RAT 1210 ANT UNIT 1-3 EXAM
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Which phase of the somatic cell cycle are ribonucleic acid and proteins synthesized
G1
An adenocarcinoma of the prostate would have a tissue origin of
glandular epithelial
Oteosarcomas occur more frequently in the
metaphysis of the long bone
DNA is synthesized during the ___________ phase of the somatic cell cycle
S
Which of the following structures is responsible for adenosine triphophate, which is a source of energy for intracellular metabolism
mitochondria
Meiosis is different from mitosis in that
Meiosis is how germ cells differentiate
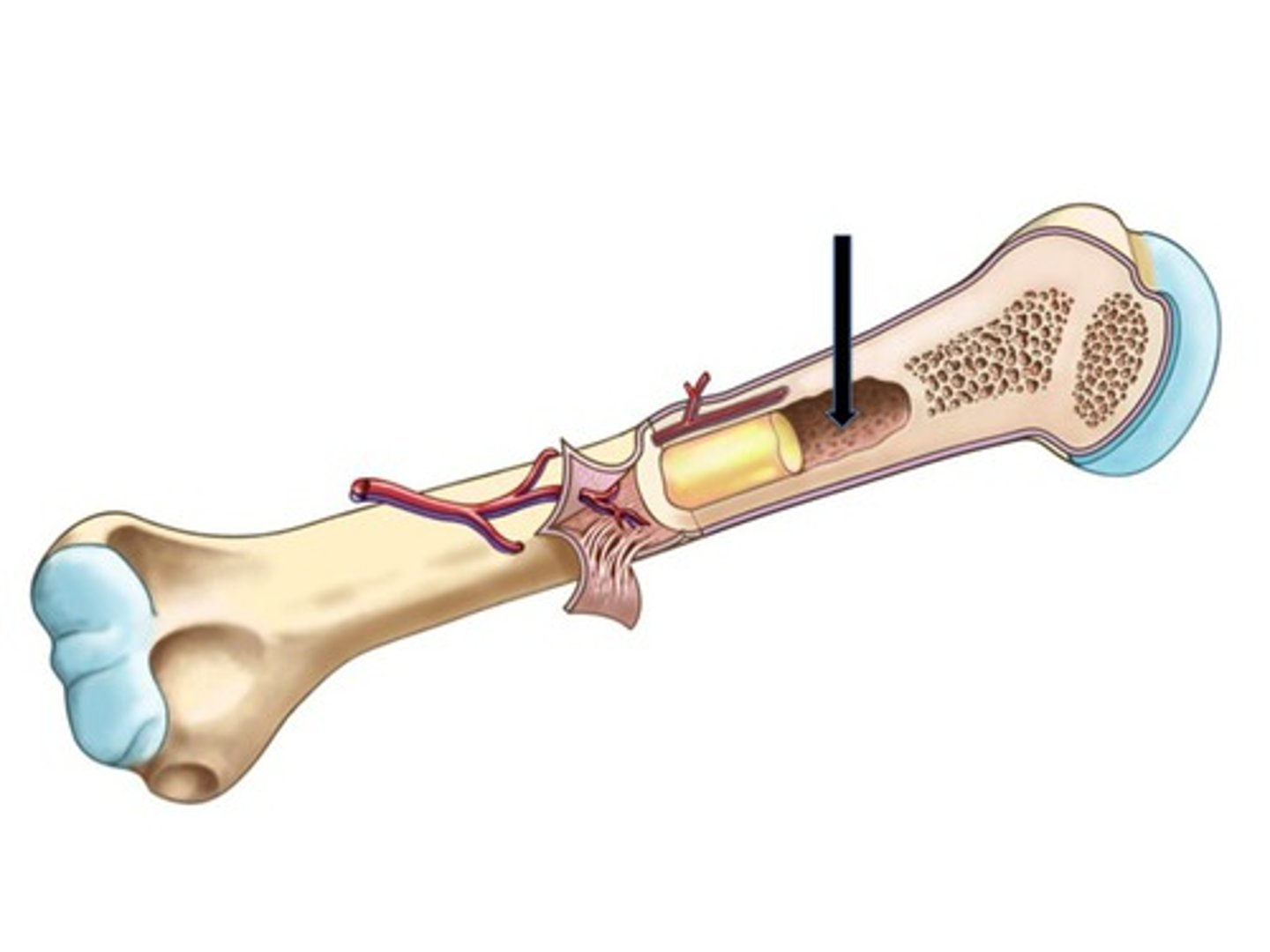
The knoblike portions located at either end of the long bone are called the
Epiphysis
Which phase is it when the chromatids are aligned in the center
methaphase
The part of the bone anatomy that plays a role in the metastic spread of cancer is the
periosteum
The bone forming cells of the skeletal system are the
osteoblasts
The joint at the thumb is called
synovial joint or a saddle joint
Which of the following organs is an exocrine gland
salivary
Which organelle, when activated by radiation, is thought to be one if the mechanisms by which radiation kills cells.
