Comprehensive Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Quantum Mechanics, and Periodic Trends
1/297
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
298 Terms
What is thermochemistry?
The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes that involve heat.
What is the most important form of potential energy in molecules?
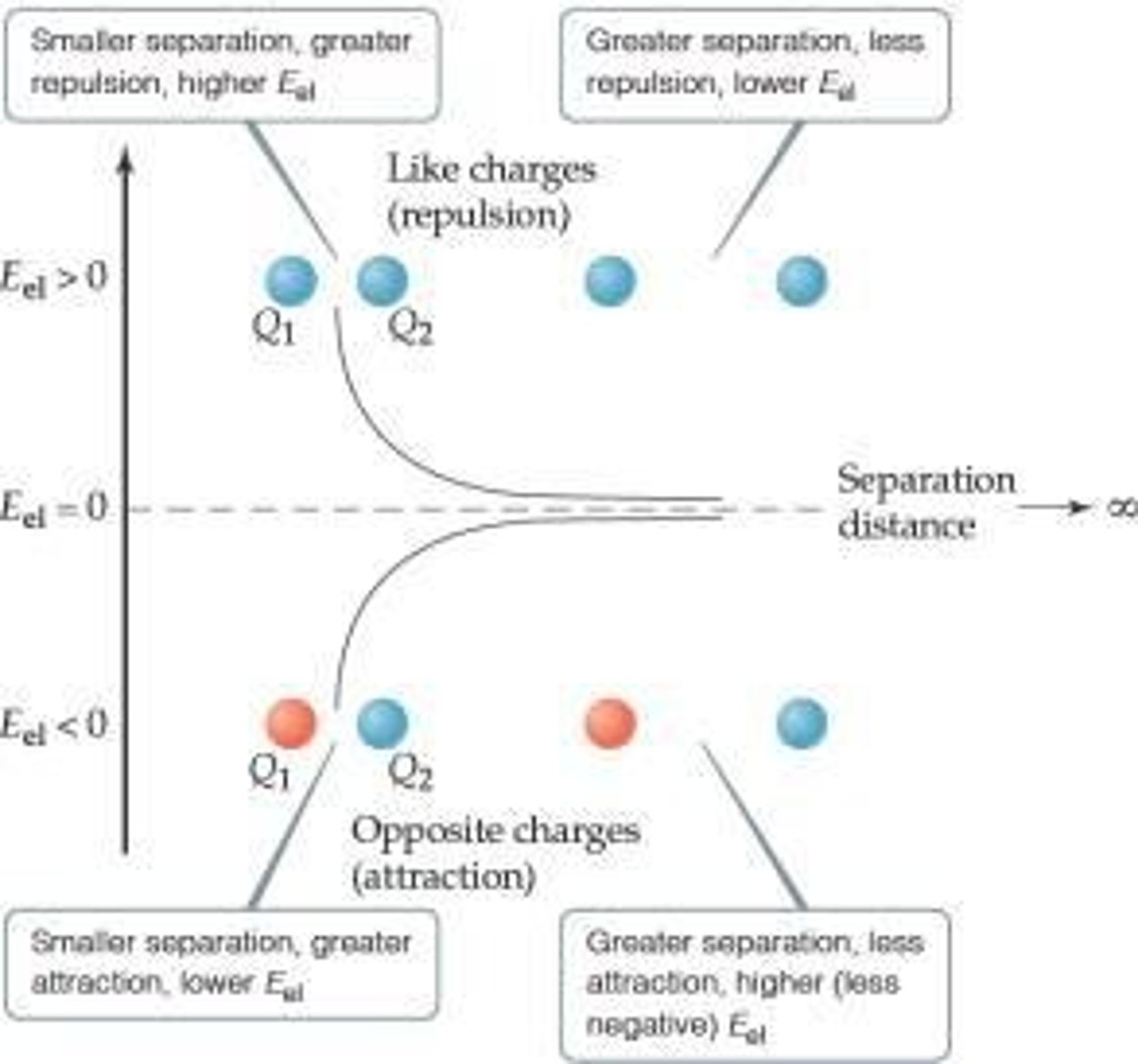
Electrostatic potential energy (Eel).
