Intro to Anatomy I - Final (copy)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/88
Last updated 6:33 PM on 5/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
What is the smallest unit capable of life?
A cell
2
New cards
Organize the levels of multicellular organisms from basic to complex: neurons, brain, human being, nerve tissue, CNS
Neuron, nerve tissue, brain, CNS, human being
3
New cards
What organelle is most of our skeletal muscle made of?
Mitochondria
4
New cards
What is epithelial tissue?
Covers body surfaces and lines body cavities to form boundaries, protect, absorb, and filter; make up glands
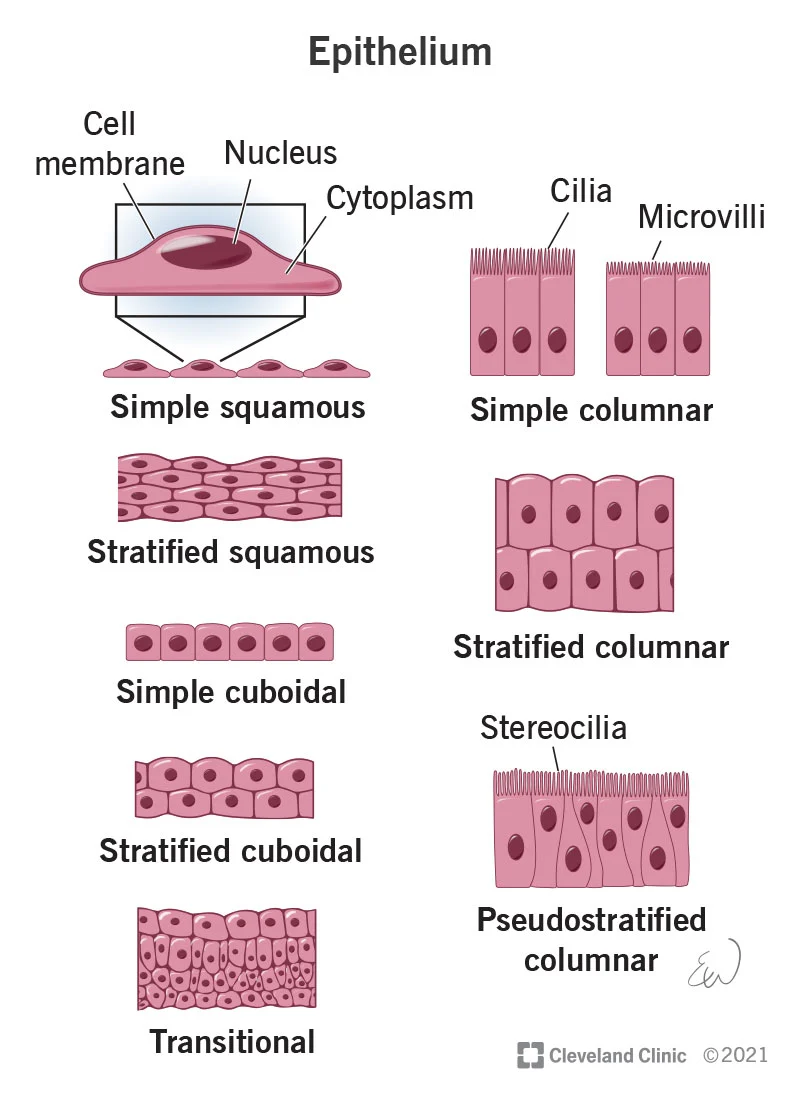
5
New cards
What is connective tissue?
Supports, protects, insulates, transports, and binds other tissues together
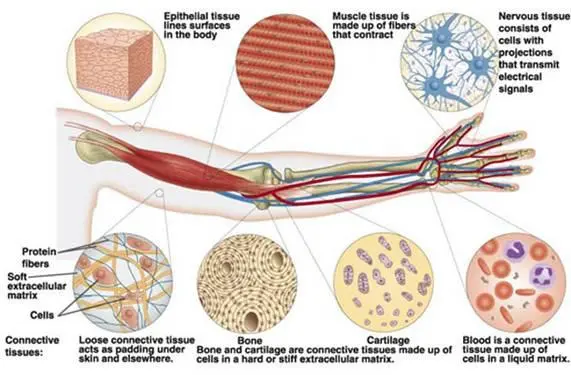
6
New cards
What is muscle tissue?
Made of tightly packed together cells that allow for contractions to cause movement
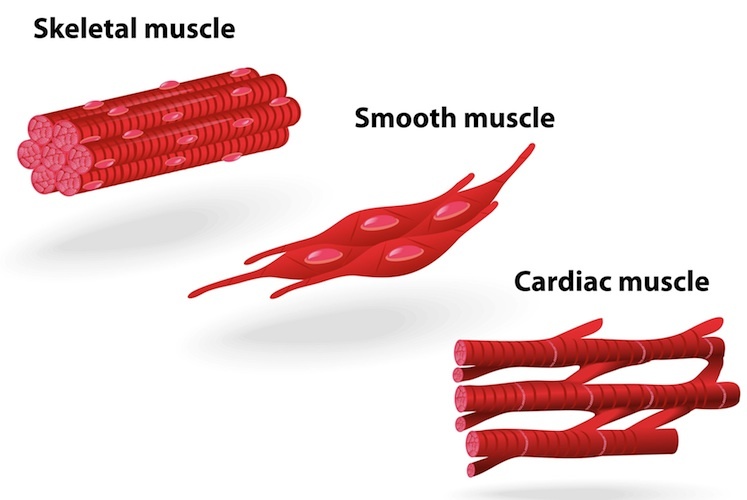
7
New cards
What is nervous tissue?
The main component of nervous system organs that control regulation and communication; mainly composed of neurons
8
New cards
What is a hypertonic solution?
Water solute is lower than the cell’s cytoplasm (low water concentration means high solute); shrivels
9
New cards
What is a hypotonic solution?
Water solute is higher than the cell’s cytoplasm; swells
10
New cards
What is a isotonic solution?
There are identical water solute within the cell’s cytoplasm and within the cell; stays the same
11
New cards
What would happen to a cell’s daughter cells that failed to go through DNA replication prior to mitosis?
Each daughter cell would contain half of the necessary chromosomes
12
New cards
What organelle specializes in the engulfment of harmful substances?
Lysosomes
13
New cards
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer
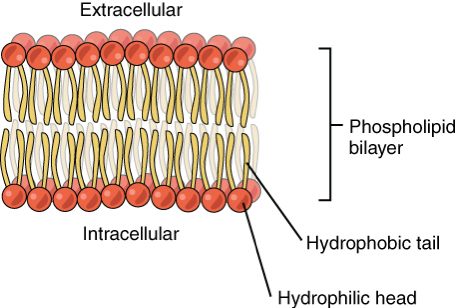
14
New cards
What two macromolecules are embedded in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates which provide structure and proteins which aid transportation
15
New cards
What is a feedback loop?
A feedback loop helps maintain homeostasis in an organism. It uses the output of a system to signal a change in input so that a system response can be stabilized or amplified.
16
New cards
What is the difference between a positive feedback loop an a negative feedback loop?
Positive: output/product of a system intensifies the response Ex: Childbirth
Negative: output/product of a system causes a counter-response to return to a set point Ex: blood glucose regulation, body temperature, etc
Negative: output/product of a system causes a counter-response to return to a set point Ex: blood glucose regulation, body temperature, etc
17
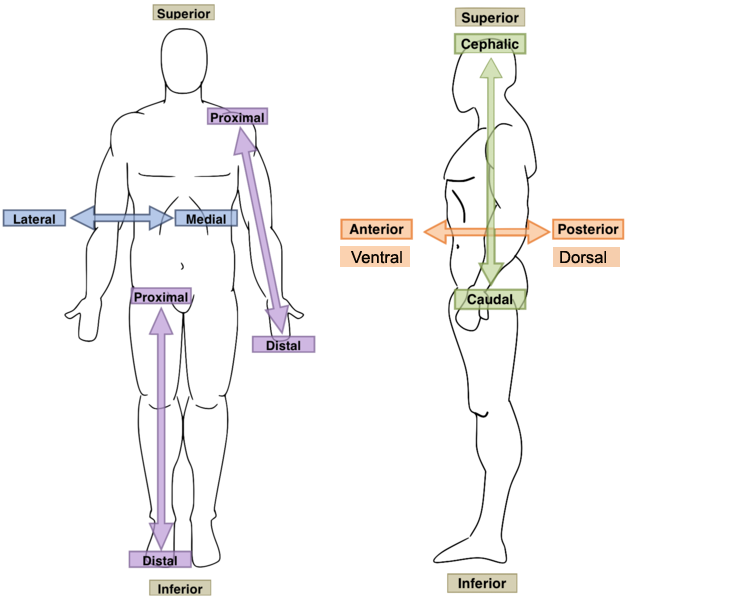
New cards
Lateral?