Lysosomes
Benign connective tissue smooth muscle neoplasms are classified as
leiomymoma
The chronologically correct order of the somatic cell cycle is
Gap1, Synthesis, Gap2, and Mitosis
Where is the medullary cavity located
The endocrine gland responsible for the production of adrenaline is the
adrenal gland
Of the four major types of tissue in the human body, which of the following is the most resist to radiation
nerve tissue
Which structure is important in the storage and management of intracellular substance
golgi apparatus
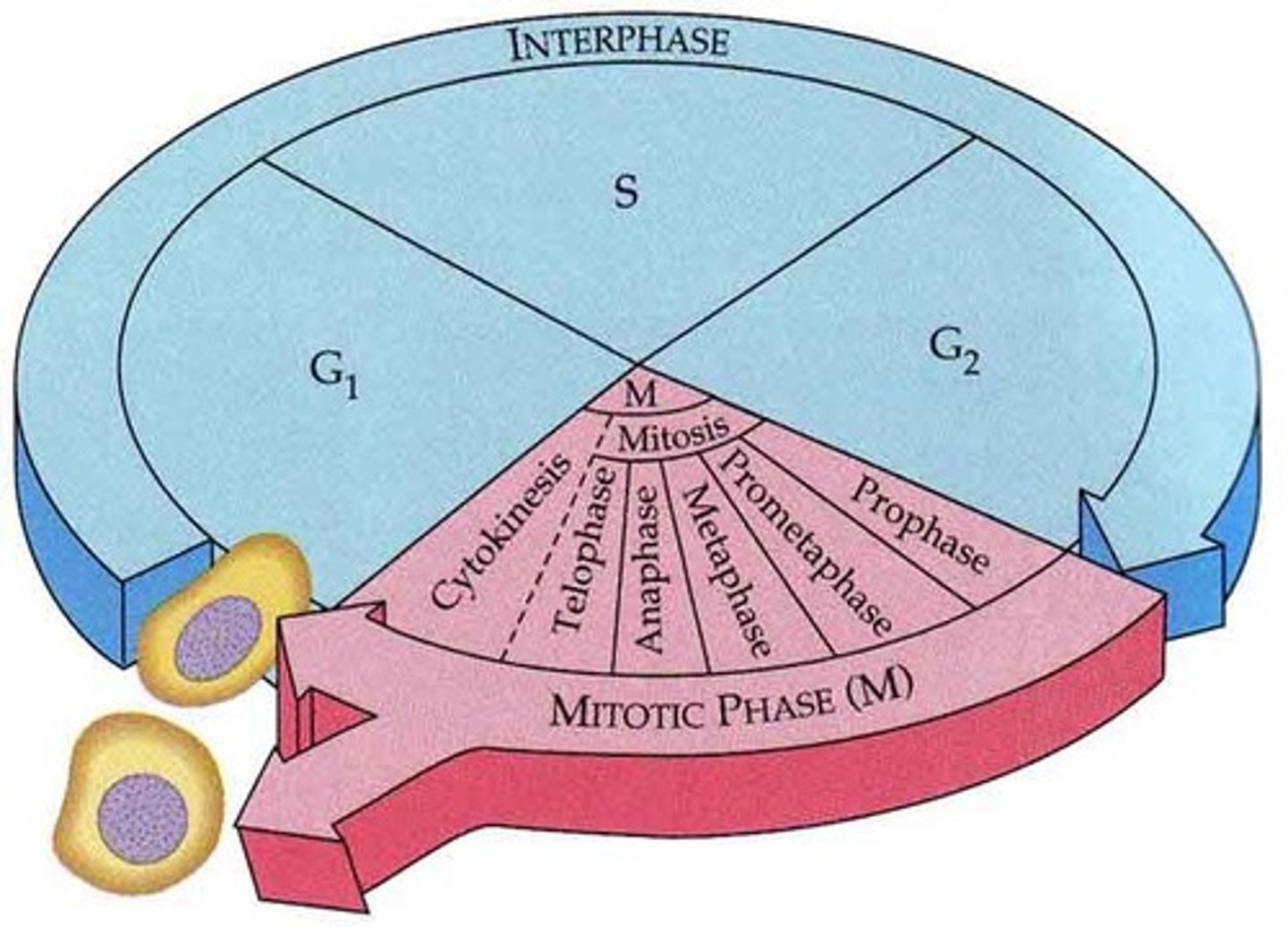
The two divisions of the somatic cell cycle are
interphase, mitosis
germ cells undergo
meiosis
Somatic cells undergo
mitosis
Program cell death is called
apoptosis
How does cancer start
with one cell that starts growing and dividing out of control
The guardian angel gene is called
P53
This is the cells control center. It is where DNA is located. And is where radiation is aimed at?
