Global change The Future LECTURE 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Projected changes in drivers
Population growth
Changes in geography of the population
Grwoth in the glocal economy
Population growth
10 billion people
Even if fertilitiy fell sharply→ still would be 9 mmillion
Chnaging geography of population
Urbanisation→ 70% in 2050
Increased efficeciency of resource use
Disproportionate growth projections in Africa
likely to double 2010-2060
note: growth is varied
Growth in the economy
projected at 130% growth porjection
per capita GDP will outstrip population growth
→ Can change relative decoupling to absolute decoupling

Relative decoupling
resources use/ $ is declining
Absolute decoupling
resource use/$ is declining faster than the global encomy is growing!
Projected changes in threat
Habitat conversion
Over harvesting
Climate change
Invasive species
pH of ocean
Pollution in ocean
Habitat conversion
More wealthy people deamnd more food
especially high footprint products e.g meat and dairy
Need more cropland than today
ESPECIALLY→ Sub-saharan Africa→ Dramatic growth but chronically low yields
Must use up even more African land→ biodivsery threat a very high
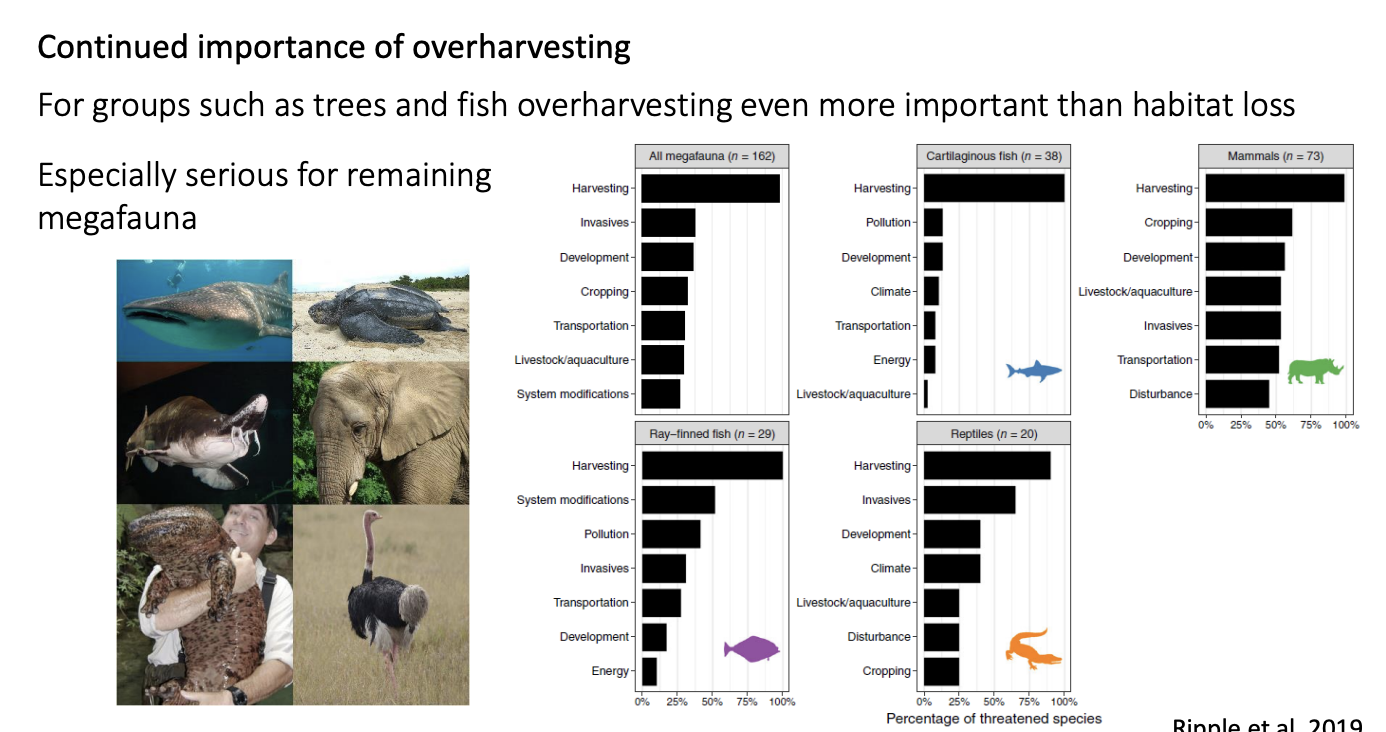
Overharvesting
Trees and fish→ more important than habitat loss
Especially
megafauna
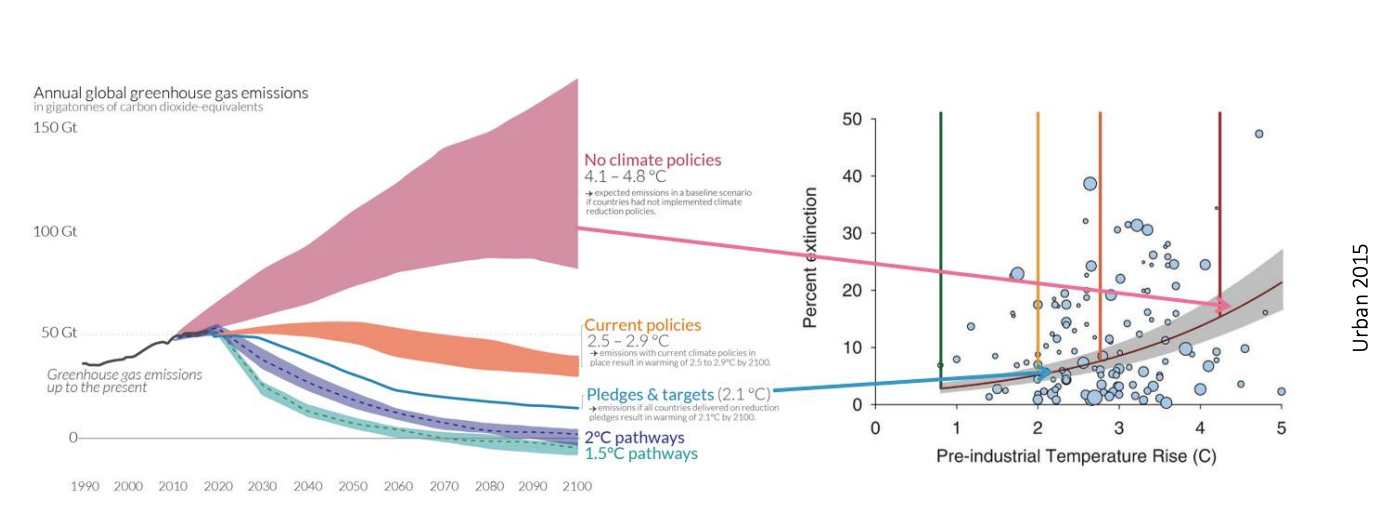
Climate change→ greenhouse gases
The near-term descion agreements now will determine emissions trajectories
