PC1- 4.1:Allergic Rhinitis, Cold and Cough Self-Care
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
True or False
There is limited evidence of dietary supplements in the treatment of common cold
True
Some dietary supplement only help in the _______________ not ________________
prevention
treatment
What are some supplements with limited evidence for possible effectiveness on common cold
Ginseng
Echinacea
Elderberry
Green Tea

What are some supplements with inconclusive or insufficient evidence for common cold
garlic
mistletoe
German Chamomile
Vitamin C
Zinc
Andrographs

mainly used to support immune system functions and prevent repeated cold infections, may reduce risk of respiratory tract infections in immunocompromised patients
American Ginseng
(Panax ginseng)
in combination with andrographis may reduce symptoms and shorten duration of symptoms
Siberian (Korean) Ginseng,
(Eleutherococcus senticosus)
True or False
American ginseng and Siberian Ginseng is the same and can be compared
FALSE
difference in extract composition!
Limitations for Ginseng in common cold
Pregnancy
(teratogenic effects)

What strength of Ginseng is safe for adults when using for common cold
100-3000 mg per day for 10 days
Should Ginseng be used short term or long term?
Short
American Ginseng standardization is _________ %of _____________ while Siberian Ginseng is _________ %of _____________
3-5%, ginsenosides
0.1-0.3%, eleutherosides
Ginseng interactions are moderate with ___________ active drugs
CNS
(alcohol, benzodiazepine)
DO NOT USE Ginseng in patients on what therapy as this is a MAJOR interaction
Warfarin
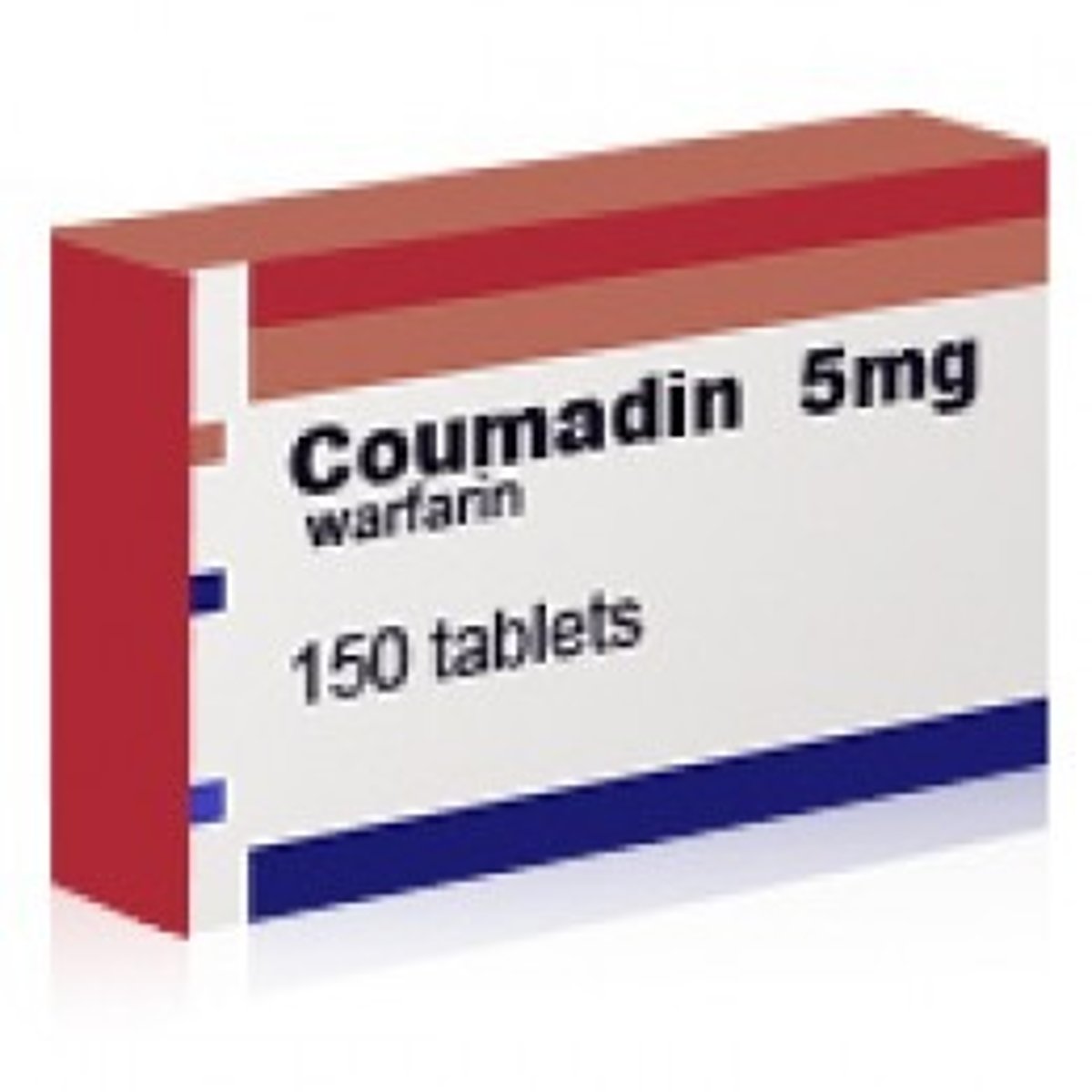
Moderate drug interactions with Ginseng
Antidiabetes
Antihypertensive
MAO inhibitors
3 species that Echinacea comes from
Echinacea pallida, Echinacea angustifolia, or Echinacea purpurea,
In clinical trials, Echinacea showed to prevent the common cold by reducing symptoms by
50-60%
Echinacea shows more evidence in the ____________ of common cold
prevention
Most preparations of Echinacea are liquid _____________ extracts and the dosing is usually _________ mL , __________ times daily
hydroalcoholic
5
2-6
Plant parts used for Echinacea are from
roots or herbs
Most common standardization of Echinacea root extracts is to _________ and _________
alkamides and polysaccharides
Above-ground Echinacea extracts are standardized to ________and __________
echinacosides and complex polysaccharides
True or False
Standardization may be linked with effectiveness in Echinacea