Nucleus
All cells are surrounded by
plasma membrane
What is a radiation therapist responsible for
for knowing the functions of the organelles and nucleus as this plays a role in radiation protection, patient outcome, and how cancer grows
Protoplasma (cytoplasm) contains mostly 70-85% of
water
Water aids in protecting the cell from
drastic temperature changes
A cell life is impossible without the presences of
Na and K
What are the organic compound in a cell
protein(15%), carbohydrate, nucleic acid , and lipids
Has an amino acid component. Its primary function is basic cell building block, Examples are insulin albumin, and hemoglobin
protein
Has carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as a component. Provides energy fir cellular functions. Examples are starch, glycogen, lactose, and sucrose
carbohydrate
Has a component of sugar and phosphate. Directs cellular information to transmit genetic info and protein synthesis. Example DNA and RNA
Nucleic acid
Componets differ. This is where energy is stored and protection is provided. Examples are cholesterol and steroids
Lipid
What is the splitting of a water molecule called
radiolysis
What will happen if the plasma membrane is ruptured
death
This is between the nucleus and outer cell wall membrane, cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough), ribosomes, golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysomes, and mitochondria
Cytoplasm
This organelle is woven throughout the cytoplasm. It is continuous with the nuclear membrane, houses the ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum
rough endoplasmic reticulum have ribosomes on them
What is synthesis?
when two or more elements or compounds combine to make a more complex substance
Ribosomes are responsible for
protein synthesis
This is where specific enzymes are harbored. These enzymes facilitate certain metabolic processes
peroxisomes
One of the initial theories concerning the mechanism by radiation kills cells.
intracellular digestion
formed in the golgi apparatus
digest bacteria and other substances that enter the cell
under normal conditions the enzymes are safely confined
Lysosomes
This is the main target within the cell from radiation exposure (radiation therapy) because it contains:
DNA(Genes and chromosomes)
Directs cellular metabolism
contains one or more nucleoli
malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause for several human cancer
the nucleus
This is a double lipid layer. The outer membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum while the inner nuclear membrane is the primary residence of several inner nuclear membrane proteins.
