Patho Exam 1: Endocrine
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Parts of the central endocrine system
pineal gland
pituitary gland
hypothalamus
Dedicated function endocrine glands
only have the function of releasing and regulating hormones
Thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands
Mixed function endocrine glands
organs that have additional functions, and release endocrine hormones
Ex: kidneys, reproductive organs
Endocrine Gland
An organ that produces and releases chemicals either through ducts or into the bloodstream.
Hormone
Produced by glands. Released into bloodstream. Reach their target slower. Have a longer lasting effect on the body. wide dispersal.
agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
partial agonist
a drug that binds to a receptor and causes a response that is less than that caused by a full agonist
antagonist
A substance that blocks normal neurotransmitter functioning.
Endocrine cells release hormones where?
into the blood stream
How do hormones achieve different effects on various organs?
Different organs have different receptor subtypes for the same hormone.
Neurotransmitters
Produced by neuron. Released into synaptic cleft of Target site. Reach their target quickly. Have short lasting effect on the body. Precise delivery.
Neurosecretory cell
a neuron that secretes a hormone or hormonelike substance
Endogenous ligand
any substance, produced within the body, that selectively binds to the type of receptor that is under study
Three basic responses a hormone has once binding to a receptor
1. Alters channel permeability by acting on pre-existing channel-forming proteins
2. Acts through second-messenger system to alter activity of pre-existing proteins
3. Activates specific genes to cause formation of new proteins
Three Types of Hormones:
Peptide and Protein hormones
Amino Acid Derived hormones
Steroids Hormones
peptide and protein hormones are made of:
chains of amino acids
amino acid hormones
hormones composed of proteins, from a single amino acid that is altered
steroids all come from what?
cholesterol
thus are lipid soluble
Important factors impacted by water-soluble hormones vs lipid-soluble Hormones
synthesis
storage
transport
interaction with target
water-soluble hormones synthesis
Synthesized as a prohormone and converted into active
fat-soluble hormones synthesis
synthesize from cholesterol
water-soluble hormone storage
usually via intracellular vesicles
fat-soluble hormone storage
often not stored, b/c they can pass through vesicle membranes,
made on demand and use hormone binding proteins
binding proteins function
They facilitate the movement of lipid-soluble hormones through the bloodstream.
help store lipid-soluble proteins
water-soluble hormone transport
usually move freely in the blood stream
fat-soluble hormone transport
bound to plasma protein
water-soluble target cell interaction
bind to membrane receptor and often use a second messenger
fat-soluble target cell interaction
usually bind to nuclear receptor, regulates gene transcription
Name the Fat-Soluble hormones
All Steroids: aldosterone, cortisol, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
Thyroid Hormones: T3 and T4
Amino Acid Derived Hormones
Thyroid hormones: T3, T4
Adrenal medulla hormones: epinephrine, norepinephrine
Dopamine and Serotonin
Important Peptide hormones
ADH
Insulin
Oxytocin
TSH
Catecholamines
subtype of amine hormones derived from tyrosine
Epi and Norepi
T3 and T4 mechanism of action
thyroid hormones
T3 is active form and T4 must be converted to T3
Fat soluble hormones that impact gene expression
Steroids
aldosterone, cortisol, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
lipoprotein
bonding of molecules of fat and protein
Which organ is responsible for synthesizing cholesterol when it is not obtained from the diet?
liver
Purpose of LDL
Low-density lipoprotein
transport cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues/organs via the blood
Steroid Hormone Synthesis
1. Cholesterol from the diet or liver is packaged with LDL for transport in the bloodstream.
2. LDL binds to cell receptors and is taken into the cell.
3. LDL is broken down, releasing free cholesterol.
Cholesterol is converted in the mitochondria to pregnenolone, which is then used to make the specific steroid hormone needed.
Each step of steroid hormone synthesis requires what?
a functioning enzyme
Example: to make testosterone you must first produce prenenolone or progesterone or to make aldosterone you must first make corticosterone
Aldosterone
"salt-retaining hormone" which promotes the retention of Na+ by the kidneys. na+ retention promotes water retention, which promotes a higher blood volume and pressure
A pharmaceutical company is developing a drug to block aldosterone's effect on sodium retention. What might be the goal of this medication?
To treat hypertension by reducing blood volume
cAMP
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Two secondary messengers for peptide hormones
cAMP & C++ release
How does cAMP function as a secondary messenager
1. The hormone binds to a receptor activating a G protein
2. G protein activates Adenyl Cyclase
3. Adenylate cyclase converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP), which acts as a second messenger by activating protein kinase
4. Protein kinase phosphorylates a protein which causes a cell responce

What is the major effect of cyclic AMP (cAMP) as a second messenger?