What is the unit of energy commonly used in thermochemistry?
The Joule (1 J = 1 kg m²/s²).
What does the First Law of Thermodynamics state?
Energy can be converted from one form to another, but it is neither created nor destroyed.
What happens to chemical energy when heating a home?
Chemical energy is converted to heat.
How is energy released or consumed during chemical bond formation?
Energy is released when chemical bonds are formed and consumed when they are broken.
What are the three types of systems in thermodynamics?
1) Open System: exchanges heat and mass with surroundings. 2) Closed System: exchanges heat but not mass. 3) Isolated System: exchanges neither heat nor mass.
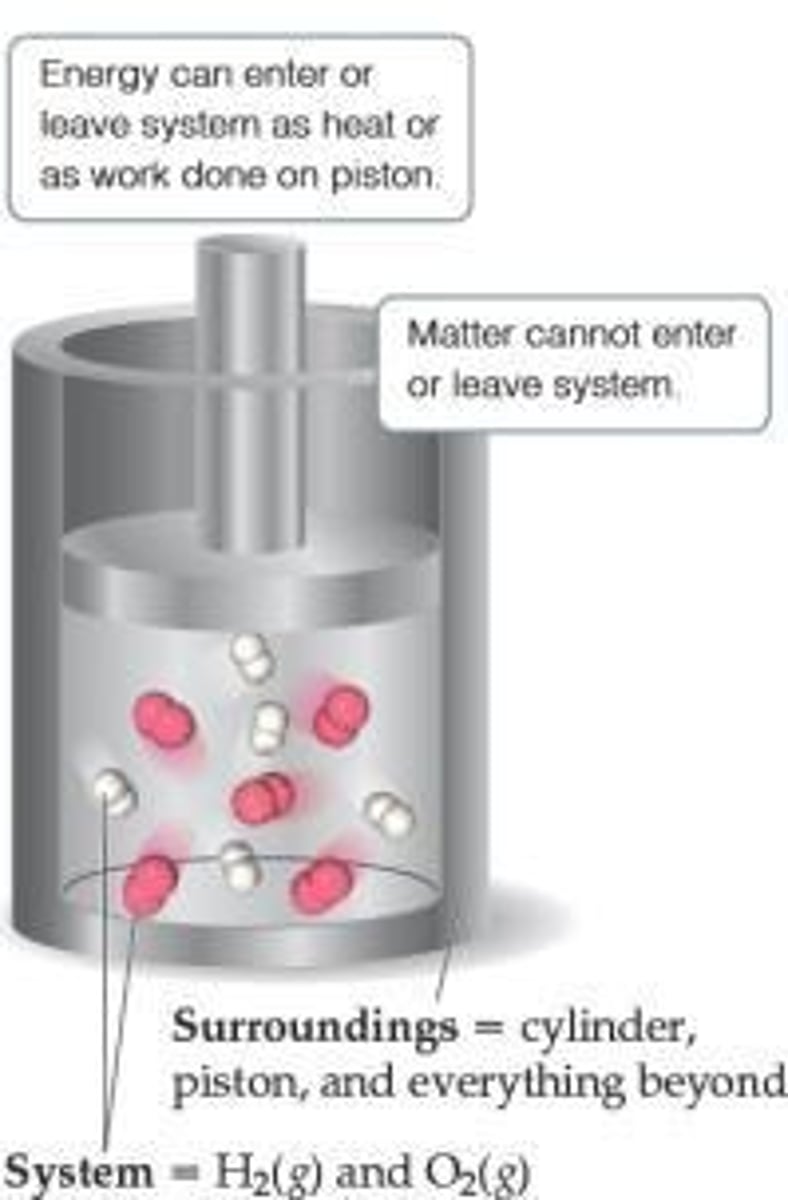
What is the definition of internal energy?
The sum of all kinetic and potential energies of all components of the system, represented as E.
How is the change in internal energy calculated?
ΔE = E_final - E_initial.
What does a positive change in internal energy (ΔE) indicate?
The system absorbed energy from the surroundings.
What does a negative change in internal energy (ΔE) indicate?
The system released energy to the surroundings.
What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic processes?