FALSE
Traditional uses for Echinacea
inflammations, fever, dizziness, blood purification, rattlesnake bites, colds, wound healing, general immune stimulant
Clinical use of Echinacea
treatment of the common cold ,anti-inflammatory effect after intravenous application
standardization of aerial parts of Echinacea purpurea
3.5% echinacoside
Dosing for Echinacea purpurea
900mg/day divided into 3 doses
MOA of Echinacea
inhibition of hyaluronidase
inhibition of prostaglandin synth
inhibition of COX-2
Root extracts of Echinacea exert what effects
antiviral and antifungal
leaf and aerial part extracts of Echinacea are linked to what effect
immunomodulatory
Proposed active ingredient of Echinacea
Echinacosides
only what part extract is standardized to Echinacosides
Echinacea purpurea aerial
true or false
Alkamides and polysaccharides in Echinacea are not usually standardized
true
Alkamides and polysacchardies are used as __________ substance substances for Echinacea
marker
Echinacea should not be given _________ due to potential allergic interactions and leukopenia
intravenously
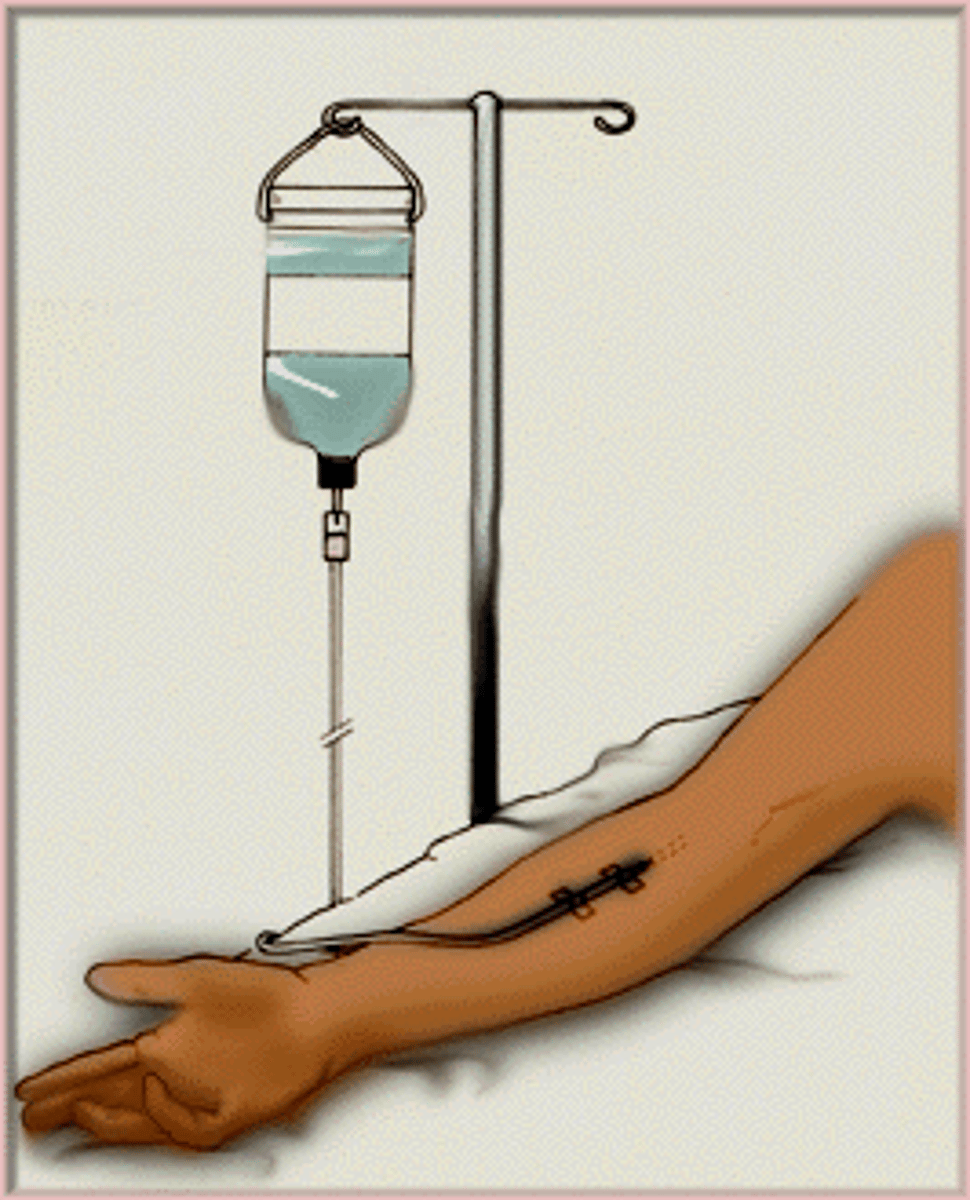
Echinacea can cause counteractive effects on patients with on what drugs
immunosuppressants

