Intro: Chapter 12, Communication and Collaboration in Professional Nursing
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Up to ___ percent of serious medical errors can be attributed to miscommunication
80
Joseph Priestley:
The more we elaborate our means of communication, the less we communicate…
George Bernard Shaw:
The single biggest problem with communication is the illusion that it has taken place…
Peplau (1952) Interpersonal Relations:
Nurse pioneer
1952- book- Interpersonal Relations (Nurse/Patient/Relationship)
“Therapeutic use of self”
Orientation phase: trust
Working phase: tasks
Termination phase
Key elements impacting communication and collaboration:
SELF AWARENESS
PROFESSIONAL BOUNDARIES
Social vs. professional relationships
AVOID STEREOTYPES
REFLECTIVE PRACTICE
NON - JUDGMENTAL
acceptance
PATIENT CENTERED CARE
Caring is key
5 Elements of the Communication Process:
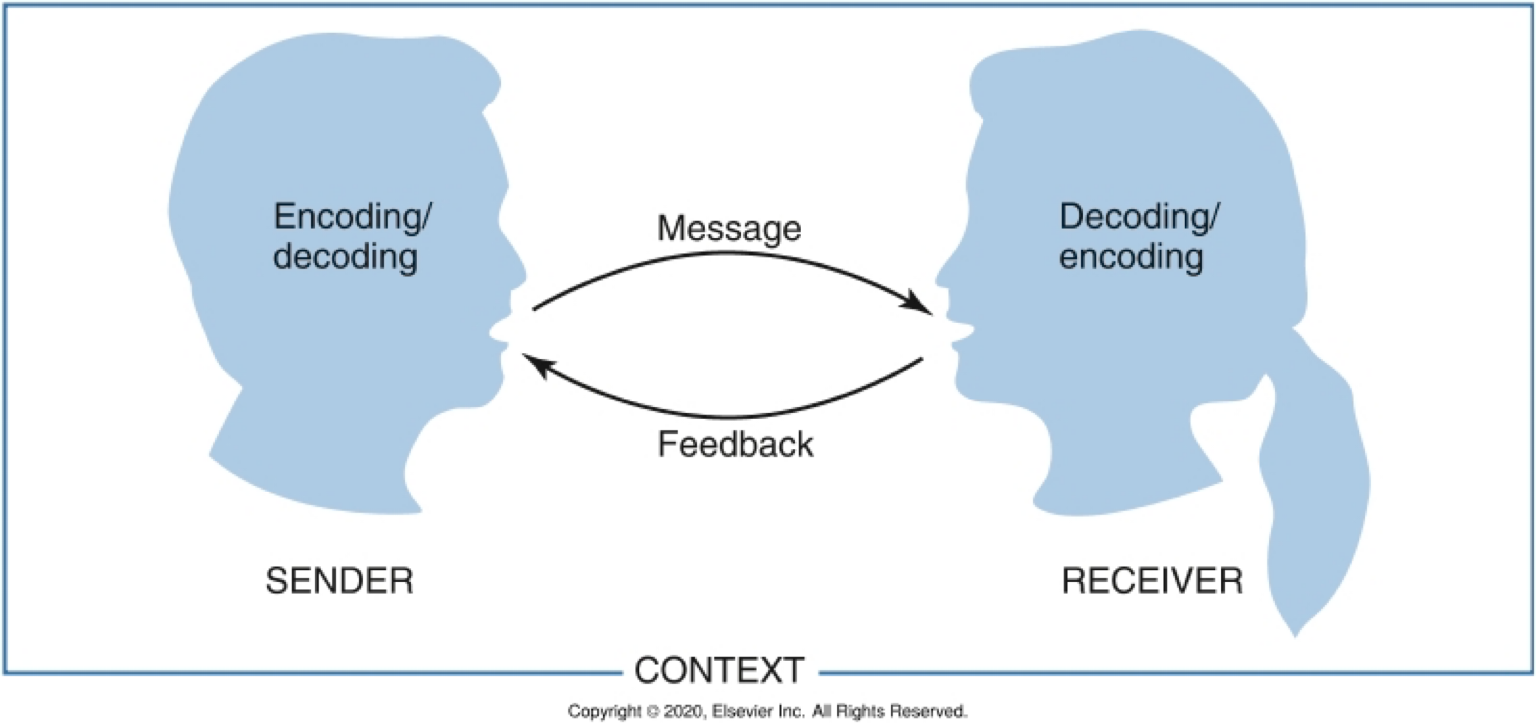
Operations in communication process:
PERCEPTION
EVALUATION
TRANSMISSION
Individualized and impacted by gender, age, culture, interest, mood, value, clarity, length of message, feedback, intellect, sociocultural conditioning….very complex
Communication Theory:
Verbal Communication: Talking or writing to share information.
Congruence: When your words match your body language.
Nonverbal Communication: Using body language, like facial expressions or gestures, to communicate without words.
Development of Human Communication:
Somatic Language: Communicating through body movements, like gestures and facial expressions.
Action Language: Communicating through actions, like waving or shaking hands.
Verbal Language: Communicating using words, either spoken or written.