Away from the mid-line of the body; on the outer side of
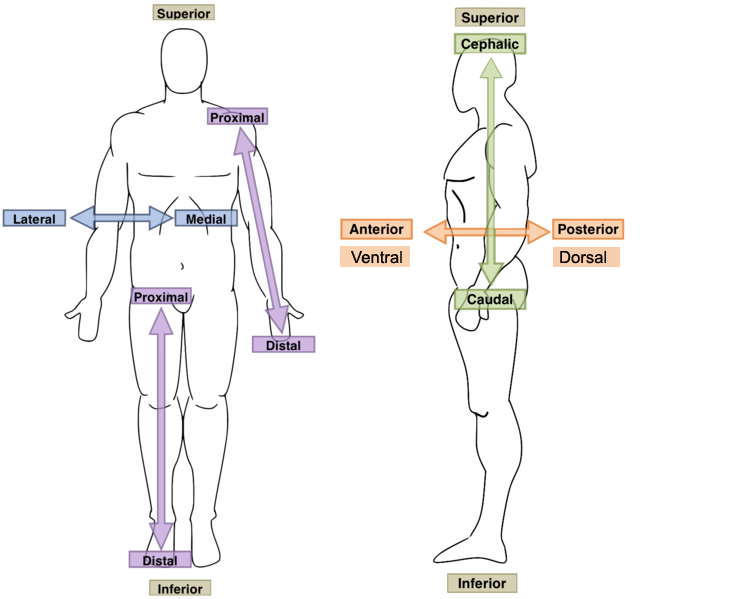
18
New cards
Medial?
Toward or at the mid-line of the body; on the inner side of
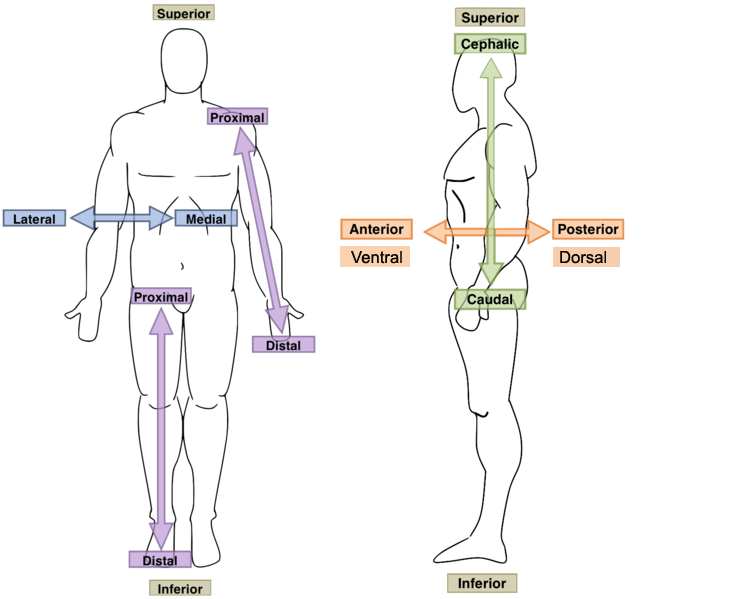
19
New cards
Superior?
Toward the upper part; above; cranial
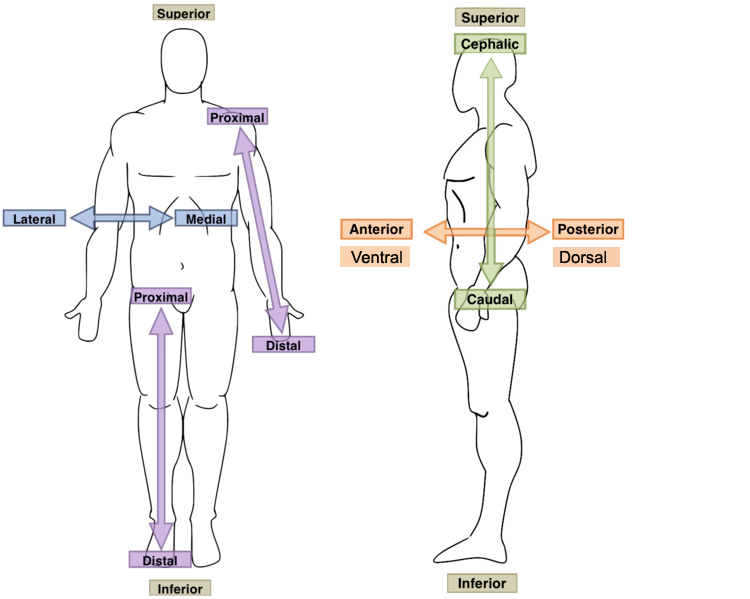
20
New cards
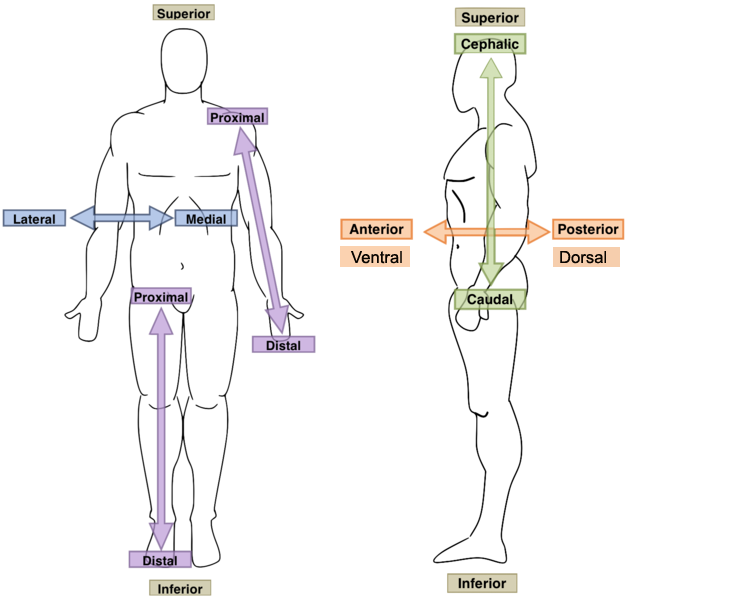
Anterior?
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of; ventral
21
New cards
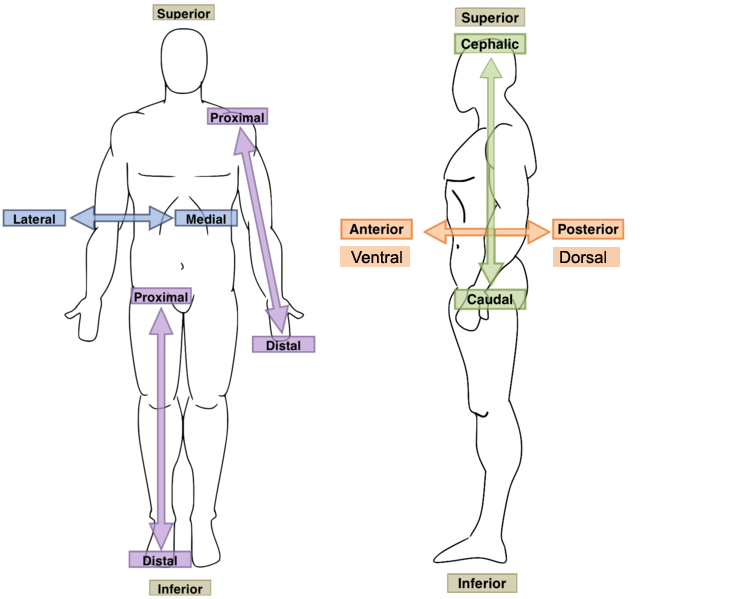
Posterior?
Toward or at the back of the body; behind; dorsal
22
New cards
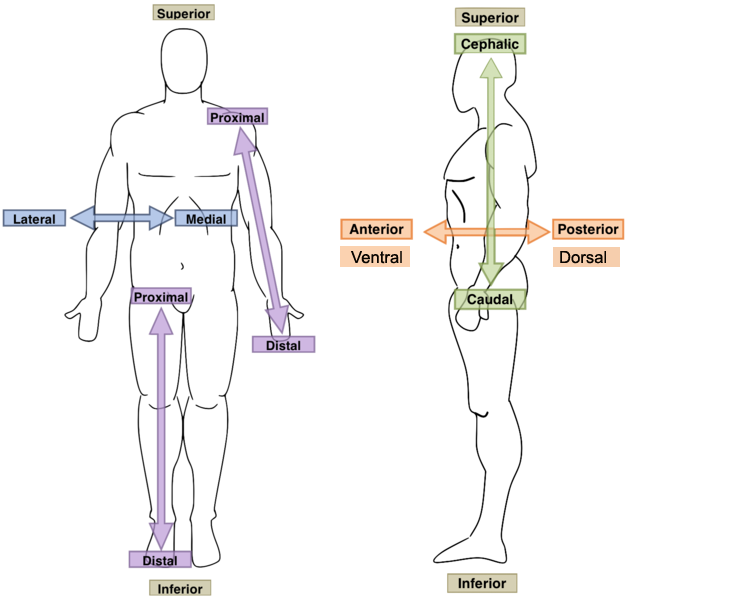
Inferior?
Away from the upper part; toward the lower part; below; caudal
23
New cards
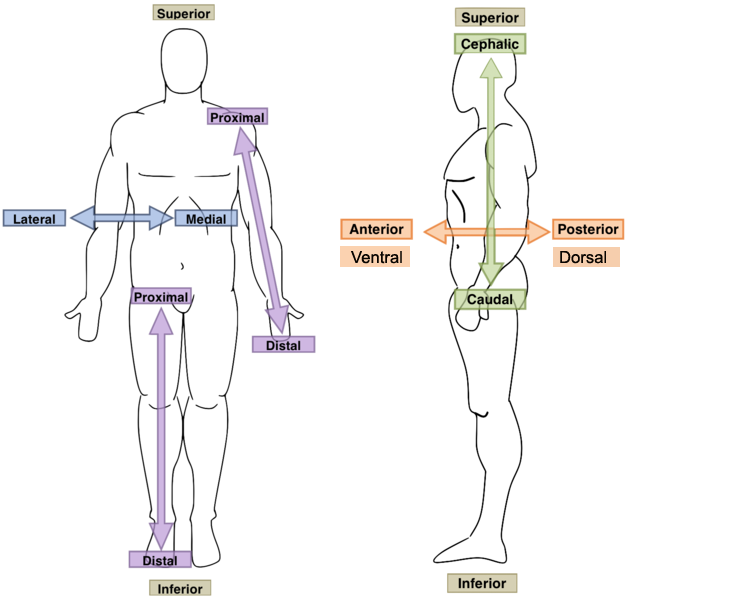
Cranial?
