Chapter 15 - Fetal Assessment During Labor
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mississippi College; NUR390: Maternal, Newborn, and Women's Health; 2nd Semester
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what is electronic fetal monitoring?
tool for visualizing fetal heart rate patterns on a monitor screen or printed tracing
when was fetal monitoring first used?
1970s
what was the anticipated effect for fetal monitoring?
a decrease in cerebral palsy, however, the rate has not ben declined
what is the primary mode of intrapartum assessment in the United States?
fetal monitoring
what is a period of physiologic stress for fetus?
labor
what is part of nursing care during labor?
frequent monitoring of fetal status
what must be maintained during labor to prevent fetal compromise?
fetal oxygen supply
fetal oxygen supply can decrease due to what 4 factors?
reduction of blood flow through maternal vessels as a result of hypertension and hypotension
reduction of oxygen content in maternal blood as a result of hemorrhage or severe anemia
alterations in fetal circulation with compression of umbilical cord
reduction in blood flow to intervillous space in placenta (maternal hypertension/diabetes mellitus)
what is uterine activity?
fetal well-being during labor measured by response of FHR to uterine contractions
what is the goal of intrapartum FHR monitoring?
to identify non-reassuring patterns indicative of fetal compromise
what are non-reassuring FHR patterns associated with?
fetal hypoxemia which if left uncorrected can progress to fetal hypoxia
what is intermittent auscultation?
listening to fetal heart sounds at periodic intervals to assess FHR
what tools can we use for intermittent auscultation?
DeLee-Hillis fetoscope
Pinard stethoscope
Doppler ultrasound device
what are some electronic fetal monitoring techniques?
external monitoring
internal monitoring (invasive)
display
what tools can we use for external monitoring?
FHR - ultrasound transducer
UC - tocotransducer
what are some tools we can use for internal monitoring?
spiral electrode
Montevideo units
what are Leopold maneuvers?
palpating the maternal abdomen to identify fetal presentation an position
what positions of the fetus do we not want to see?
mentum, brow presentation, transverse
what positions of the fetus do we want to see?
occiput
what is the most common fetus presentation do we want to see?
what is the normal range for fetal heart rate?
110-160 bpm
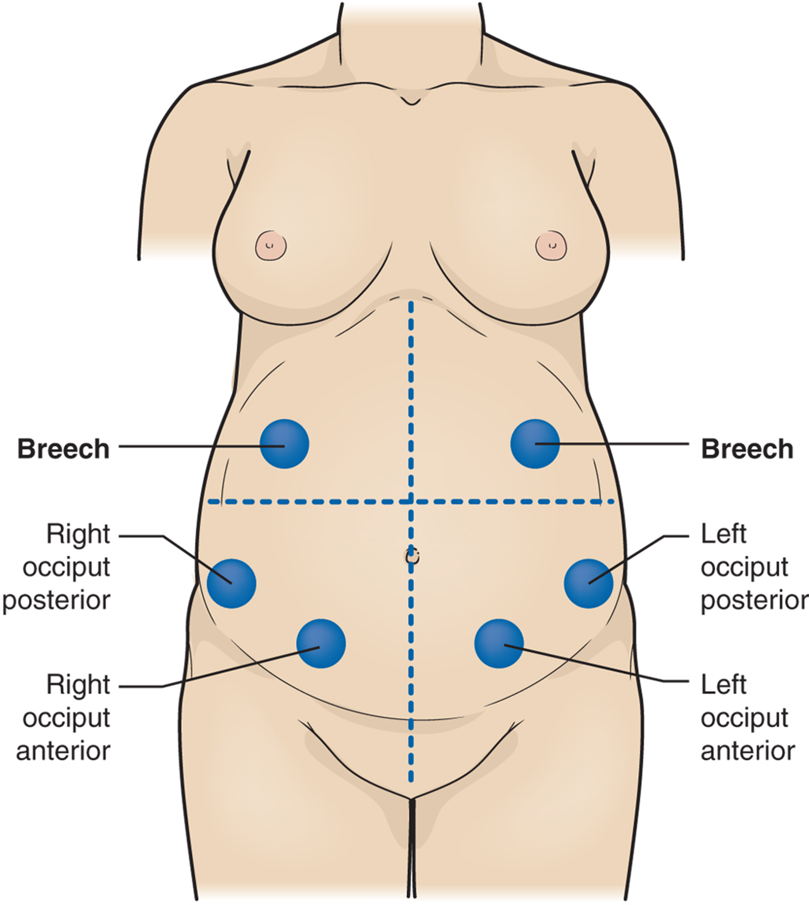
Know this! will have a question on test where you have to place in the right spot
baseline fetal heart rate is averaged during a __________ segment?
