Brain plasticity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
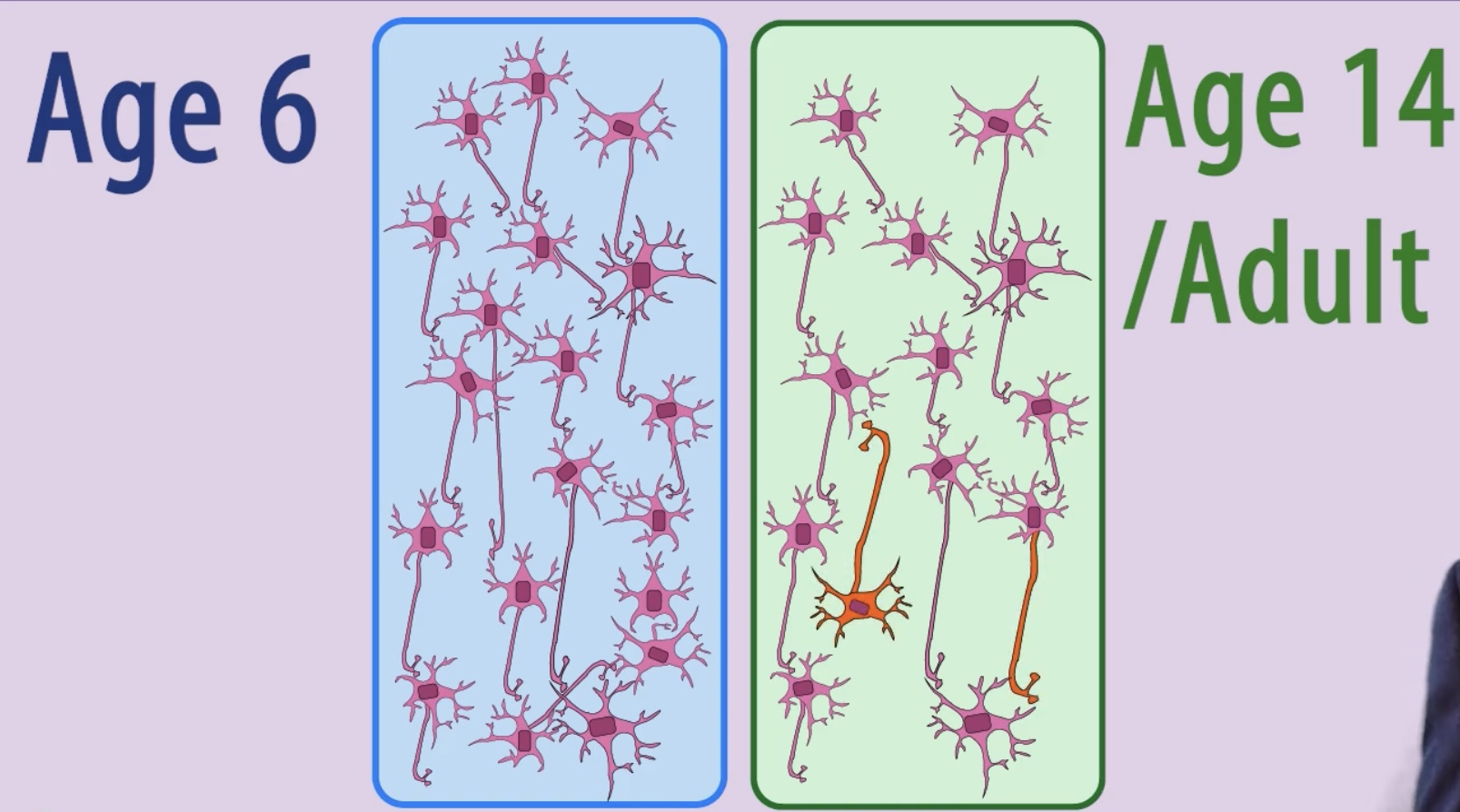
Brain Plasticity
The brain adapts in both its function and structure as a result of a change in the enviroment. These changes could be due to damage, or to meet the cogntive demands of learning new skills
Reasons for Plasticity
Learning new skills
A result of developmental changes
Response to direct trauma to area of the brain
Response to indirect effects of damage such as brain swelling or bleeding (from stroke)
