1.6 Nucleic acids
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exclusion statement: the molecular structure of specific nucleotides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Nucleic acids
polymers made of nucleotide monomers
store, transmit, and express hereditary information
2 forms: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Components of nucleic acids: nucleotides—> polynucleotides—>nucleic acids
Nucleotides
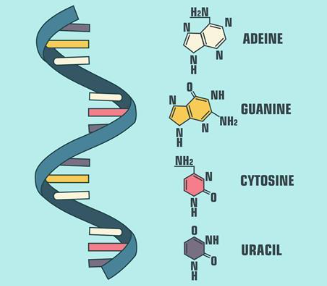
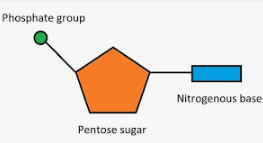
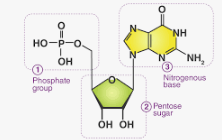
Contains 3 parts: nitrogenous base(adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine,or uracil), five carbon sugar(deoxyribose or ribose), and phosphate groups (in polynucleotides each monomer only has one phosphate group)
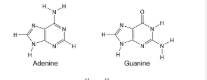
Nitrogenous base
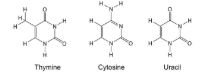
2 types: Pyrimidines and Purines
Pyrimidines are one ring with 6 atoms: Cytosine, Thymine(only found in DNA), Uracil(only found in RNA)
Purines are one ring with 6 atoms bonded to one ring with 5 atoms: adenine and guanine
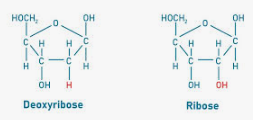
Five Carbon Sugar
A sugar is bonded to the base
in DNA the sugar is deoxyribose (OH H at the base)
in RNA the sugar is ribose (OH OH at the base)
difference in structure and function between the two
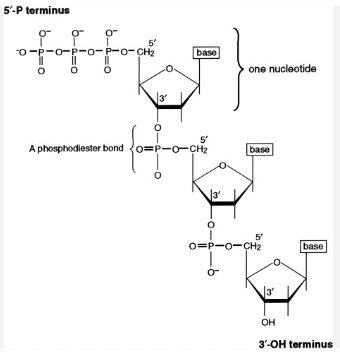
Phosphate Group
A phosphate group is added to the 5’ carbon of the sugar(which is attached to the base) to form a nucleotide
a nucleoside is a portion without a phosphate group
Polynucleotides
Phosphate groups link adjacent nucleotides
phosphodiester linkage
directionality( the measures of the phosphate and hydroxyl ends of the polynucleotides) is 5’ to 3’
the sequences of bases along the DNA or mRNA is unique for each gene
dictates AA sequence
dictates primary structure of a protein
dictates 3D structure of a protein
during nucleic acid synthesis(dehydration reaction), nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the growing strand, resulting in the formation of covalent bonds between nucleotides
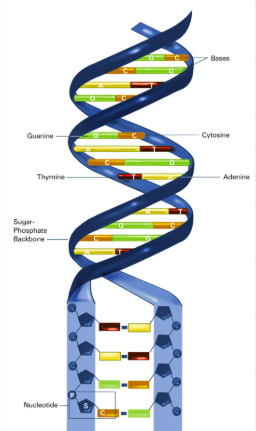
DNA
consists of two polynucleotides
forms a double helix
strands are antiparallel( 2 strands of its double helix run in opposite directions, one in 5’ to 3’ direction and the other in the 3’ to 5’ direction)
strands are antiparallel for the sugar phosphate backbone to form a stable structure and have proper DNA replication and transcription
held together by hydrogen bonds between bases
cytosine binds to guanine (C to G) with 3 hydrogen bonds
adenine binds to thymine (A to T) with 2 hydrogen bonds
the backbone is the sugar phosphate backbone
sugar is deoxyribose
more stable than RNA
double stranded
function is to store long term genetic info
found in the nucleus of a cell
RNA
single stranded polynucleotide
variable in shape due to base pairing within RNA
adenine bonds to uracil (A to U)
cytosine bonds to guanine (C to G)
sugar is ribose
more reactive than DNA
function is to be a messenger and carry genetic info
found in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria in eukaryotic cells