Activates Protein Kinases
How does Ca2+ function as a secondary messenager
1. The hormone binds to a receptor activating a G protein
2. the G protein opens the Ca++ ion channel allowing Ca++ to flow in causing a cell responce

Steps of how lipid soluble hormones act on the cell
1. Hormone enters through the cell membrane and travels to the nucleus
2. It binds to a nuclear receptor that controls expression of a gene and activates expression
3. The gene is transcribed and a protein is synthesized
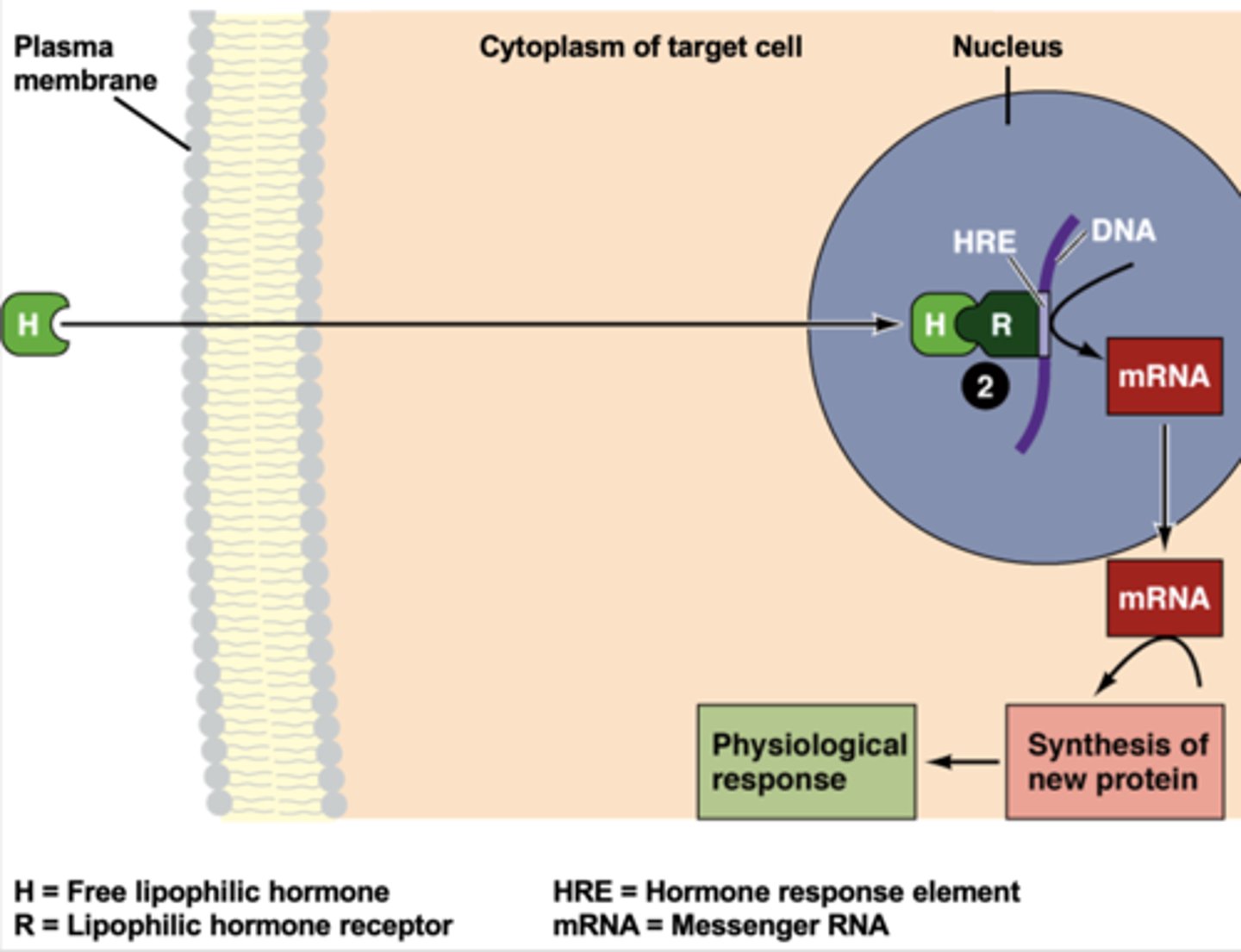
Nuclear receptors
Protein inside a eukaryotic cell that, on binding to a signal molecule, regulates transcription.