Exothermic: heat is released by the system. Endothermic: heat is absorbed by the system.

What does the symbol 'q' represent in thermodynamics?
Heat exchanged between the system and surroundings.
What does the symbol 'w' represent in thermodynamics?
Work done by or on the system.
What does a positive 'q' value indicate?
The system gains heat.
What does a negative 'q' value indicate?
The system loses heat.
What does a positive 'w' value indicate?
Work is done on the system.
What does a negative 'w' value indicate?
Work is done by the system.
What are state functions in thermodynamics?
Properties that are independent of the path taken to achieve a particular state.
Why is it difficult to know the internal energy of a system?
Finding the exact value of internal energy is too complex.
What is the relationship between internal energy and the path taken to achieve a state?
The internal energy is independent of the path taken.
What is electrostatic attraction in the context of thermochemistry?
Attraction between oppositely charged ions.
What is the significance of energy conversion in green plants?
Sunlight is converted to chemical energy.
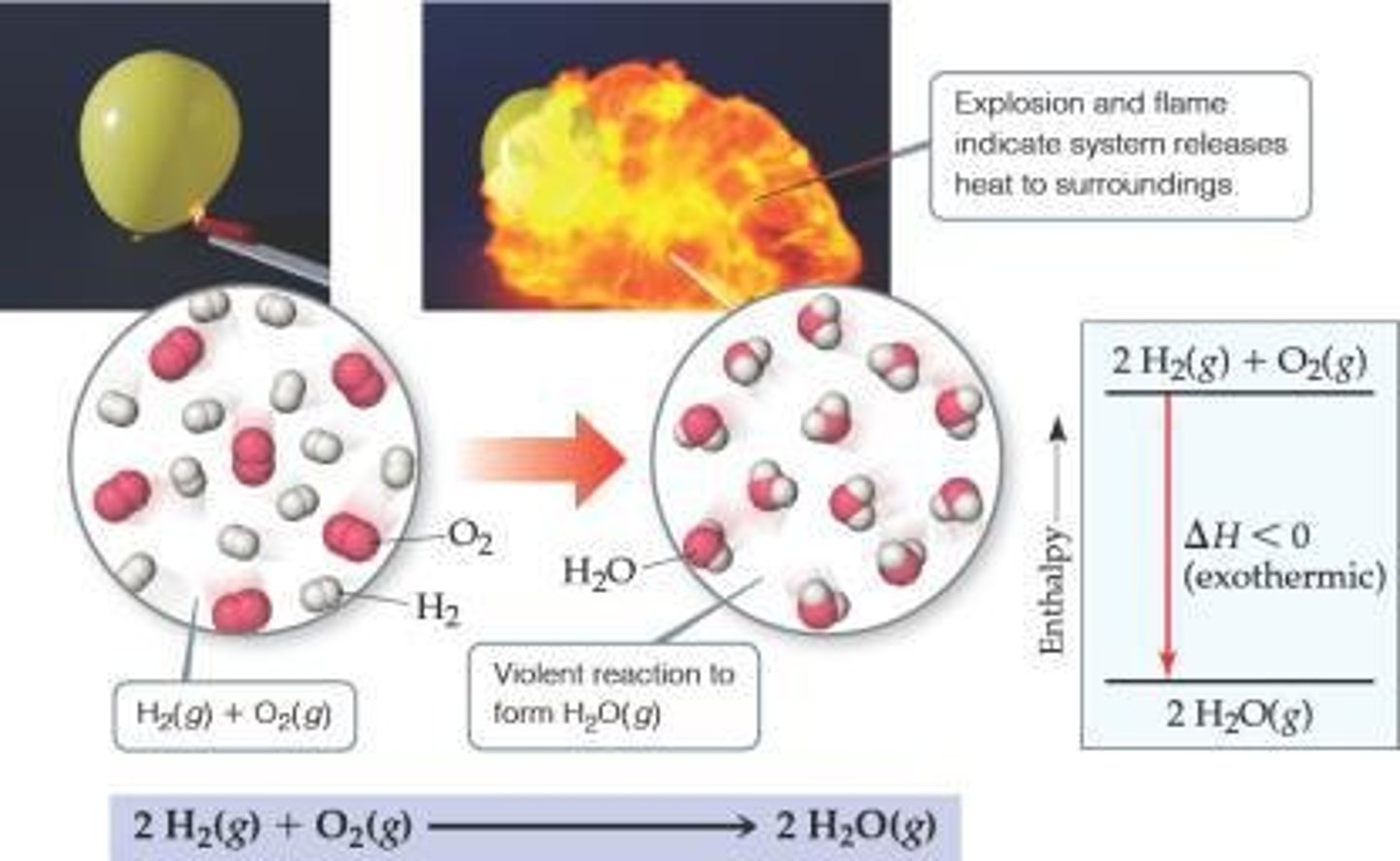
What is the result of the reaction between H2(g) and O2(g) to form H2O(l)?
