Insect Sensory Systems
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What are the 5 types of environmental stimuli
touch, sound, heat, smell, light
touch is a _ stimuli
mechanical
sound is a _ stimuli
mechanical
heat is a _ stimuli
thermal
smell is a _ stimuli
chemical
light is a _ stimuli
visual
what are the two types of touch mechanical receptors?
trichoid sensilla and proprioceptor
trichoid sensilla are:
hair-like cuticular projections
what are the 3 parts of trichoid sensilla:
trichogen cell, tormogen cell, sensory neuron
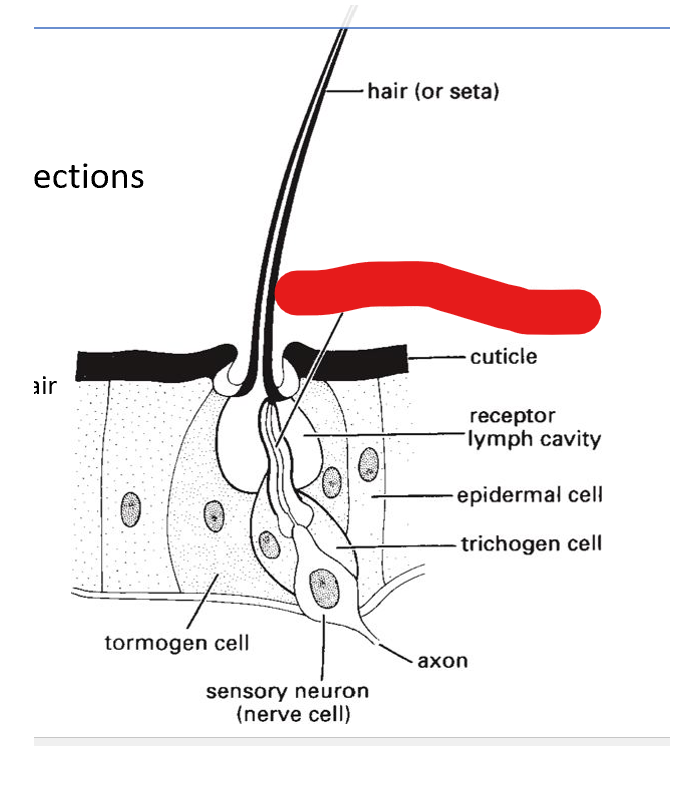
dendrite of sensory neuron
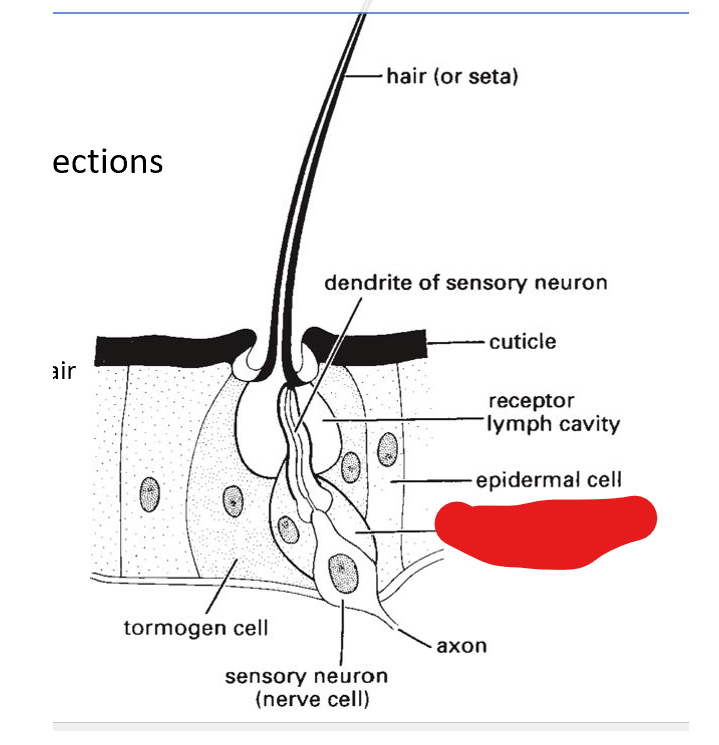
trichogen cell
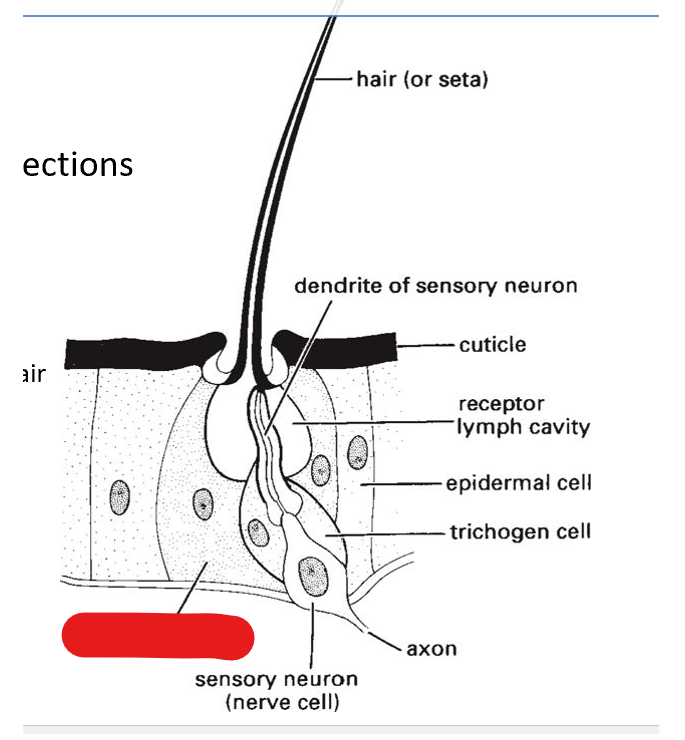
tormogen cell
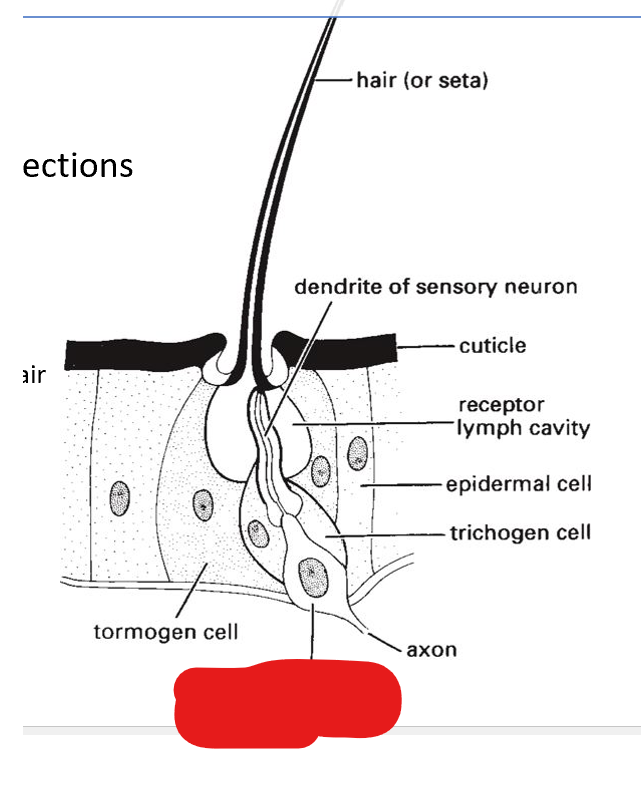
sensory neuron
hair-like cuticular projections involved in touch are:
trichoid sensilla
in trichoid sensilla, the trichogen cell:
grows the hair
in trichoid sensilla, the tormogen cells acts as the:
socket
in trichoid sensilla, the sensory neuron dendrite:
extends into the hair
what part of trichoid sensilla grows the hair?
trichogen cell
