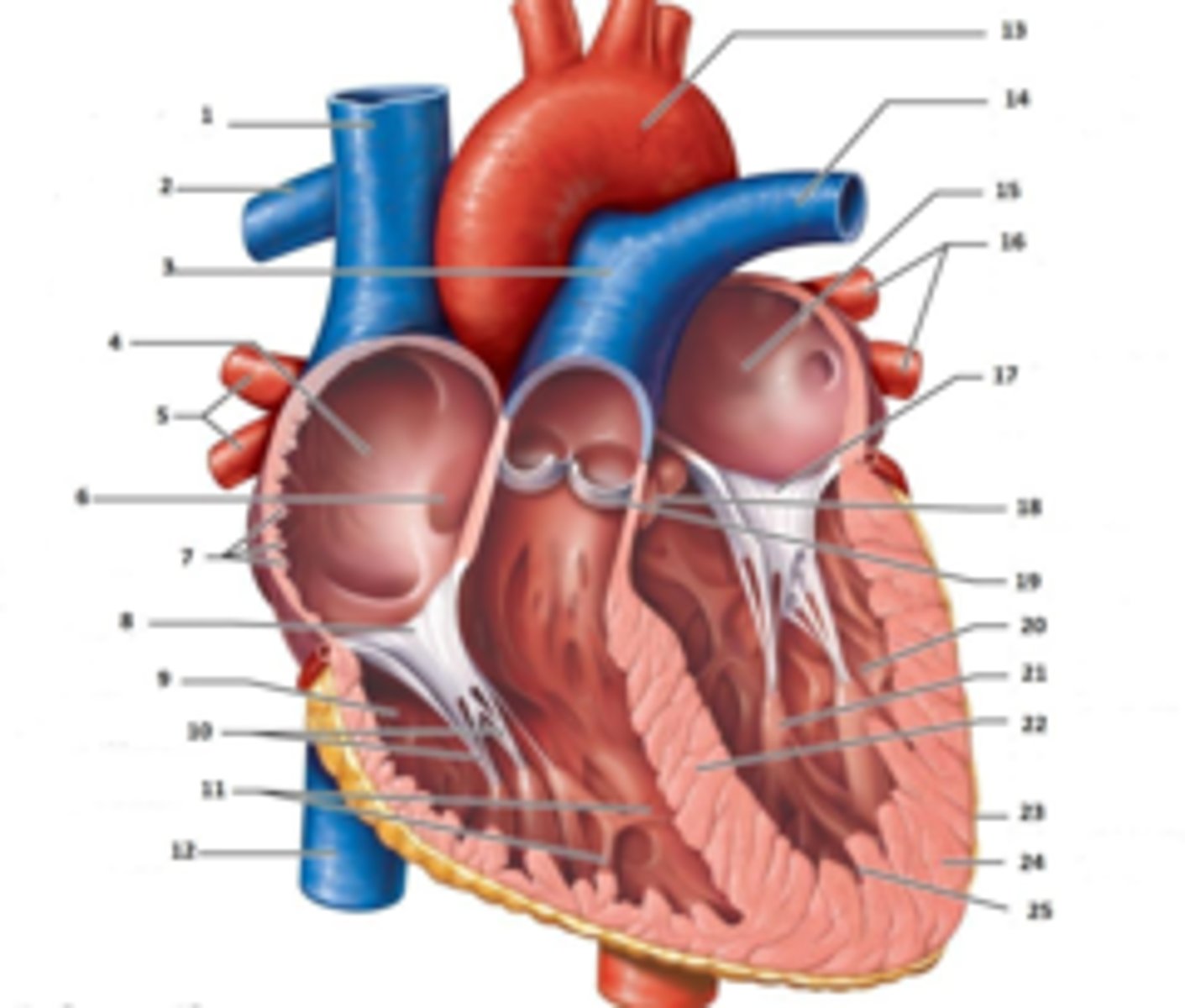
RT Pulmonary Veins
What is #5
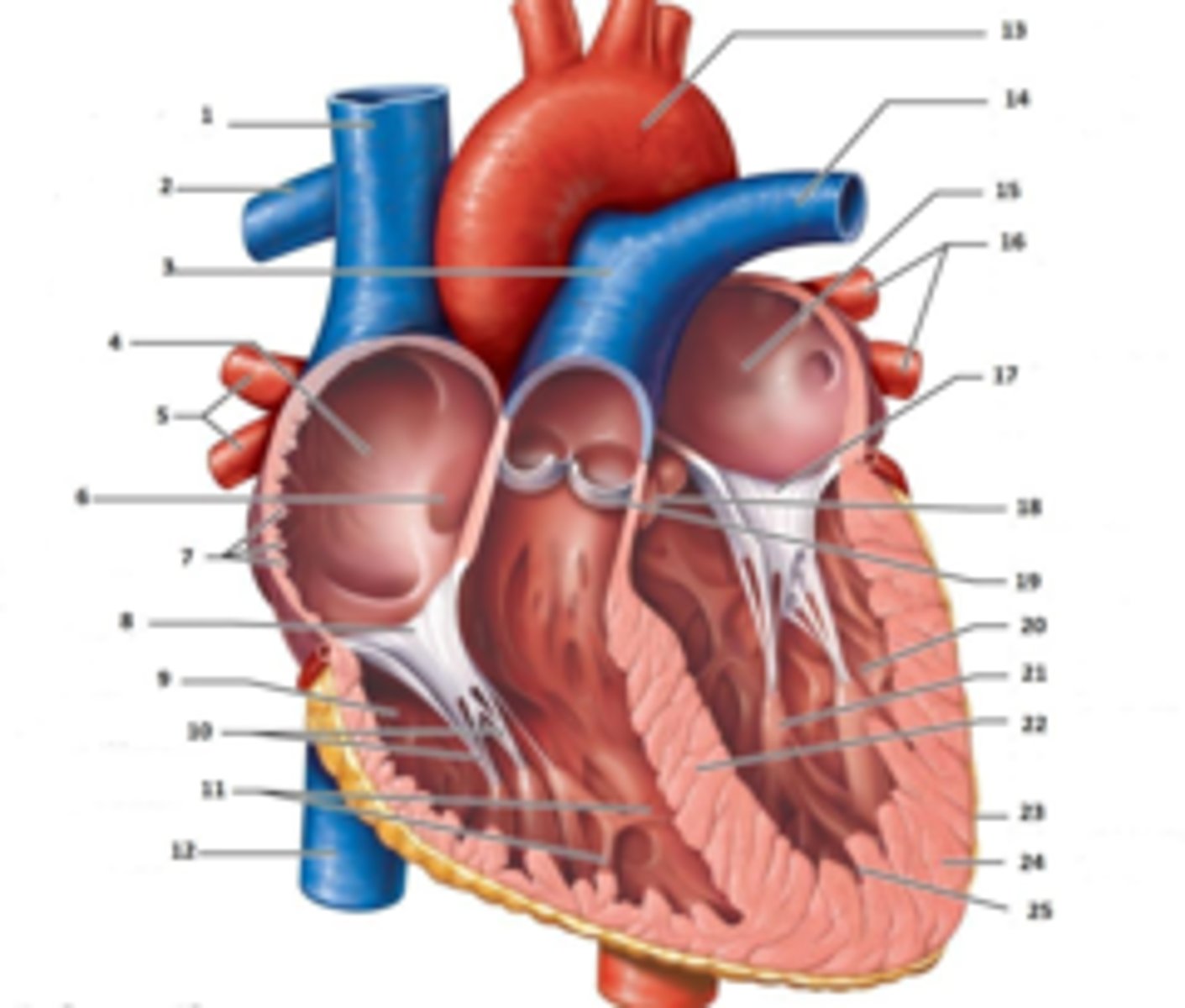
Fossa Ovalis
What is #6
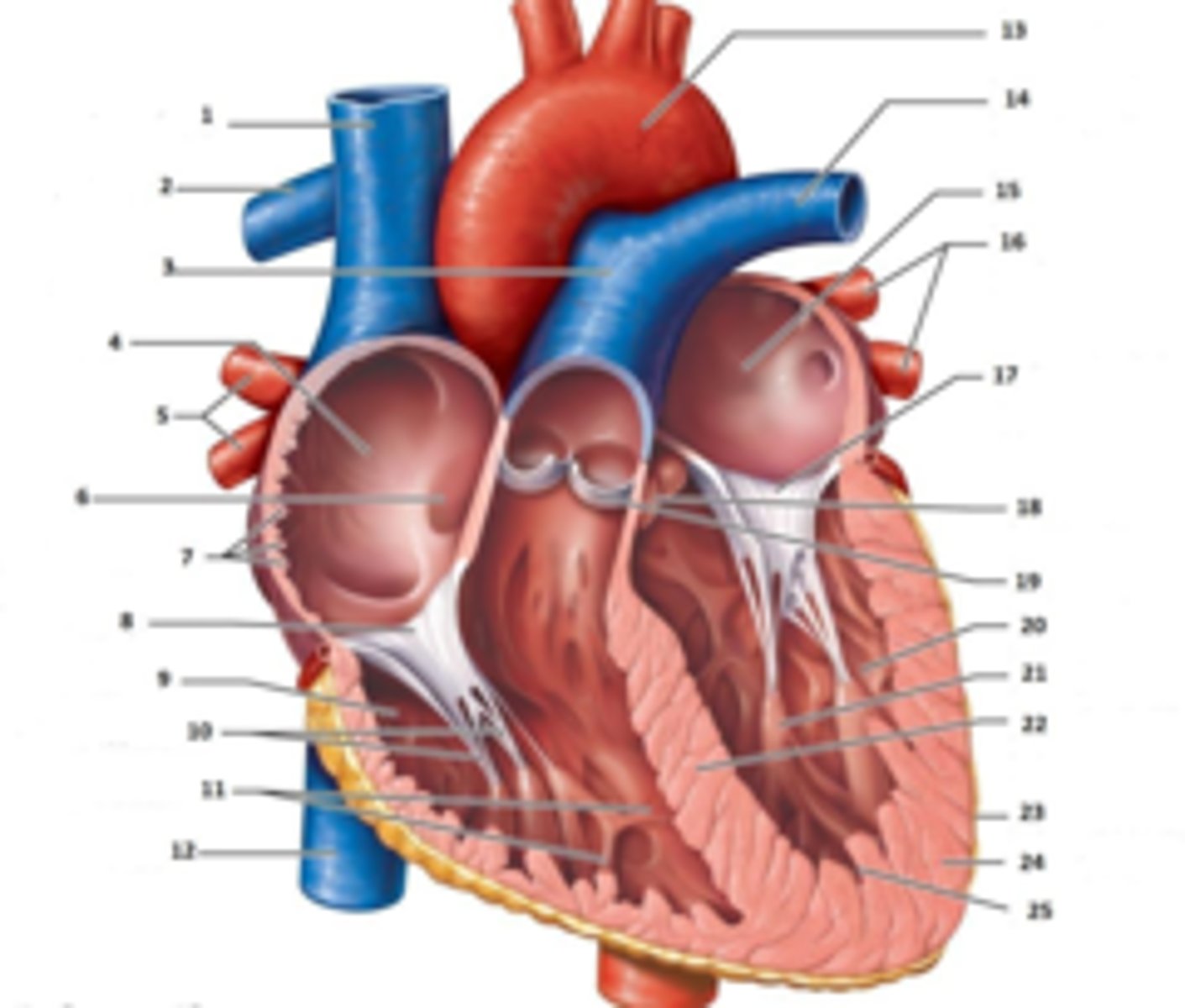
Pectinate muscles
What is #7
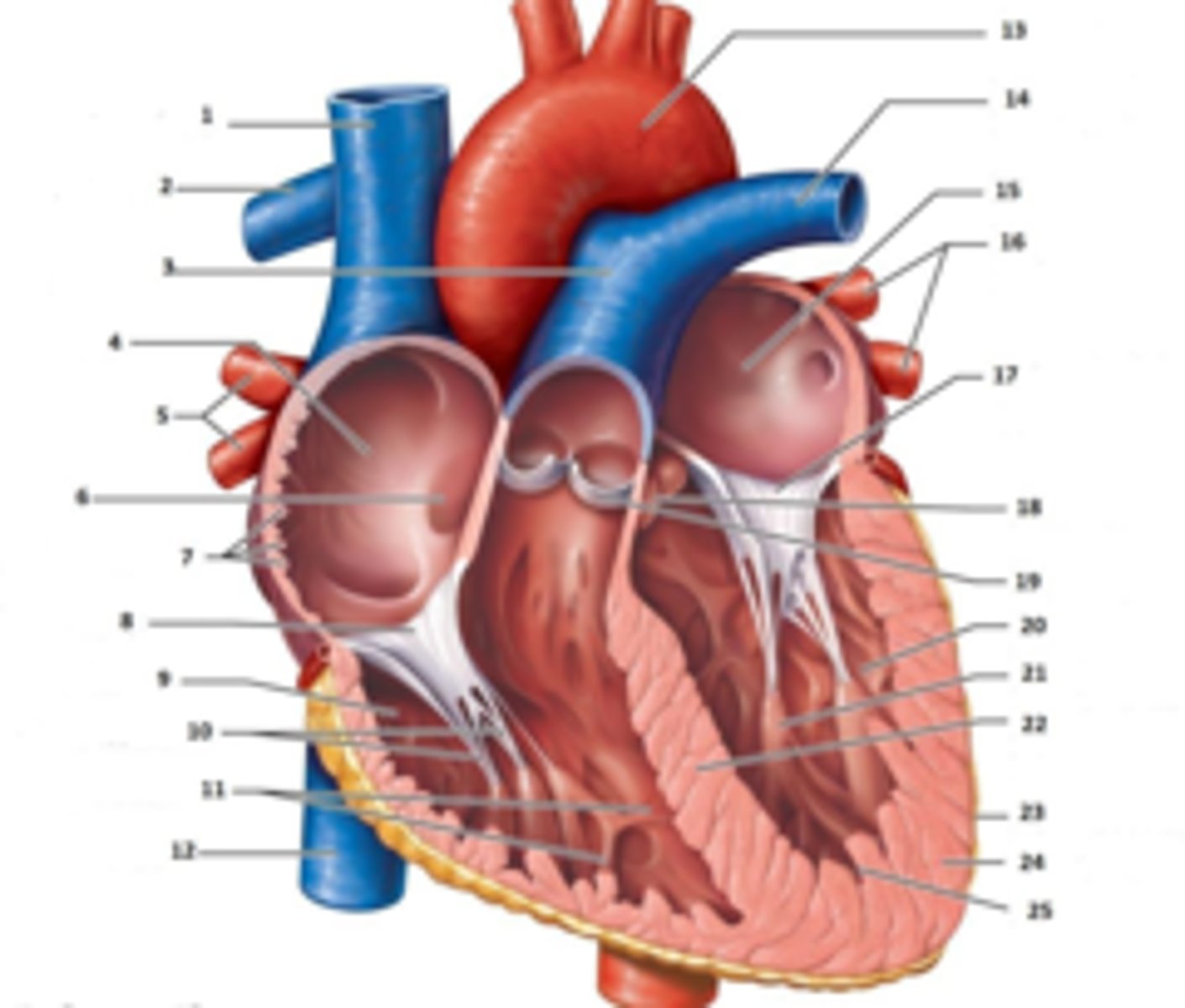
Tricuspid Valve
What is #8
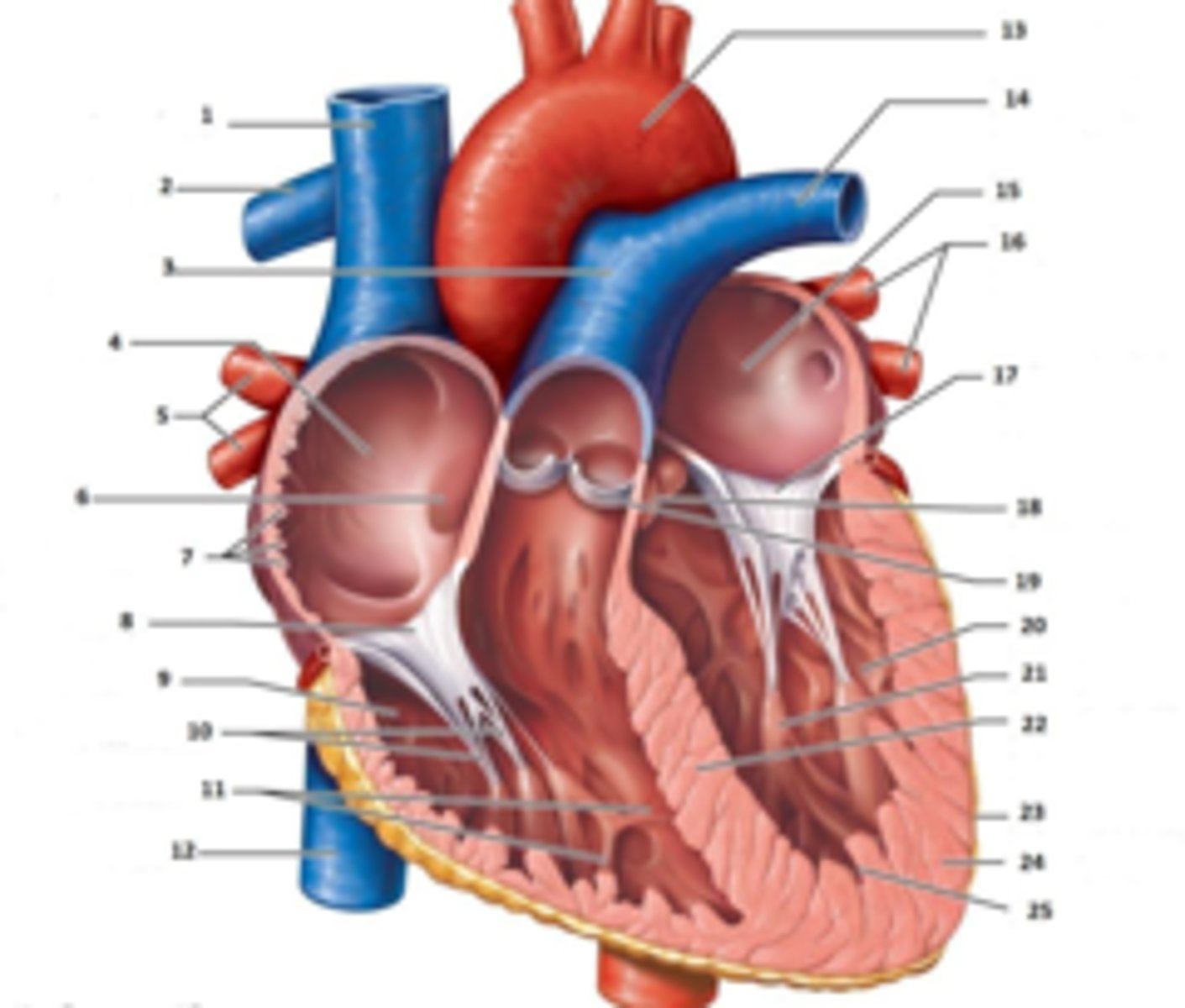