Heat is released to the surroundings.
Is the reaction of forming H2(g) and O2(g) from H2O(l) exothermic or endothermic?
Endothermic, because heat is absorbed from the surroundings.
What is a state function in thermodynamics?
A property that depends only on the current state of the system, not on the path taken to reach that state.
Which quantities act like state functions: the amount of calories consumed, weight, or calories burned through exercise?
Your weight is a state function.
What is the formula to measure work done by a gas in a piston?
w = -PΔV.
Why is the work done by a system considered negative?
Because it is work done by the system.
What is enthalpy (H) defined as?
The internal energy plus the product of pressure and volume.
What is the relationship between change in enthalpy (ΔH) and heat flow at constant pressure?
ΔH is the heat gained or lost during the process.
What is the formula for change in enthalpy at constant pressure?
ΔH = ΔE + PΔV.
What indicates an endothermic process in terms of enthalpy change (ΔH)?
ΔH is positive.
What indicates an exothermic process in terms of enthalpy change (ΔH)?
ΔH is negative.
What is the enthalpy of reaction (ΔH_rxn)?
The enthalpy of the products minus the enthalpy of the reactants.
What is true about the enthalpy change for a reaction and its reverse?
It is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign.
How does the enthalpy change depend on reactants and products?
It depends on their states.
What happens if a system does not change its volume during a process?
It does not do pressure-volume work.
What is the significance of internal energy in a thermodynamic system?
It is independent of the path taken to achieve that state.
What does the term 'extensive property' refer to in relation to enthalpy?
It means that enthalpy depends on the amount of substance present.
What can be said about q and w in terms of state functions?
They are not state functions.
What is the implication of measuring enthalpy at constant pressure?
It allows for accounting heat flow during the process.
What is the relationship between internal energy (E) and work (w) in a chemical reaction?
They are related but not the same; work can vary while internal energy remains constant.
What happens to the internal energy of a system when it releases heat?
The internal energy decreases.
What is the primary type of work done by chemical or physical changes?
Mechanical work associated with a change in gas volume.
What does the symbol Δ represent in thermodynamics?
It represents a change in a quantity, such as energy or enthalpy.
What is the equation for work in thermodynamics?
w = -PΔV
What is the value of ΔH for the reaction 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ⟶ 2 H2O(g)?
ΔH = -483.6 kJ
If the volume change (ΔV) is zero, what can be said about the enthalpy change (ΔH)?
ΔH would be the same as in the equation.
What sign does ΔH have when a reaction in a flask causes it to get colder?
ΔH has a negative sign (b. -).
What is the process when an ice cube melts in terms of enthalpy change?
It is an endothermic process with a positive ΔH.
What happens to the enthalpy change (ΔH) when 1 g of butane is combusted?
It is an exothermic process with a negative ΔH.