intracellular change = _______ change
physiological change
Negative feedback loop
A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving
Hierarchical Levels Of Control
when many levels of endocrine glans and hormones are involved with the secretion of a final hormone that acts on a target organ
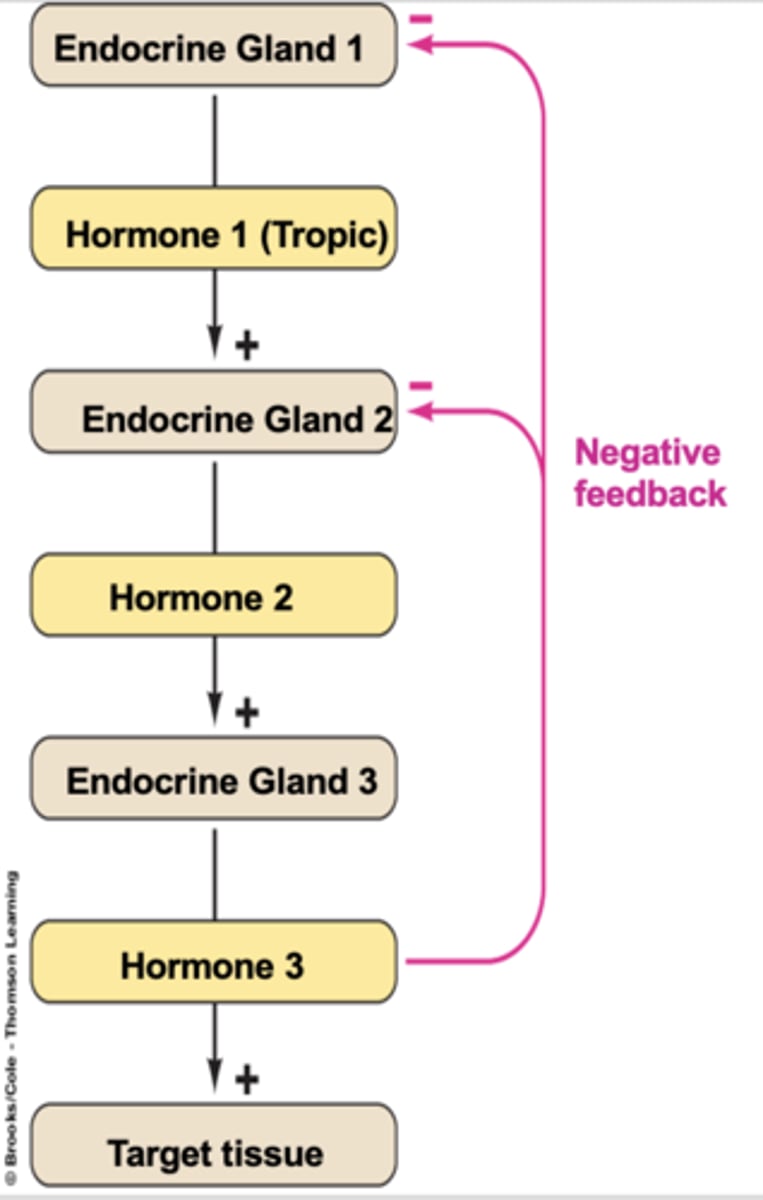
What would happen if hormone three in a hierarchical control system is not produced?
Negative feedback to gland one and gland two would stop, leading to increased production of hormones one and two.
What would happen if the hypothalamus is damaged reducing activity, in a hierarchical control system?