True or False
Echinacea is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation
FALSE it is actually not!
Clinical trials reported reduction in _________ of the common cold but it not significantly different compared to placebo
duration
Adverse effects of Echinacea are _______ with mostly just mild _______ upset
rare
GI
Patients with an __________ allergy should caution use of Echinacea and you should counsel them about using __________ or _________ instead
Asteraceae
Chamomile or calendula
Avoid use of ____________ agents and ___________ drugs with Echinacea
chemotherapeutic
immunosuppressant
Can Echinacea be used in children?
Yes, but short term
Echinacea effectiveness depends on
extract formulation
dosing
Moderate drug int with Echinacea
Caffeine
CYP 1A2 substrates
CYP 3A4 substrates
Immunosuppresants
Minor drug Interaction with Echinacea
Midazolam
Sambucus nigra, Caprifoliaceae
Elderberry
Traditional uses for Elderberry
flavoring agent
diuretic
laxative
astringent
Clinical uses of Elderberry
treatment of influenza, potential immune system activation, anti-hepatotoxi
Most preparations of Elderberry contain
100-150 mg of anthocyanins or flavonoids,
Daily doses of Elderberry in clinical trials range from
400 mg to 2 g dried berry extract
MOA of Elderberry
prevention of hemagglutination of release of viral particles for influenza A and B strains
reduction in HIV and herpes simplex replication through antigen production stimulation
Active ingredients in Elderberry
anthocyanins
sambunigrin
plant lectins
Which ingredient in elderberry is responsible for hemagglutination
plant lectins
Elderberry has moderate interaction with
immunosuppressant drugs
Is pregnancy contraindicated in Elderberry use?
No
Green tea latin name
Camellia sinensis, Theaceae