10 minute
*excluding periodic changes, episodic changes, periods of marked variability, segments of the baseline that differ by more than 25 bpm
what is variability?
described as irregular waves or fluctuations in the baseline FHR of two cycles per minute or greater
what is absent variability?
not detected with unaided eye
what is minimal variability?
detectable but less than 5 bpm
what is moderate variability?
normal (indicator of normal fetal acid-base balance)
what is marked variability?
unclear significance
what is a sinusoidal pattern variability?
regular smooth, undulating, wavelike patterns (associated with fetal anemia)
on the monitor display, FHR is displayed in the _____ section and UA is displayed in the _____ section
upper
lower
each small square on the monitor paper or screen represents how many seconds?
10 seconds
each larger box of six squares equals how many minutes?
1 minute
what are the four types of variability?
absent
minimal
moderate
marked
which variability do we want to see?
moderate variability
what is fetal tachycardia?
baseline more than 160 beats/min for a duration of 10 minutes or longer
what are some causes of fetal tachycardia?
maternal/fetal infection
maternal hyperthyroidism
fetal anemia
in response to medications such as atropine, hydroxyzine (Vistaril), terbutaline (Brethine), and/or illicit drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamines
abnormalities involving fetal cardiac pacemakers and/or cardiac conduction system
early signs of fetal hypoxemia especially when associated with late decelerations and minimal or absent variability
what is fetal bradycardia?
baseline less than 110 beats/min for duration of 10 minutes or longer
what are some causes of fetal bradycardia?
fetal cardiac issues/structural defects
maternal hypoglycemia
maternal hypothermia
viruses (like cytomegalovirus)
do not get true bradycardia mixed up with prolonged decelerations
when do periodic changes in baseline FHR occur?
with contractions
are episodic changes in baseline FHR associated with contractions?
no
what are accelerations?
visually apparent, abrupt (onset to peak <30 seconds) increase (15 bpm) in FHR above baseline
acceleration with fetal movement signifies fetal well-being representing fetal alertness or arousal states
the peak is at least 15 beats/min above the baseline, and the acceleration lasts 15 seconds or more, with the return baseline less than 2 minutes from the beginning of the acceleration
decelerations can be either said as _____ or _____?
benign or abnormal
what are the four categories of decelerations?
early
late
variable
prolonged
what are early decelerations?
response to fetal head compression
are early decelerations “good” or “bad”?
good! usually benign and is a “mirror image” of a contraction
what are late decelerations?
gradual decrease in and return to baseline FHR associated with UC
what are late decelerations caused by?
uteroplacental insufficiency (disruption of O2 transfer)
when does late decelerations occur?
begins after contraction
when does the lowest point of deceleration occur?
after peak of contraction
when does baseline FHR return after a deceleration?
after contraction is over
what are some nursing interventions for late decelerations?
drug of choice = oxytocin
assist woman to side-lying position
administer oxygen at 10 L/min (nonrebreather mask)
correct hypotension (elevate legs)
increase rate of maintenance IV fluid
palpate uterus for tachysystole
notify HCP
may need internal monitoring
assist with birth if pattern cannot be corrected
what are variable decelerations caused by?
compression of the cord and vessels within with or without contractions
what are some specific examples of cord compression?
maternal position with cord between fetus and maternal pelvis
cord around fetal neck, arm, leg, or other body part
short cord
knot in cord
prolapsed cord
variable decelerations’ decrease is at least _____ beats/min or more below the baseline, lasts at least _____ seconds, and returns to baseline in less than _____ minutes from the time of onset.
