Chemistry Unit 1
1/263
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
264 Terms
Formulae of Sulfur Dioxide
SO2
Formulae of Methane
CH4
Formulae of Hydrochloric Acid
HCl
Formulae of Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4
Formulae of Nitric Acid
HNO3
Formulae of Ammonia
NH3
Formulae of Ammonium Chloride
NH4Cl
Formulae of Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH
Formulae of Sodium Chloride
NaCl
Formulae of Sodium Carbonate
Na2CO3
Formulae of Sodium Hydrogencarbonate
NaHCO3
Formulae of Sodium Sulfate
Na2SO4
Formulae of Calcium Hydroxide
Ca(OH)2
Formulae of Calcium Carbonate
CaCO3
Formulae of Calcium Chloride
CaCl2
Formulae of Copper (II) Oxide
CuO
Formulae of Copper (II) Sulfate
CuSO4
How to find charge of ion?
Use group number
e.g. group 7 has charge of -
Charge for Hydrogencarbonate
HCO3-
What is a redox reaction?
A reaction where one substance is reduced and another is oxidised.
What is a reducing agent?
reduce other species
give electrons
are themselves oxidised
What is a oxidising agent?
oxidise other species
accept electrons
are themselves reduced
What is the oxidation of an uncombined element?
0
e.g. O2 = 0
What is the oxidation of a simple ion?
Charge of the ion
e.g. O2- = -2
What is the oxidation of a compound?
The sum must equal 0
What is the oxidation of group 1 and 2 metals in a compound?
Same as their group number
e.g. BaSO4 = Ba=+2
What is the oxidation of a complex ion?
The sum must equal the charge
e.g. CO32- = C=+4, O=-2
What is the oxidation of Hydride?
H = -1
What is the oxidation of Fluorine?
F = -1
What is the oxidation of Peroxide?
O = -1
Steps to work out ionic equations
word equation
balanced symbol equation
balanced ionic equation (usually for precipitate (s) )
spectator ions
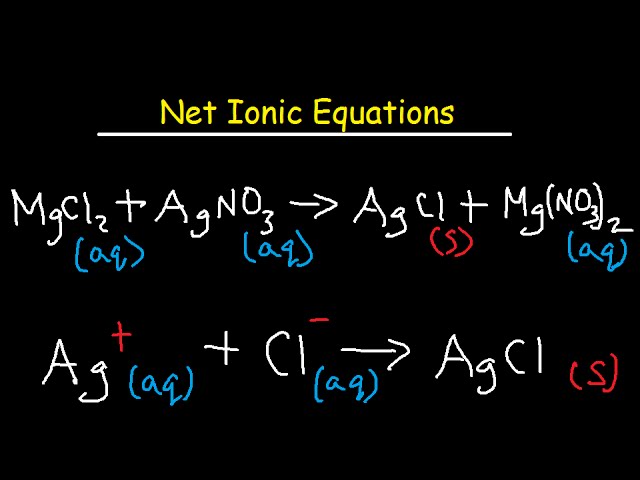
Charge for Hydroxide
OH-
Charge for Nitrate
NO3-
Charge for Oxide
O2-
Charge for Sulfide
S2-
Charge for Carbonate
CO32-
Charge for Sulfate
SO42-
Charge for Phosphate
PO43-
Charge for Ethanoate
CH3COO-
What is the mass/charge of proton/neutron/electrons?
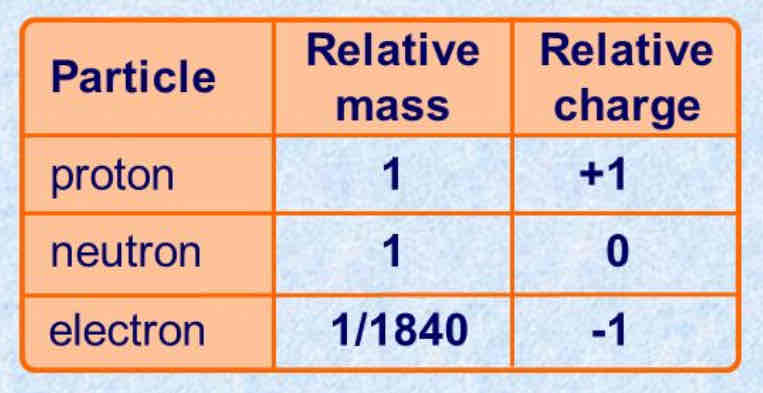
What charge does the nucleus have?
Positive - contains protons and neutrons
What charge does an atom have in general?
Neutral - same amount of protons and electrons
What is an ion?
Charged atoms caused by the gain or loss of electrons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons.