Nuclear membrane (nuclear envelope)
What are the cellular division
meiosis
mitosis
What are the 2 divisions in the somatic cell cycle
interphase
mitosis
G1, Synthesis, G2 are the
3 divisions of interphase
What are the phases of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
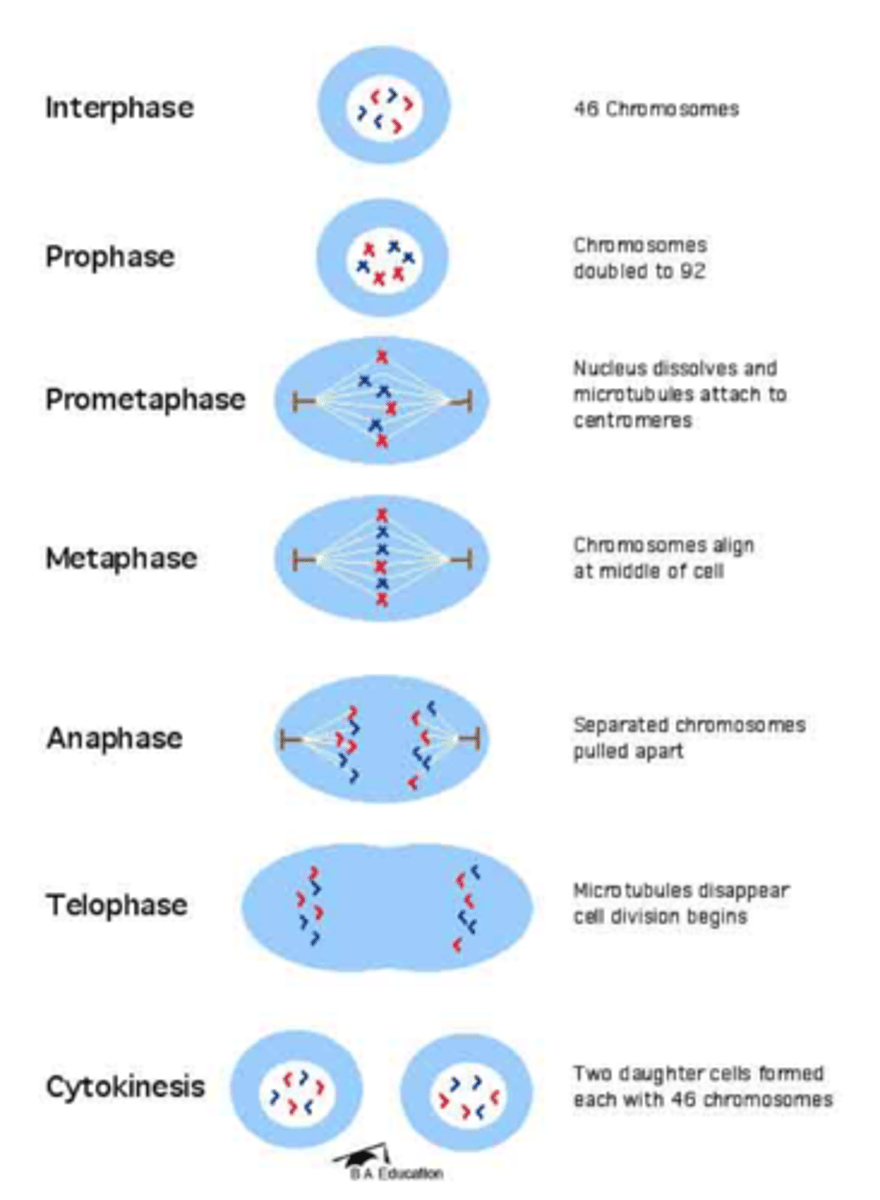