RT Ventricle
What is #9
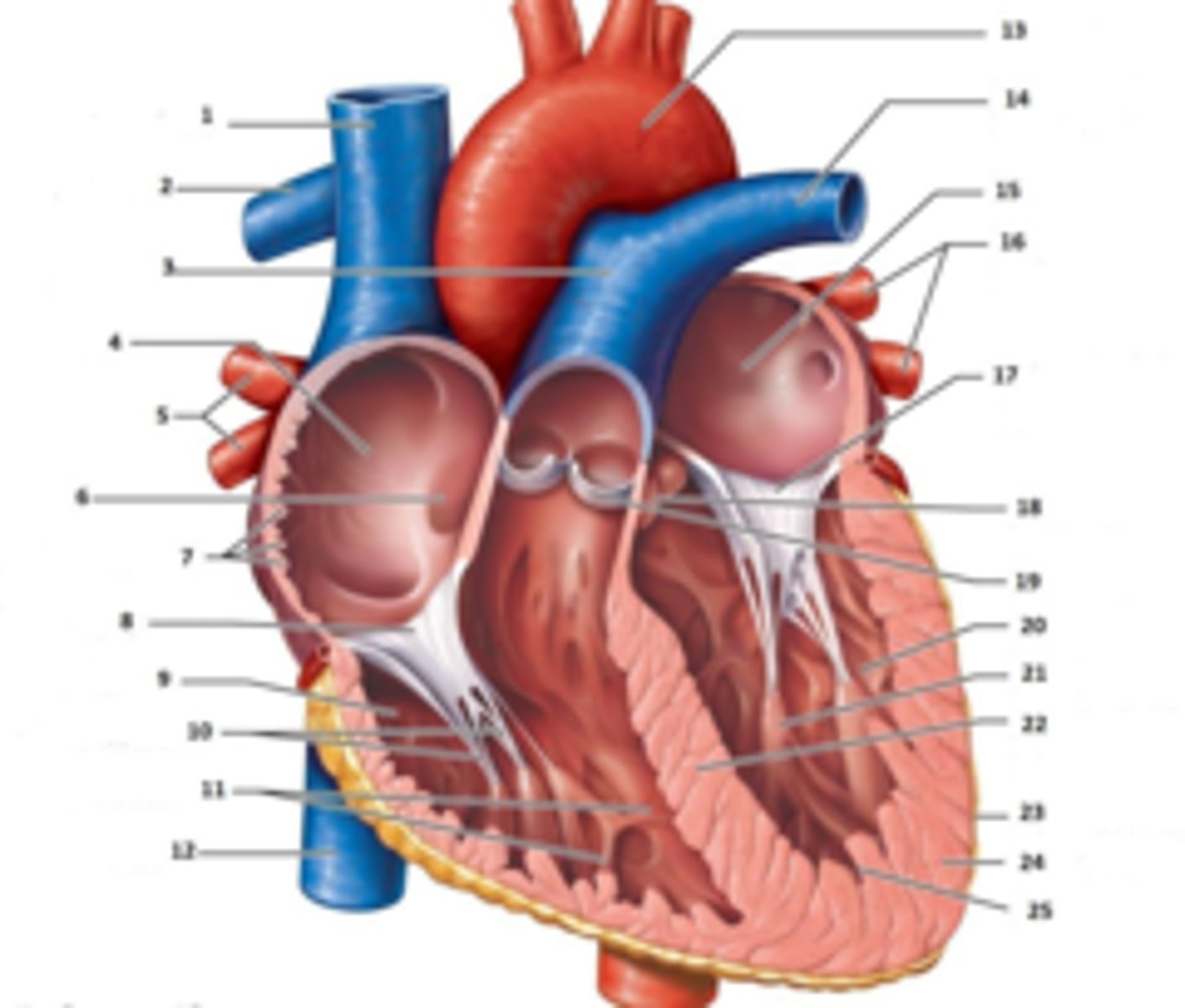
Chordae Tendinae
What is #10
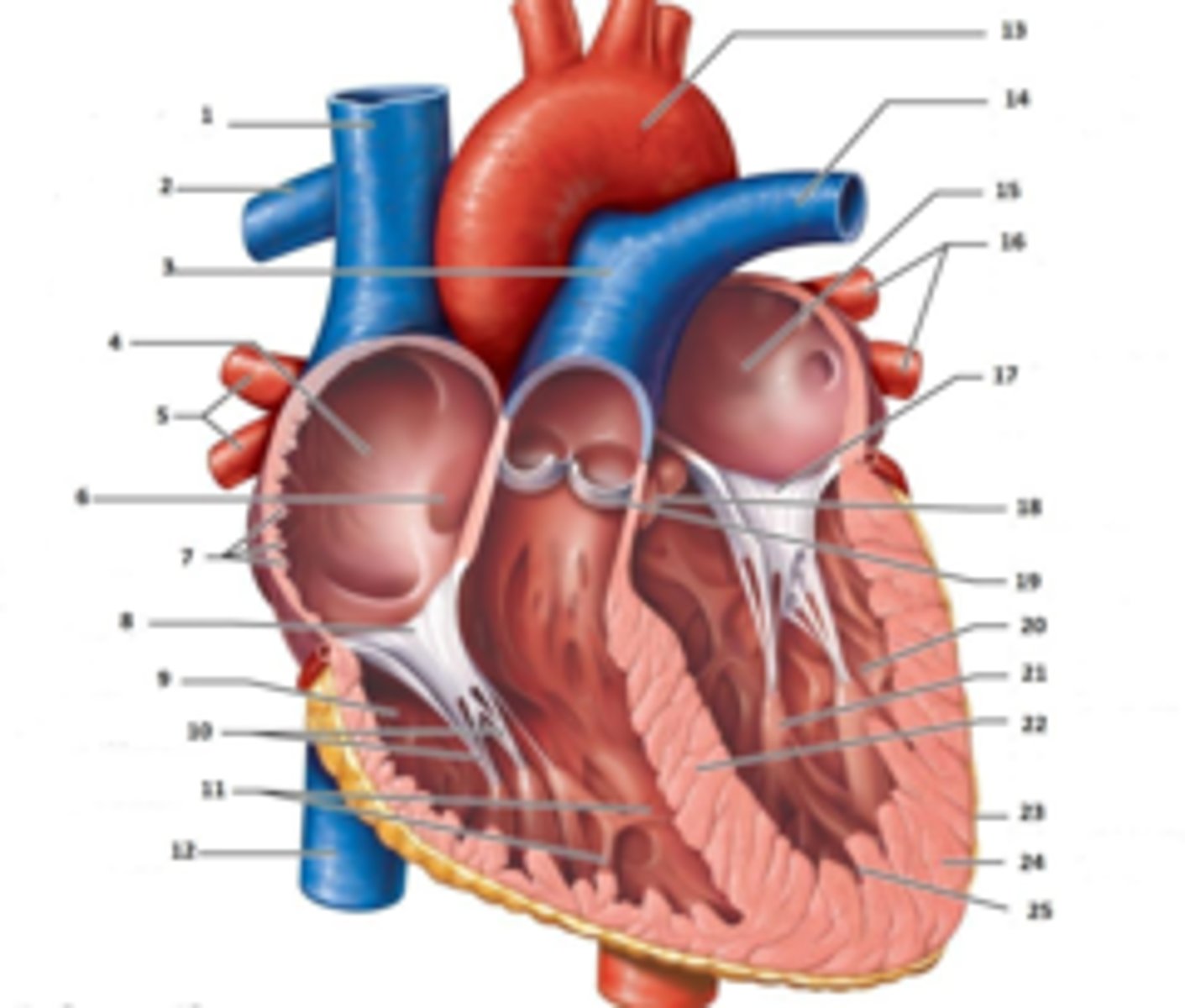
trabecluae carneae
What is #11
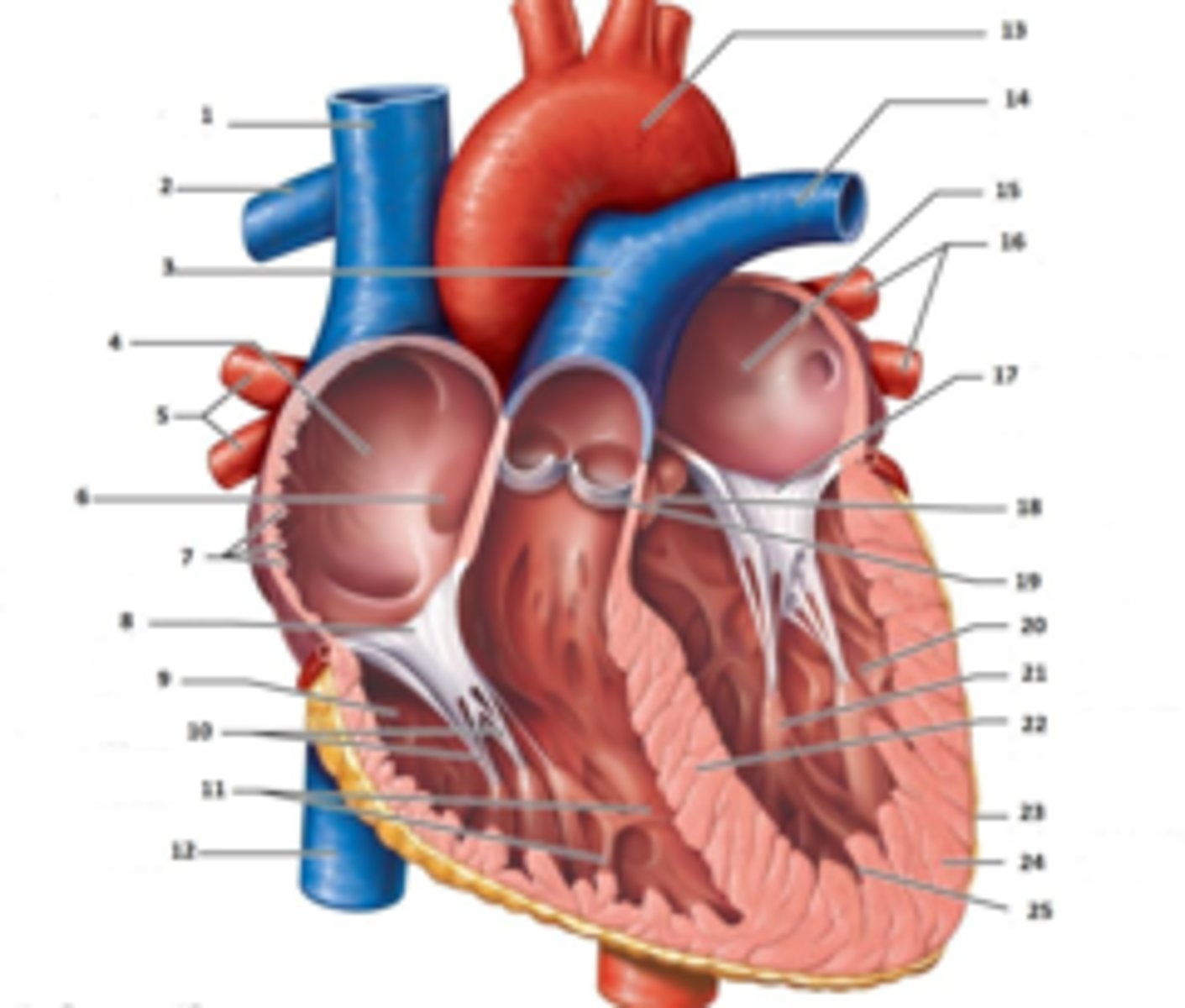
Inferior Vena Cava
What is #12
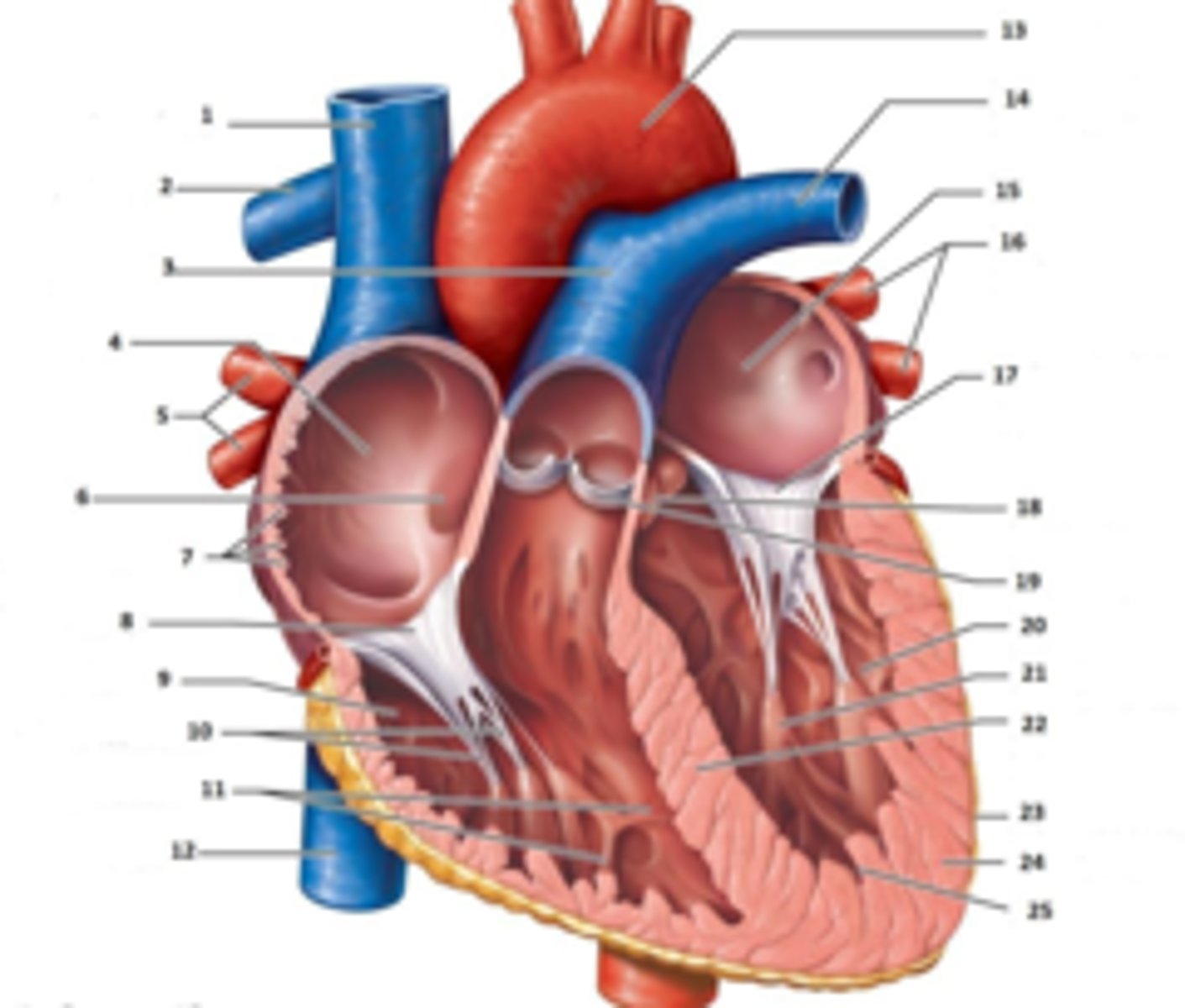
Aorta
What is #13