Alpha particle
Helium nucleus
Mass - 4 units
Absorbed by - paper or few cm of air
High ionising power
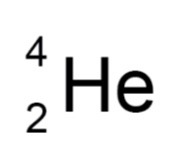
Beta particle
Fast moving electron
Mass - negligible
Absorbed by - Aluminium
Medium ionising power
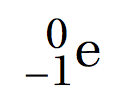
Gamma ray
Electromagnetic wave
Mass - 0
Absorbed by - thick lead
Low ionising power
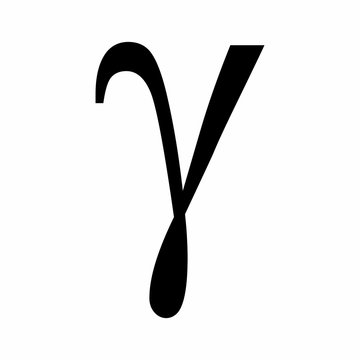
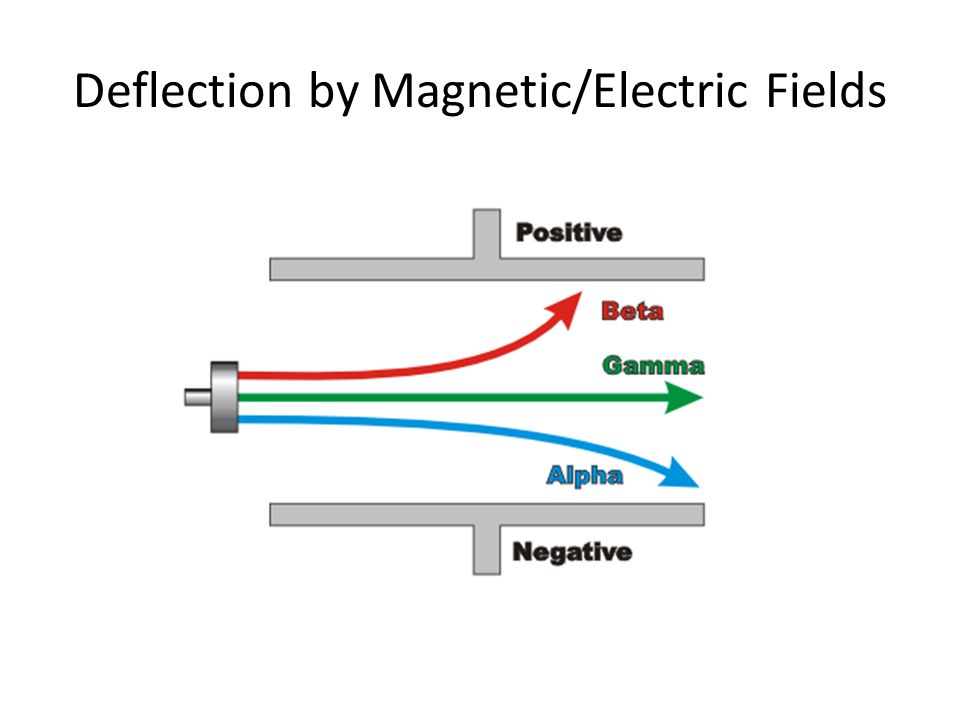
Electric field effect on radioactive particles
Beta - light so fully attracted
Alpha - heavy so slightly attracted
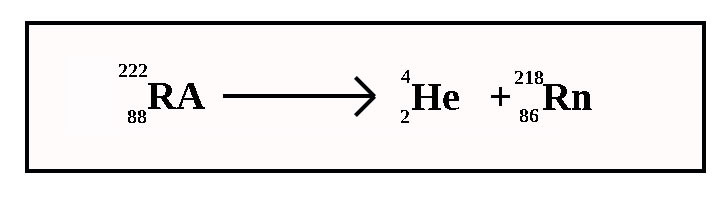
Alpha decay
mass number decreases by 4
atomic number decreases by 2
Beta decay
mass number remains the same
atomic number increases by 1
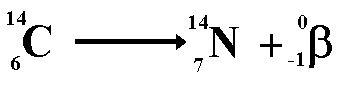
Positron
mass number remains the same
atomic number decreases by 1
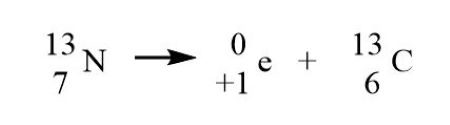
Electron capture
mass number remains the same
atomic number decreases by 1

Why is ionising radiation unsafe for humans?
Damages cells and DNA causing mutations to occur
What are the safe uses of radioactivity?
tracers
carbon dating
smoke alarms
What is tracers?
radioactive isotopes are inserted into a sample and tracked using x-rays
medical tracers/water pipe blockages/biochemistry of plants
must be low ionising power and short half life if used in the body
What is carbon dating?
Carbon-14 is a beta emitter
When an organism is living the amount of Carbon-14 is consistent
When an organism dies the amount of Carbon-14 decreases
This allows scientists to determine the age of organisms that have been dead for many years
What is half life?
Time taken for the mass/activity of a radioactive isotope to fall to half of its original value
What is an orbital?
Volume where there is a high probability of finding an electron
How many electrons can each orbital have?
2 electrons each
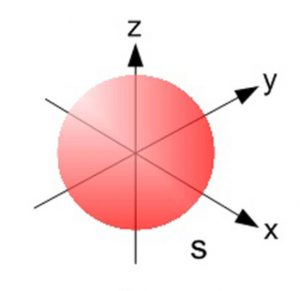
S orbital
spherical
all energy levels
groups of 1
size increases with energy level
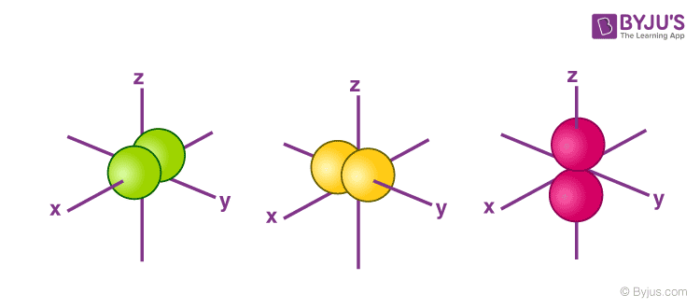
P orbital
dumbbell shape
all energy levels except n=1
groups of 3
lobes become longer and larger with energy level
How many D orbitals are in a group?
groups of 5
How many F orbitals are in a group?
groups of 7
How many G orbitals are in a group?
