Chapter 26 Oxidation of Fatty Acids
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
brapa pathway oxidation of fatty acids?
1.beta oxidation (major)
2.peroxisomal oxidation
3.alpha oxidation
4.w (omega) oxidation
Beta oxidation of FA
E kena release dari FA
si acyl coA kena oxidised pg acetyl coA
kena panggil b O sebab oxidation start at b carbon atom of FA
Location B O
Tissues: liver, muscle, renal cortex, adrenal medulla, heart etc
intracellular site: mitochondria
brapa stage B oxidation?
activation of Fatty acid
transport of fatty acyl coA into mitochondria
degradation (b- oxidation reactions)
activation of Fatty acid
Fatty acid + CoA-SH —> Fatty acyl CoA guna enzyme thiokiase dan perlu Mg2+
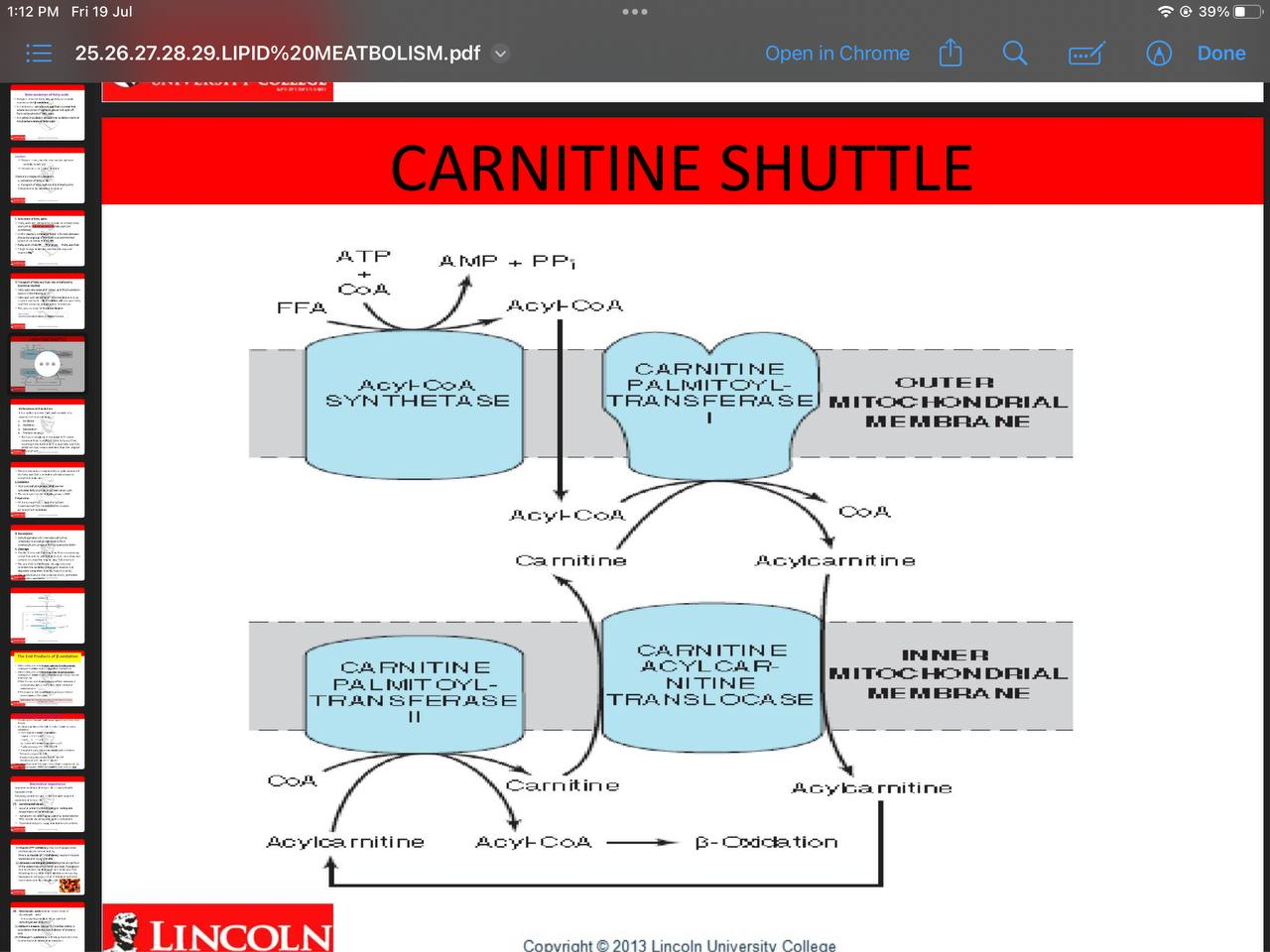
transport of fatty acyl coA into mitochondri
Guna carnitine shuttle. hafal picture dia sebab ini sangat penting
Reactions of β-oxidation
Reactions of β-oxidation:
Cyclical process
Four reactions per cycle: Oxidation, Hydration, Reoxidation, Thiolytic cleavage
Each cycle removes 2 carbon compound as acetyl CoA
Repeated cycles break down fatty acyl CoA to acetyl CoA
Oxidation
Oxidation:
Acyl CoA dehydrogenase converts fatty acyl CoA to Δ2 trans enoyl CoA using FAD
Hydration
Hydration:
Δ2 trans enoyl CoA is hydrated to 3-hydroxyacyl CoA by Δ2 -enoyl-CoA hydratase
Reoxidation
Reoxidation:
3-hydroxyacyl CoA is dehydrogenated to 3-ketoacyl-CoA by -3-ketoacyl-CoA dehydrogenase using NAD+
Cleavage
Cleavage:
3-ketoacyl-CoA is cleaved by thiolase to produce acetyl-CoA and acyl CoA derivative
Acyl-CoA re-enters pathway for further degradation to acetyl CoA via citric acid cycle
End product of B oxidation
Even no. C atom: Acetyl coA
Odd no. C atom: Acetyl coA and propionyl coA
Energetic of beta oxidation
Palmitic acid is the commonly occurring fatty acid in the food and body
E yang kena hasil dari palmitic acid (guna Beta O)
1 NADPH = 2.5 ATP
1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
1 cycle of Beta O produced 4 ATP
7 cycle of Beta O produced 7×4= 28 ATP
A total of 8 acetyl coA are produced; each one enters TCA cycle and gives 10 ATP.
8 Acetyl coA: 8×10 ATP= 80 ATP
Therefore 28 ATP + 80 ATP = 108 ATP
But the activation of fatty acid utilizes 2 high energy bonds. So, the net production of ATP from palmitic acid: 108-2= 106 ATP
Biomedical importance
Carnitine deficiency
infants yang ada renal leakage
symptom dia hypoglycemia, muscle weakness dan lipid accumulation
treatment: oral supplementation of carnitine
Hepatic CPT 1 deficiency
hypoglycemia and low plasma ketone bodies
Hepatic CPT 2 deficiency
muscle weakness and myoglobinuria
Jamaican vomiting sickness
eating unripe ackee tree. ni ada toxin hypoglycin yang inhibit beta oxidation dan cause hypoglycemia
Decarboxylic aciduria lead to excretion of dicarbocylic acids. sebab dia ada acyl coA dehydrogenase deficiency
Refsum’s disease - inherited defect alpha oxidation that allow accumulation of phytanic acid
Zellweger’s syndrome (cerebrohepatorenal) inherited deficiency of peroxisomes