Business as usual emissions→ causes >4 degree heating by 2100 over preindustrial levels
IMPACT→ 16% of all species to extinction
marine extinctions comparable to end-Permian event by 2300
But even if pledges were met
→ still eliminate 7 to 8% of species
Need more stringent measures!
Invasice species
Likely to rise:
Increase in global shipping→ 1200% by 2050
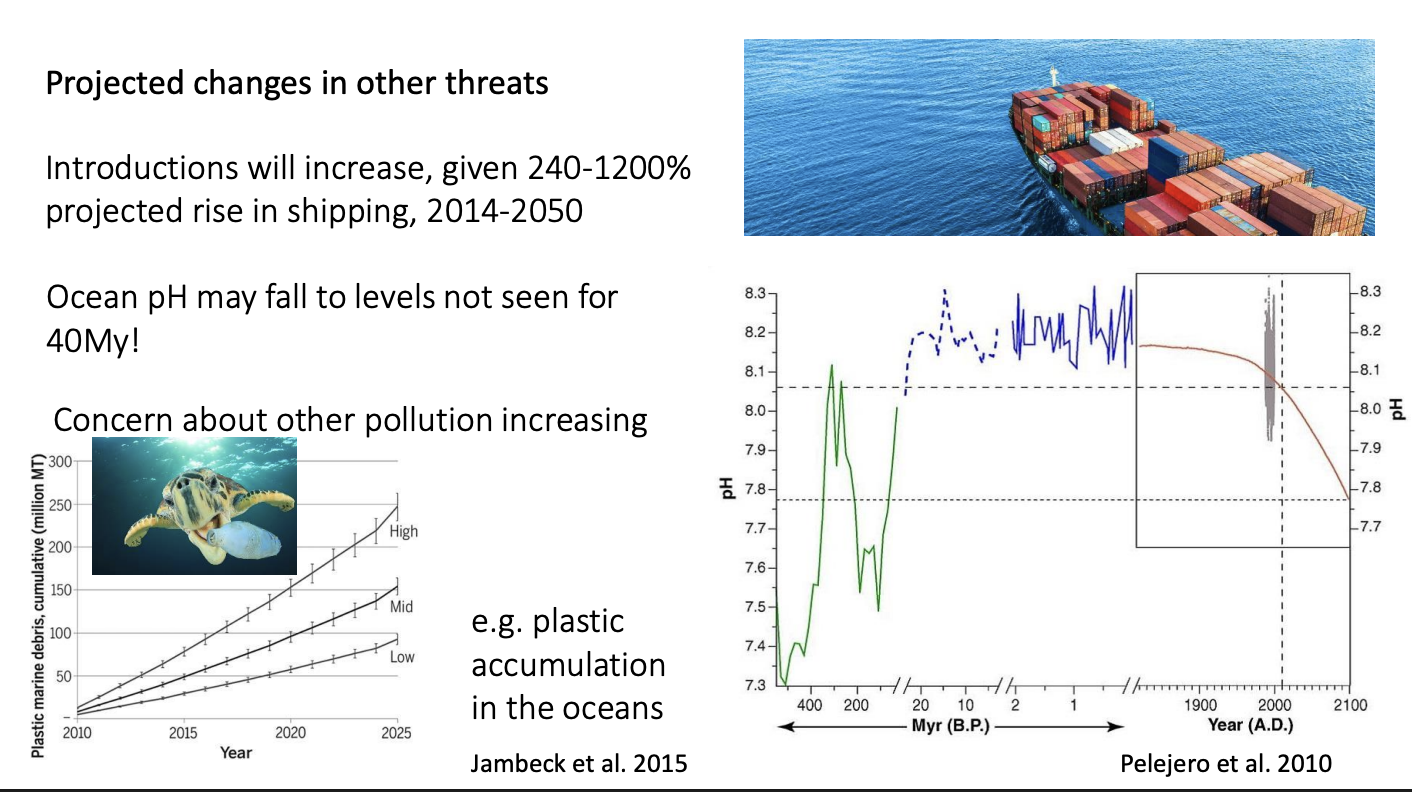
pH of oceans
fall by -.3pH unites by 2100
more acidic than they were past 40My
Pollution in the ocean
Eutrophication
accumulation of plastic debris
bioaccumulation os persistant organochlorines in the tissues of apex predators
like the killer whales
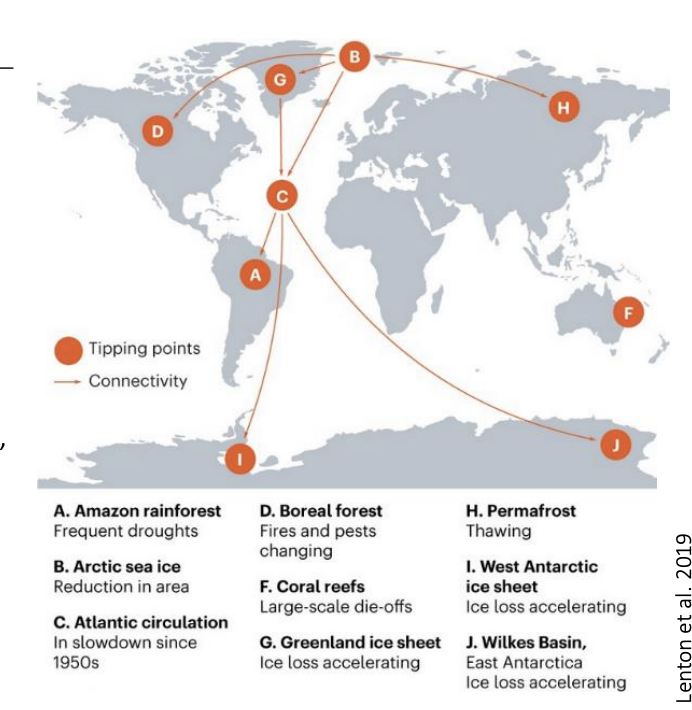
Cumulative effects of projected threats!