all hormones in the system would have reduced secretion due to a cascade effect of a lack of the first hormone released from the hypothalamus
What is the value of a hierachical control?
there is a lot of feedback so specific control over secretion can be kept
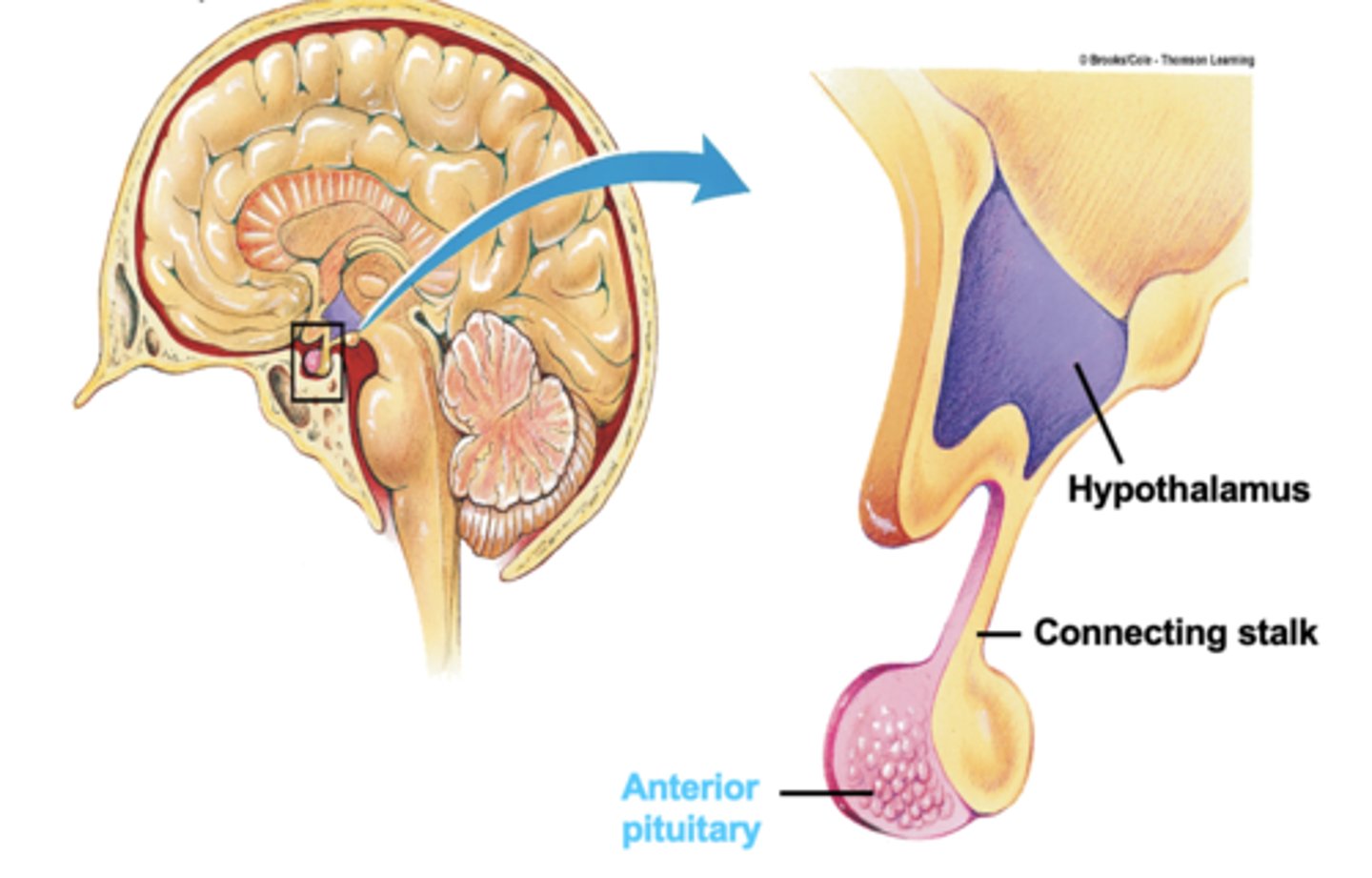
Hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
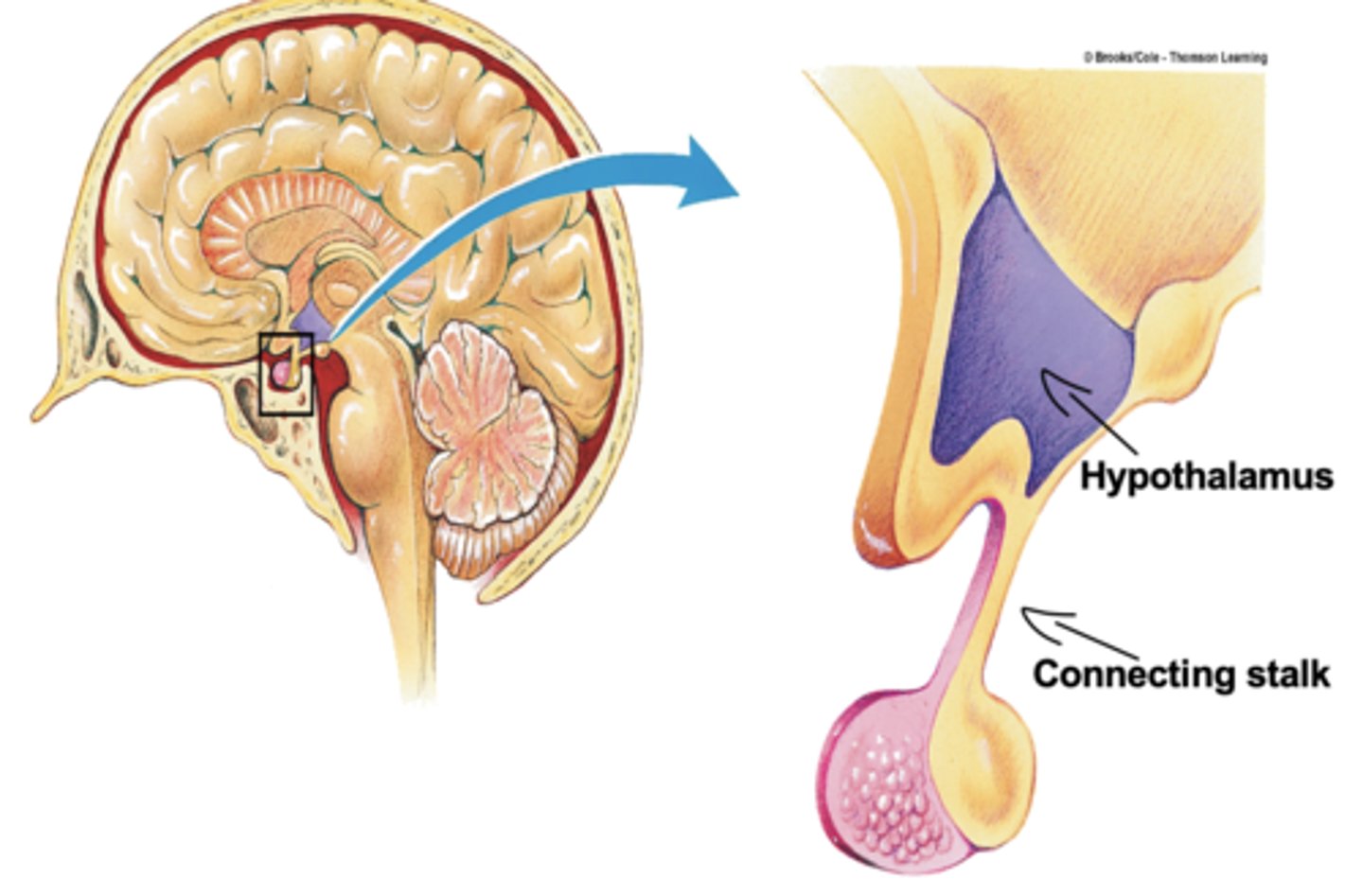
Connecting Stalk
connection between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
anterior pituitary gland
the anterior part of the pituitary gland
an endocrine gland whose secretions are controlled by the hypothalamic hormones
Posterior pituitary
Stores and releases hormones from hypothalamus.
