PA Envirothon - Soils, PA Envirothon Soils
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
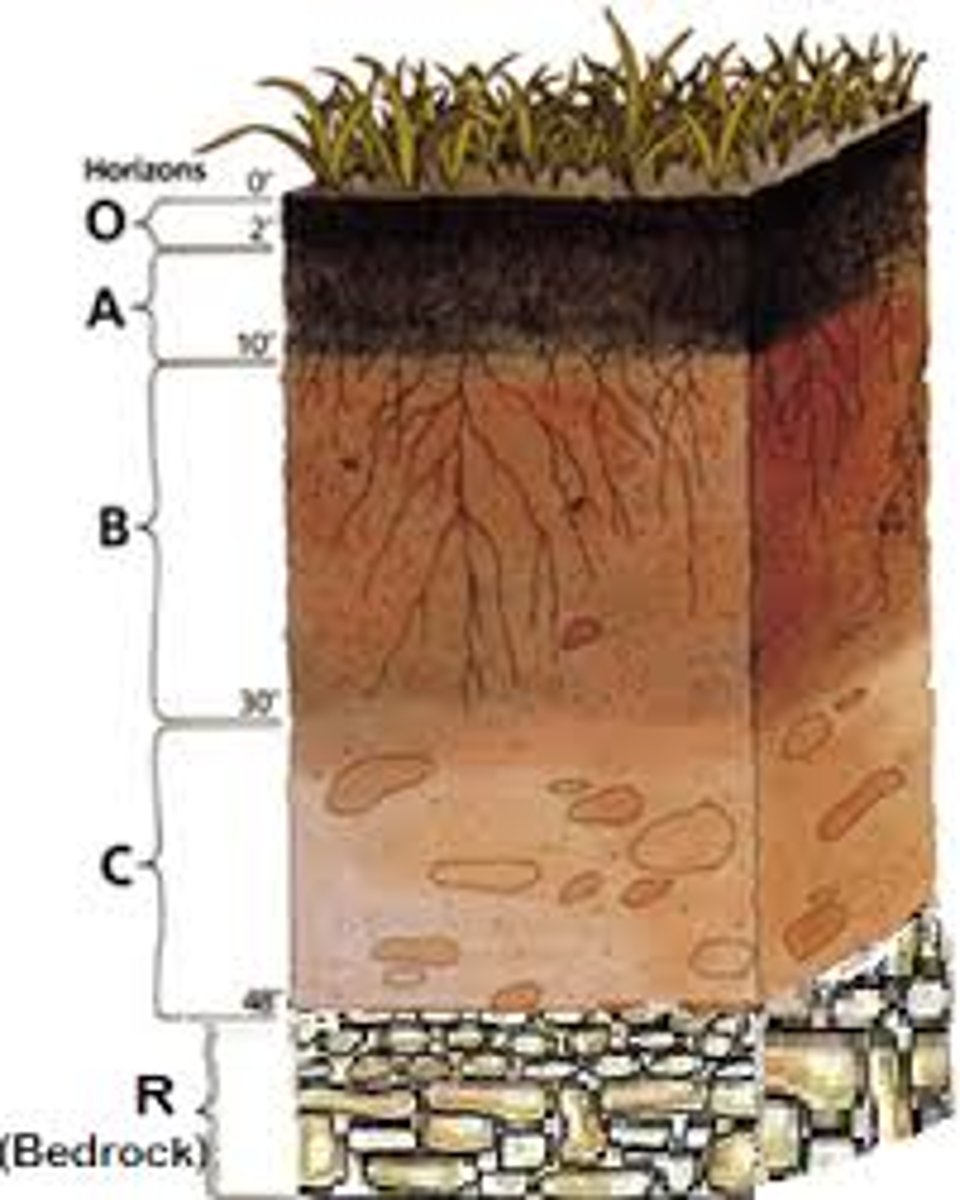
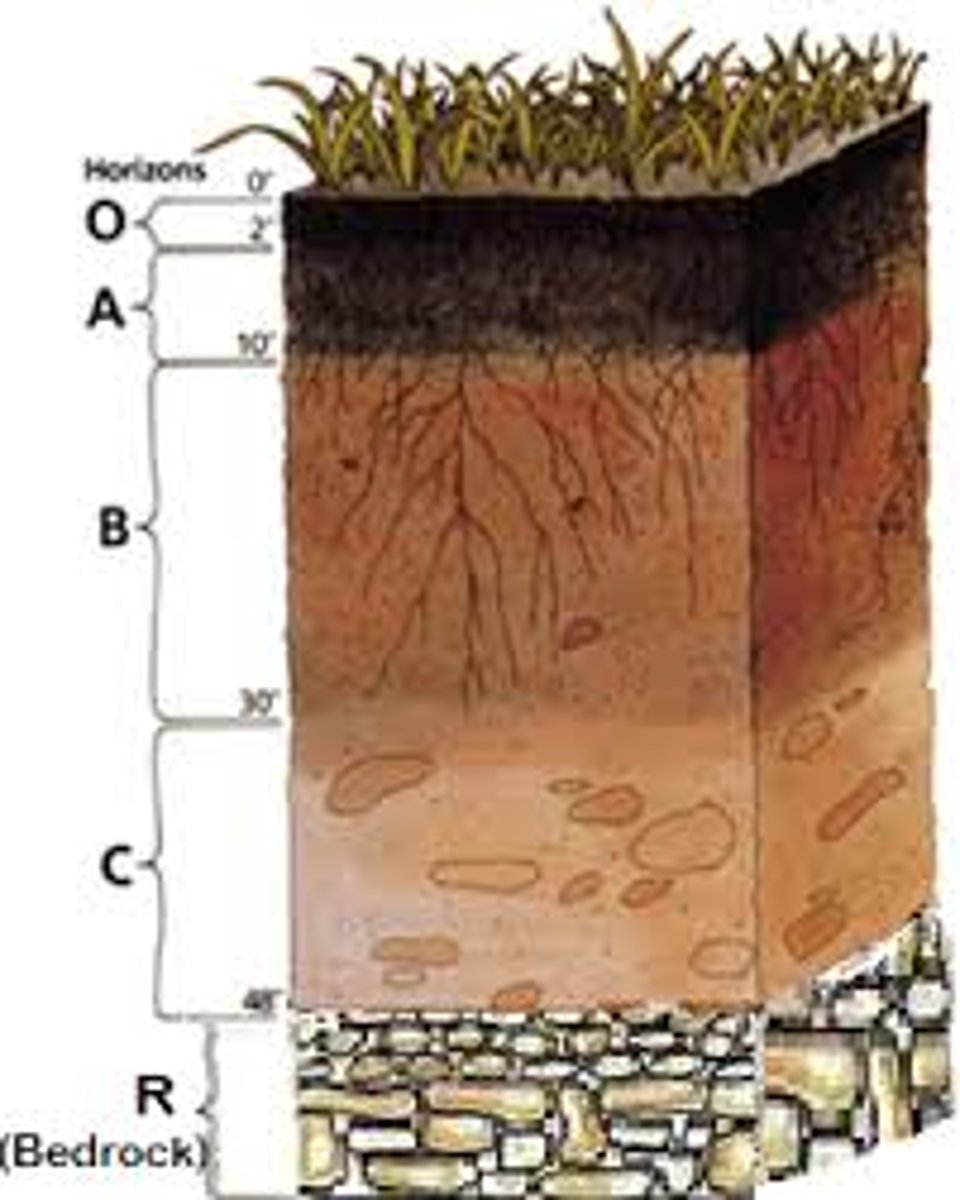