groups of 9
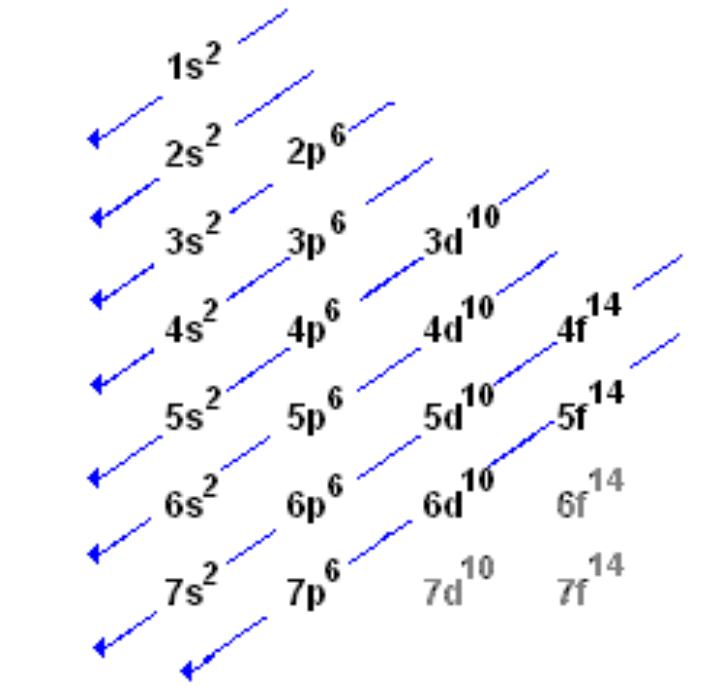
What is the order of orbitals?
S, P, D, F, G
Subshells
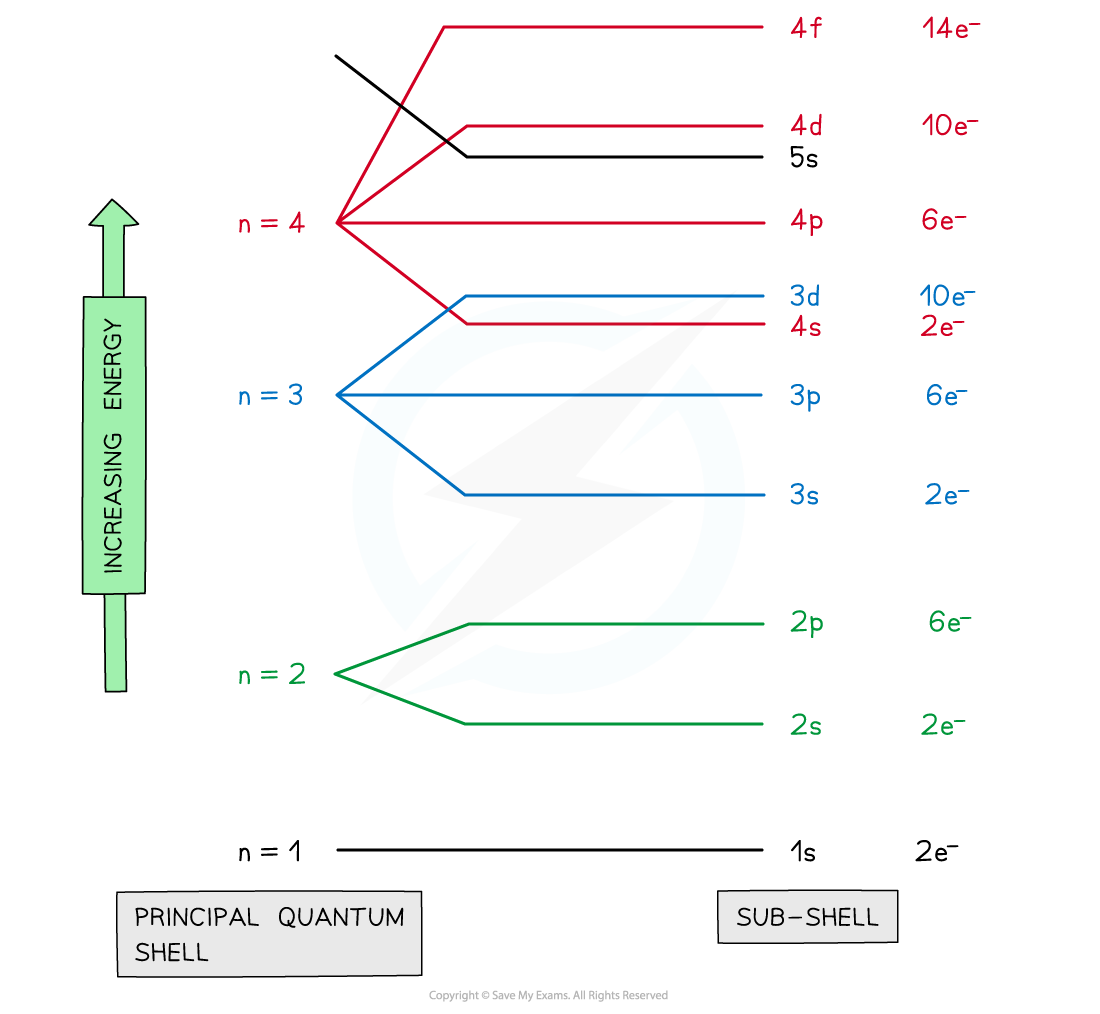
What is the electronic configuration?
gives information on atom
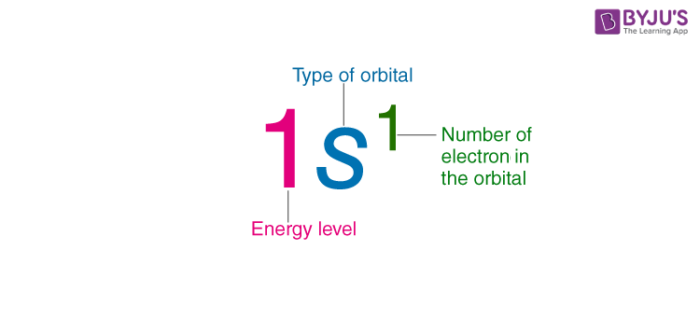
What are the rules of electronic confurguration?