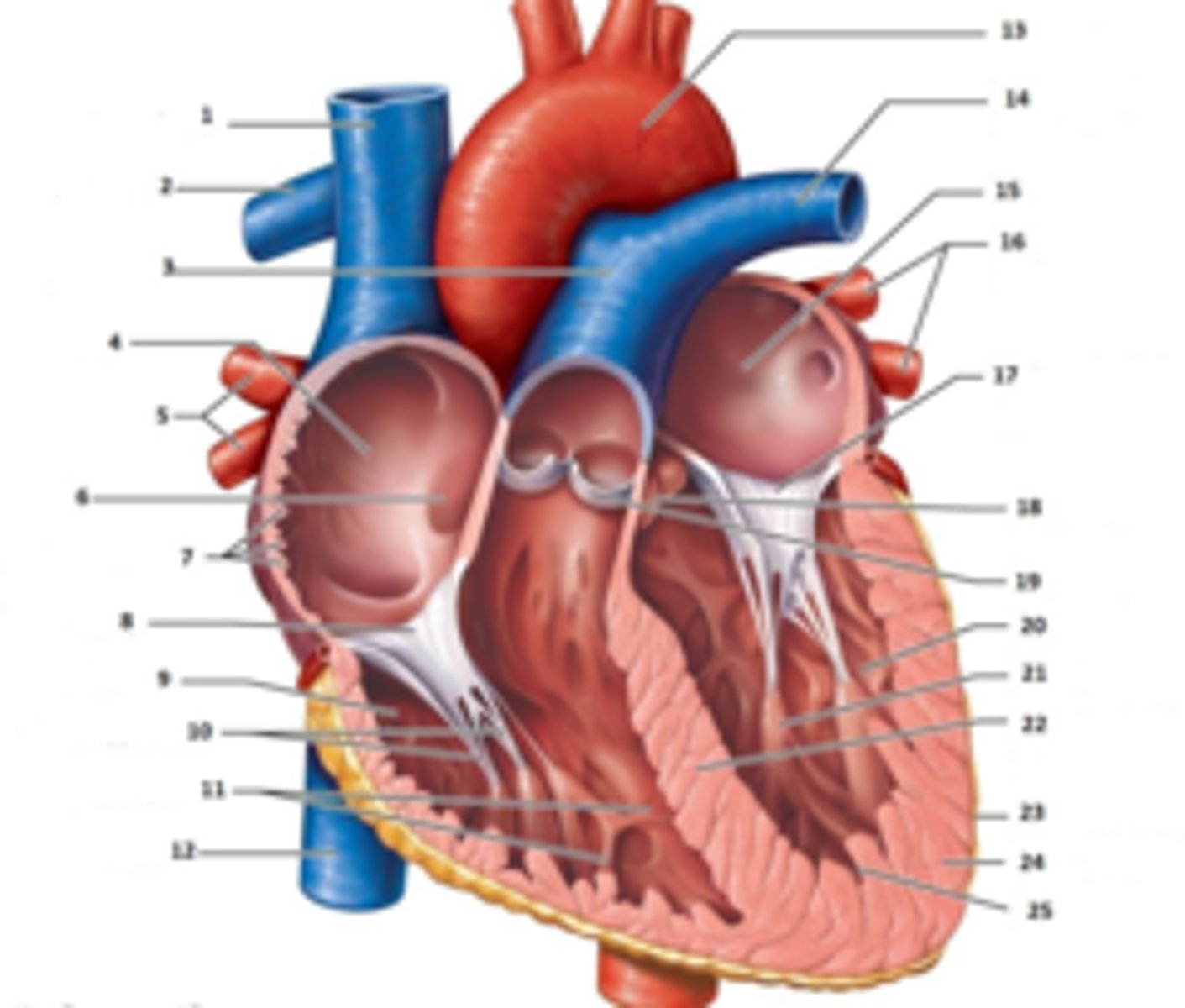
LT Pulmonary Artery
What is #14
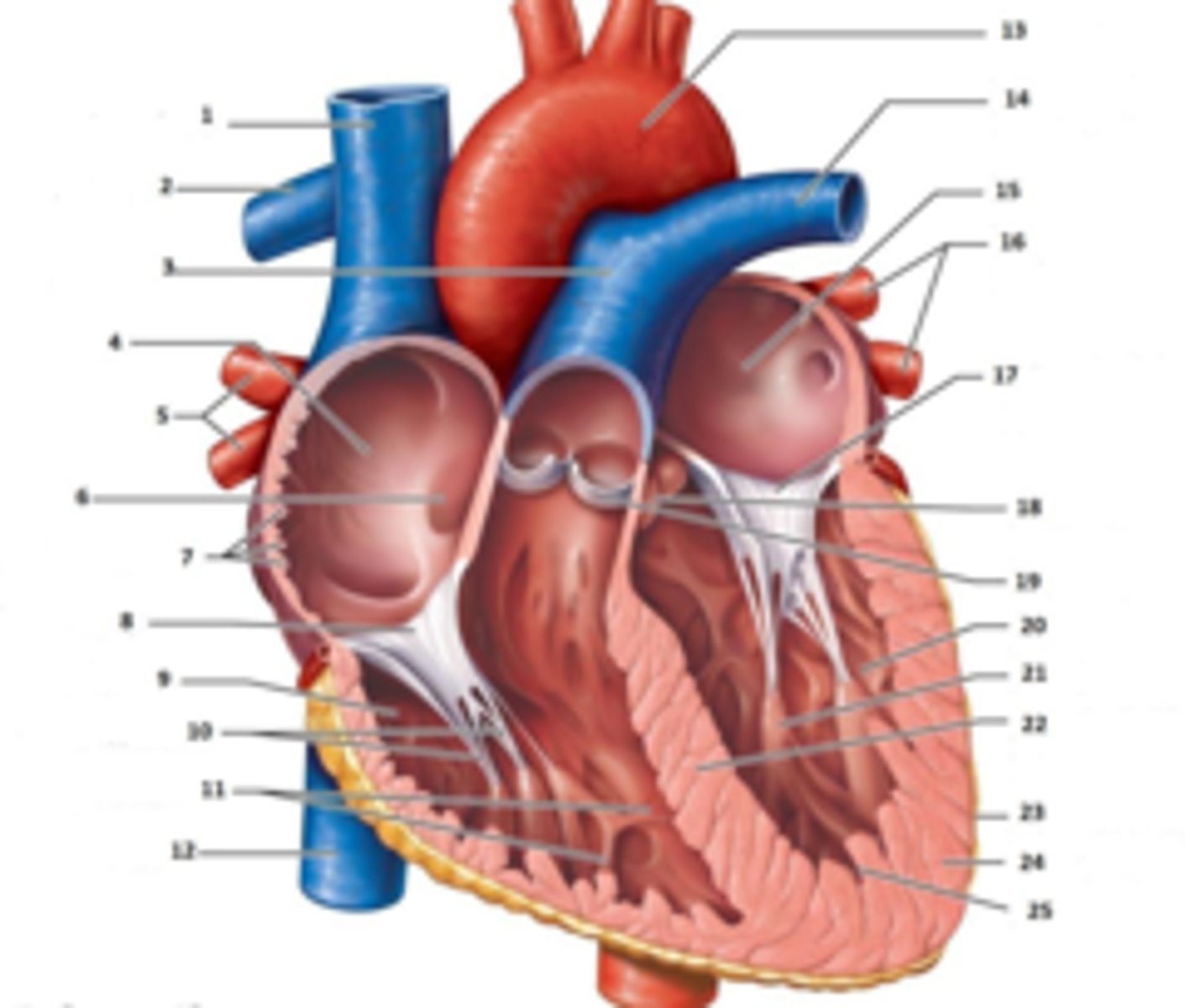
LT Atrium
What is #15
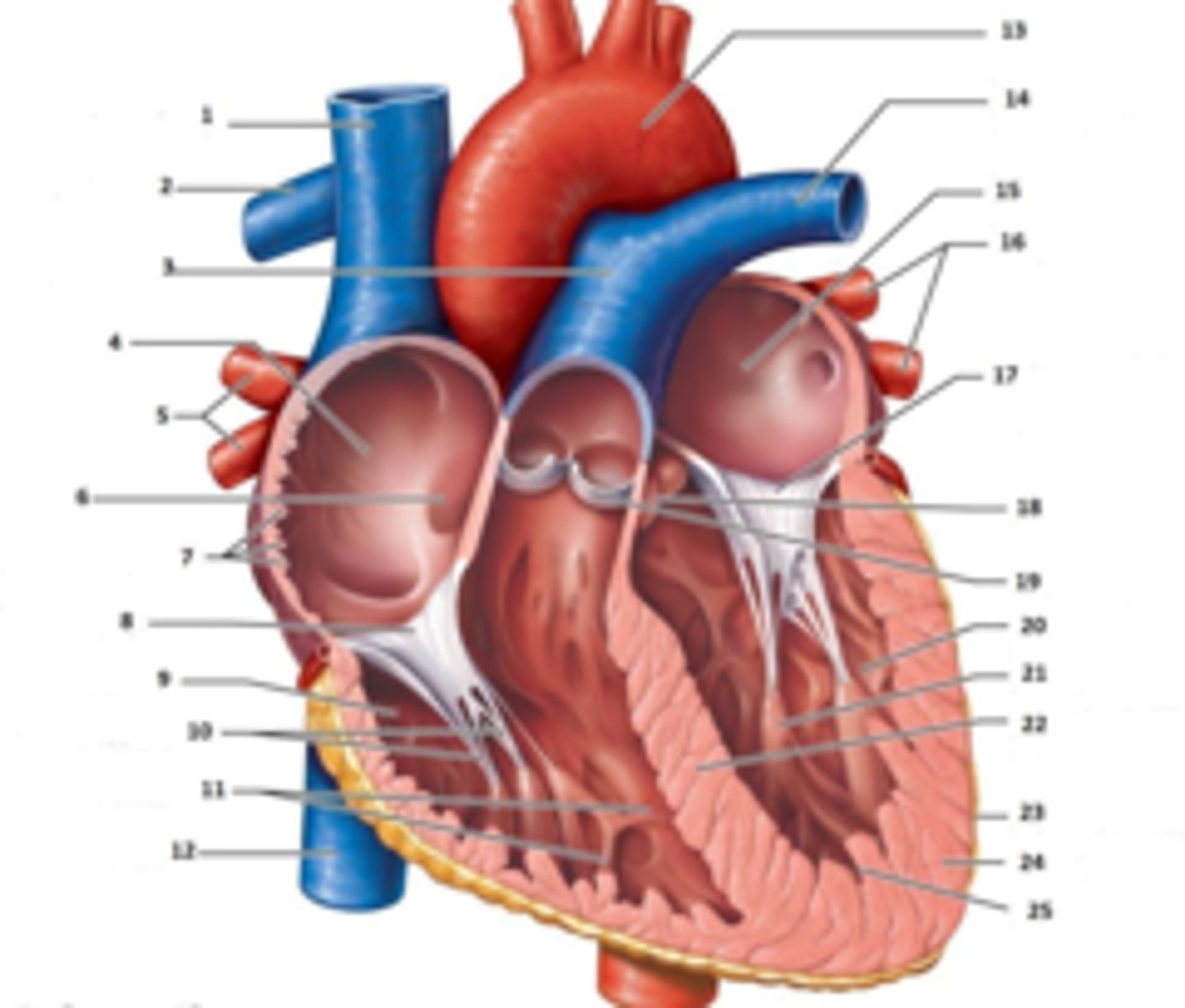
LT Pulmonary Veins
What is #16
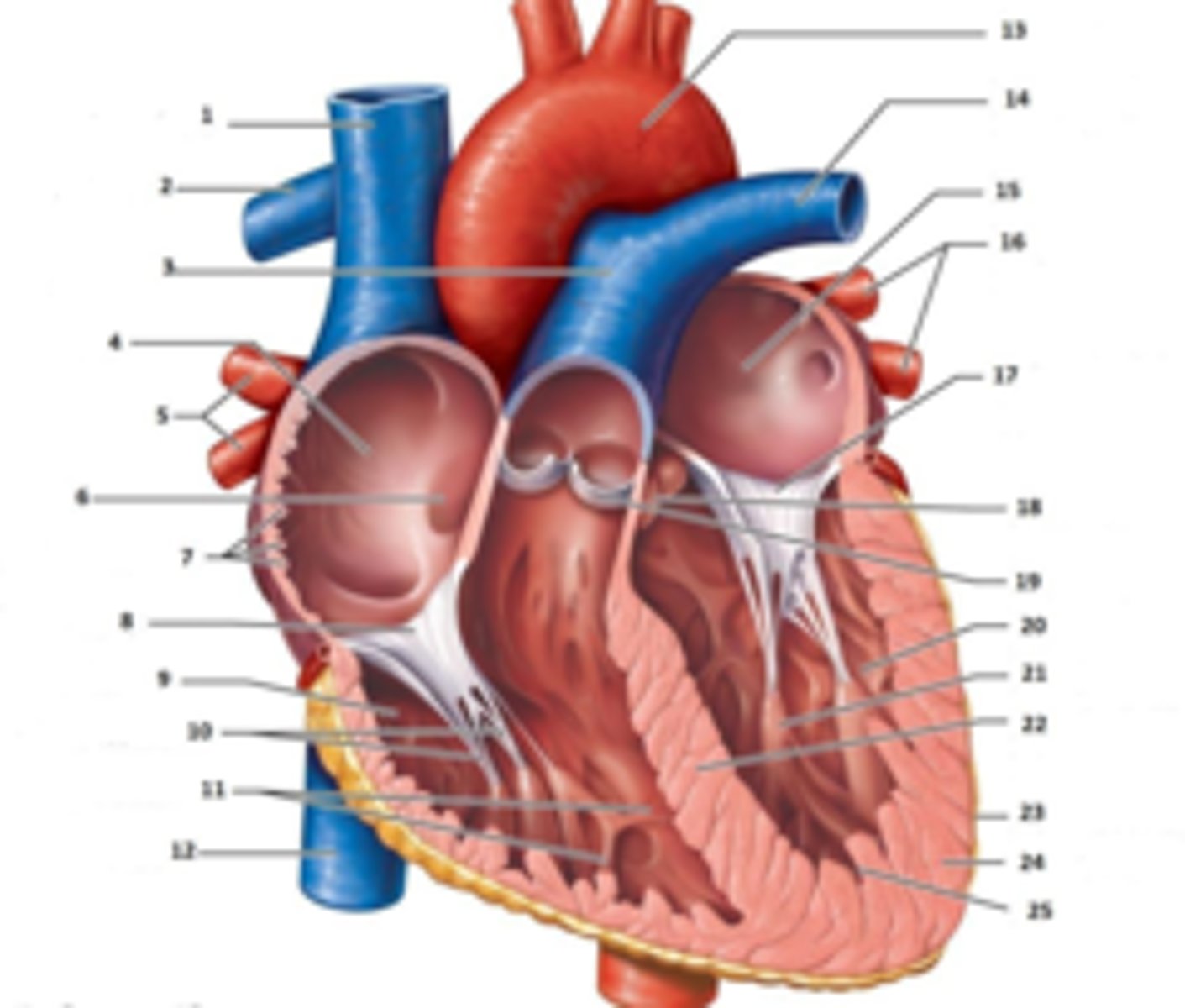
Mitral Valve
What is #17
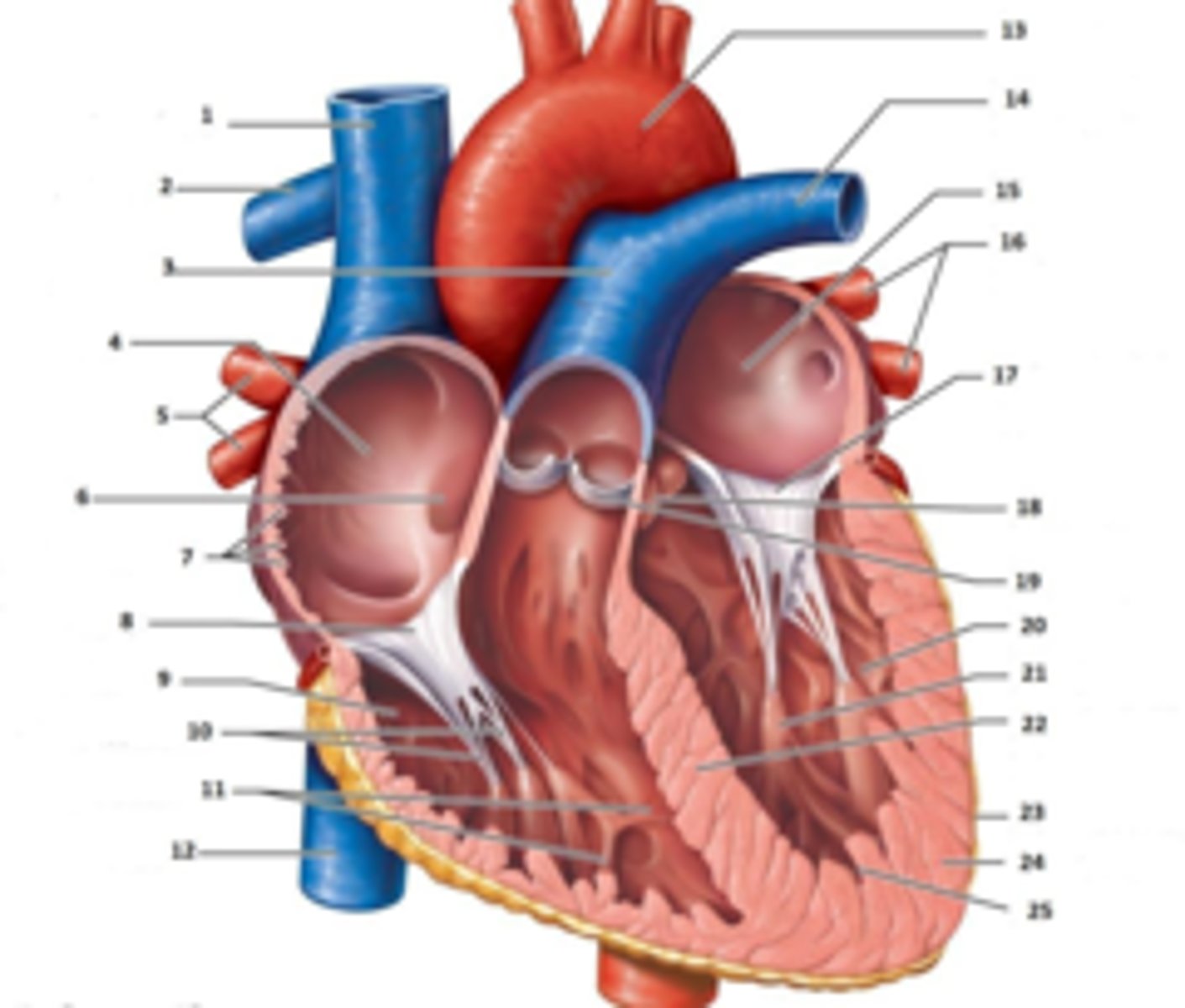
