TCA cycle
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
glucose to pyruvate - what then?
Glycolysis released less than a quarter of the chemical energy in glucose that can be released by cells. Most of the energy remains stockpiled in the 2 molecules of pyruvate. If molecular oxygen is present, the pyruvate enters a mitochondrion (in eukaryotic cells), where the oxidation of glucose is completed
in prokaryotic cells…
this process occurs in the cytosol
glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
Upon entering the mitochondrion via active transport, pyruvate is first converted to a compound called acetyl coenzyme A, or acetyl CoA.
Pyruvate produced by glycolysis is converted into acetyl CoA, the fuel of the citric acid cycle.
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
In the mitochondrial matrix, pyruvate is oxidatively decarboxylated by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to form acetyl CoA.
This irreversible reaction is the link between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.

TCA cycle
Each pair of electrons from NADH will generate ~2.5 ATP when used to reduce oxygen in the electron-transport chain.
Each pair of electrons from FADH2 will power the synthesis of ~1.5 ATP with the reduction of oxygen in the electron-transport chain.
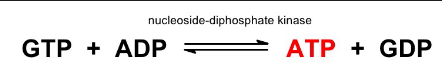
GTP vs ATP
ATP is universally used for general energy needs, while GTP is usually found in processes like protein synthesis and signalling
GTP can be converted to ATP
The energy released when ATP or GTP id hydrolysed to ADP is identical (∆G = -30.5 KJ/mol).
TCA cycle net reactions
Two carbon atoms enter in the form of an acetyl unit
Two carbons leave in the form of CO2 molecules
Four pairs of electrons leave on the reduced form of electron carriers (3 NADH and 1 FADH2)
One NTP (usually ATP) is generated
Two water molecules are consumed: one in the synthesis of citrate by the hydrolysis of citryl CoA and the other in the hydration of fumarate
Regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase
The synthesis of acetyl CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a key irreversible step in the metabolism of glucose.
control of the citric acid cycle
The rate of the citric acid cycle is precisely adjusted to meet an animal cell's needs for ATP.
regulation of the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle is regulated primarily by the concentration of ATP and NADH.
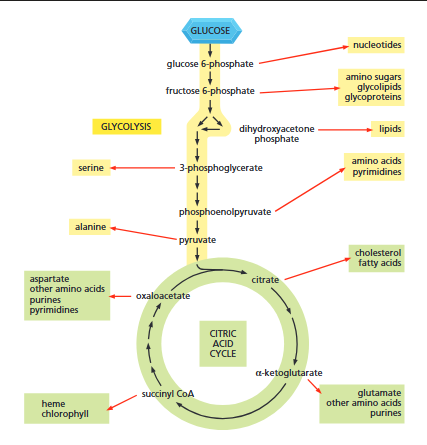
glycolysis and the citric acid cycle provide
the precursors needed to synthesise many important biological molecules.
diagram
Each black arrow in the diagram denotes a single enzyme-catalysed reaction. Red arrows generally represent pathways with many steps that are required to produce the indicated products.
observations made by Krebs
in the presence of oxygen certain organic acids (citrate, succinate, fumarate, and malate) are readily oxidised to carbon dioxide
these reactions depend on a continuous supply of oxygen
the oxidation of these compounds falls into a pair of linear, sequential pathways
The synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A from pyruvate required
3 enzymes and 5 coenzymes