what part of trichoid sensilla acts as the socket?
tormogen cells
when trichoid sensilla are moved, they send a _to the brain, _
impulse, indicating movement
sensilla differ in their _
sensitivity
proprioceptors are used to detect:
self-positioning
proprioceptors are associated with:
joints, muscles, cuticle
propriorecepts function by:
sensilla on plate rubbing against another part of the body
sound is mainly used for what 2 functions?
find a mate and detect predators
the two main forms of sound reception are:
non-tympanal and tympanal
non-tympanal detects sound through:
specialized sensory hair
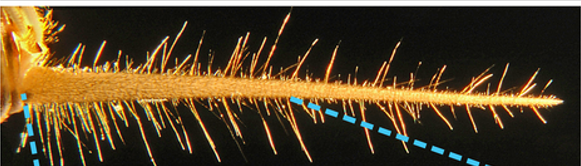
why are the trichoid sensilla on the cersi of this cricket different lengths?
to detect different frequencies
what is an example of a chordotonal organ?
Johnston’s organ
chordotonal organs are composed of:
scolopidia
scolopidia make up:
chordotonal organs
scolopidia, making up chordotonal organs, are composed of what 2 types of cells:
cap and scolopale
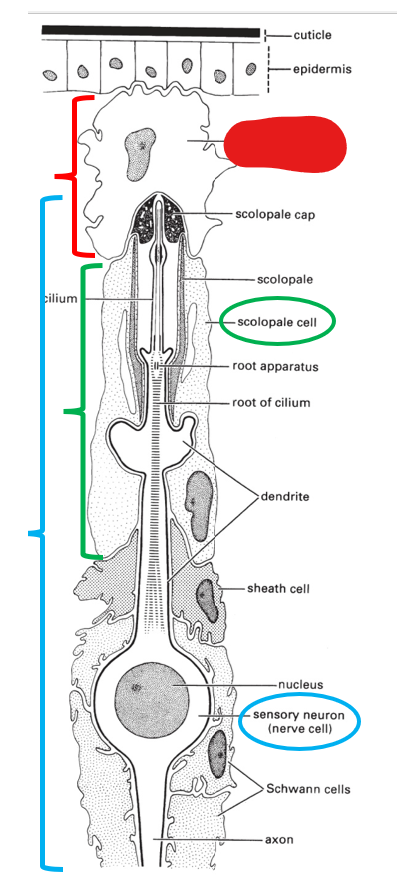
what is this portion of the scolopidium (making up chordotonal organs) called?