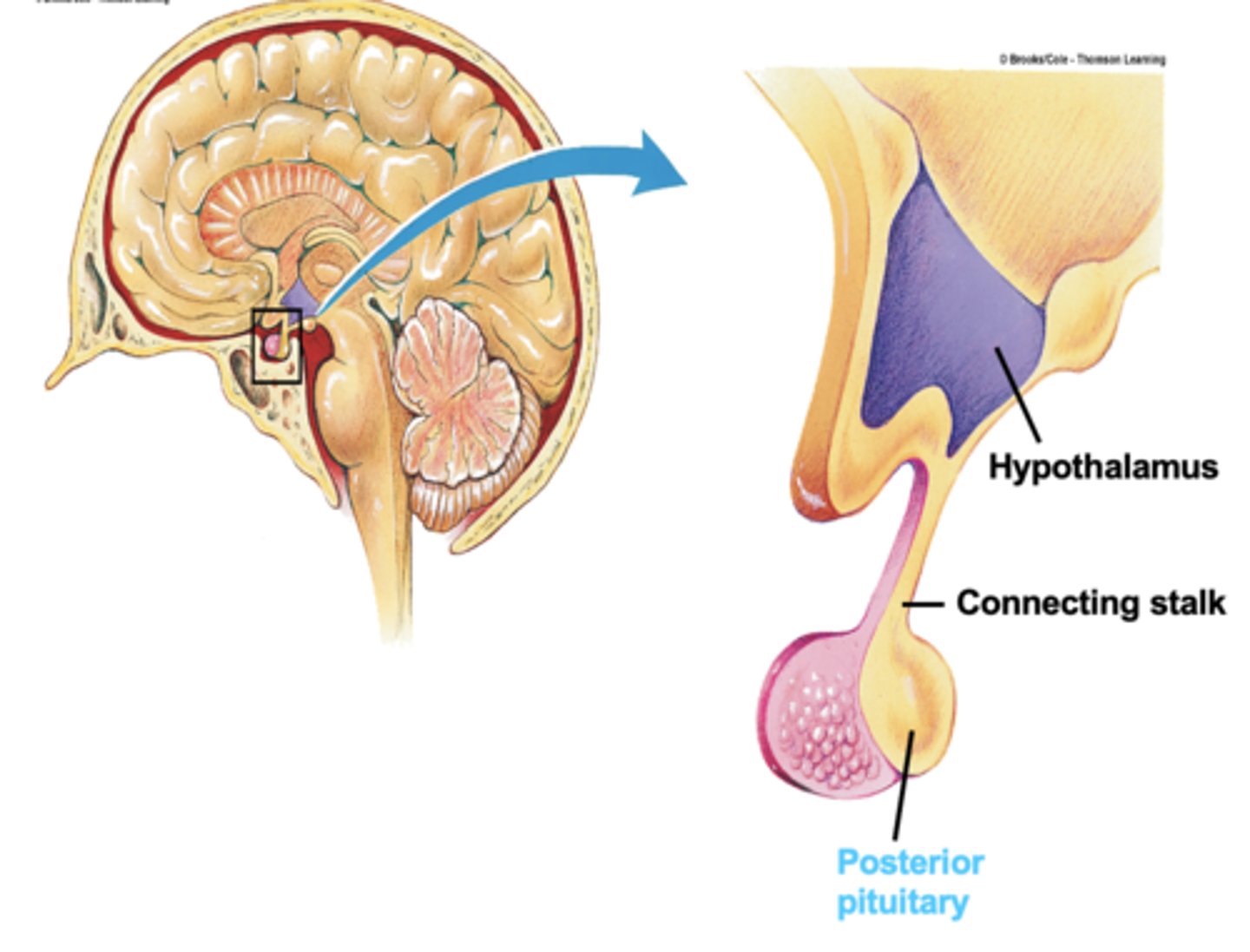
Which gland is not considered a true independent endocrine gland?
posterior pituitary
Difference between the Anterior Pituitary and Posterior Pituitary
Anterior is the real endocrine gland, with secretory cells
Posterior: mostly just an extension of the hypothalamus
Neurosecretory neurons
Neurons releasing hormones into the bloodstream.
Describe the connection between the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary
1. Neurosecretory neurons leave the hypotalamus, and travel to the posterior pituitary, via the connecting stalk.
2. In the posterior pituitary the Neurosecretory neurons release hormones into the blood stream
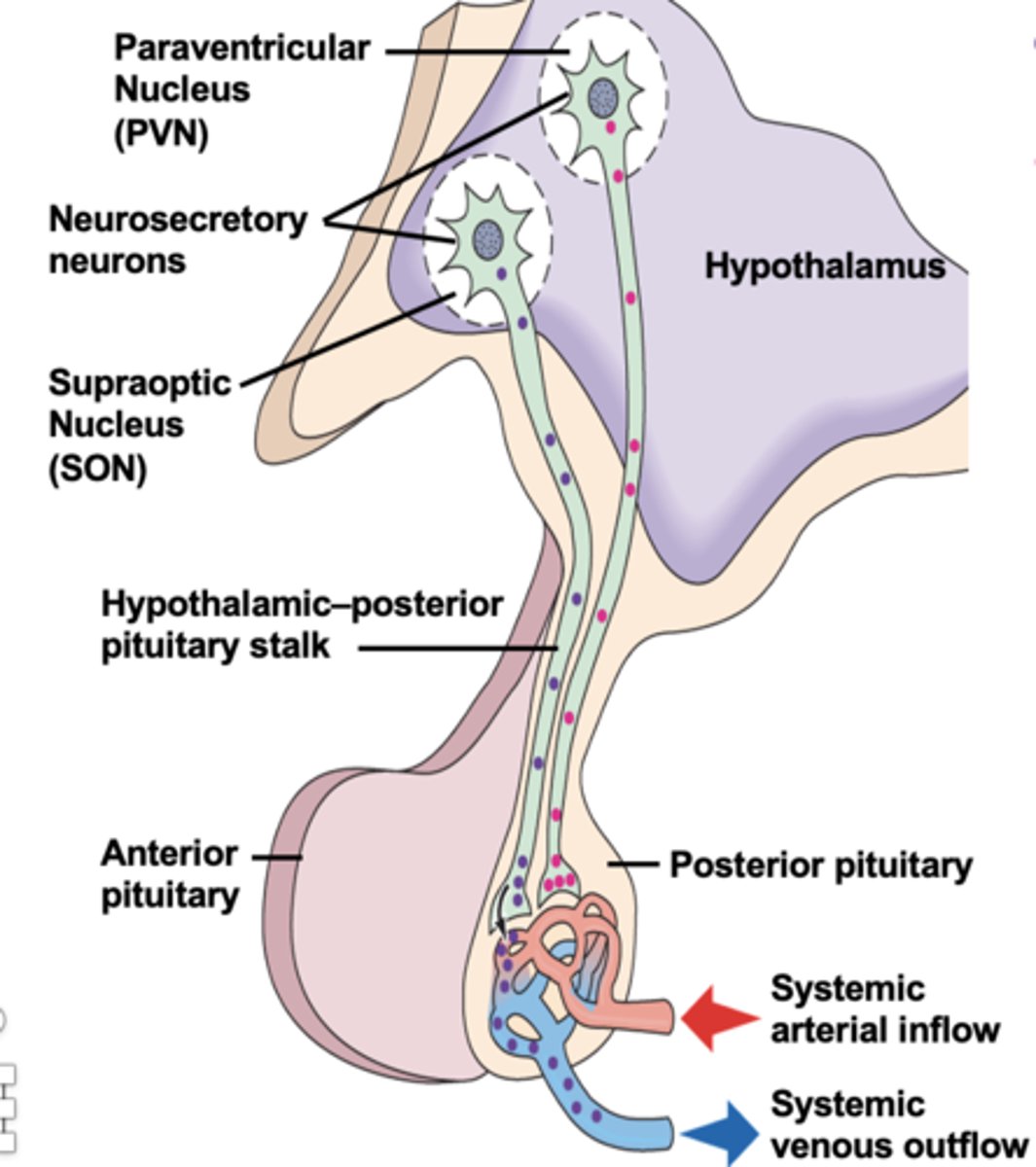
What hormones are released in the posterior pituitary
Vasopressin (ADH)
Oxytocin
Describe the connection between the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary (AP)
1. Neurosecretory neurons leave the hypotalamus, and release hormones into the blood stream
2. The hormones travel, via blood, down the connecting stalk to the AP
3. The hormones stimulate endocrine cells in the AP to produce hormones which are released into blood circulation and travel to target organs
What hormones are produced by the anterior pituitary gland
TSH, ACTH, Prolactin, GH, LH, FSH
TSH
thyroid stimulating hormone
Stimulates the Thyriod glad and produce T3 and T4
Thyrotrophs
secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
ACTH
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Stimulates the Adrenal cortex to release cortisol
Prolactin
stimulates milk production and mammary gland growth
Prolactin and Dopamine dynamic
dopamine inhibits the release of prolactin
GH
growth hormone
stimulates liver and many other tissues
LH and FSH
luteinizing hormone & Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
stimulate ovaries/testes
Lacotrophs
secrete prolactin (PRL)
Gonadotrophs
secrete FSH and LH
corticotroph cells
Pituitary cells producing ACTH.
What hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates FSH/LH release
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
What hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates ACTH release
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
What hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates TSH release
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
What hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates Prolactin release
Prolactin-Releasing Hormone (PRH)
When is Prolactin-Releasing Hormone (PRH) released?
During childbirth and breast/chest feeding to stimulate milk production
What hormone from the hypothalamus inhibits Prolactin release
dopamine
What hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates GH release
Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
What hormone from the hypothalamus inhibits GH release
Somatostatin
What type of cells release GH
Somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary
When is GH released?
During deep sleep: stage II non-rem sleep
GH effects
acts on the liver to produce IGF 1 and 2
increases the availability of glucose in the blood stream
IGF 1 and 2
Insulin-like Growth Factor
Acts similar to insulin by allowing cells to take up the glucose, that was released by GH, and use the glucose to grow and divide
A patient presents with low levels of IGF-1 but normal levels of growth hormone. What might be malfunctioning?
liver
When is IGF released?