O horizon
The top horizon, made up of a little soil and mostly humus (leaves, sticks, organic matter, etc.), above the A horizon, called humus
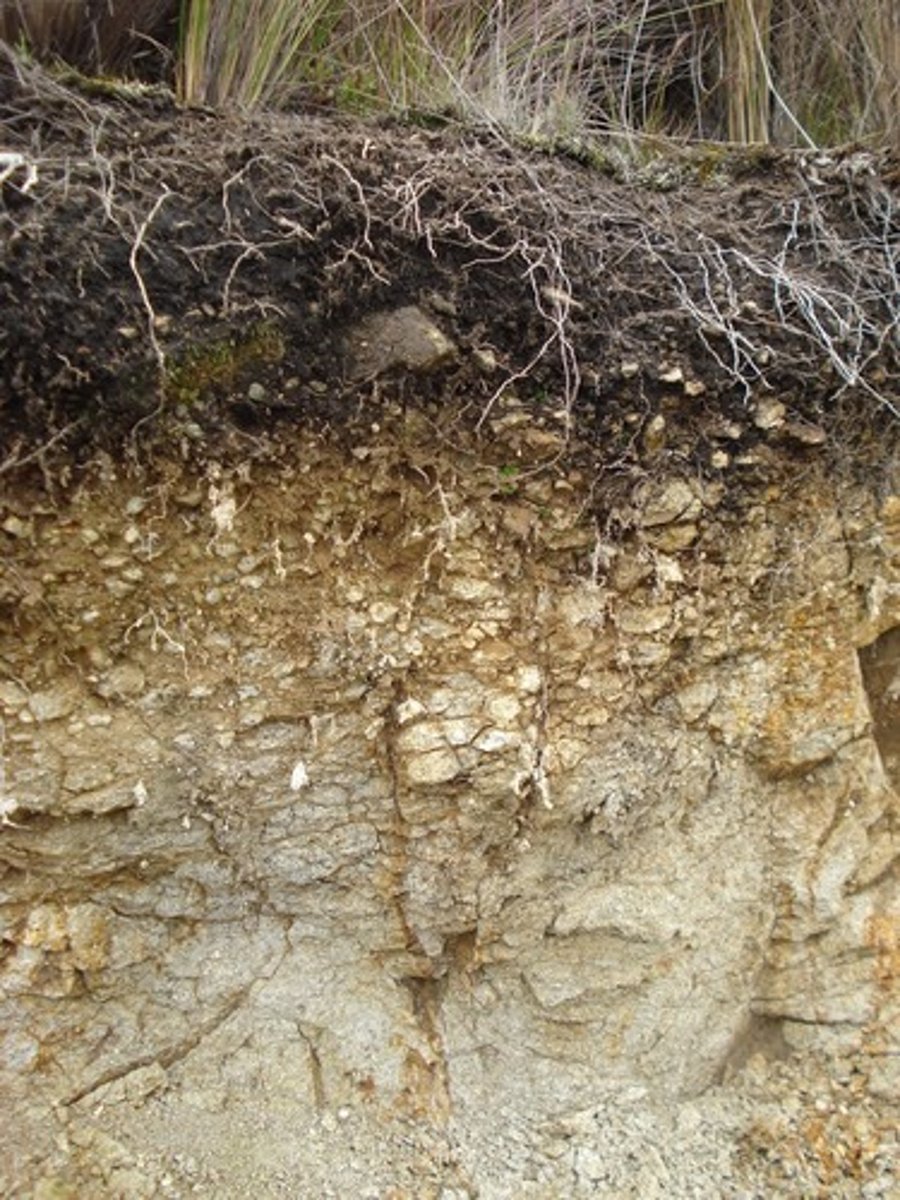