Aortic Valve
What is #18
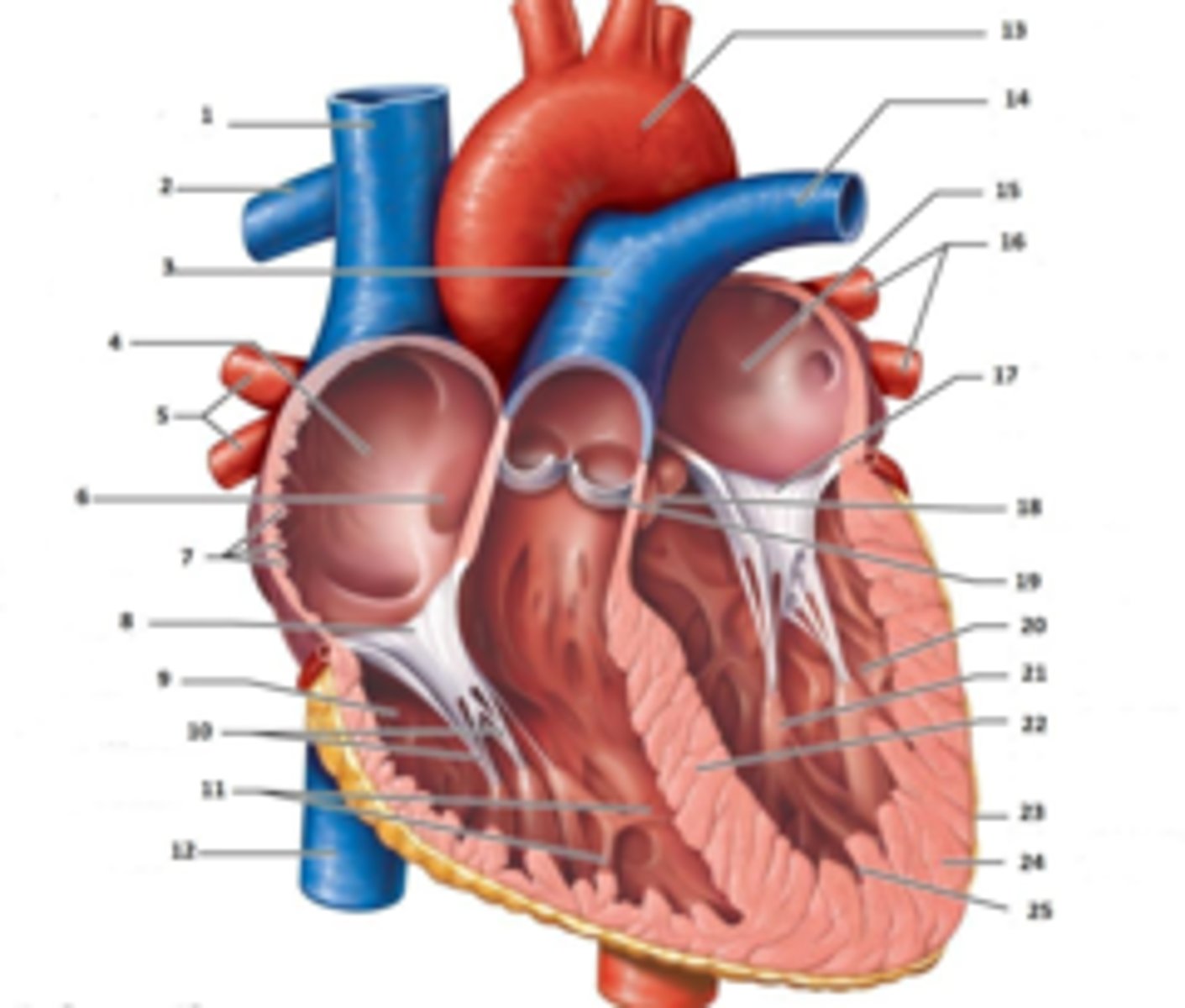
Pulmonary Valve
What is #19
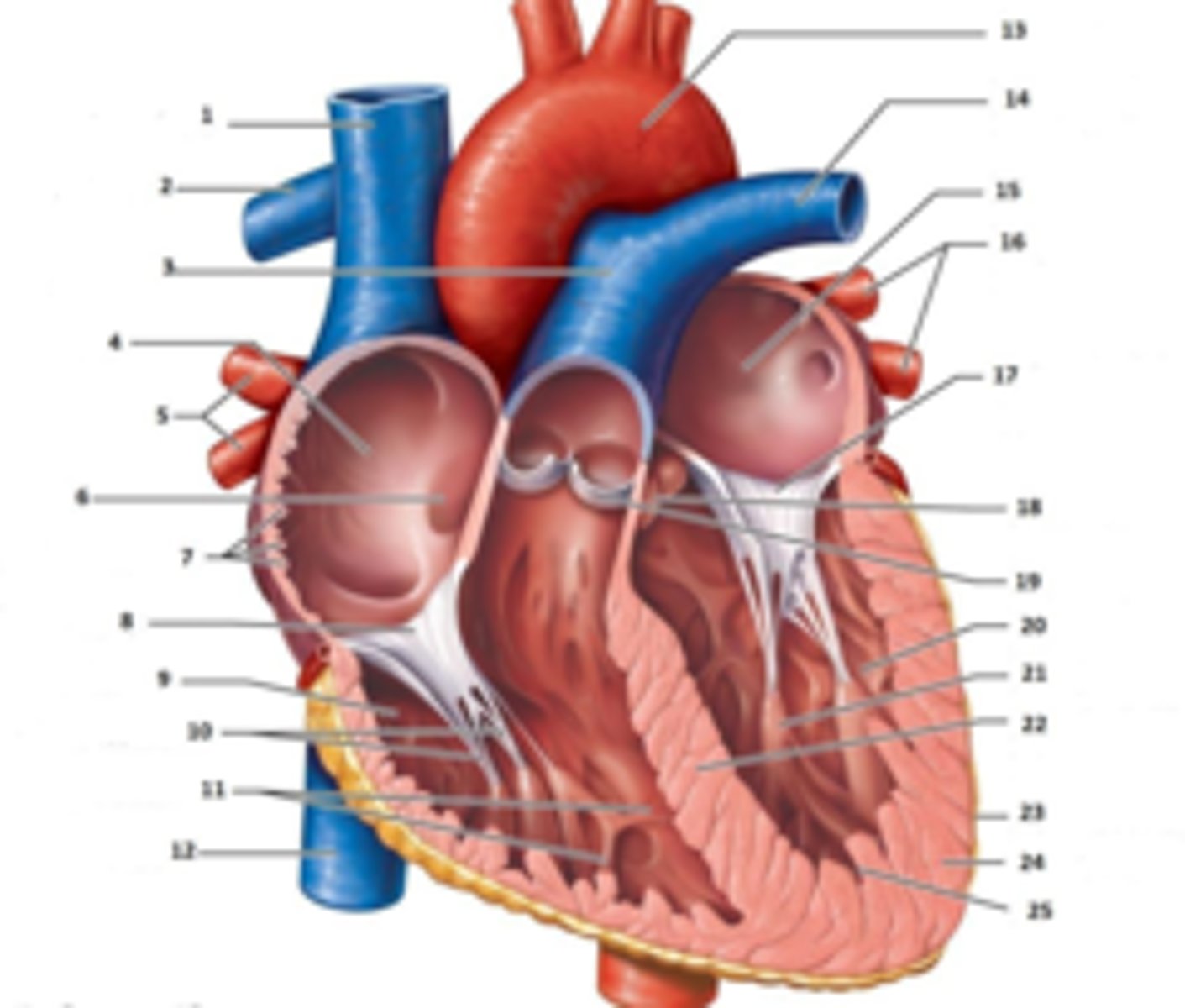
LT Ventricle
What is #2
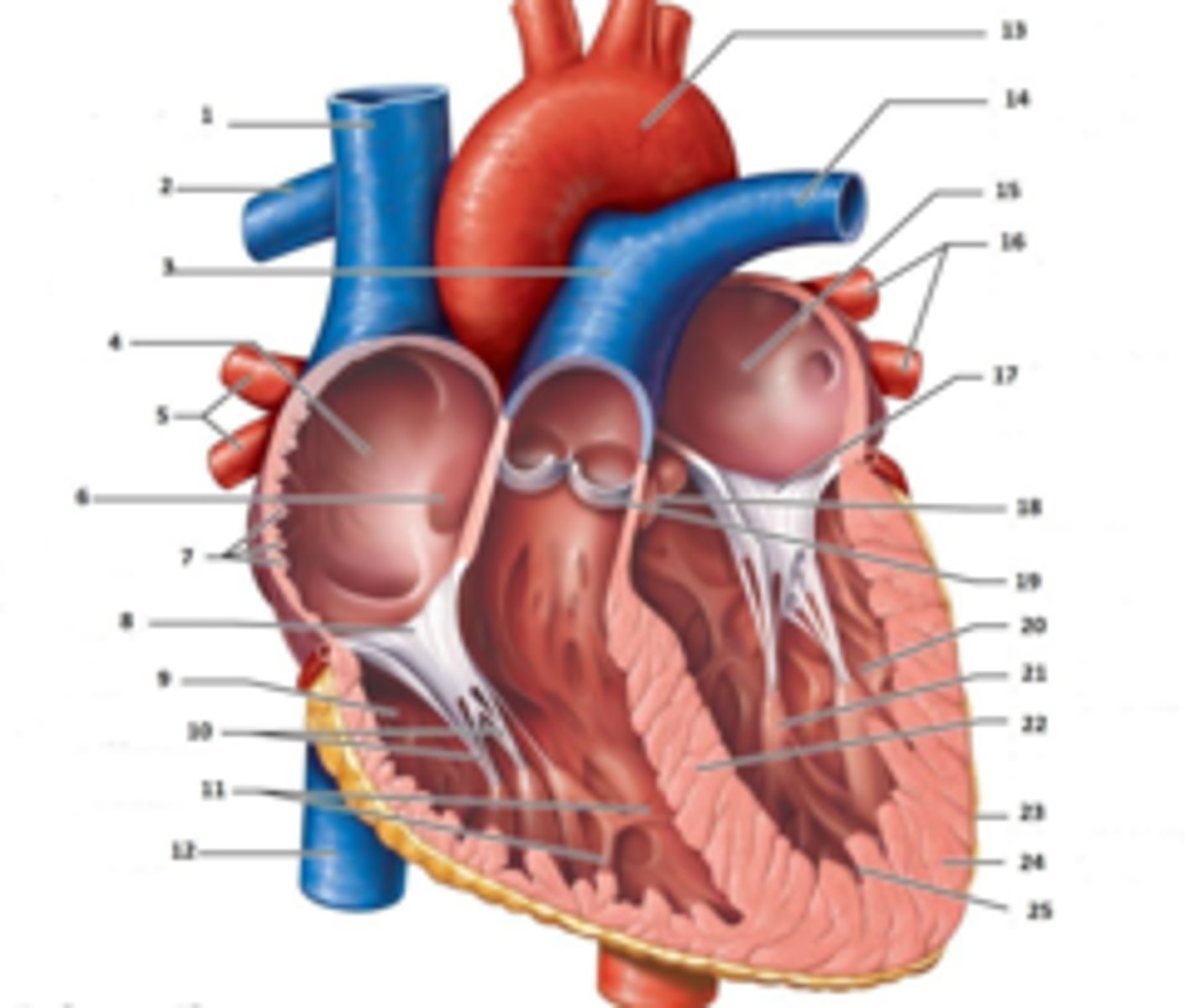
Papillary Muscle
What is #21
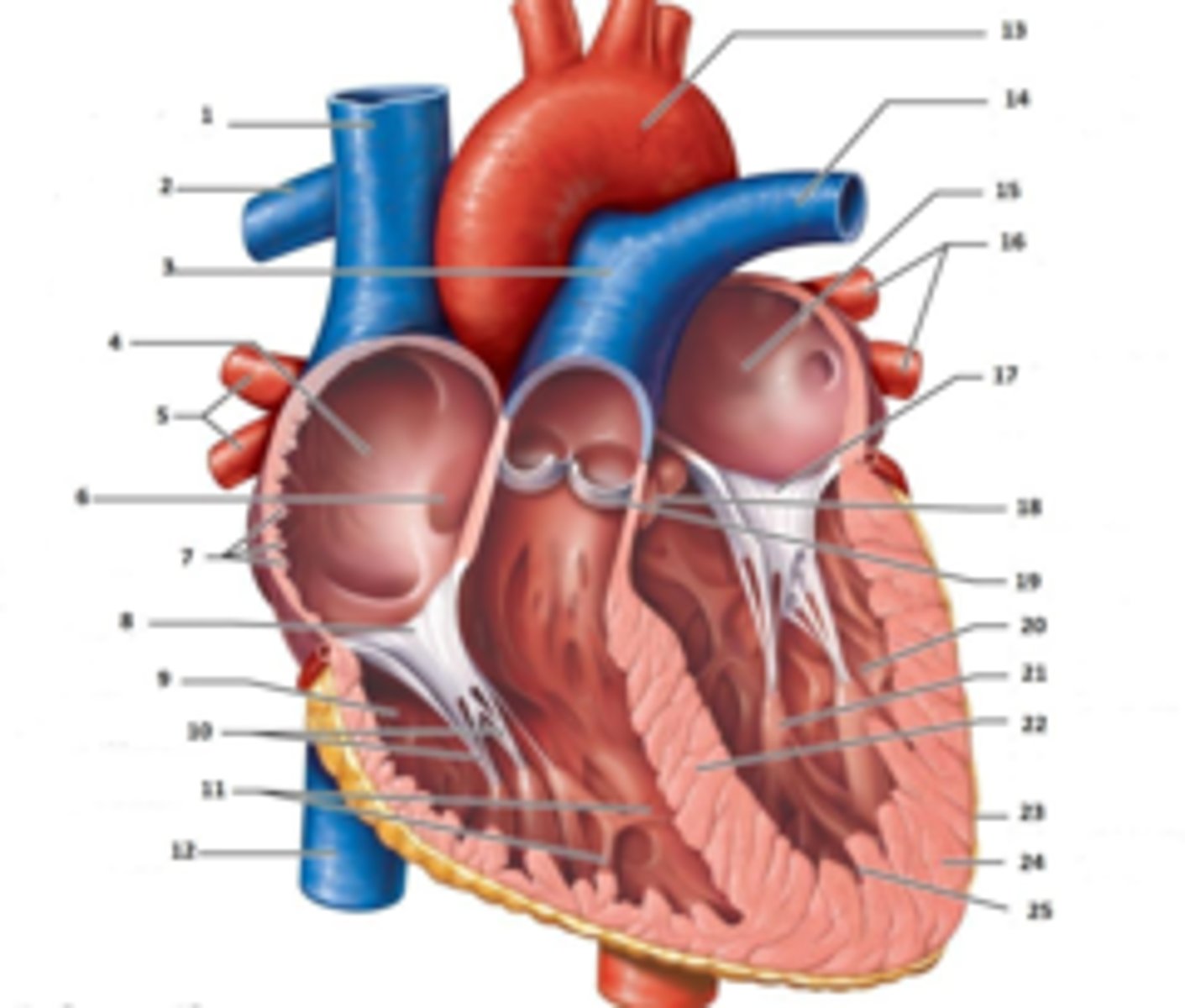
Interventricular Septum