Put electron in lowest possible energy level as there’s more energy away from nucleus
Fill electrons into orbitals singly before adding 2 electrons to minimise electron repulsion
Example of electronic configuration
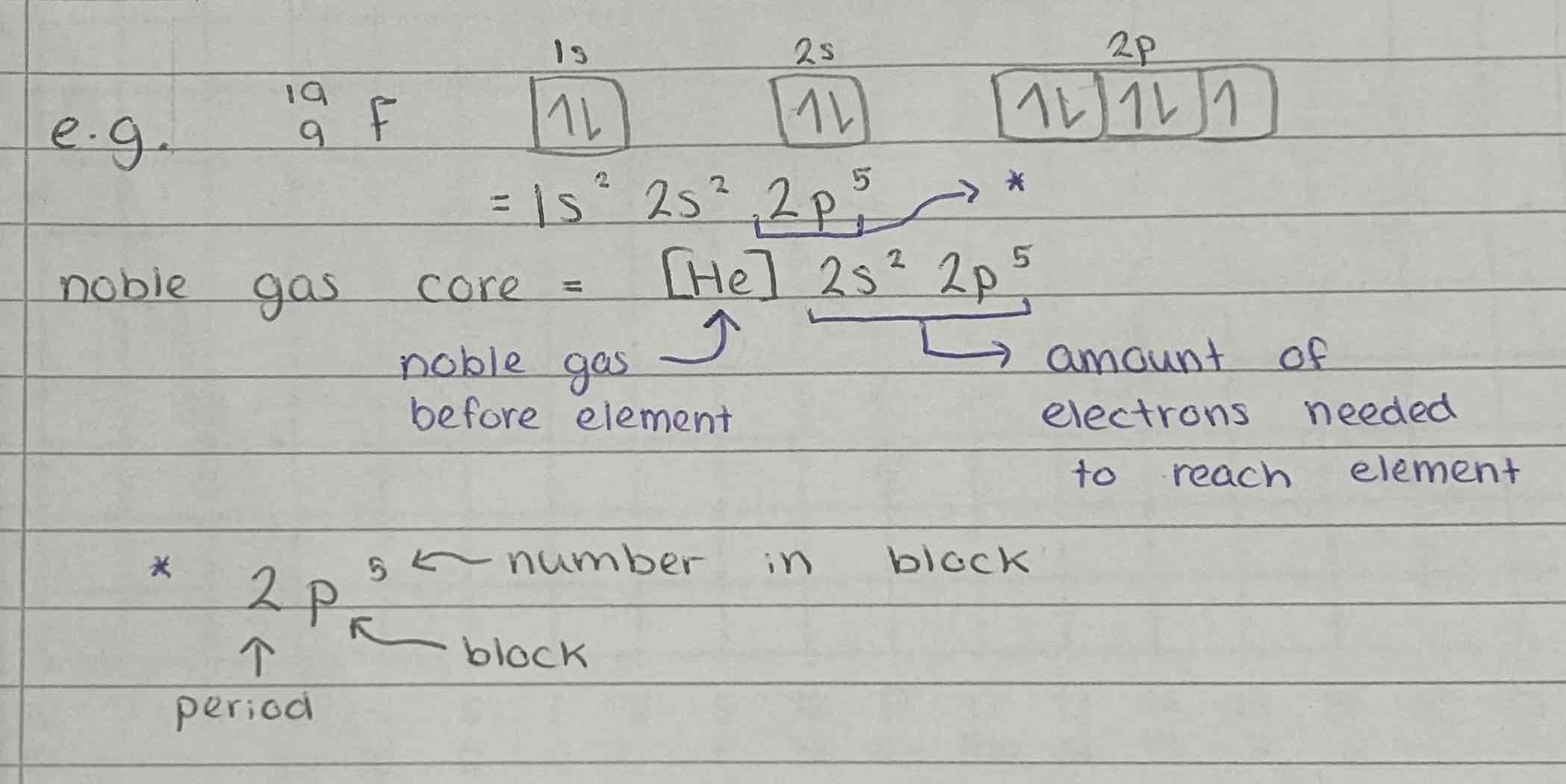
Exceptions to the electronic configuration rules
Copper and Chromium
Orbitals are more stable if half-filled or fully-filled
4s and 3d are similar in energy one electron can move from 4s to 3d
Copper - [Ar] 4s1 3d10
Chromium - [Ar] 4s1 3d5
What is the Molar first ionisation energy?
The energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous ions
What is the equation for Molar first ionisation energy?