Toward the upper part; above; superior
24
New cards
Caudal?
Away from the upper part; toward the lower part; below; inferior
25
New cards
Distal?
Farther from the point where the limb attaches to the body trunk
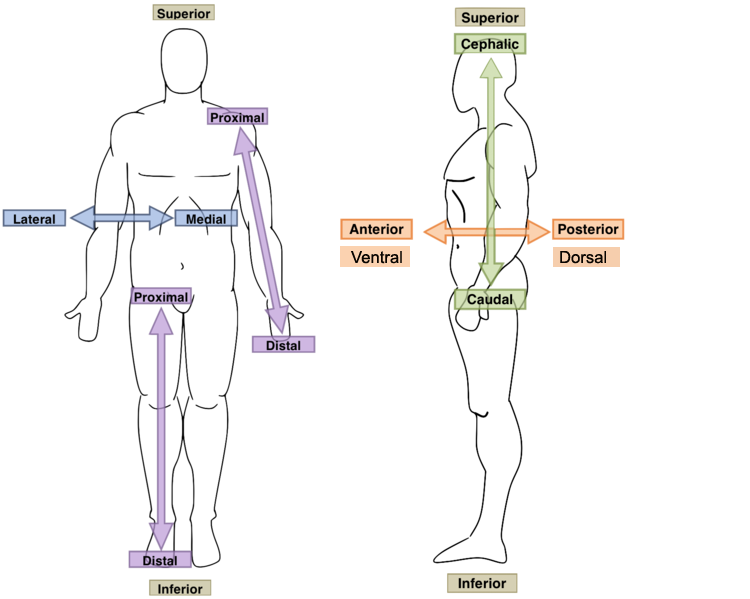
26
New cards
Proximal?
Closer to the point where a limb attaches to the body's trunk
27
New cards
Superficial?
Toward or at the body surface; external
28
New cards
Deep?
Away from the body surface; internal
29
New cards
What is the axial skeleton?
Used for organ protection and consists of the trunk section of the body (chest, pelvis, shoulder, skull, spinal cord)
30
New cards
What is the appendicular skeleton?
Used for movement and consists of the limbs
31
New cards
What are cords of connective tissue that connect muscle to bone?
Tendon
32
New cards
What are the bones that make up the ankle called?
Tarsals
33
New cards
What leg bone aids and stabilizes the ankle joint but does not bear any weight?
Fibula
34
New cards
What is the prime mover in inspiration?
Diaphragm
35
New cards
What does it mean if a muscle is a prime mover?
It is the muscle responsible for producing a certain movement
36
New cards
What does it mean if a muscle is an antagoinst?
It opposes the prime mover or does the reverse of a certain movement; located on the opposite side; can regulate prime movers by adding resistance
37
New cards
What does it mean if a muscle is a stabilizer?
It supports and sometimes immobilizes other areas to increase the prime mover’s effectiveness
38
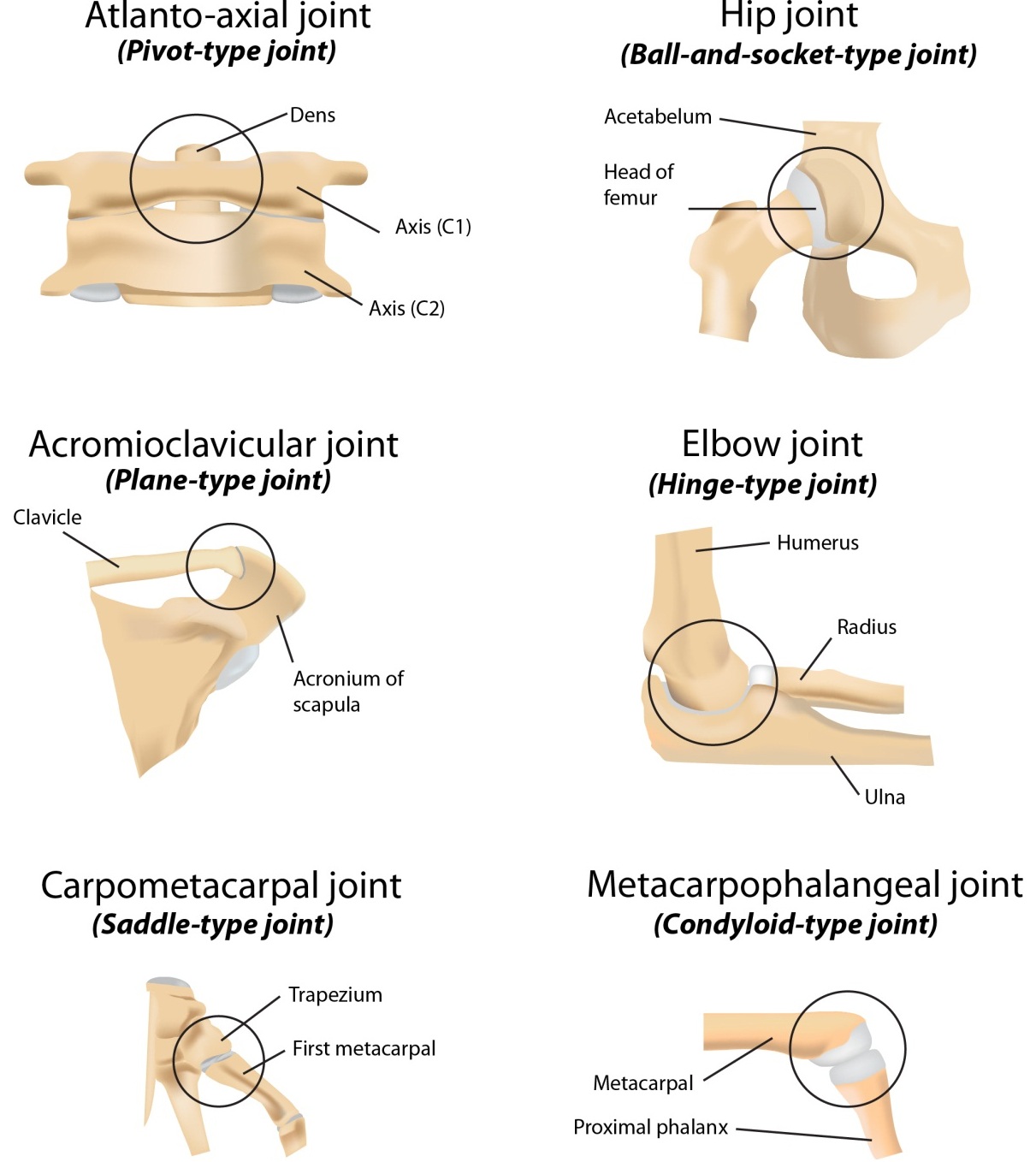
New cards
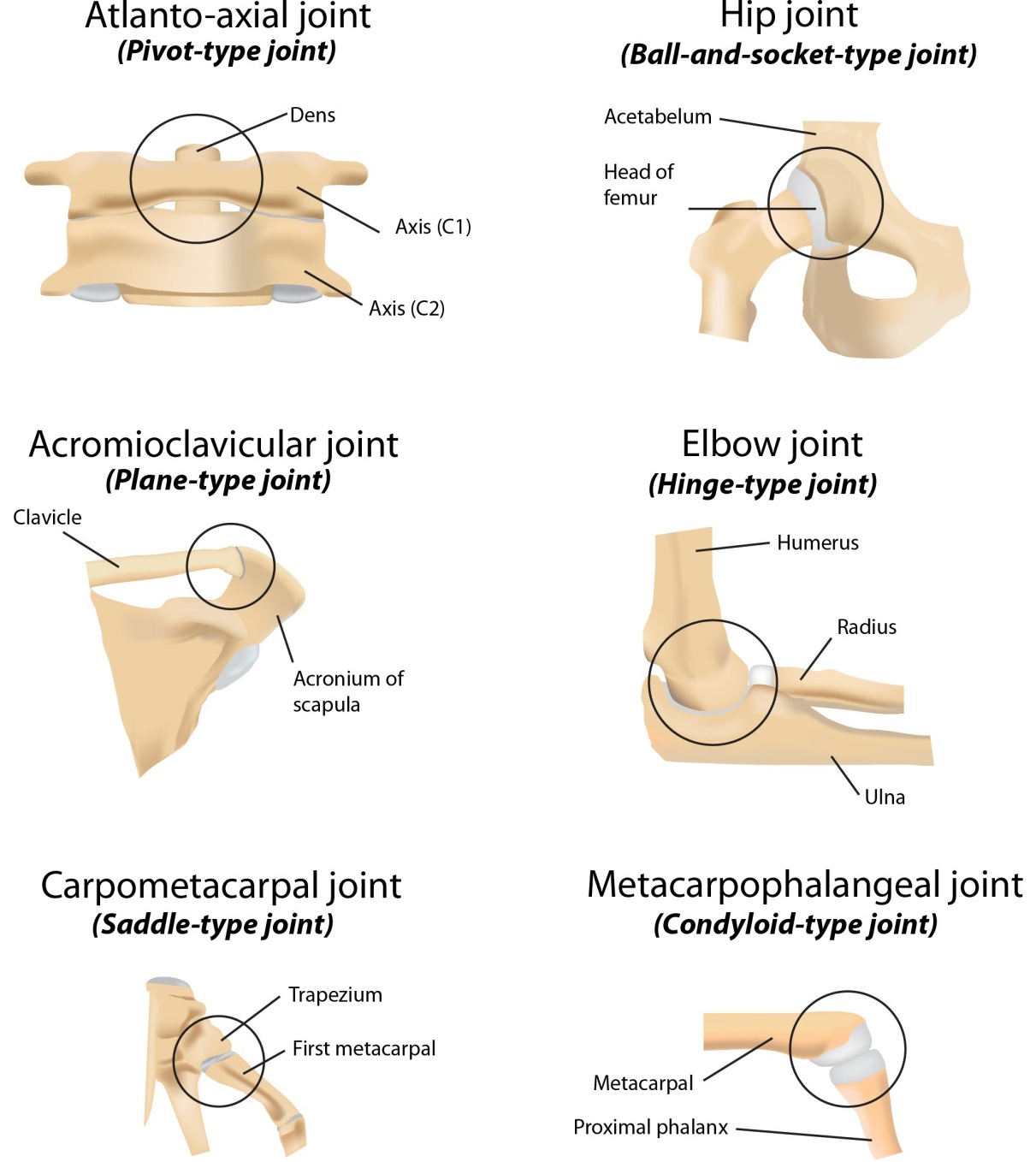
What is a hinge joint?
Only moves in one direction; allows angular movements like flexion and extension
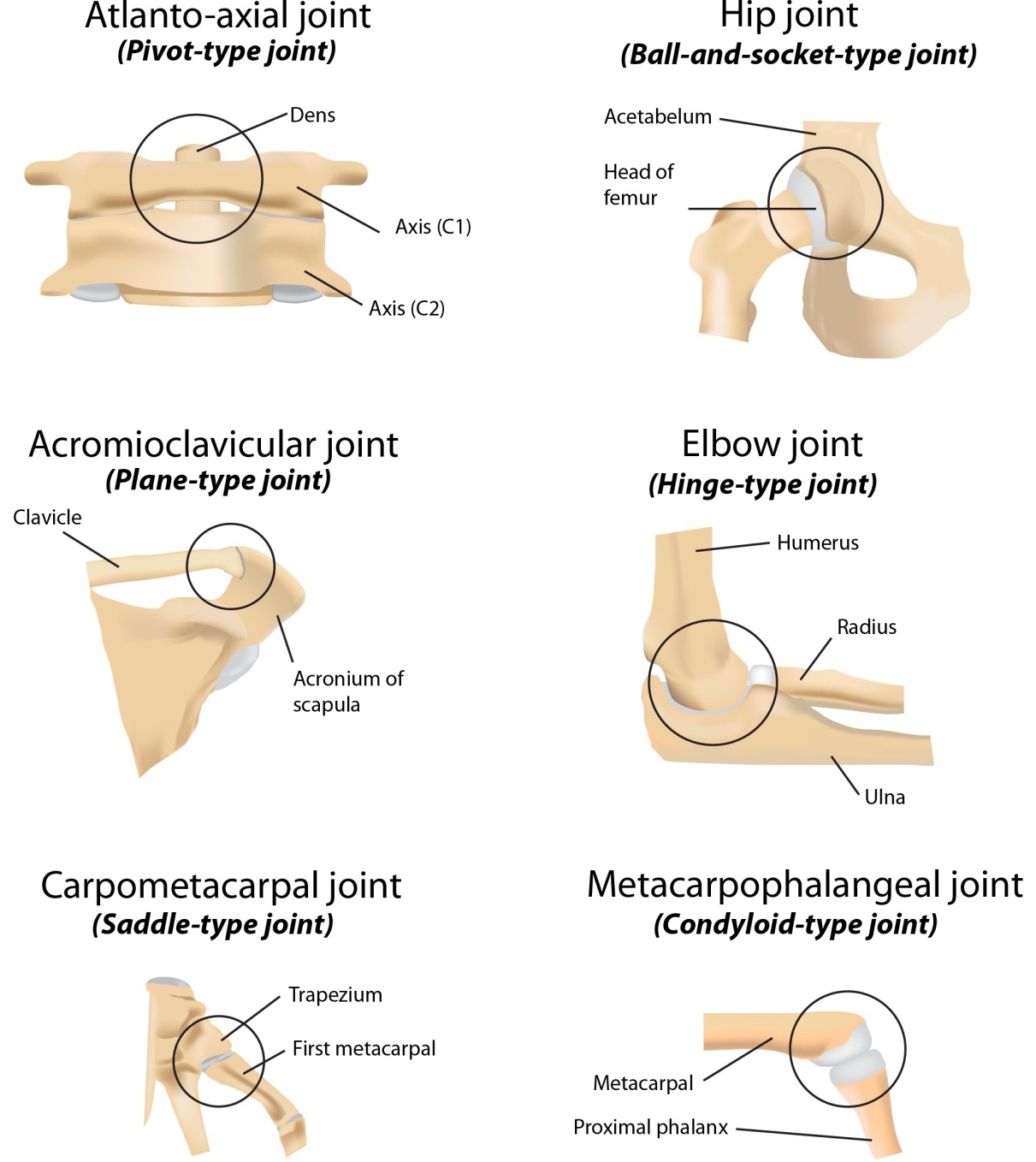
39
New cards
What is a gliding joint?
AKA plane joint; allows for gliding movements
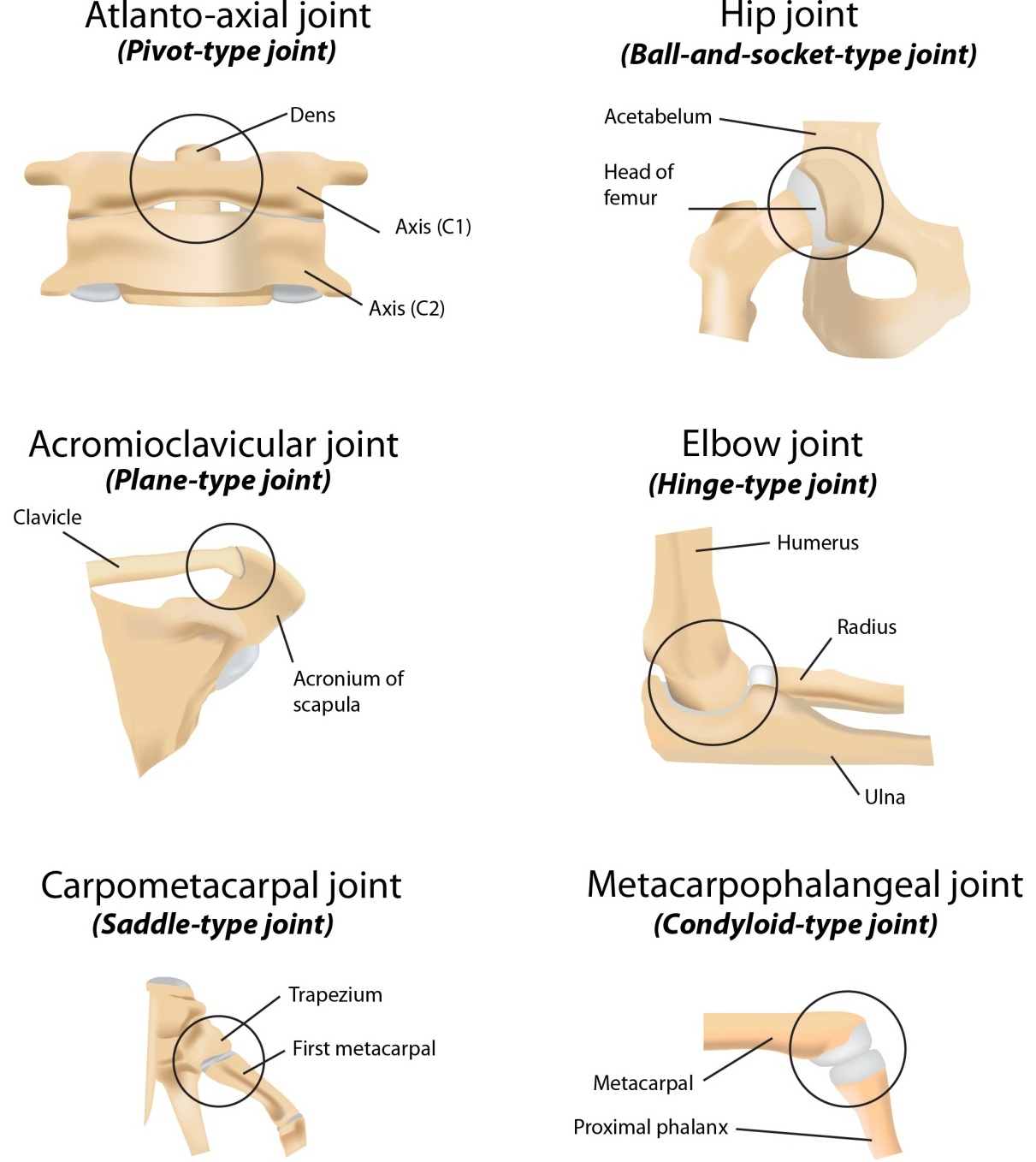
40
New cards
What is a pivot joint?
Allow rotations as well as twisting movements such as supination and pronation
41
New cards
What is a condylar joint?