cap cell
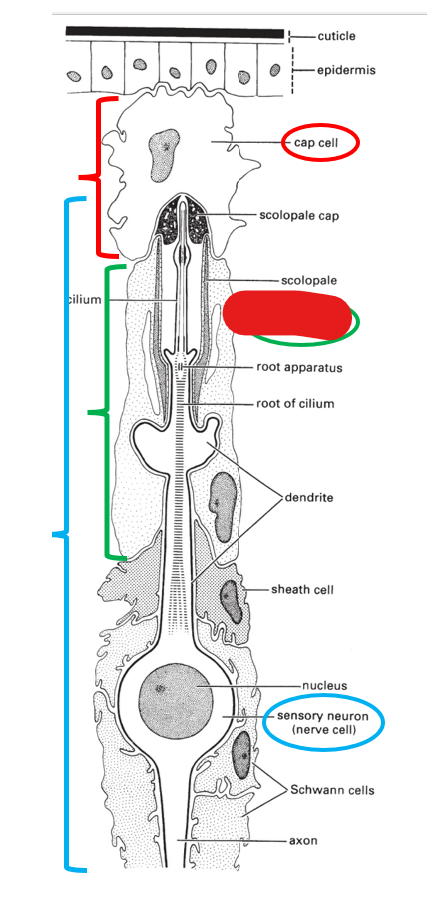
what is this portion of the scolopidium (making up chordotonal organs) called?
scolopale cell
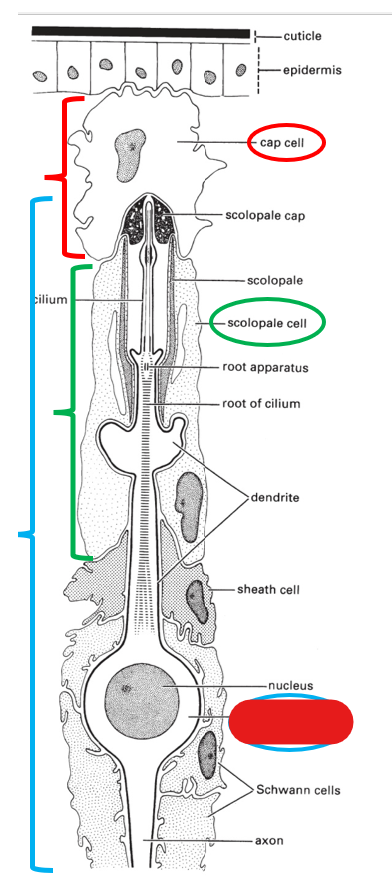
what is this portion of the scolopidium (making up chordotonal organs) called?
sensory neuron
the cap cell in scolopidia act similar to a:
tympanum
the scolopale cell in scolopidia:
house the dendrite of a nerve cell
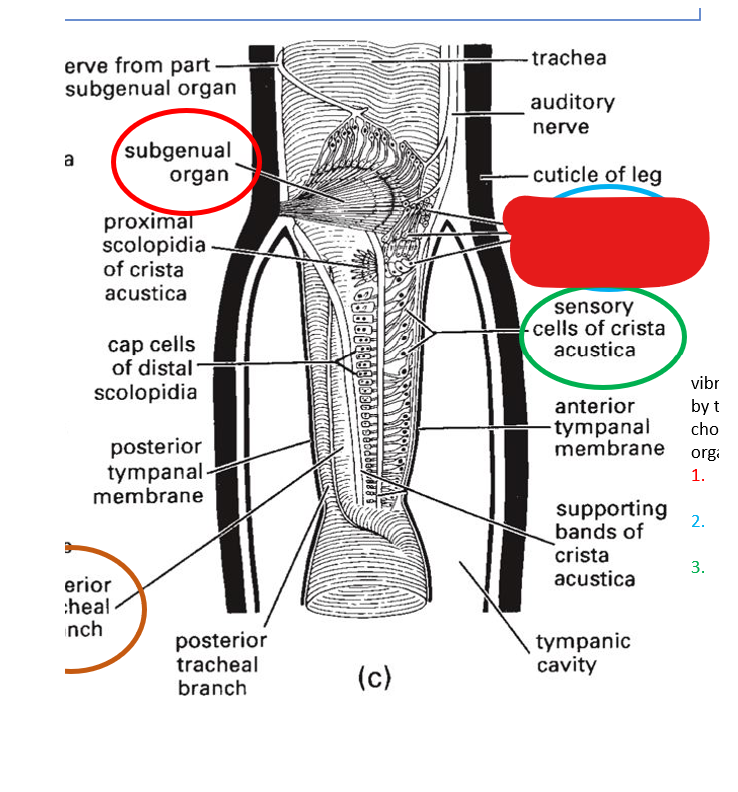
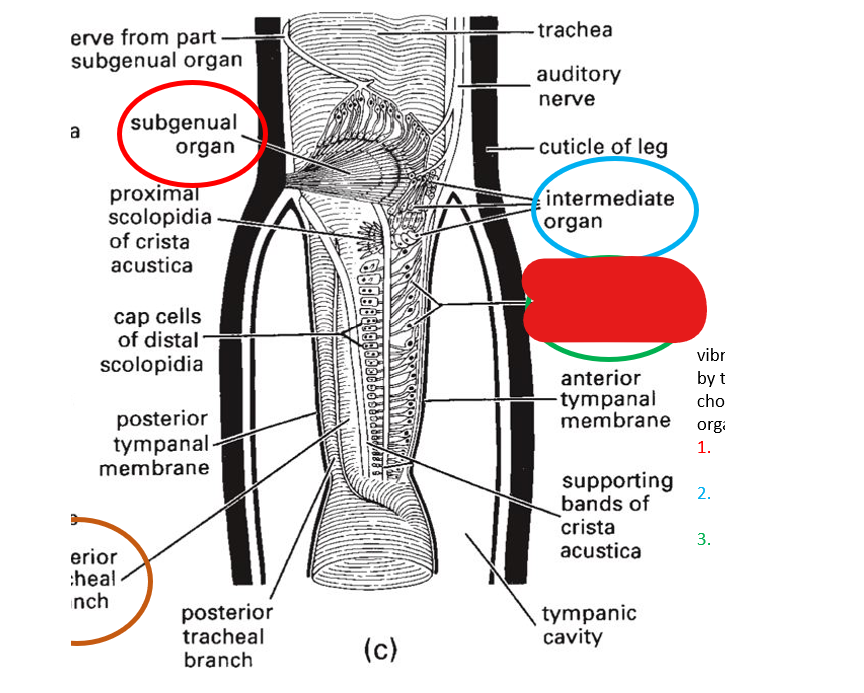
the subgenual organ detects:
substrate vibrations
where is the subgenual organ located?
hemocoel of the tibia
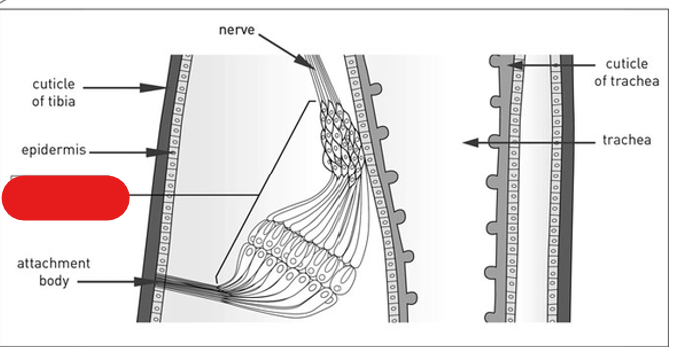
subgenual organ
where is the johnston’s organ located?