X(g) → X+(g) + e-
X4+(g) → X5+(g) + e-
What happens down a group with Molar first ionisation energy?
distance from nucleus increases
shielding from inner electrons increases
weaker electrostatic forces of attraction
outer electron easier to remove
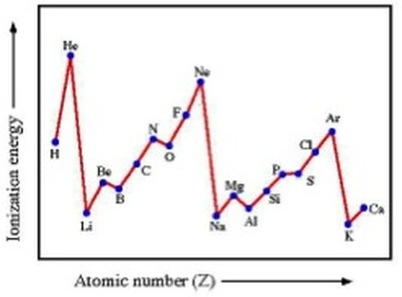
What happens across a period with Molar first ionisation energy?
increased nuclear charge
outer electron harder to remove
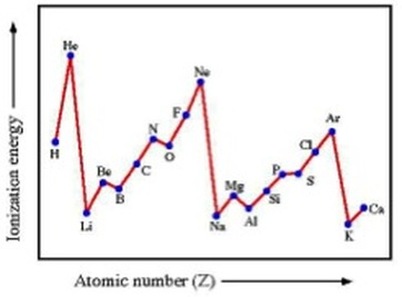
What happens in successive ionisation energy?
A single atom loses it’s electrons one by one
outer electron is easiest to remove as most shielding and furthest
3rd shell/2nd shell harder to remove as closer, slowly increases as protons are holding electrons more tightly because charge becomes imbalanced (effective nuclear charge)
1st shell hardest as no shielding and closest
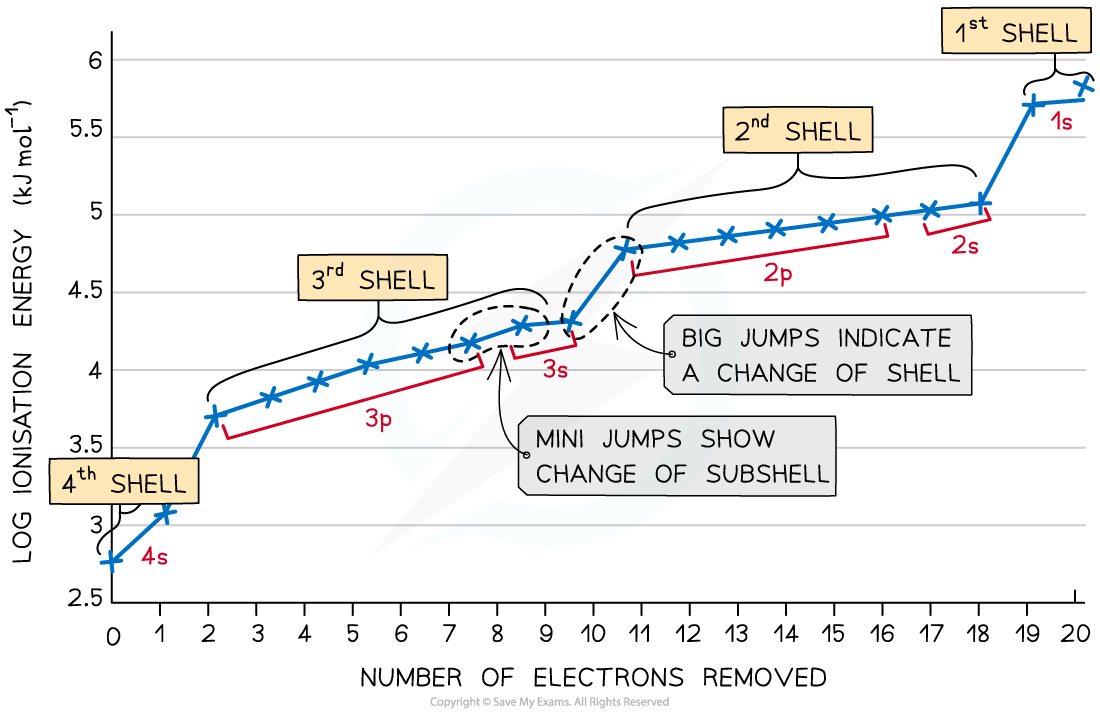
Order of electromagnetic spectrum
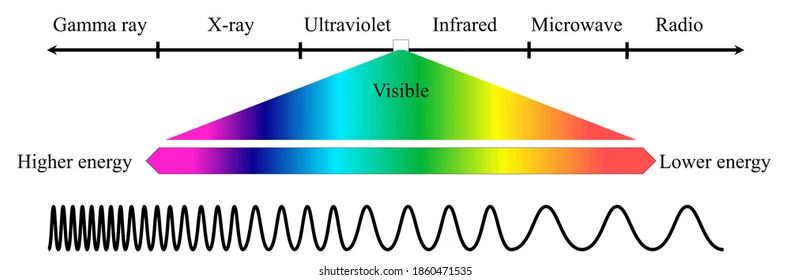
What is quantisation?