Extinction rates→ increase by x5
CO2 and temperature increase and habitat conversion» last deglaciation
Several regional scale state-shifts
irreversible transitions from one state to another
AND
They can interact→ making glocal-scale state shift plausible!
Reasons for thinking these effects could be solved!
Trends in the level of conservation responses
Conservation improves habitas and populations
Conservation is tackling the drivers underlying core threats
Public levels of concern are growing
Many of the changes being made can also positively impact other issues
Trends in the level of conservation responses
conervation seems to have accelerated
Now targets to protect at least 30% of terrestrial, freshwater, coastal and marine areas in PAs and OECMs
Although:
These must really be effective in helping meet rising human deamnd for food, fibre and energy!
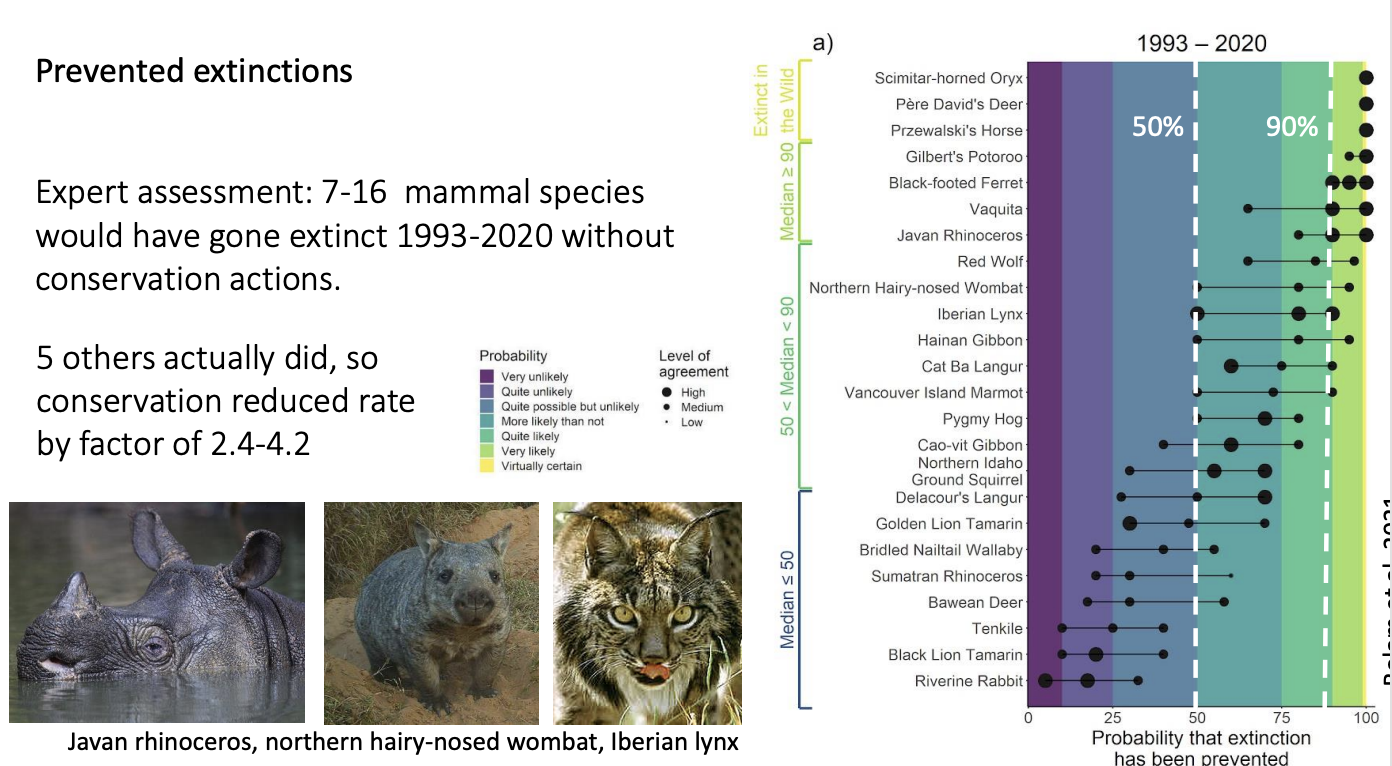
Conservation improves habitats and populations
Conservation seems to be improving habitats and populations
AND slowing down exticntion rates
e.g 26 highly endangered mammals species→ 7-16 would have gone extinct by now, BUT HAVE NOT!
