AP Statistics Unit 4
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
(4.2) Law of Large Numbers?
Simulated probabilities seem to get closer to the true probability as the number of trials increases.
(4.3) The probability of an event is between what two numbers?
The probability of any event is a number between 0 and 1, inclusive.
(4.3) Probability of an Event Formula?

(4.3) Probability of the Complement of an Event Formula?
E’ (aka EC or not E) = 1 - P(E)
(4.4) What is a mutually exclusive event?
Two events are mutually exclusive (disjoint) if they cannot occur at the same time. If two events are mutually exclusive, then the probability of their intersection is 0; in other words if two events are mutually exclusive, P(A and B) = 0.
(4.4) What is Joint Probability?
The joint probability is the probability of the intersection of two events; P(A and B).
(4.5) What is conditional probability?
Conditional probability is the probability that an event happens given that another event is known to have already happened.
(4.5) General multiplication rule for two events A and B?
Note that it can be manipulated to give the conditional probability formula as well; P(B | A) = P (A ⋂ B) / P (A).

(4.6) What are the conditions for two events to be independent?
Two events A and B are independent iff
P(A | B) = P(A) and P(B | A) = P(B)
P(A and B) = P(A) ⋅ P(B)
(4.6) How do you calculate the probability of the union of two events?
The probability of the union of two events can be found by the formula:
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Using proper notation it is:
P(A ⋃ B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ⋂ B)
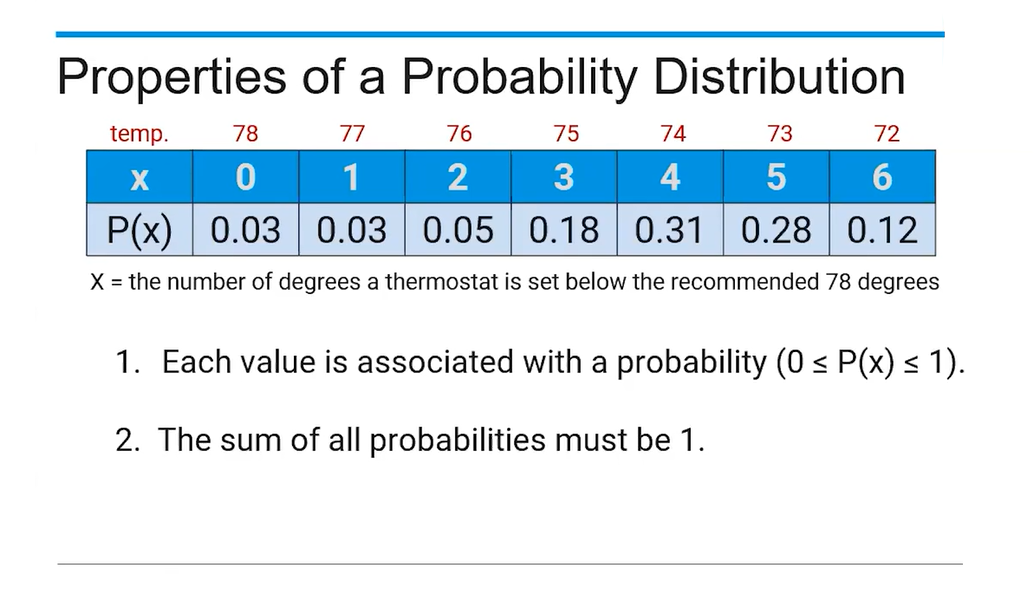
(4.7) Properties of a probability distribution?
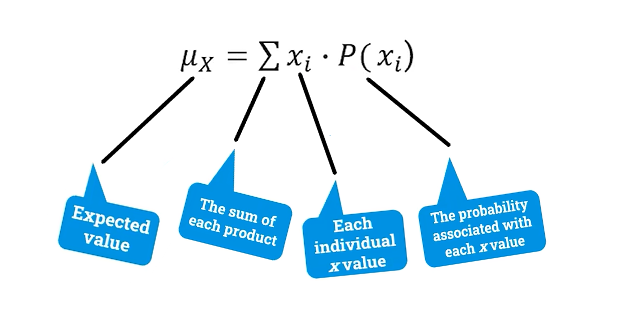
(4.8) Mean (Expected value formula)?