in opposite cycle of GH
When GH is low IGH is high, during sleep
Impact of GH + IGH on cells
increases linear bone growth
increases organ size
decreases adiposity
increases lean body mass
allows for increased cell division
General maintenance of tissue
Thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
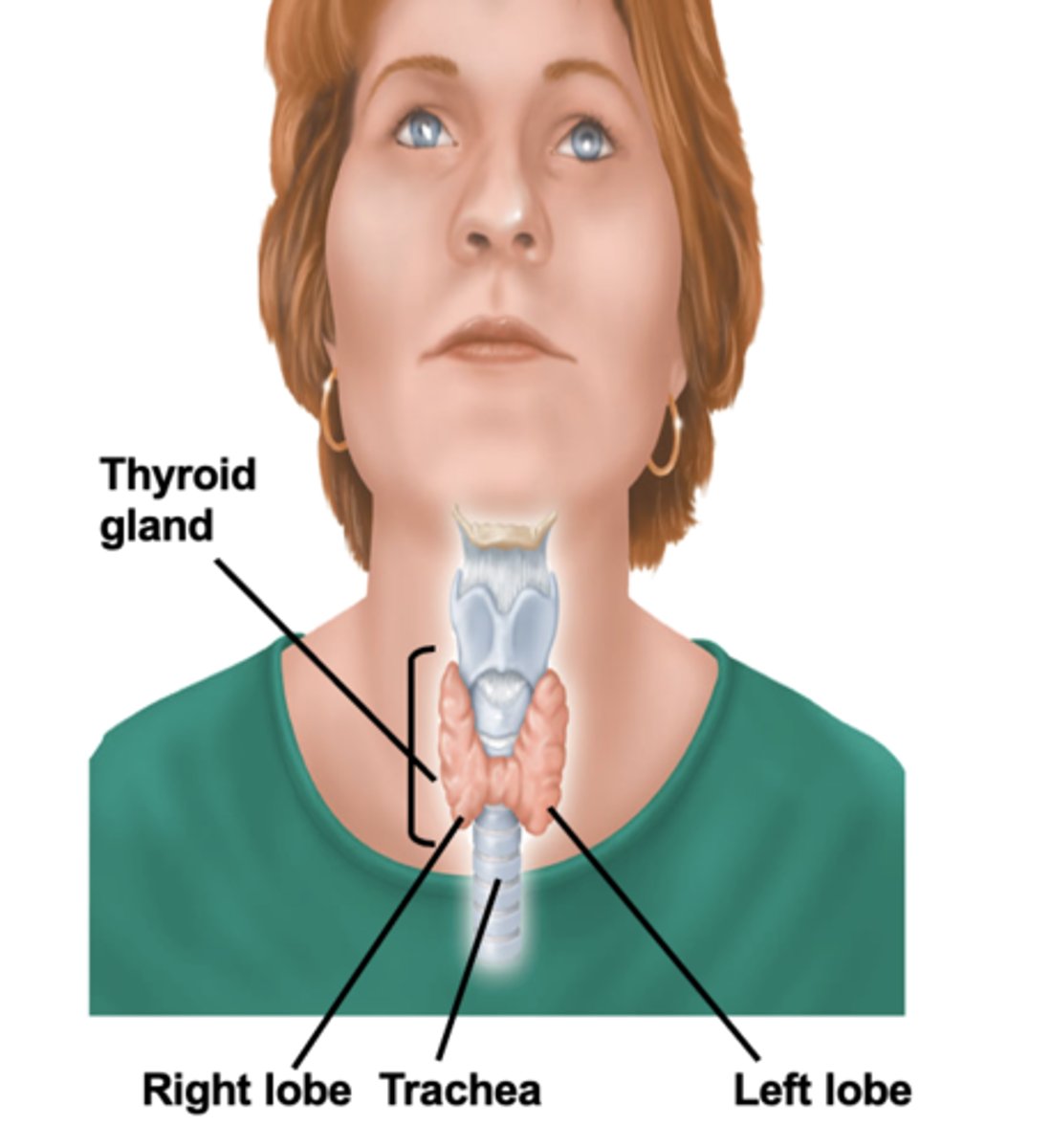
Cell structures of the thyroid gland
- arranged in follicles
- within the follicles is a protein material called colloid
- follicular cells produce thyroid hormones and store them in the colloid with thyroglobulin
- C-cells and blood capillaries are between the follicles
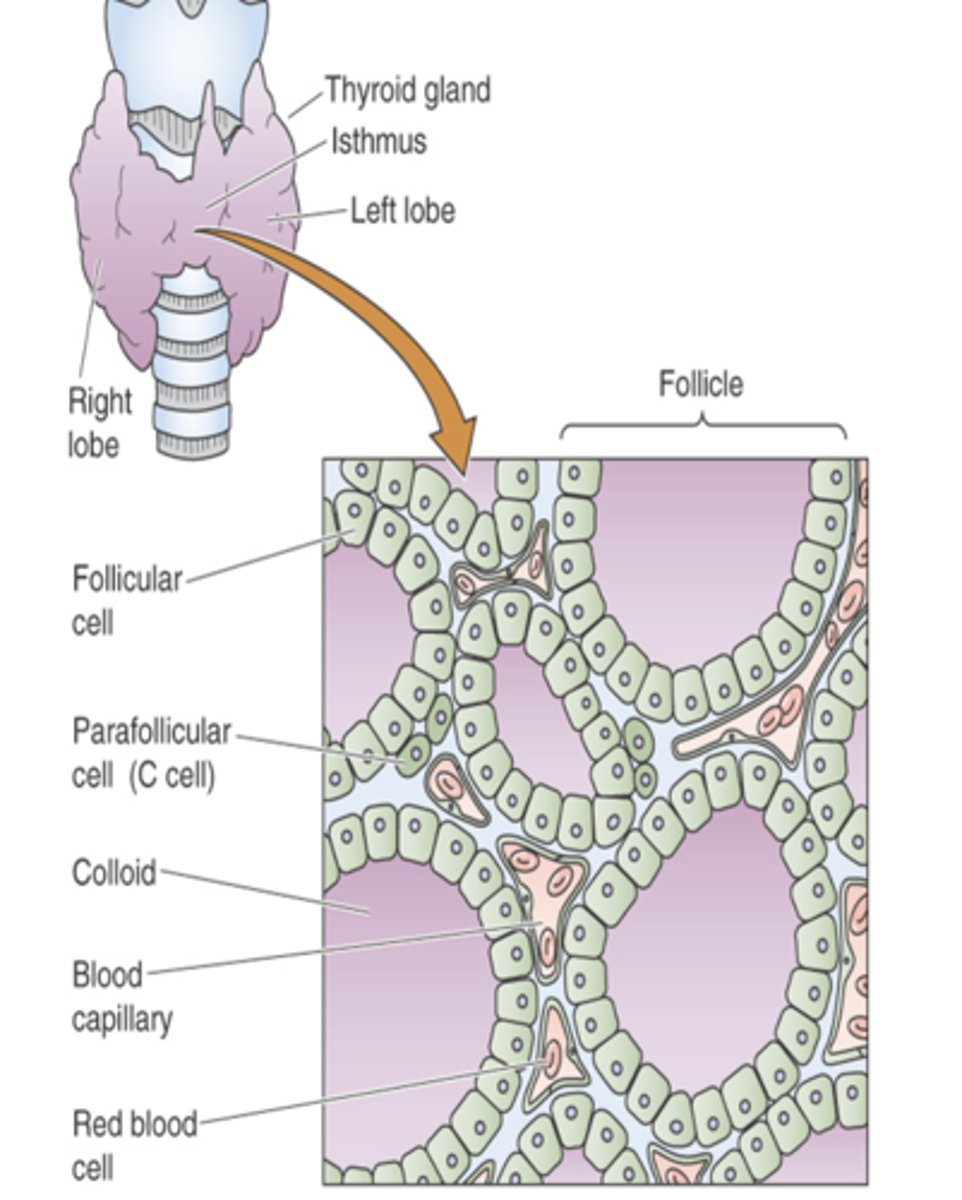
thyroglobulin
secreted by follicle cells
binds with iodine to produce T4 and T3 and makes up colloid
C-cells
produce calcitonin which controls calcium levels in the body
