Lit Circles Literary Terms
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
simile
a figure of speech in which "like or "as" is used to make a comparison between two basically unlike ideas (e.g. "Her eyes were as blue as a clear sky.")

antagonist
the character(s) in conflict in a literary work; typically the ones we want to fail

dialogue
a conversation between characters.

first-person point of view
the narrator is a character in the story and refers to him/herself with the pronoun "I."

flashback
a scene within a story that interrupts the sequence of events to relate events that ocurred in the past.

hyperbole
exaggerated statements or claims not meant to be taken literally.

imagery
visually descriptive or figurative language.
person vs. self conflict
a character is in conflict with his/her own inner feelings or thinking.

irony
a contradiction between what happens and what is expected. Usually, this involves a complete reversal of expectations and possibly a cruel twist of fate.

mood
The feeling created in the reader by a literary work or passage.

onomatopoeia
the use of words that imitate sounds (e.g., cuckoo, sizzle ).

oxymoron
a pair of words that are opposites or contradictory, like "jumbo shrimp," "awfully good," "alone together," and "open secret."

anecdote
a brief story about an interesting, amusing, or strange event. Writers use this device to entertain or to make a point.
allusion
a reference to a well-known person, event, place, literary work, or work of art. Use of this device allows the writer to express complex ideas without spelling them out. Understanding what a literary work is saying often depends on recognizing this device and the meaning it suggests.
alliteration
the repetition of initial consonant sounds. Writers use this device to create musical effects and to draw attention to certain words or ideas

tone
the writer's attitude toward his or her audience and subject.

symbol
anything (usually an object) that stands for or represents something else.

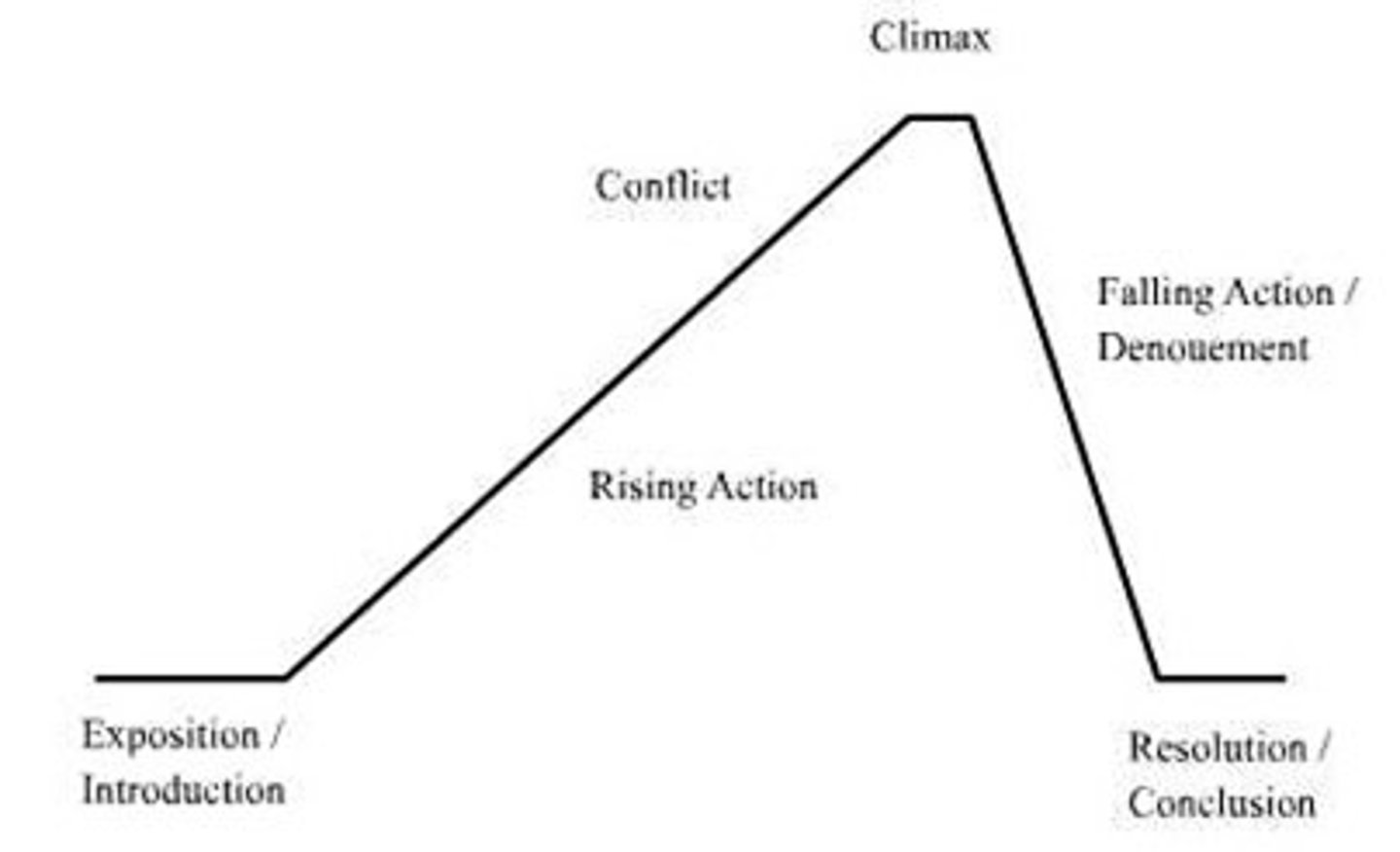
climax
the highest point of interest or suspense in a story, novel, or play; this usually occurs near the end of the story and is the turning point at which the fate of the protagonist is often decided.
exposition
the necessary background information for understanding a story. It introduces the setting, the characters, and the basic situation. It is the first part of the plot.
person vs. person conflict
a character is in conflict against another character.

conflict
a struggle between two opposing forces

figurative language
writing or speech not meant to be interpreted literally. It is often used to create vivid impressions by setting up comparisons between dissimilar things.

foreshadowing
the use of clues in a literary work that suggests events that have yet to occur. This technique helps to create suspense, keeping readers wondering what will happen next.