Similar to a pedestal with a joint on top; allows movements like flexion and extension as well as adduction and abduction
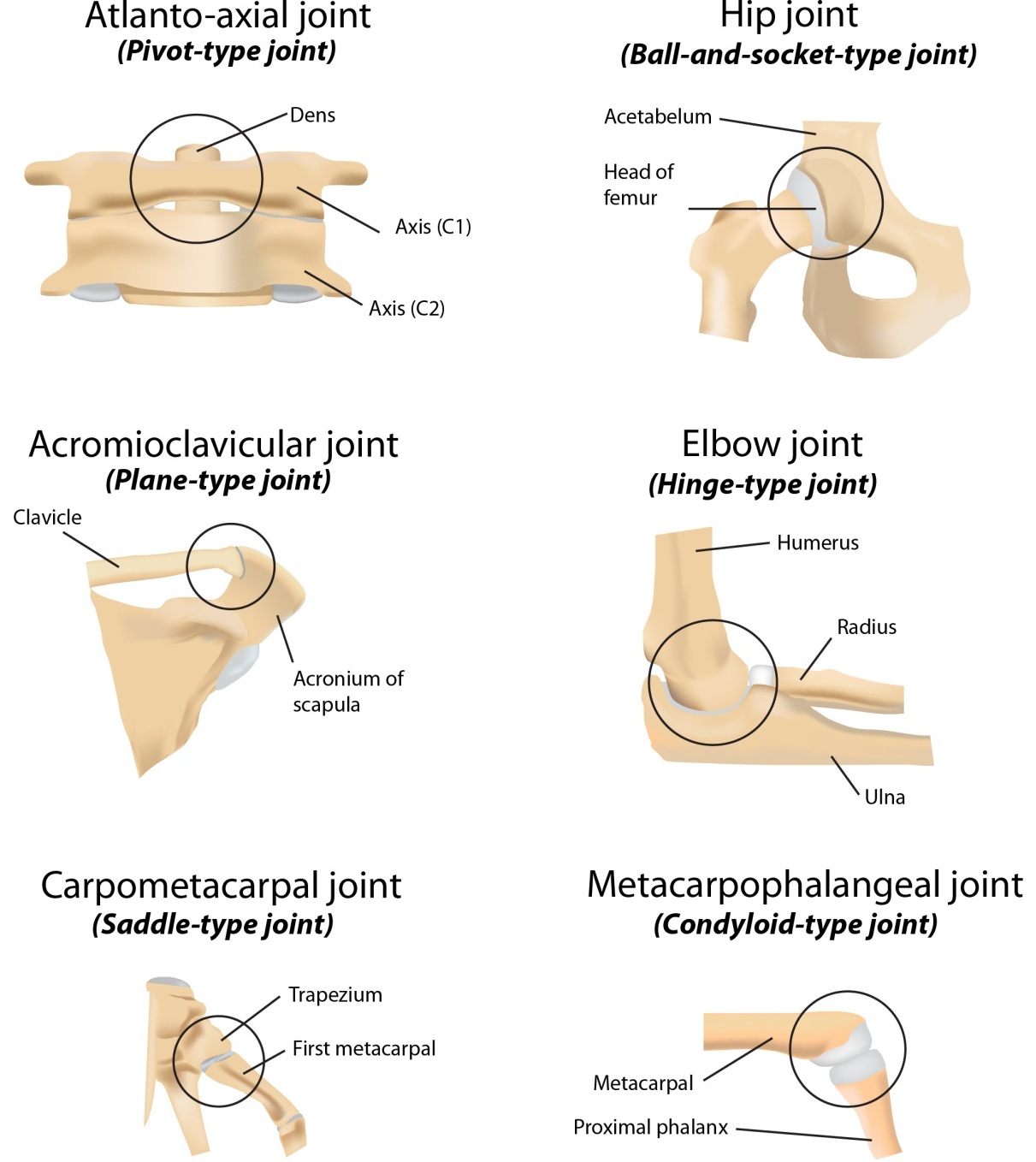
42
New cards
What is a saddle joint?
Allows opposition movements as well as flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
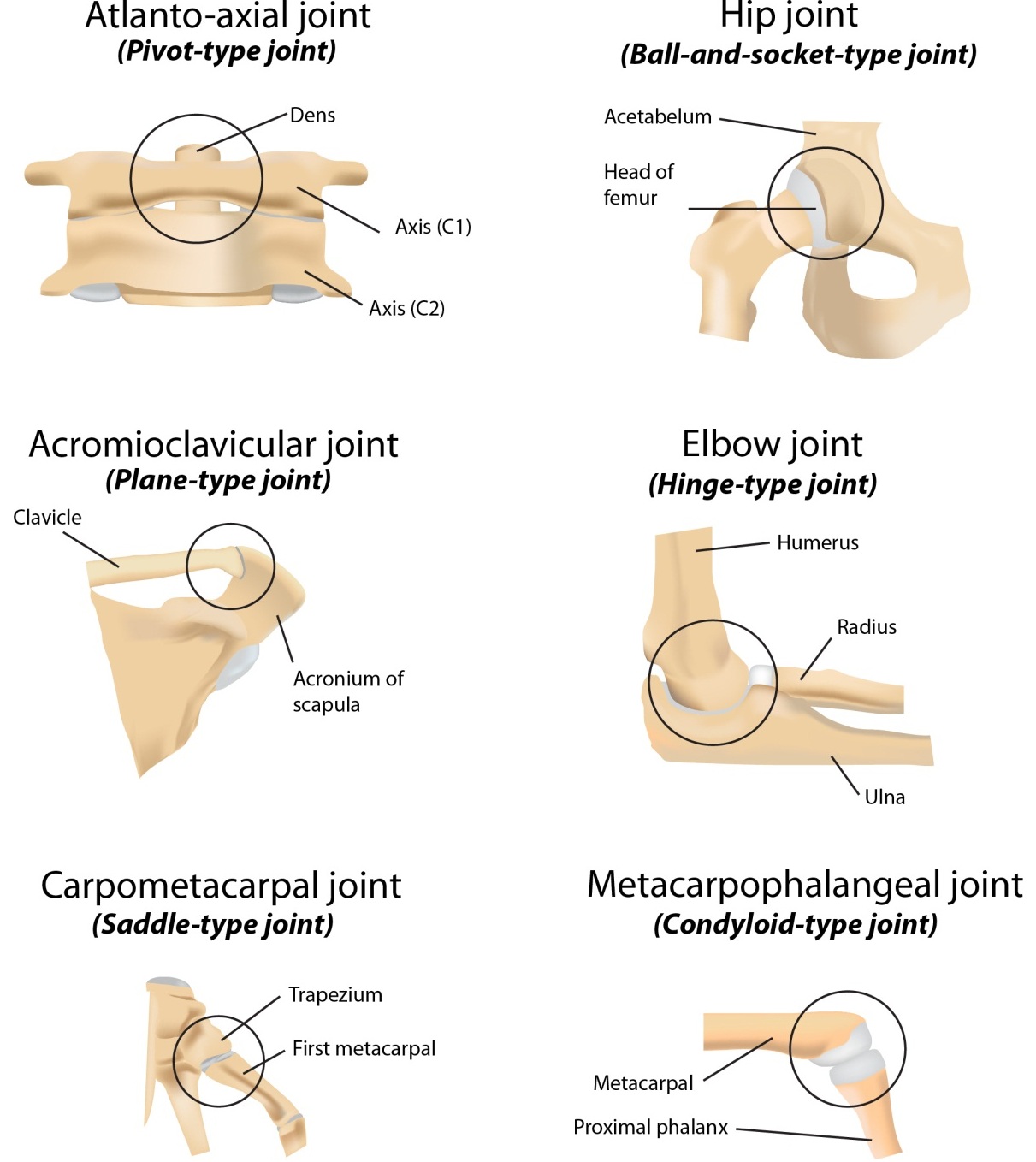
43
New cards
What is a ball and socket joint?
Lots of maneuverability; allows for rotational movements, abduction, adduction, flexion, and extension
44
New cards
Why is there an abundance of mitochondria in our muscle cells?
Muscles require high amount of energy/ATP
45
New cards
Why is the nervous system critical for muscle contraction?
The nervous system signals the muscle system to contract in response to varying stimuli causing contraction.
46
New cards
Explain why people who experience paralysis in their lower limbs have thinner, weaker bones in their legs and thighs.
This is due to the lack of use. If the bones are not being used, they thin out as they do not need to bear as much weight.
47
New cards
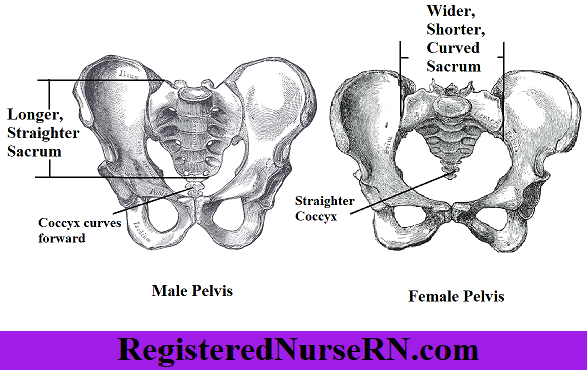
What are the differences between a female and male pelvis?