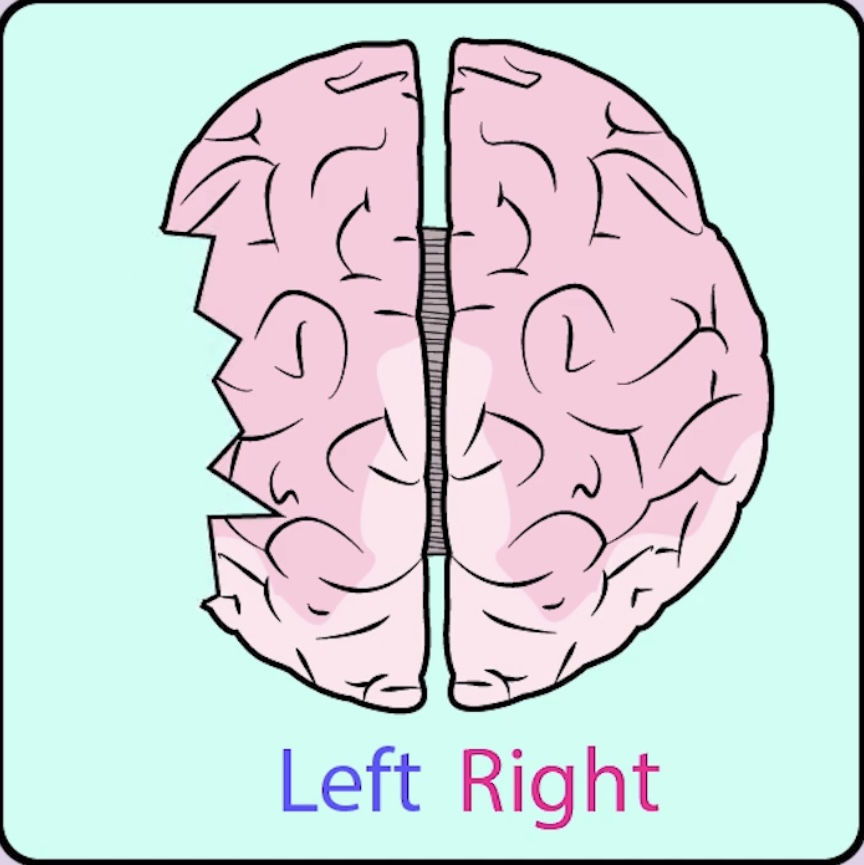
Functional Recovery
The fuctions that were performed by areas of the brain that are lost (nuronal cell death) or damaged are performed by undamaged areas of the brain. - Functional reogansiation
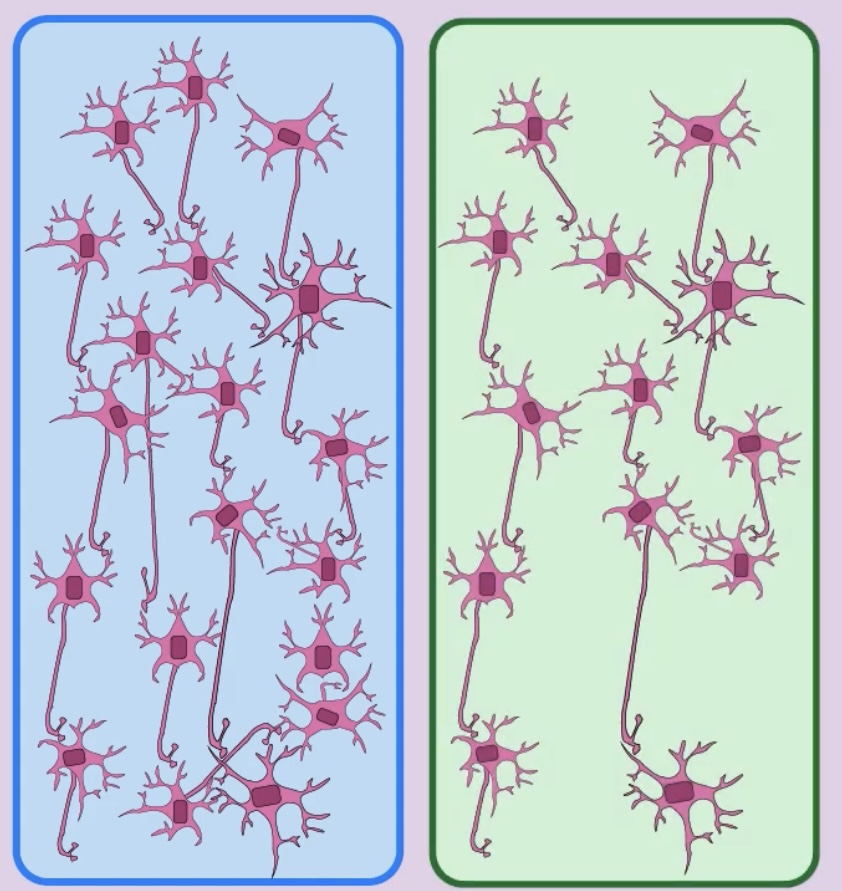
Synaptic Pruning
Synapses that are used frequently become stronger over time, however unused synaptic connections are lost. this makes the brain a more efficient communication system over time.