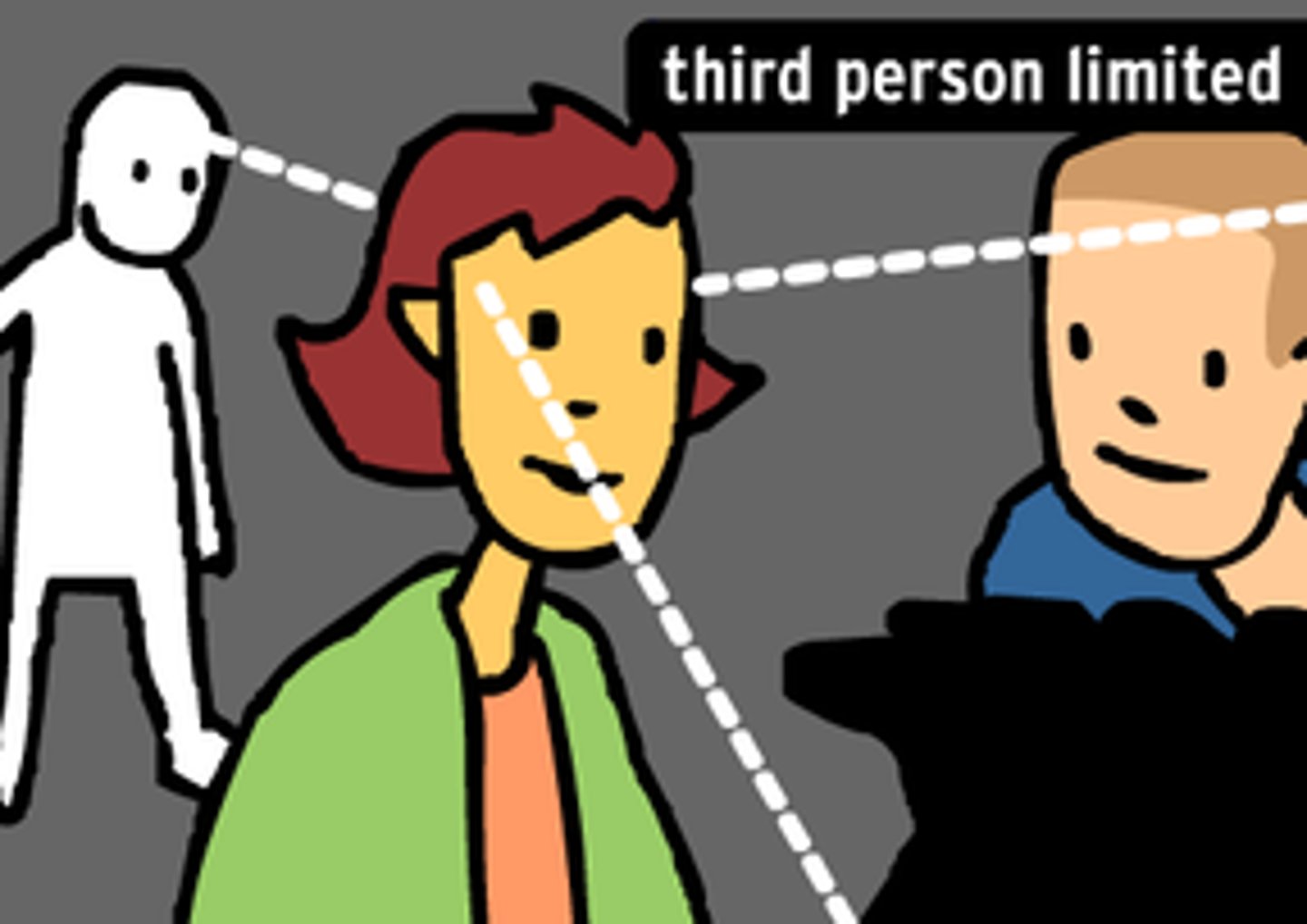
limited third person point of view
the narrator relates the inner thoughts and feelings of only one character, and everything is viewed from this character's perspective. Pronouns like "he," "she," and "they" are used rather than "I," "me," or "we."
metaphor
a figure of speech in which one thing is spoken of as though it were something else. This device implies a comparison between the two things, but without using "like" or "as." (E.g. "Her lips were rose petals.")

narrator
the one who is telling the story.

omniscient third person point of view
the narrator knows and tells about what each character thinks and feels. The narrator knows all.

personification
a type of figurative language in which a nonhuman subject is given human characteristics

plot
the sequence of events in a literary work.
protagonist
the main character(s) in a literary work; the ones the reader usually wants to succeed

theme
a central message or insight into life revealed through a literary work.

point of view
the perspective or vantage point from which a story is told.

setting
the time and place of the action.

verbal irony
irony in which a person says or writes one thing and means another, or uses words to convey a meaning that is the opposite of the literal meaning.

situational irony
irony involving a situation in which actions have an effect that is opposite from what was intended, so that the outcome is contrary to what was expected.
dramatic irony
Irony that occurs when the meaning of the situation is understood by the audience but not by the characters.

Person vs. Society Conflict
a character has a problem with some element of society: the school, law, the accepted way of doing things, and so on.