Production pathway from hypothalamus to T3/4 release
Hypothalamus => TRH release => anterior pituitary stimulation => TSH release => thyroid stimulation => T3/4 release => target organ stimulation
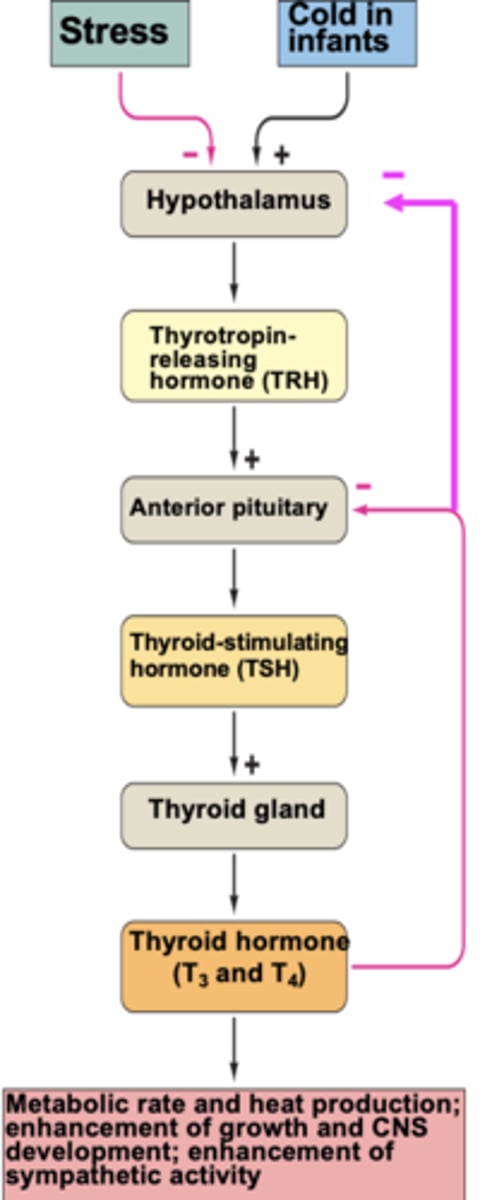
Impact of T3 and T4 in the body
increase the production of proteins that require energy (ATP) so it increases metabolic rate
- increased Metabolic rate and heat production
- enhancement of growth and CNS development
- enhancement of sympathetic activity
Is T3/T4 release continuous or on an as needed basis
continuous controlled release
Adrenal gland
A pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress.

adrenal cortex location
outer section of each adrenal gland

adrenal cortex secretes what hormones
secretes cortisol, aldosterone, and sex hormones