Genetic Bone and Connective Tissue Syndromes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is Craniosyostosis?
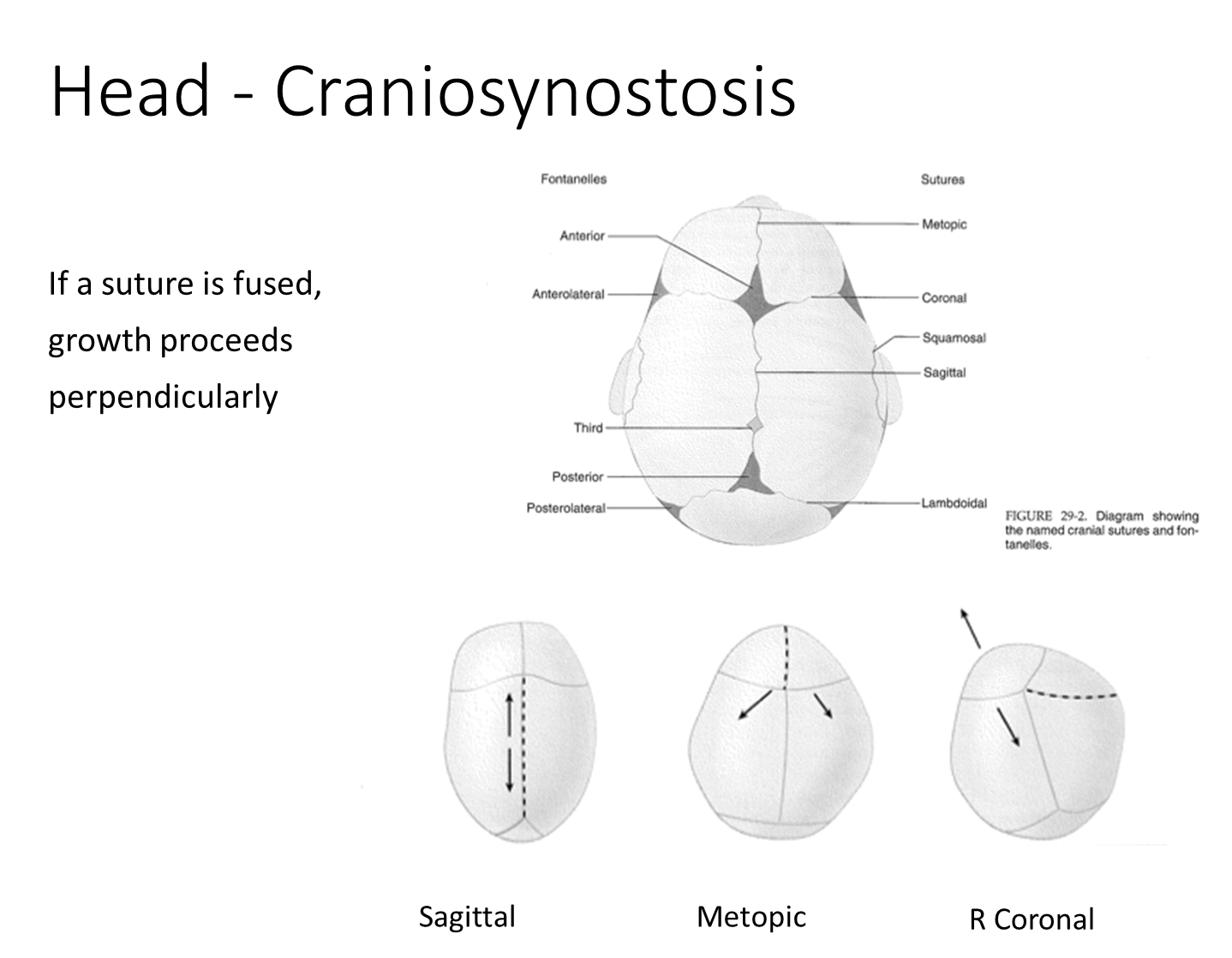
Craniosynostosis is premature fusion of the cranial sutures and can be primary or secondary
1) With craniosynostosis, you can identify the prematurely fused suture based on the shape of the head
→ for example if the sagittal sutures fuse the only direction the skull can grow is longer front to back
2) Secondary craniosynostosis is due to premature closure of the sutures because the bone is not receiving growth signals underneath
→ associated with microcephaly
What three syndromes are associated with craniosynostosis?