pedicel of antennae
tympanal sound reception involves:
specialized proprioceptors
define tympanum
cuticular membrane that vibrates from airborne vibrations
what is like an ear
tympanum
sound enters through the _ and is amplified in the _
acoustic spiracle, acoustic trachea
sound enters the _ where it vibrates the _
tibia, tympanum
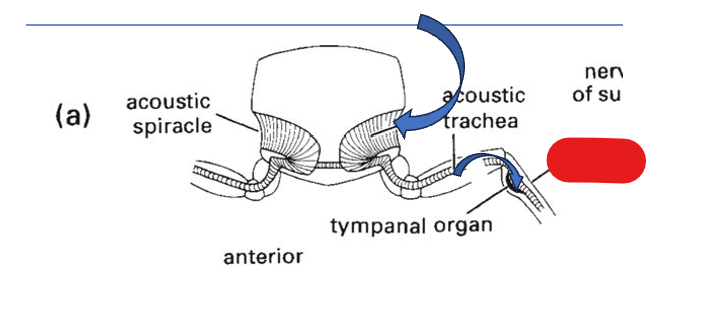
tibia
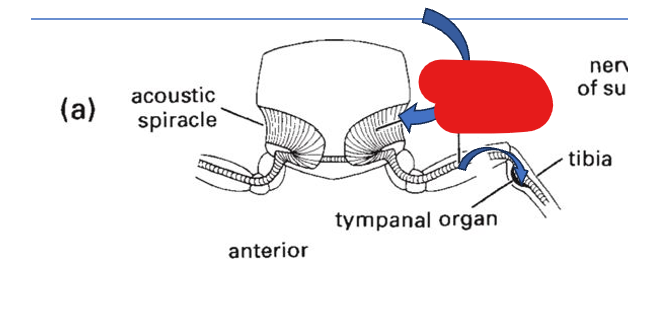
acoustic trachea
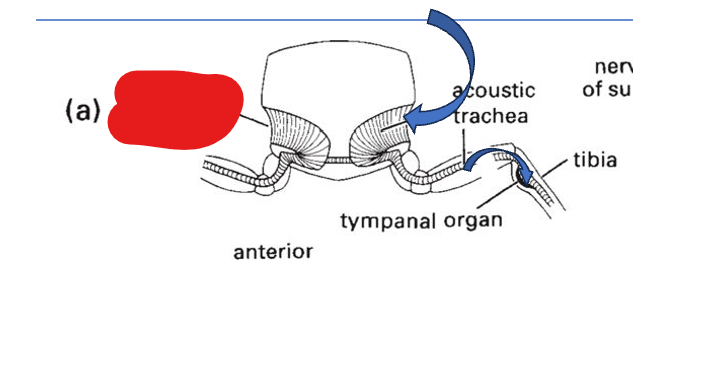
acoustic spiracle
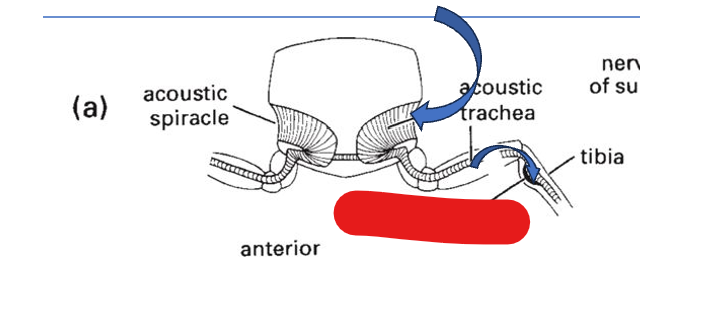
tympanal organ
specialized proprioceptors make up:
tympanal sound reception
what may allow for directional hearing?