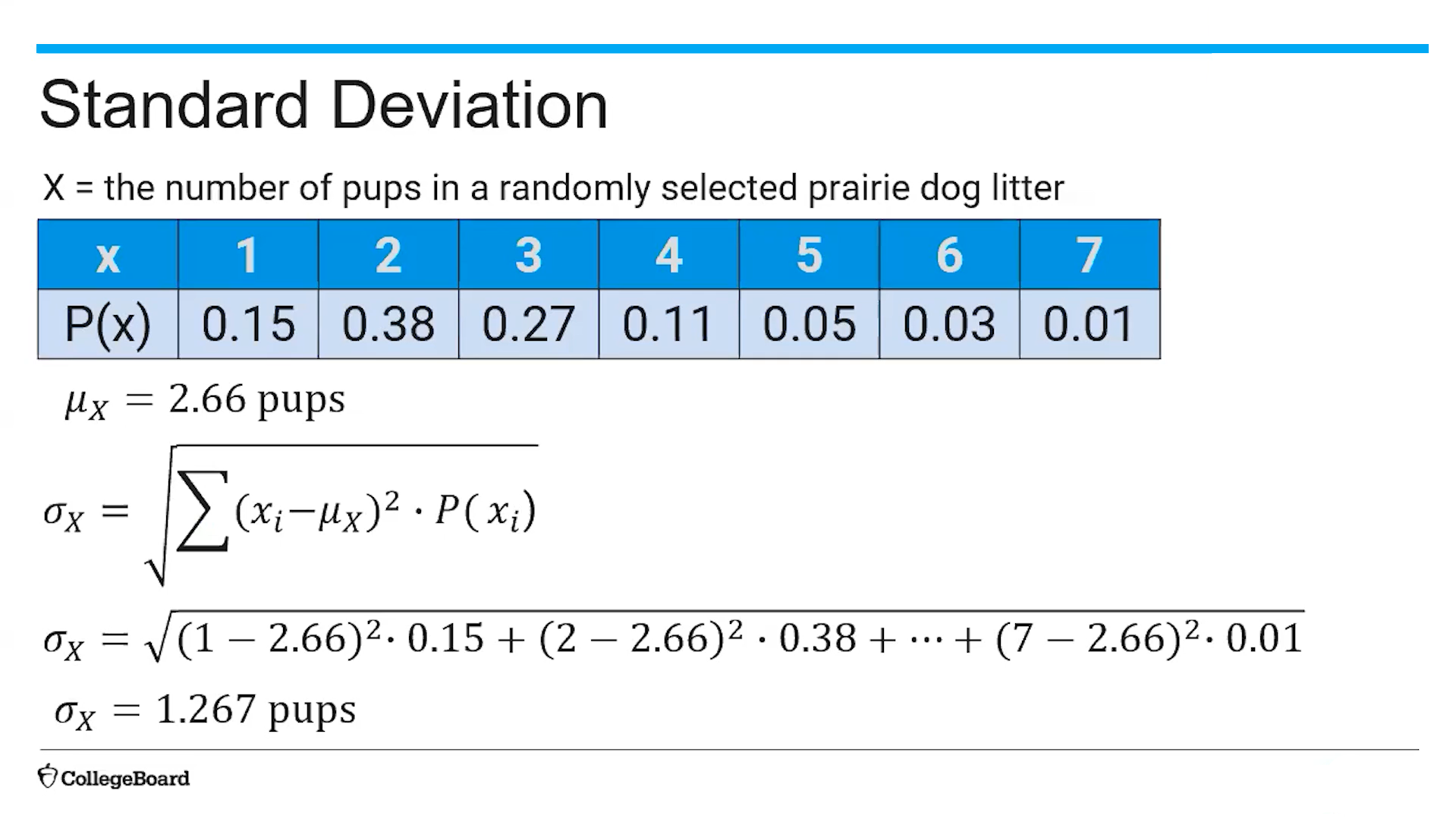
(4.8) Standard Deviation Formula (σx)?
(4.8) Variance Formula (σx2)?