Somatic Cell Cycle
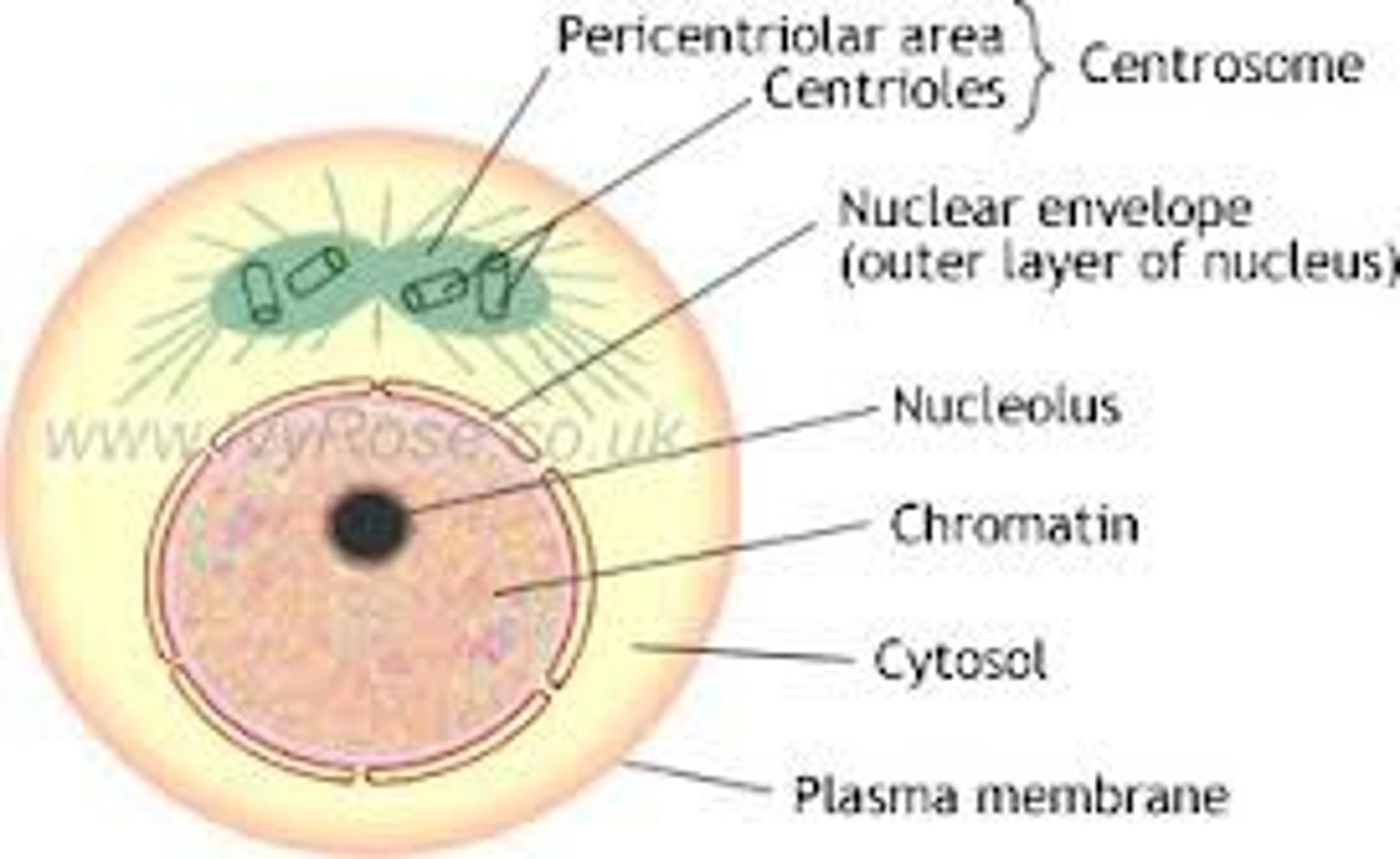
Cell growth replication of chromosomes cell not actively dividing
Interphase
The chromatin condense into vesible chromosome . chromatids become attached at the centromeres . spindle fibers appear, the nucleus and nuclear envelope disappear