The amount of energy that the molecule can absorb/emit and is a specific value, this allows us to identify a molecule
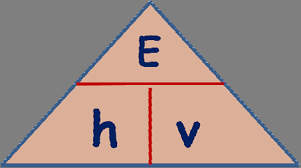
Energy =
energy (J) = Planck’s constant x frequency (Hz)
Speed of light =
speed of light = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
Absorption spectra
Electrons are in ground state so lowest energy levels
Giving atoms energy can cause electrons to move to a higher energy level. They are then in an excited state
The difference between energy levels is a fixed value
The energy relates to a particular frequency (E=hf), the frequency relates to a specific wavelength/colour of light (C=fλ)
The missing wavelengths show dark bands on a coloured background
Emission spectra
Electrons have been absorbed so in an excited state
The electron falls to a lower energy level
The difference between energy levels is a fixed value
The energy relates to a particular frequency (E=hf), the frequency relates to a specific wavelength/colour of light (C=fλ)
The emitted wavelengths show coloured bands on a dark background
Atomic spectrum of Hydrogen
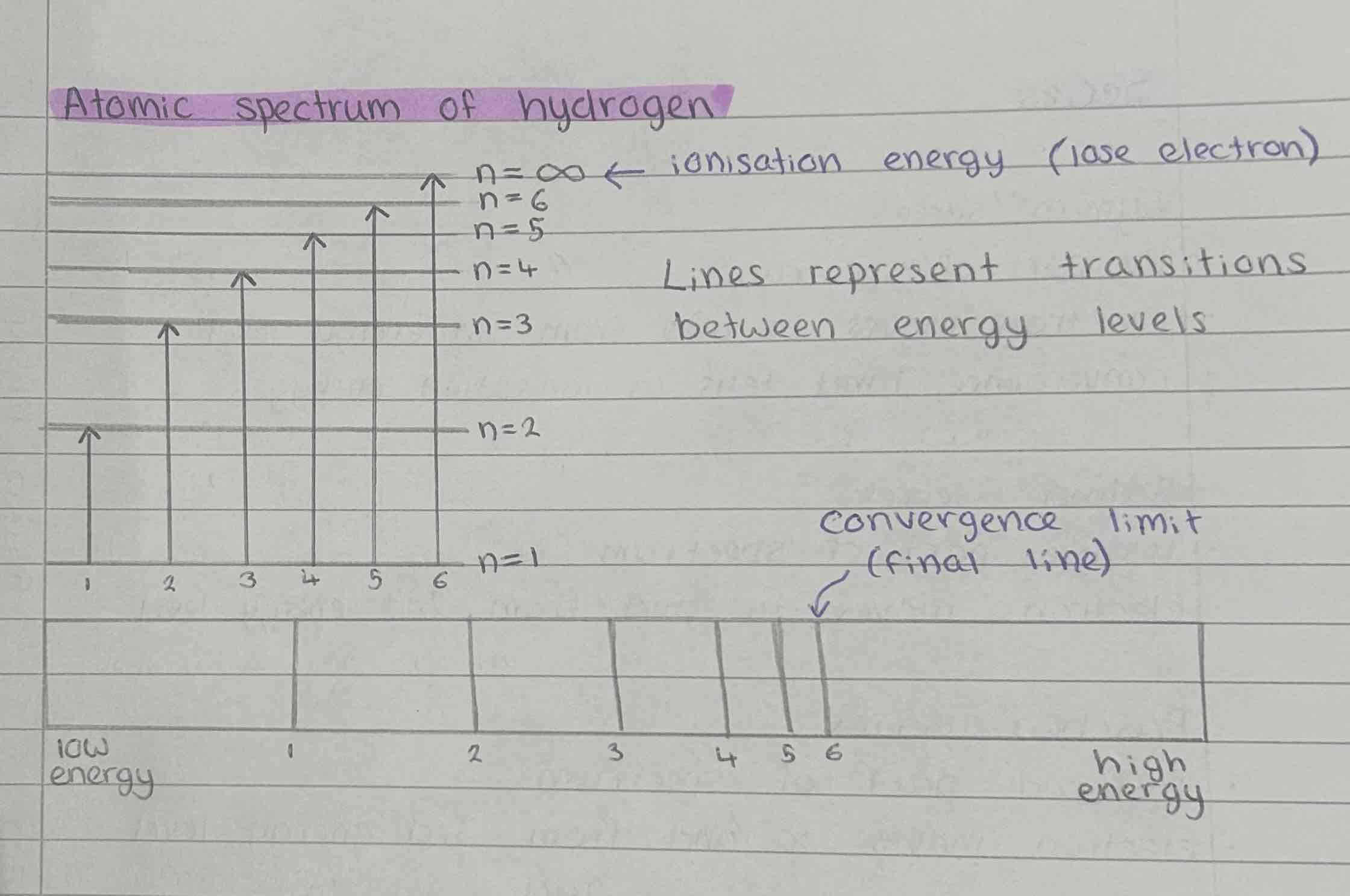
Why is the spectrum a series of lines?
Each line is equal to the difference in energy between particular energy levels which is a fixed value
Why do the lines converge?
The energy levels become closer and eventually converge
What is the significance of the convergence limit?