slits in the tympanic cavity
vibrations are detected by what 3 chordontal organs?
subgenual organ, intermediate organ, crista acustica
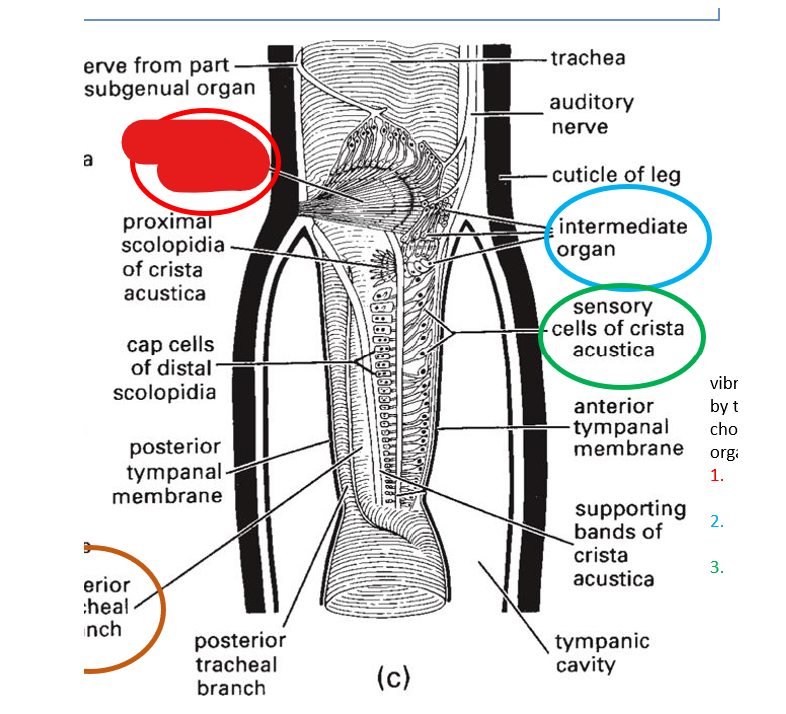
subgenual organ
intermediate organ
sensory cells of crista acustica
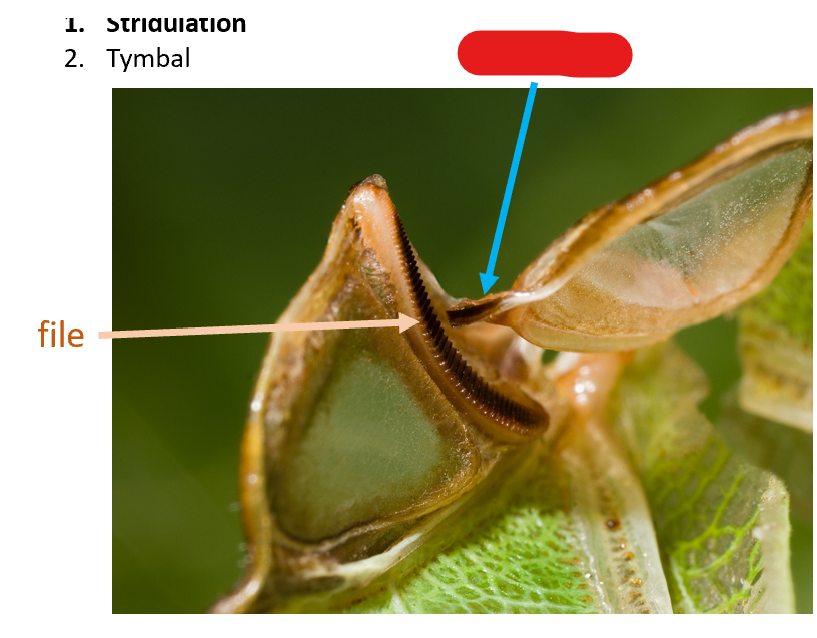
what are the two types of sound production?