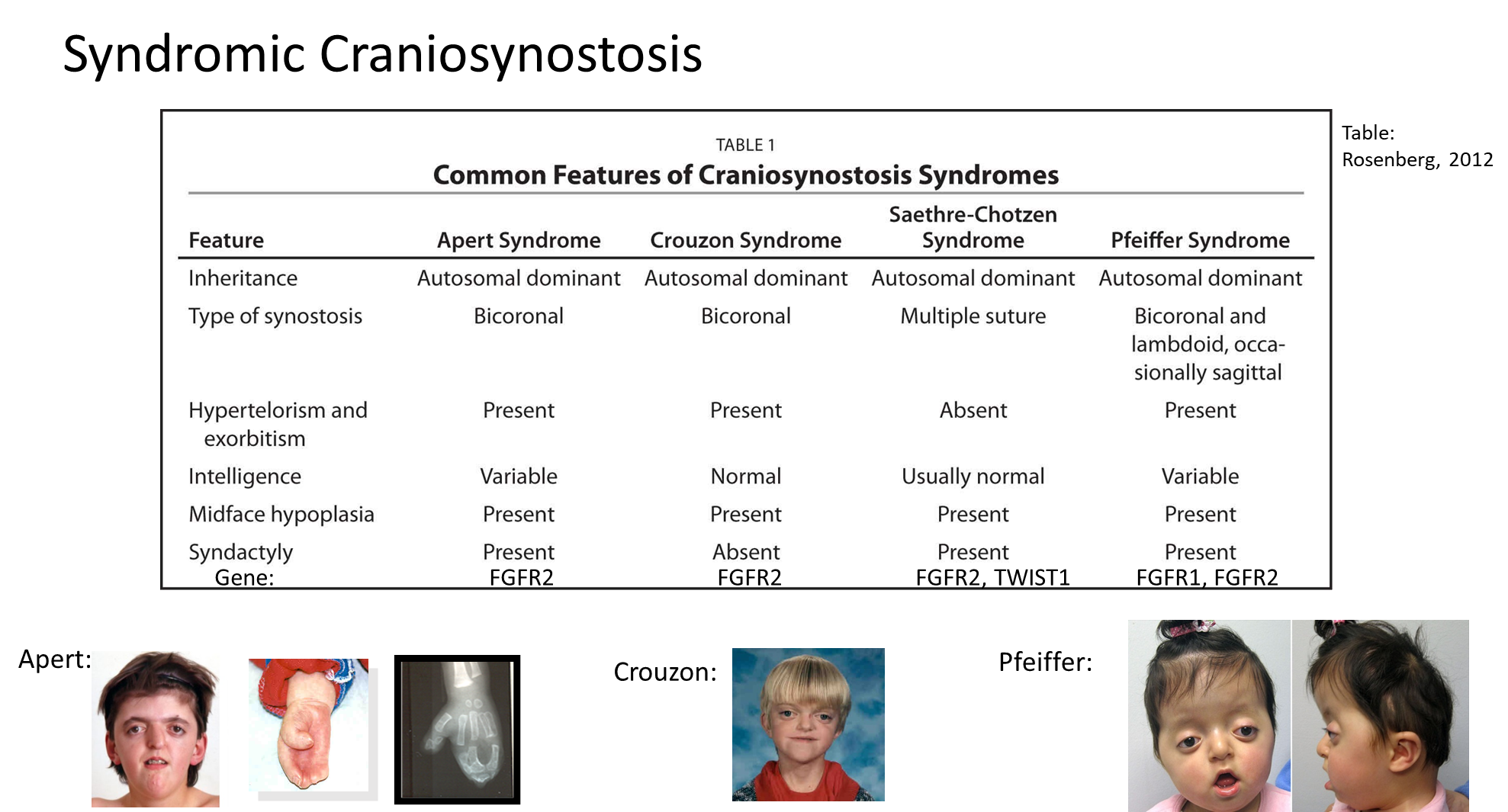
There are a group of three disorders associated with fibroblast growth factor receptors that can cause syndromic craniosynostosis
→ typically affects the FGFR1 and FGFR2 genes
1) Apert Syndrome
→ bicoronal craniosynostosis which is premature fusion of the coronal sutures of the forehead, resulting in a short wide skull
→ will also have severe hand deformities with their fingers fused together like a mitten
→ mid face hypoplasia
2) Crouzon Syndrome
→ can have bicoronal craniosynostosis but will have normal hands
→ mid face hypoplasia
3) Pfeiffer Syndrome
→ can have bicoronal craniosynostosis
→ patients will often have a large thumb
→ mid face hypoplasia
What is Achondroplasia?