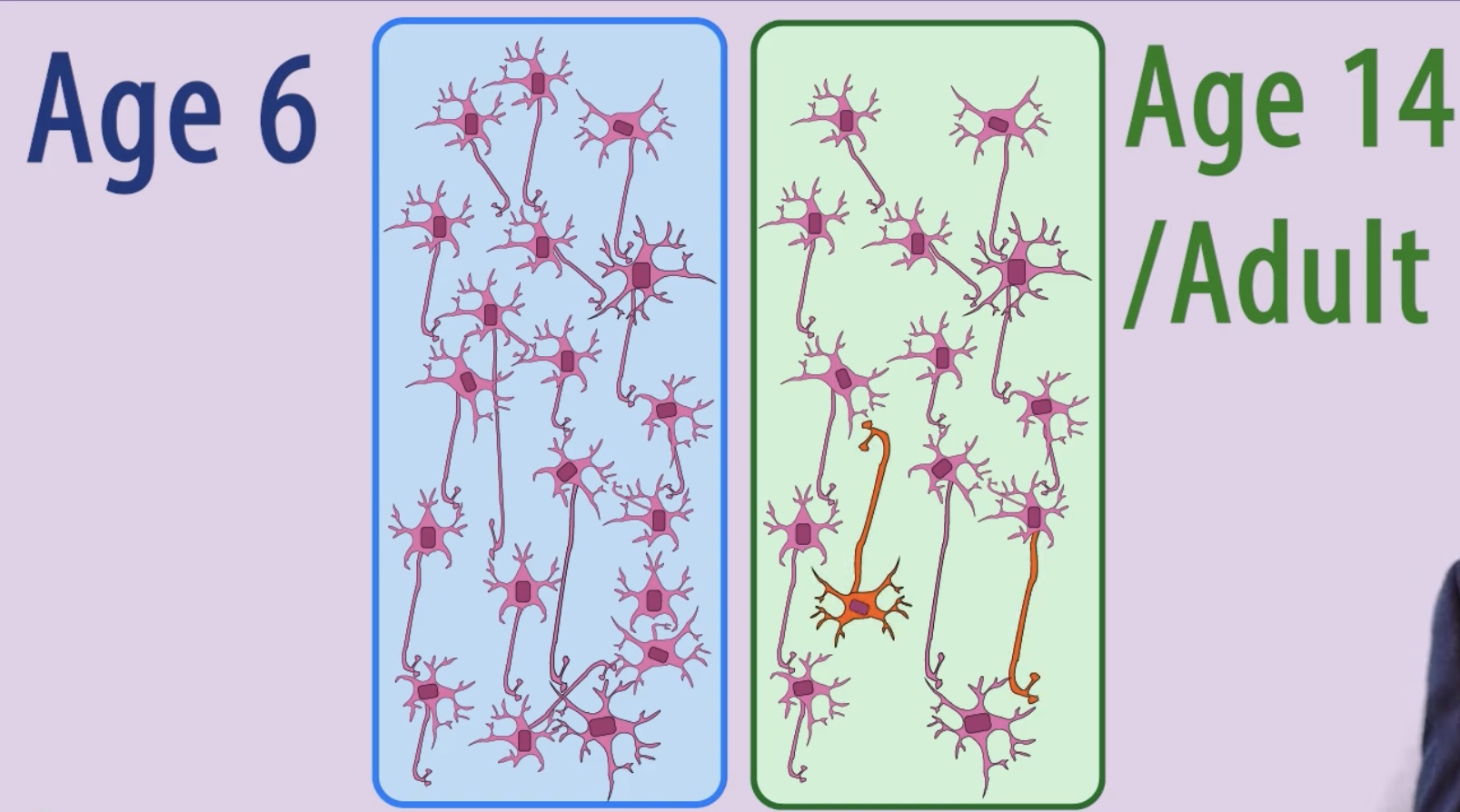
Axonal Sprouting
Existing neurons growing new axons to connect to ajacent neurons. Neural regeneration is the growth of new nuronal cells.