In the Lymans series, it is the ionisation energy
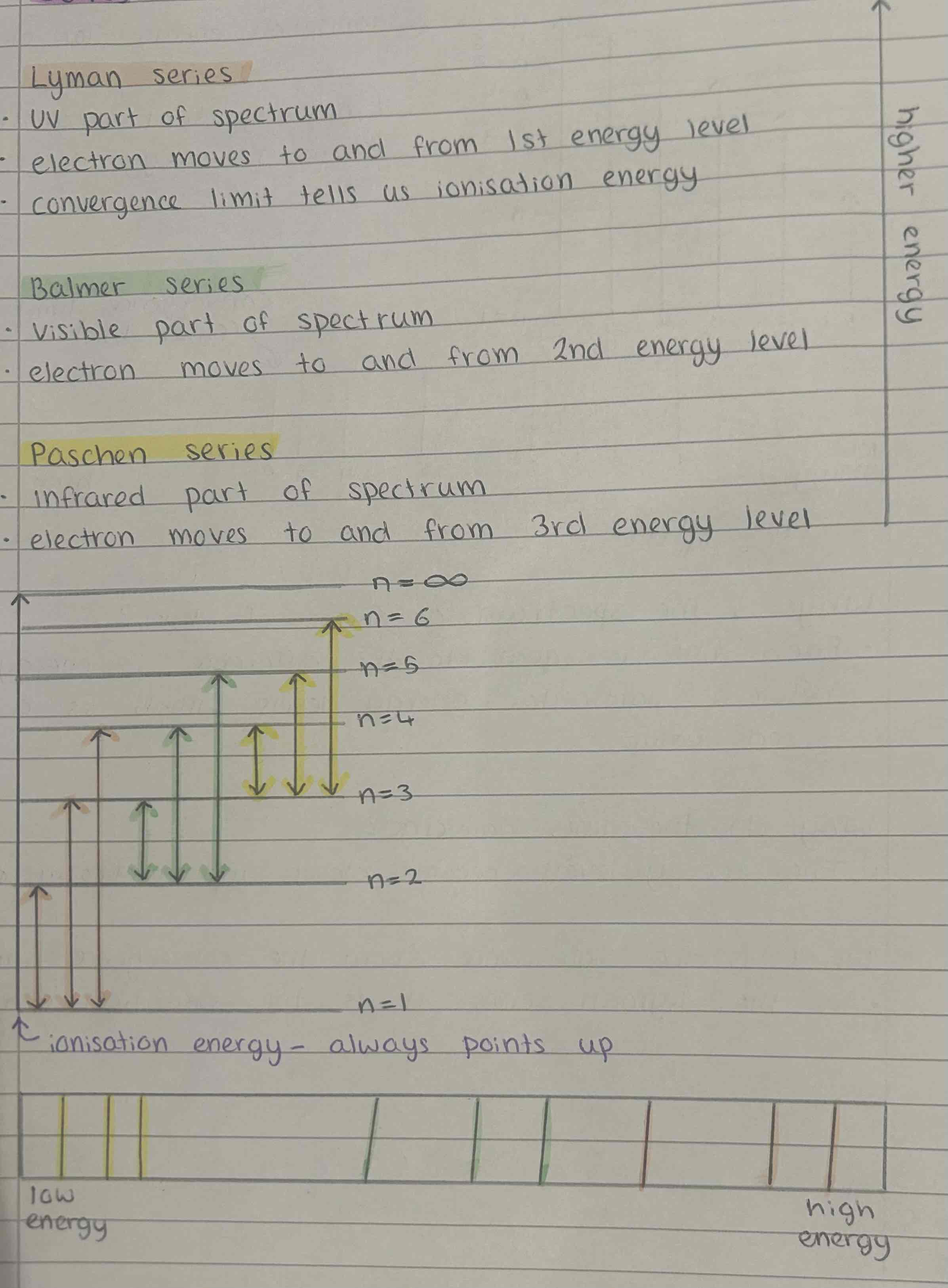
Lyman series
UV part of spectrum
electron moves to and from 1st energy level
convergence limit tells us ionisation energy
highest energy
Balmer series
visible part of spectrum
electron moves to and from 2nd energy level
Paschen series
infrared part of spectrum
electron moves to and from 3rd energy level
lowest energy
Series on a graph
What is the relative isotopic mass?
The mass of an atom of an isotope relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
e.g. 35Cl has a relative isotopic mass of 35
What is the relative atomic mass (Ar)?
The average mass of one atom of the element relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
found on a periodic table
What is the relative formula mass (Mr)?
The average mass of a molecule relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
add up all the Ar
e.g. CaCO3 40.1 + 12 + (16×3) = 100.1
What is a mole?
One mole is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms of carbon in exactly 12g of carbon-12.
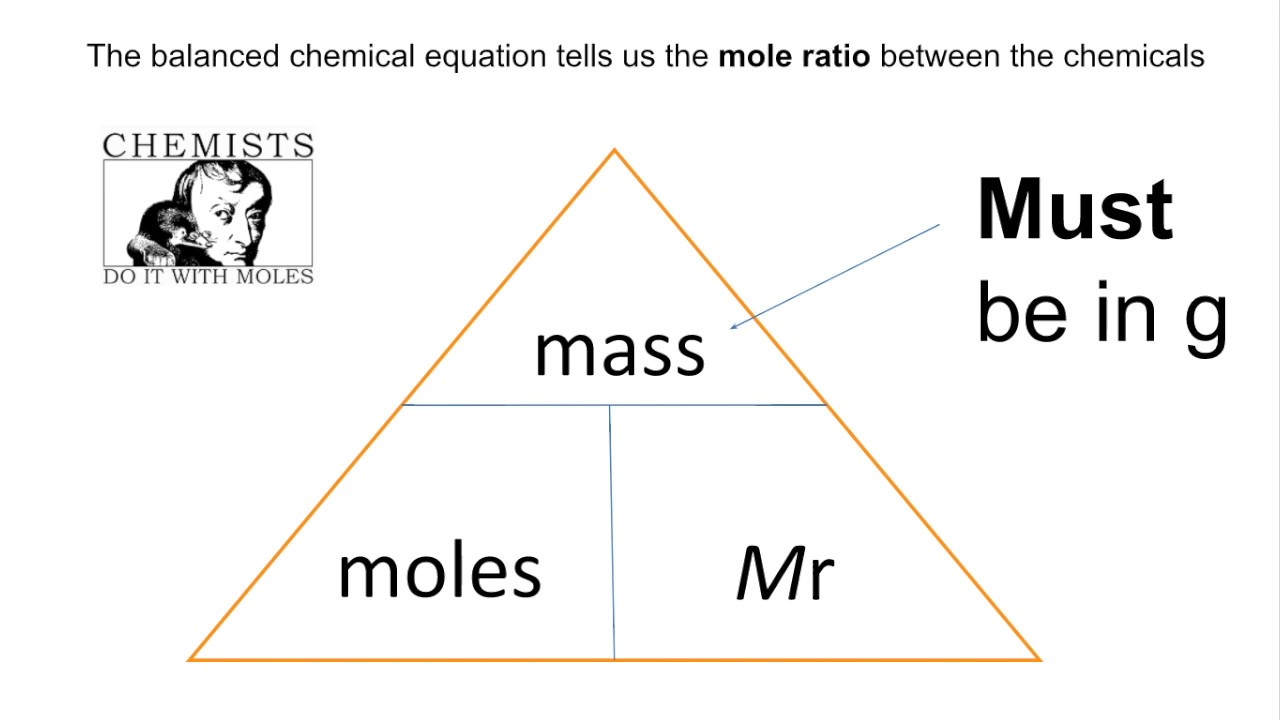
Mass =
Mr x moles
What is the molar mass?