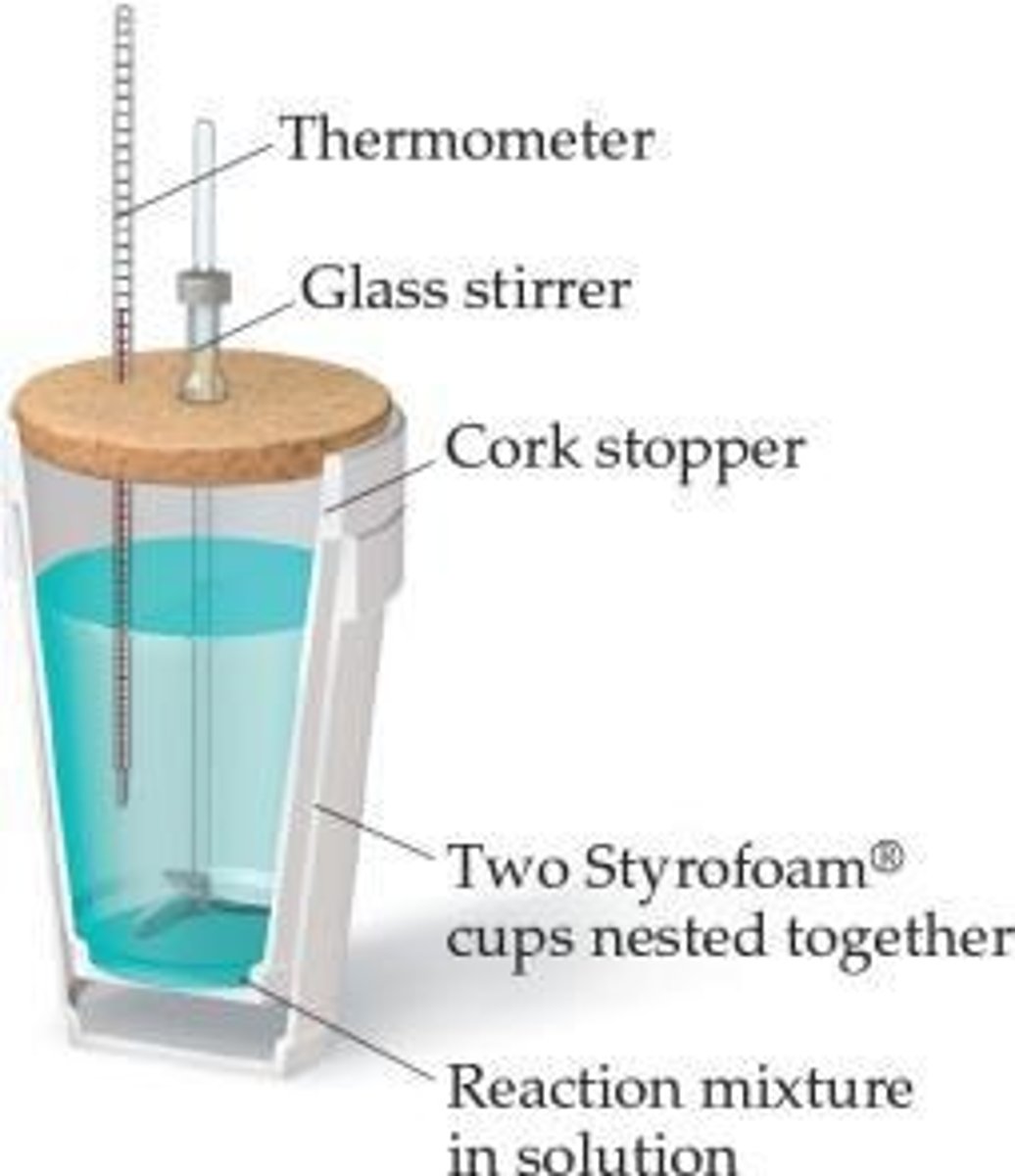
What is the definition of calorimetry?
Calorimetry is the measurement of heat flow.
What is the specific heat of water?
4.184 J/g∙K.
How do you calculate ΔH for a reaction using calorimetry?
ΔH = q / (m × C × ΔT) where q is heat, m is mass, C is specific heat, and ΔT is temperature change.
Which substance undergoes the greatest temperature change when absorbing the same quantity of heat?
H2O(l) (water).
What is the specific heat capacity trend among copper, silver, and gold as atomic weight increases?
The specific heat capacity decreases as atomic weight increases.
What is Hess's Law?
Hess's Law states that ΔH can be calculated using published ΔH values and the properties of enthalpy.
What is the specific heat of aluminum (Al)?
0.90 J/g-K.
What is the specific heat of iron (Fe)?
0.45 J/g-K.
What is the specific heat of mercury (Hg)?