Prophase

Spindle fibers attach to each chromatid align
Metaphase
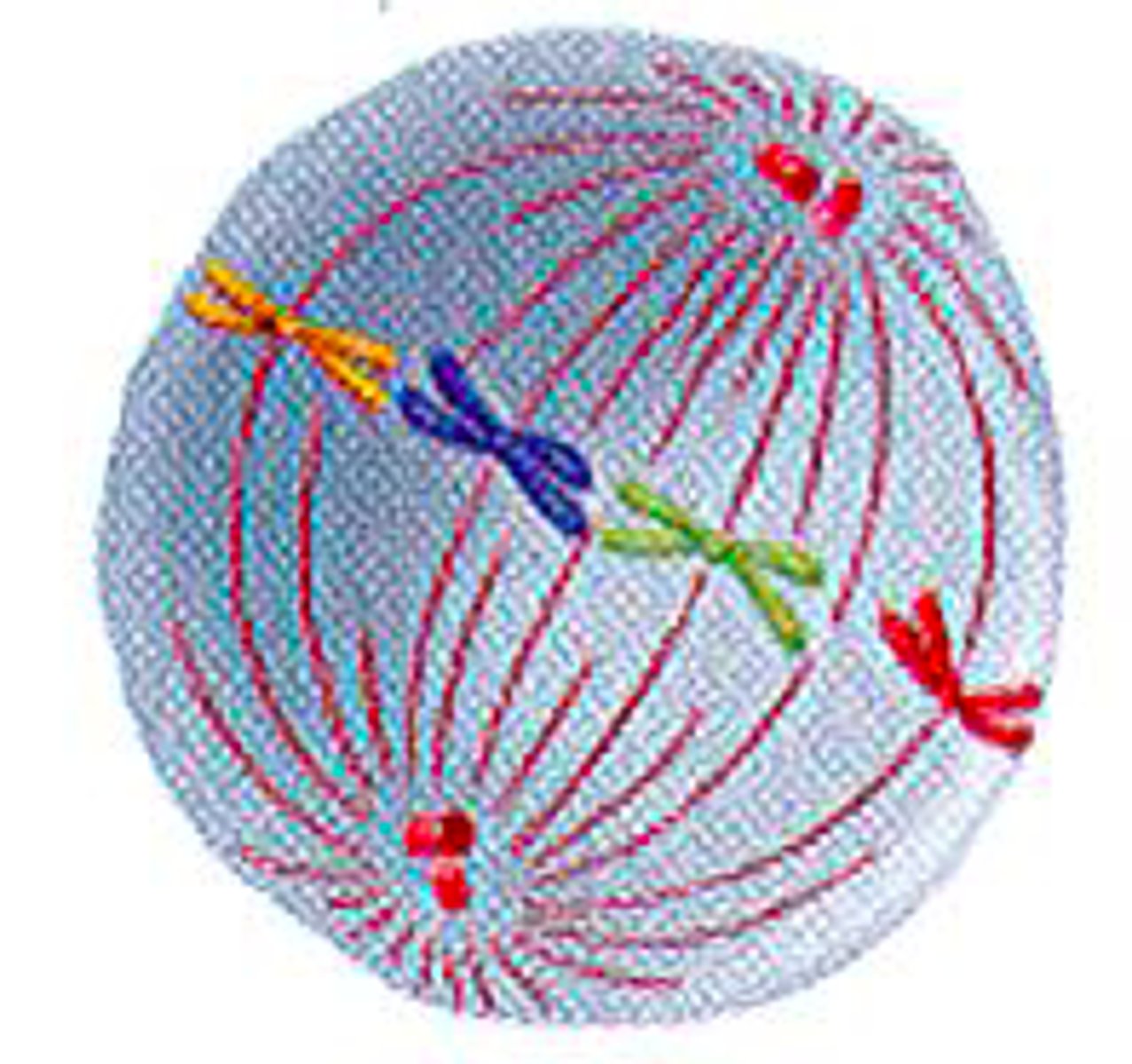
Centromeres break apart. Chromosomes move away
Anaphase
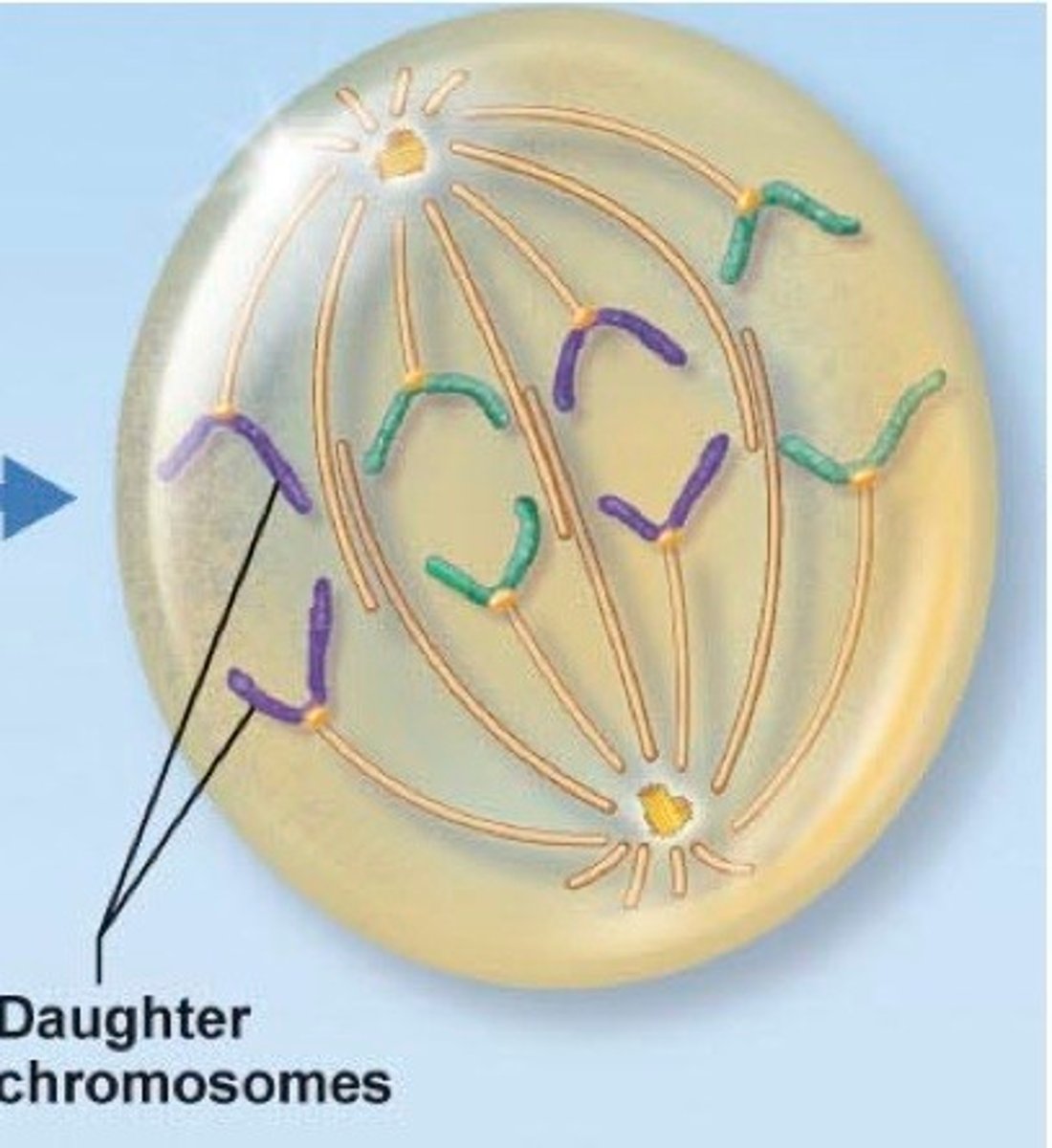
The nuclear envelope and both nuclei appear. The cytoplasm and organelle divide. Division complete