What is #22
Epicardium
What is #23
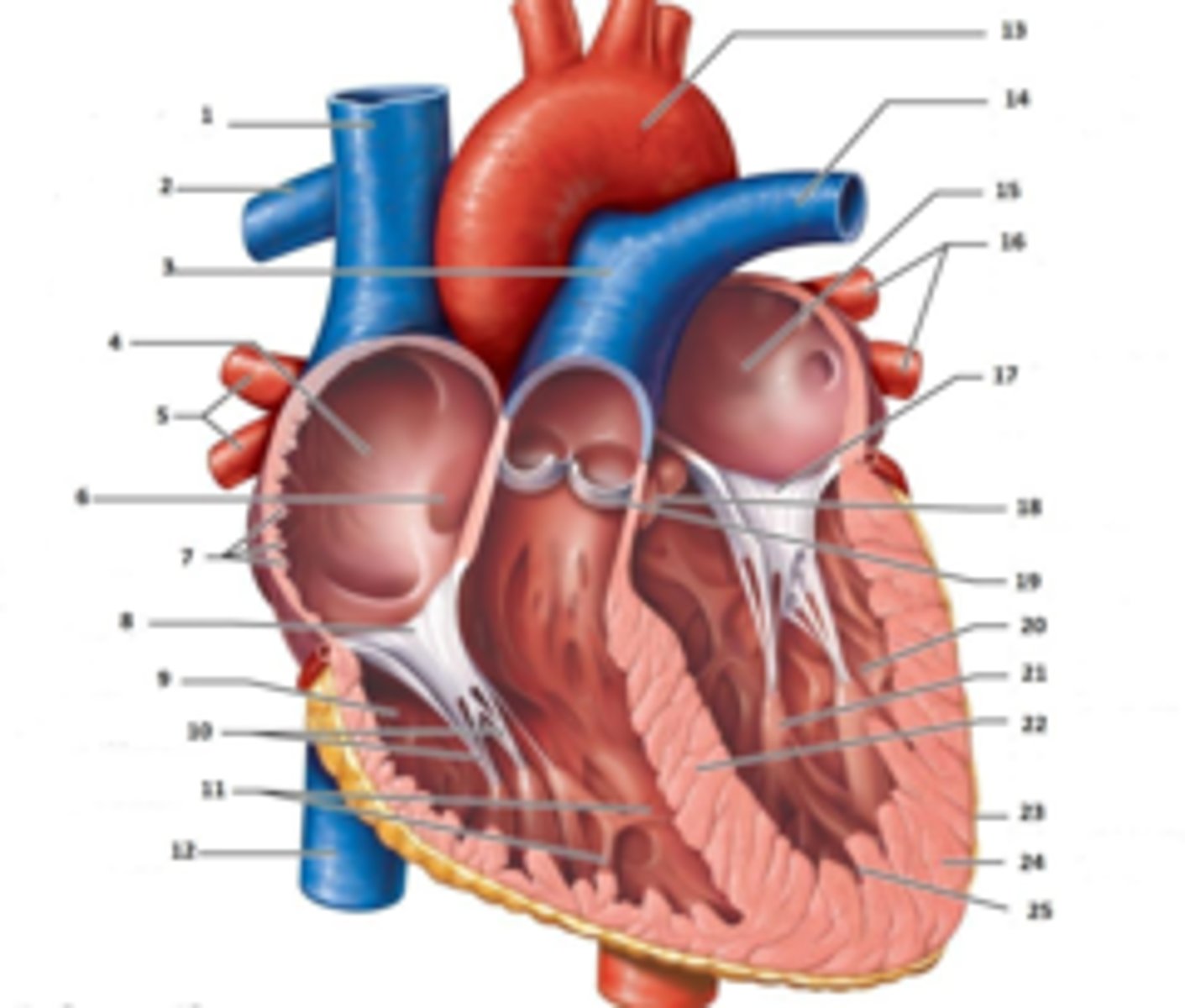
Myocardium
What is #24
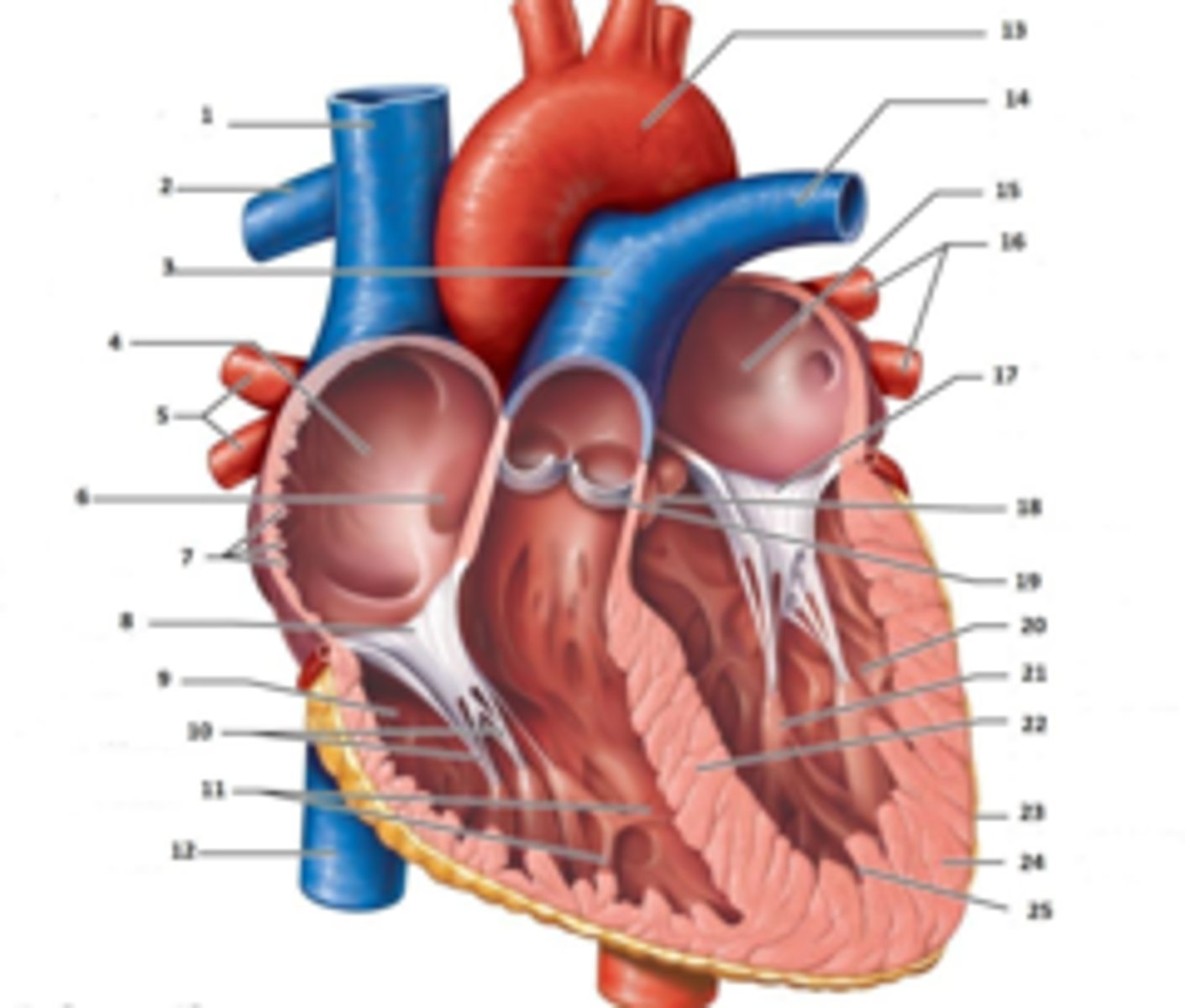
Endocardium
What is #25
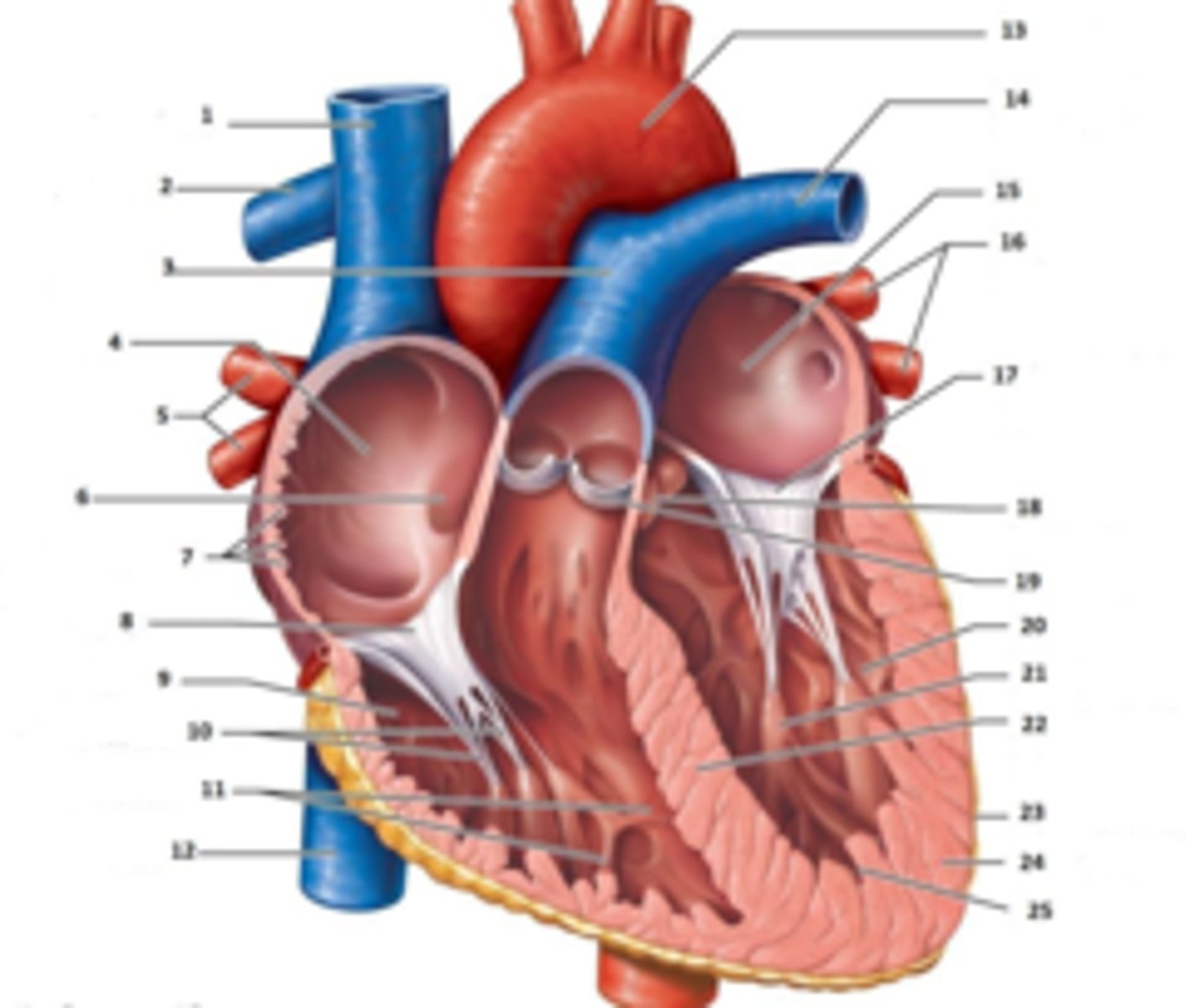
Right Coronary Cusp
What is #1
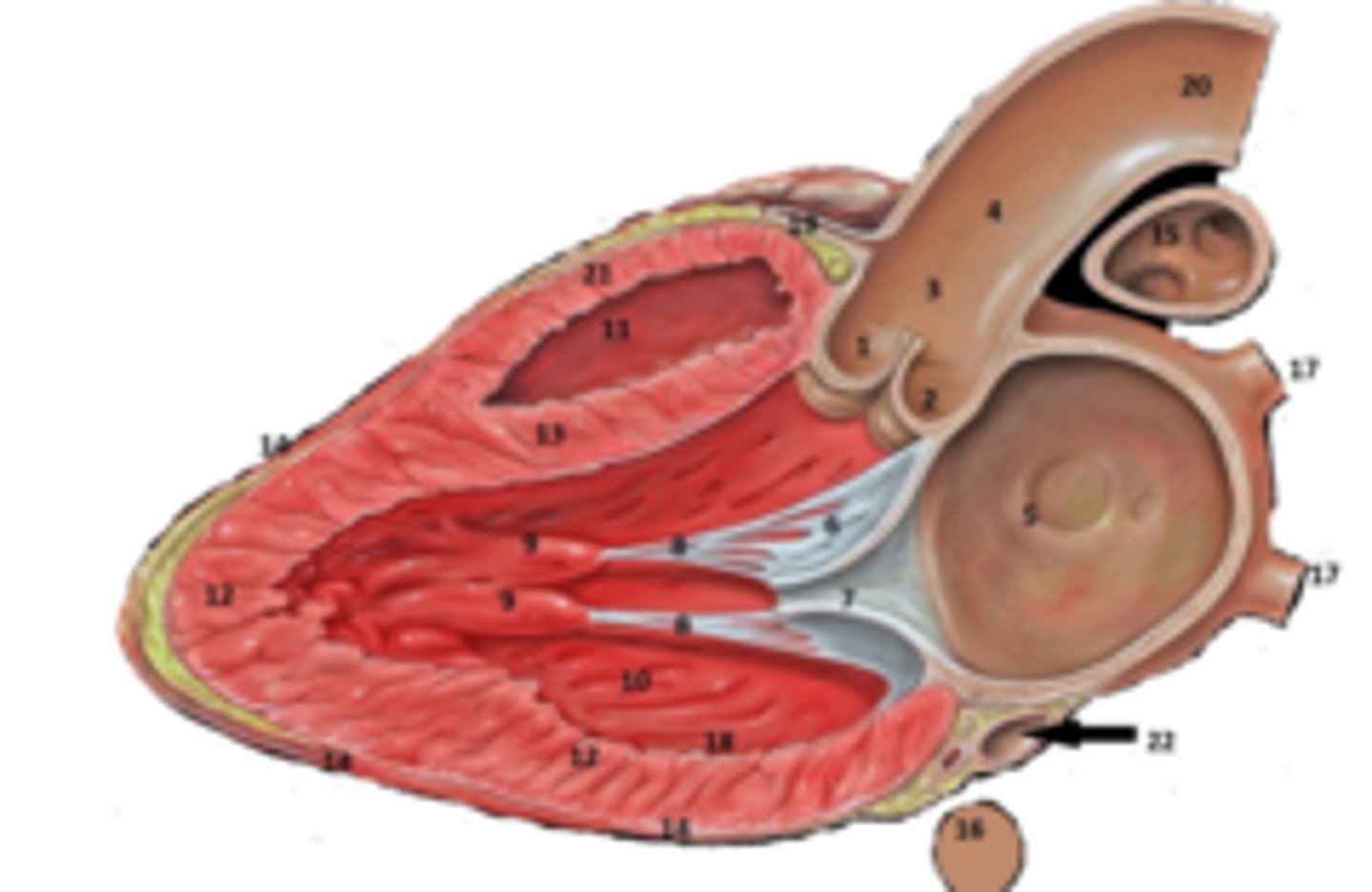
non coronary cusp
What is #2