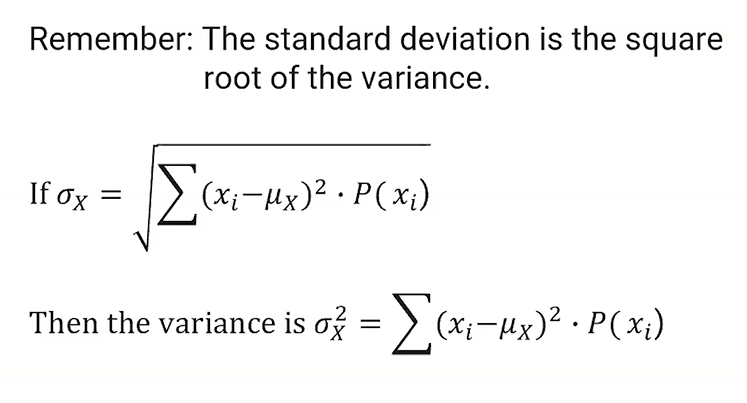
(4.9) Finding the mean and standard deviation using a linear transformation

(4.9) When are two random variables independent?
Two random variables are independent if knowing information about one of them does not change the probability distribution of the other.
(4.9) How do you calculate the mean and standard deviation of independent random variables X and Y and real numbers a and b?
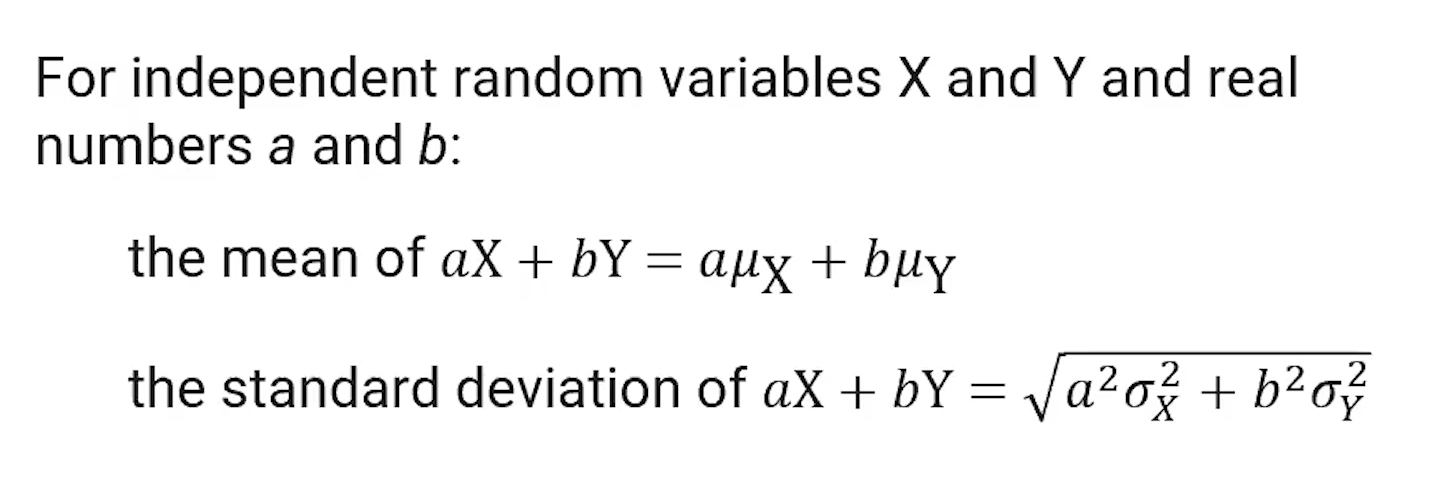
(4.10) Definition and conditions for a binomial setting?