Telophase
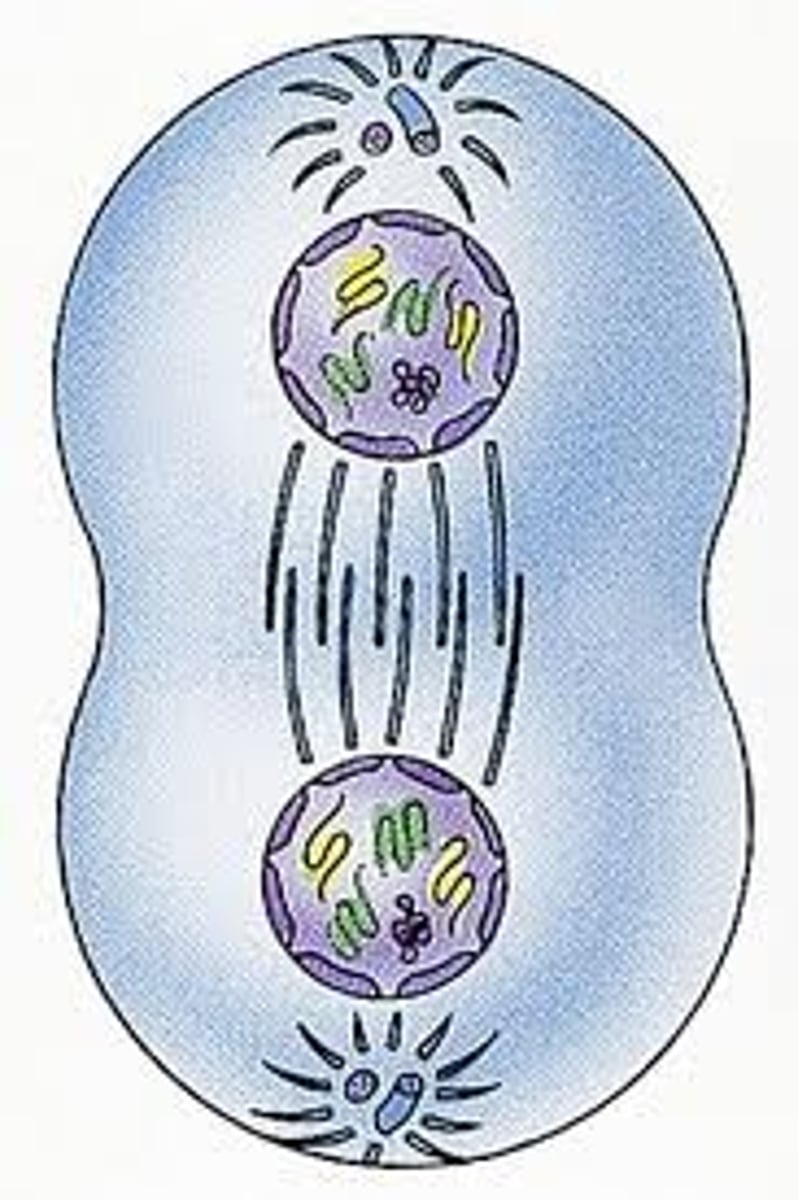
Two daughter cells are formed each with 46 chromosomes
Cytokinesis
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
When the process of cellular division stops and the cell does not divide further, this usually occurs at what point?