stridulation and tymbal
stridulation creates sound by:
file and scraper

scraper
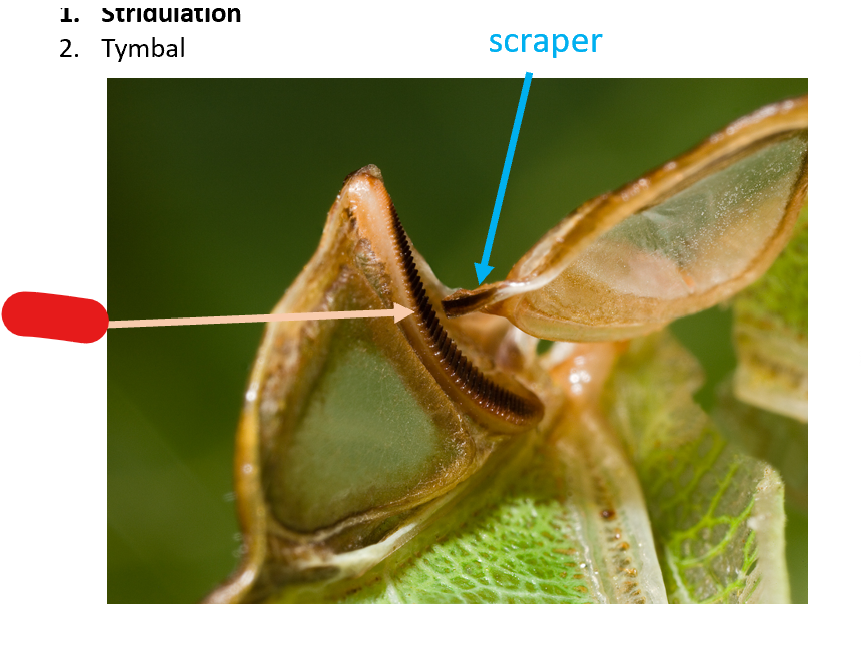
file
what sound is created by a file and scraper mechaism?
stridulation
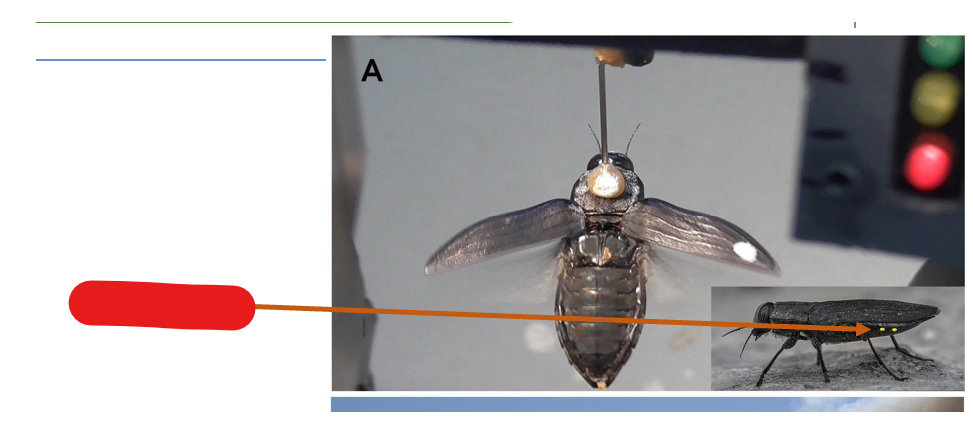
the tymbal creates sound when:
an elastic cuticle deforms
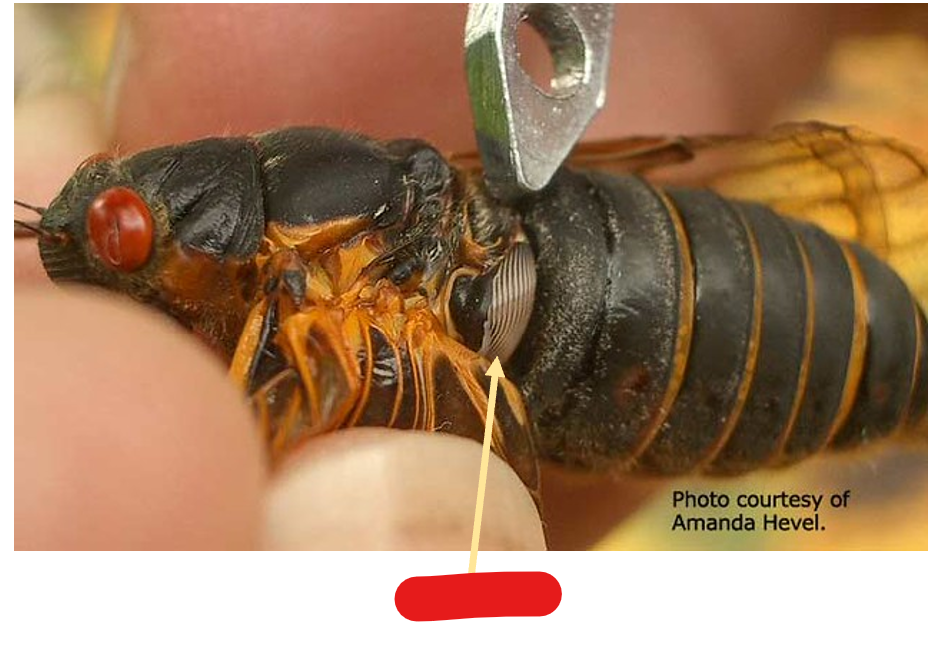

tymbal
elastic cuticles deforming creates what type of sound?