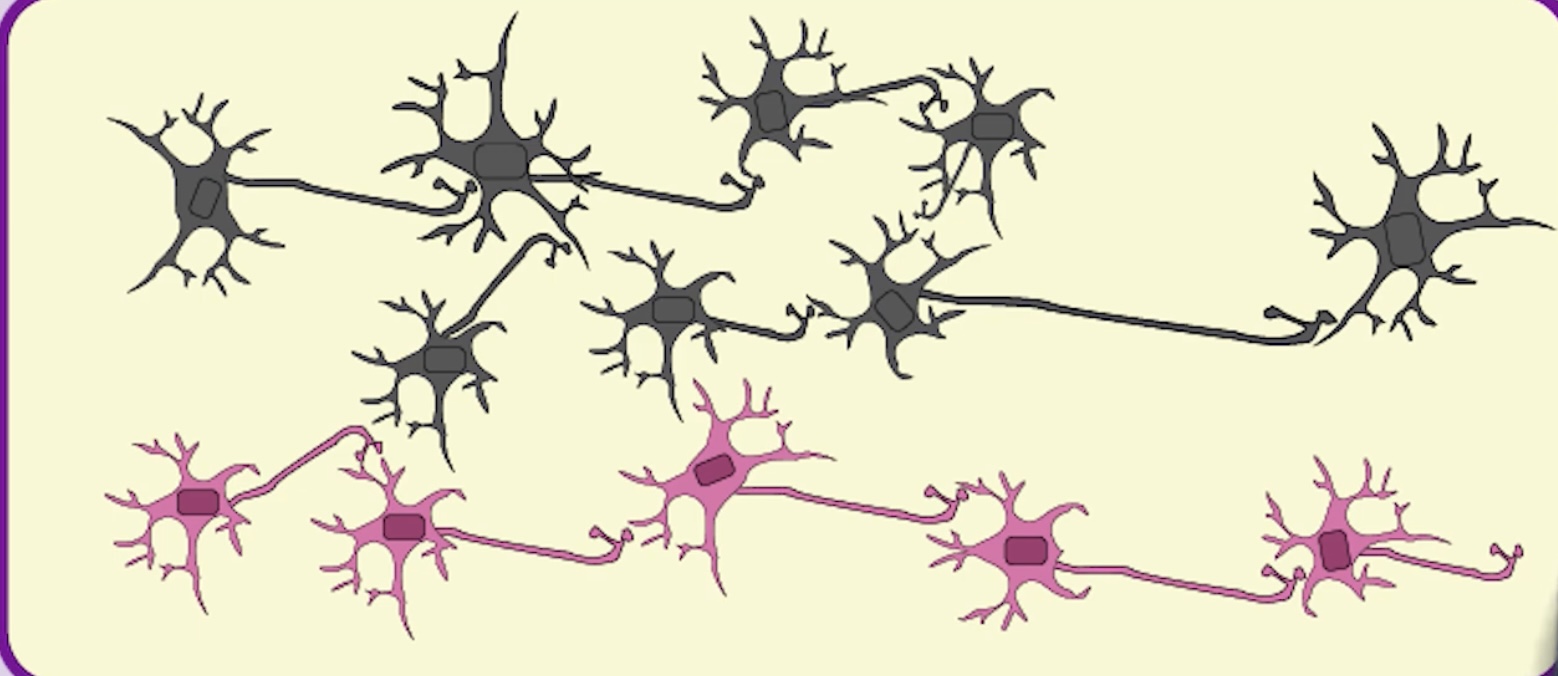
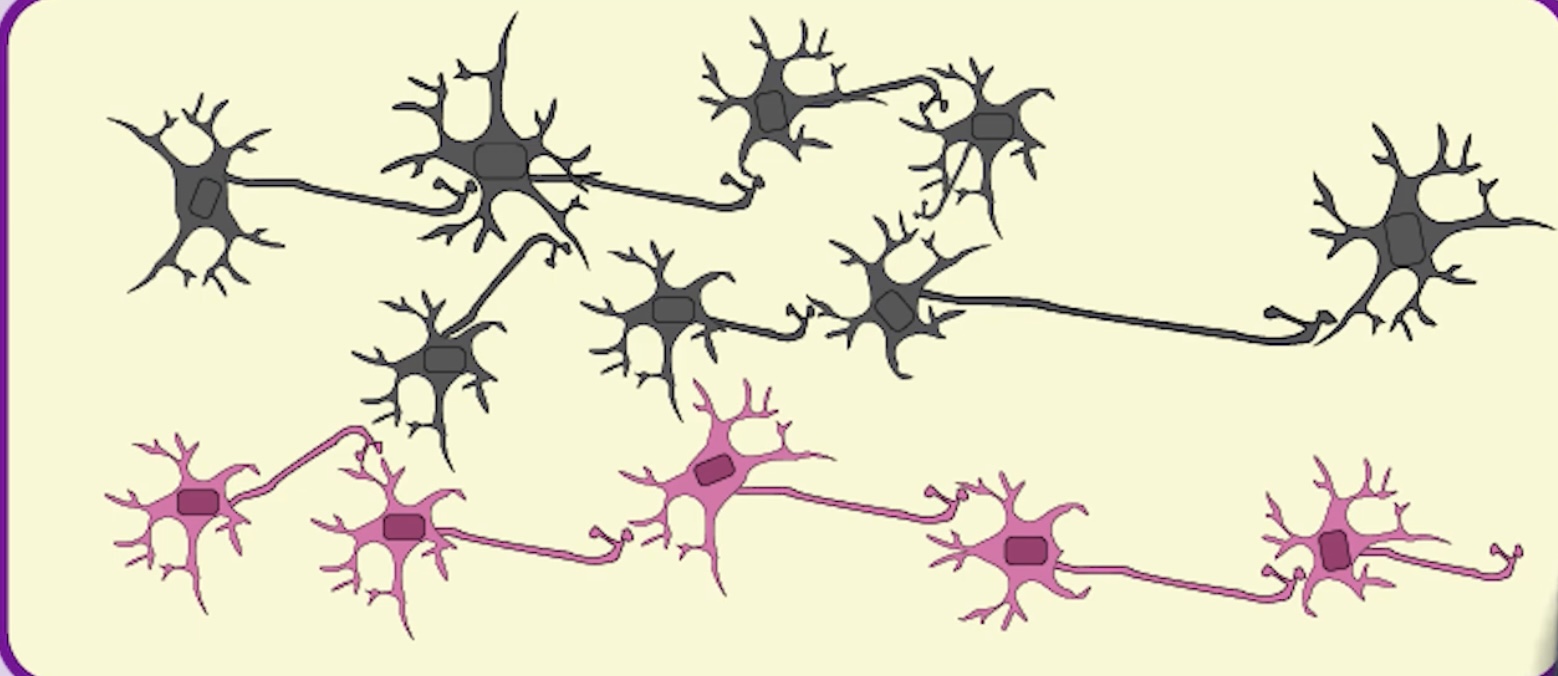
Denervation Supersensitivity
To compensate for the loss of axons in a pathway the remaining axons become more sensitive. (more likely to fire). This can result in side effects such as pain.
Factors affecting functional recovery
Age: Children have the best ability to recover, then young adults.
Gender: Women are more able to recover from brain damage Rehabilitative Therapy: Focused effort results in improvement
Constraint induced therapy
Stopping patients from using coping strategies (like body language for communication or using undamaged limbs for tasks) makes them improve via functional reorganisation.
Research support by Maguire et al. (2000)(Procedure, Findings and Conclusion)
Procedure: Structural MRI Brain scans of 16 male taxi drivers were compared to the brain scans of 16 matched (age, gender) non taxi driver controls.
Findings:The posterior hippocampi in the London taxi drivers were found to be significantly larger than the controls. Also, the size of the posterior hippocampi was positively correlated with the amount of time working as a taxi driver.
Conclusion:This suggests the physical structure of the brain is plastic, able to reconfigure itself to better adapt to psychological demands, in this case to improve memory formation.
Case study by Danelli et al. (2013)
Procedure:Case study of 14-year-old EB. At the age of two and a half EB had a hemispherectomy of the left side of his brain to remove a tumour. This removed the language centres of Broca's and Wernicke's areas.
Findings:Immediately after surgery EB had lost all language ability (aphasia). However, after two years of recovery EB had recovered his language ability. Even without his left hemisphere EB developed normally as he aged asides from some dyslexia like symptoms. researchers noted FMRI scans showed the right hemisphere followed a "left-like blueprint" for language.
Conclusion:This research suggests that the brain can adapt and recover after significant damage, especially early in life, with the right hemisphere taking roles usually performed by the left.
Practical Applications
Research on brain plasticity and functional recovery has practical benefits.
It has been useful in rehabilitative therapy, helping people return to their lives and productive work, ultimately benefiting the wider economy.
Individual differences in recovery
Mathias (2015): Metanalysis demonstrated IQ and educational background are positively correlated with better outcomes after traumatic brain injury, suggesting some individuals have a greater cognitive reserve, helping in recovery.