0.14 J/g-K.
What is the specific heat of carbon dioxide (CO2)?
0.84 J/g-K.
What is the specific heat of methane (CH4)?
2.20 J/g-K.
What happens during the solidification of molten gold at atmospheric pressure?
It is an exothermic process.
What is the specific heat of nitrogen gas (N2)?
1.04 J/g-K.
What is the heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 K (1 degree Celsius).
What is the difference between heat capacity and specific heat?
Heat capacity is for any amount of substance, while specific heat is for one gram.
What is the molar heat capacity?
The heat capacity of one mole of a substance.
What is the significance of measuring ΔH through calorimetry?
It allows us to determine the heat changes in reactions without knowing the exact enthalpy of reactants and products.
What is Hess's Law?
Hess's law states that if a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, the overall enthalpy change (ΔH) equals the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.
What is the enthalpy of reaction for the combustion of carbon (C) to carbon dioxide (CO2)?
-393.5 kJ/mol.
What is the enthalpy change for the combustion of carbon monoxide (CO) to carbon dioxide (CO2)?
-283.0 kJ/mol.
How can you calculate the enthalpy for the combustion of carbon (C) to carbon monoxide (CO)?
Using Hess's Law, by rearranging the enthalpy changes of known reactions.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → N2O4(g)?
-55.2 kJ.
What are the enthalpy changes for the combustion of graphite and diamond?
Graphite: -393.5 kJ/mol; Diamond: -395.4 kJ/mol.
How do you calculate the enthalpy change for the conversion of graphite to diamond?
Use the enthalpy changes of the combustion reactions of graphite and diamond.
What is the definition of an enthalpy of formation (ΔHf)?
The enthalpy change for the reaction in which a compound is made from its constituent elements in their elemental forms.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)?
-393.5 kJ.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 CO(g) + O2(g) → 2 CO2(g)?
-566.0 kJ.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(g)?
-483.6 kJ.
How do you calculate ΔH for the reaction C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g)?
Use the enthalpy changes from the given thermochemical equations.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction NO(g) + O(g) → NO2(g)?
Calculate using the enthalpy changes from the given reactions involving NO and O3.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction O3(g) → O2(g)?
-142.3 kJ.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction O2(g) → 2 O(g)?
495.0 kJ.
What is the overall enthalpy change when calculating ΔH using Hess's Law?
The sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps must equal the overall reaction.
What is the enthalpy change for the combustion of propane (C3H8) in terms of its decomposition?
The enthalpy change can be calculated by summing the enthalpy changes for each step of the reaction.
What is the significance of standard enthalpies of formation (ΔHf°)?
They are measured under standard conditions (25 °C and 1.00 atm pressure) and provide a reference for calculating reaction enthalpies.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g)?
-393.5 kJ.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction C(diamond) + O2(g) → CO2(g)?
-395.4 kJ.
What is the relationship between enthalpy changes and the steps of a reaction?
Enthalpy changes are the same whether the reaction occurs in one step or multiple steps.
How does the enthalpy of combustion differ between graphite and diamond?
The enthalpy of combustion for diamond is slightly more negative than that for graphite.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 C(s) + H2(g) → C2H2(g)?
This reaction's enthalpy change can be calculated using Hess's Law based on known enthalpy changes.
What is the effect on ΔH when reversing a reaction?
The sign of ΔH changes.
What happens to ΔH when the coefficients of a reaction are multiplied by 2?
The value of ΔH doubles.
What is bond enthalpy?
The enthalpy associated with breaking one mole of a particular bond in a gaseous substance.
What is the general formula for calculating ΔH using bond enthalpies?
ΔH = Σ(bond enthalpies of bonds broken) - Σ(bond enthalpies of bonds formed).
What is the fuel value of glucose on a per gram basis?
The amount of energy released is 2803 kJ/g.
What is the heat of formation of H2O(l)?
-286 kJ/mol.
Which reaction represents a standard enthalpy of formation?
2 Na(s) + O2(g) → Na2O(s) is a standard enthalpy of formation.
How is the enthalpy change for the combustion of ethanol calculated?
Using the reaction: C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l).