A horizon
The second soil layer, made up of humus mixed with mineral particles, this is where plant roots penetrate and grow, has a very dark color, called the topsoil
E horizon
The third soil horizon, mostly made up of sand and silt, characterized by eluviation (AKA leaching, infiltration, or water dripping through and taking minerals and clay along with it), this is a very light colored horizon, called the eluviation layer
B horizon
The fourth soil horizon, made up of mostly clay and mineral deposits that it receives from the eluviation layer above it when water drips through, called the subsoil
C horizon
The fifth soil horizon, made up of slightly broken up bedrock, plant roots do not penetrate into this layer, little organic matter is found here, also called the regolith
R horizon
The sixth soil horizon, made up of unweathered bedrock, called the bedrock layer
Horizon
The horizontal layers in soil starting from the top layer of humus to the bottom layer of bedrock
A slope
0-3% slope
B slope
3-8% slope
C slope
8-15% slope
D slope
15-25% slope
E slope
25-30% slope
F slope
30% and above slope
Hazelton
Pennsylvania's state soil
Hugh Hammond Bennett
The father of soil conservation, helped resolve the dust bowl and prevent something like that from happening again
21,000
number of types of soil in the US
sand
The largest soil classification, larger than silt and clay
silt
The second to largest, second to smallest soil classification (larger than clay, smaller than sand)
clay
The smallest soil classification, smaller than silt and sand
Pesticides
Synthetic or organic chemicals used to control weed growth in crops and lawns or unwanted/harmful pests

upland
a general term for higher ground in contrast to a valley, floodplain, or other low lying ground
residuum
unconsolidated, weathered, or partly weathered soil material that accumulates in place by disintegration of the bedrock

loess
soil material transported and deposited by wind, and predominantly of silt size

local alluvium
soil deposited in drainageways and on footslopes by sheet, rill, and gully erosion of adjacent and nearby slopes. Created by stormwater runoff rather than overflowing streams.
flood plain
a flat area that borders a stream or river and is subject to flooding; soil material has been deposited by stream overflow and deposition

drift (glacial)
a general term applied to all material transported and deposited by glacial ice. The term applies to deposits that no longer contain glaciers.

colluvium
soil material that has accumulated at the footslope of a ridge or mountainside due to mass soil movement or landslide

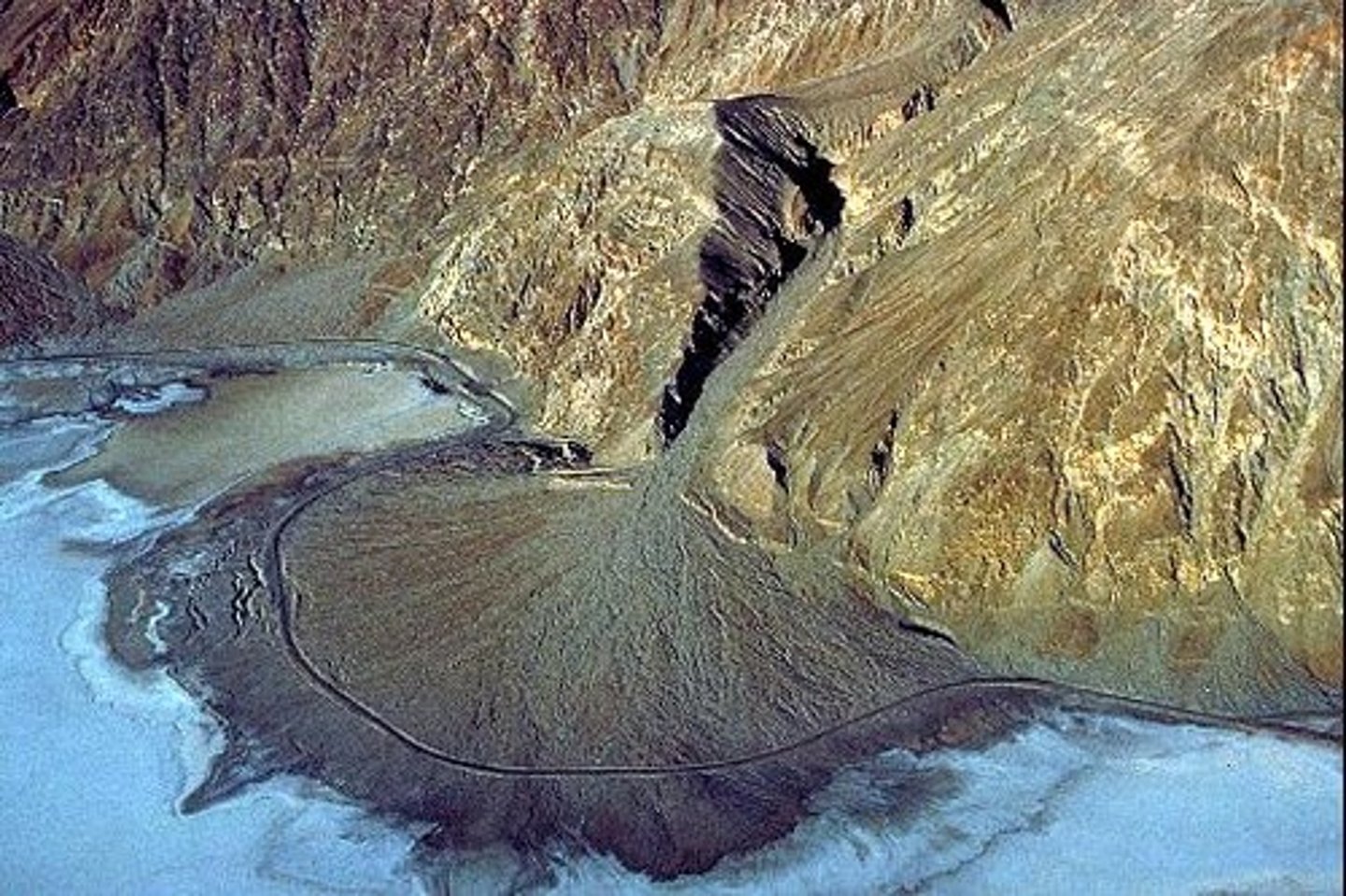
alluvial fan
a low, outspread mass of soil and/or rock, deposited by a stream,s shaped like an open fan or cone. Commonly found at the mouth of streams where they enter a larger valley.

ABC Soil
a soil having horizons A, B, and C
Aeration
the exchange of air in soil with air from the atmosphere;
well aerated soil
the air in the soil is similar to that of the atmosphere
poorly aerated soil
the air in the soil is higher in Carbon Dioxide and low in Oxygen
Aggregate
many fine particles held in a single mass or cluster
Peds
natural soil aggregates, such as granules, blocks, or prisms
Alkali or Sodic
a soil having so high a degree of alkalinity or so high a percentage of exchangeable sodium, or both, that plant life is restricted
alluvium
unconsolidated material, such as gravel, sand, silt, clay, and various mixtures of these, deposited on land by running water

calcareous soil
a soil containing enough calcium carbonate (commonly combined with magnesium carbonate) to effervesce visibly when treated wit cold, dilute hydrochloric acid
capillary water
water held as a film around soil particles and in tiny spaces between particles.
capillarity
ability for moisture to be drawn upward into soil
loamy sand
a gritty soil texture that is mostly sand with much less silt and clay
elluviation
the movement of material in true solution or colloidal suspension from one place to another within the soil
eolian deposit
sand, silt, or clay sized clastic material transported and deposited primarily by ind, common in the form of a dune or a sheet of sand or loess
fertility
the quality that enables soil to provide plant nutrients, in adequate amounts and in proper balance
till
dominantly unsorted and unstratified drift, generally unconsolidated and deposited directly by a glacier
soil texture
relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in a mass of soil
soil
has properties resulting from the integrated effect of climate and living matter acting on earthy parent material
solum
the upper part of a soil profile; above the C horizon.
What are the five soil forming factors?
Climate, Organisms, Parent material, Topography, Time
Why are organisms important to soil formation?
provides organic matter and reduces soil erosion
Why is topography important in the formation of soils?
It affects the temperature and moisture of the soil
This soil forming factor allows for greater soil horizon development.
Time
What is the best pH range for most crops?
6.0-7.5
Soil pH that is too high or too low can cause______?
Nutrient deficiencies, decrease in crop yield, decrease in microbial activity
This nutrient provides plants with energy and helps with internal functions. Too little and the plant yellows and growth is stunted.
Nitrogen
This nutrient helps in photosynthesis, energy transfer and efficient use of water. Too little and growth is stunted and leaves turn bluish-green.
Phosphorus
This nutrient helps plant metabolism; controls water and chemicals inside the plant. Too little of this nutrient and the plant has weak stems and roots; leaves appear burned and more easily affected by bugs.
Potassium
This soil feature is important to sustaining biological activity, diversity and productivity. Regulates water flow and nutrient availability. Stores and recycles nutrients. Filters, buffers, degrades and detoxifies organic and inorganic materials that are potential pollutants. Essential to plant growth.
Soil Food Web
This biological component is a single-celled animal that eats bacteria, soluble organic matter and fungi which releases nitrogen for plant use. Help control bacteria populations.
Protozoa
Non-segmented worms that are important to mineralizing nutrients for plants. They suppress disease and are a food source for microbial predators.
Nematodes
Invertebrates that are shredders and predators that help mineralize nutrients, control pests, stimulate microbial activity and enhance soil aggregation.
Arthropods
Major decomposer of dead and decomposing organic matter. Dramatically change soil structure, water movement, nutrient dynamics and plant growth.
Earthworms
This factor is important to soil health by improving structure, infiltration and water-holding capacity; reducing disease and pollution; and recycling nutrients.
Soil organisms
This farming practice plants crops in long rotational strips along the contour of the slope to help prevent water and wind erosion.
Contour strip cropping
This conservation practice helps prevent erosion, improves soil physical and biological properties, supplies nutrients, suppresses weeds, improves water holding capacity and can break pest cycles.
Cover crops
This is a vegetated area next to a stream that helps protect the stream from adjacent land use. It helps filter and slow runoff and provides shade for stream.
Riparian buffer
Hard stable area where cattle and equipment can cross stream without damaging streambed or banks.
Stream crossing
Soils that are saturated for long periods of time and cannot hold much oxygen.
Hydric soils (wetland soils)
Hydric soils because of their anaerobic conditions are what color?
grey (gleyed)
This type of wetland soil contains noticeable amounts of partially decomposed plants that look like black muck.
Organic wetland soils
Wetland soils that contain little or no organic matter. Mineral soils are mottled and are usually gray, greenish or bluish gray.
Mineral wetland soils
What are some benefits of wetland soils
wildlife habitat, improves water quality, flood control, erosion control, groundwater recharge, recreation
What are the two parts of a soil mapping unit?
Soil Series and Slope
Areas of equal elevation on a topographic map.
Contour lines
Distance between adjacent contour lines.
Contour interval
A platform in a stream valley parallel to the stream; abandoned floodplain at a higher elevation.
Stream terrace
Waterlogged swampy area
Bog
Outspread mass of soil and rock deposited at the mouth of a stream where it enters a larger valley.
Alluvial fan
A large flat area at high elevation near the summit
Plateau
Topographically highest position
Summit
Area bordering a stream subject to flooding.
Flood plain
A long narrow water course that lacks a channel, but has intermittent water flow.
Drainageway
Topography with sinkholes and underground drainage formed in limestone.
Karst