Female has a wider pubic arch, a flexible and shorter coccyx, and a large birth canal in the center
Male has a more narrow pubic arch, a stiff and longer coccyx, and a fairly narrow center area
Male has a more narrow pubic arch, a stiff and longer coccyx, and a fairly narrow center area
48
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Support, protection, movement, storage, hematopoiesis (blood cell formation), and hormone production
49
New cards
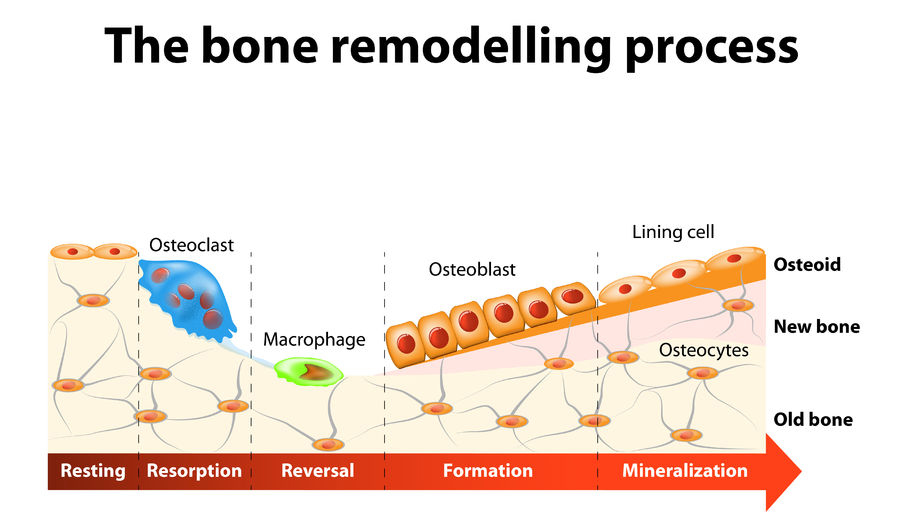
What are the steps in bone remodeling?
1) Osteocytes release chemical signals to tell osteoclasts to go to the damage
2) Osteocalsts release enzymes there that allow them to digest the calcium phosphate, putting the calcium and phosphate back into the blood (resorption)
3) Macrophages promote bone tissue remodeling
4) Osteoblasts come in and build new bone before they undergo apoptosis
2) Osteocalsts release enzymes there that allow them to digest the calcium phosphate, putting the calcium and phosphate back into the blood (resorption)
3) Macrophages promote bone tissue remodeling
4) Osteoblasts come in and build new bone before they undergo apoptosis
50
New cards
What two things are needed in order for muscle contraction to occur?
Access for myosin to “attach” to actin and ATP
51
New cards
Summarize the sliding filament model.
The heads of the myosin filament grab onto the actin filament which pulls the actin to slide past the myosin. This results in more overlap of actin and myosin filaments and the shortening of a sarcomere

52
New cards
What organelle is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft?
Synaptic vesicles
53
New cards
What division is responsible for the “fight or flight” response?
Sympathetic Division
54
New cards
What division is responsible for controlling voluntary movements?
Somatic Division
55
New cards
What are mechanoreceptors?
Activated by mechanical force: vibration, pressure, stretch, and touch
56
New cards
What are photoreceptors?
Activated by light
57
New cards
What are thermoreceptors?
Activated by a change in temperature
58
New cards
What are chemoreceptors?
Activated by chemicals
59
New cards
What are nociceptors?
Activated by pain
60
New cards
What is the function of the adrenal glands?
Synthesizing and secreting mineralocorticoids like aldosterone; fight or flight functions; bodily stress response
61
New cards
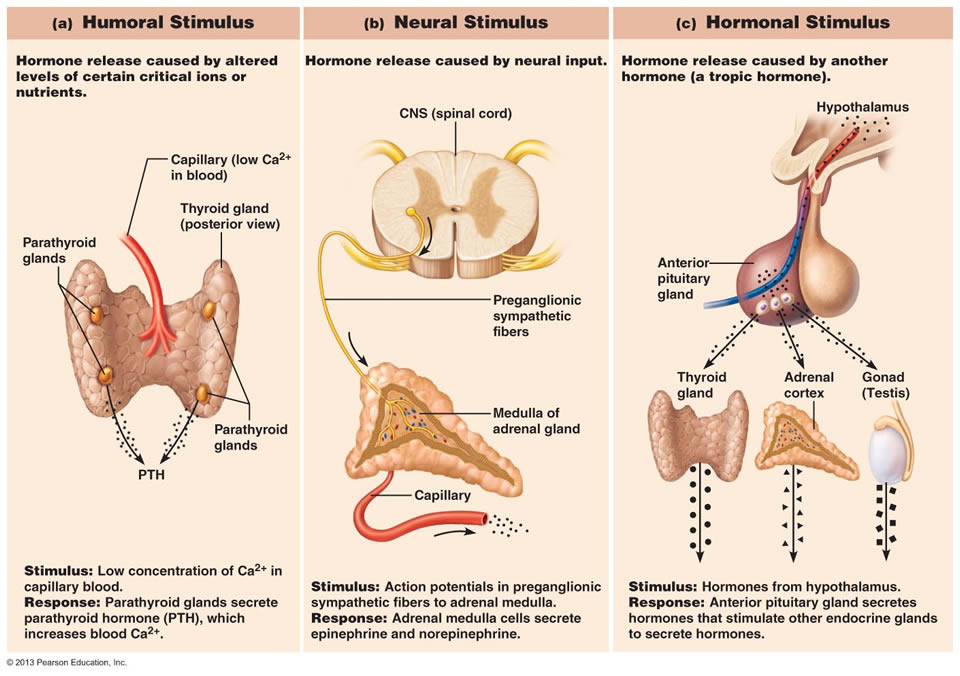
What are the three types of stimuli that can trigger endocrine glands to make and release hormones?
Humoral, Neural, and Hormonal
62
New cards
What are humoral stimuli?
Hormone release caused by altered levels of critical ions or nutrients; simplest endocrine control
63
New cards
What are hormonal stimuli?
Hormone release caused by another hormone
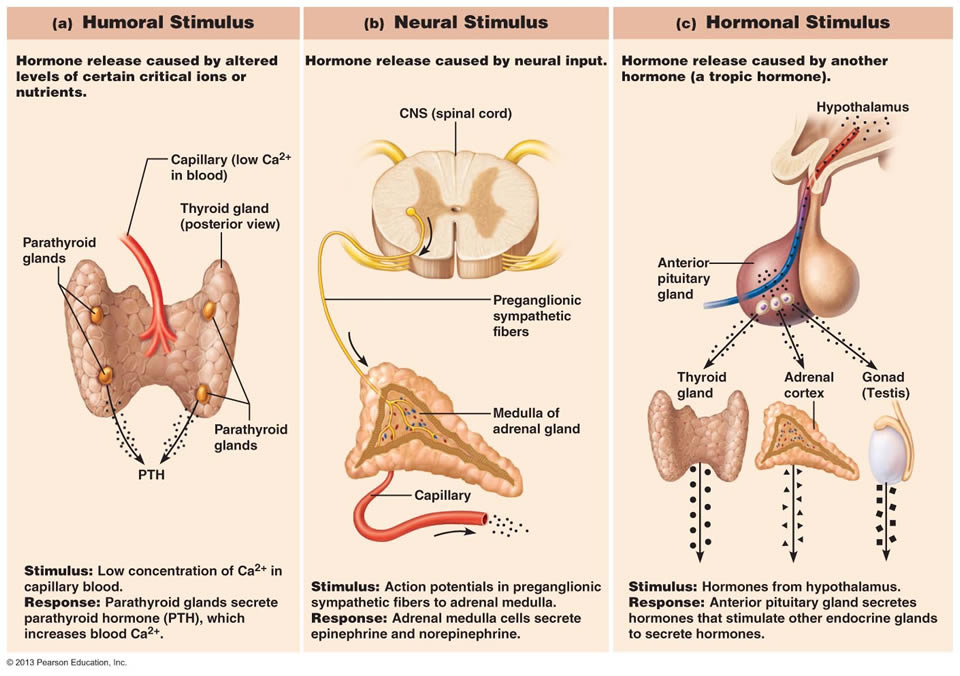
64
New cards
What are neural stimuli?
Hormone release caused by neural input
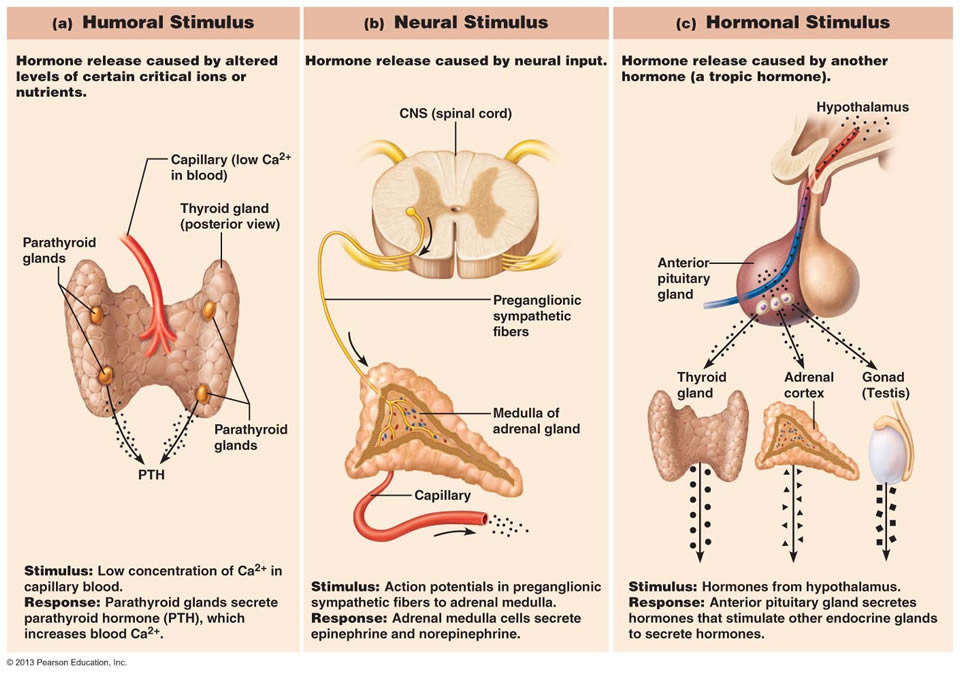
65
New cards
What is the difference between a membrane receptor and an intracellular receptor?
