Vitals, Secondary, SMR
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Heart Rate/Pulse Rate
Palpate for 10secs (x6)
Rate, rhythm, volume
Adequate cardiac output produces palpable pulses (CO = SV x HR)
Normal: 60-100 bpm
Tachycardia > 100 bpm
Bradycardia < 50 bpm
Heart Rate/Pulse Rate Issues
Make sure you’re not feeling your pulse
Become confident in finding pulses
Don’t cut off circulation
If irregular hr, count 60 secs
Blood Pressure
Measures pressure exerted by blood against the arterial walls (mmHg)
Normotensive SBP > 100mmHg
Hypertensive SBP > 140mmHg
Hypotensive SBP < 90mmHg
Non-Invasive BP (NIBP)
Mean Arterial Pressure
Average pressure in arteries in cardiac cycle
MAP = CO x SVR (system vascular resistance: tightly arteries are squeezed)
MAP = 1/3 SBP x 2/3 DBP (70-110mmHg) (<60 mmHg affects organ perfusion)
Korotkoff Sounds
P1: Sharp Tapping
P2: Whooshing Sound
P3: Soft Thump
P4: Muffled Fading Sounds
P5: Silence
Blood Pressure Issues
Positioning, loud noises and movement
Respiratory Rate
15 secs (x4)
Rate, rhythm, depth
Normal: 12-20 breaths/min
Tachypneic > 28 bpm
Bradypneic < 10bpm
Respiratory Rate Issues
Can’t see
Change breathing pattern
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
Red vs IR light absorption through periphery
Measures haemoglobin % saturation
Finger, toe, ear
Aerobic cell metabolism
Normal: 94-100%
COPD: 88-92%
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) Issues
Nail polish (try sideways)
Cold (inaccurate reading)
Light (other light gets in) (use blanket)
Motions (sometimes opens & closes)
Dirty Hands (alcohol wipe)
Fidget with it (blanket)
Carbon Monoxide (CO makes high reading)