15
15
2
what are some nursing interventions for variable decelerations?
discontinue oxytocin if infusing
change maternal position (side to side, knee-chest on all fours)
notify physician or nurse-midwife
assist with vaginal or speculum examination to assess for cord prolapse
assist with amnioinfusion if ordered
assist with birth (vaginal assisted or cesarean) if pattern cannot be corrected
what are prolonged decelerations caused by?
an interruption to fetal oxygen supply
what are some things that can occur that lead to the fetus not receiving oxygen?
maternal apnea during an eclamptic seizure
cord compression, stretch, or prolapse
a prolonged deceleration is a visually apparent decrease (may be either gradual or abrupt) in FHR of at least _____ beats/min below the baseline and lasting more than _____ minutes but less than _____ minutes
15
2
10
a deceleration lasting more than _____ minutes is considered a baseline change
10
what are the five essential components of the FHR tracing that must be evaluated regularly?
baseline rate
baseline variability
accelerations
decelerations
changes/trends over time
Category I, II, or III FHR tracings are abnormal. Immediate evaluation and prompt intervention are required when these patterns are identified
category III
what are some nursing considerations for abnormal fetal monitoring patterns?
begin intrauterine resuscitation
assist client to side-lying position
increase maternal blood volume by increasing the rate of the primary IV infusion
what are some other FHR monitoring methods of assessment techniques?
fetal scalp stimulation
vibroacoustic stimulation
umbilical cord acid-base determination
fetal scalp blood sampling
what does fetal scalp stimulation (digital pressure on scalp) increase?
heart rate
what does vibroacoustic stimulation (device on maternal abdomen over fetal head) increase?
heart rate
what does umbilical cord acid-base determine?
obtained from cord/vein when FHR tracings have been abnormal
how is fetal scalp blood sampling done?
performed after ROM through dilated cervix
not common practice in the US anymore
what is amnioinfusion?
infusion or room-temperature isotonic fluid (NS or LR) in the uterine cavity for low amniotic fluid
what does amnioinfusion relieve?
intermittent umbilical cord compression
how do we perform amnioinfusion?
through gravity or a pump
less than 1000 mL infused by bolus over 20-30 minutes
monitor for distension/uterine resting tone
what is tocolytic therapy?
tocolysis causes relaxation of the uterus (slows or stops contractions)
improves oxygenation to the fetus
what is the most common tocolytic drug?
Terbutaline (Brethine)
what are some common adverse effects of tocolytic therapy?
palpitations
chest pain
rapid heart rise
tremor
nervousness
what are some patient and family teaching points for amnioinfusion and tocolytic therapy?
explain purpose and procedure
reassure woman and partner that use of monitoring does not imply fetal jeopardy
reassure woman and partner that prepared childbirth techniques can be implemented without difficulty
what are some things you want to document for amnioinfusion and tocolytic therapy?
clear and complete documentation in the woman’s medical record is essential
each FHR and UA assessment must be documented completely
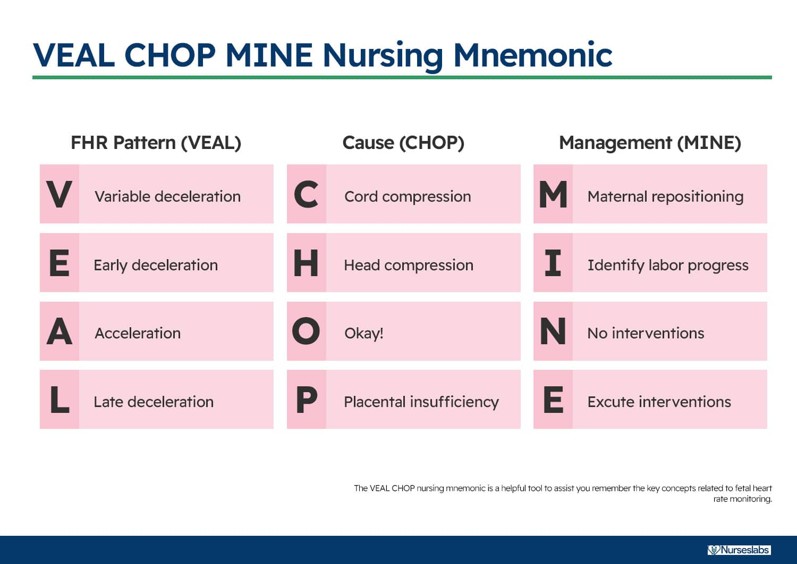
Use this to help :)
fetal tachycardia is most common during which of the following situations/conditions?
A. maternal fever
B. umbilical cord prolapse
C. regional anesthesia
D. MgSO4 administration
A. maternal fever