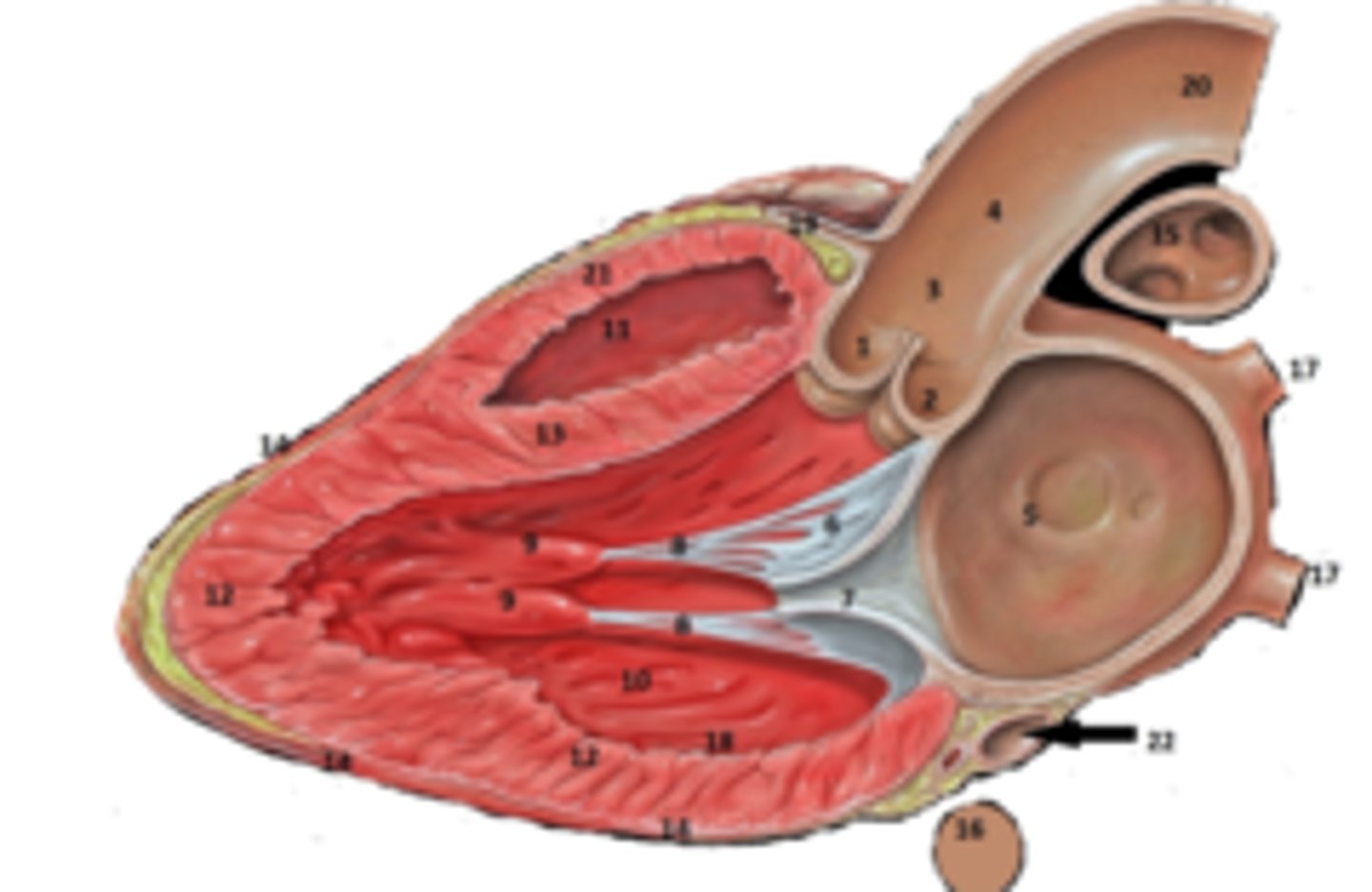
RT Pulmonary Artery
What is #15
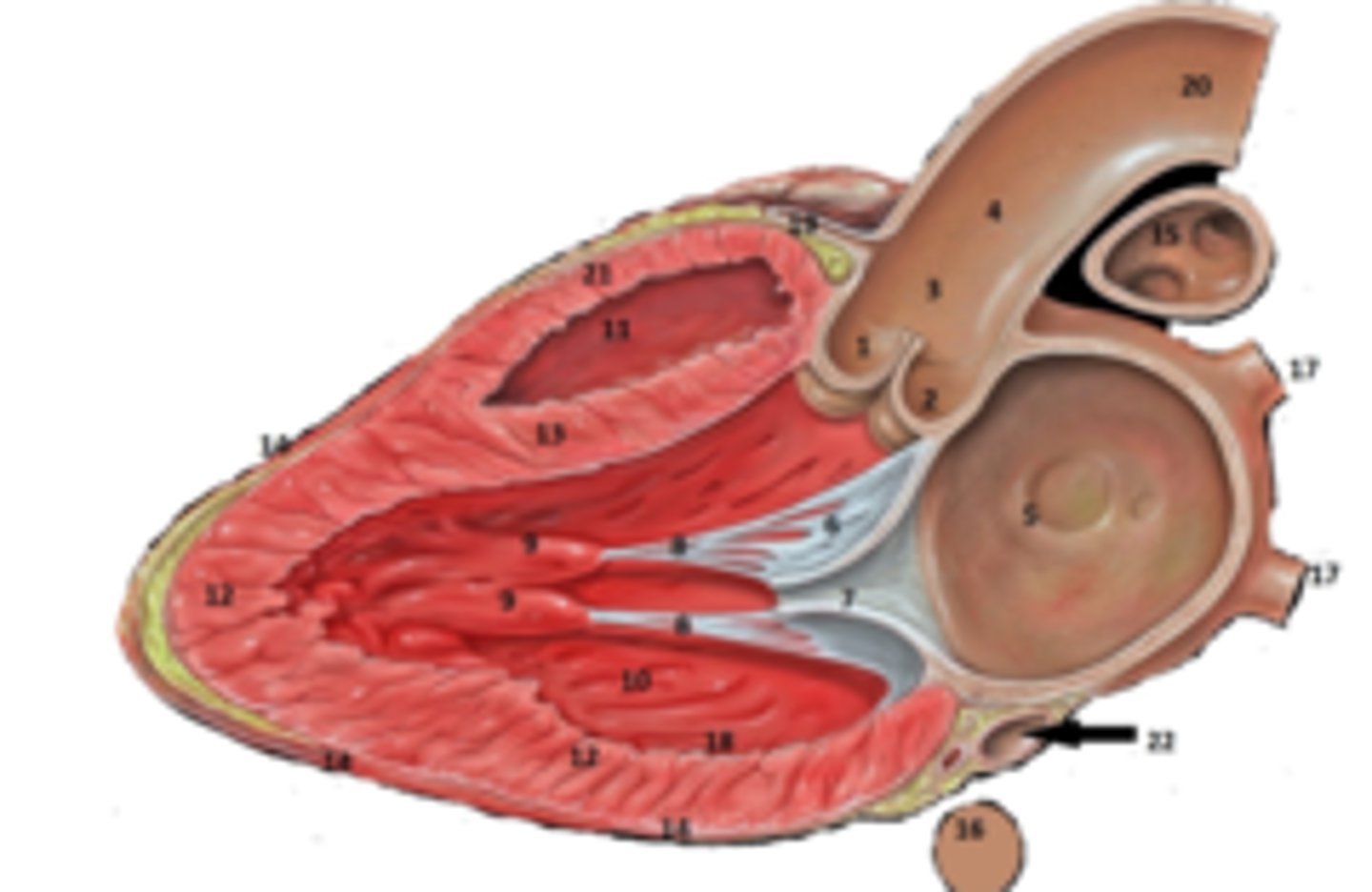
RT Coronary Artery Sulcus
What is #19
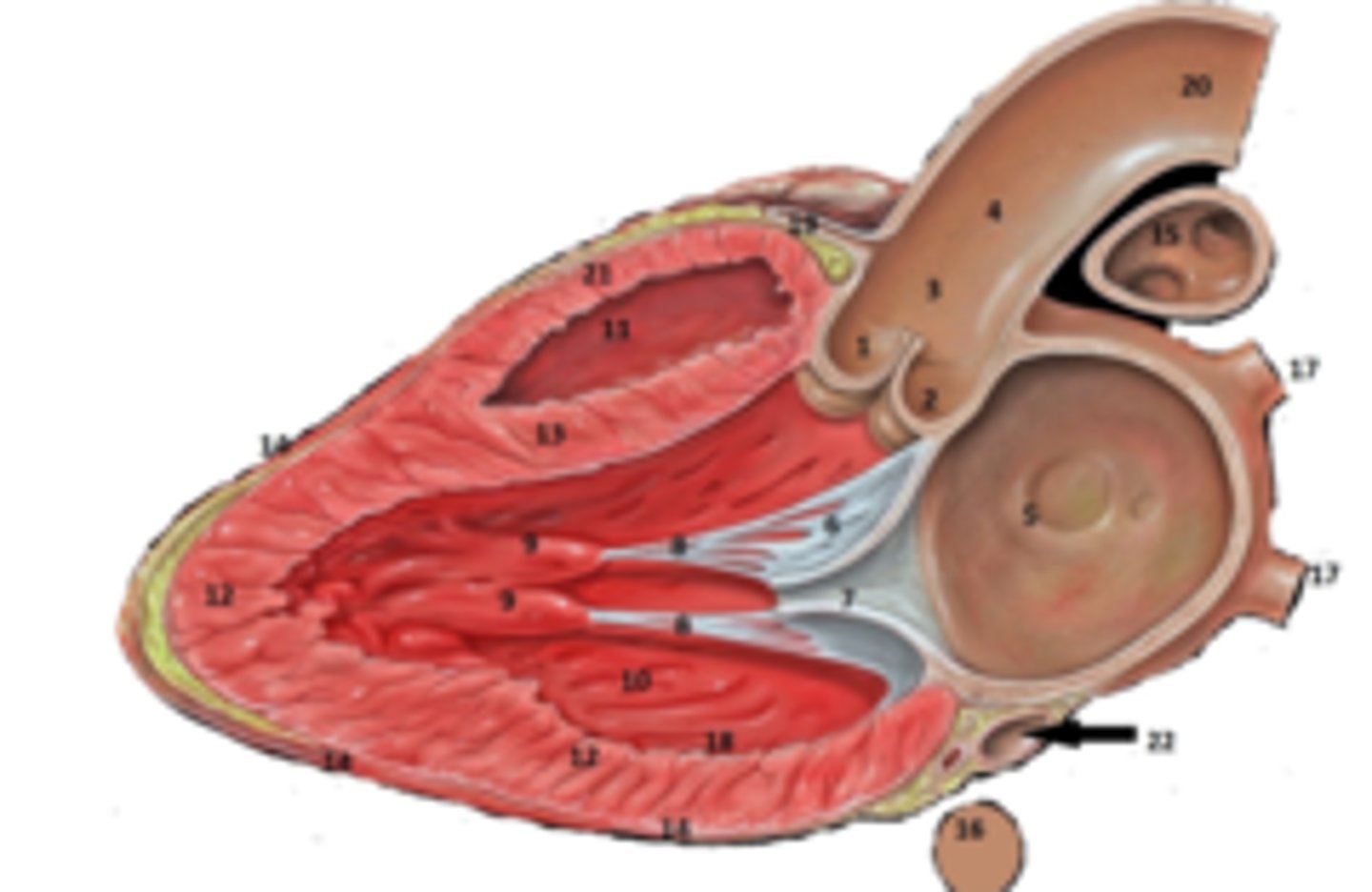
RT Ventricular Anterior Free Wall
What is #21
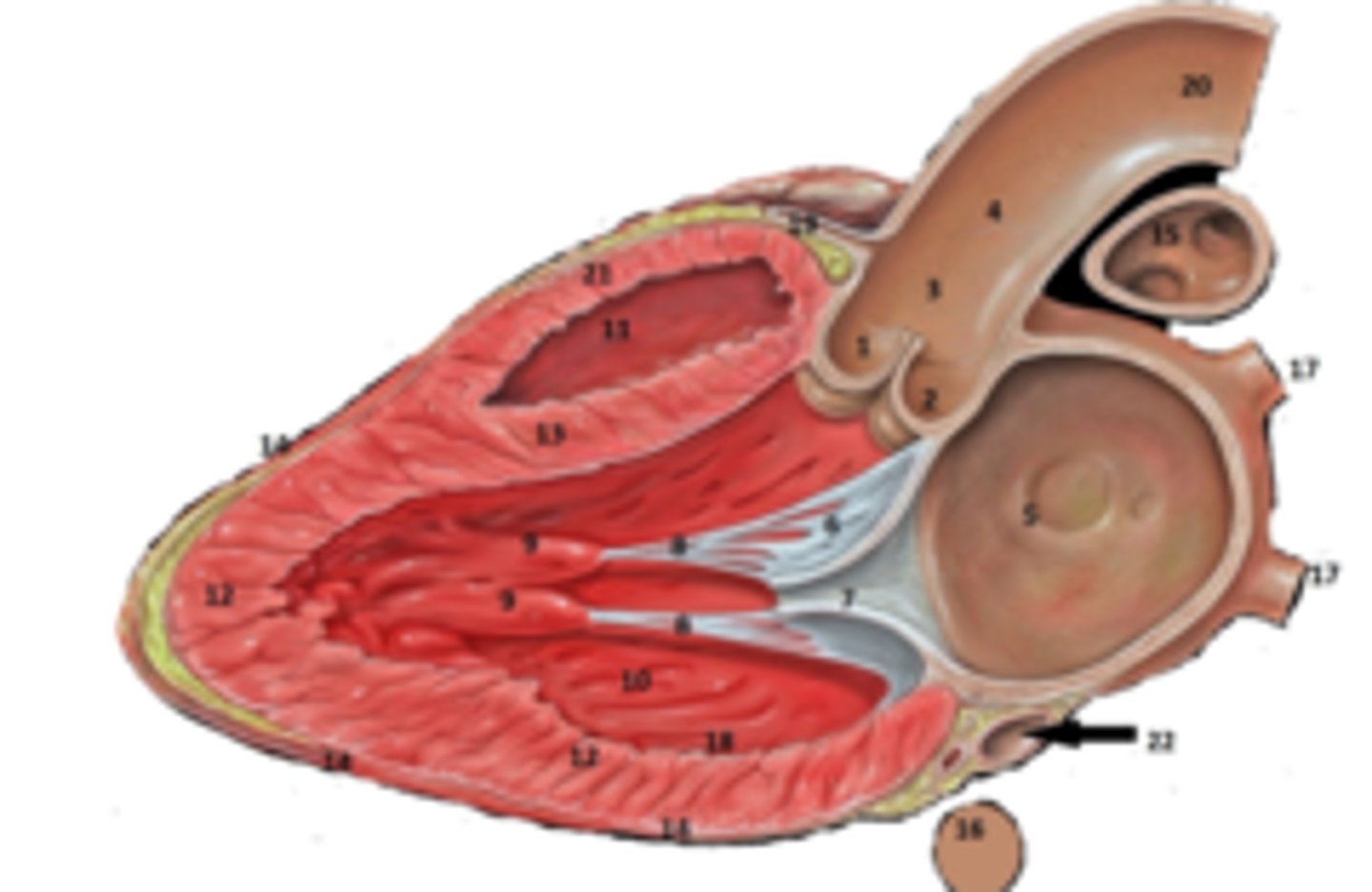
Coronary Sinus
What is #22.