SpO2 Waveform
Normal Signal

SpO2 Waveform
Low Perfusion
SpO2 Waveform
Noise Artifact

SpO2 Waveform
Motion Artifact
Temperature
Tympanic (ear), oral (mouth), axillary (armpit), rectal (anus), infrared (forehead)
Used for diseases and environmental illnesses
Normal: 36-37 C
Hyperthermic > 38 C (febrile)
Hypothermic < 35 C
Temperature Issues
Placement of tympanic
Hearing aids increase temp (wait a few)
Blood Glucose Levels (BGL)
Glucometer and test strip or finger prick (lancet)
Ensure optimal levels of glucose in body
Normal: 4-8mmol/L (different for diabetics 12-20 is normal)
Hyperglycaemic > 18mmol/L
Hypoglycaemic < 4mmol/L
Blood Glucose Levels (BGL) Issues
Cold fingers (not enough blood)
Use on side of finger (blood thinners)
If just squeezing (run fingers down to encourage bloodflow)
Wait for alcohol wipes to dry (get lower reading)
Don’t clean fingers (higher reading)
Glucometer doesn’t like cold
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Access neurological function (what’s normal for them)
Eyes (none, pain, verbal, spontaneous)
Verbal (none, incomprehensible sounds, inappropriate words, confused, oriented)
Motor (none, decerebrate, decorticate, withdraws from pain, localizes to pain, obeys commands)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Issues
Not suitable for people that are drunk, ods, not wanting to speak or dozing off
Pupils
Access neurological function
Size, equal, reactive, consensual
PEARL (pupils are equal and reactive to light)
Mydriasis (big ass pupils) (drugs, dead, dark areas)
Miosis (small ass pupils) (opioids)
Anisocoria (different sized pupils) (pressure on one side, ask if normal)
Slow reaction/no reaction
Pupils Issues
Light situations
Shining in both eyes
ECG
3-Lead (4 stickers, 3 views of heart)
12-Lead (10 stickers, 12 views of heart)
Check regularly and match pulses
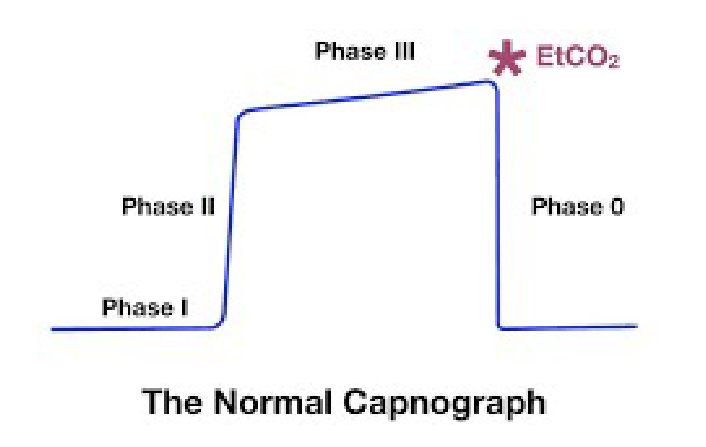
ETCO2
Capnography Line (measures CO2 levels during expiration)
Levels of perfusion, ventilation, circulation, correlates PACO2 (Arterial CO2)
Normal: 35-45mmHg
ETCO2 Issues
Plug into machine before using on patient
Fluid getting into tube
Fidgeting
Mouth breathing (use face mask)
Head & Neck
Bones: Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible
Hair can cover bleeding
TMJ (open and close mouth)
Check eyes oot near nose, csf (halo), oral cavity, drooling, swallowing
Palpate larynx, move neck
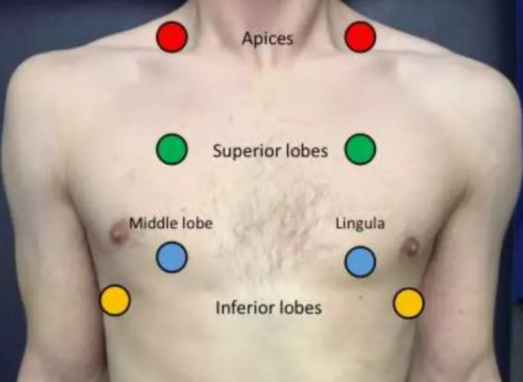
Chest
Palpate clavicles, sternum, anterior and lateral chest walls (symmetry) and subcutaneous emphysema
Feel expansion during expiration
6-point auscultation
Abdomen
Visualize
Palpate all four quadrants, gentle then deep
Flanks
Percuss, lay finger over area and tap first knuckle
Pelvic Fracture
Pubic Rami Fracture

Pelvic Fracture
Straddle Fracture
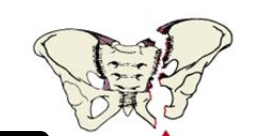
Pelvic Fracture
Vertical Sheer (5-15%)
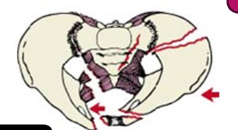
Pelvic Fracture
Lateral Compression Fracture (60-70%)
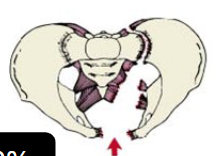
Pelvic Fracture
Anterior and Posterior Compression Fracture (15-20%)
Pelvis
Treat for one, don’t hunt for one
If no obvious injury gentle squeeze, only inspect genitals if needed
Tenderness over lateral pelvis/hip joints (hip dislocations/Neck of
femur fractures)
Legs
Assess pedal pulse and ROM
Look for shortening
Extremities
Assess CSM and look for left/right inequality
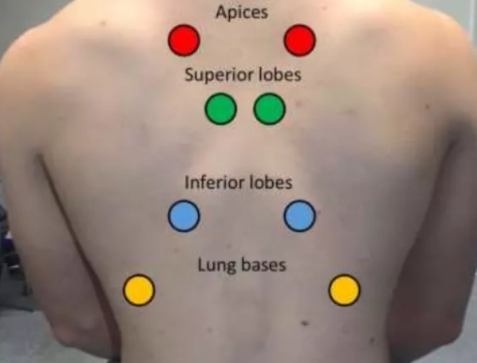
Back
Palpate scapula, vertebrae and ribs on back
SMR
C3/4/5 keeps you alive
Use smr for seniors that fall from standing height
Pulses
Temporal (head), carotid (neck), apical (chest), brachial (arm), radial (wrist), femoral (groin), popliteal (behind knee), posterior tibial (ankle), pedal (foot)