A binomial setting involves repeated trials of the same random process, where these conditions are met:
Two possible outcomes: success or failure
Independent trials
Fixed number of trials
Each trial has the same probability of success
(4.10) Binomial Coefficient Formula
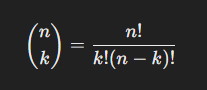
(4.10) Binomial Probability Function

(4.10) Note about calculating binomial probabilities
When calculating binomial probabilities, be sure to define the random variable, identify the distribution and values of interest, calculate the correct probability and answer the question in context
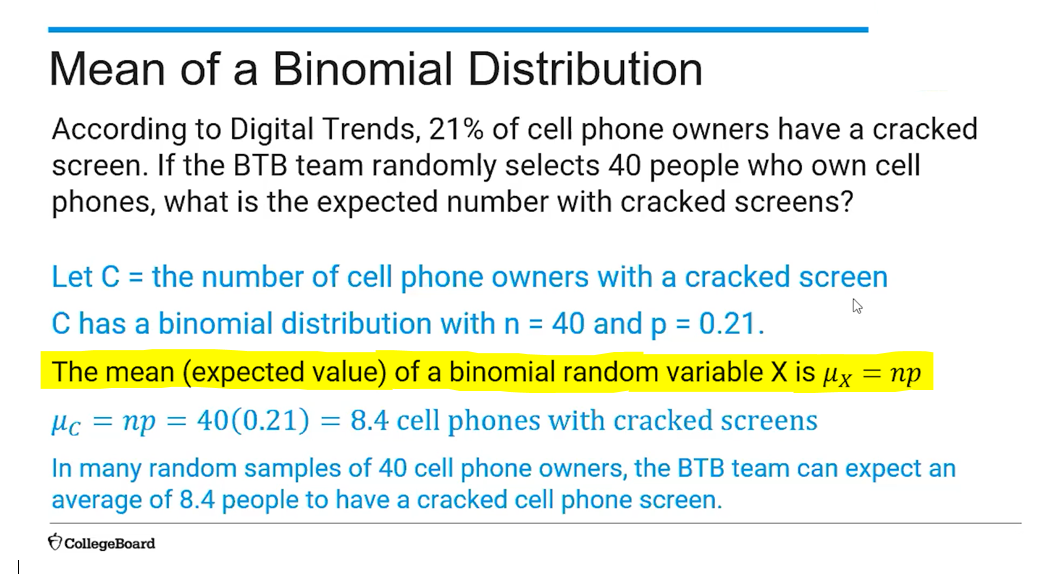
(4.11) Mean of a Binomial Function Formula?
μX=np
(4.11) Standard Deviation of Binomial Function Formula?
σx=√np(1-np)

(4.12) Geometric Setting vs Binomial Setting
A geometric setting involves the same elements as a binomial setting:
Two possible outcomes: success or failure
Independent trials
Each trial has the same probability of success
The only difference is this:
No fixed number of trials (Trials will be continued until there is success)
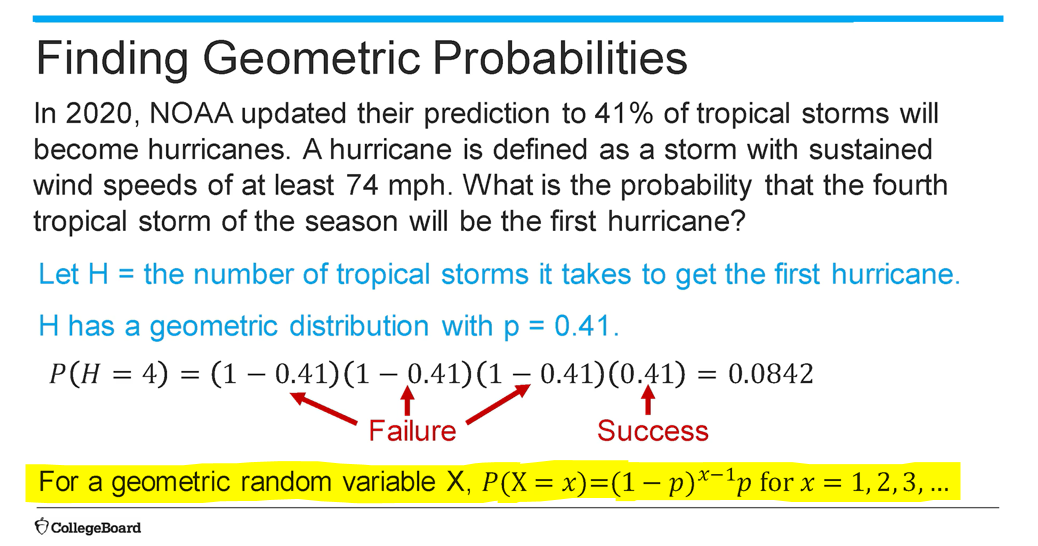
(4.12) Geometric Random Variable Probability Formula?