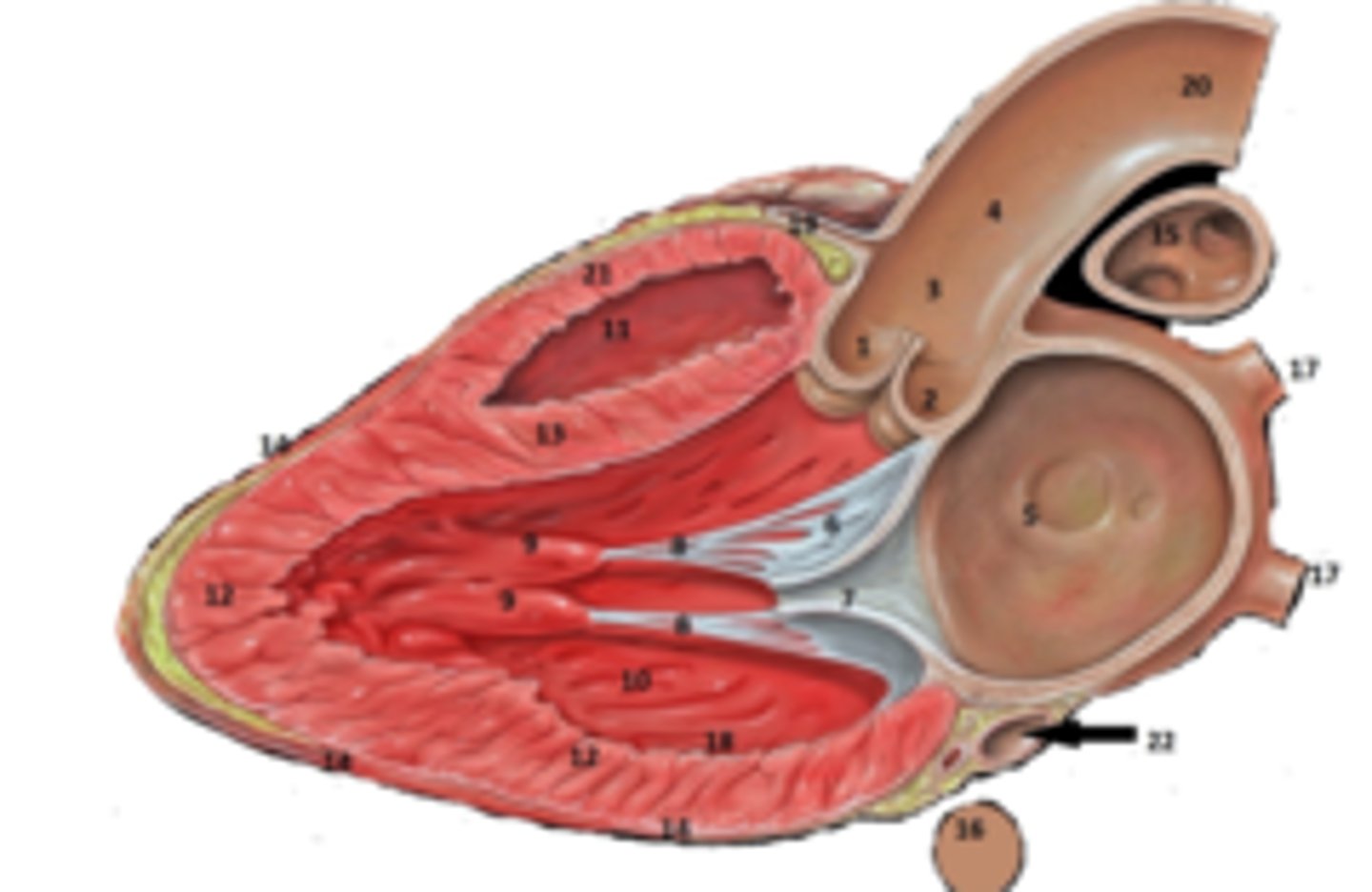
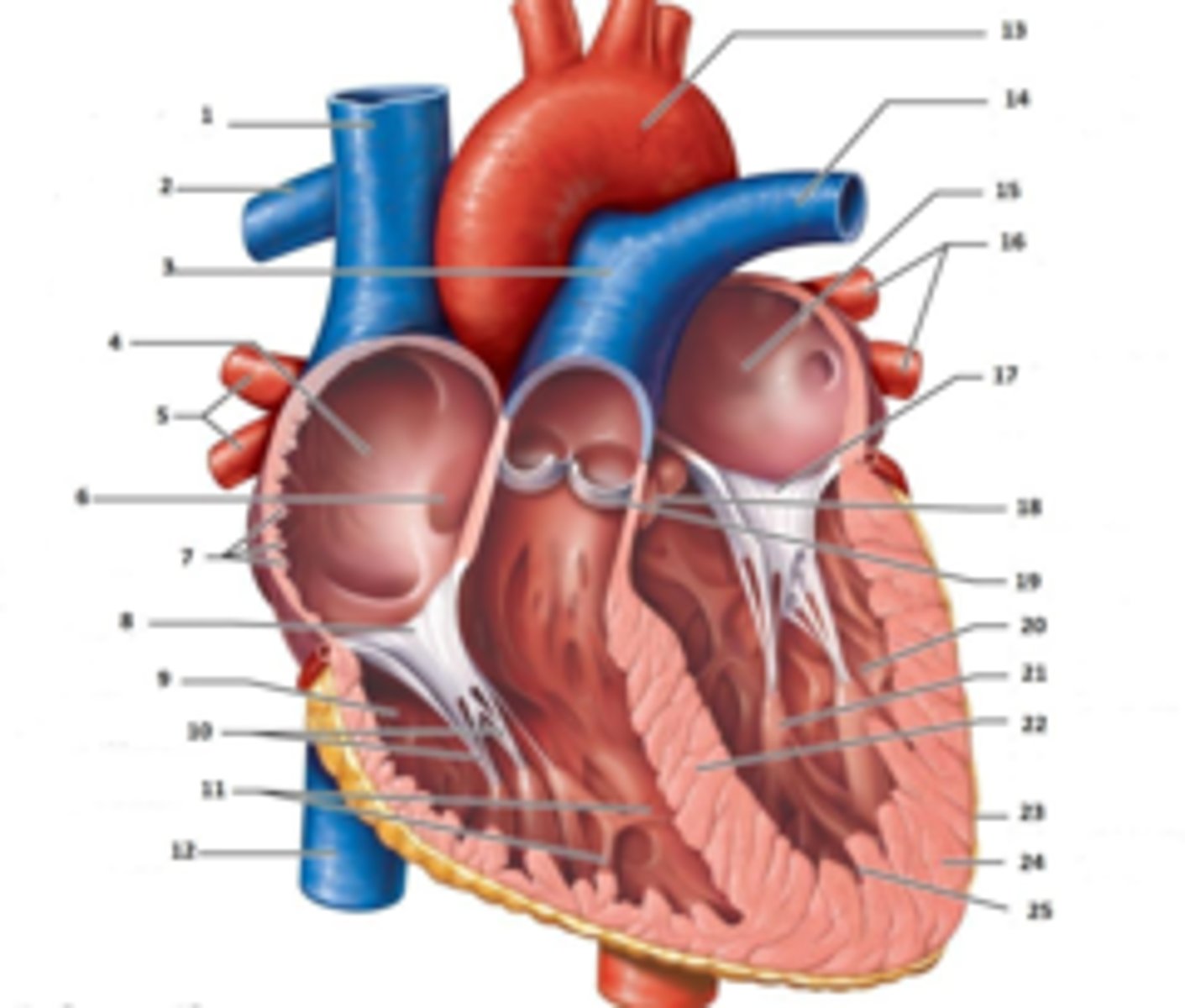
Left Ventricle
What is A
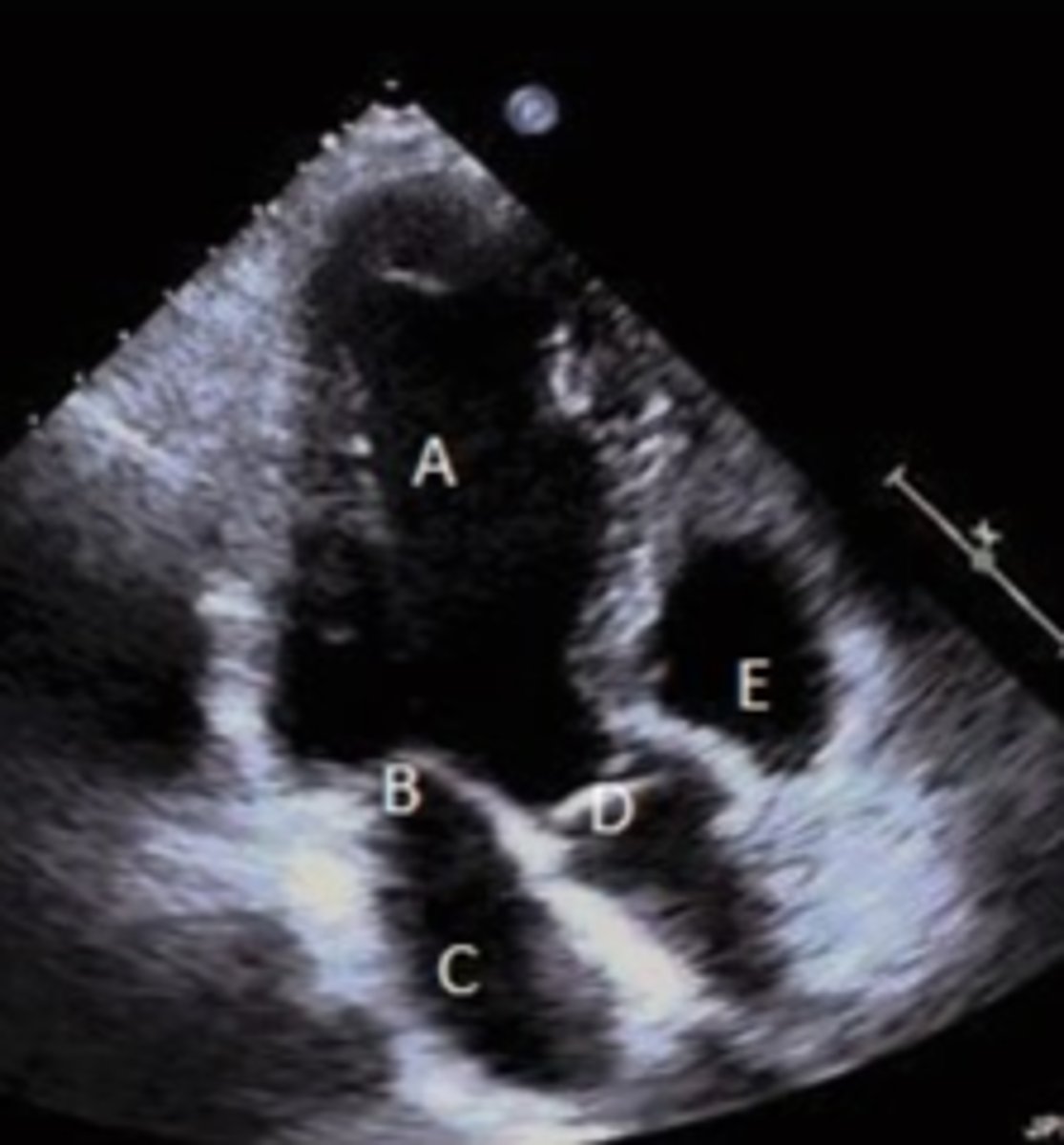
RV
A?
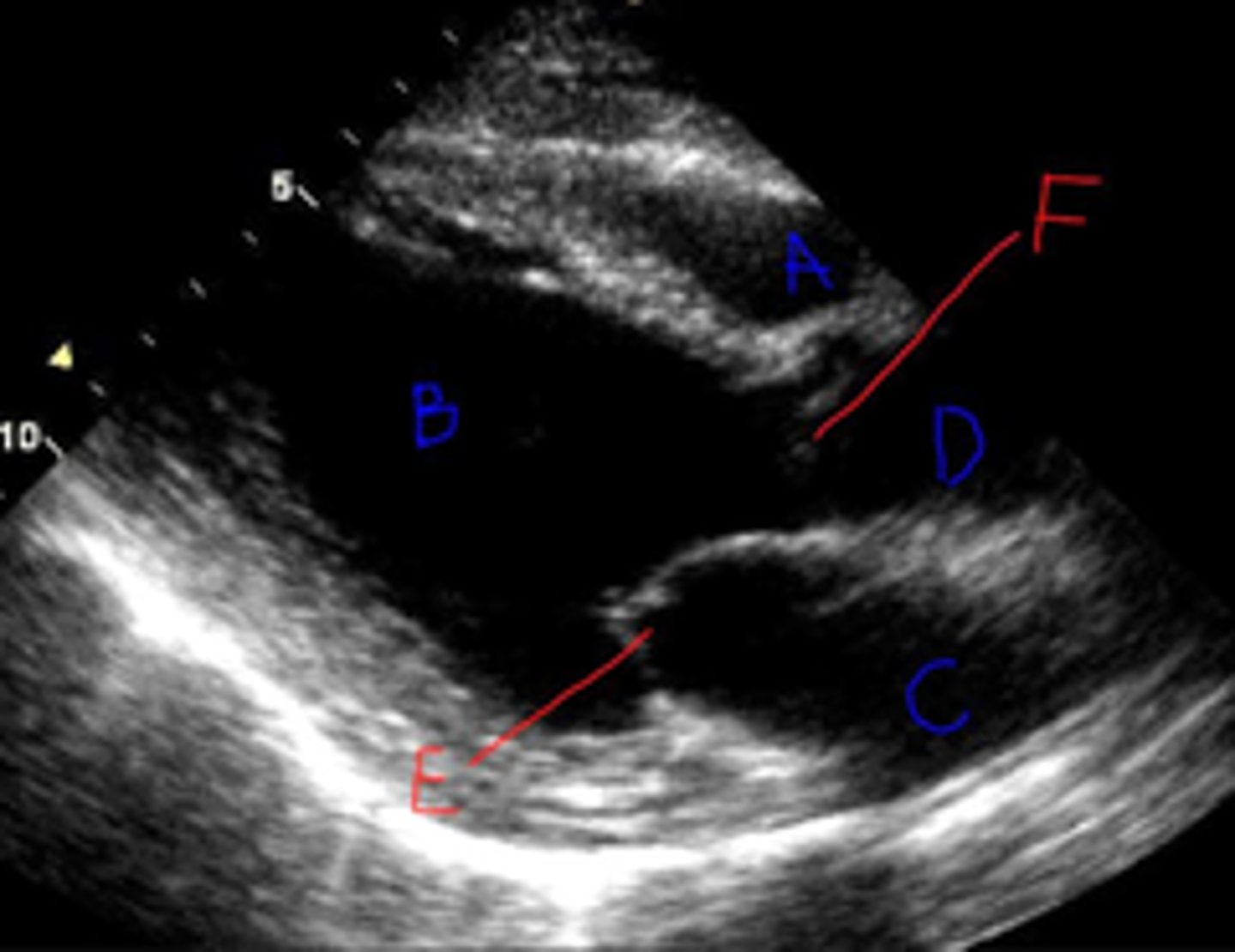
LV
B?