tymbal
thermal pits
there are thermal receptors in:
antennae, legs, pits
insects are temperature conformers, aka _
poikilothermic
ectothermic behaviors include:
sun basking and stilting
an endothermic behavior is:
flight
surface are to volume ratio impacts:
thermal regulation
insect generally gain and lose heat easily because of their:
large surface area and small volume
taste occurs with:
physical contact
receptors for taste are found in:
mouthparts, ovipositors, antennae, tarsi
receptors for taste in ovipositors are used to:
determine adequate substrate
receptors for taste in tarsi are used to:
cue feeding response
smell is detected through:
air
sensilla are:
chemoreceptors
sensilla can be _ or _
uniporous, multiprous
uniporous sensill are used for _, while mutiporous sensilla are used for _
taste, olfaction
multipored sensillum on the antenna include what 3 cells:
trichogen cell, tormogen cell, sensory neuron
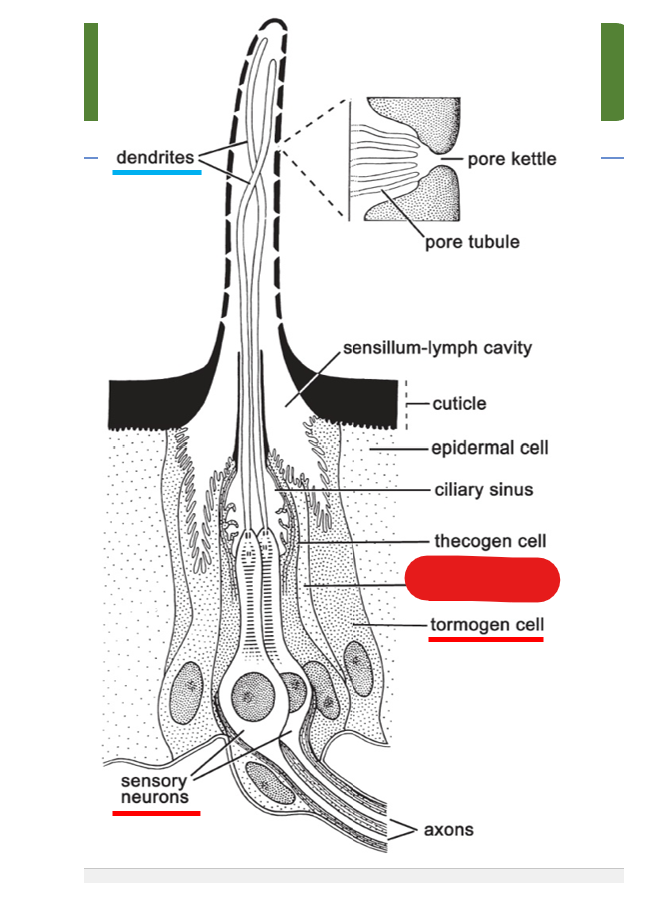
what is shown on this diagram of multipored sensillum on the antenna?
trichogen cell
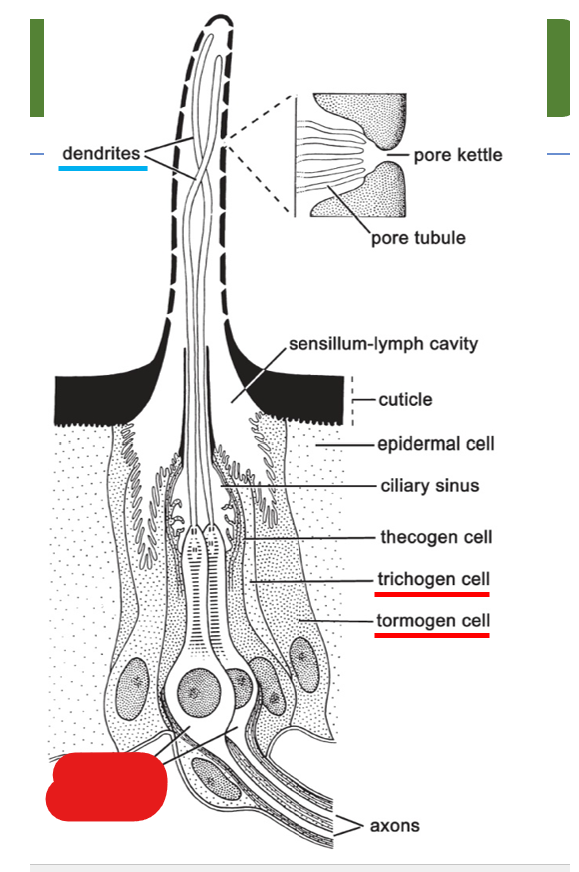
what is shown on this diagram of multipored sensillum on the antenna?