P(X=x) = (1-p)x-1p
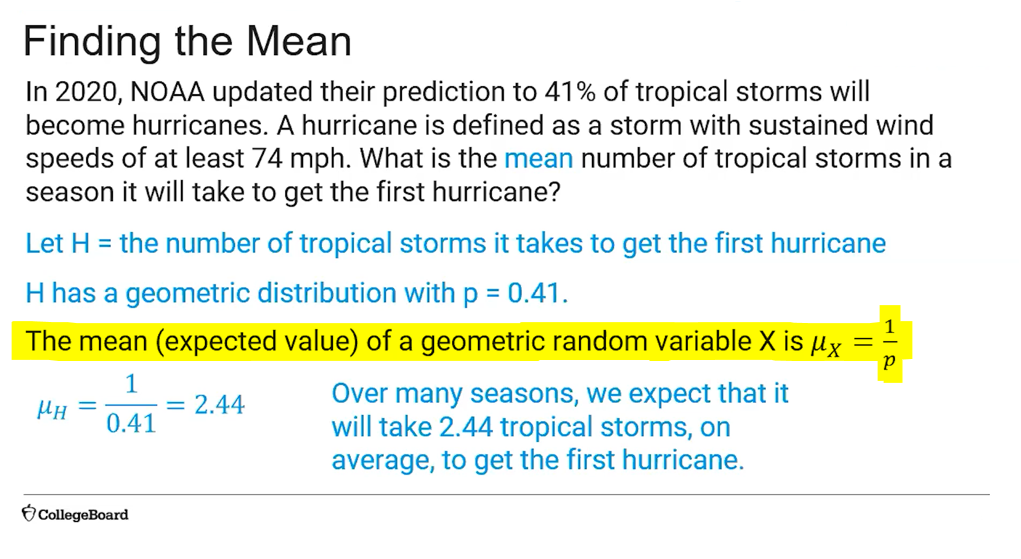
(4.12) Mean of a Geometric Random Variable Formula?
μX=1/p
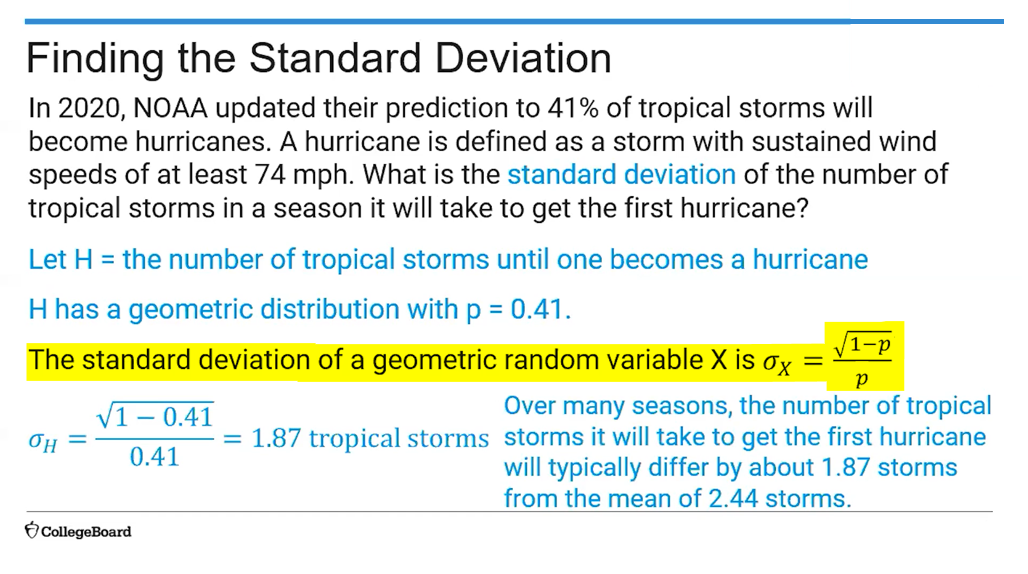
(4.12) Standard Deviation of a Geometric Random Variable Formula?