RVOT/RV
A?
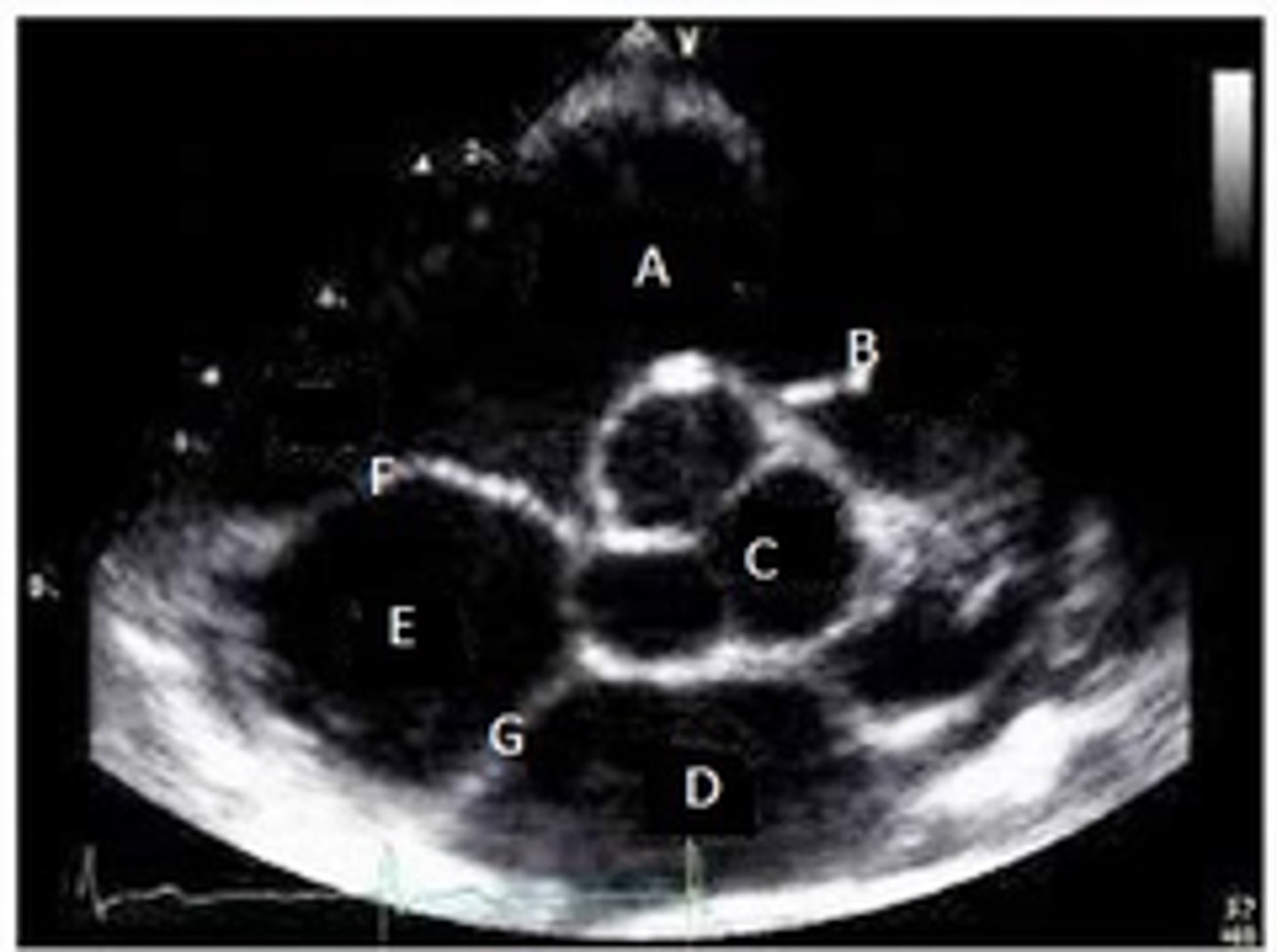
PV
B?
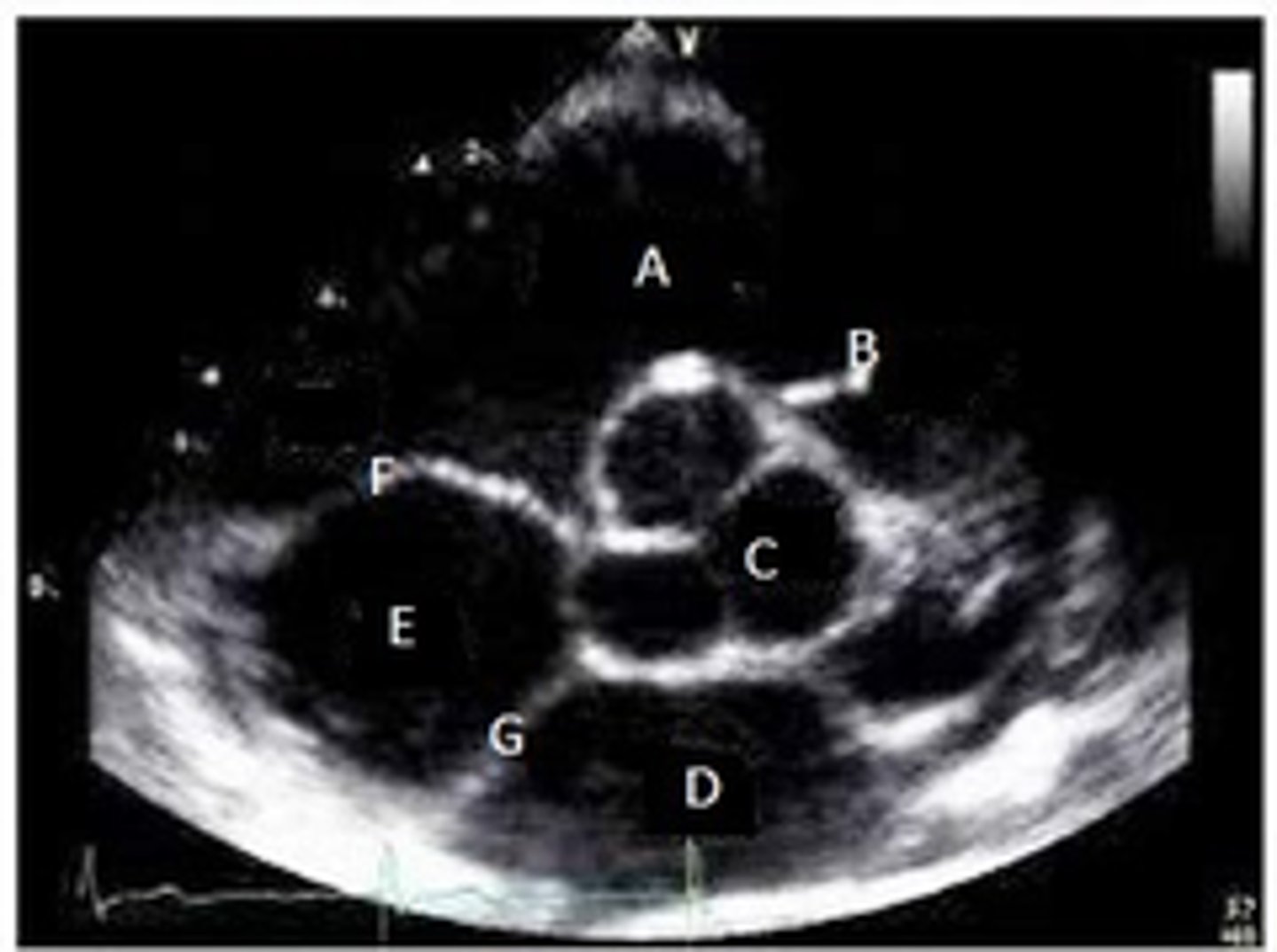
MV
2?
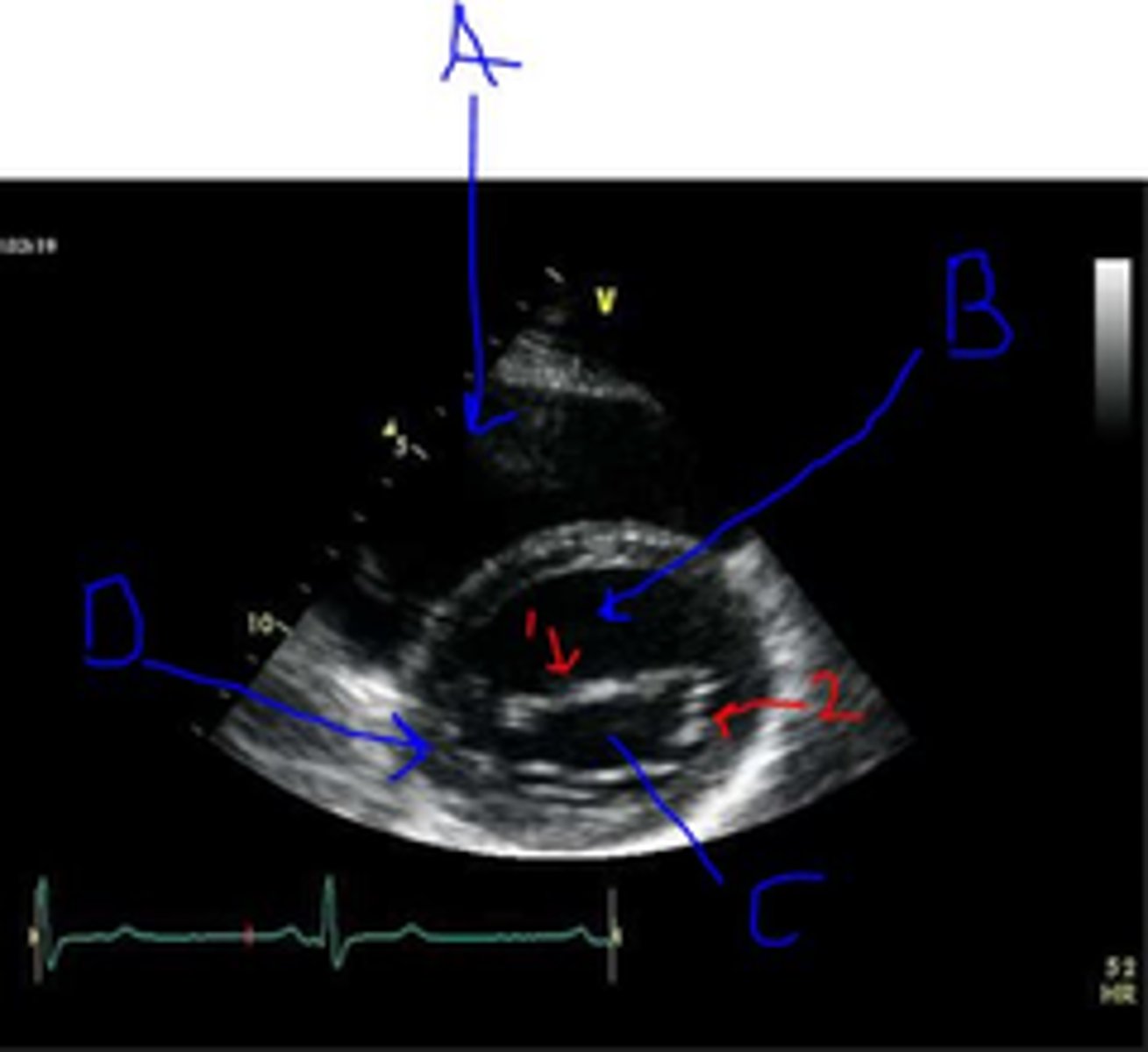
Anterior MV leaflet
1?
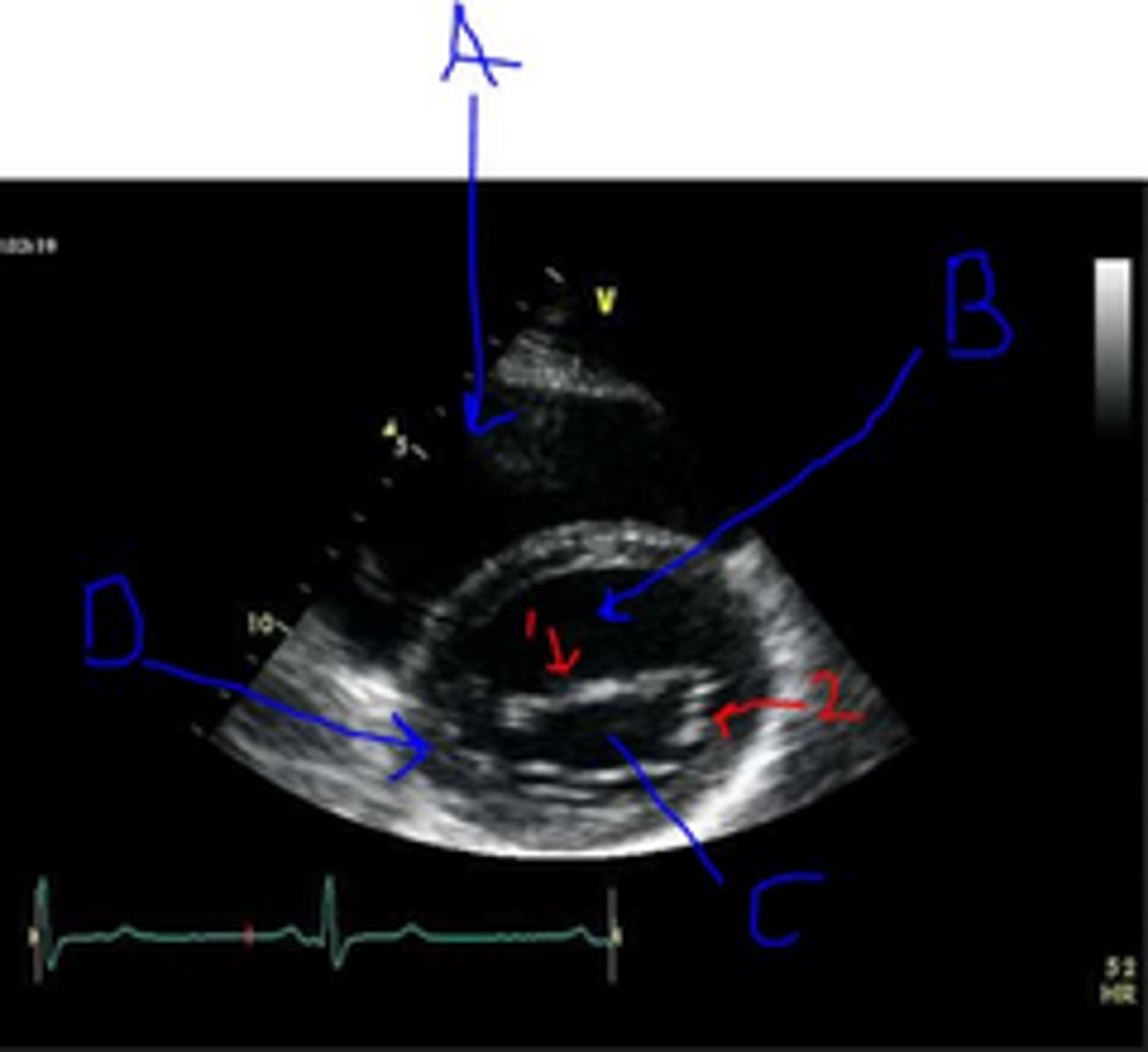
base wall
D?