Traditional uses of Green Tea
appetite suppressant
increase sexual drive,
malaria,
dysentery,
diuretic,
stimulant,
immune modulator
Clinical uses of Green Tea
ergogenic,
neuroprotective, & nootropic effects, cardiovascular protection,
antimicrobial
Pure caffeine green tea can be taken in doses of _____________ but no more than _____________a day
100-200 mg
500 mg
Polyphenol-rich extracts in green tea may contain up to ____________ mg of epigallocatechin-gallate
800
What is responsible for stimulant and nootropic effects in green tea
Caffeine

What ingredient in green tea is responsible for calming and anxiolytic effects through action on central GABAA receptor
L-theanine
What has strong antioxidant and antiviral effect in green tea
Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG)
Green tea ____________-rich extracts exert antiviral effects,
polyphenol
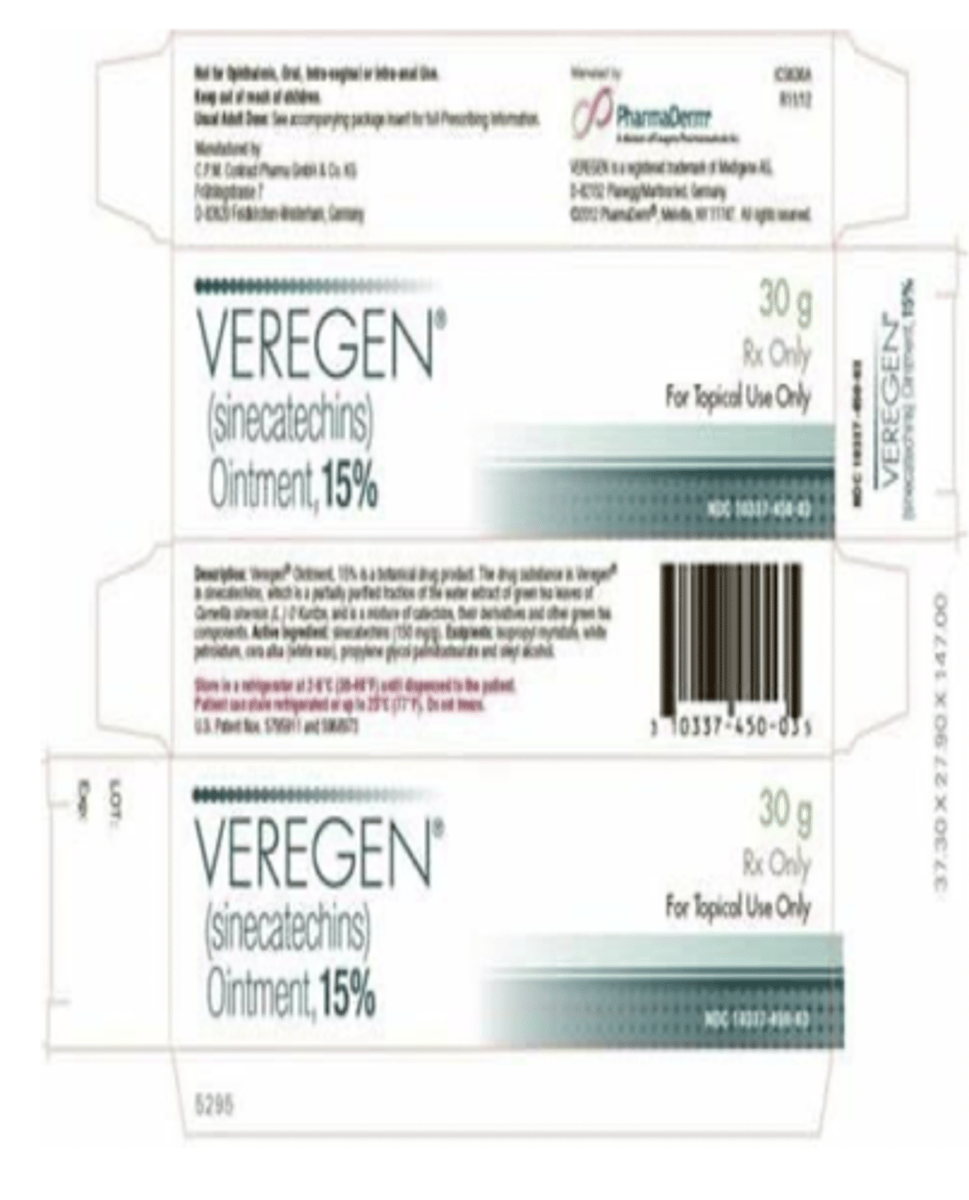
FDA approved green tea extract marketed as __________ and _______________ ointment is used for genital warts, special formulation of sinecatechins
Veregen
Polyphenon E
Due to the caffeine content in green tea, there are moderate drug interactions with
diuretics
antihypertensive drugs
Minor interactions with Green Tea
Alcohol
antidiabetes
contraceptives
Fluconazole
Mexiletine
Terbinafine
Major interaction with Green tea
Ephedra
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) showed modest effects of reducing common cold duration by _________ days but is inconsistent between studies
1-1.5

Higher doses of Vitamin C are needed to achieve potential benefit of more than _______
2g
Doses above 2g may results in adverse effects such as
kidney stones
GI upset
No relationship between vitamin C ______________ and reduced risk of contracting common cold in adults or children alike
supplementation
Only route of Vit C supplementation is ________; any other route is not a dietary supplement but _____ administration is FDA-approved drug
oral
IV

________ is a micronutrient electrolyte that is essential in enzymatic processes and cellular processes including immune regulation and response
Zinc
Upper daily limit of Zinc intake is _______ mg, should not be exceeded through supplementation
40
Oral supplementation with zinc lozenges can contain between _________ mg of elemental zinc as its sulfate or acetate salt
9-34
Zinc May reduce ______ and __________ of common cold if taken at symptom onset although clinical studies are limited and show only marginal improvement
severity
duration

Zinc ______ __________ remains controversial since it may lead to high absorption with subsequent copper deficiency
nasal spray
___________ was associated with certain Zicam products, since been withdrawn from US market
Loss of smell
Zinc lozenges can be taken every____ hours until symptom improvement, do not exceed more than ____ lozenges per day in adults, ______ in children (also consider upper daily limit 40mg!)
2
6
4
______-term Zinc use is regarded as safe, adverse effects are limited to potential ______ and ___________
short
constipation
N/V

Do not recommend supplement use in immunocompromised patients, including ________ or_______
toddlers
elderly