Extinction have reduced by a factor of 2.4-4.2
Conservation is tackling the drivers underlying core threats
E.g Tackling the need for more cropland by:
cutting food waste
shifting towards plant-based diets
increasng crop yeilds
e.g in AFrica
80% yield gap closed
→ halves the area of extra crop land needed
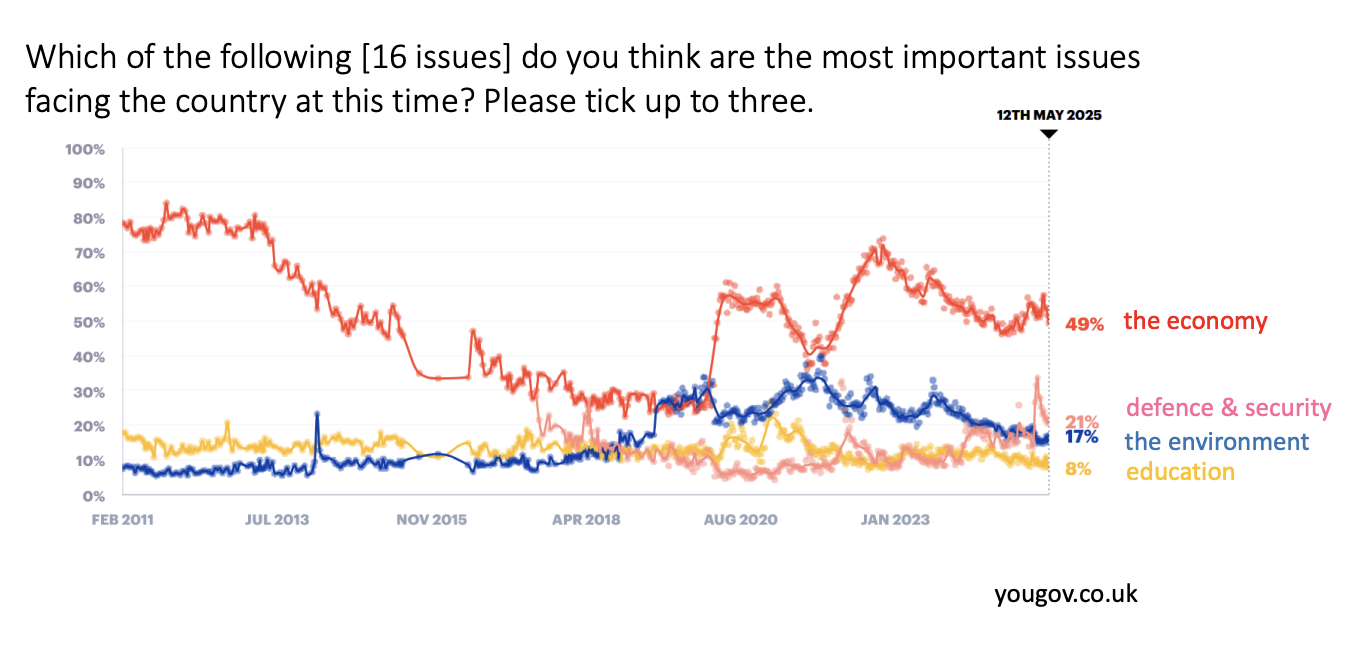
Public levels of concern are increasing
higher than education
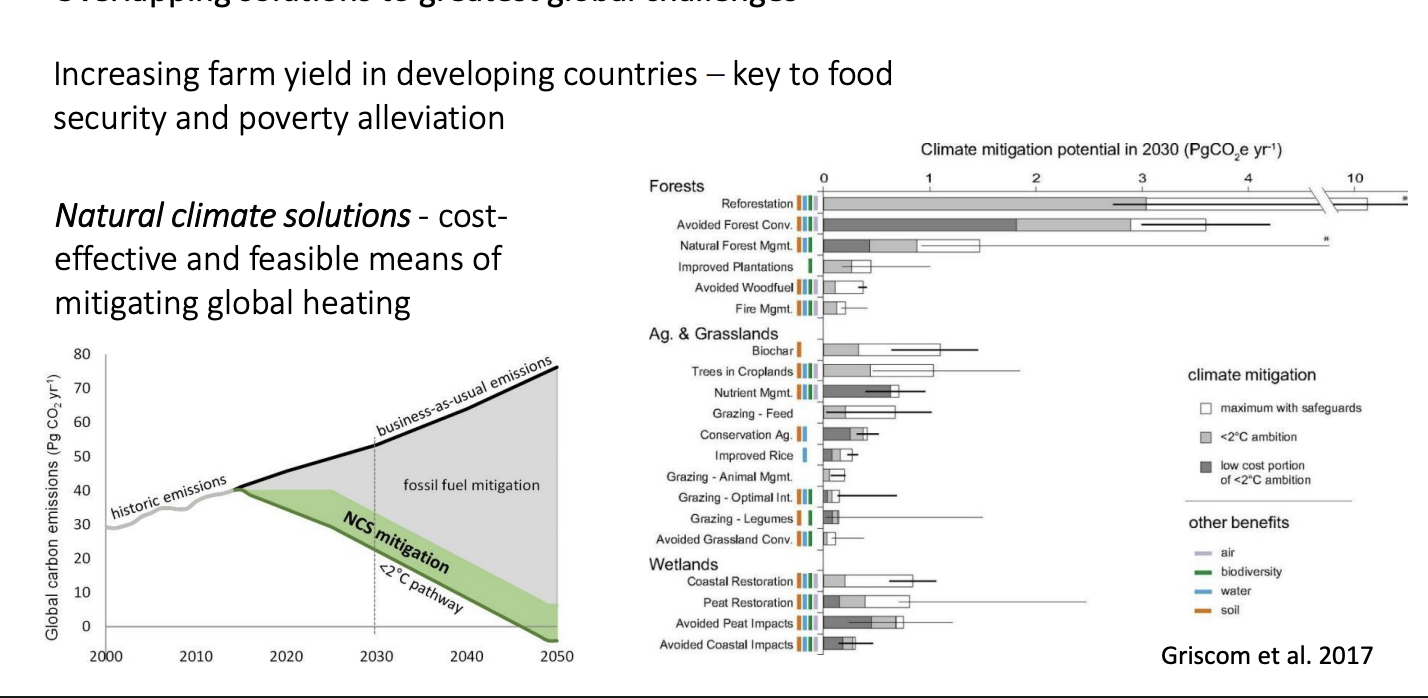
Many of the changes being made can also positively impact other issues
e.g Tackling food security→ ALSO natural climate solution
cutting food waste
increase yields
→ ALSO HELPS
restore forest on low-yielding grasing lands
stops further deforestation
→ Adds a 20% reduction in emissions needs to achieve net-zero
Case Study 1: Mauritius→ How it is going
intensive hands-on managmenet of several critically endangered birds
promoted more species managment
Re-introductions into the wild!
Case Study 1: What needs to be done next?
Extend to overlooked species
e.g endemic invertebrates and habitats (caves)
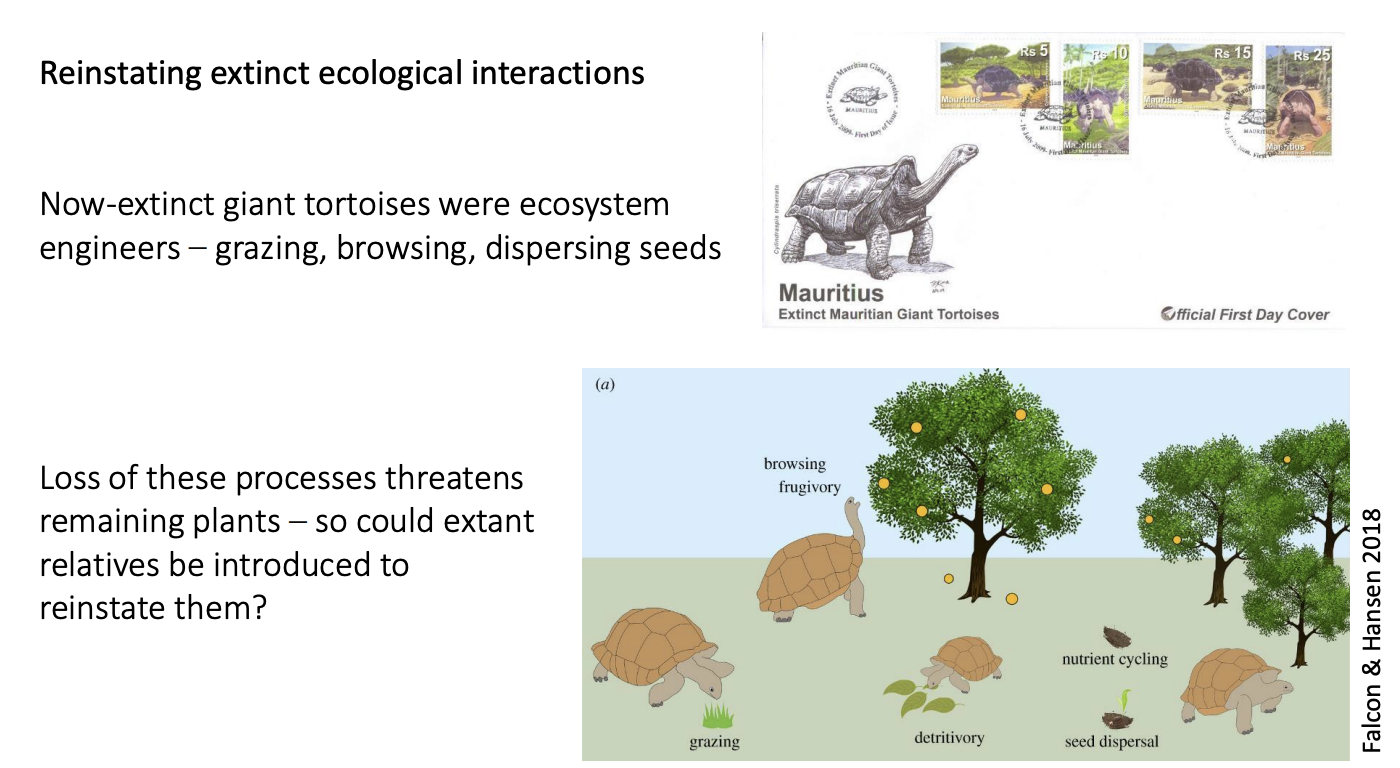
Case Sudy 1: Next steps→ Rewilding
Ecological replacement (taxon substritution)