One mole of any substance has a mass equivalent to the Mr of that substance in grams (gmol-1).
e.g. MgCl2 - Mr=95.3, molar mass = 95.3 gmol-1
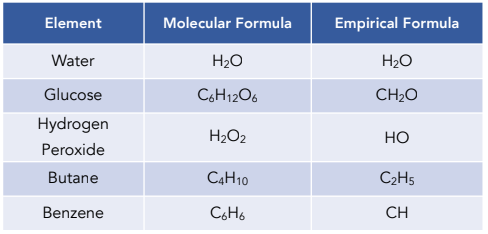
What is the empirical formula?
Simplest formula of a substance
symbol of elements
% or mass
Ar
moles
divide by smallest mole
ratio
How to calculate reacting masses?
balanced equation
moles of one
ratio for moles of what we need
mass=mrxmoles
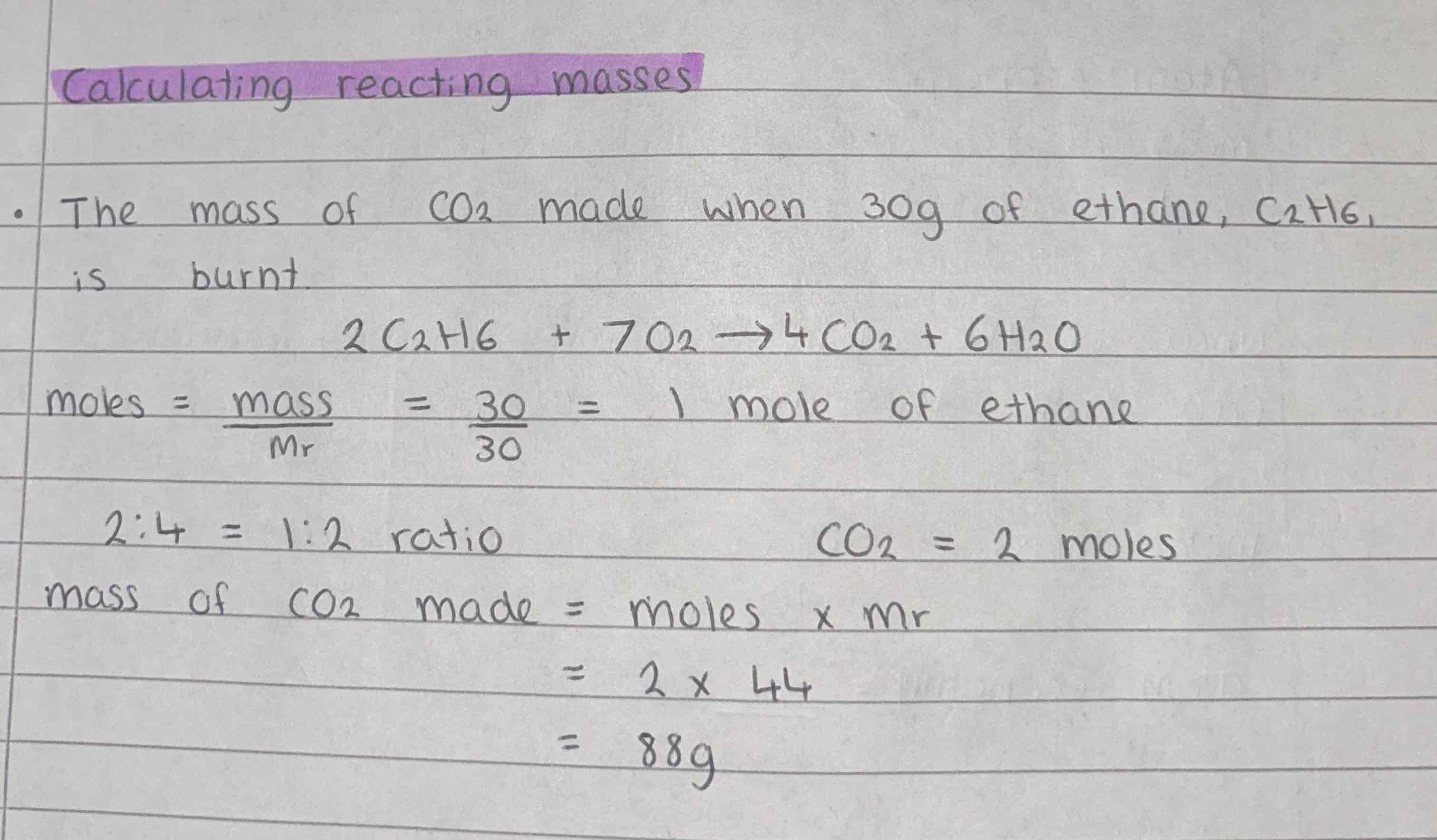
Percentage yield =
mass of product obtained / maximum theoretical mass x 100
Why will percentage yield always be less than 100%?
Due to loss of product during transfer,separation or an incomplete reaction
Atom economy =
mass of required product / total mass of reactants x 100