Intracellular: inside the cell, usually receive lipid-soluble hormones
Membrane: On the cell membrane and usually receive water-soluble hormones
Membrane: On the cell membrane and usually receive water-soluble hormones
66
New cards
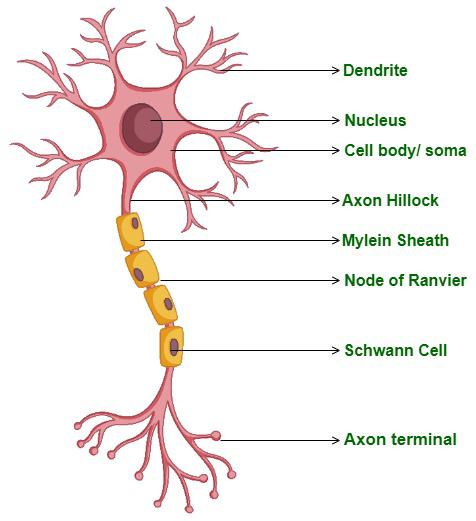
What are the parts of a neuron?
Soma, dendrites, axon, axon terminals, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, and the nucleus
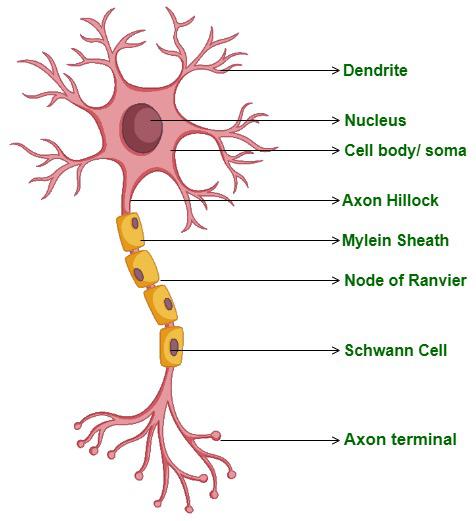
67
New cards
Function of cell body or soma and the nucleus
The life support containing the nucleus and most organelles (ex: a lot of mitochondria)
68
New cards
Function of dendrites.
The main receptor of signals; conducting region
69
New cards
Function of axon.
Generates and transmits nerve impulses; conducting region known as the nerve fiber
70
New cards
Function of myelin sheath.
Covers long axons to protect and electrically insulate them to increase the speed of nerve impulse transmission
71
New cards
Function of nodes of Ranvier.
Unmyelinated gaps in the myelin sheath that aid in increasing the velocity of nerve signal conduction
72
New cards
Function of axon terminals.
The end of the axon that releases neurotransmitters at a synapse when a nerve impulse is received; secretory region
73
New cards
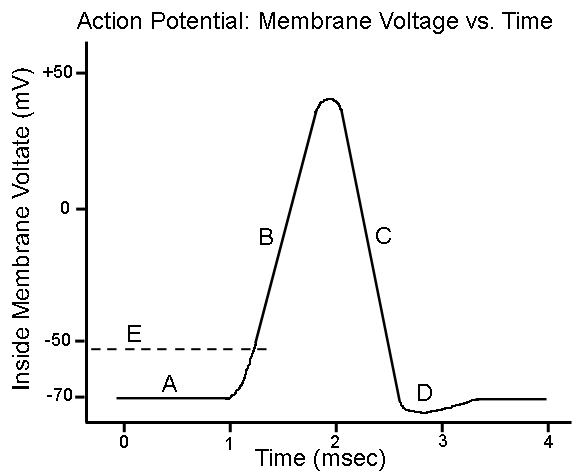
What does “A” show?
Resting state
74
New cards
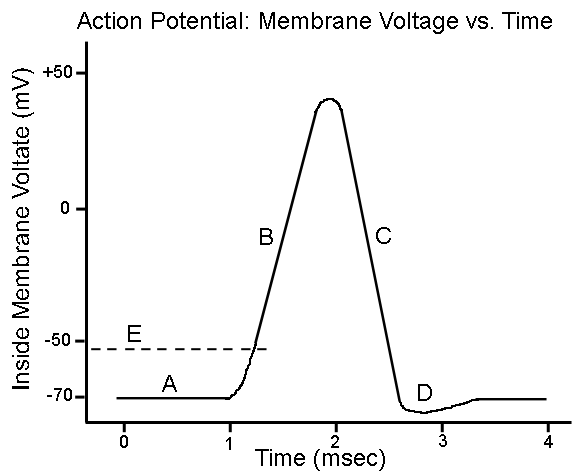
What does “B” show?
Depolarization
75
New cards
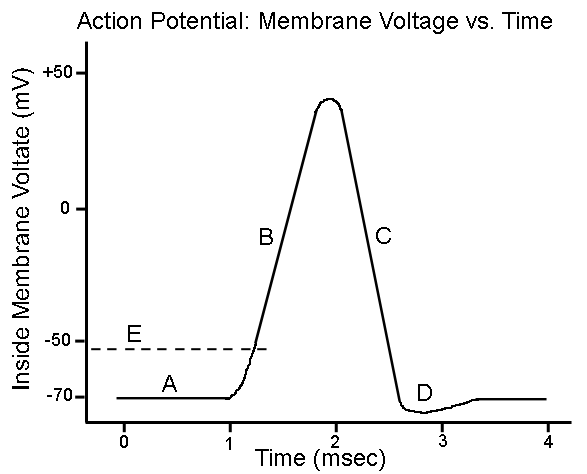
What does “C” show?
Repolarization
76
New cards
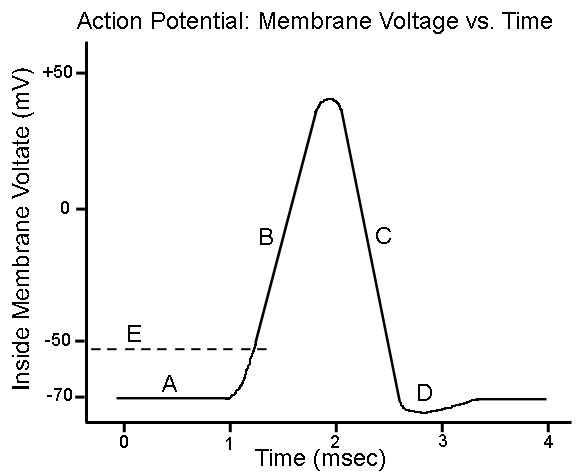
What does “D” show?
Hyperpolarization
77
New cards
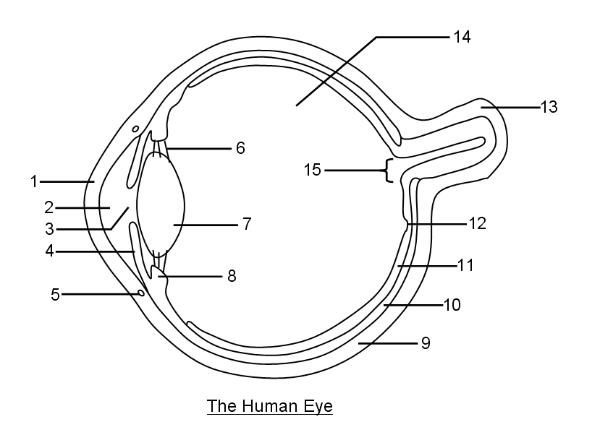
What is 1?
Cornea
78
New cards
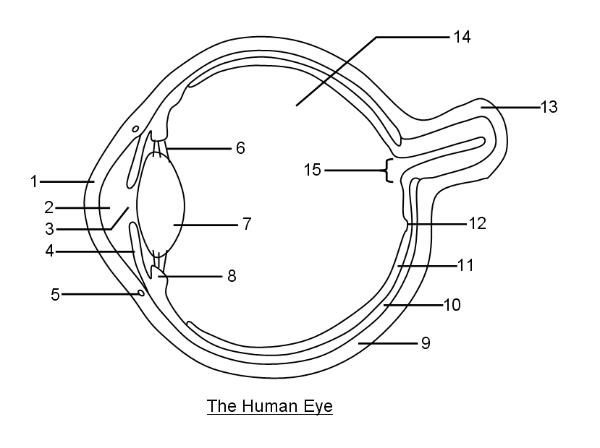
What is 2?
Aqueous humor
79
New cards
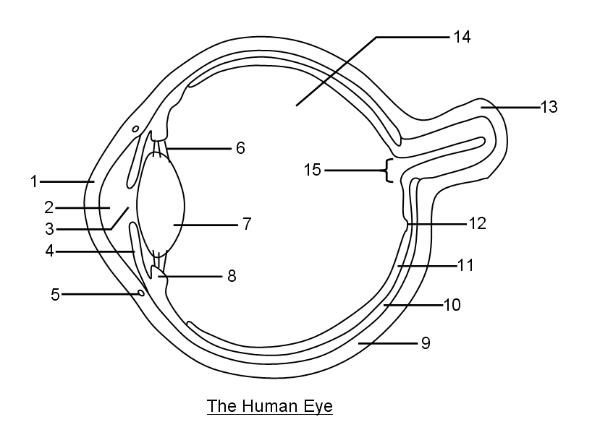
What is 3?