replacing extinct species witht the next best thing to take up the ecologial niche
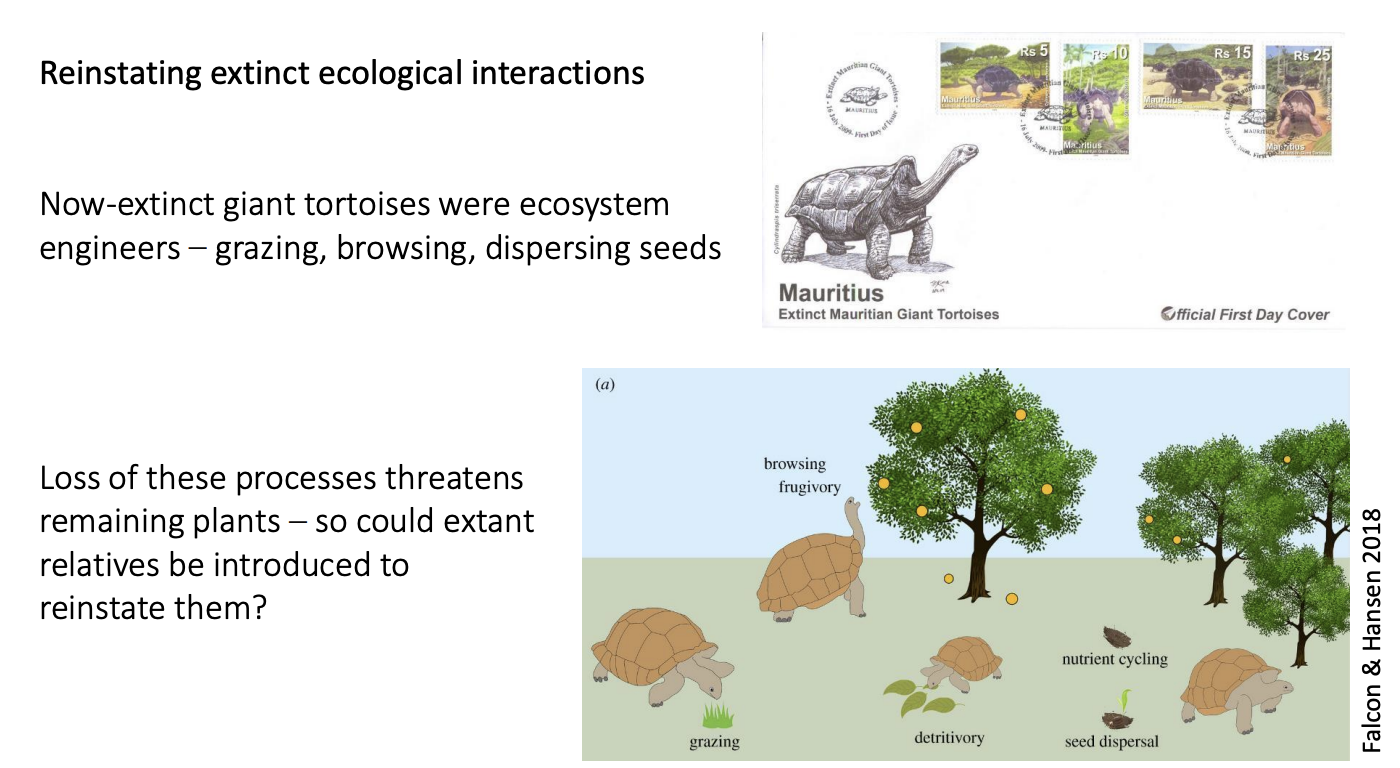
E.g example of rewilding
Species that went extinct→ tortoises, needed for
large seed dispersal
exerted strong selesction for grazing herbs and grasses
Replacement→ new tortoises
To Ile aux Aigrettes
Effect:
seedlings appear right across islet
not beneath plants any more
pass through gut→ Increased germination
promoted palm-rich habitat important for endemic skinks and geckos
Other ways to rewild
Genetic engineering→ e.g dodos
but many argue these are unhelpful distractions!
Case study 2: Great Whales→ How it is going
Norway and Japan still doing it for research
Japan banned
Jan withdrew from International whaling commission
Still whaling!
Case study 2: Positives that may help?
INcrease in whalewatching
13M people worldwide paying to see whales
2.1B/y to regional economies
Even in Japan
Case study2: Effect of this?
Japan whale meat prices→ too high→ uptake is limited
→ Globally no longer a majoe threat
5/7 whale species with reliable population estimates now considered to be increasing!
Case Study 2: New threats coming?
Noise pollution growing from (although causation is not clear)
