Breeding and Genetics Exam 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Place the steps of transcription below in the correct order of occurrence
____The DNA helix is unwound and RNA is synthesized
____Transcription is stopped by a hairpin loop
____The RNA polymerase II binds to the promotor
__2__The DNA helix is unwound and RNA is synthesized
__3__Transcription is stopped by a hairpin loop
__1__The RNA polymerase II binds to the promotor
What two roles are played by RNA polymerase II during transciption?
Going to unwind DNA helix
Synthesizes mRNA
After RNA is transcribed, the RNA must be processed before translation into protein. What are the three steps of RNA processing?
Add a 5’ modified guanesine
Add a 3’ poly A tail
Remove introns
The formation of the ____________ ends transcription.
hairpin loop
What is the function of the spliceosome?
Spliceosome removes introns from mRNA
What is the difference between an exon and an intron?
Only exons are translated into protein
What is alternative splicing?
When introns become exons or vice versa based on environmental changes, development state, or tissue type.
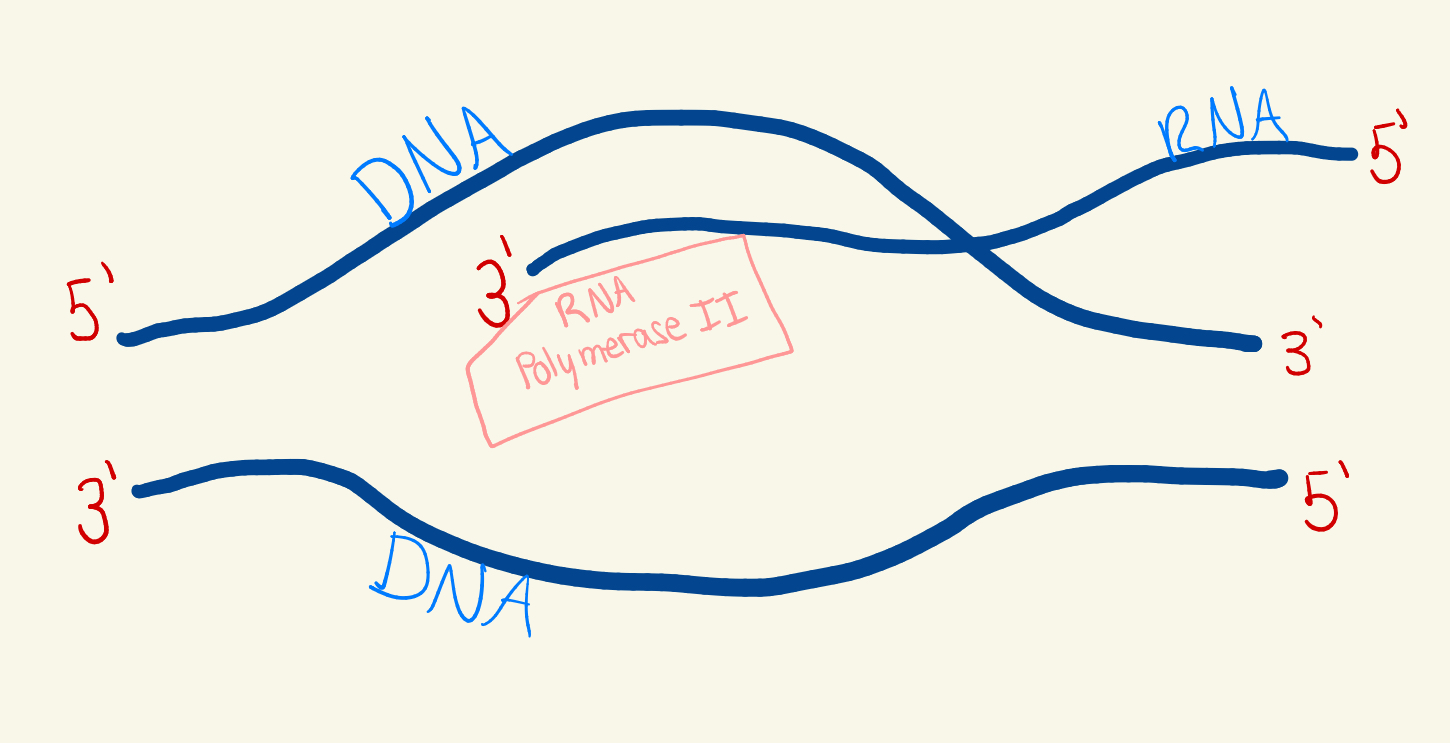
Below is a gene actively being transcribed. Please identify each of the following:
A. Label all 5’ and 3’ ends (6 total)
B. Circle the direction of transcription (below)
Left to Right OR Right to Left
C. Label the location of the RNA strands
D. Label all the DNA and RNA strands
What happens at the Aminoacyl (A) site in translation?
tRNA with anticodon complementary to the mRNA codon enters the ribosome.
What happens at the Peptidyl (P) site in translation?
Links the amino acids together with peptide bonds.
What are the functions of the three types of RNA required for translation to take place?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)-the sequence that the ribosome translates into protein
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)-forms part of the ribosome
Transfer RNA (tRNA)-links codons in the mRNA to specific amino acids
Place the steps of translation below in the correct order of occurrence (1-6)
____The amino acids on the tRNA in the peptidyl region are transferred to the amino acid on the tRNA in the aminoacyl region
____The ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA
____A tRNA with an anticodon complementary to the mRNA start codon in the aminoacyl region enters the aminoacyl region
____The small ribosomal subunit identifies the start codon and the large ribosomal subunit binds to the small ribosomal subunit to complete the ribosome
____The ribosome shifts three nucleotides such that the codon/tRNA in the aminoacyl region is now in the peptidyl region and a new codon enters the aminoacyl region. A new tRNA enters the aminoacyl region.
____Repeat steps 4-5 until a stop codon enters the aminoacyl region
__5__The amino acids on the tRNA in the peptidyl region are transferred to the amino acid on the tRNA in the aminoacyl region
__1__The ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA
__3__A tRNA with an anticodon complementary to the mRNA start codon in the aminoacyl region enters the aminoacyl region
__2__The small ribosomal subunit identifies the start codon and the large ribosomal subunit binds to the small ribosomal subunit to complete the ribosome
__4__The ribosome shifts three nucleotides such that the codon/tRNA in the aminoacyl region is now in the peptidyl region and a new codon enters the aminoacyl region. A new tRNA enters the aminoacyl region.
__6__Repeat steps 4-5 until a stop codon enters the aminoacyl region
What is the start codon?
AUG
What are the three stop codons?
UAA
UAG
UGA
Here is a codon from some gene: 5’ GCC 3’
A. What is the sequence of the anticodon that could paid with this codon during translation?
3’_________5’
B. Using the genetic code table, identify all possible tRNA anticodons that code for Ile (isoleucine). There may be more blanks that needed.
3’______5’ 3’______5’ 3’______5’ 3’______5’