Successful Communication:
Feedback
Appropriateness
Efficiency
Flexibility
Communication Skills:
ACTIVE LISTENING
OPEN POSTURE
EMPATHY
OPEN ENDED QUESTIONS
GIVING INFORMATION
REFLECTION
SILENCE
LANGUAGE BARRIERS
Why does communication fail?
Fail to see uniqueness of individual
Fail to recognize level of meaning
Use value statements and clichés
False reassurance
Failure to clarify
Ineffective use of electronic communication devices
Failure to value culture or generation differences
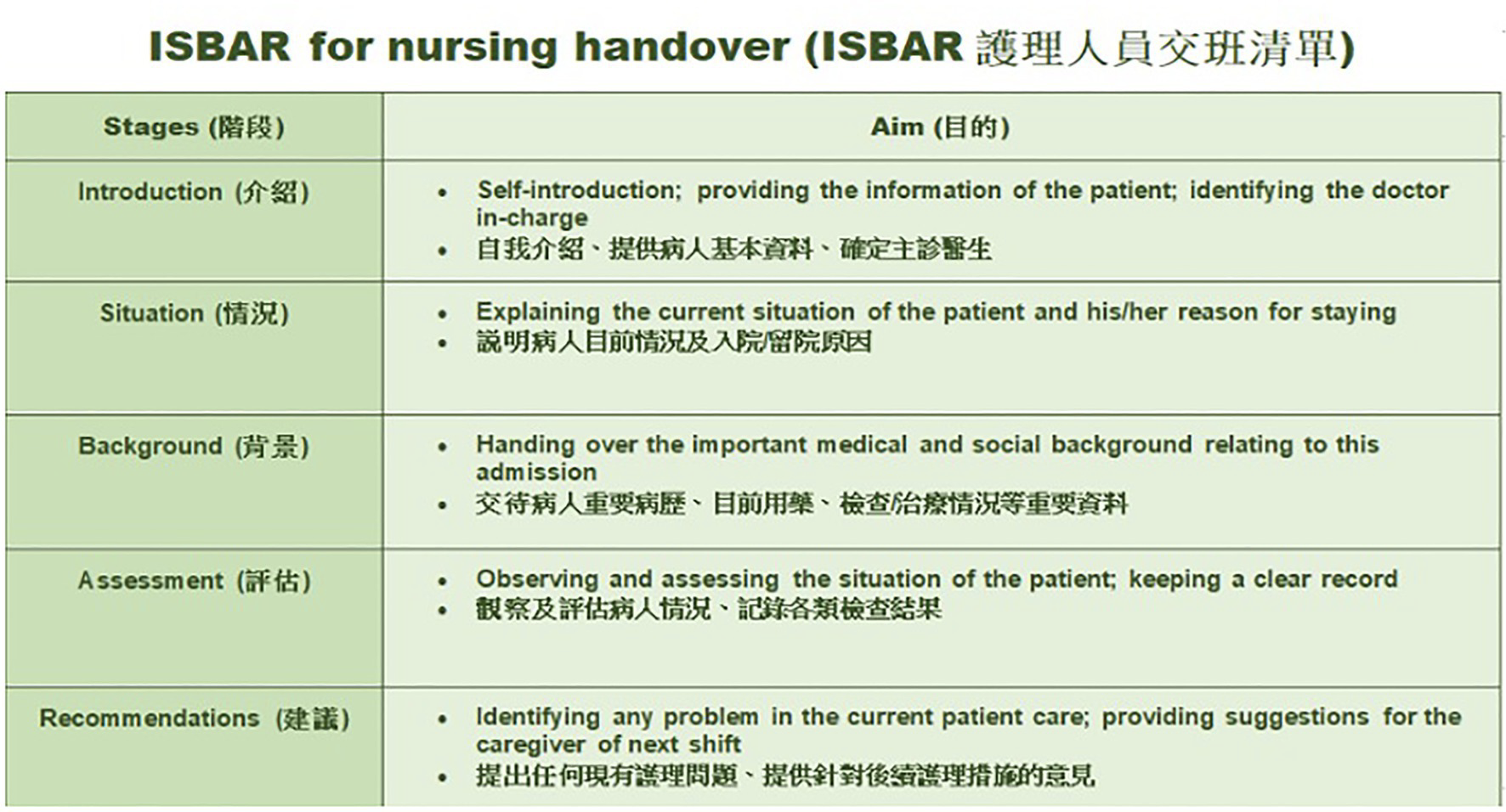
ISBAR:
Introduction
Situation
Background
Assessment
Recommendation
ISBAR Defined:
I - Introduction: Identify yourself, your role, and the patient.
Example: "Hi, this is Nurse Jane Doe, calling about Mr. John Smith in Room 12."
S - Situation: Describe the situation or reason for communication.
Example: "Mr. Smith is experiencing shortness of breath and his oxygen levels have dropped."
B - Background: Provide relevant background information about the patient’s condition.
Example: "Mr. Smith has a history of COPD and is currently on 2L of oxygen."
A - Assessment: Share your assessment or findings.
Example: "His oxygen saturation is 88%, and he is tachypneic at 24 breaths per minute."
R - Recommendation: Offer a recommendation or request for action.
Example: "I recommend increasing his oxygen to 4L and possibly contacting the doctor for further evaluation."
Leadership: