2- hypothalamus + pituitary physio
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
where’s the pituitary gland
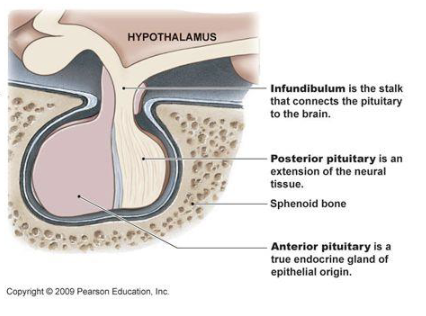
base of the brain, sitting in the sella turcica + connected to the overlying hypothalamus via pituitary stalk (infundibulum)
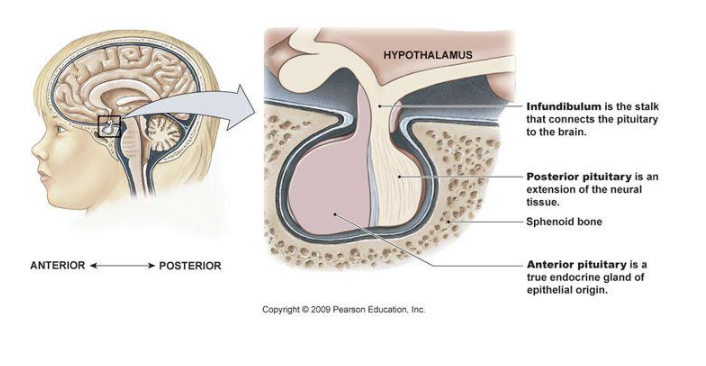
structure of pituitary gland
2 lobes:
anterior (adenohypophysis), bigger one
posterior (neurohypophysis)
what controls the secretion of hormones from pituitary gland
hypothalamus
how does the hypothalamus control the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones
neurons in hypothalamus secrete releasing/inhibitory hormones into hypothalamic capillaries that form long hypothalamic-pituitary portal veins that descend to anterior pituitary → where a 2nd capillary network combines w/ the portal veins to deliver the hormones to “troph” cells that control release of anterior pituitary hormones how
what type of hormones does the anterior pituitary secrete
6 peptide hormones:
FSH → reproductive system
LH → reproductive system
TSH → thyroid gland
ACTH → adrenal glands
prolactin → mammary glands
GH → liver, bone, muscles
F L T A P G
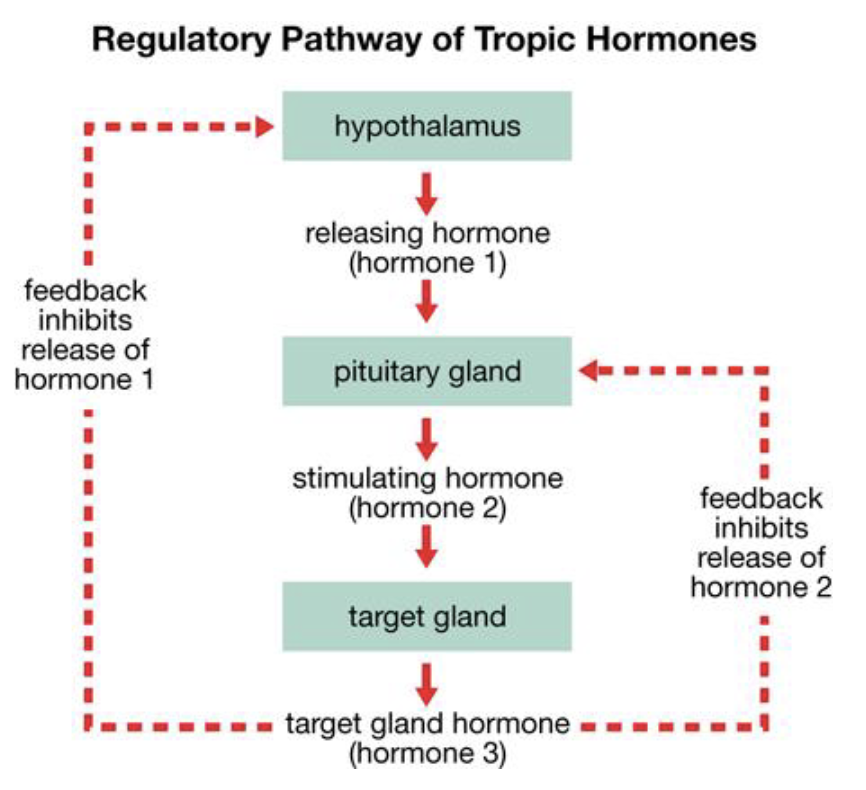
3 levels of the pituitary hormone pathway
hypothalamus
pituitary gland
target gland
each one producing hormones
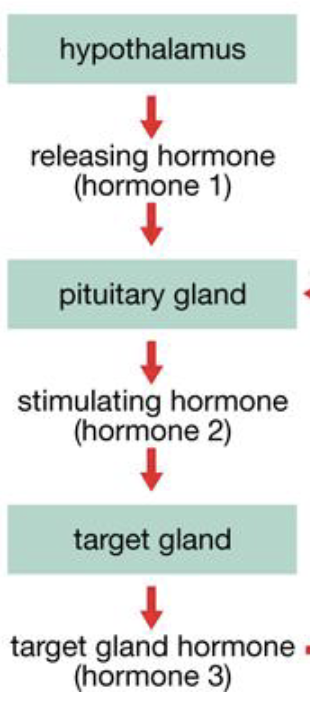
how is the pituitary hormone pathway regulated
hormones released by target glands can feedback inhibit hormone release from both pituitary gland + hypothalamus
which hormones are released by the hypothalamus that stimulates the pituitary
CRH → ACTH
TRH → TSH
GnRH/LHRH → FSH/LH
GHRH/somatostatin → GH
PRH/dopamine → PRL
how does GH (growth hormone) elicit cellular response
binds to surface receptors on muscle, adipose tissue, liver → activates JAK 2-STAT signaling pathway
4 short term effects of GH
lipolysis in liver
gluconeogenesis in liver
inhibition of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle
maintains normal pancreatic islet function
GH’s effect on insulin
GH deficiency → decline in insulin secretion
GH excess → rise in insulin to compensate for reduction of glucose uptake in muscle
overall function of GH
raises blood levels of energy substrates, fatty acids, glucose
inhibiting glucose uptake by muscle → ensures that enough glucose is available for other tissues, especially the CNS
long term effects of GH
secretes IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor) → promotes linear growth between birth + puberty by stimulating proliferation of cartilage in epiphyseal (growth) plates of long bones + by increasing organ size/function
what happens once linear growth stops after puberty
GH-IGF-1 continues to regulate body composition + promote anabolic actions in muscles
GH deficiency leads to what
dwarfism
poor jaw development
delayed dentition with late loss of deciduous teeth
missing permanent teeth
GH excess leads to what
prepubertal → gigantism
postpubertal → acromegaly (thickening of bones + soft tissues of hands, head, feet), glucose intolerance, hyperinsulinemia
PRL (prolactin) is produced by which cells in the anterior pituitary
lactotrophs
T/F: PRL (prolactin) is secreted at low levels throughout life in males + females
true
PRL (prolactin) is stimulated/inhibited by what
stimulated: TRH
inhibited: dopamine
main function of PRL (prolactin)
breast development + milk production
excess PRL (prolactin) secretion can lead to what
females: infertility, dysmenorrhea, galactorrhea (inappropriate milk production)
males: decreased testosterone/sperm production, gynecomastia
most common cause of PRL (prolactin) excess secretion
prolactinoma, usually treated w/ dopamine agonist
what 2 hormones are secreted by the posterior pituitary
2 peptide hormones:
oxytocin (OT)
arginine vasopressin (AVP/ADH)
how are OT + AVP/ADH synthesized
by neurons in the hypothalamus located in supraoptic nucleus (SON) + paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
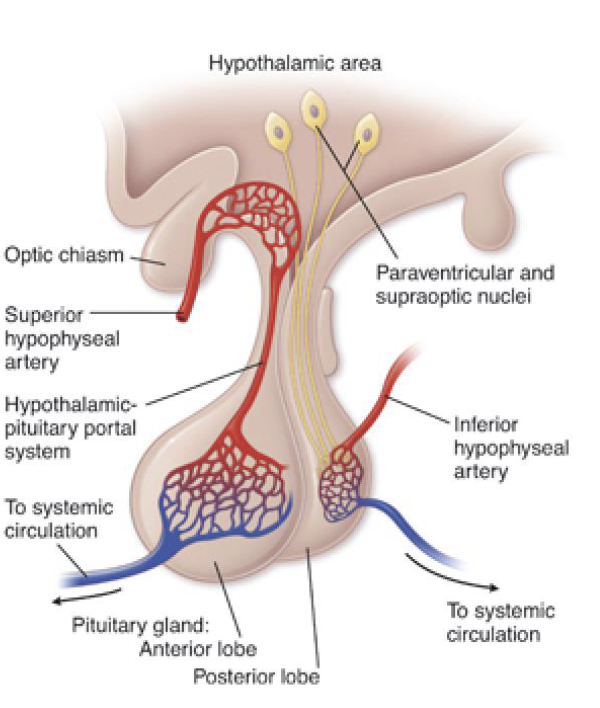
how do OT + AVP/ADH get to the posterior pituitary
OT + AVP/ADH are packaged in vesicles → travel down axons of the hypothalamus neurons that project down the pituitary stalk + terminate in posterior pituitary
how are OT + AVP/ADH made from their preprohormone form
preprohormone forms are cleaved into their bioactive forms w/ their signal peptide + inactive neurophysin fragment
when is AVP/ADH secreted
plasma osmolality increases: osmoreceptor cells signal to the SON + PVN in the hypothalamus
plasma volume decreases: sensed by vascular baroreceptors
3 effects of AVP/ADH
kidney: binds to basolateral side of collecting duct cells, via cAMP dependent kinases to insert aquaporins into luminal membrane → increased water reabsorption → reduced urine
blood vessels: vasoconstriction via PLC pathway
anterior pituitary: enhances ACTH secretion
AVP/ADH deficiency leads to
diabetes insipidus
2 main actions of oxytocin
milk let-down in lactation
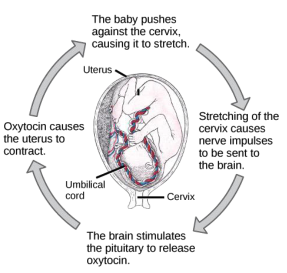
parturition: postive feedback cycle
definition of milk let-down in lactation
neuroendocrine reflex stimulated by nipple suckling → myoepithelial cells surrounding the lactiferous ducts + acinar cells of the breast contract + eject milk from the mammary glands
definition of parturition
positive feedback cycle:
increased stretching of cervical myometrium increases oxytocin release from posterior pituitary → stimulates myometrial contractions in labor that push fetus further into cervical, further increasing stress-induced neural signals + OT release