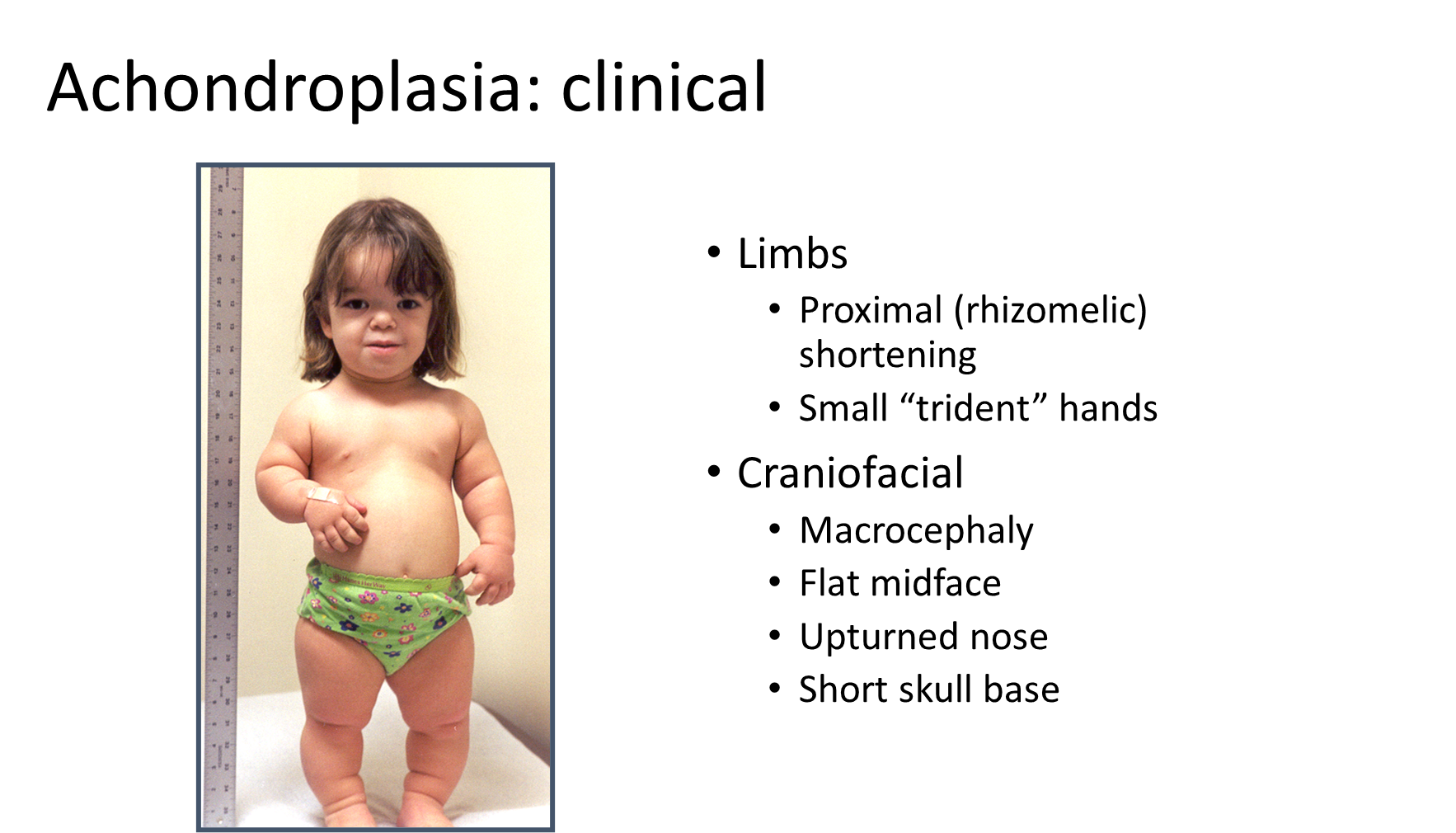
Achondroplasia is the most common form of dwarfism
1) Achondroplasia is autosomal dominant with most cases being sporadic
→ the gene has complete penetrance with very little variation in expression
→ most are caused by FGFR3 pGly380Arg variant
2) Patients will have shortening of their proximal limb bones with small “trident-shaped” hands along with characteristic facial features
→ have a large head comparative to their body with a flat face
→ have a upturned nose and short skull base
3) For any neonate you perform a sleep study and MRI
→ babies with achondroplasia often have apnea and foramen magnum compression
What are the classic radiographic findings associated with achondroplasia?
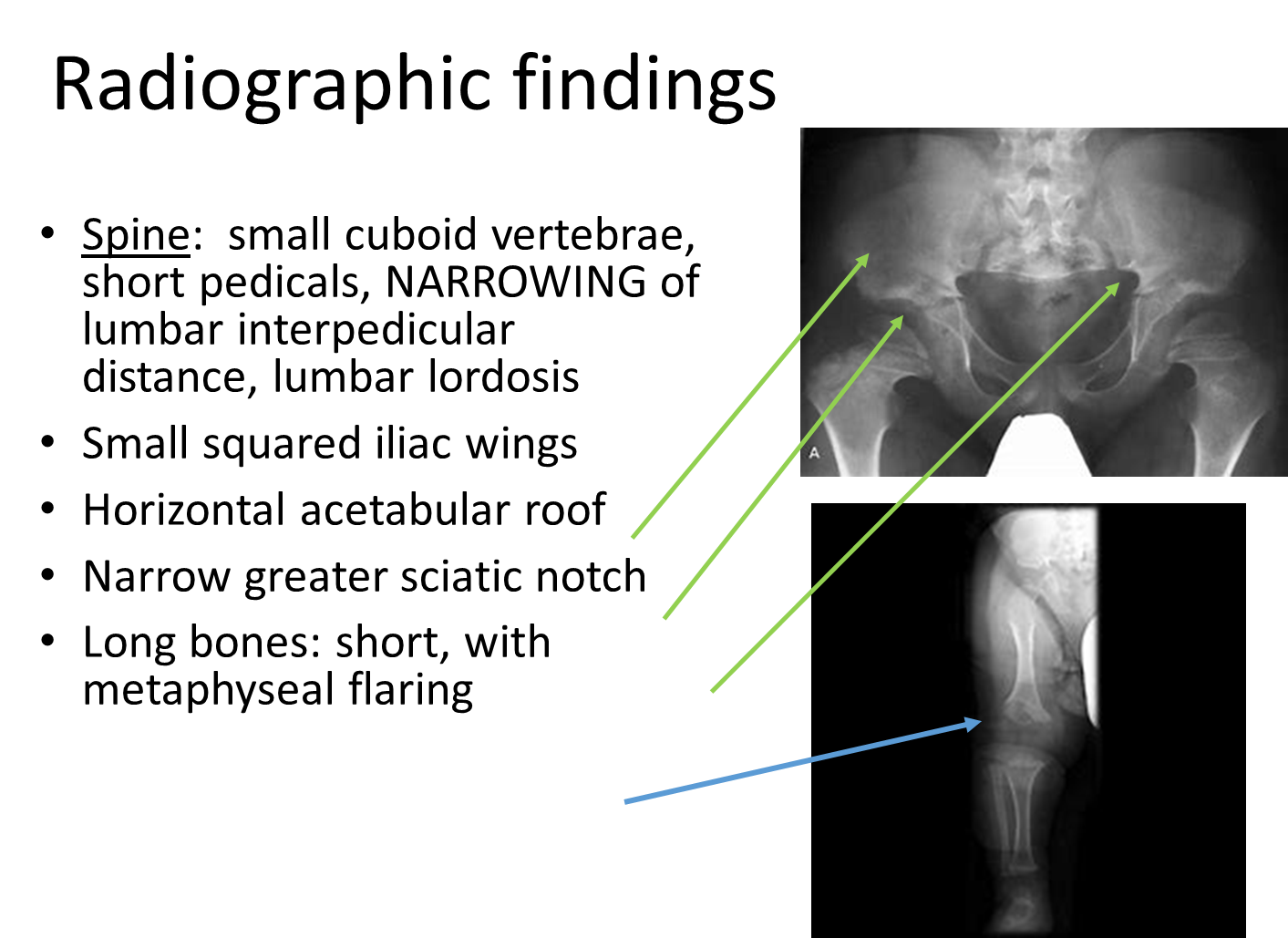
There are classic radiographic findings associated with achondroplasia
→ squared iliac wings
→ horizontal acetabular roof
→ narrow greater sciatic notch
→ long bones will be short and have metaphyseal flaring
What are the two other FGFR3 syndromes aside from achondroplasia?
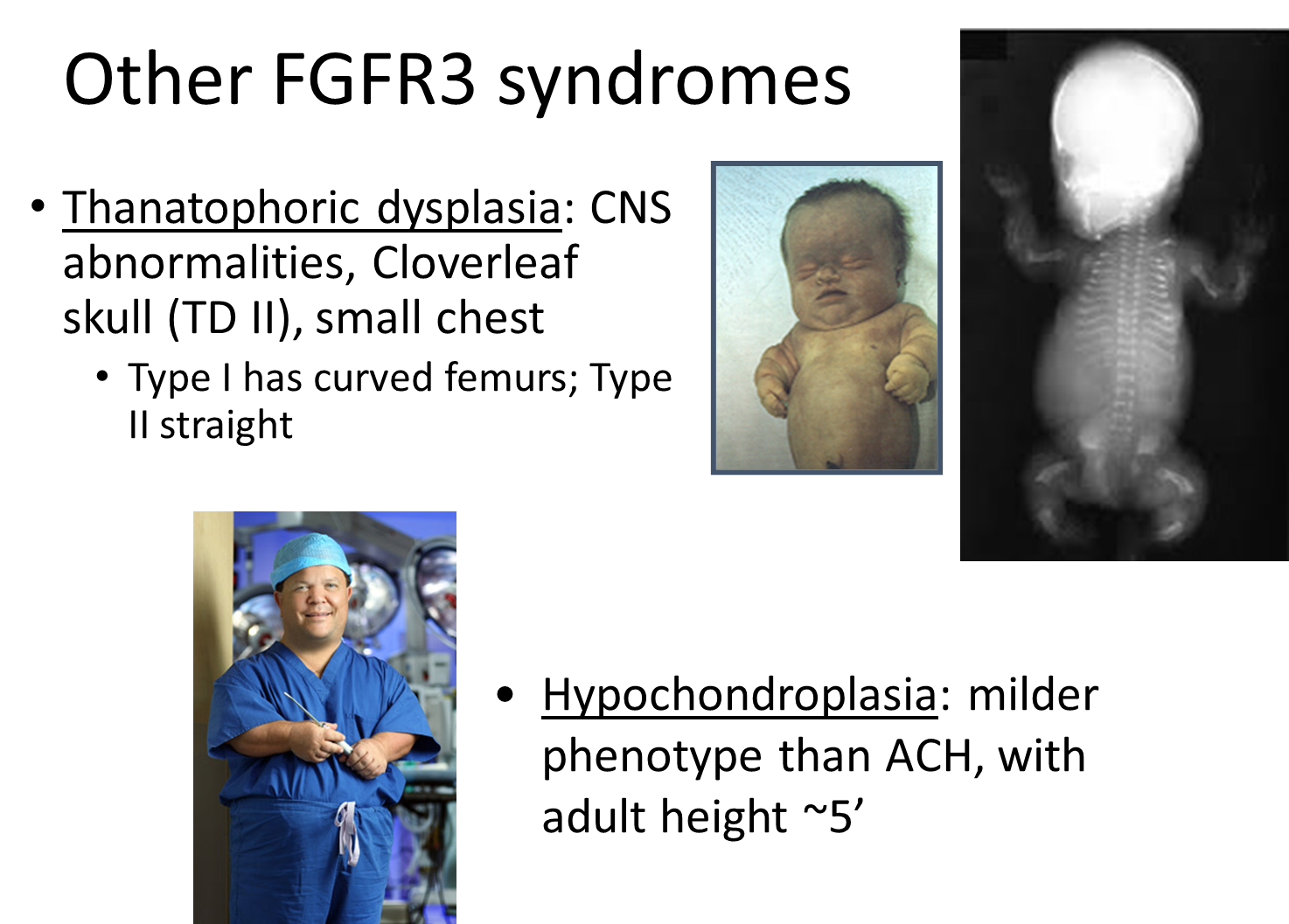
There are two other FGFR3 syndrome aside from achondroplasia:
1) Thanatophoric Dysplasia
→ causes CNS abnormalities, cloverleaf skull, and a small chest
2) Hypochondroplasia
→ milder version of achondroplasia with adult height around five feet tall
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta?


Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a common genetic disease that presents as multiple fractures in younger kids
1) Caused by mutations in either COL1A1 or COL1A2 which leads to a disruption in the formation of Type 1 collagen
→ patients will fracture easily and have progressive hearing loss
→ soft and discolored teeth (dentogenesis imperfecta)
→ blue sclerae
2) On imaging you should identify osteopenia, so the bones appear less dense and are thinner
→ Wormian bones are identifiable, which are extra bone in between the sutures of the skull
What are the subtypes of osteogenesis imperfecta?


1) Type 1 - most common
→ non-deforming: meaning the bones will heal without losing their shape
→ often have normal stature and may not have fractures until they are older
→ have blue sclerae with half having progressive hearing loss
2) Type 2
→ more severe and can have intrauterine fractures, or fractures while developing
→ often lethal in perinatal
3) Type 3
→ individuals have more severe fractures and have deformities when the bones heal
4) Type 4
→ have normal sclera
5) Type 5, 6, 7
→ unimportant
What is a Non-Accidental Injury

Non-Accidental Injury (NAI) are injuries inflicted on a child deliberately, without an accidental cause. Basically it is abuse
→ most commonly in kids under the age of 2
→ have specific radiographic features that are not consistent with OI
1) Osteogenesis Imperfecta is often used as a excuse for NAI
How is Osteogenesis Imperfecta treated?

Bisphosphonates
→ class of drug inhibits osteoclast activity, decreasing bone resorption
→ can increase cortical thickness but it is unclear if it reduces pain and fracture rate in patients with severe osteogenesis imperfecta
What is Marfan Syndrome?

Marfan Syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition associated with a mutation in Fibrillin 1 (FBN1) resulting in overactivity of TGF-beta
→ Fibrillin 1 is responsible for binding and sequestering TGF-beta, but this is defective causing TGF-beta to be overactive
1) Patients will present with characteristic cardiovascular, ocular, and skeletal features
→ ectopia lentis or where the lens becomes dislocated from its position
→ can have mitral valve prolapse and issues with the aorta as well|
2) The classic physical presentation is patients with very long bones and flexible joints
→ can have pectus excavatum
→ poor wound healing
What is Ehlers Danlos Syndrome?

Ehlers-Danlos is a group of diseases that are characterized by hyperextensible skin, fragile tissue, and hypermobile joints. There are three kinds
1) Classical (Type V Collagen/COL5A1)
→ joint hypermobility, skin hyper-elasticity
→ associated with fragile skin and wound healing
2) Vascular (Type I Collagen)
→ most serious form and causes sudden ruptures of internal vessels, organs, and uterus
→ life threatening
3) Hypermobile (most common)
→ importantly hypermobility is not specific to connective tissue diseases
→ requires other musculoskeletal involvement such as joint pain