sensory neurons
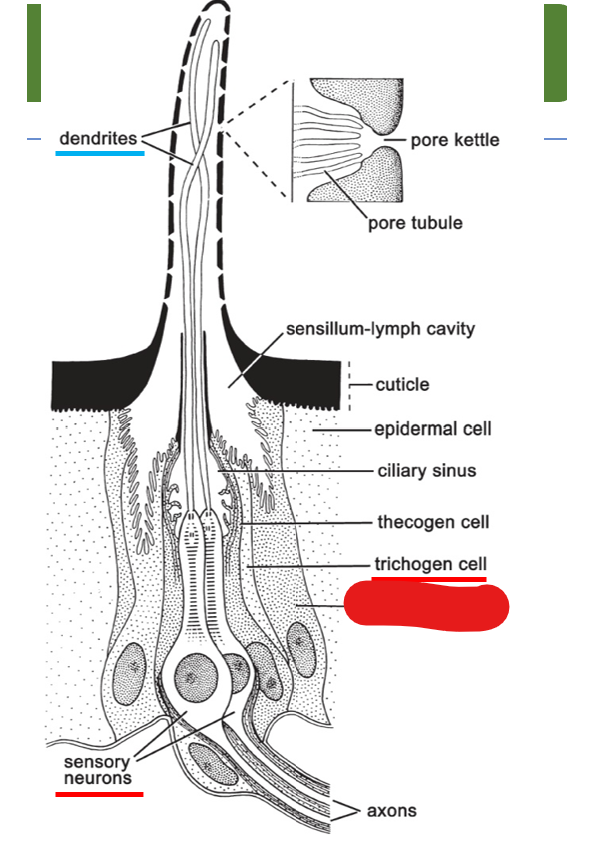
what is shown on this diagram of multipored sensillum on the antenna?
tormogen cell
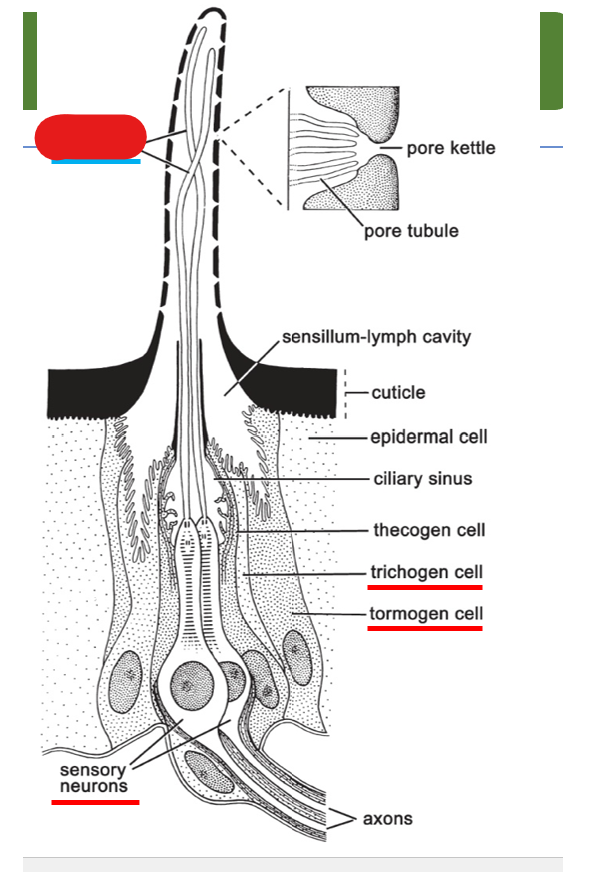
what is shown on this diagram of multipored sensillum on the antenna?
dendrites
describe the general function of sensilla on the antennal flagellum
chemical odorant enters pore, binds with olfaction binding proteins, interacts with chemical-specific receptors, then if chemical is a match it induces a signal and fires the nerve
why do dendrite have different types of sensilla?
to respond to different chemicals
what are two ways that scientists can determine what chemicals insects respond to?
electroantennogram and single-sensillum recording
what does an electroantennogram measure?
electrical response for an entire antenna to a particular volatile compound
single-sensillum recording allows you to:
record the response of a single sensillum to a volatile chemical
what are pheromones?
chemicals produced by insects for attracting other insects
what are 5 types of pheromones?
sex, aggregation, spacing, trail-marking, warning
kairomones have what effects?
producer (-), receiver (+)
an example of a kairomone:
predator hijacks a producers signal
Allomones have what effects?
producer (+), receiver (neutral)
an example of an allomone:
producer telling predators “I don’t taste good”
synomones have what effects?
producer (+), receiver (+)
an example of a synomone:
plant producing pheromone to attract predators of parasites
pheromone with producer (-) and receiver (+) effects:
kairomone
pheromone with producer (+) and receiver (neutral) effects:
allomone
pheromone with producer (+) and receiver (+) effects:
synomone