shipping (which is growing)
seimis surveys
military sonar
Shipping strikes is series
Solution?
Decrease speeds
re-routing shipping lanes
training pilots
Entanglement in fishing gear abandomned
300K deaths/y
solution?
The marine lobsters are overfished
so if decrease fishing effort
would boost profit and help right whale recovery!
Climate-linked shifts in prey e.g for North Atlantic right whale
Case study 3: Amazon→ How it is going
Hunting is a growing problem
Deforestation is accelerating
Case study 3: How to decrease hunting
Tried to suggest chicken substriture
→ DID NOT reduce wild meat consumption
Give cookery lessons and public commitments to reduce wild meat consumption
→ Did help!
Note: reducing unsustainable hunting may require similary nuance interventions elsewhere
Why was deforestation accelerating
Bolsonaro regime
Consequences of further deforestation
Extinctions accelerate→ 25% of Amazon’s tree species and contiues to 57%
Carbon sink lost
Moist forest→ savanna
deforestation lowers evapotranspirative loss, reducing rainfall, turn further reduces evapotranspitation
Rapid switch to savanna-like vegetation
Bad for agricultureal areas!
Case study 3: Optimism?
Political and economic pressure
Proven tools for slowing deforestation
Abandoned by farmers→ Restoration
Carbon credits
Increasing yields
Political and economic pressure
National and international
return of Lula de Silva
committed to net-zero deforestation by 2030
Proven tools for slowing deforestation
Proved that things can slow deforestation substationally!
protect areas
market and regulation driven carrot and stick interventions on private land
→ Deforestation rates have rouhly halved!
Abandoned by farmers→ Restoration
23% of recently cleared forest has been abandoned
could support deforestation
restoriation!
Carbon credits
Glocal carbon prices increased 16-fold
payments of carbon creits could be a good incsetise to reatin forest cover!
Increasing yields
Cattle stocking is only at about 1/3 carrying capactiy
raise to 50%→ meets Brazil’s target for agriculture
At the same time as
stopping further deforestation
ALSO: meet Chinease soy demand
Conclusion
If we continue business-as-usual, a sixth mass extinction will probably be triggered and climatic tipping points breached –
but the evidence suggests already we have much of the knowledge and the means to avert these outcomes, if we choose