Late G1 phase
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
Most radio sensitive or least radioresistant
Late G and mitosis
most radio resistant part of cell cycle or least radio sensative
S
ring formation
single chromatid's ends unite to form ring
What are the four major tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
Epithelial tissue is
radio sensitive
This tissue lines the cavities and surface structure throughout the body
Epithelial epithelium
What are the 3 type of epithelial tissue
Squamous epithelium
cuboidal epithelium
columnar epithelium
Which cancer originated from epithelium
carcinomas
Where do squamous cell carcinomas originate from
the lining of organs
Where do adenocarcinomas arise from?
epithelial cells that are glandular
This tissue connects, supports or separates different types of tissues. This is found everywhere in the body except the central nervous system
connective tissue
Connective tissue is found in
adipose tissue
cartilage
bone
blood
Which type of cancers are connective tissue cancers
sarcomas
Sarcomas arise from
mesenchymal cells
Mesenchymal cells develop into distinct tissue
bone
tendons
muscle
adipose
cartilage
nerve
blood and blood vessels
Which tissue are responsible for changing and maintaining posture and movement of internal organs
muscular tissue
What are the three types of muscular tissue
skeletal (voluntary movement)
cardiac (involuntary movement myocardium)
smooth (involuntary movement, internal organs)
What is the main component of the two parts of the nervous system
nerve tissue
Central nervous system contains
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
branching nerves that control bodily functions and activities
Nerve tissue is composed of
of neurons & connective tissue cells that are referred to as neuroglia
Benign: Expanding, Pushing
Malignant: Infiltrative and invasive
What is its characteristic
local spread
Benign: Rare
Malignant: Metastasize early or late by lymphatics, blood, or seeding
What is its characteristic
Distant spread
Benign- well-differentiated cells in one mass
Malignant- well differentiated to undifferentiated
What is its characteristic
differentiation
Benign: normal
Malignant: normal to increased mitotic rate
what is its characteristic
mitotic activity
Benign: Normal
Malignant: normal to pleomorphic
What is its characteristics
morphology
Benign: Little(depending in treatment and location of tumor)
Malignant: Life-threatening
What is its characteristics
effect on host
Benign: Normal
Malignant: Normal to accelerated
What is its characteristics
doubling time
Tissue origin: Glandular Epithelium
Benign: Adenoma
Malignant: Adenocarcinoma
Tissue of origin: Squamous epithelium
Benign: Papilloma
Maligant: Squamous cell carcinoma
Tissue of origin: connective tissue smooth muscle
Benign: Leiomyoma
Maligant: Leiomyosarcoma
Tissue of origin: hemtaopoletic
Benign: none
Malignant: Leukemia
Tissue or origin: Lymohireticular
Benign: none
Malignant: Lymphoma
Tissue of origin: neural
Benign: Neuroma
Malignant: Blastoma
What are the sites for squamous cell carcinoma
Oral Cavity
Pharynx
Lung
Anus
Cervix
What are the sited for adenocarcinoma
colon/ rectum
endometrium
prostate
What site is infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) located
Breast
What site is astrocytoma located
brain