Pupil
80
New cards
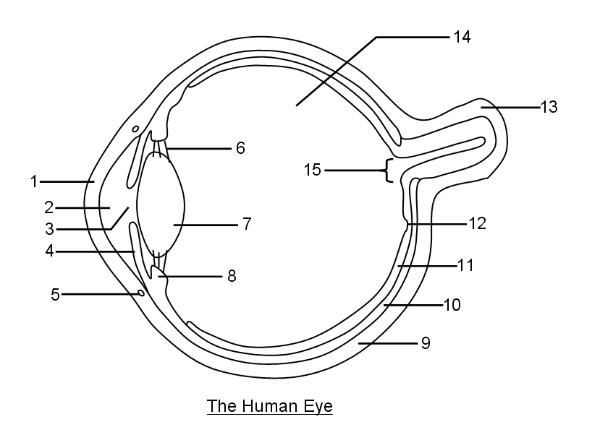
What is 4?
Iris
81
New cards
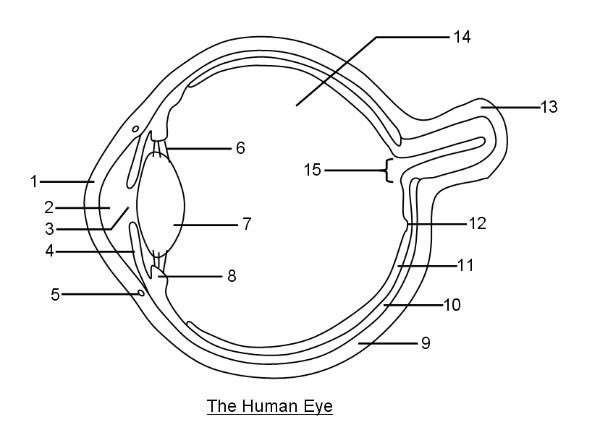
What is 6?
Suspensory ligaments
82
New cards
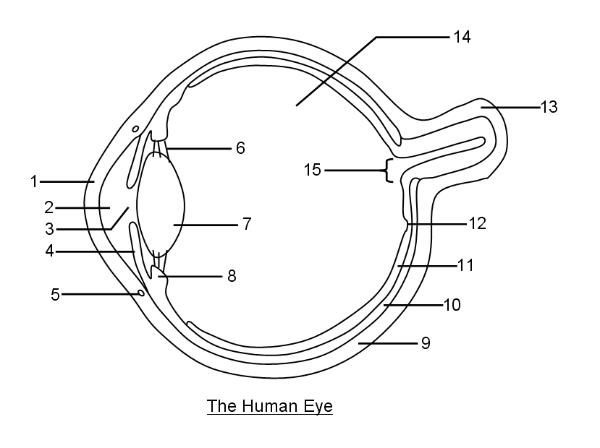
What is 7?
Lens
83
New cards
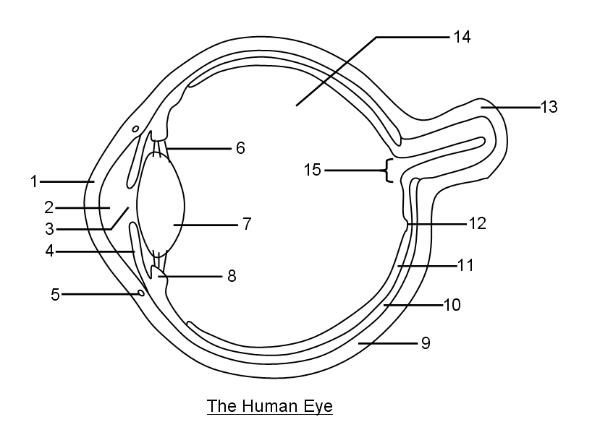
What is 8?
Ciliary body
84
New cards
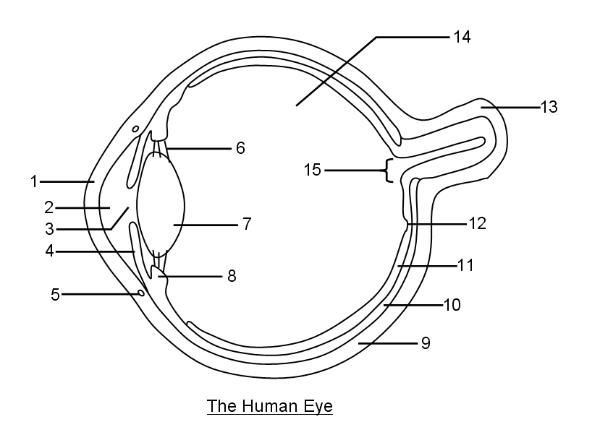
What is 9?
Sclera
85
New cards
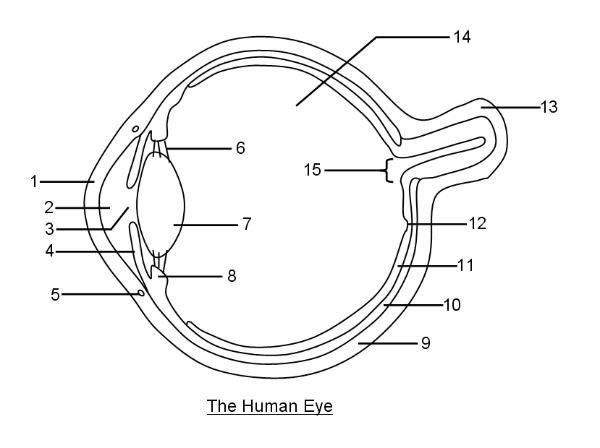
What is 10?
Choroid layer
86
New cards
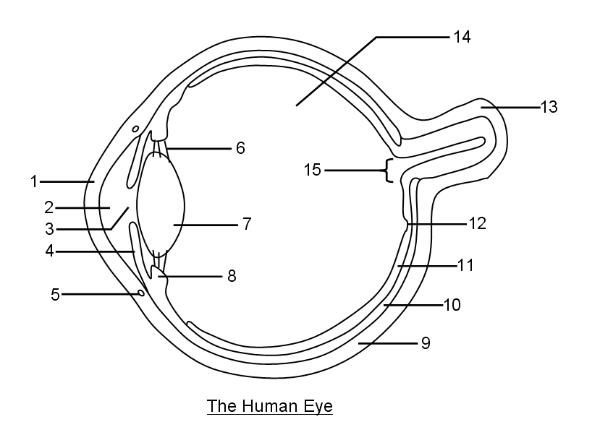
What is 11?
Retina
87
New cards
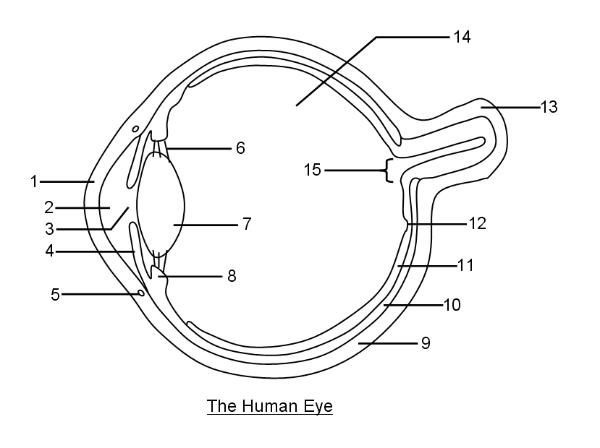
What is 12?
Fovea Centralis
88
New cards
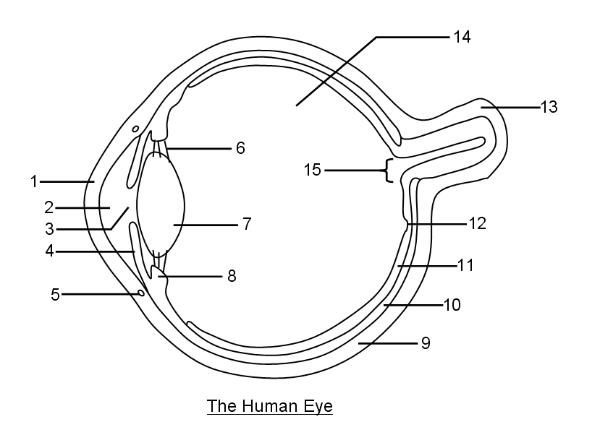
What is 14?
Vitreous humor
89
New cards
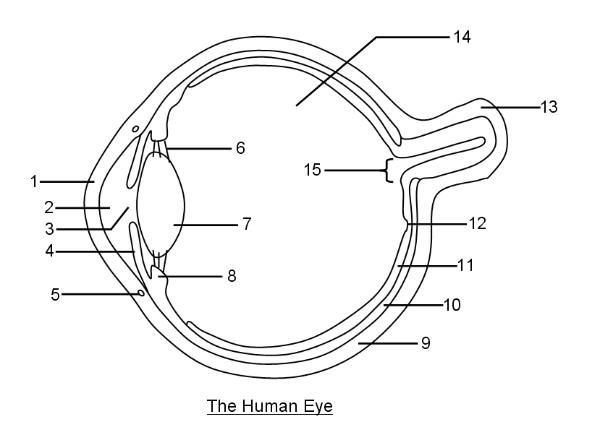
What is 15?
Optic disc to optic nerve